IGCSE Chemistry: Measurement, Techniques, States, and Solutions
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Stopwatch
Measures time in seconds/minutes.
Thermometer
Measures temperature/change in temperature.
Balance
Measures mass in grams.
Burette
Accurate volume to 0.1cm3 for any volume between 0.0 and 50.0 cm3.
Pipette
Accurate volume to 0.1cm3 for a fixed volume only.
Measuring cylinder
To measure an approximate volume.
Excess reagent
More than was required.
Filtration
Removes a solid from a liquid/solution.
Crystallisation
Removes a solvent from a solution.
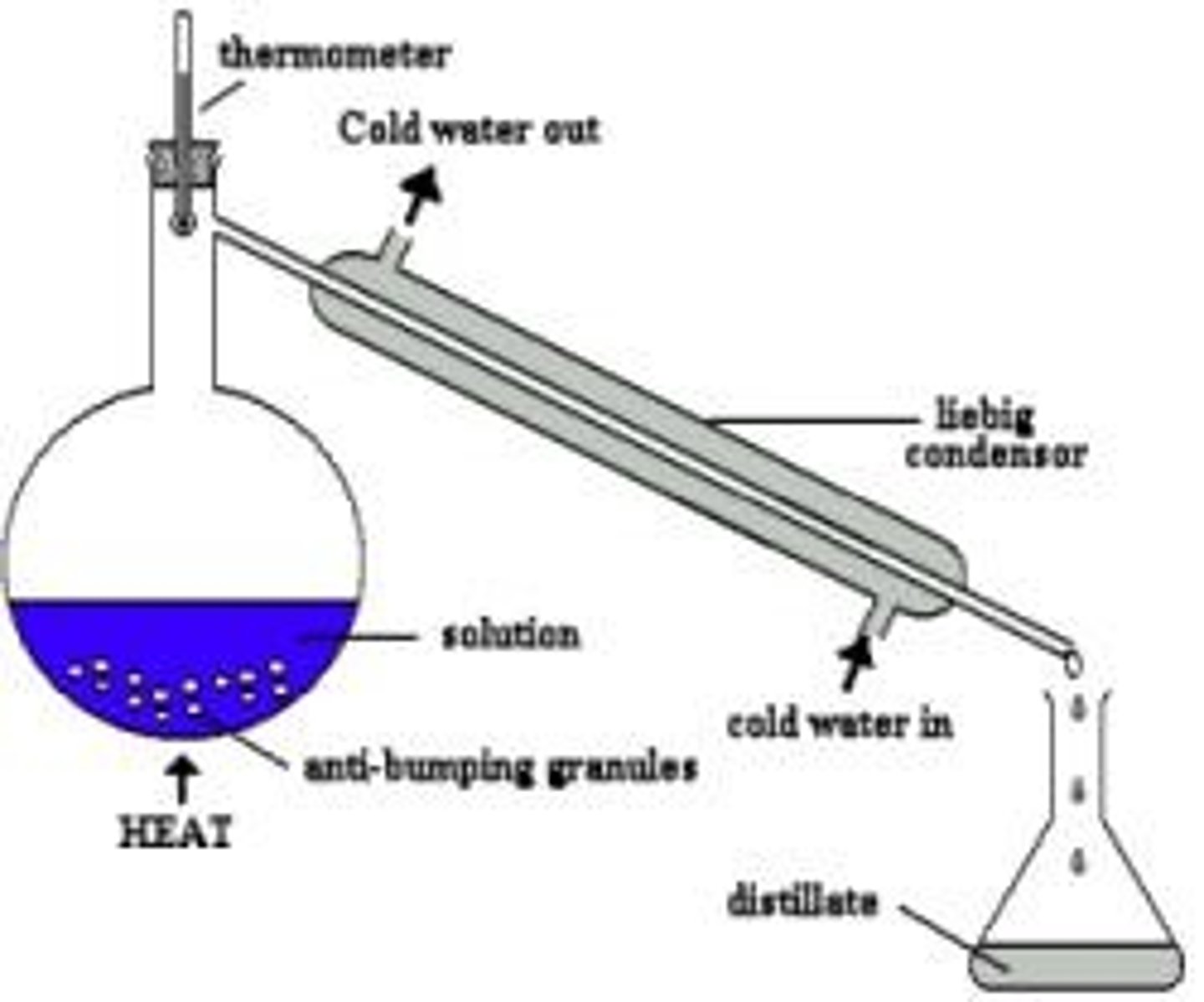
Simple Distillation
Separates substances with very different boiling points.
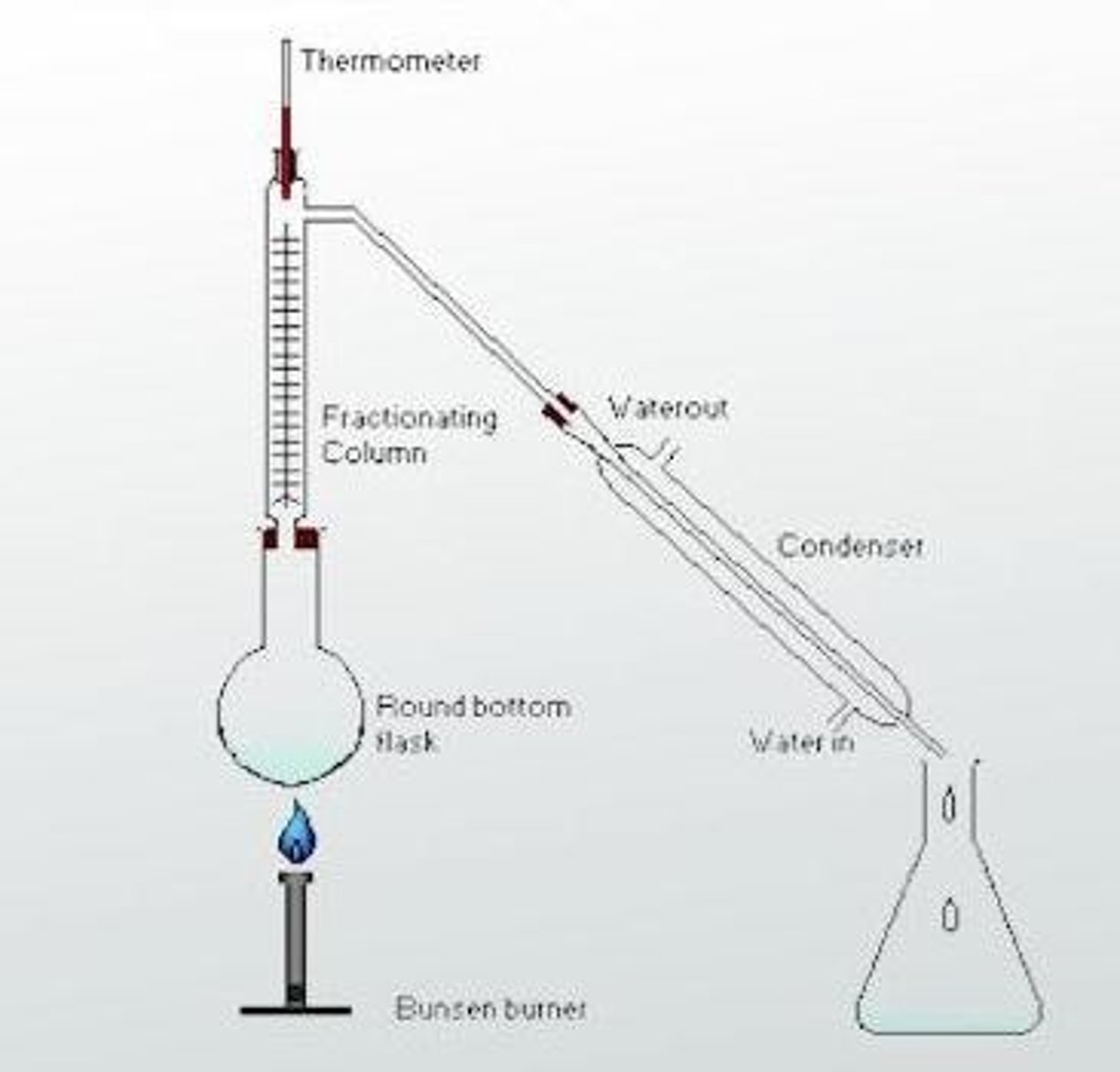
Fractional Distillation
Separates substances with different boiling points using a temperature gradient.
Determining crystallisation/saturation point
If crystals form, the solution is at crystallisation point.
Purity
Check melting point/boiling point.
Impure substance
Melts/boils at a range of temperatures around the melting point/boiling point.
Fractionating column
A component used in fractional distillation that has a temperature gradient, hotter at the bottom and cooler at the top.
Condenser
A device required for both simple and fractional distillation that cools vapour and condenses it back into liquid.
Anti-bumping granules
Granules used in distillation to prevent the flask from bumping too much.
Boiling point (bp)
The temperature at which a substance changes from liquid to gas.
Rf value
A value used in chromatography to identify a substance, calculated as Distance moved by substance ÷ Distance moved by solvent.
Chromatography
A technique that separates molecules by size, mass, and solubility, often used for dyes or coloured substances.
Baseline/origin
The starting line on chromatography paper where samples are placed.
Solvent front
The furthest point reached by the solvent in chromatography.
Distance moved by substance
The distance a substance travels from the baseline in chromatography.
Distance moved by solvent
The distance the solvent travels from the baseline in chromatography.
Temperature gradient
A variation in temperature along the length of the fractionating column in fractional distillation.
Mixture
A combination of two or more substances that can be separated by physical means.
Flask
A container used to collect the liquid in distillation.
Beaker
A container that can also be used to collect the liquid in distillation.
Vapour
The gaseous state of a substance that is typically liquid at room temperature.
Chromatography paper
The medium used in chromatography to separate substances.
Watch glass
A glass dish used to cover the chromatography paper to prevent solvent evaporation.
Unknowns
Samples of substances whose identities are to be determined through chromatography.
Solvent
A liquid that dissolves a solute to form a solution, used in chromatography.
Collection
The process of gathering the separated substances after distillation or chromatography.
Separation
The act of dividing a mixture into its individual components.
Kinetic Particle Theory
The theory that explains how energy must be supplied or removed to change one state of matter to another.
Melting
The change from solid to liquid.
Boiling
The change from liquid to gas.
Freezing
The change from liquid to solid.
Condensation
The change from gas to liquid.
Sublimation
The direct change of a solid to a gas or gas to a solid without passing through the liquid state.
Brownian Motion
The random movement of particles, evidenced by suspended particles in a liquid moving in random directions.
Diffusion
The random movement and mixing of particles causing the substance to spread.
States of Matter
Matter may be solid, liquid, or gas.
Atoms
The basic units that make up all matter.
Molecules
Atoms combined together.
Compounds
Substances composed of two or more different types of atoms chemically bonded at a fixed ratio
Elements
Substances composed of only one type of atom.
Gas Laws
Properties of gases, including how they exert pressure and respond to temperature changes.
Pressure in gases
The force exerted by gas particles colliding with the surface of a container.
Temperature effect on gas
Increased temperature leads to faster movement of particles, causing more collisions and increased pressure.
Elasticity of gases
Increases in pressure lead to increases in volume as the container stretches.
Suspension
A mixture where solid particles are dispersed in a liquid.
Antibody based locating agent
A substance added to indicate the location of separated substances that have no color.
Rate of diffusion factors
Dependent upon molecular mass; lower molecular mass = faster diffusion, higher molecular mass = slower diffusion.
Temperature effect on diffusion
Higher temperature = faster diffusion, lower temperature = slower diffusion.
Evidence of diffusion
A perfume sprayed in one corner of the room spreads until the entire room is filled with that perfume.
Pure substances properties
Have a fixed mp and bp
Impure substances
Melt or boil at a range of temperatures, usually close to the mp/bp of the pure substance.
Salt on roads
Salt is put on roads during winter because water freezes at about -5°C rather than 0°C.
Dilution
A way of changing the concentration of a solution in a measured way.

Diluted solution example
The solution has been diluted to 10% of the original at each step.
Solute
A solid that can dissolve.
Solution
A solvent containing a dissolved solid.
Soluble meaning
A solid that can dissolve.
Insoluble
A solid that cannot dissolve.
Saturated solution
A solution with the maximum mass of a solute dissolved.
Crystallisation of saturated solutions
Saturated solutions crystallise quickly.
unit of solubility
Measured in grams per litre (g/L).
Solubility per 100g of solvent
The mass of solute that can dissolve in 100g of solvent.
Solubility curves
Plotted to determine the theoretical solubility of a substance at a particular temperature.
Mixtures
Made up of a range of different substances that are easily separated.
Identifying substances
Use the name and/or formula to identify what a substance is.
Atom
The simplest unit of matter.
Compound
Two or more atoms chemically joined in a fixed ratio.
Element
Composed of only one type of atom.
Impure
Contains more than one substance.
Pure
Contains only one substance.
Water of crystallisation/hydration
The water present in a fixed ratio when crystals form.