2.2.8(Proteins)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Define the term amino acid
Monomers of all proteins with the same basic structure
Describe the role of proteins
They are structural components of animals
They adopt specific shapes which makes them important as enzymes, antibodies and some hormones
Membranes have proteins that act as carriers ad pores for active transport and facilitated diffusion
State the elements which make up an amino acid
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
Nitrogen
some contain sulfur
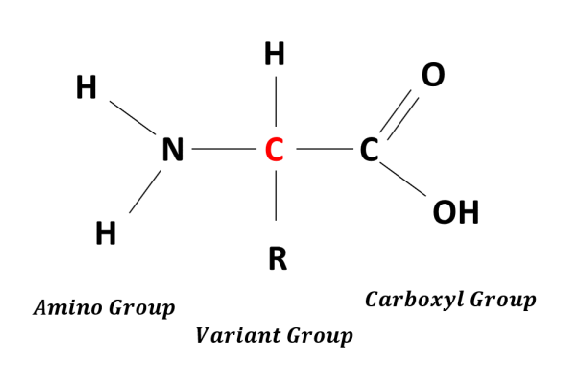
State the functional groups of amino acids and draw the standard amino acid structure
Amino group(-NH2)
Carboxyl group(-COOH)
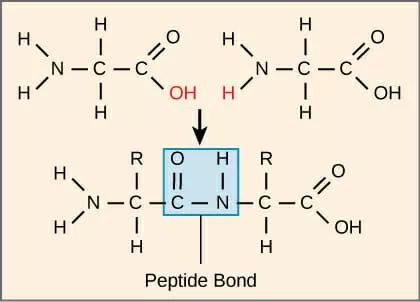
State the name of the bond which holds amino acids together
Peptide bonds
State the enzyme which helps to catalyse the break down of proteins
Protease - by breaking peptide bonds
What is the peptide bond structure
C double bond O, N H
What is meant by the primary structure of a protein
The sequence of amino acids in a protein chain is its primary structure
What is meant by the secondary structure
The coiling or folding of an a primary structure, due to hydrogen bonding between different parts of the polypeptide chain
What are the 2 main Secondary structures?
alpha helix sturcture
beta pleated sheet
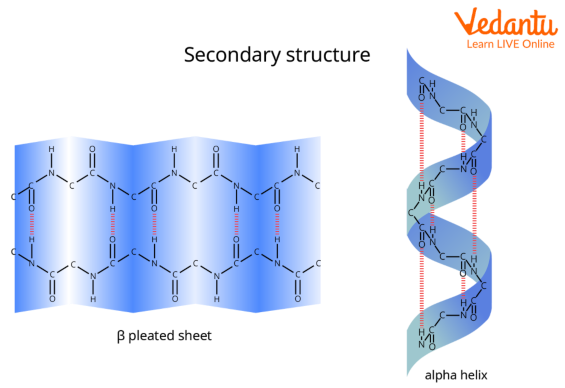
Describe the structure of an alpha helix structure
Helix structure which is spiraled
The helix is held together by lots of hydrogen bonds between the -NH group of one amino acid and the -C=O of another amino acid, 4 places ahead of it in the chain
Describe the structure of a beta pleated sheet structure
It has a zigzag structure which is folded in on itself
Hydrogen bonds form between the -NH of one amino acid and the C=O of another amino acid further down the strand which holds the sheet together
Explain why secondary structures are stable.
Although hydrogen bonds are weak, many of them are formed between -NH and -C=O groups which makes the entire structure strong and stable at optimal temperatures and pH
What meant by a tertiary structure
It is the overall 3D shape of a protein molecule, that arises due to hydrogen bonding, disulphide bond, ionic bonds and hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions
Describe how hydrogen bonds are formed between amino acids in polypeptide chains
They form between a slightly positive hydrogen and a slightly negative oxygen, in amino acids, these form between hydroxyl, carboxyl and amino groups
State the importance of hydrogen bonding in proteins
Hydrogen bonds are important in keeping the tertiary and quaternary structure of the protein in the correct shape.
The presence of multiple hydrogen bonds can give protein molecules a lot strength
Describe how ionic bonds form
They form between carboxyl and amino groups that are part of R groups
These ionise into NH3+ and COO- groups
Positive and negative groups like thus are strongly attracted to each other to form ionic bonds
Describe how disulfide links form
The R group of the amino acid cysteine contains sulfur. Disulfide bridges are formed between the R groups of 2 cysteines
These are strong covalent bonds
Describe how hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions take place in proteins?
Hydrophobic parts of the R groups tend to associate together in the centre of the polypeptide to avoid water. In the same hydrophilic parts are found at the edge of the polypeptide, close to water
Hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions cause the twisting of the amino acid chain, which changes the shape of the protein
Explain why hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions are important
The hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions are important as most proteins are found surrounded by water inside a living organism
What are the 2 main categories of tertiary and quaternary structured proteins
Globular
Fibrous
State structure and function of fibrous proteins
They have a regular, repetitive sequences of amino acids
Usually insoluble in water
These features enable them to form fibres which tend to have a structural function
State the structure and function of Globular proteins
They roll up into an almost spherical shape.
Any hydrophobic R-groups are turned inwards towards the centre of the molecule, while hydrophilic groups are on the outside.
This makes the proteins soluble in water
They often have very specific shapes, which help them to take up specific roles
Compare Globular and fibrous proteins
Fibrous:
Shape: Long, Narrow
Role: Structural(strength)
Solubility: generally insoluble in water
Sequence: Repetitive amino acid sequences
Stability: Less sensitive to changes in Heat, pH, etc.
Examples: Collagen, Keratin, Elastin, Myosin
Globular:
Shape: Rounded
Role: Functional(catalytic, transport etc.)
Solubility: Generally soluble in water
Sequence: Irregular amino acid sequence
Stability: More sensitive to changes in temperature, pH
Examples: Haemoglobin, Insulin, Pepsin
State the function of collagen as a fibrous protein and 4 examples of their function being used.
Function: Provide mechanical strength:
Examples:
Artery walls: Collagen prevents bursting and withstands high pressure
Tendons: made of collagen and connect muscle to bone
Bones: Made of collagen and reinforced with calcium phosphate - making them hard
Cartilage and connective tissue: Made from collagen
State the function of cross links in collagen
They are staggered to avoid weak points
State the structure and function of keratin
Function:
Provide mechanical protection
Impermeable barrier to infection which prevents entry of water-born pollutants
Structure:
Rich in cysteine, causing lots of disulfide bridges from between its polypeptide chains.
Along side hydrogen bonds makes the molecule very strong
State where keratin is found in the body
It is found in body parts that need to be hard and strong:
Fingernails
Hair
Claws
Hoofs
Horns
Scales
Fur
Feathers
State the structure and function of elastin
Structure: Crosslinks and coiling make the structure of elastin strong and extensible.
Function: To provide stretch and adapt shape as part of their processes
State 3 ways in which elastin is used in the body
Skin: Skin can stretch around our bones and muscles because of elastin which allows skin to go back to normal after being pinched
Lungs and bladder: It is found in out lungs to allow them to inflate and deflate and in out bladder, which helps it expand to hold urine
Blood vessels: Elastin helps out blood vessels stretch and recoil, helping maintain pressure of blood
State what collagen, keratin and elastin are examples of
Fibrous proteins
State the structure and function of haemoglobin
Structure: (Quaternary structure)
Made up of 4 polypeptide chains:
2 alpha-globin chains and 2 beta-globin chain
Each of these has its own tertiary structure, but when fitted together they form one haemoglobin molecule
The shape of the molecule is held together by hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions and ionic bonds which gives it a very specific shape
Each polypeptide subunit has a haem group which are called prosthetic groups
Haemoglobin is a conjugated, globular protein
When oxygen binds, haemoglobin turns from a purple red colour to bright red
Function:
To carry oxygen from lungs to respiring tissue. It does this by binding to the iron group in each haem group
State the structure and function of insulin
Structure:
Made of 2 polypeptide chains:
The A chain begins with a section of alpha helix, and the B chain ends with a section of Beta pleat.
Both chains fold into a tertiary structure and are then joined by disulfide links
Amino Acids with hydrophilic R groups are on the outside of the molecule, which makes it soluble in water
Function:
Binds to glycoprotein receptors on the outside of the muscle and fat cells to increase their uptake of glucose from the blood and to increase their rate of consumption
State the strucure and function of pepsin
Structure:
Made up of a single polypeptide chain of 327 acids, but it folds into a symmetrical tertiary structure.
Pepsin has a few amino acids with only 4 basic R groups
Pepsin has 43 amino acids with acidic R groups
there are few basic groups that accept H+ ions and therefore can be little effect on the enzyme’s structure which explains it’s stability in acidic environments
Functions:
An enzyme which digests proteins in the stomach
State and explain 2 ways in which structures of proteins can be predicted
Ab initio protein modelling:
A model built based on the physical and electrical properties of atoms in each amino acid in the sequence. There can multiple solutions to the same amino acid sequence and other methods sometimes need applying to reducing the number of solutions
Comparative protein modelling:
Protein threading is one approach, which scans the amino acid sequence against a data base of known structures and produced a possible set of models which would match that sequence