8. AQA GCSE Physics (9-1) Circuits
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
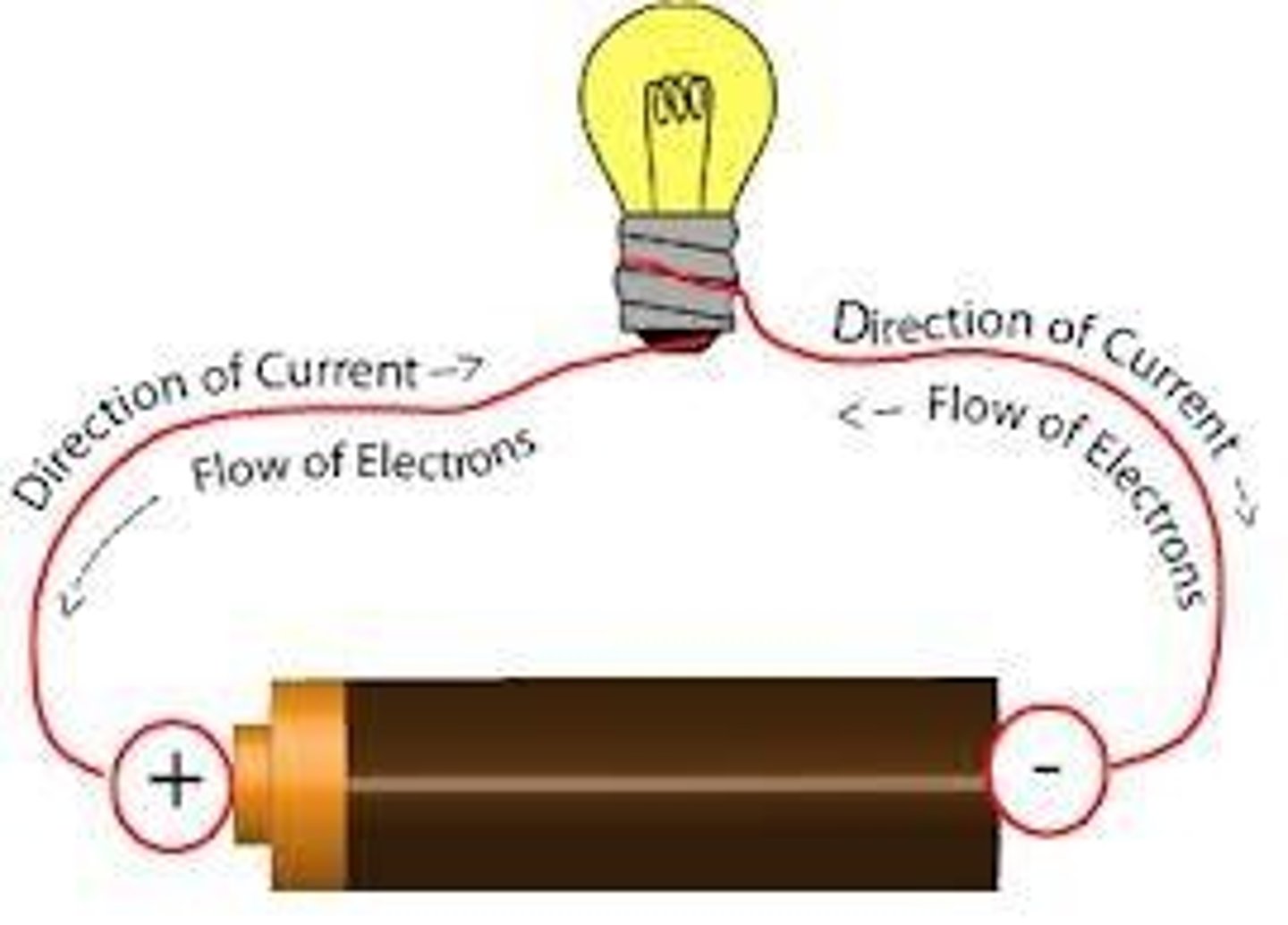
What is electric current
This is the rate of flow of electric charge
What is Potential difference (p.d)
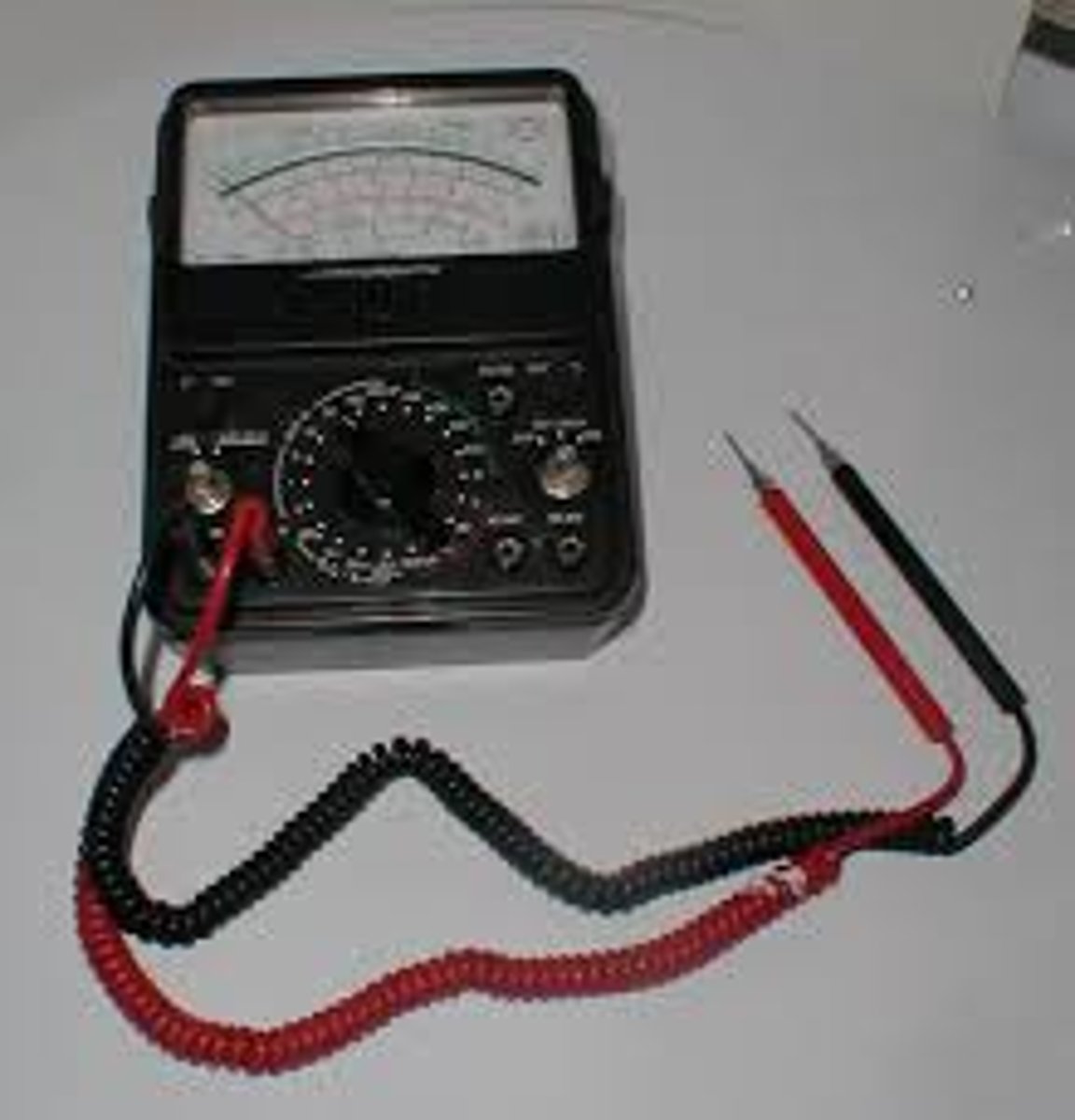
A measure of the electrical work done by a cell as charge flows around a circuit. This is also called voltage.

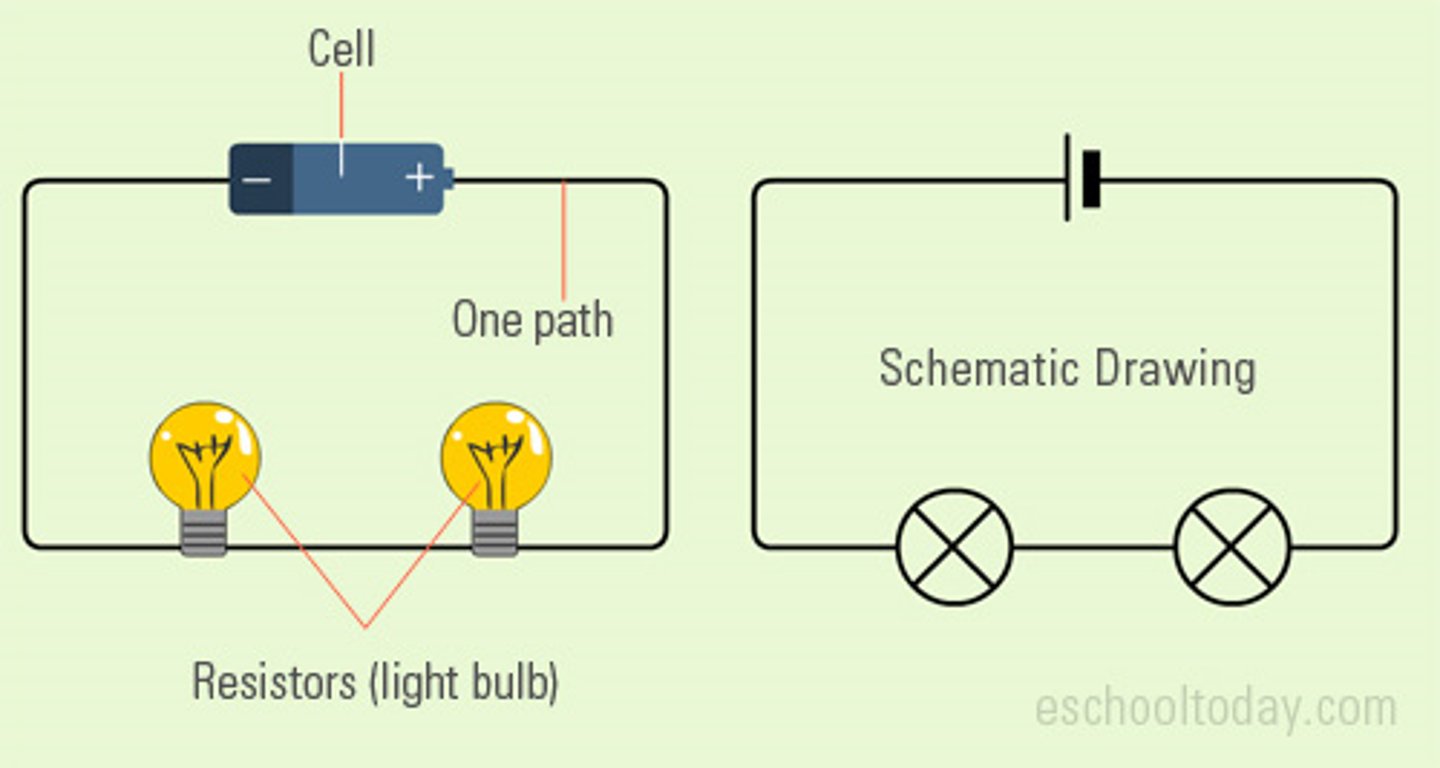
What is a series circuit?
A circuit that only has one loop (one route for the current to flow around)
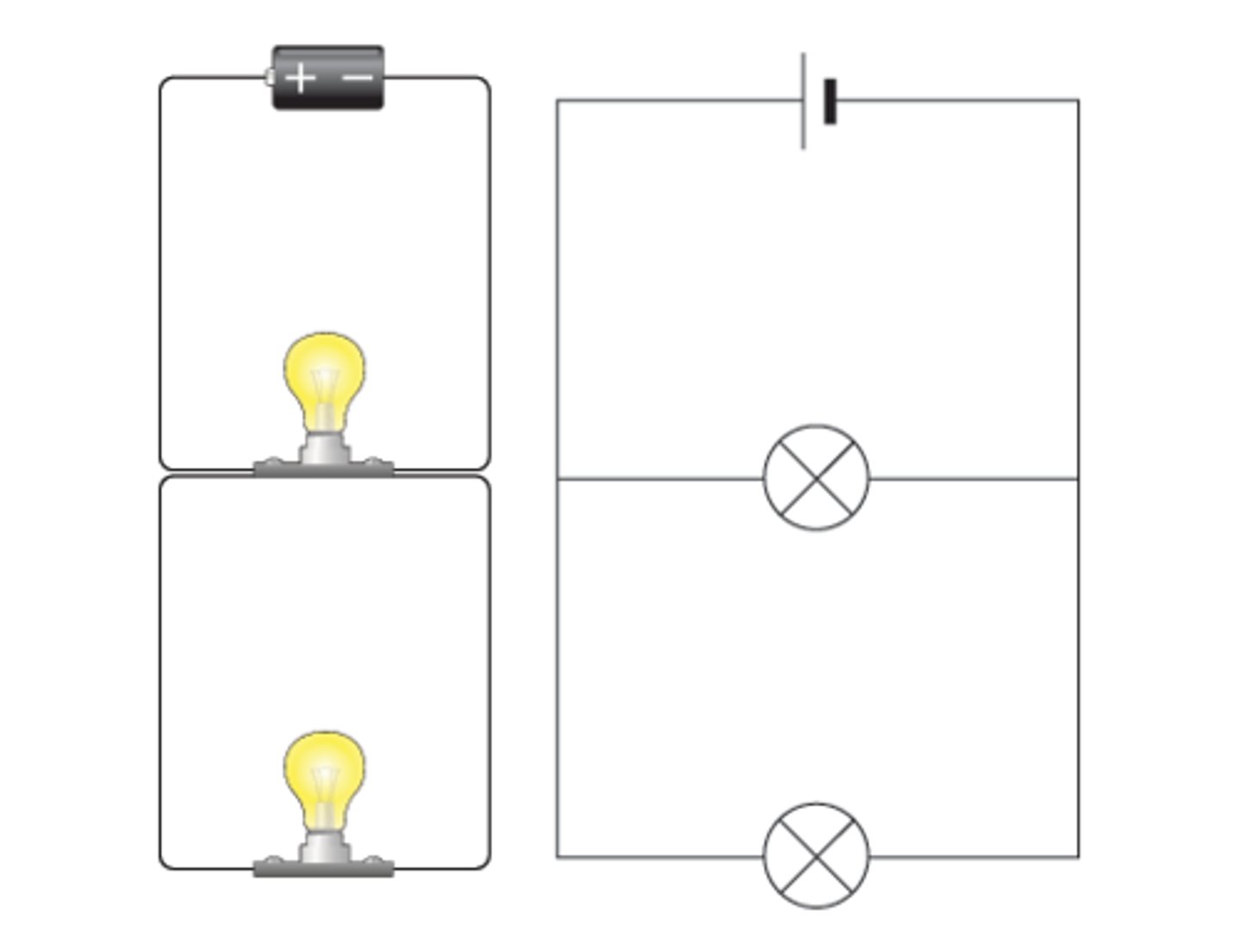
What is a parallel circuit
A circuit that has two or more loops that current can flow around
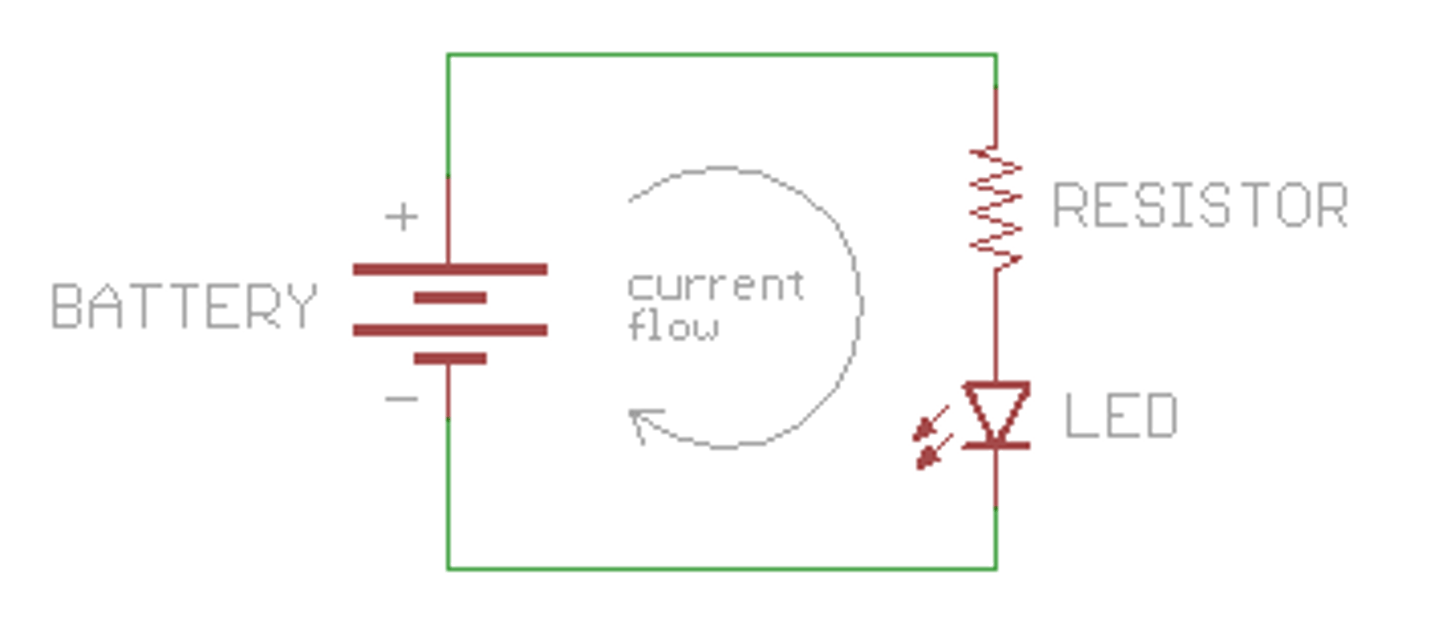
What causes current to flow around a closed circuit?
A cell, battery or power supply ( i.e. a source of potential difference) pushes the charge around the circuit
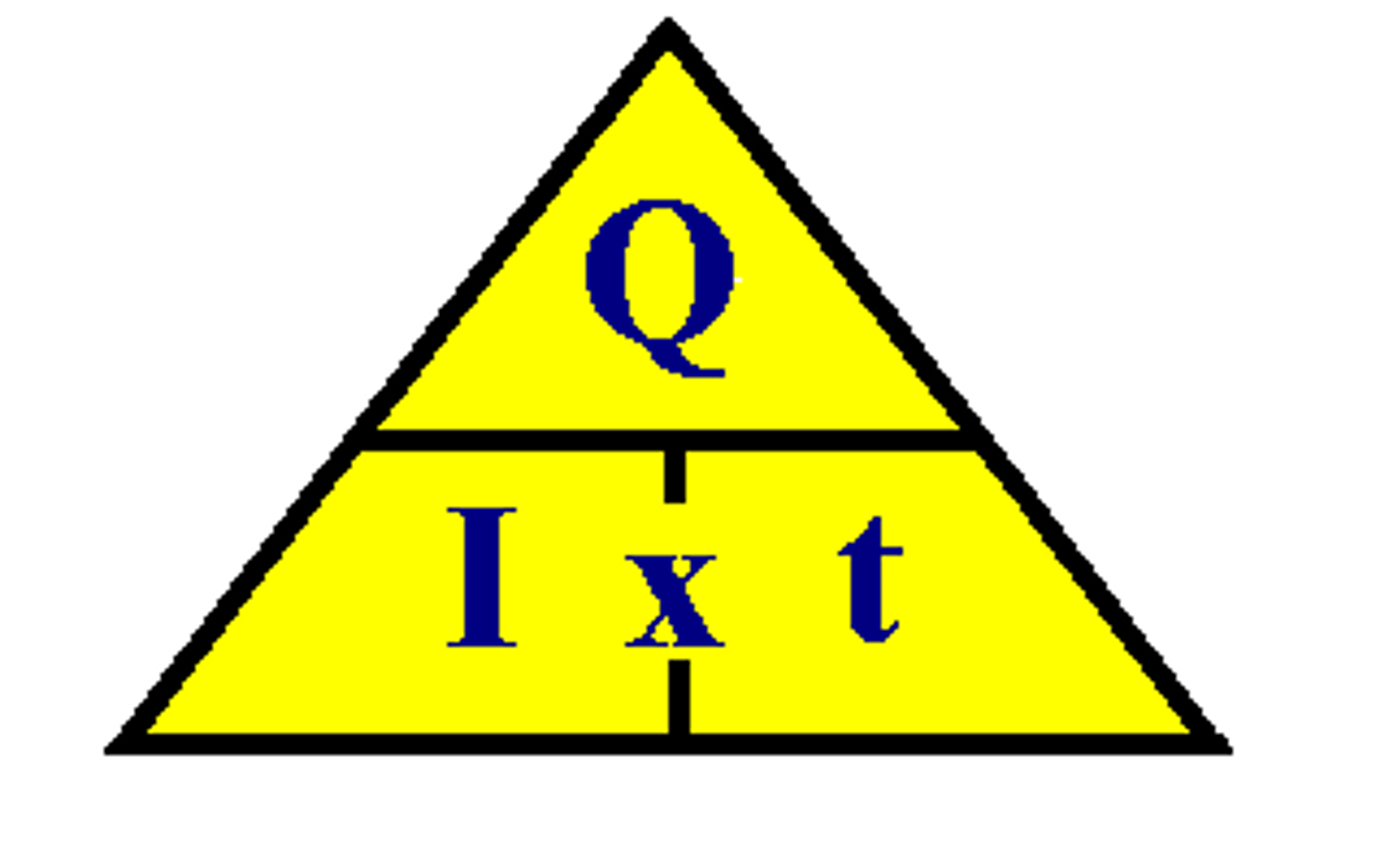
What equation links charge, current and time?
Charge = current x time or Q = I x t
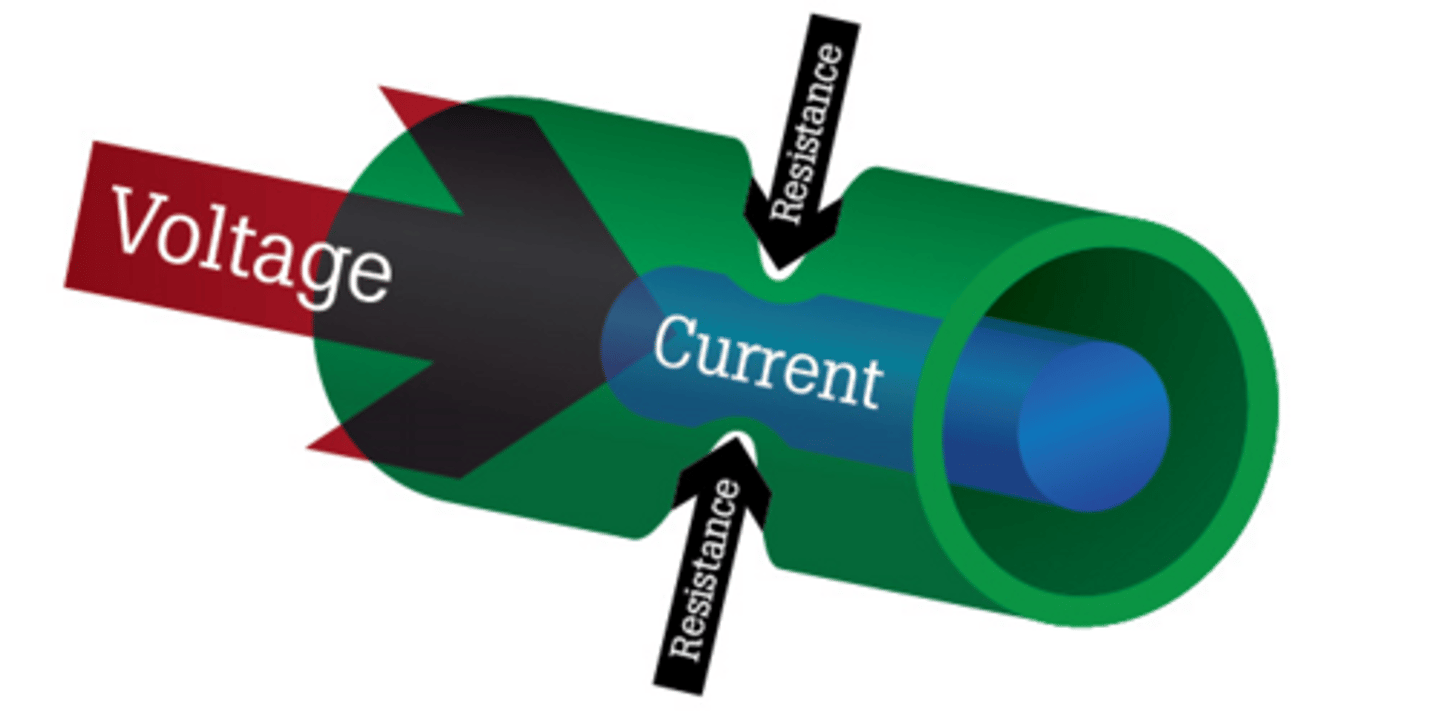
What is resistance?
Resistance opposes (resists) the current flowing round a circuit. The larger the resistance, the smaller the current flow for a given potential difference
What is resistance measured in?
Ohms, symbol Ω
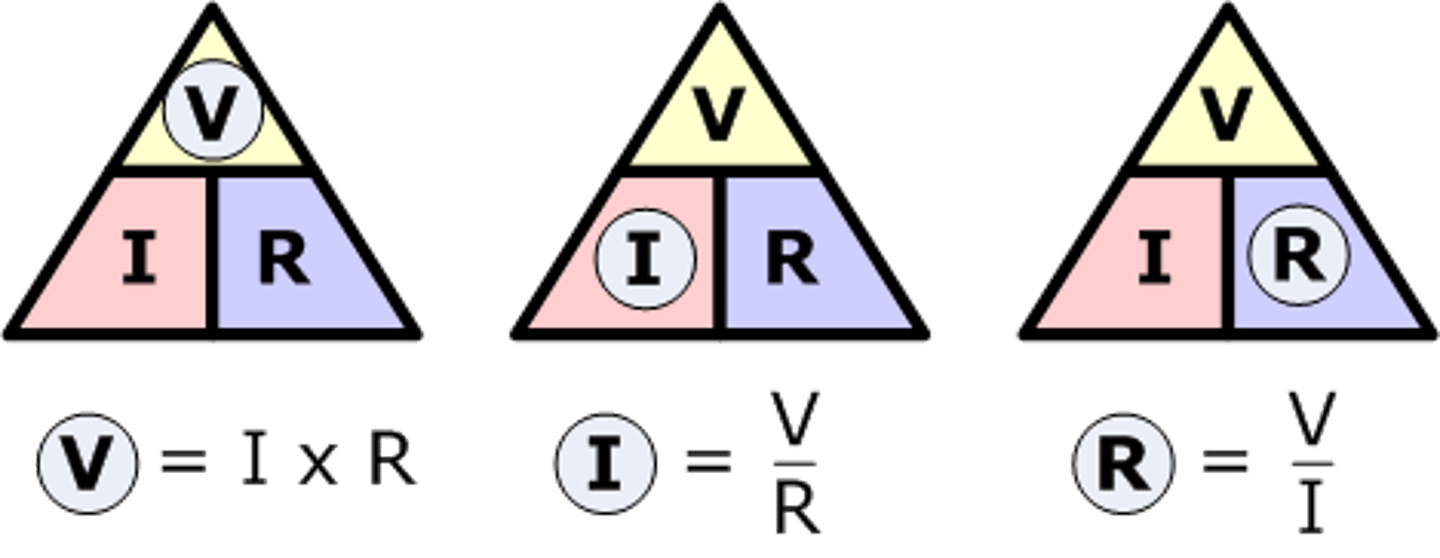
What equation links resistance, potential difference and current?
Ohms law: Potential difference = current x resistance
How do you measure current?
Using a ammeter
What is current measured in?
Amperes (amps), symbol A
How is an ammeter connected in a circuit.
In series
How is potential difference measured?
Using a voltmeter
What is potential difference measured in?
Volts, symbol V
How is a voltmeter connected in a circuit?
In parallel (across) the component
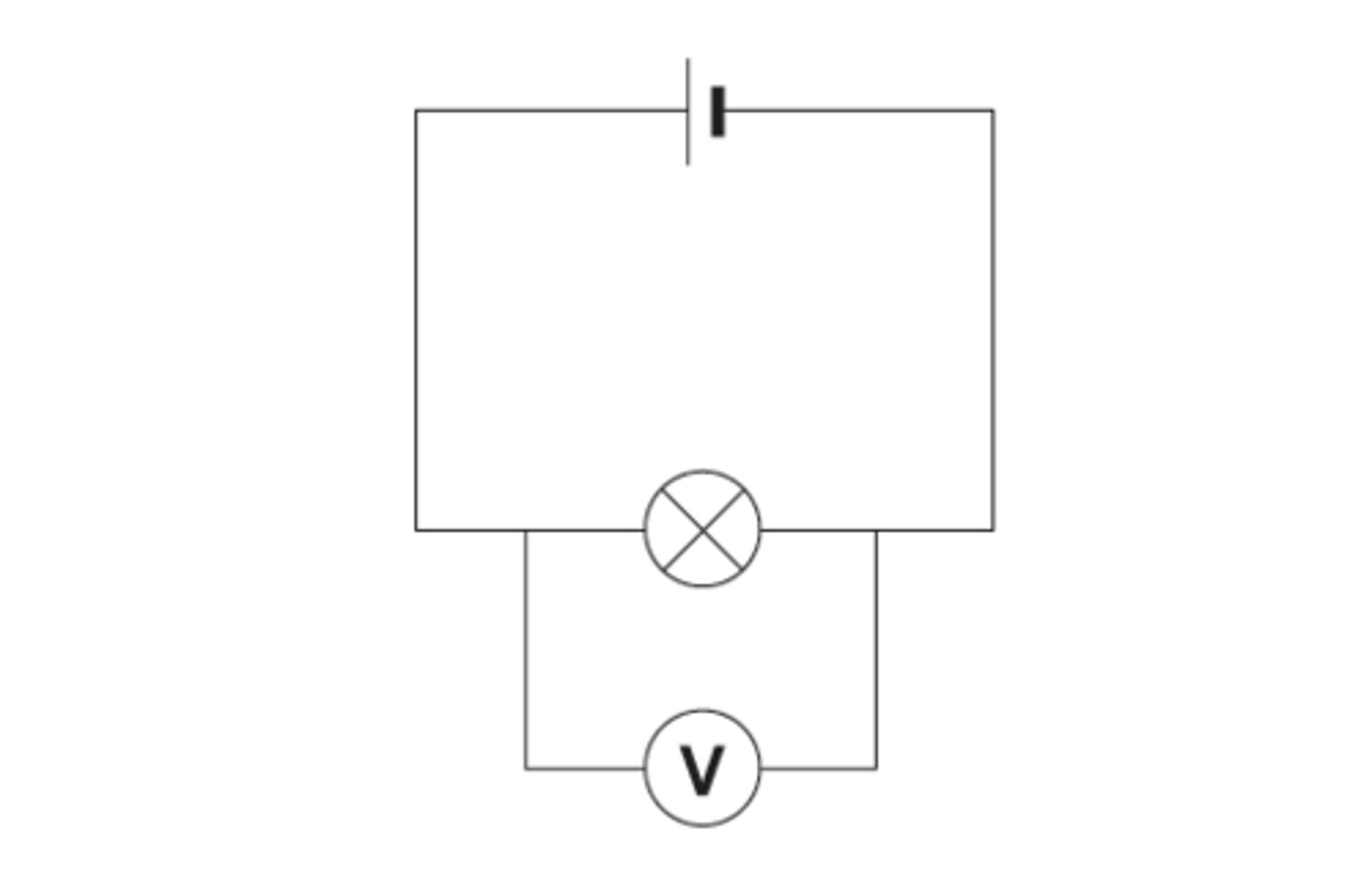
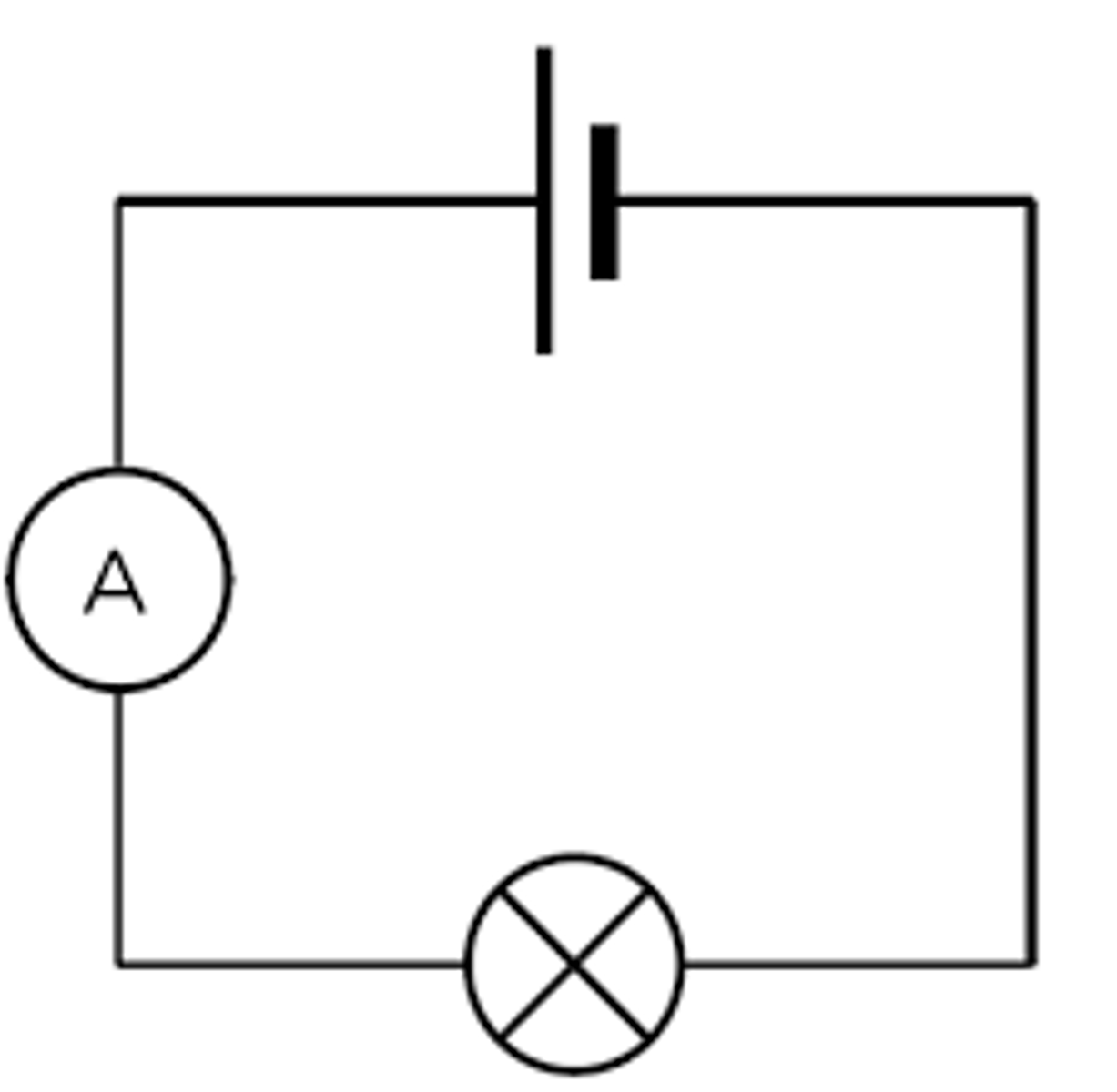
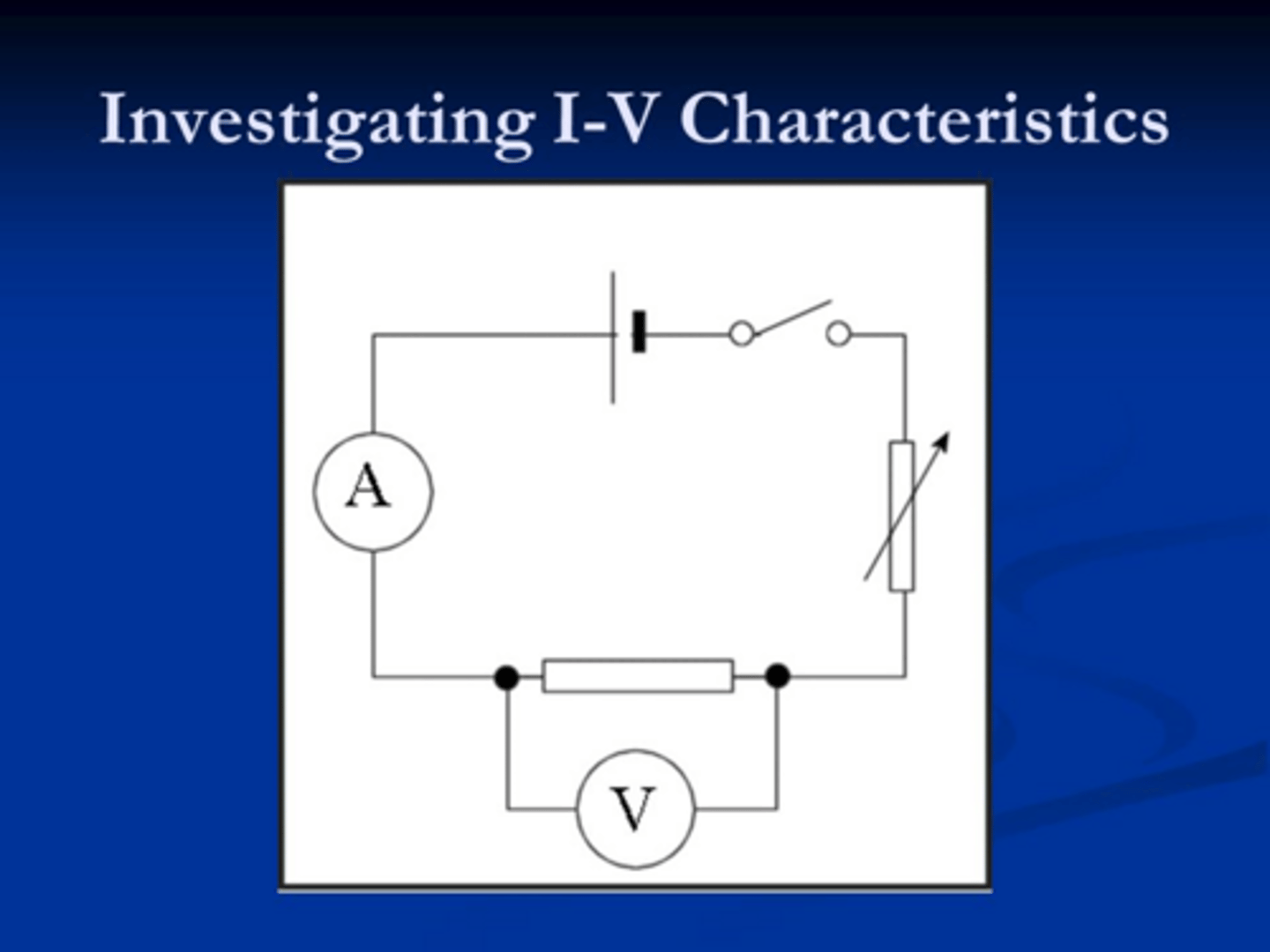
What circuit could you use to investigate the IV characteristics of a component?
This is the example for a resistor.
Note: the variable resistor is used to change the potential difference and current.
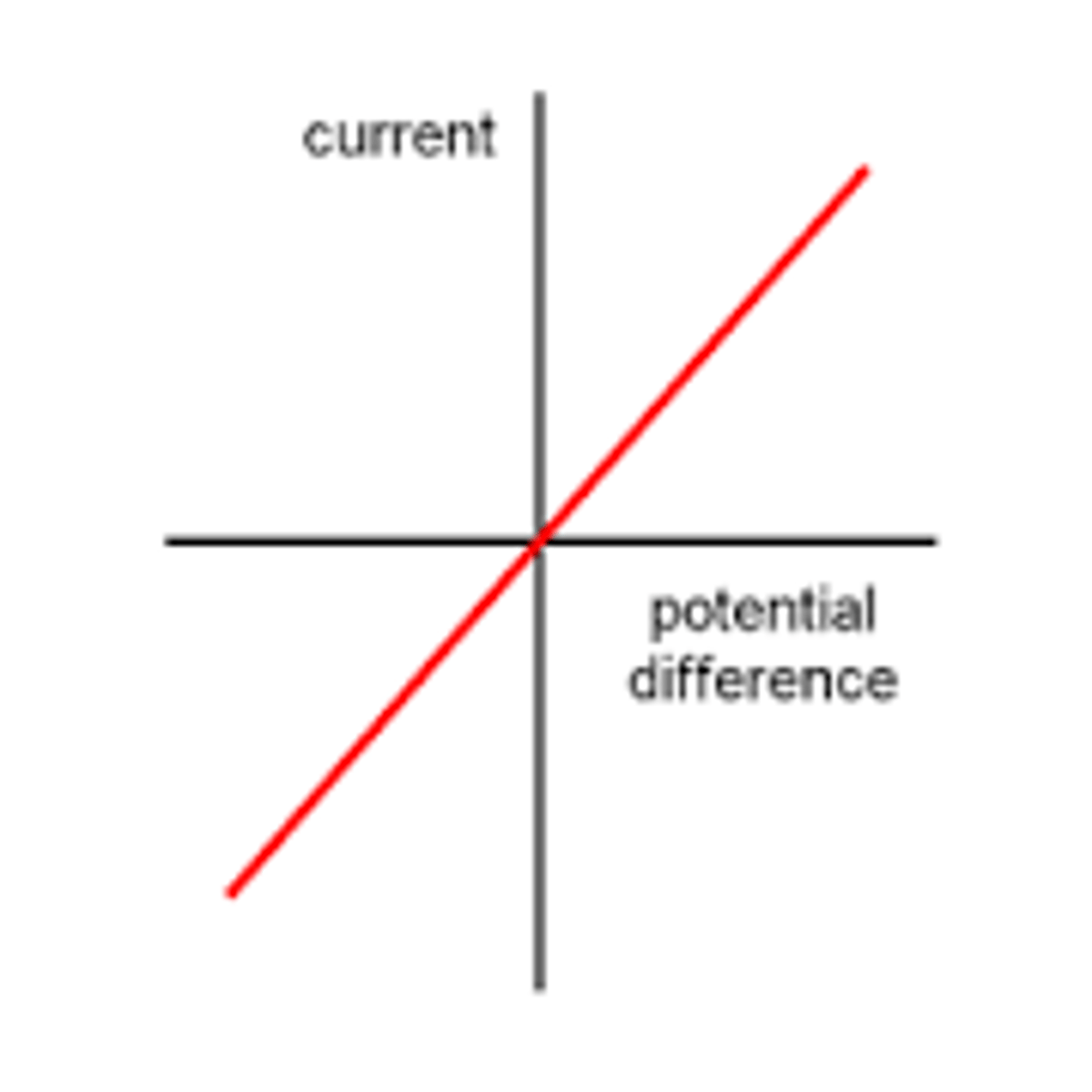
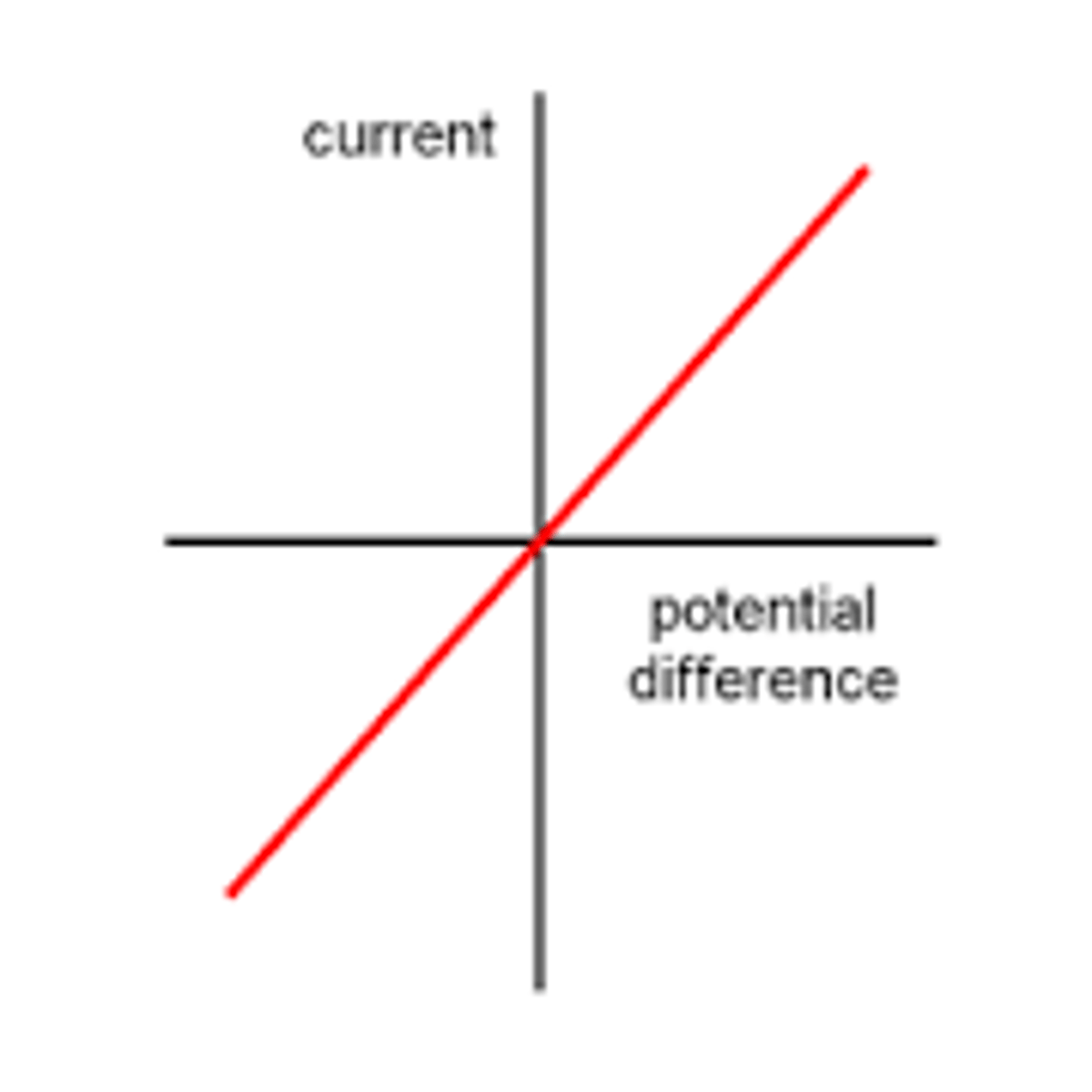
What is the IV graph for a fixed resistor (at constant temperature?
The p.d. and current are directly proportional showing the resistance is constant.
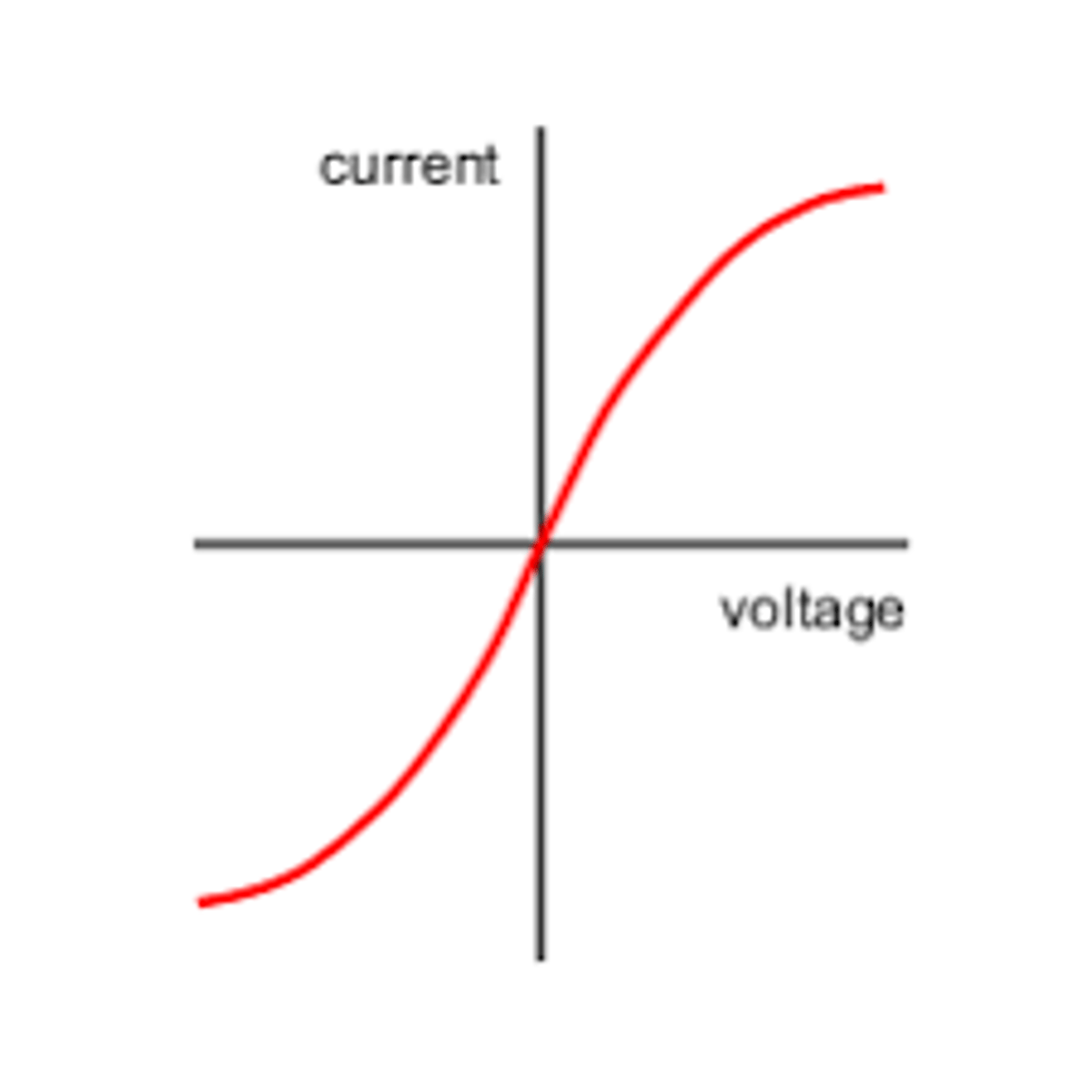
What is the IV graph for a filament lamp?
The p.d. and current are not directly proportional showing that resistance is changing. The higher the p.d. the higher the resistance as the temperature of the lamp increases.
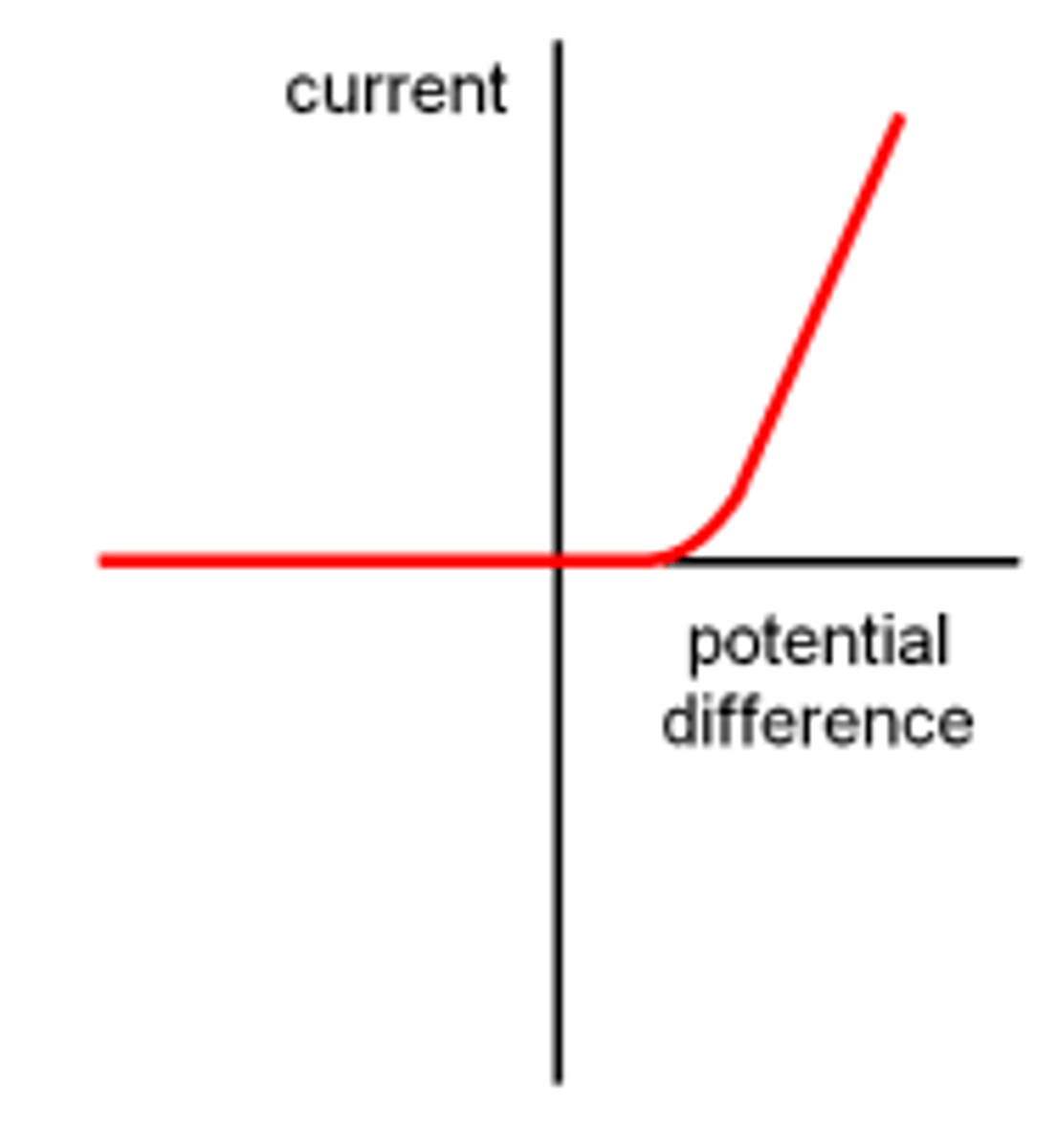
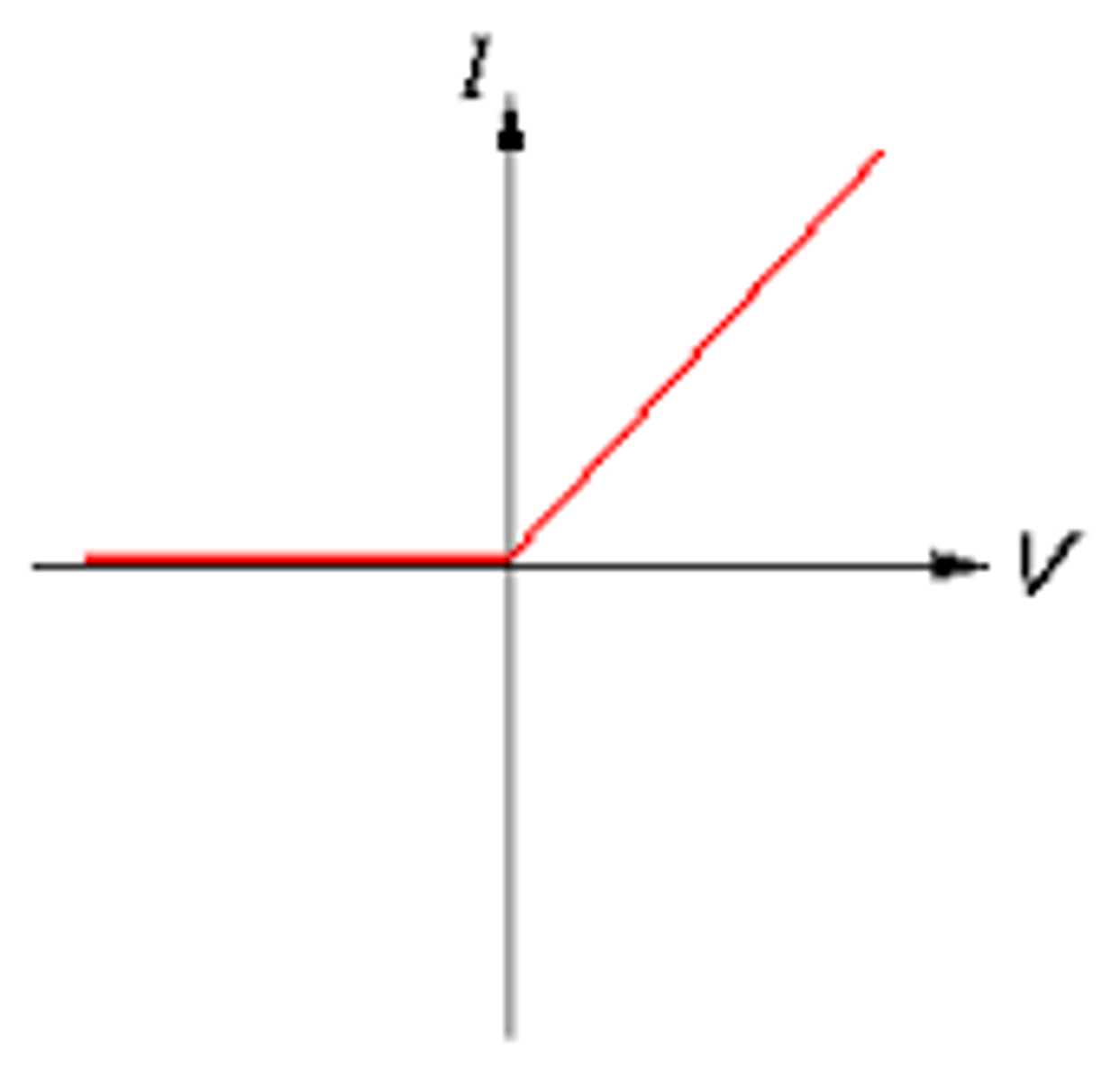
What is the IV graph for a diode?
The resistance of a diode is very low in one direction so current can flow. In the other direction the resistance is very high so no current flows.
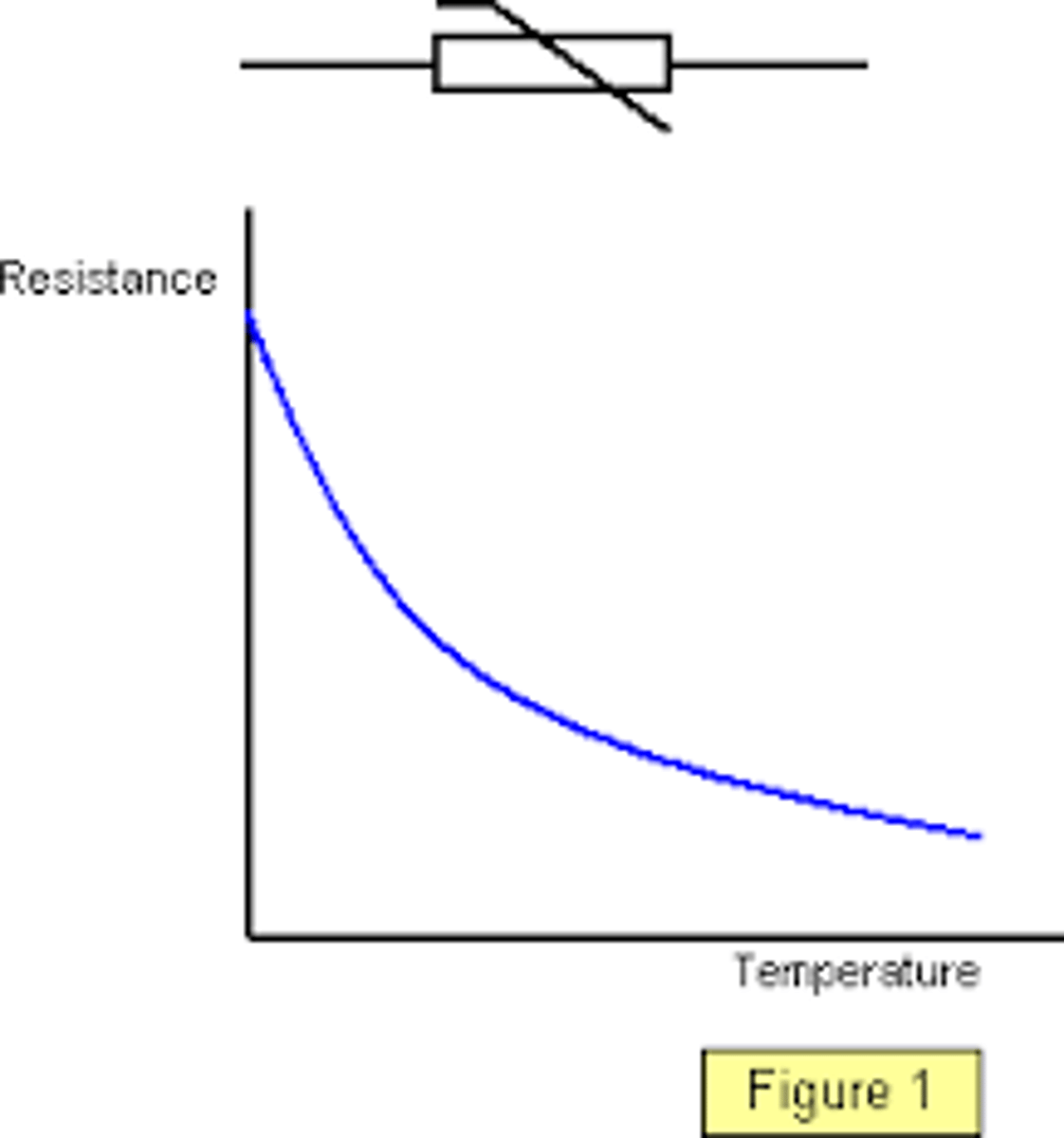
How does the resistance of a thermistor change as the temperature increases?
The resistance gets smaller so more current can flow.
Name some uses of thermistors
As a thermostat to turn on a heater if the temperature gets to hot.
In a fire alarm circuit.
In an electronic thermometer
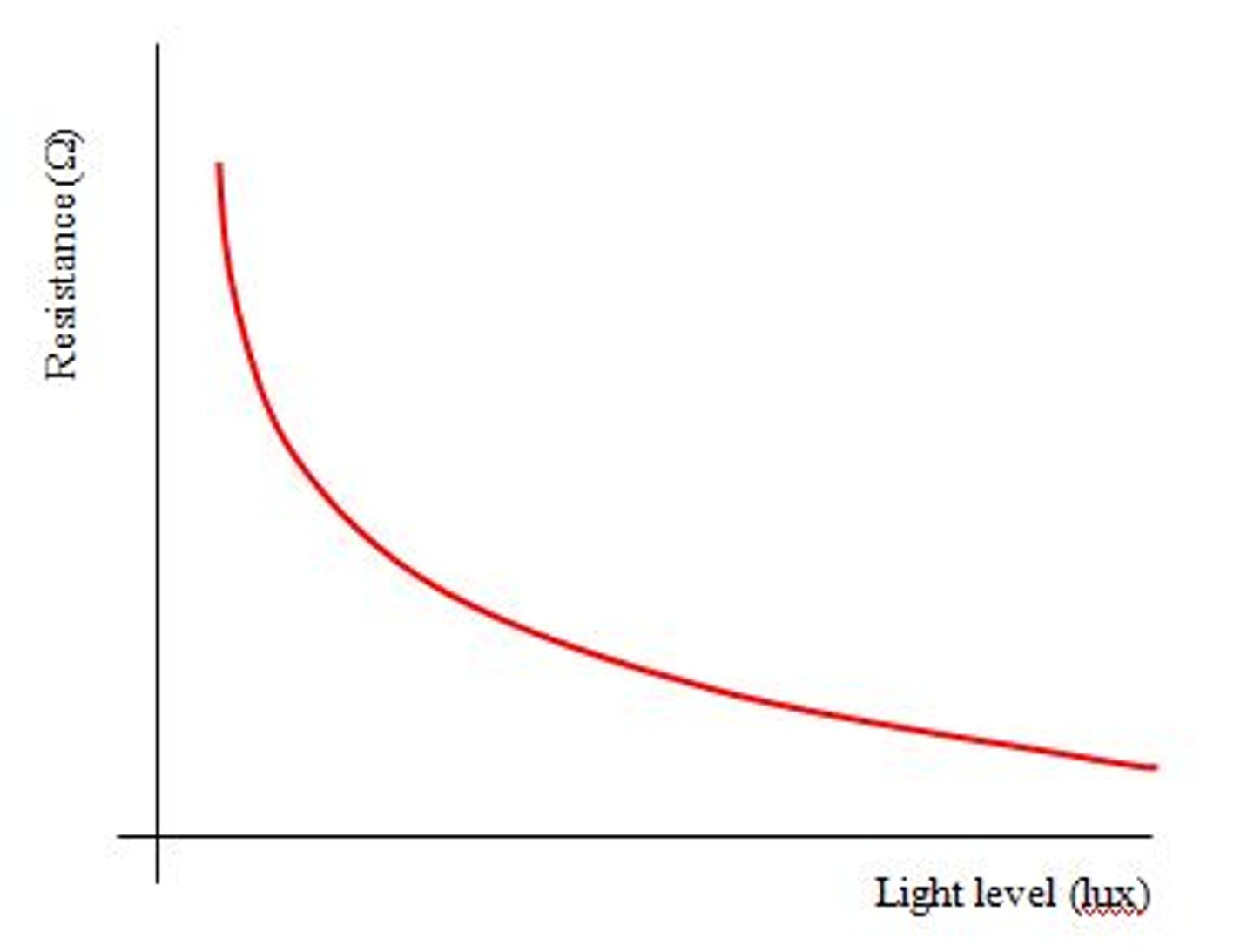
How does the resistance of a LDR change as light intensity increases?
The resistance gets smaller so more current can flow.
Name a use (application) of LDRs
To turn on street lights as it get dark.
Name an ohmic (linear) component
A fixed resistor where the IV graph is a straight line, resistance is constant.
Name some non-ohmic (non-linear) components
Lamp, diode, LED, LDR, thermistor. The resistance changes depending on the applied p.d. The IV graph is not a straight line.
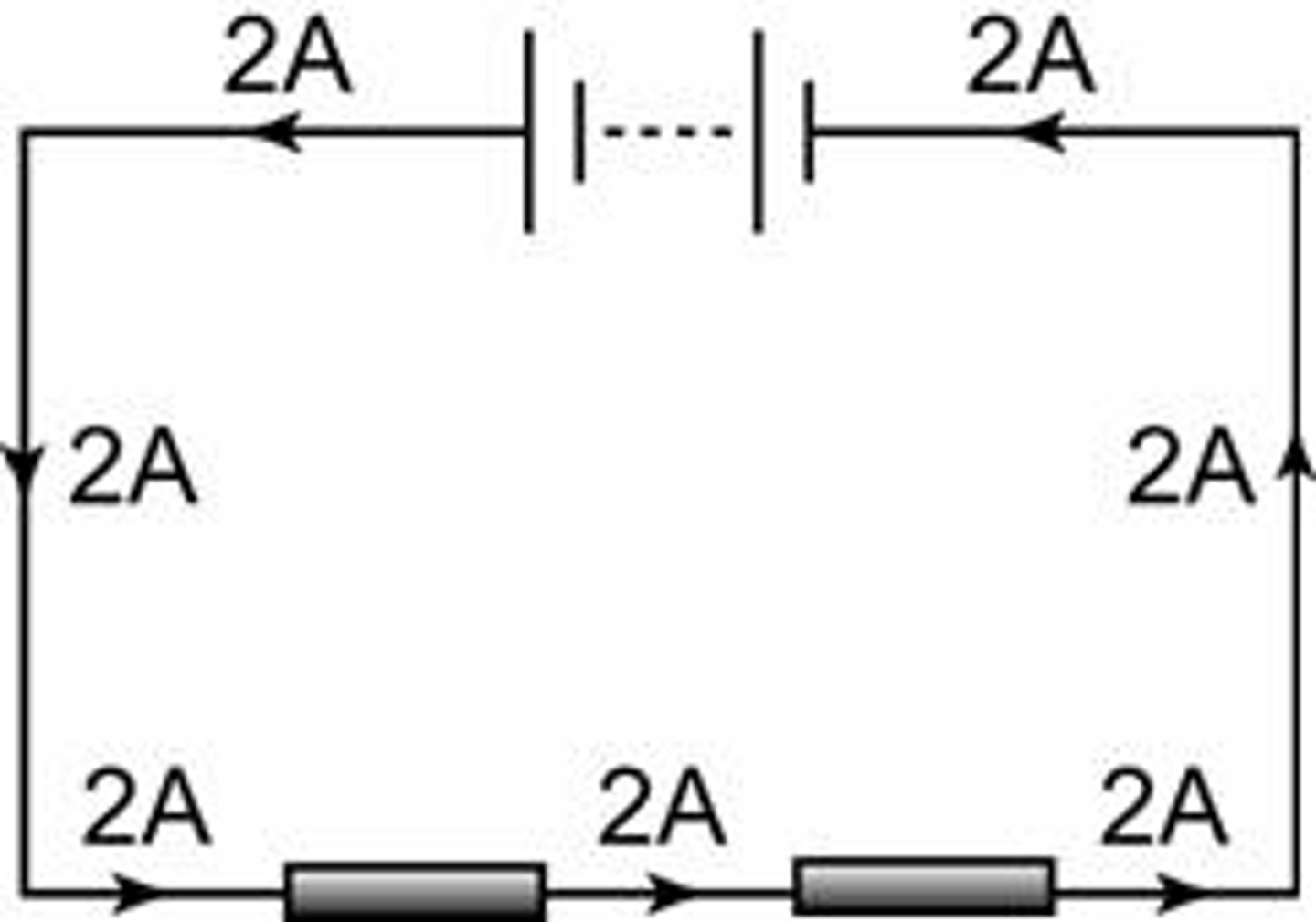
Describe the current in a series circuit
The current has the same value at every point in a series circuit
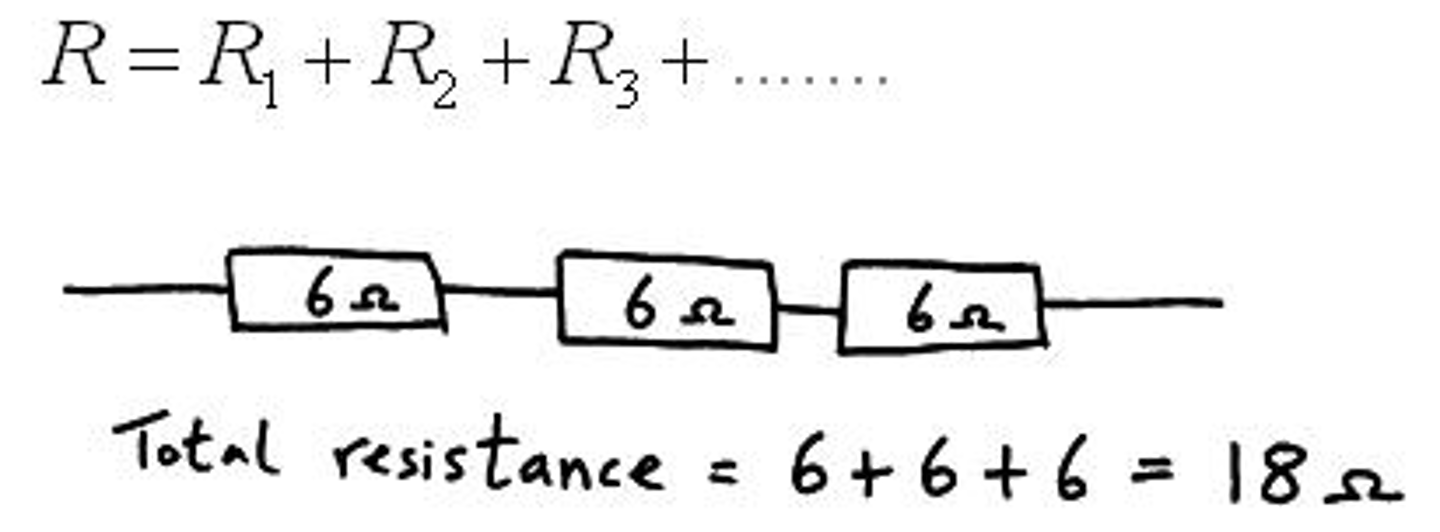
In a series circuit, how is the total resistance of the circuit calculated?
By adding up the individual resistances
What happens to the overall resistance of a series circuit as more components are added?
The overall resistance will increase as it is harder for current to flow.
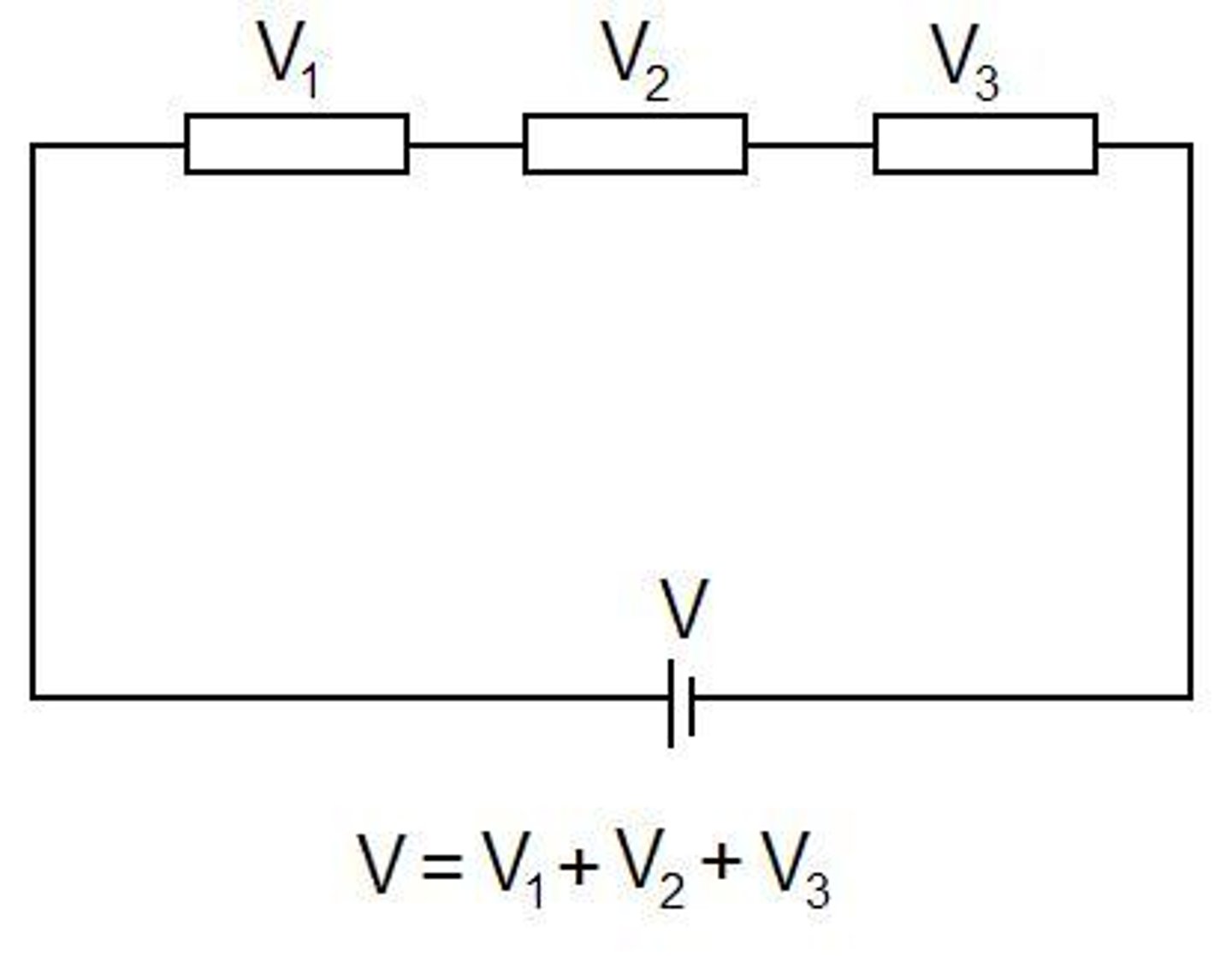
What happens to the supply potential difference in a series circuit?
It is shared between the circuit components. The components with higher resistance get more of the supply p.d.
What happens to current in a parallel circuit?
The current from the supply is divided up between the different loops of the circuit
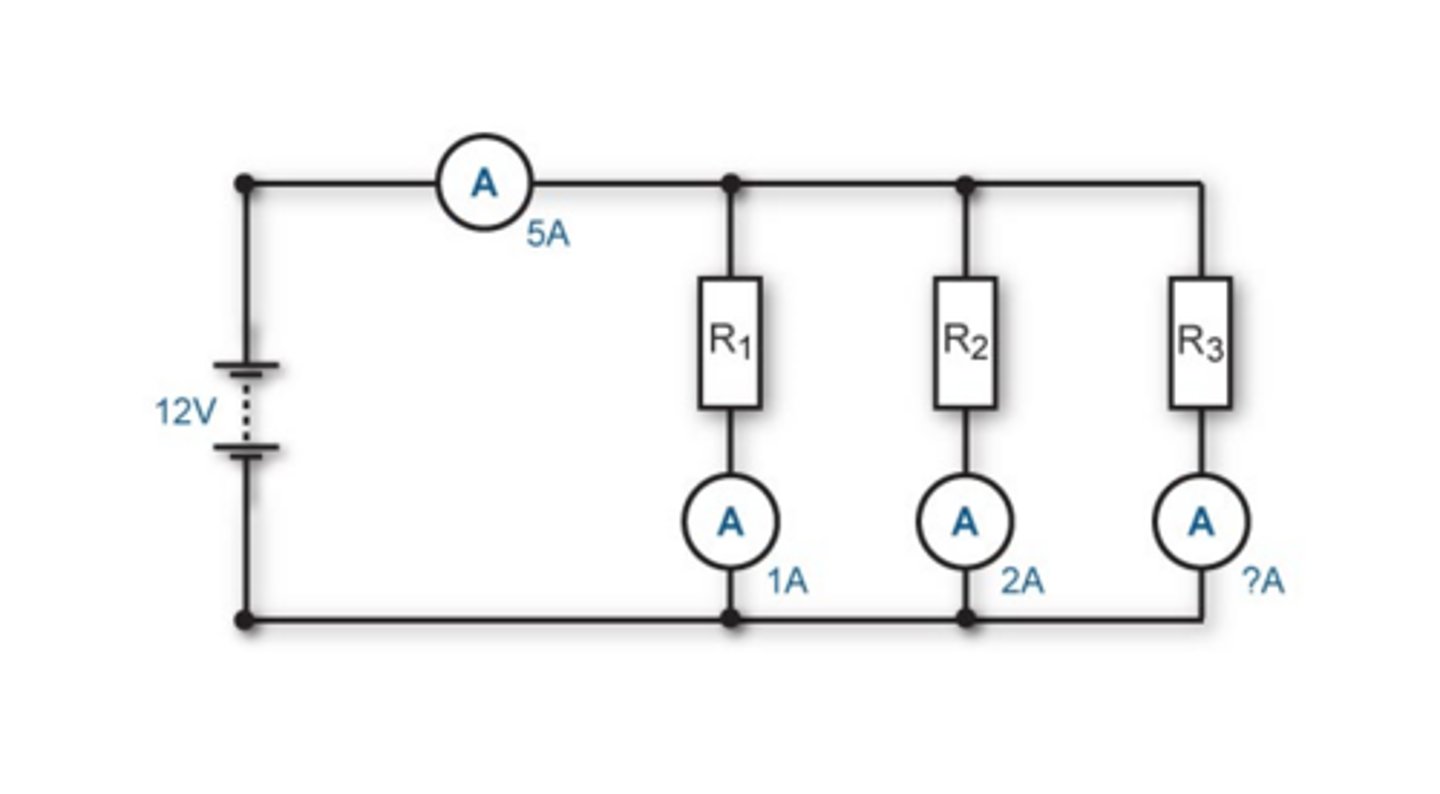
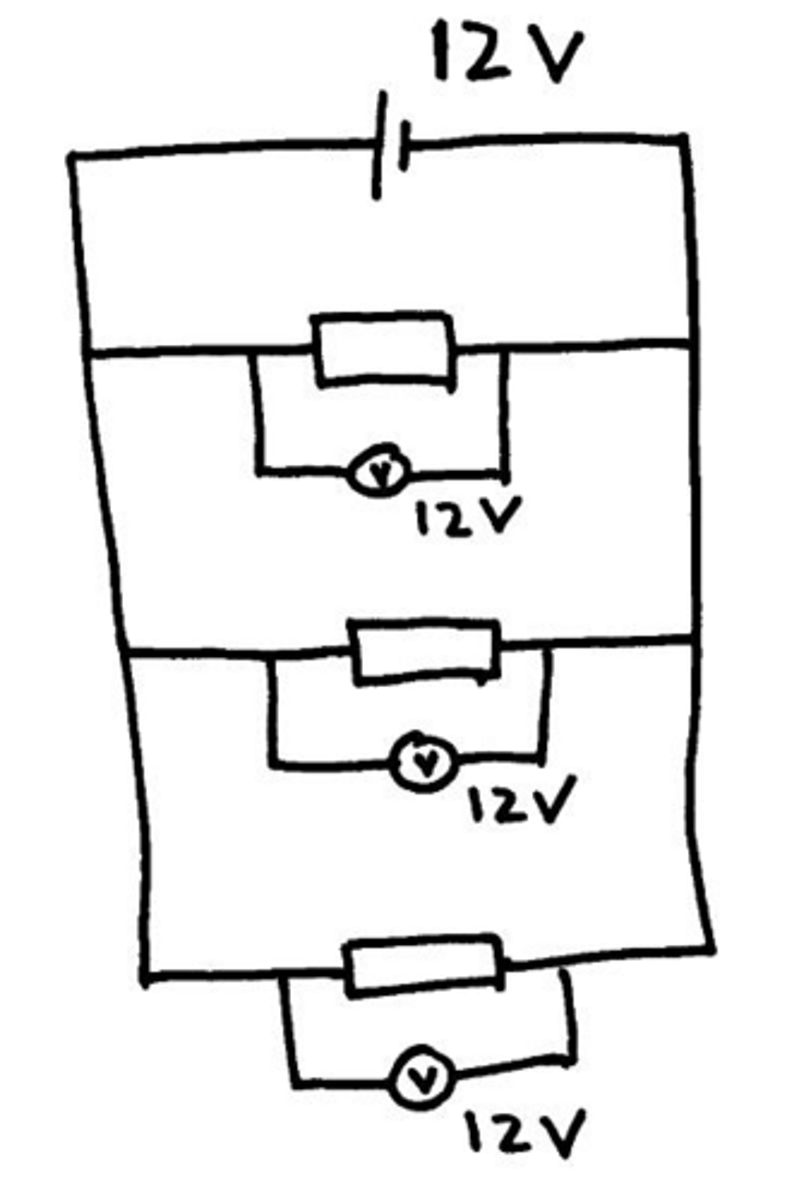
What happens to the potential difference in a parallel circuit?
The p.d. across each loop of the circuit is the same
What happens to the overall resistance of a parallel circuit as more resistors are added in parallel?
The overall resistance will decrease. This is because there are extra routes for the current to flow through so the overall current will increase. (Think about opening extra turnstiles at Thorpe Park, it is easier for the people to flow through the entrance.)