Honors Chemistry- Ksp
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Solubility Product Constant
Ksp=concentration of ions
If a solid dissolves well, then KSP value is…
Bigger
The smaller the KSP is…
The less souble the ionic soild is
The name of a solution when a solid of the solution has dissolved as much as it can
Molar solubility “s”
THE 3 EXCEPTIONS TO TRANSITION ELEMENT CHARGES
Ag+1, Zn +2, Cd +2
How to caculate KSP
Write the dissociation chemical reaction, where the ions will separate from each other on the ionic soild
Balance out the reaction, check the subscripts of the soild and balance it out on the right hand side
Check out the mol ratio of the reaction, if given a molar soublity of the solid, use that for the ratio and multiply as needed
Write out KSP expression, dont forget exponets, and then plug values in and solve. You do NOT need units for KSP
Calculating molar solubility
Write the solubility reaction: Start by writing the balanced chemical equation for the dissolution of the solid compound in water.
Set up an ICE problem but using S instead of X, ensure to account for molar solubility already given, and CHECK THE MOL RATIOS IN THE REACTION
Once done, set up a Ksp equation, solving for S this time
Plug S in if needed to find concentrations for the ionic solid and/or ions
Saturated solution
Solution that already has dissolved as much solid as it can and have as much ions as it can
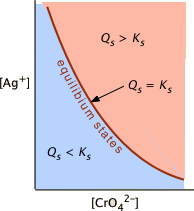
What does Qsp mean?
Like K, but can be compared to K to figure out if a precipitate will form
Q=Ksp
Saturated solution, no more soild will dissolve
Q < Ksp
Too little ions and below the max, hence it is unsaturated and there is no precipitate
Q > Ksp
There are too many ions, and a precipitate will form instead, making the solution super saturated
Q and KSP relationship on a graph…
When will the dilution equation need to be used?
If there is a mention about mL or L, and states that it is ADDED to something else also with mL or L. Ensure you have the TOTAL volume as V2, in most cases you will solve for M2
Common Ion
When an ion is already found in water, which means a soild will not be able to dissolve as much if ions are already in the water
Rule of common Ions in problems
When a solution dissolves in something that already has that, the moliarty of the compound/element with a common ion will also have the same MOLARITY, can change however based on mole ratio
Double replacement reactions
Write the unbalanced equation:
Write the reactants and their products in the general format AB + CD → AD + CB, where A and C are cations, and B and D are anions.
Predict the products:
Swap the cations and anions from the reactants to form the products. Remember to use the correct charges to determine the subscripts in the new compounds.
Balance the equation:
Count atoms: Determine the number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation.
Adjust coefficients: Add coefficients (numbers in front of the compounds) to balance the number of atoms of each element on both sides.
Check and adjust: Ensure that all elements are balanced after adjusting the coefficients. You may need to adjust the coefficients several times to reach a balanced equation
Titration goal
Determine the concentration of ions present in a soultion by reacting it with a solution with a KNOWN concentration until it reaches completion
Burette, and what is that liquid’s name?
Top section of the titration filled with a chemical of known molarity called the TITRANT
Flask, and what is that liquid called?
Bottom section of a flask containing of the known volume but unknown molarity, called the ANALYTE
Which important unit returns in titrations?
Stoichemistry