Pathology CVS Labs Flashcards
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Goodluck <3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Aschoff Bodies
pathognomonic heart lesions in RF
Rheumatic Valvulitis
- thick valves
- warty vegetations
- along the line of closure of leaflets and cusps
- great mechanical stress on the valves of the left heart
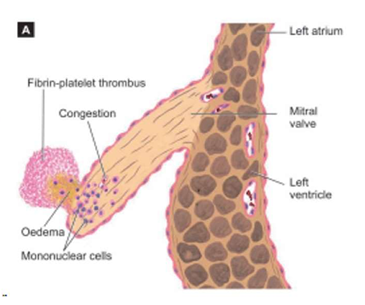
Rhuematic Endocarditis: Rheumatic valvulitis
Acute RF
- edema of the valvue leaflet
- aschoff nodule
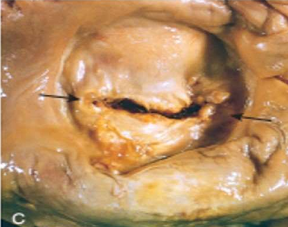
Rheumatic valvulitis
chronic healed mitral valve is
'fish mouth' or 'button hole' stenosis
permanent deformity
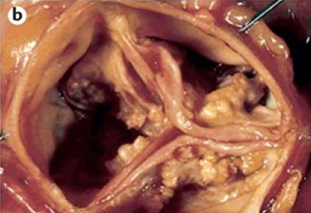
Rheumatic valvulitis
chronic stage of RHD
Calcified aortic stenosis GROSS
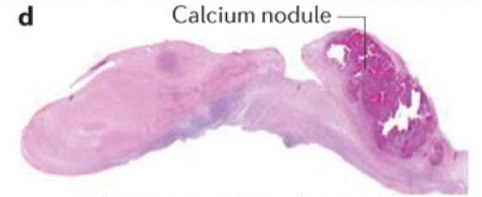
Rheumatic valvulitis
chronic stage of RHD
Calcified aortic stenosis MICROSCOPIC
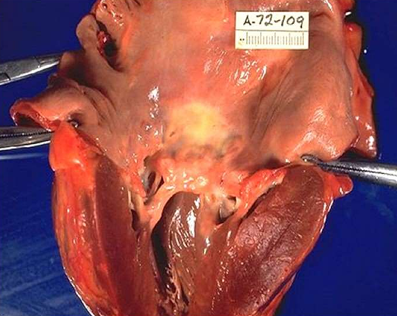
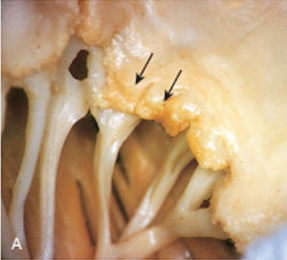
Rheumatic Mural Endocarditis
Gross appearance of heart showing dilated left atrium with MacCallum plaque and vegetations
lesions are commonly seen in the region of endocardial surface in the posterior wall of left atrium
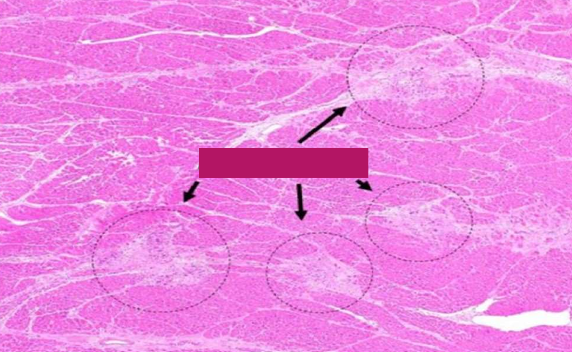
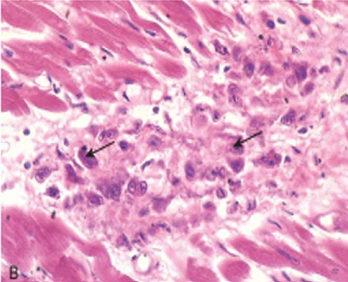
Rheumatic Myocarditis
Aschoff bodies are seen between myocardial bundles as paravascular fusiform collection of mononuclear cells around fibrinoid necrosis
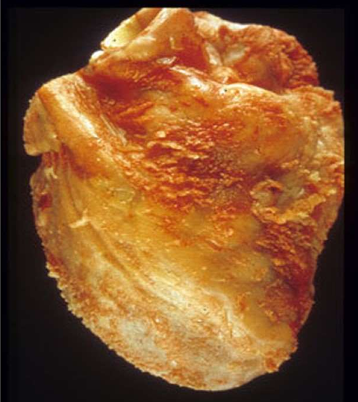
Rheumatic Pericarditis
'bread and butter appearance'.
[surfaces are shaggy due to thick fibrin covering them].
Rhematic Vegetations
on mitral alone, or mitral and aortic combined.
occur along the line of closure.
small, multiple, warty, grey brown, translucent firmly attached produce permanent valvular deformity
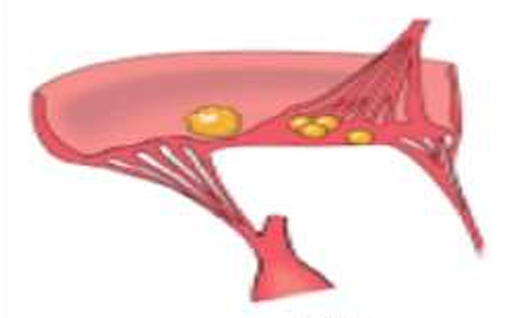
Libman Sack Vegetations
occur on both surfaces of the valve leaflet
Medium sized, multiple, DO NOT produce permanent valvular deformity
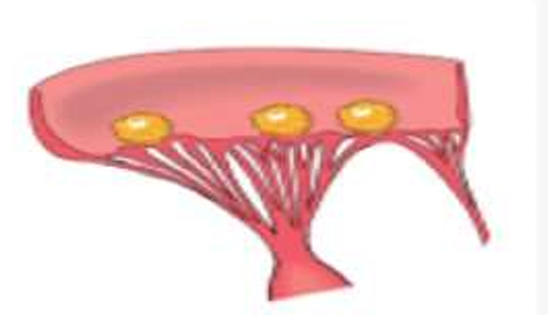
NON-Bacterial Thrombotic Vegetations
occur on along the line of closure
larger than of that in RHD, More friable than RHD
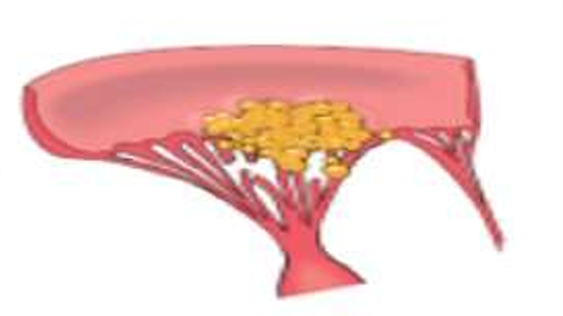
Bacterial INFECTIVE Vegetations
SABE = on diseased valves
ABE = on normal valves
LARGE, green tawny, irregular, single/multiple, TYPICALLY FRIABLE
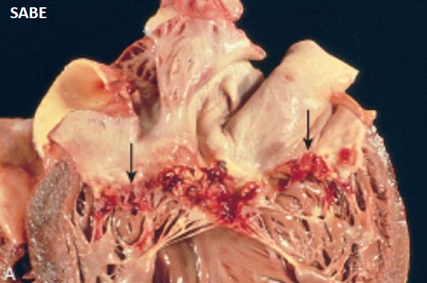
SABE Non RH Endocarditis: Infective Bacterial
- valve thickened and fibrotic
- firm, gray vegetations
- organized
- sometimes may show calcification
- chronic inflammatory granulation
- healing scars
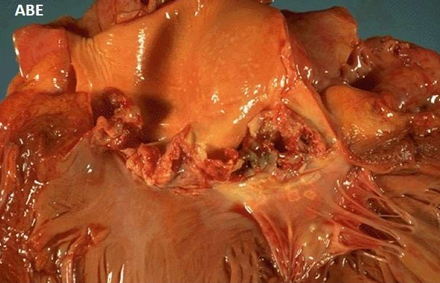
ABE Non RH Endocarditis: Infective Bacterial
- valve ulcerated and destroyed
- soft, bulky, easily detached (sometimes causes emboli)
- grey yellow vegetations
- typically friable
- underlying valves shows necrosis, suppuration and abscess
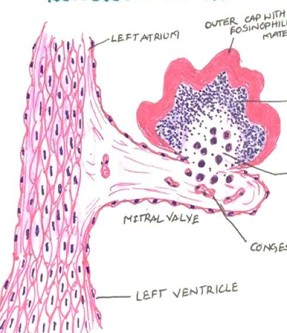
Non RH Endocarditis: Infective Bacterial
The vegetations of BE consist of 3 zones:
i) Outer cap consists of eosinophilic material composed of fibrin and platelets.
ii) Middle basophilic zone containing colonies of bacteria.
iii) Deeper zone consists of non-specific inflammatory reaction in the cusp itself
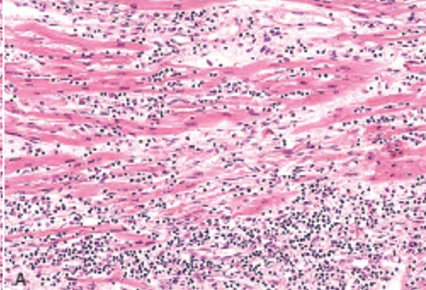
Idiopathic (Fiedler’s) Myocarditis
Diffuse idiopathic myocarditis
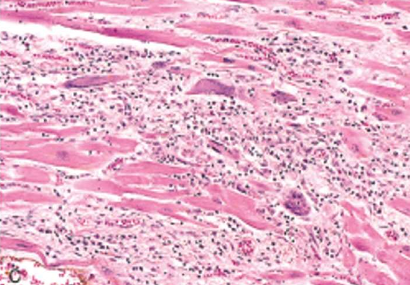
Idiopathic (Fiedler’s) Myocarditis
Giant Cell idiopathic granulomatous
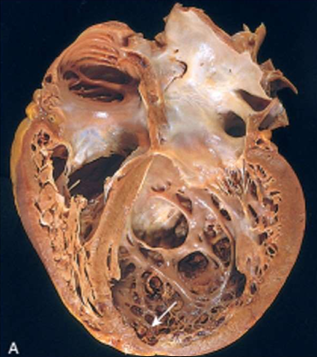
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
four chamber dilation and hypertrophy
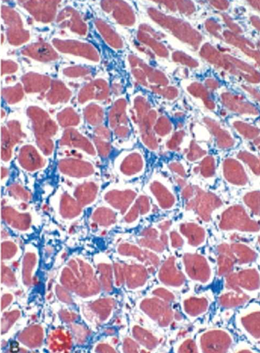
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Myocyte hypertrophy and interstitial fibrosis (Blue with masson trichrome stain)
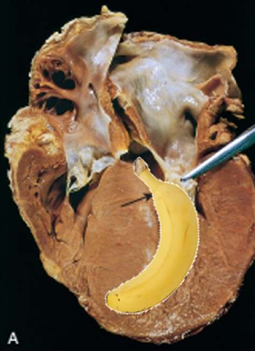
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
asymmetric septal hypertrophy, septal muscle bulges into the left ventricular outflow tract, "banana-shaped" ventricular lumen
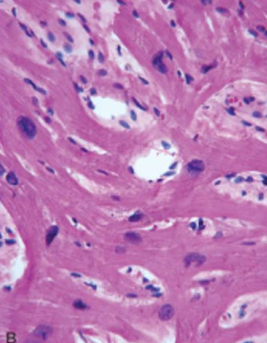
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Myocyte disarray, extreme hypertrophy, and characteristic branching, & interstitial fibrosis.
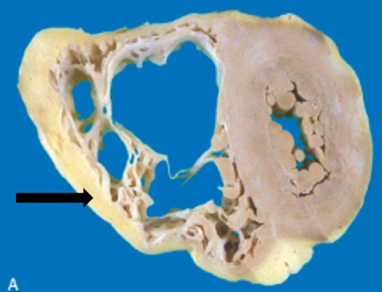
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy
Morphologically, the right ventricular wall is severely thinned owing to myocyte replacement by fatty infiltration and lesser amounts of fibrosis. (Gross)
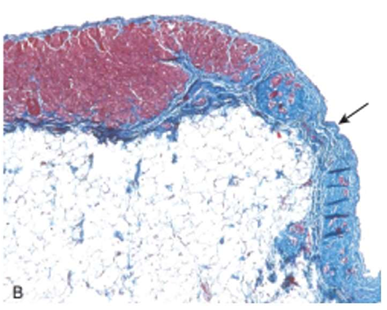
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy
Morphologically, the right ventricular wall is severely thinned owing to myocyte replacement by fatty infiltration and lesser amounts of fibrosis. (Microscopy)
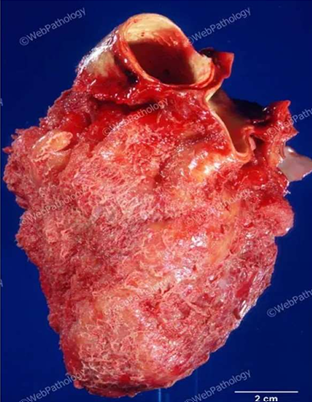
Fibrinous pericarditis
most common form of pericarditis.
In RF & Uraemia
The pericardial cavity contains a mixture of fibrinous exudate with serous fluid.
When two layers of pericardium are pulled apart, 'bread and butter' appearance
(GROSS APPEARANCE)
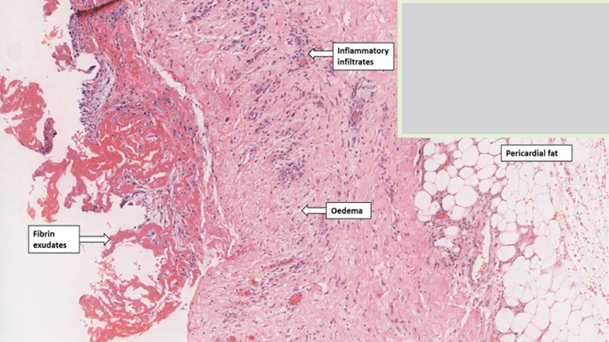
Fibrinous pericarditis
i. Pericardial surface contains pink fibrinous exudate.
ii. pericardium shows congestion and an acute inflammatory infiltrate composed predominantly of neutrophils.
(MICROSCOPIC APPEARANCE)
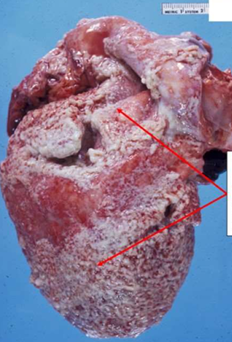
Suppurative/Purulent pericarditis
Acute Bacterial
. Exudate: Fibrinopurulent
. Pericardial cavity may contain pus.
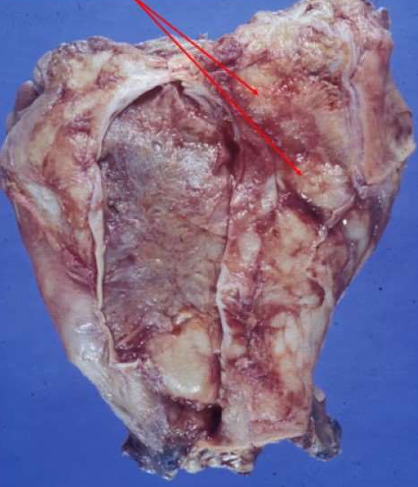
Tuberculous pericarditis
Caseating granulomatous inflammation.
Thickened pericardium with yellow plaques of caseous necrosis.
Outcome: Healing by fibrosis, sometimes causing constrictive pericarditis.
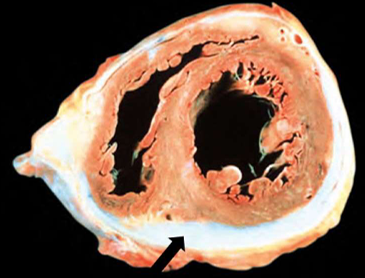
Chronic pericarditis
Dense fibrotic scars that may obliterate the pericardial space, leading to constrictive pericarditis.
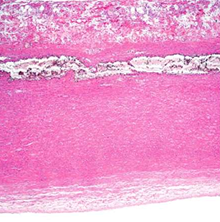
Dissecting aneurysm
begins in the arch of aorta. most often located in the ascending aorta.
The dissection is seen most characteristically separates the intima and inner two third of the media on one side from the outer one-third of the media and the adventitia on the other.

Dissecting aneurysm
begins in the arch of aorta. most often located in the ascending aorta.
The dissection is seen most characteristically separates the intima and inner two third of the media on one side from the outer one-third of the media and the adventitia on the other.
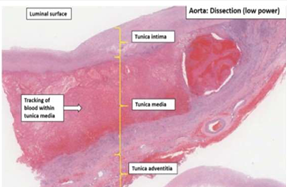
Dissecting aneurysm
begins in the arch of aorta. most often located in the ascending aorta.
The dissection is seen most characteristically separates the intima and inner two third of the media on one side from the outer one-third of the media and the adventitia on the other.
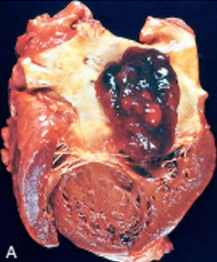
Cardiac neoplasm: Myxoma
- most common in adults
- left atrium (attached to fossa ovalis by stalk)
- gelatinous, lobulated mass
- may obstruct mitral valve → syncope/sudden death
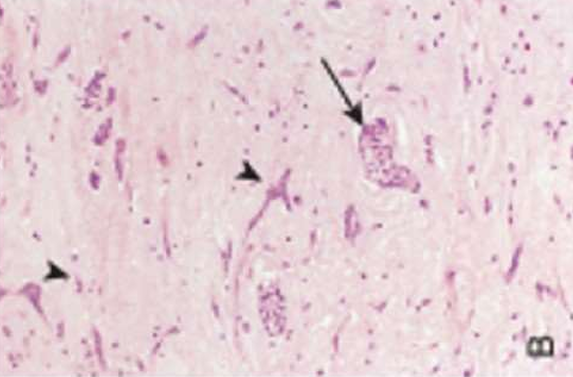
Cardiac neoplasm: Myxoma
- Scattered polygonal or stellate myxoma cells in myxoid (mucoid) stroma.
- May form cords, rings, or gland-like structures.
- May show hemorrhage and inflammation.
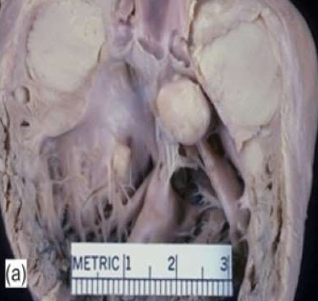
Cardiac neoplasm: Rhabdomyoma
- Mostly in children
- associated with tuberous sclerosis
- Grey white nodular mass
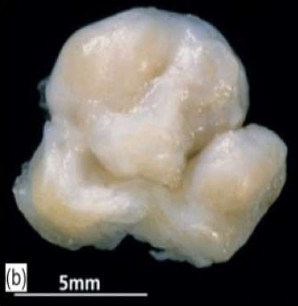
Cardiac neoplasm: Rhabdomyoma
- Mostly in children
- associated with tuberous sclerosis
- Grey white nodular mass
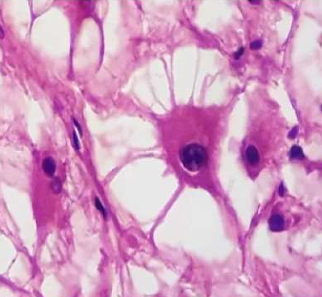
Cardiac neoplasm: Rhabdomyoma
- Large spider Cells
- Abundant cytoplasm, radial cytoplasmic strands extending to cell membrane
- May regress spontaneously
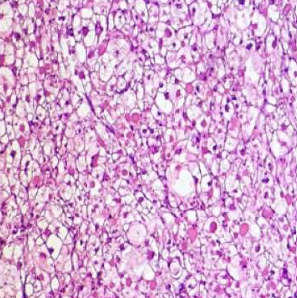
Cardiac neoplasm: Rhabdomyoma
- Large spider Cells
- Abundant cytoplasm, radial cytoplasmic strands extending to cell membrane
- May regress spontaneously
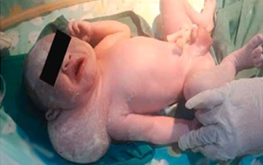
Vascular neoplasm: Benign
Cystic Hygroma cavernous lymphangioma GROSS
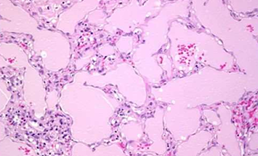
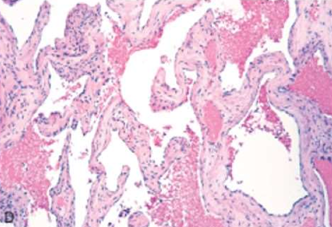
Vascular neoplasm: Benign
Cystic Hygroma cavernous lymphangioma MICROSCOPY
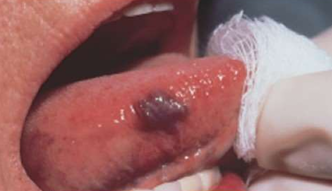
Vascular neoplasm: Benign
Pyogenic Granuloma, Lobular capillary hemangioma GROSS
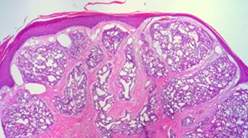
Vascular neoplasm: Benign
Pyogenic Granuloma, Lobular capillary hemangioma MICROSCOPY
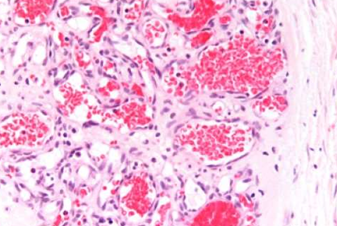
Vascular neoplasm: Benign
Capillary hemangioma MICROSCOPY
Vascular neoplasm: Benign
Cavernous hemangioma MICROSCOPY
Vascular neoplasm: Intermediate
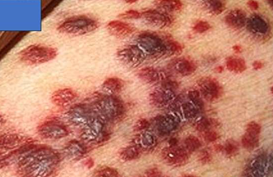
KAPOSI SARCOMA
Reddish macules that become raised plaques and nodules over time; begins in skin GROSS
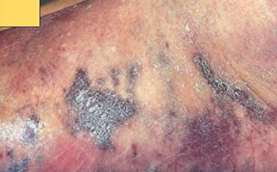
Vascular neoplasm: Intermediate
KAPOSI SARCOMA
Reddish macules that become raised plaques and nodules over time; begins in skin GROSS
Vascular neoplasm: Intermediate
KAPOSI SARCOMA
Reddish macules that become raised plaques and nodules over time; begins in skin GROSS
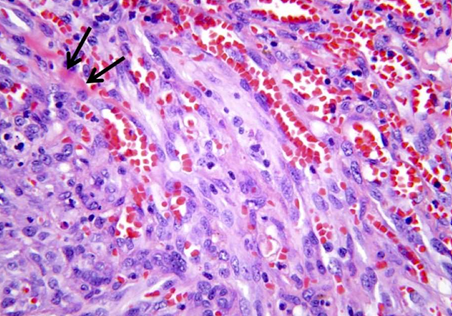
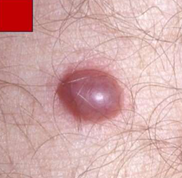
Vascular neoplasm: Intermediate
KAPOSI SARCOMA
Dilated blood vessels with an endothelial mononuclear infiltrate; will progress to see spindle cells with hyaline globules, mitotic figures, and hemosiderin pigment MICROSCOPY
Vascular neoplasm: Malignant
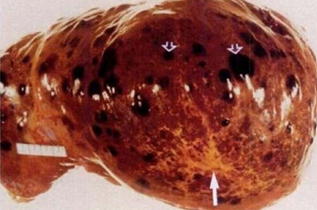
Angiosarcoma
.Highly malignant tumor of endothelial origin.
.Site: liver
.Gross: Large, hemorrhagic, necrotic mass.
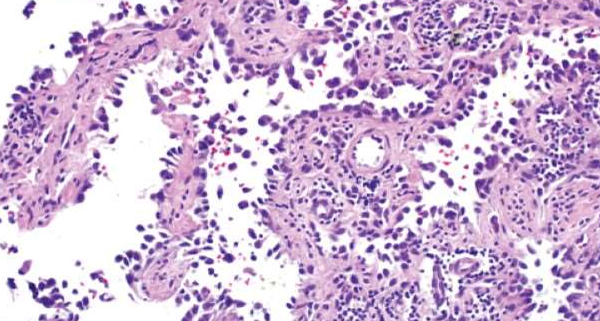
Vascular neoplasm: Malignant
Angiosarcoma
.Malignant endothelial cells forming irregular, anastomosing vascular channels.
.Atypia, mitotic activity, and multilayering of endothelial cells.
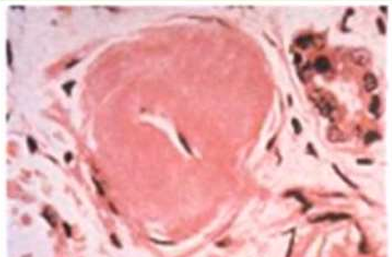
Arteriosclerosis
Hypertensive vascular disease: Benign Hypertension
Hyaline arteriolosclerosis.
The arteriolar wall is thickened with the deposition of amorphous proteinaceous material (hyalinized), and the lumen is markedly narrowed.
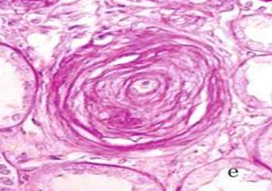
Arteriosclerosis
Hypertensive vascular disease: Benign Hypertension
Elastosis
Splitting of internal elastic lamina into multiple layer
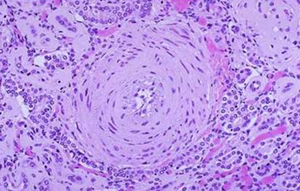
Arteriosclerosis
Hypertensive vascular disease: Malignant Hypertension
Hyperplastic ("onion-skinning") obliteration arteriolosclerosis causing luminal
Arteriosclerosis
Hypertensive vascular disease: Malignant Hypertension
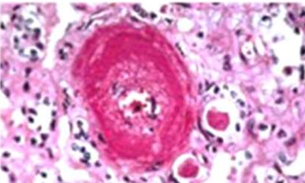
Necrotizing arteriolosclerosis
Fibrinoid necrosis showing fragmented collagen & inflammation
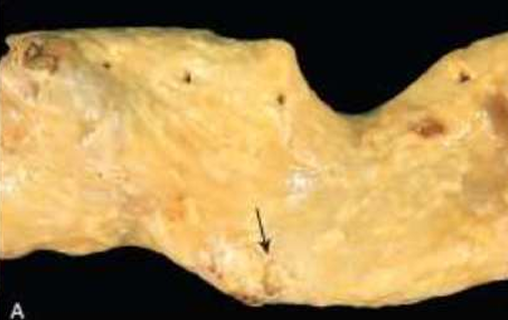
Atherosclerosis
Atheromatous lesions
Aorta with mild atherosclerosis composed of fibrous plaques, one denoted by the arrow.
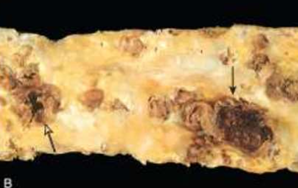
Atherosclerosis
Atheromatous lesions
Aorta with severe diffuse complicated lesions, including an ulcerated plaque (open arrow), and a lesion with overlying thrombus (closed arrow).
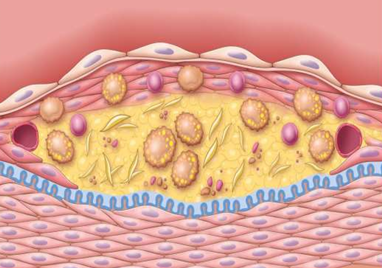
Atherosclerosis
Atheromatous plaque
· FIBROUS CAP
· CELLULAR ZONE (smooth muscle cells, macrophages, foam cells, lymphocytes, collagen, elastin, proteoglycans, neovascularization)
· NECROTIC CENTER (cell debris, cholesterol crystals, foam cells, calcium)
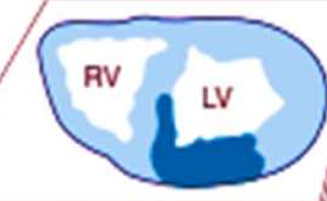
IHD: Myocardial infarction
40-50%
left anterior descending artery obstruction
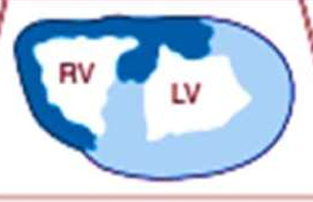
IHD: Myocardial infarction
30-40%
Right coronary artery obstruction
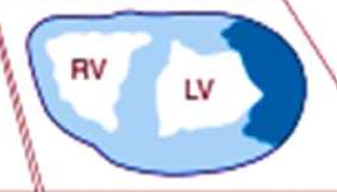
IHD: Myocardial infarction
15-20%
Left circumflex artery obstruction
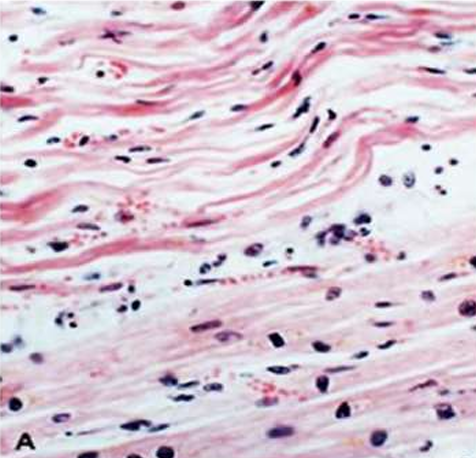
IHD: Myocardial infarction
Acute Myocardial Infarction
1d: Beginning of coagulative necrosis with few neutrophils, wavy fibers with elongation, and narrowing, compared with adjacent normal fibers (lower right).
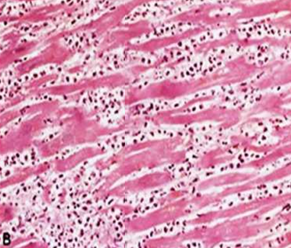
IHD: Myocardial infarction
Acute Myocardial Infarction
2-3 ds: Coagulative necrosis, Dense neutrophilic infiltrate in an area of acute myocardial infarction
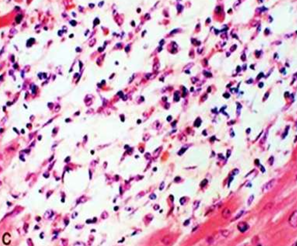
IHD: Myocardial infarction
Acute Myocardial Infarction
7-10 ds: Nearly complete removal of necrotic myocytes by phagocytosis
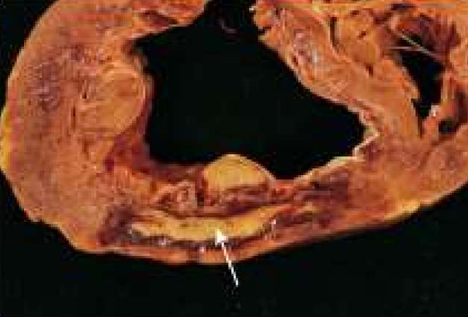
IHD: Myocardial infarction
Acute Myocardial Infarction
7-10 ds: the posterior wall of the left ventricle.
The yellow area (arrow) of necrosis is surrounded by a rim of dark, red granulation tissue.
IHD: Myocardial infarction
Acute Myocardial Infarction
10-14 ds: Granulation tissue
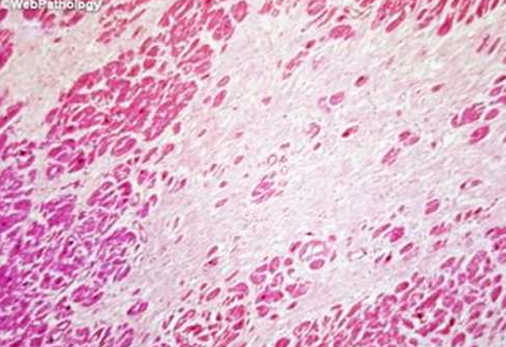
IHD: Myocardial infarction
Acute Myocardial Infarction
After 8 wks: Healed MI with replacement of the necrotic fibers by dense collagenous scar. Residual cardiac muscle cells are present
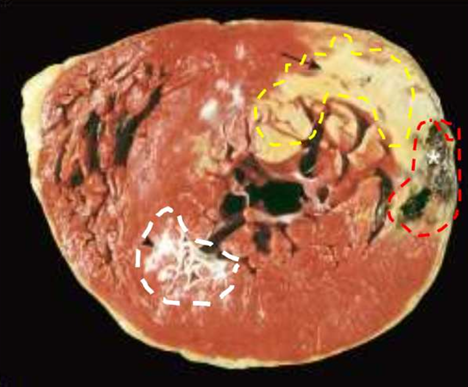
IHD: Myocardial infarction
Acute Myocardial Infarction
Yellow area = necrosis
arrow head = anterior scar (remote infarction)
star = myocardial haemorrhage due to ventricular rupture (was the acute cause of death
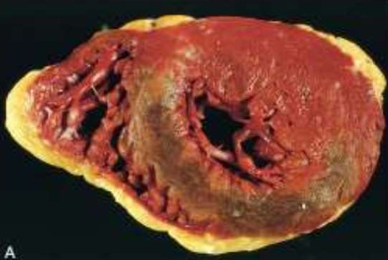
IHD: Myocardial infarction
Acute Myocardial Infarction
Reperfused myocardial infarction
Reperfused myocardial infarction. The transverse heart slice exhibits a large anterior wall myocardial infarction that is hemorrhagic because of bleeding from damaged vessels. The posterior wall is at the top.
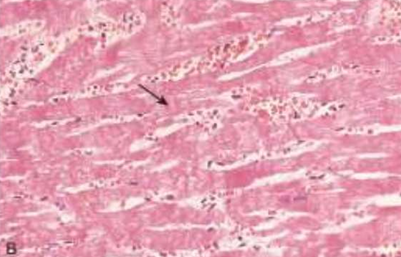
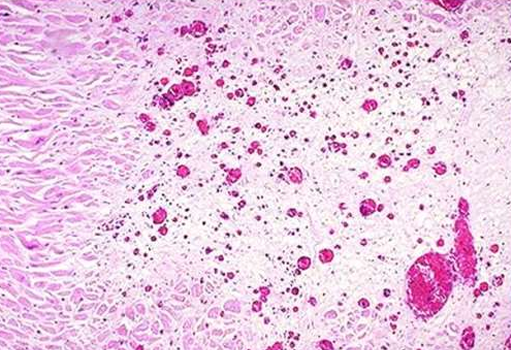
IHD: Myocardial infarction
Acute Myocardial Infarction
Reperfused myocardial infarction
Hemorrhage and contraction bands, visible as prominent hyper eosinophilic cross-striations spanning myofibers (arrow), are seen microscopically.
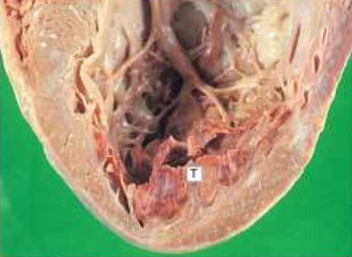
IHD: Myocardial infarction
Acute Myocardial Infarction
Mural thrombus
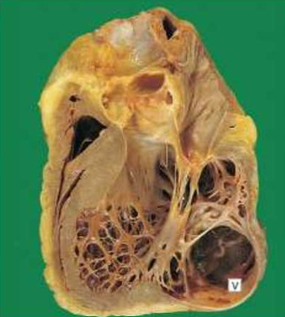
IHD: Myocardial infarction
Acute Myocardial Infarction
Left Ventricular aneurysm
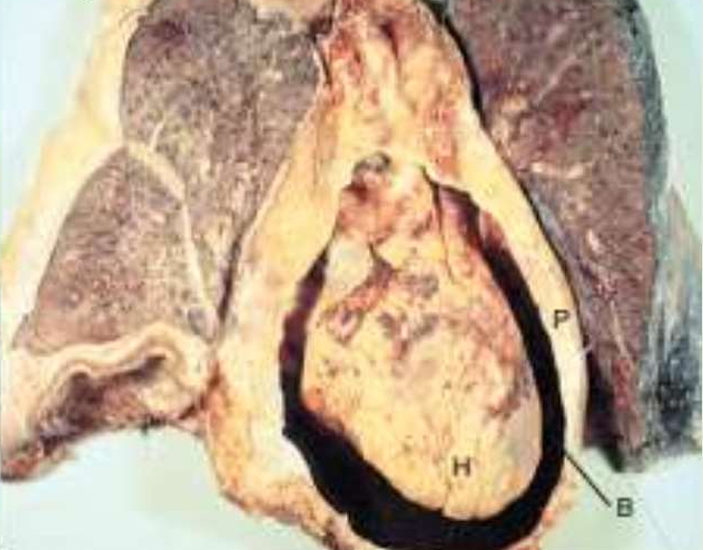
IHD: Myocardial infarction
Acute Myocardial Infarction
Hemopericardium (caused by rupture of infarcts
P= Pericardial sac
B= Filled with blood
H= Surrounding the heart