Viral Diseases - Clin Med
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What is this referring to
15-year-old female presents to urgent care with a few days of fever and sore throat.
She had recently gone to an outdoor music festival and shared multiple drinks and cigarettes with friends, who had similar symptoms.
She denies having a cough. She also had not taken anything for it
Physical exam, she has palatal petechiae and cervical lymphadenopathy.
A peripheral blood smear showed atypical lymphocytes and a Monospot test confirmed the diagnosis.
She is counseled to avoid any contact sports.
Epstein-barr virus (mono)
What is this referring to
“Epstein Barr virus (EBV) (AKA Human Herpes Virus – 4 (HHV-4))”
Epstein Barr Virus (Mono)
What is this referring to
MC teens and young adults
Risk Factors
Asian descent
Living in endemic areas
Transplant recipient
Poor sanitation
“Kissing”
Daycare centers
Epidemiology Epstein Barr Virus (Mono)
What is this referring to
Linear strand DNA virus
Transmitted via respiratory secretions
Causes Mononucleosis
Etiology Epstein Barr Virus (Mono)
What is this referring to
Fatigue
Pharyngitis
Maculopapular rash
Clinical history Epstein Barr Virus (Mono)
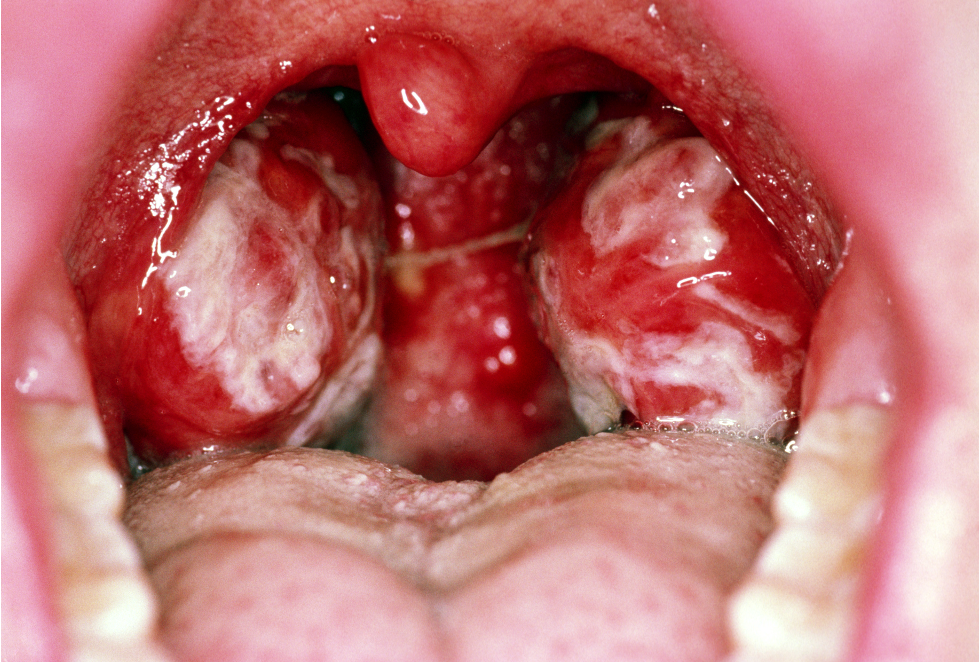
What is this referring to
Fever
Posterior cervical lymphadenopathy
Hepatosplenomegaly
Palatal petechiae
Tonsillar exudate
+/- rash
Physical exam Epstein Barr Virus (Mono)
What is this referring to
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Mono
Presents with mono type sx
Likely have more myalgias and cough
Strep Pharyngitis
Differential diagnosis of Epstein Barr Virus (Mono)
What is this referring to
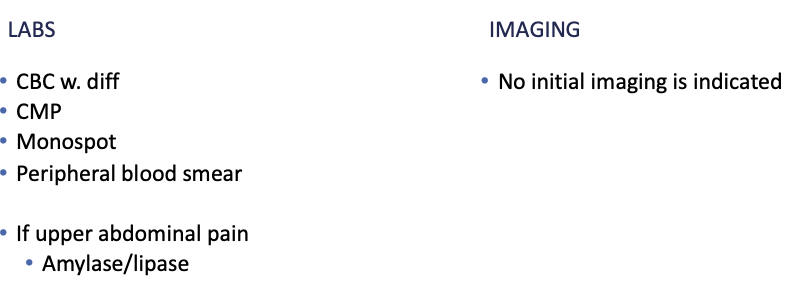
Workup for Epstein Barr Virus (Mono)
What is this referring to
+ Monospot
↑ atypical lymphocytes on peripheral blood smear
How to diagnose Epstein Barr Virus (Mono)
What is this referring to
Supportive care
Avoidance of contact sports
Supportive care
Acetaminophen
Ibuprofen
Hydration
Clinical intervention of Epstein Barr Virus (Mono)
What is the treatment for Epstein Barr Virus (Mono)
No antiviral or antibiotic medications
What is this referring to
Complications
Can lead to nasopharyngeal CA
Can cause Burkitt lymphoma
Splenic rupture
Malignancy
Hemolytic anemia
Tx with rituximab (Rituxan)
Good hygiene
Prevention/morbidity/mortality Epstein Barr Virus (Mono)
What is the prognosis of Epstein Barr Virus (Mono)
Most patients make a full recovery
What is this referring to
A 26-year-old teacher presents to his primary care physician for a low-grade fever, swollen jaw, and painful testes.
He teaches at an elementary school in Oregon, where many parents decline vaccination for their children.
The patient immigrated from China when he was 5 and does not recall if he had been vaccinated prior to immigrating.
On physical exam, he has right-sided swollen and tender parotid glands.
His bilateral testes are also swollen and tender.
He is prescribed antipyretics and analgesics and instructed to be isolated for at least 5 days.
Mumps
What is this referring to
Paramyxovirus
Classified in the family Paramyxoviridae
Also includes parainfluenza
Mumps
What is this referring to
Decreased cases due to effective vaccination
MC in winter and spring
MC children
Risk Factors
Exposure to patient with mumps or unvaccinated people
Crowded living environment
Lack of vaccination
Epidemiology Mumps
What is this referring to
Paramyxovirus
Transmission – respiratory secretions
Causes parotitis and orchitis
Virus replication in the nasopharynx and regional lymph nodes
Etiology of Mumps
What is this referring to
Presenting as Parotitis
Otalgia
Jaw pain
Prodromal
Low-grade fever
Malaise
HA
Presenting with orchitis
Bilateral testicular pain
Clinical history of Mumps
What is this referring to

Clinical Presentation Mumps
What is this referring to
Epstein-Barr virus
Mononucleosis
Acute Bacterial Parotitis
Differential of Diagnosis of Mumps
What is this referring to
Although not diagnostic – amylase is often elevated
Antibody (Ab) detection IgG and/or IgM
Buccal or oral swab with viral isolation
+ reverse transcriptase (RT)-PCR
How to diagnose Mumps
What is this referring to
Prevention with MMR vaccination in childhood
Supportive care
Antipyretics
Analgesics
Hydration, hydration, hydration
Clinical Intervention of Mumps
What is the treatment for Mumps
No antiviral therapy available
What is this referring to
Green tea to strengthen immune system
Chinese herbal medicine
Complementary and alternative therapy – Mumps
What is this referring to

Complications
Sterility in males who have orchitis after puberty
Sensorineural deafness
Most patients are asx
Prognosis of Mumps
What is this referring to
25-year-old woman presents to the clinic for routine check-up.
She reports that about a month ago, she had what she thought was mononucleosis.
She had fevers, chills, a red rash, muscle pain, and joint pains.
She works in a daycare center, and some of her colleagues had similar symptoms.
This resolved in 1 week.
Today, there are no significant findings on physical exam.
Laboratory evaluation reveals that she is positive for CMV-specific immunoglobulin M (IgM).
Other laboratory tests are negative.
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Adult
What is this referring to
DS-DNA virus
Associated conditions
Congenital CMV infection
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Adult
What is this referring to
Common viral illness
Risk Factors
Immunosuppression
MSM
Poor socioeconomic status
Working in childcare
Transplant recipients
Epidemiology Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Adult
What is this referring to
DS DNA virus
Classified as CMV or HHV-5
Largest virus that causes human infection
Primary infection or reactivation of latent infection
Transmission
Body fluids
Vertical transmission
Etiology Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Adult
What is this referring to

Clinical history Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Adult
What is this referring to
Fever
Cervical lymphadenopathy
Hepatomegaly
Maculopapular rash
Retinitis
Clinical presentation Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Adult
What is this referring to
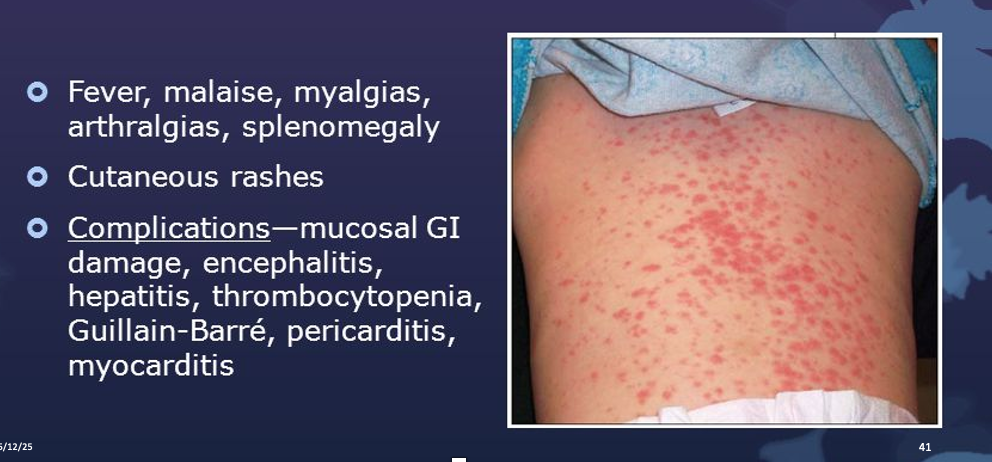
CMV in Immunocompetent
What is this referring to
Mononucleosis
EBV (Epstein Barr v.)
CMV
Differential diagnosis Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Adult
What is this referring to
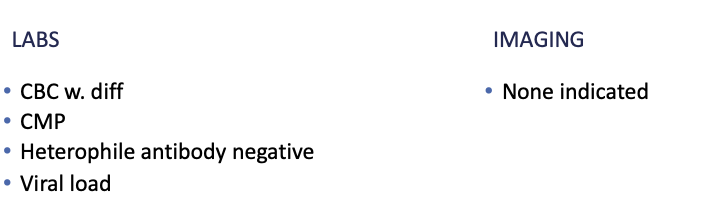
Diagnostics Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Adult
What is this referring to
CMV-specific immunoglobulin G (persists for 4-6 months)
CMV-specific immunoglobulin M (2-3 weeks)*
Active infection
How Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Adult is diagnosed
What is this referring to
Support care
Antipyretics
Analgesics
Hydration, hydration, hydration
Clinical intervention Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Adult
What is this referring to
1st line antivirals
Ganciclovir (Cytovene)
Valganciclovir (Valcyte)
Clinical pharmacotherapeutics Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Adult
What is the prognosis for Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Adult
Often self-limiting in immunocompetent patients
What is this referring to
A 13-year-old boy in rural Asia presents to a local hospital after a dog bite.
The dog did not belong to anybody and is often seen running around the area.
His parents report that this occurred a few weeks ago, but that they weren’t concerned until the boy started having low-grade fever and chills.
While the physician explains that they can administer both active and passive immunity, as symptoms have already started, the parents must prepare for the worst.
Rabies
What is this referring to
Negative, single stranded linear RNA virus
Rhabdovirus
Rabies
What is this referring to
MC in children
MC in Asia and Africa
Interaction with non-domestic animals is significant risk factor
Epidemiology Rabies
What is this referring to
Transmission
Bites of infected animals
Bats > raccoons and skunks > dogs (US)
Rare aerosol transmission
Bats
Incubation period weeks to months
Etiology Rabies
What is this referring to
Non-specific prodrome
Malaise
Fever
HA
Clinical history of rabies
What is this referring to

Clinical presentation of Rabies
What is this referring to
Botulism
Temporal lobe HSV-1 encephalitis
Differential Diagnosis of Rabies
What is this referring to
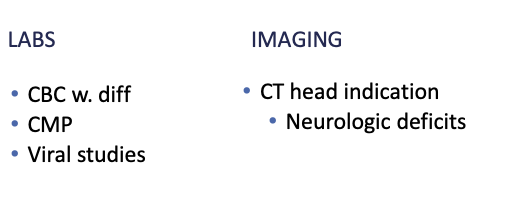
Diagnostics for Rabies
What is this referring to
Viral studies
Reverse transcription and PCR
Virus isolation
Histology
Brain biopsy
+ negri bodies
Eosinophilic inclusion bodies are pathognomonic
How is rabies diagnosed
What is this referring to
Wound cleaning
Wound healing by secondary intention if possible
Clinical intervention of rabies
What is this referring to
Indications
Bitten by known rabid animal
Bite from rapid or potentially rabid animal can’t be ruled out
Domestic animal
Observe for signs of rabies in domestic animals for 24-48 hours
If animal euthanized
Brain bx specimen to test for rabies
Drug regimen
Rabies vaccine monotherapy if patient has had previous rabies vaccine in the past
Rabies vaccine (IM) + rabies immune globulin
Patients who have not had a rabies vaccine in the past
Dosing schedule
Administered as soon after the bite as possible THEN
on days 3, 7, and 14
Clinical pharmacotherapeutics post-exposure prophylaxis
What is this referring to
Animal bites
1st line abx
Amoxicillin-Clavulanic Acid (Augmentin)
Alternative regimens
Clindamycin
Ciprofloxacin
Clinical pharmacotherapeutics Rabies
What is this referring to

Full recovery with early diagnosis and treatment
Respiratory failure leading to death if not managed aggressively
Prognosis of rabies