Women's Health Exam 1 JMU
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Signs of Pregnancy: Presumptive
those changes felt by the woman (e.g., amenorrhea, fatigue, breast changes, nausea)
Signs of Pregnancy: Probable
those changes observed by an examiner (e.g., Hegar sign, ballottement, pregnancy tests)
Signs of pregnancy: positive
those signs attributed only to the presence of the fetus (e.g., hearing fetal heart tones, visualizing the fetus on an ultrasound, palpating fetal movements)
Probable sign of pregnancy: Hegar sign
softening of the lower uterine segment that is classified as a probable sign of pregnancy can increase the need for urination
Probable sign of pregnancy: Ballotement
fetal part is displaced by a light tap of examiners fingers on the cervix and then rebounds quickly
Cervix changes: Godell's sign
softening of the cervix tip, making it highly elastic
Chadwick's sign
Bluish purple discoloration of the cervix, vagina, and labia during pregnancy as a result of increased vascular congestion.
Naegele's Rule
add 7 days to first day of LMP, subtract 3 months, add 1 year
Gravidity
Total number of pregnancies a woman has had regardless of duration, including a present one
Gravida/Para
Gravida (gravidity): # of Pregnancies
Para (parady): # of live births (past 20 weeks)
Term (# of births)
woman has had a baby at 37 week or more (early, full, late, post-term)
Preterm (# of births)
# of births between 20-36 weeks
Abortion
birth of fetus before 20 weeks or baby weighing less than 500g
Living
# of current living children
A 30 year old female is 25 weeks pregnant with twins. She has 5 living children. Four of the 5 children were born at 39 weeks gestation and one child was born at 27 weeks gestation. Two years ago she had a miscarriage at 10 weeks gestation. What is her GTPAL?
G: 7, T: 4, P:1, A:1, L:5
Urine testing during pregnancy
Protein, ketones, glucose, urine culture
Abnormal reading of protein in the urine of a pregnant woman
greater than 300mgterm-18
sign of preeclampsia
preeclampsia
a complication of pregnancy characterized by hypertension, edema, and proteinuria
can cause inhibition of oxygen to fetus
ketones in urine
Body doesnt have adequate glucose or calories in the body and starts to break fast and muscles down for energy
caused by nausea and vomiting or diabetes
Bacteria in urine culture
woman could develop kidney infection (pyelonephritis) which can increase risk of pre term labor
hyperemesis gravidarum
severe nausea and vomiting in pregnancy that can cause severe dehydration in the mother and fetus
needs IV fluids
H & H norms during first trimester
HGB: 12-16 G/dl
Hct: 37-47%
If a woman's HGB drops below __________ she is considered anemic:
11 g/dl
What blood type do nurses need to look out for in a pregnant woman?
O type
What Rh sign in the mother can cause alarm if baby is Rh positive?
Rh negative
STDs tested during preganancy
gonnorhea, chlamydia, syphilis, HIV, Hep B
If a woman has this STD, it is recommended that she doesnt breast feed
HIV +
Can you give a Rubella vaccine to a pregnant woman?
no
Other vaccines that pregnant women canNOT recieve during gestation include:
Mumps and varicella vaccines
Vaccines women can receive during pregnancy
Hep ABC, Flu, Tdap
Second trimester: Supine hypotension syndrom
caused by woman laying on their back and uterus pushing up on their aorta and IFV
decrease in cardiac output
Second trimester: femoral venous pressure
due to growing of the uterus the blood return from the legs and pelvis area to the heart are decreased making pregnant women more prone to clots and DVTs
lightening
The movement of the fetus down into the pelvis late in pregnancy.
What disease has put newborn babies at most risk for infections such as sepsis, pneumonia, and meningitis?
Group B Strep
nullipara
a woman who has never borne a viable child
primipara
a woman who has borne one viable childterm-36
multipara
woman who has given birth to two or more children
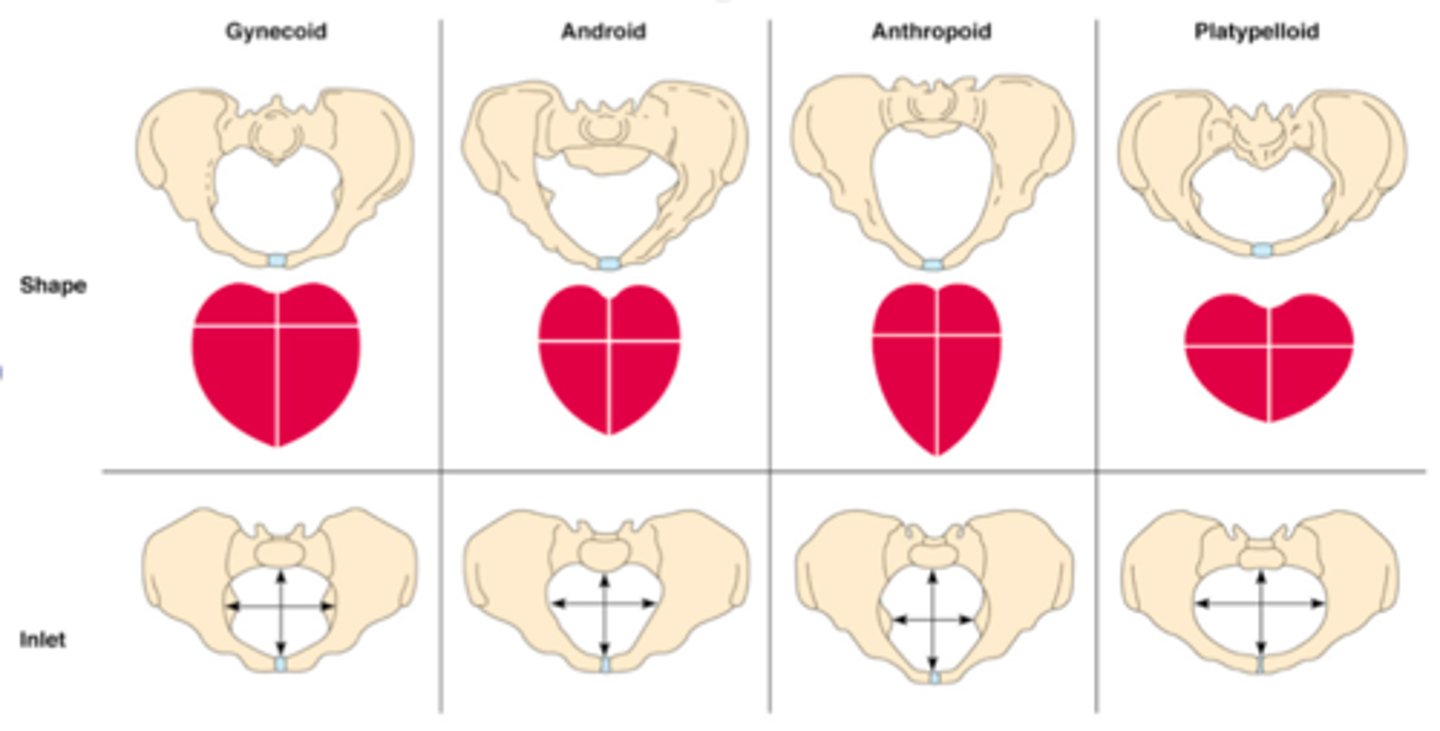
gynecoid pelvis
typical female pelvis and most favorable pelvis for successful vaginal labor.
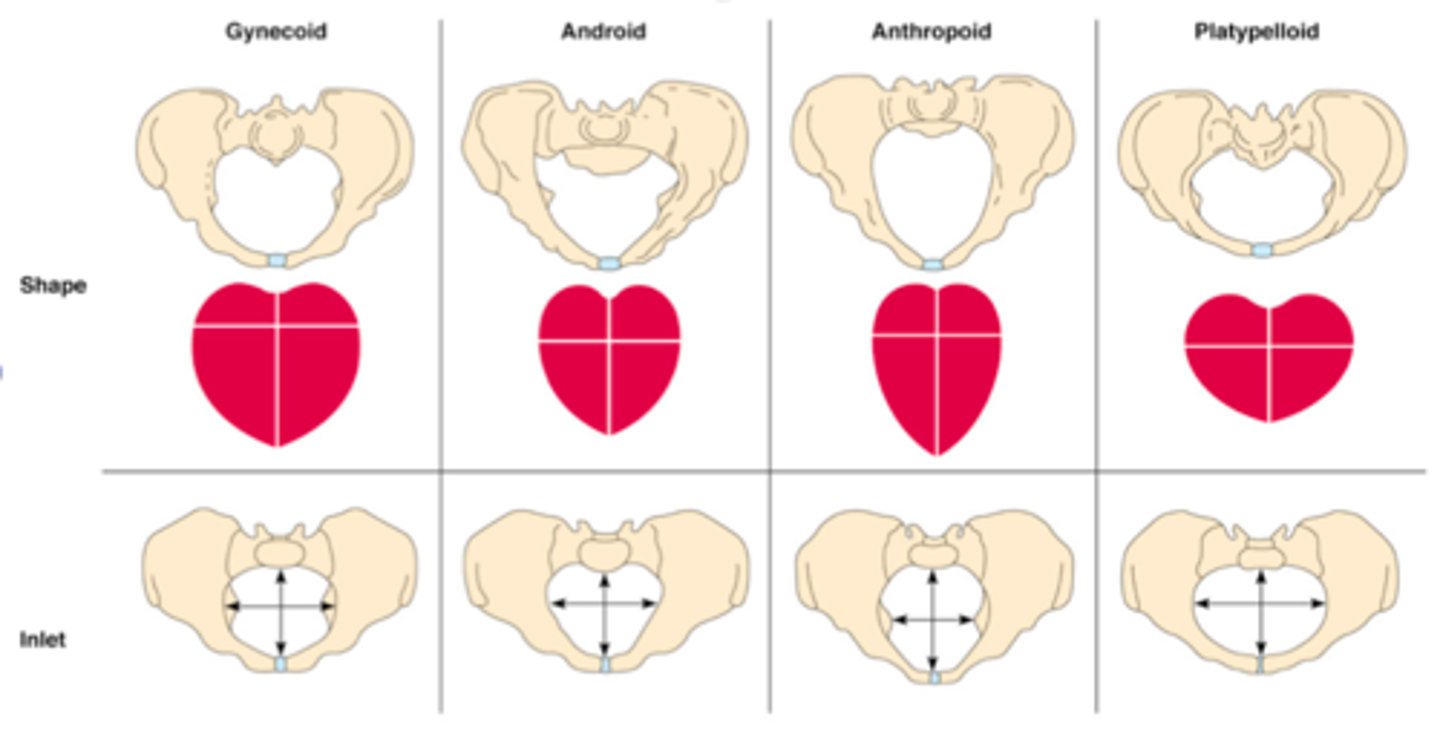
anthropoid pelvis
oval shaped, with a wider anteroposterior diameter
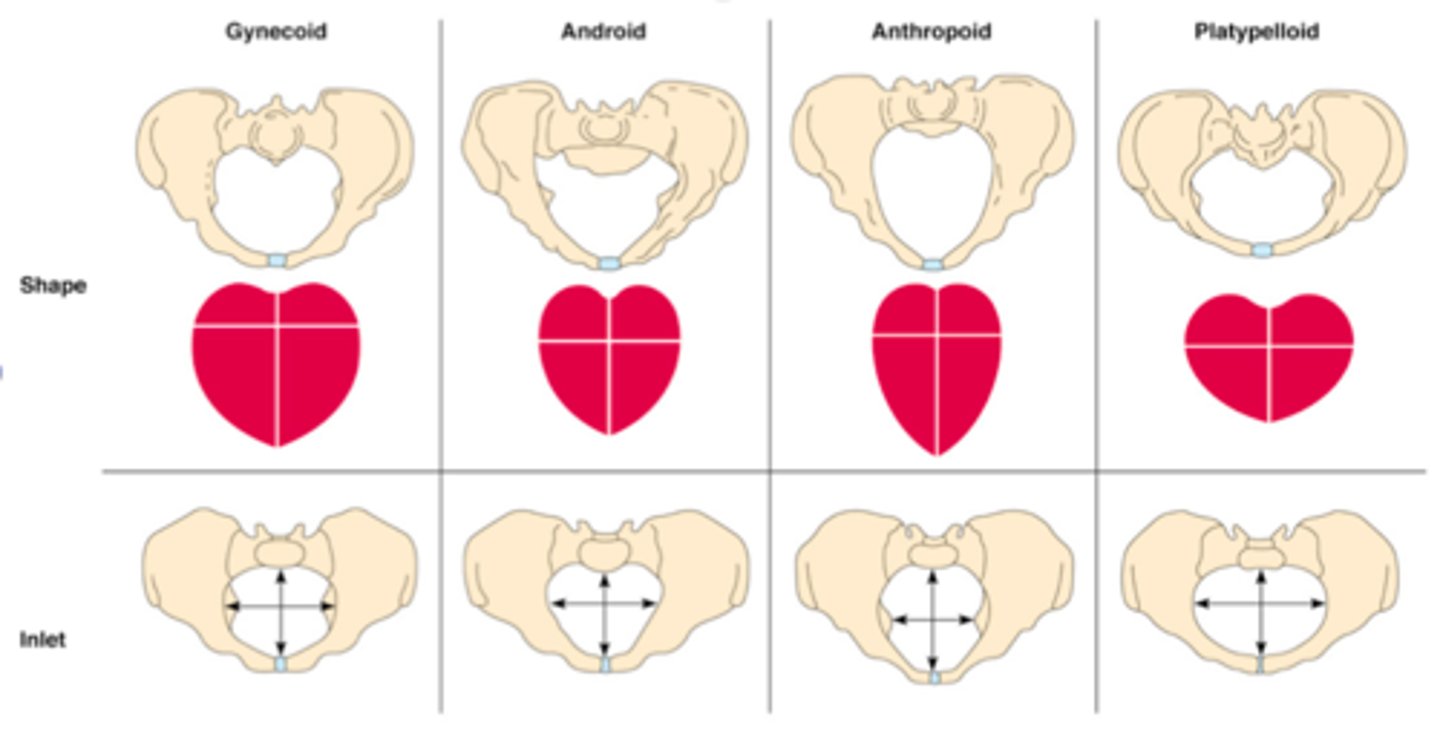
android pelvis
the typical male pelvis; in the woman, the heart shape of the android pelvis is not favorable to a vaginal delivery so c-section is recommended
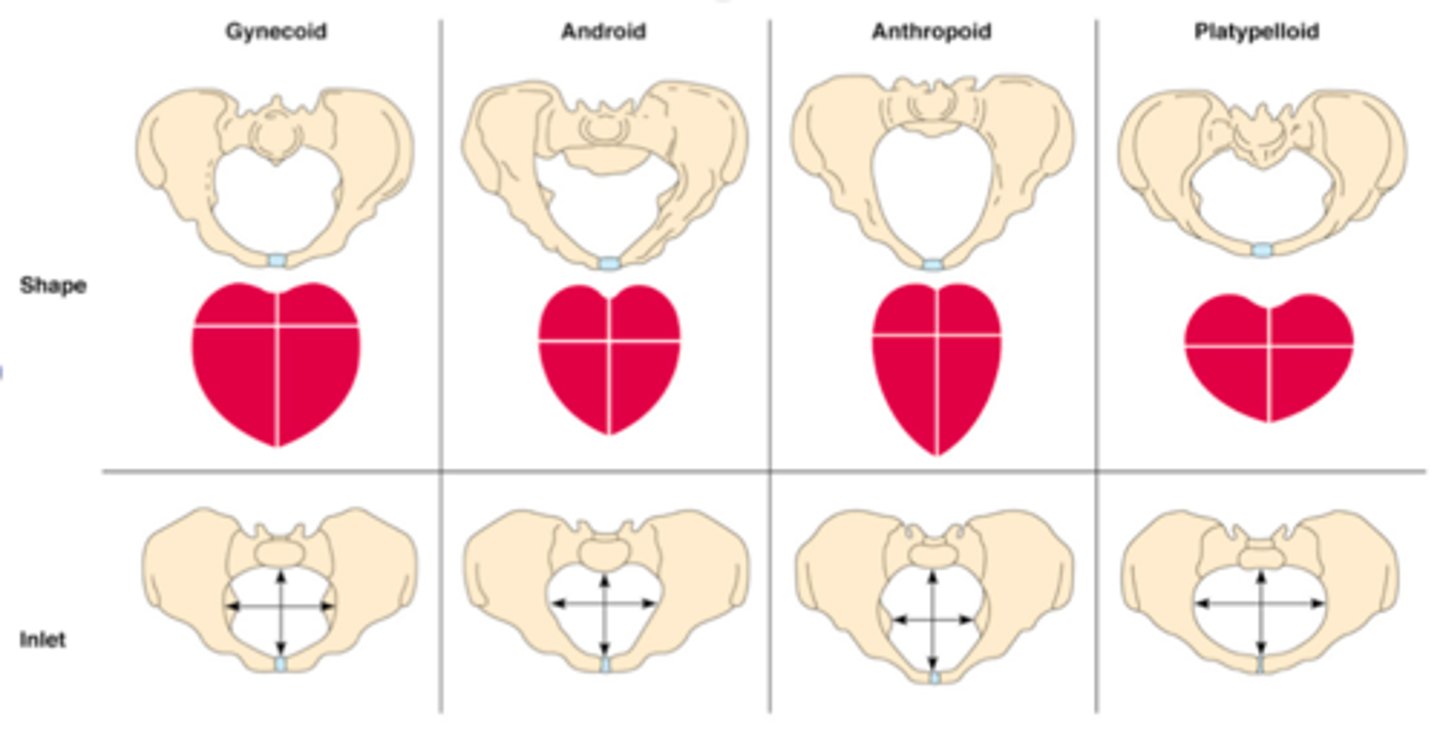
platypelloid pelvis
pelvis that is flat in its dimensions with a very narrow anterior-posterior diameter and a wide transverse diameter; this shape makes it extremely difficult for the fetus to pass through the bony pelvis
which fetal skull diameter is the most important?
suboccipitobregmatic
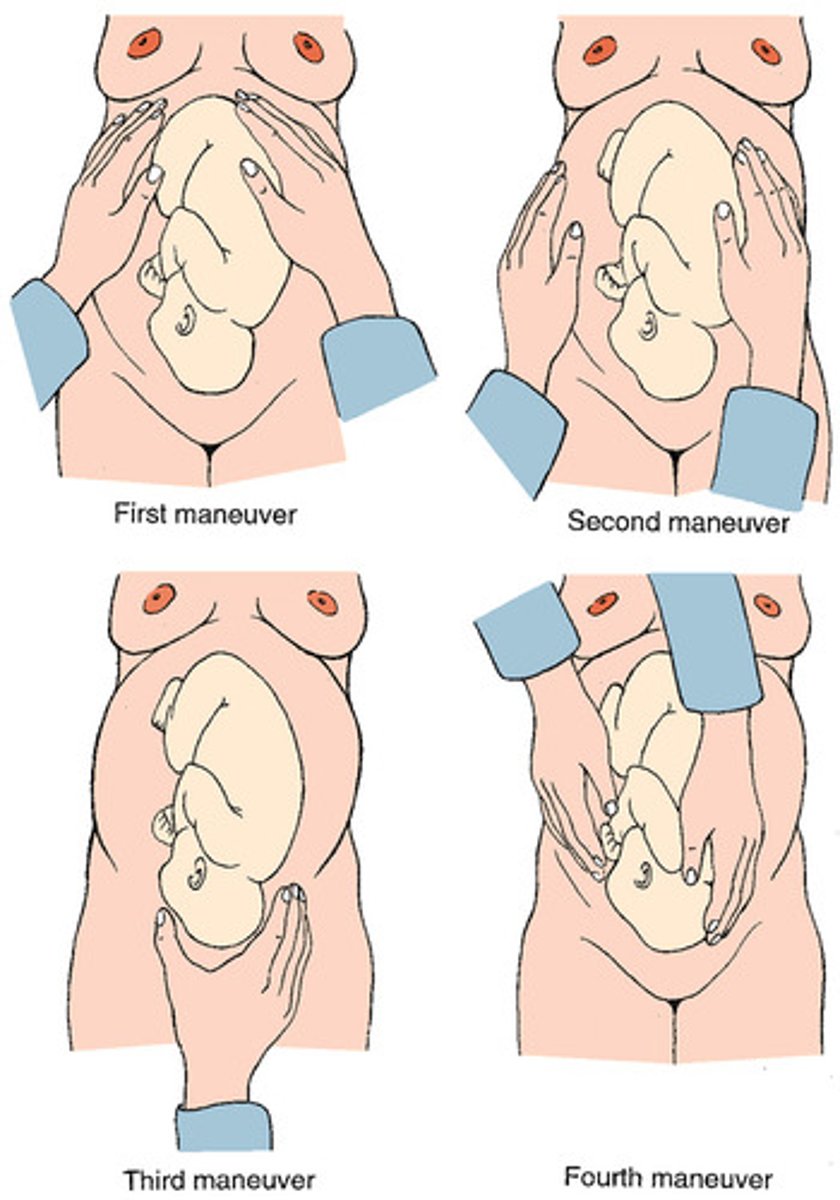
Leopold's Maneuvers
A series of four maneuvers designed to provide a systematic approach whereby the examiner may determine fetal presentation and position.
Cardinal movements of labor: step 1
Engagment
Cardinal movements of labor: step 2
Descent
Cardinal movements of labor: step 3
flexion
cardinal movements of labor: step 4
internal rotation
cardinal movements of labor: step 5
extension
Cardinal movements of labor: step 6
restitution/external rotation
cardinal movements of labor: step 7
external rotation
cardinal movements of labor: step 8
expulsion
A woman is having irregular contractions and says that walking helps alleviate the pain. what type of labor is she in?
False
a woman is having contractions that keep increasing in duration and intensity. What type of labor is she in?
true
What two things must you always document after ROM?
TACO and FHT
what does TACO stand for?
Time, Amount, Color, Odor
Percipitous labor
extremley fast labor (<3 hrs)
when is the best time to educate a pregnant woman about pain management?
before labor
What must you do before administer an epi?
administer 1000 cc of fluid bolus
spinal anesthesia
smaller dose (subarachnoid space)
quicker onset (5 min)
smaller needle (25-27g)
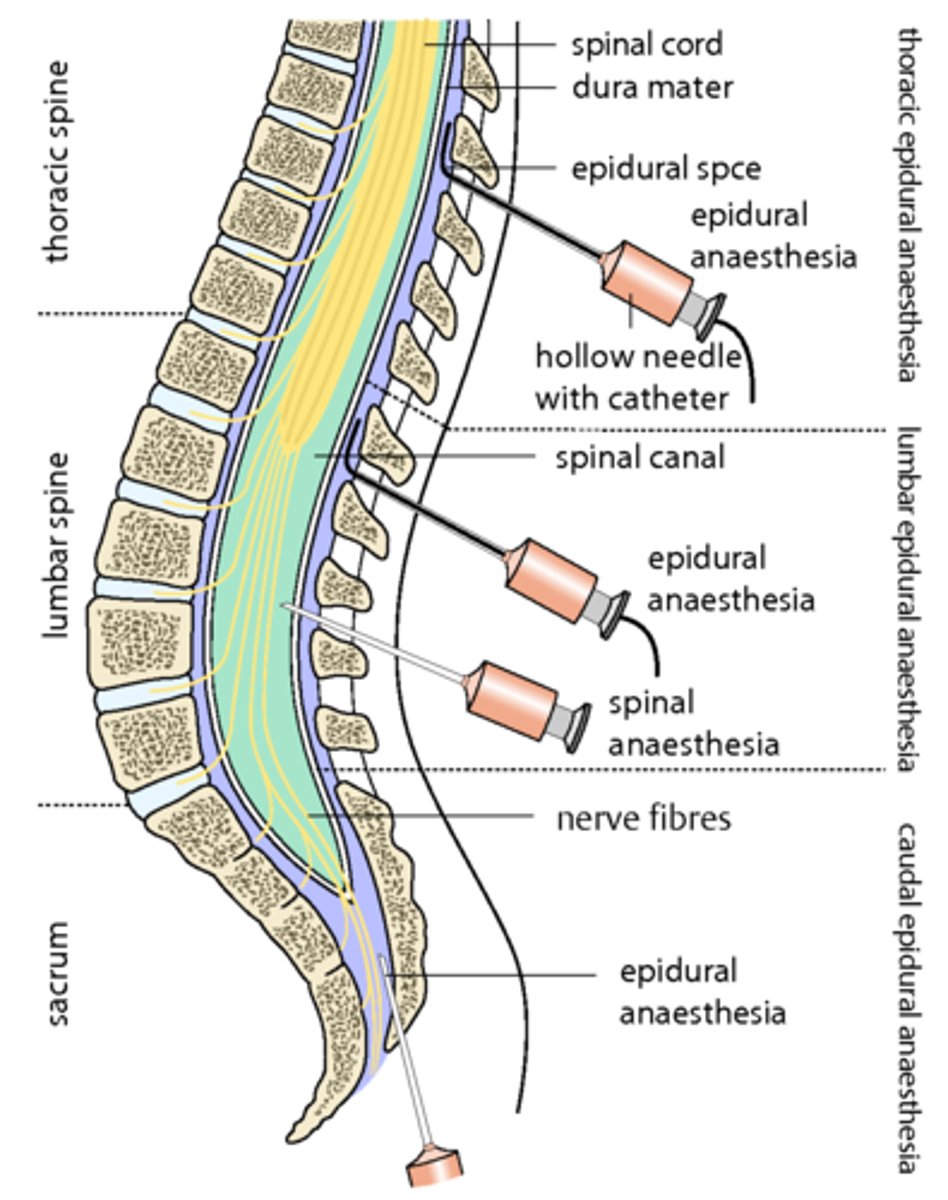
epidural anesthesia
larger dose (5x-10x)
longer onset (20 min)
larger needle (17g)
epidural space
Side effects of opioids and regional anesthesia/analgesics
urine retention
respiratory depression
postural hypo-tension
pruritus
increase HR
may slow labor <4-5cm dilation
Which hormone needs to decrease in order to stimulate lactation?
Progesterone
8 point part assessment
(BUBBLEEE) Breasts, Uterus, Bladder, Bowels, Lochia, Episiotomy, Extremities, Emotions
What is involution?
the return of the uterus to a non pregnant state after birth. Uterus contraction
Lochia rubra
Reddish or red-brown vaginal discharge that occurs immediately after childbirth; composed mostly of blood., 2-4 days
Lochia serosa
Pinkish/brown, serosanguineous. Lasts day 4-10 postpartum
Lochia alba
Yellowish, white cream color. Lasts approx 11 days-6 weeks postpartum
Rubins framework: Taking in
Focus: self, Behavior: dependent
Rubins framework: Taking hold
Focus: baby, Behavior: independent/dependent
Rubins framwork: Letting go
Focus: family as unit, Behavior: interdependent
Is the mom bonding with the baby?
(TEST): Talking, Enface, Smile, Touch
what is the most common cause of Postpartum hemorrhage?
Uterine atony
If a woman presents with a firm fundus but some gushes of blood, what is causing her PP hemorrhage?
laceration
If a woman presents with a boggy fundus but it is firm during massage, what may be causing this?
Retained placental fragments
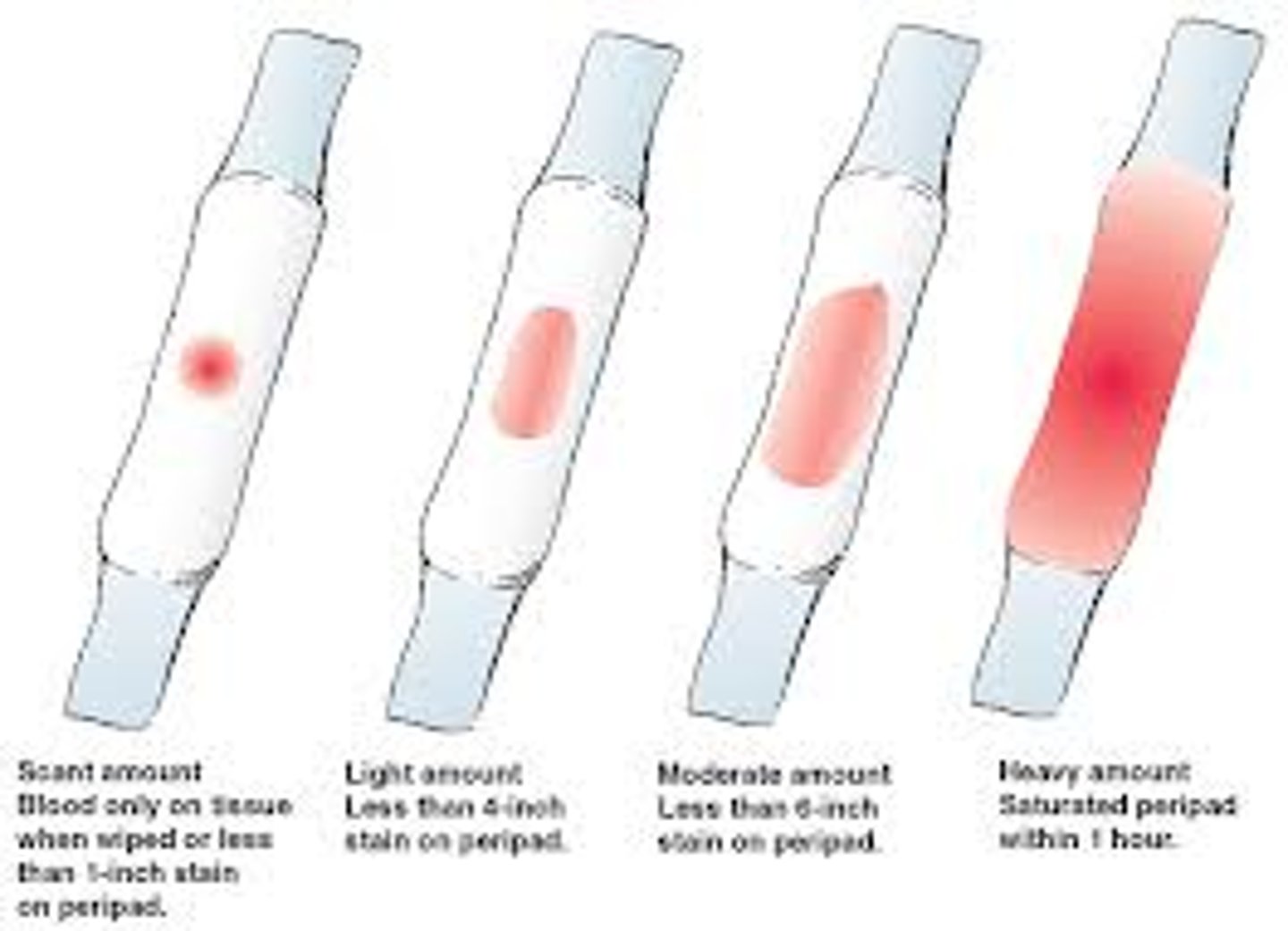
if a woman presents with a boggy fundus and soaked peri pad after 20 min PP, what may be the cause?
uterine atony
accreta
superficial invasion of the placenta into the uterine myometrium
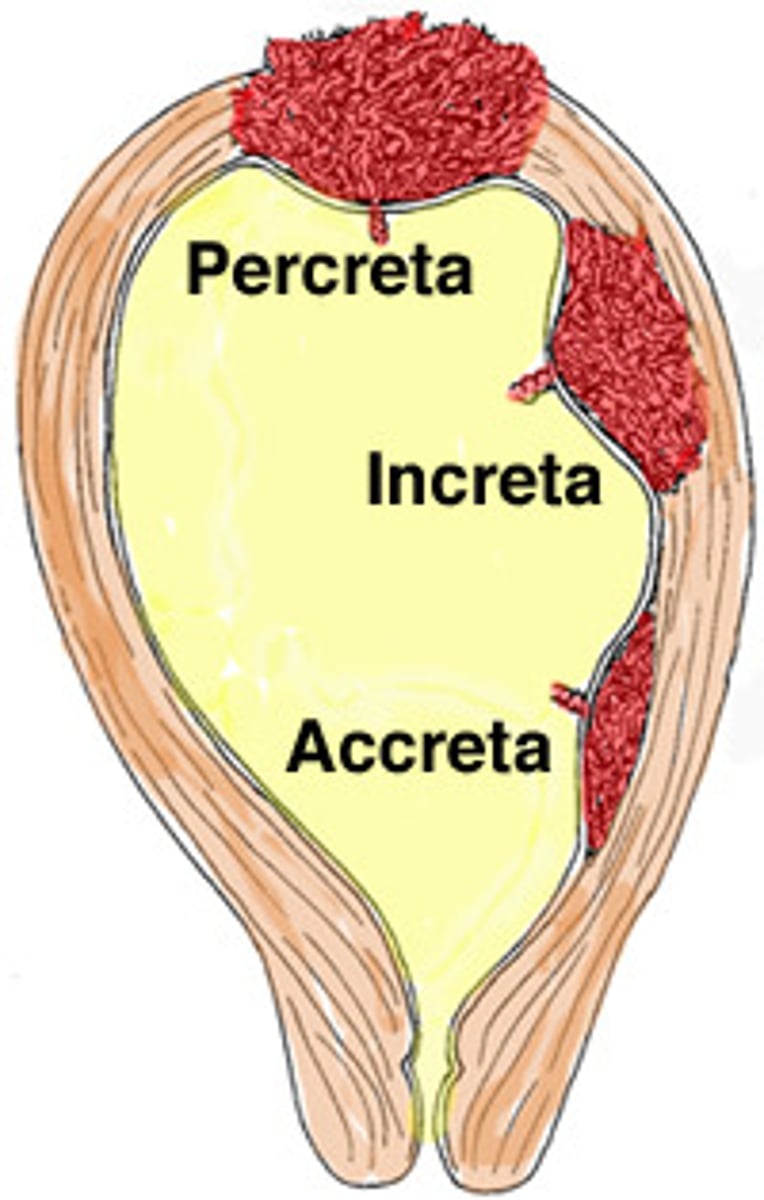
increta
placenta invades myometrium
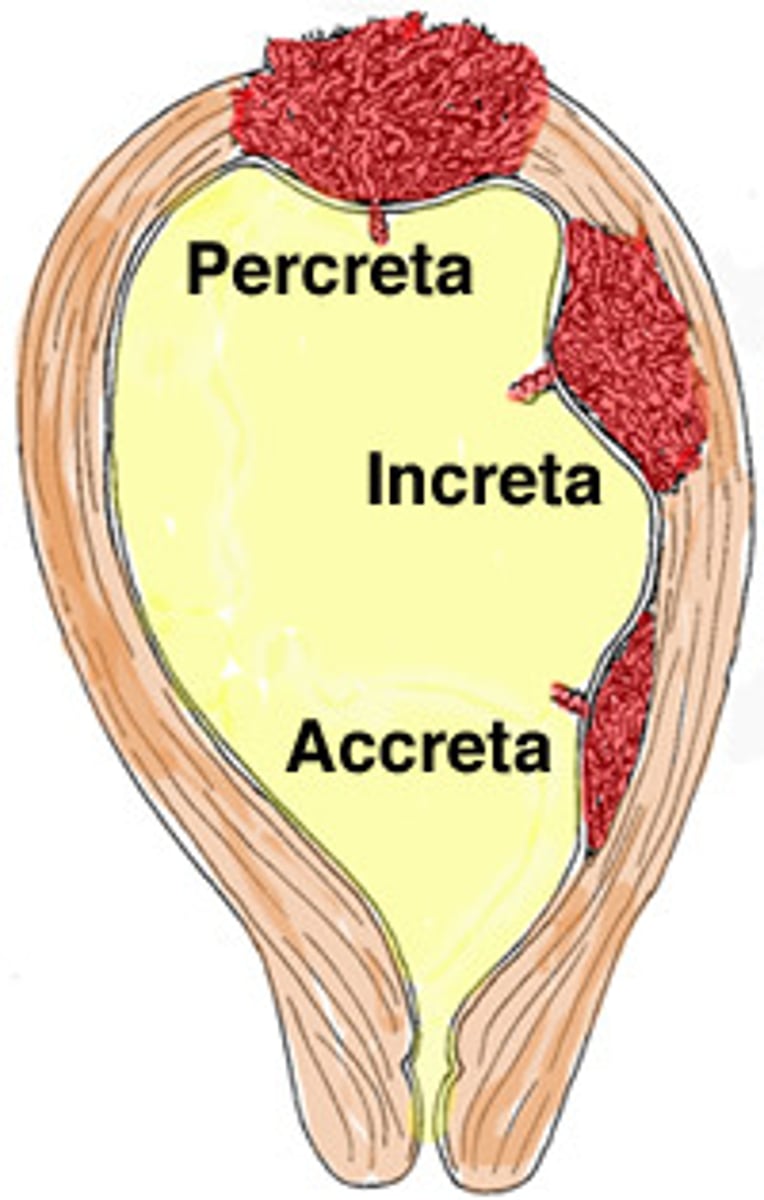
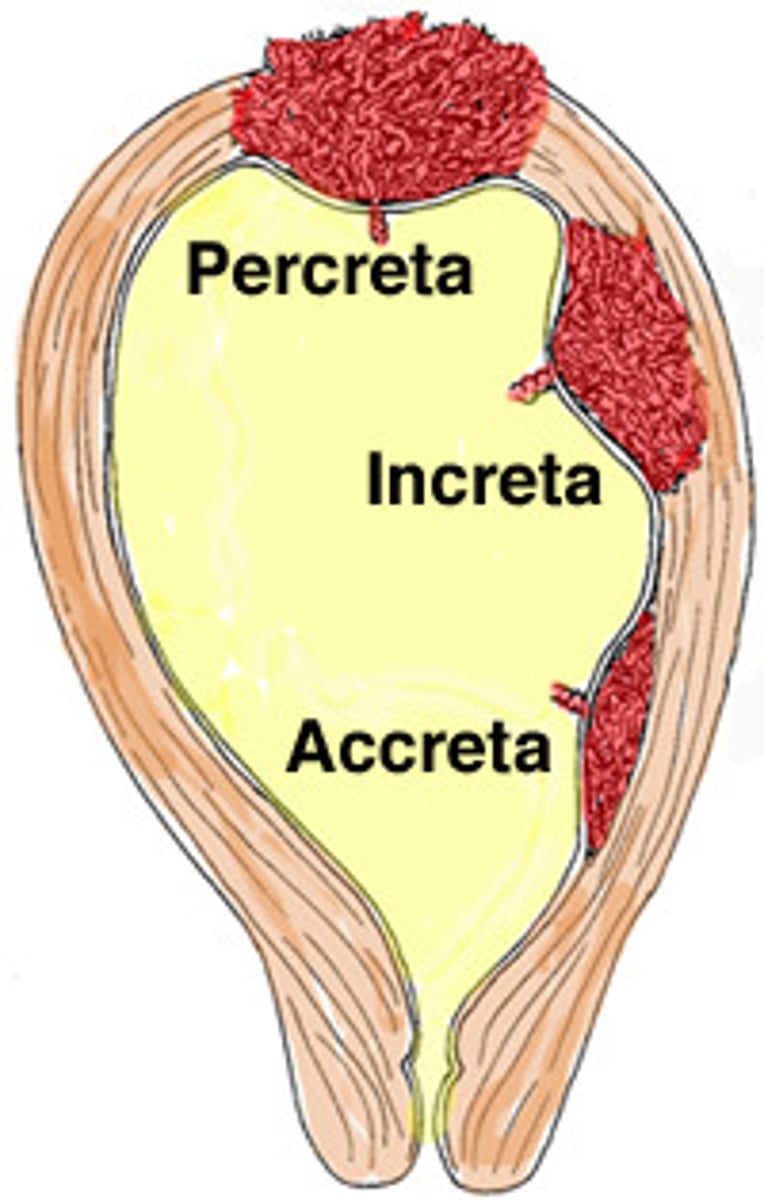
Percreta
placenta invades through the myometrium into the uterine serosa
Which PP bleeding medication should NOT be given to someone with hypertension?
Methergine
Which PP hemorrhage drug is first line AFTER pitocin?
cytotec
Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)
coagulation/autoimmune disorder in which a deficiency of platelets results in abnormal blood clotting, antibodies attack platelets, marked by tiny purple bruises (purpura) that form under the skin
Von Williebrand Disease
Hereditary defect, affects clotting factor, platelet dysfunction
Diseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
rare disease that causes abnormal clotting in blood and can cause bleeding
Post partum infection
The 7 W's
Womb (endometritis)
Wind (pneumonia)
Water (UTI)
Walk (DVT/PE)
Wound (incision site)
Weaning (engorgement/mastitis)
Wonder (Drug fever)