Grade 11 Pre-AP Biology - Unit 3 Test Review
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
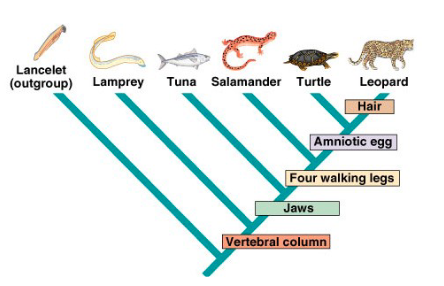
Phylogenetic Tree
diagram that shows the relationships between different species like a family tree
Dichotomous Tree
type of phylogenetic tree that branches off in pairs
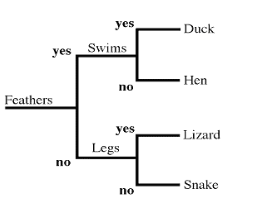
Cladogram
type of phylogenetic tree that is arranged to emphasize which species are more primitive vs. more evolved
most primitive species are on the left
most evolved species are on the right
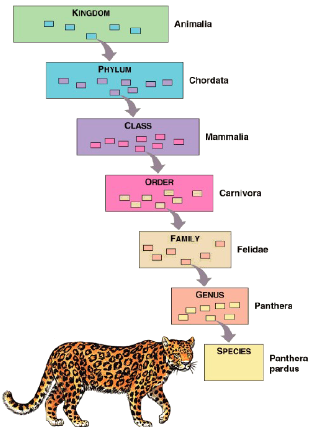
Levels of Classification
Domain → Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species
Dumb King Phillip Can’t Order Fried Garlic Sauce
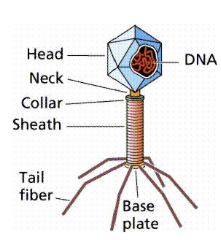
How do Viruses work?
virus lands on the surface of the cell and injects its own DNA into the host
the viral DNA then incorporates itself into the host DNA without the host knowing
lysogenic cycle → lytic cycle
Lysogenic Cycle
host divides and copies the viral DNA along with its own, creating new cells that also carry the infection
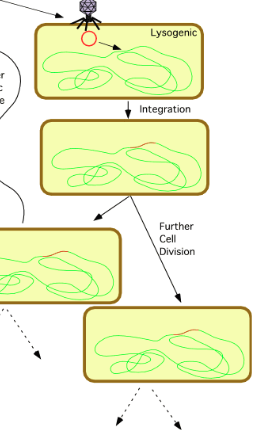
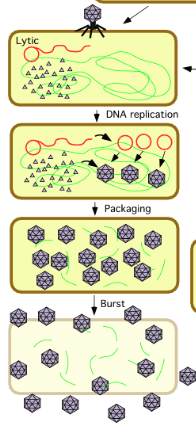
Lytic Cycle
viral DNA takes over the host’s cell and forces the cell to make viruses
once the viruses are made, the cell bursts open - spraying more viruses and leading to more infection
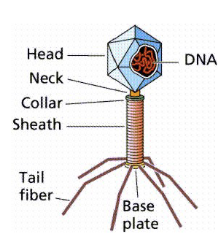
Why are viruses considered non-living?
consist of little more than strands of DNA/RNA surrounded by a protective protein coat
have no cellular organelles - must hijack other organisms in order to survive
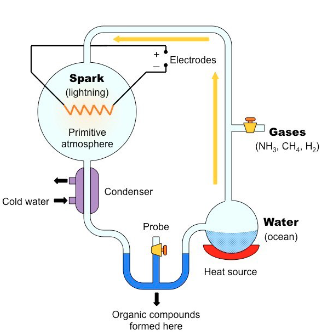
Abiogenesis: Oparin and Haldane
proposed that it was possible for organic molecules to be synthesized from non-living things, and that the first cells could have been made this way
very little oxygen in the atmosphere (oxygen prevents random formations of organic molecules)
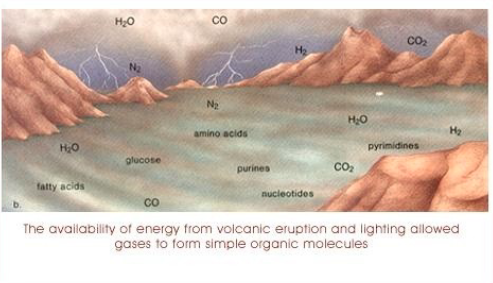
Miller-Urey Experiment
tested Oparin and Haldane’s hypothesis by recreating the conditions of the early Earth inside glass tubes
Panspermia
the idea that life exists throughout the universe
the Earth may have been struck by an asteroid containing traces of life
Heterotroph
need to obtain energy by gathering materials from its environment
Autotroph
can generate its own energy using sunlight (e.g. photosynthesis)
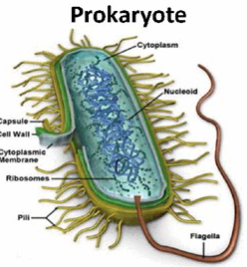
Prokaryotic
cellular components just thrown in the cell; no organization
no nucleus (DNA/RNA floats around)
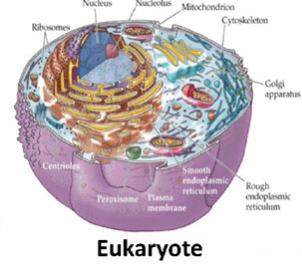
Eukaryotic
have organelles + nucleus + organization
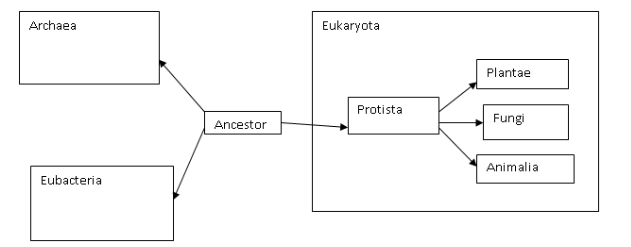
Domains
Archaea
Eubacteria
Eukaryota
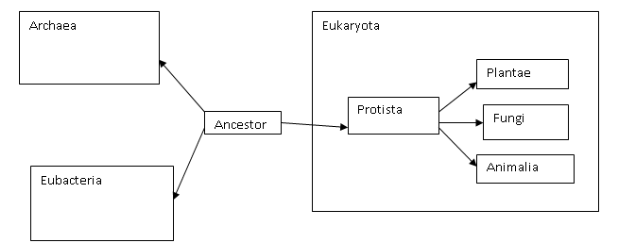
Kingdoms
Archaea
Eubacteria
Protists
Plants
Fungi
Animals
Archaea
unicellular, prokaryotic
ancient bacteria
found in extreme environments where no other cells could survive
Eubacteria (Bacteria)
unicellular, prokaryotic
more ‘modern’ type of bacteria found today
How do Bacteria Reproduce?
asexually
cells divide in a process called binary fission
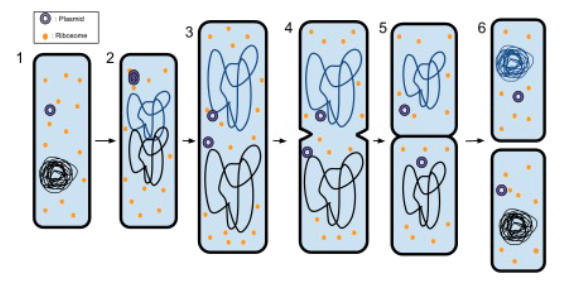
Binary Fission
the method in which bacteria asexually reproduce
DNA is stored in a loop (circular chromosome)
usually one main loop and some smaller loops called plasmids
loops are copied and the cell divides sending one of each loops to either side
Plasmid
small loops of DNA within bacteria
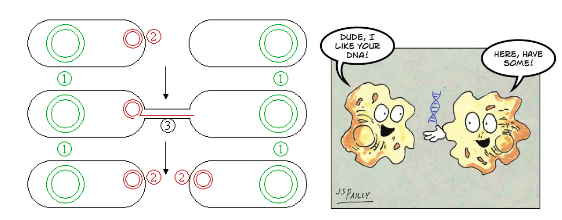
Conjugation
direct transfer of a plasmid from cell to cell
Most Accurate way to Classify Bacteria
analysis of the genetic sequence
Coccus

Diplococci
Streptococci
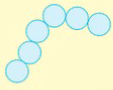
Staphylococci
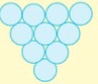
Sarcina
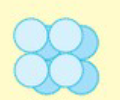
Tetrad

Bacillus

Diplobacilli

Streptobacilli
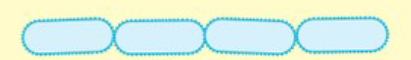
Palisades

Metabolic Needs of Bacteria (classification of bacteria)
autotrophic vs heterotrophic
aerobic (uses oxygen) vs anaerobic (doesn’t use oxygen)
Obligate Anaerobic Organism
will die if exposed to oxygen
Facultative Anaerobic Organism
can choose to use or not use oxygen
Gram Staining (classification of bacteria)
stain that stains some bacteria purple (Gram +) but others pink/red (Gram -)
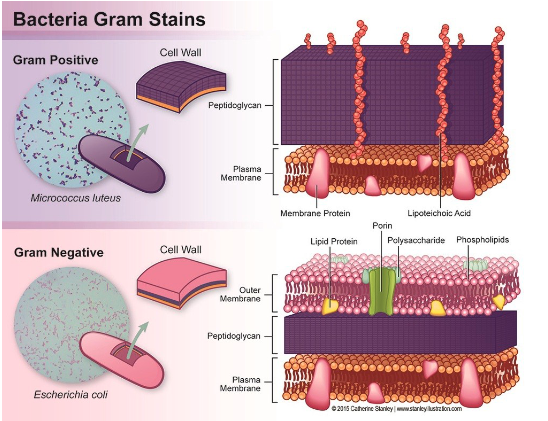
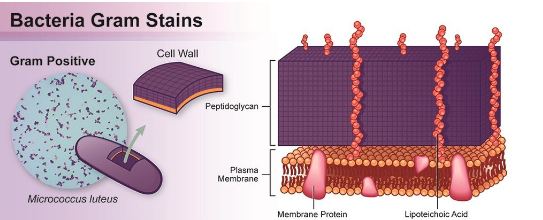
Gram +
thick protein layer on their cell wall (stain purple)
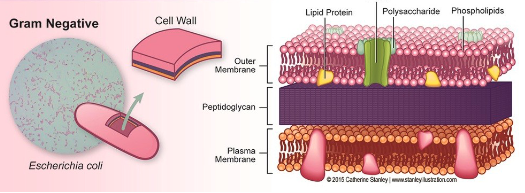
Gram -
thin protein layer on their cell wall (stain pink)
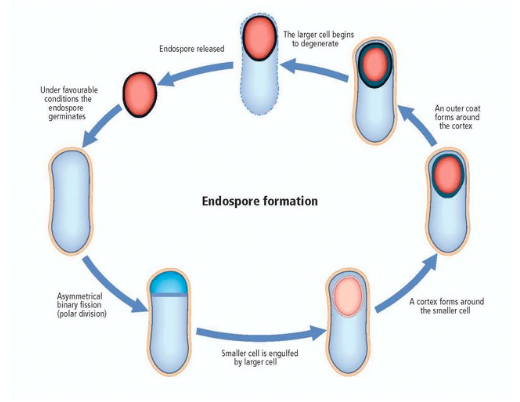
Endospore Formation (classification of bacteria)
endospore is a small extremely tough pod that acts as an “escape pod”:
DNA and bare minimum of cellular material are stored in the endospore while the rest of the cell can deteriorate
endospore stays dormant until conditions improve and the cell can regenerate
Colony Morphology (classification of bacteria)
grow bacteria in petri dishes with agar (jelly-like substance with basic nutrients)
bacteria grows large enough to see with the naked eye called colonies
shape + colour of the colonies can help indicate the species
Protists
unicellular, eukaryotic
gave rise to animals, plants and fungi
3 Types of Protists
Animal-Like
Plant-Like
Fungi-Like
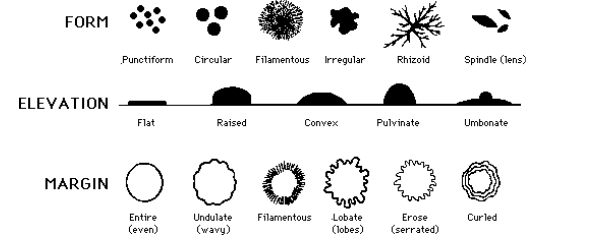
Animal-Like Protists
heterotrophs
move around to capture food
e.g. some move around using small hairs (cilia) or by shifting their cytoplasm creating ‘feet’ called pseudopods
some use a tail to swim (flagellum)
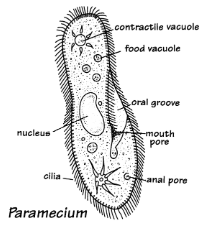
Plant-Like Protists
capable of photosynthesis
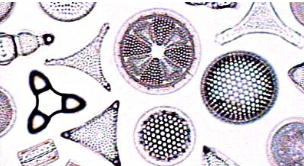
Fungi-Like Protists
heterotrophic
specialize in feeding on dead organic matter
e.g. unicellular slime molds
Endosymbiosis
one organism lives inside another, forming a mutually beneficial relationship → helps explain how eukaryotic cells may have formed from prokaryotic cells
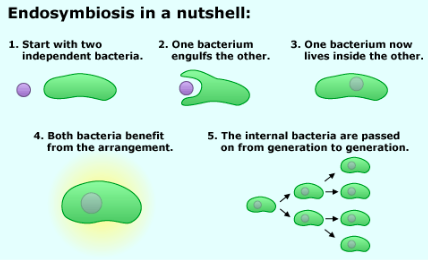
Endosymbiosis: Mitochondria
certain cells evolved to be highly efficient at generating energy from food
one of these cells was consumed by another bacterium
the predator retains the other cell inside of it to get it to generate food
the two cells are dependent on each other and essentially act as a single cell
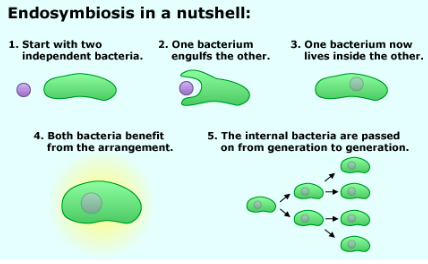
Endosymbiosis: Chloroplast
certain cells evolved to have the ability to create food from sunlight (photosynthesis)
one of these cells was consumed by another bacterium
predator retains the other cell
two cells are dependent on each other and essentially act as a single cell
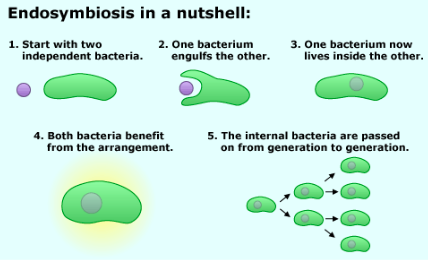
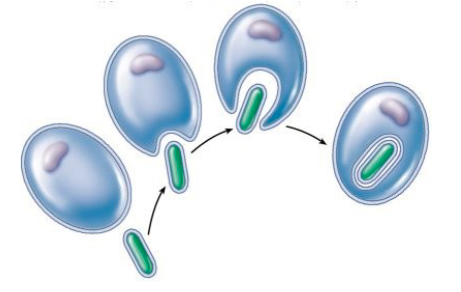
Evidence for Endosymbiosis
mitochondria + chloroplasts have a double membrane layer → inner membrane is the original membrane (got engulfed)
mitochondria + chloroplasts have their own separate DNA
in animals, mitochondria in inherited from mother, as sperm only gives DNA
Fungi
multicellular, eukaryotic
use external digestion
cell walls made from chitin
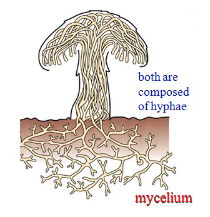
body is the mycelium
may have gills that are lined with thousands of basidia that hold the spores
External Digestion
excrete digestive enzymes to break down food and then absorb the nutrients into their cells
Chitin
type of carbohydrate that makes up the cell walls of fungi
Hyphae
formed by long chains of fungal cells
make up the mycelium
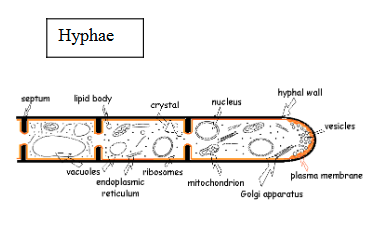
Mycelium
body of a fungus
made up of hyphae
Types of Fungus (Nutrition)
Decomposers
feed off of dead organic matter
Parasites
feed off organisms while they are still alive
Mutualists
live in the roots of plants
fungi helps plant absorb nutrients from soil, plant gives fungi sugar
Predatory
have modified hyphae that trap microscopic organisms for food
Fungal Reproduction
both asexual and sexual reproduction
asexual: fungus produces spores that drop to the ground and form a new fungus
sexual: hyphae filaments of 2 nearby fungi will grow towards each other and merge haploid cells to form a new diploid cell
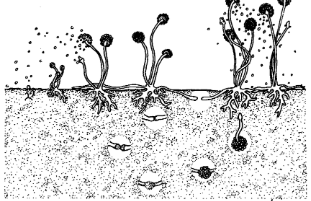
Fungal Networks in Forests
fungi and trees may connect underground and share nutrients and chemicals that help against disease
Plants
multicellular, eukaryotic
capable of photosynthesis
have cell walls made of cellulose
believed to have evolved from photosynthetic protists

Features that Helped Plants move from Water to Land
Vascular Tissue
Seeds
Flowers/Fruits
Vascular Tissue (Water to Land)
structures designed to pump fluids through the plant (e.g. roots) → on land, allows plant to absorb and move water without drying out
Seeds (Water to Land)
a structure that protects newly formed plants inside a hard covering → on land, allows young plants to move from place to place without drying out
Flowers/Fruits (Water to Land)
flowers allow for pollination which increase the chances of sexual reproduction
flowers become fruits which store the seeds → on land, allows for the spread of haploid gametes + extra covering for seeds without them drying out
Bryophytes (plants)
photosynthesize
multicellular

Ferns (plants)
photosynthesize
multicellular
vascular tissue

Gymnosperms (plants)
photosynthesize
multicellular
vascular tissue
seeds

Angiosperms (plants)
photosynthesize
multicellular
vascular tissue
seeds
fruits/flowers

Animals
multicellular, eukaryotic
heterotrophic

Order of Evolution for Animals
From Unicellular to Multicellular
From Unspecialized Cells to Specialized Cells
From Radial Symmetry to Bilateral Symmetry
From Cells being Packed Together to Leaving Some Space
From No Segmentation to Segmentation
From No Spinal Cord to Having a Spinal Cord
From Protostome to Deuterostome
From Unicellular to Multicellular (ANIMALS)
first multicellular animals were sponges

From Unspecialized Cells to Specialized Cells (ANIMALS)
first animals to develop specialized cells were jellyfish
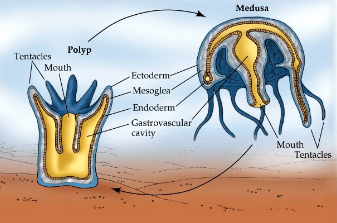
From Radial Symmetry to Bilateral Symmetry (ANIMALS)
first animals to develop bilateral symmetry were flat worms
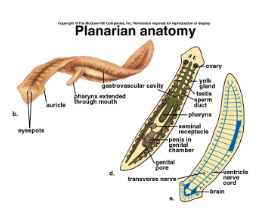
Cephalization
having a head and a butt
From Cells being Packed Together to Leaving Some Space (ANIMALS)
first animals to have a pseudocoelome were roundworms
first animals to have a coelom were mollusks
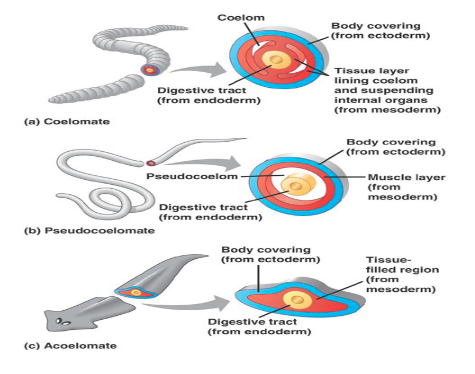
Coelom
fluid-filled cavity in the body that contains organs
Coelomate
have a coelom
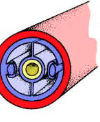
Acoelomate
don’t have a coelom
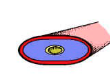
Pseudocoelomate
in between having and not having a coelom
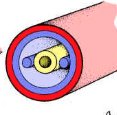
From No Segmentation to Segmentation (ANIMALS)
3 phyla that exhibit segmentation: annelids (earth worms), arthropods (insects, arachnids, crustaceans), and chordates (animals with a nerve cord)
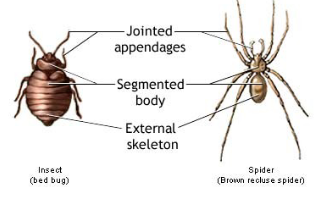
From No Spinal Cord to Having a Spinal Cord (ANIMALS)
first animals to have a spinal cord were the jawless fish
Vertebrate
animals with a properly developed spinal cord protected by vertebrae
From Protostome to Deuterostome (ANIMALS)
all animal phyla are protostomes EXCEPT chordates and sea stars
Protostome
all organisms where the blastopore becomes the mouth
Deuterostome
all organisms where the blastopore becomes the anus
Blastopore
opening in the central cavity of an embryo during development
The Big Picture
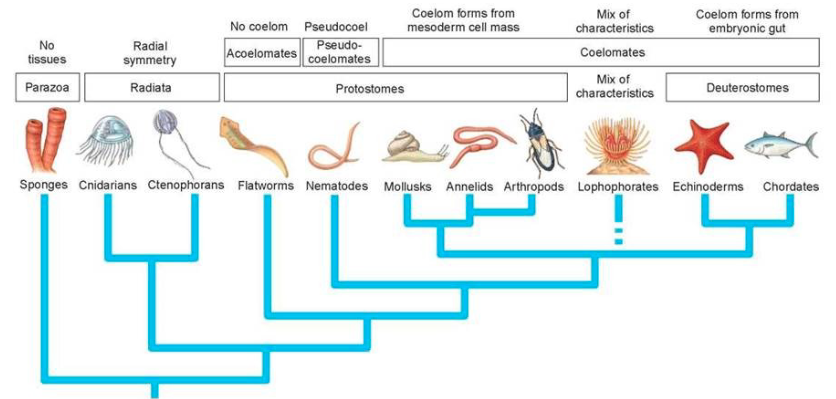
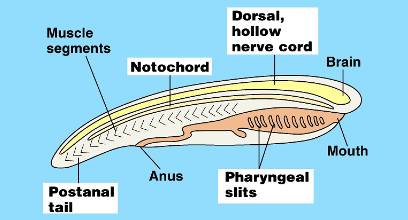
Common Features Among the Chordates
Nerve cord
Brain at the front
Notochord/Vertebrae
Pharyngeal slits (gills)
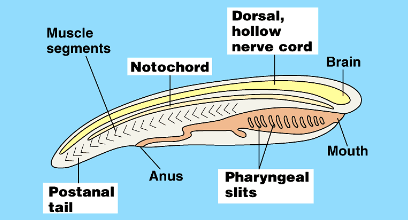
Notochord
tissue that supports the nerve cord
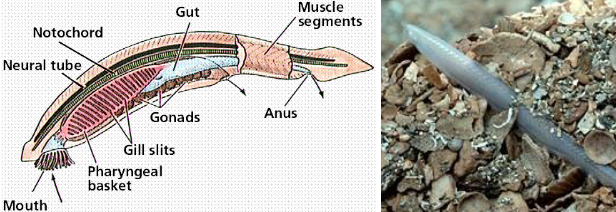
Tunicates
most primitive chordate

Lancelet
primitive chordate
considered to be the ancestor of the fish
Hagfishes & Lampreys
jawless fish
have vertebrae
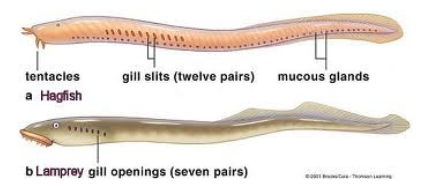
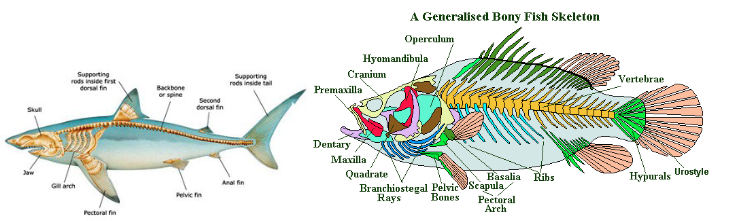
Cartilaginous Fishes vs. Bony Fishes: Sharks vs. Fish
first skeletons were made of cartilage (sharks) then later calcified to become proper bone (fish)
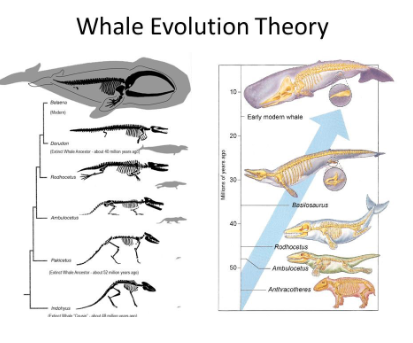
The first fish to move onto land would have given rise to the __________, and later ______, _____ and _______.
amphibians, and later reptiles, birds and mammals

Mammals are known for…
Having fur/hair
Having mammary glands that produce milk (females)
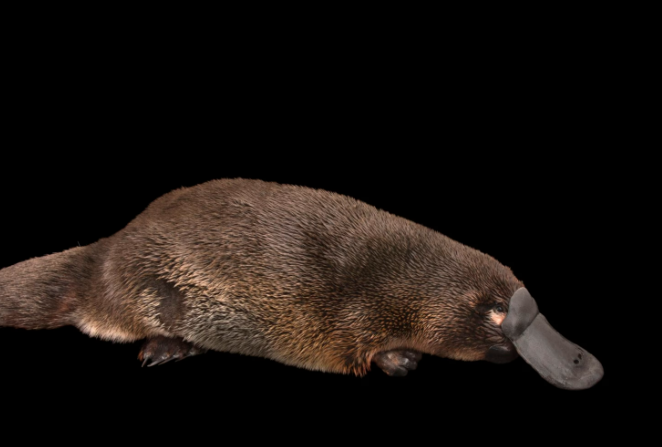
Monotreme Mammals
mammals that lay eggs

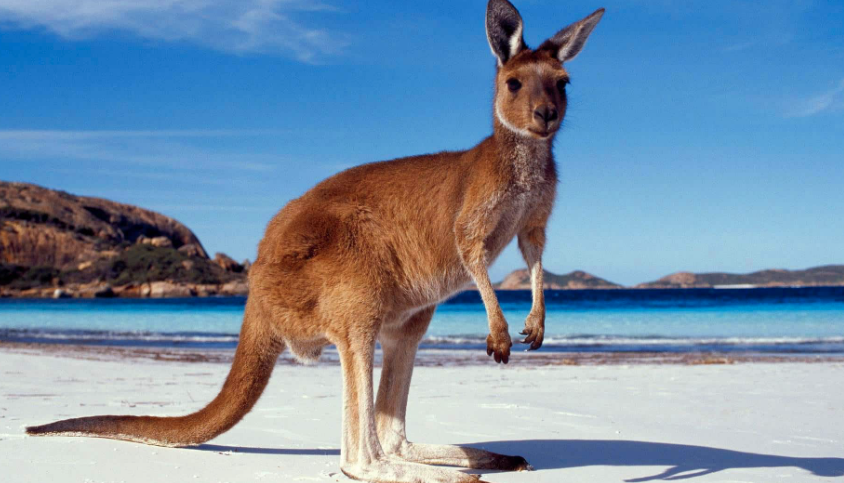
Marsupial Mammals
mammals that give birth and have pouches for offspring

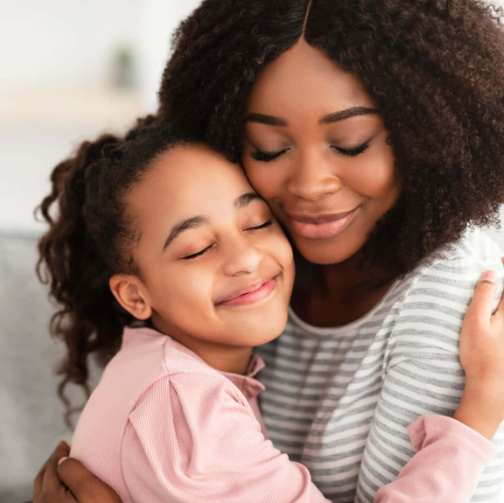
Placental Mammals
mammals that have an internal placenta for the offspring to develop inside the mother

Whales and Dolphins are…
Mammals
How would you write the name of a species?
genus, species (italicized, with genus starting with capital letter)