Rutgers Functional Human Anatomy Lec 16 (Reproductive System)
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
Reproductive system function
Gametes (germ cell, haploid:
sperm (male)
oocytes (female)
Fertilization
zygote
Gonads:
Testes/Ovaries
- produces gametes and hormones
Reproductive tract
Accessory glands
External genitalia
fertilization
- where: in the ampulla region of the uterine tube (fallopian tube)
- when: 12-24 hours after ovulation
- result: the formation of a diploid zygote
Gametes are _____________ by reproductive system
produced
stored
nourished
transported
Principle structures of male reproductive system
scrotum:
testis
epididymis
Ductus deferens
Urethra
Accessory Glands:
Seminal gland
Prostate gland
Bulbo-urethral gland
Penis
male testes during development
2nd month:
abdominal cavity
3rd month:
pelvic cavity
epididymis forms
4th month:
still inside body cavity
7 months:
scrotal cavity opened
-testes descending
Birth:
completely descended
testes & sperm development temp
testes:
develop at body temp
98.6 degrees F
sperm:
slightly cooler temp
96.6 degrees F
inguinal hernia
part of intestines protrudes in a weak spot in muscles of inguinal canal (wear testes droped from)
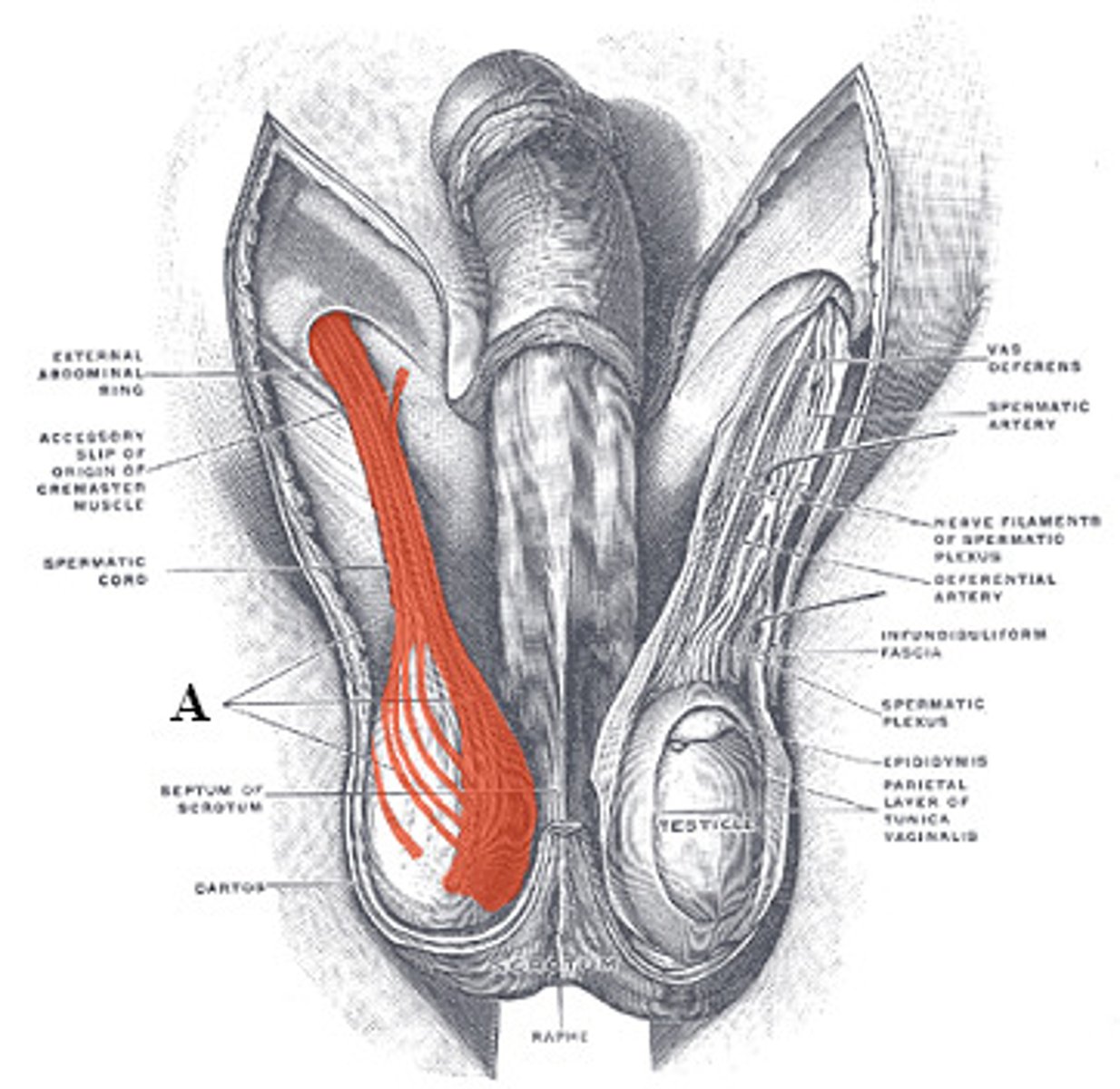
Spermatic cord
structure connected to testicles
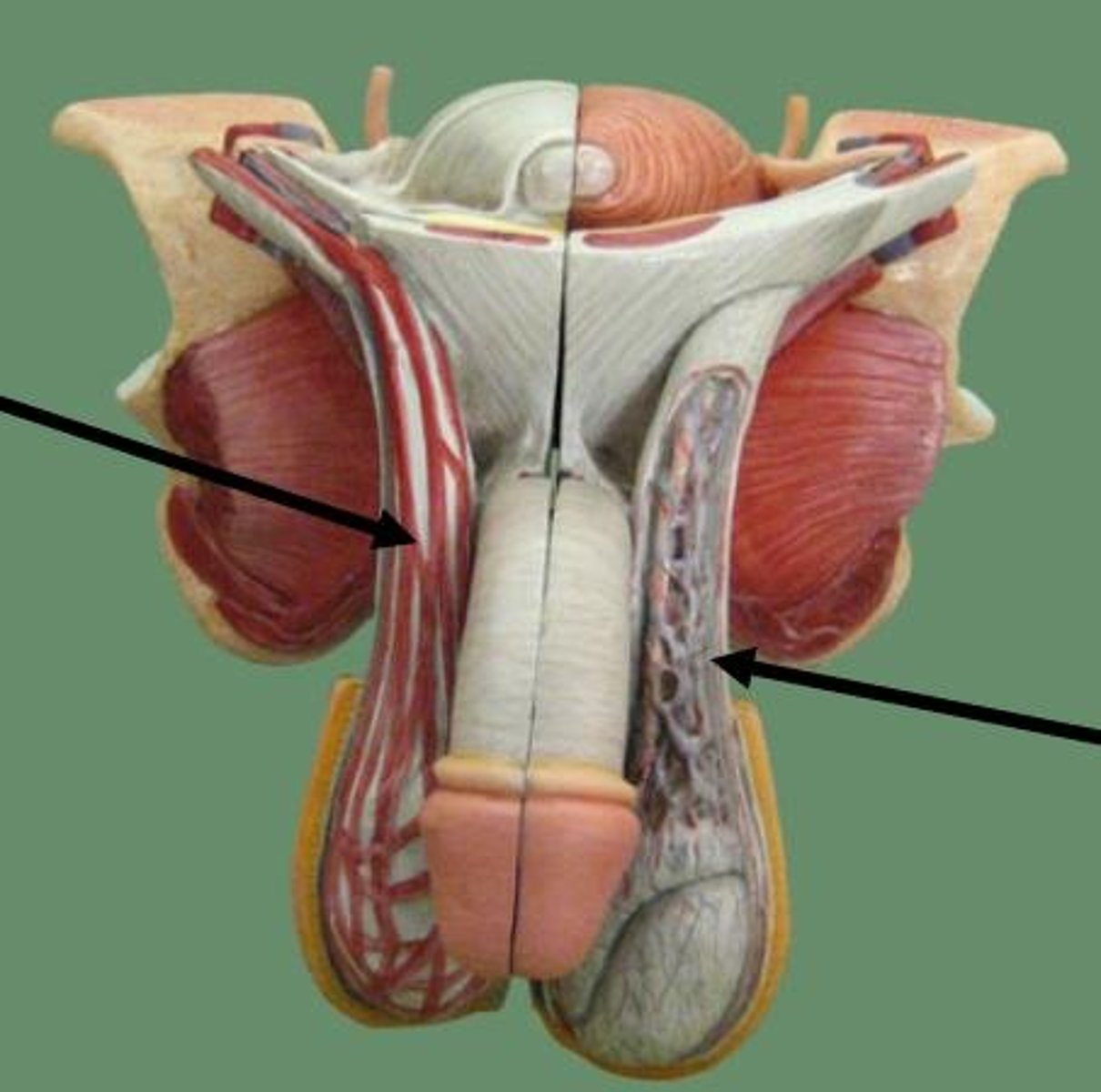
structures in spermatic cord
- ductus (Vas) deferens - transports sperm
- testicular artery
- pampiniform plexus - venous network that helps cool arterial blood
- cremaster muscle fibers - help raise/lower the testis
- genital branch of genitofemoral nerve - innervates cremaster muscle
- lymphatic vessels
scrotum
- soft tissue surrounding testes
- chamber each testicle is in, across scrotum, anterior surface of penis
tunica vaginalis
- inner lining of serous membrane (cavity)
- reduces friction between outer and inner serous layers
Dartos muscle
- superficial
- encapsulate area around testicles
- smooth muscle
- not under voluntary control
- contracts causing wrinkling of scrotal surface (in cold weather)
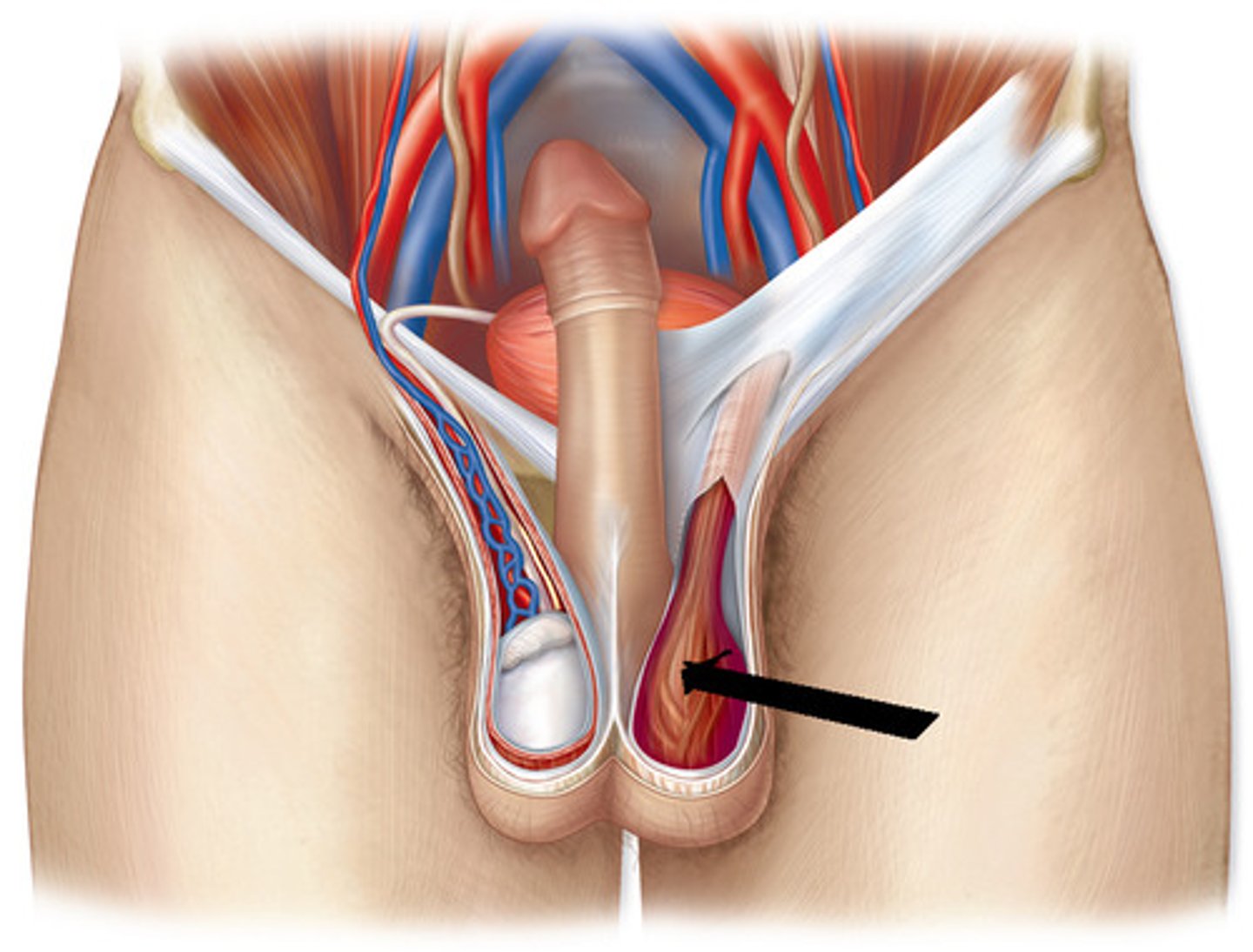
cremaster muscles
- within cremaster fascia covering the testicles
- help pull testicles closer to body
cremasteric reflex
stroking the upper inner thigh causes the ipsilateral cremaster muscle to contract, raising the testis
septa testis
separating testes into lobules
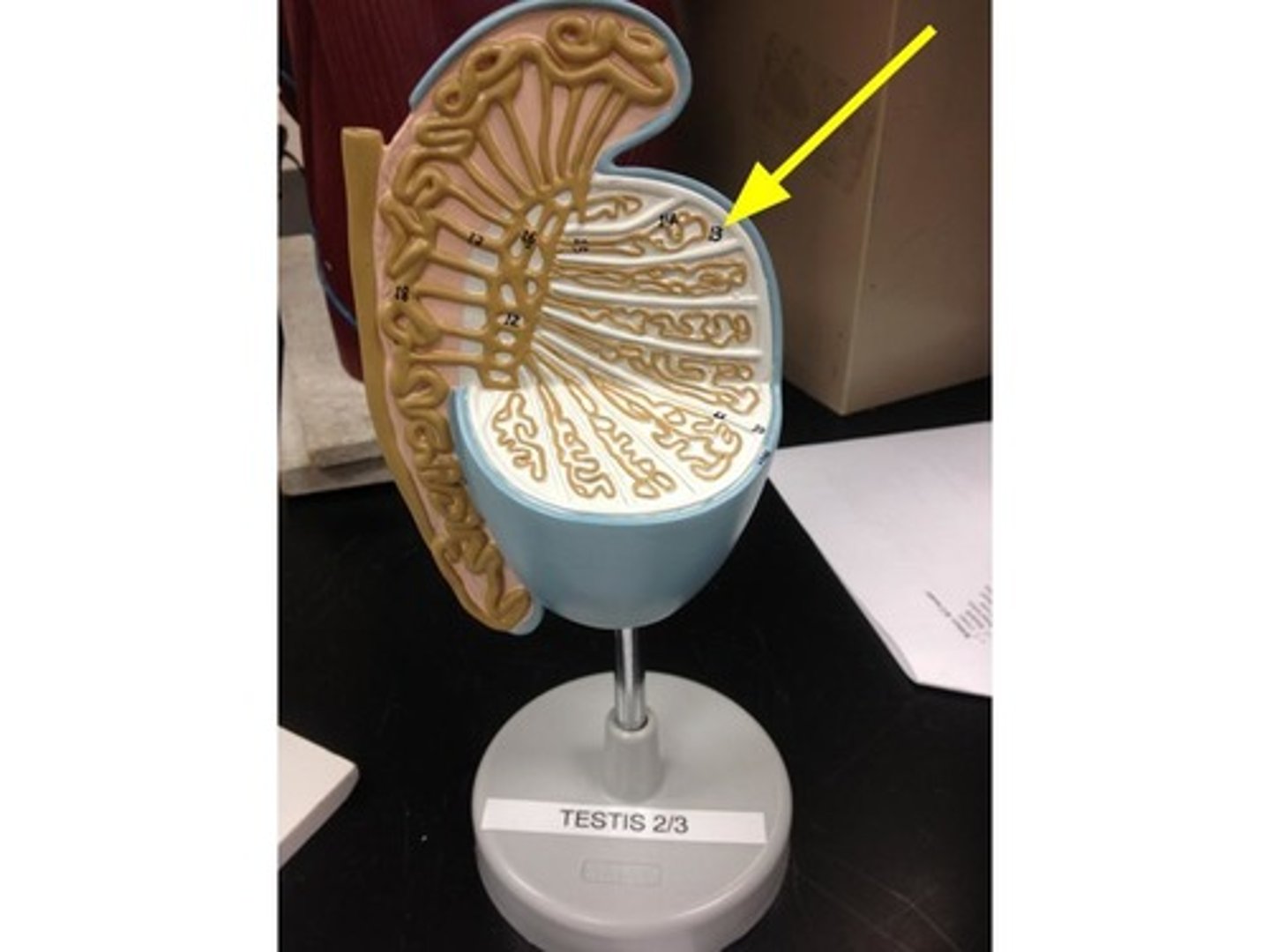
lobule
contain coiled seminiferous tubules (80cm)
> mediastinum area:
- straight tubule interconnecting forming rete testis
- rete testis > efferent ductule > epididymis
leydig cells
- interconnecting endocrine cells
- between seminiferous tubules
- testosterone produced and gets released
Testosterone
- hormone
- stimulate spermatogenesis (creation of sperm)
- promotes sperm maturation
- helps maintain accessory organs
- develop secondary sex characteristics
- stimulate growth hormone/metabolism
- stimulate sexual behavior/ sex drive
FSH and LH in males
- FSH stimulates sperm production in the seminiferous tubules
- LH stimulates Leydig cells to produce testosterone
primary/secondary sex characteristics
Primary:
- appear at birth
- physical structures
Secondary:
- appear w/ puberty
- facial & body hair
- adam's apple (larger pharynx)
- increase musculature
sperm anatomy
head:
contains chromosomes & acromsone (enzyme for fertilization of egg)
neck:
mitochondria
centrioles
tail:
flagella (only flagellum in human body)
- allows to become mobile
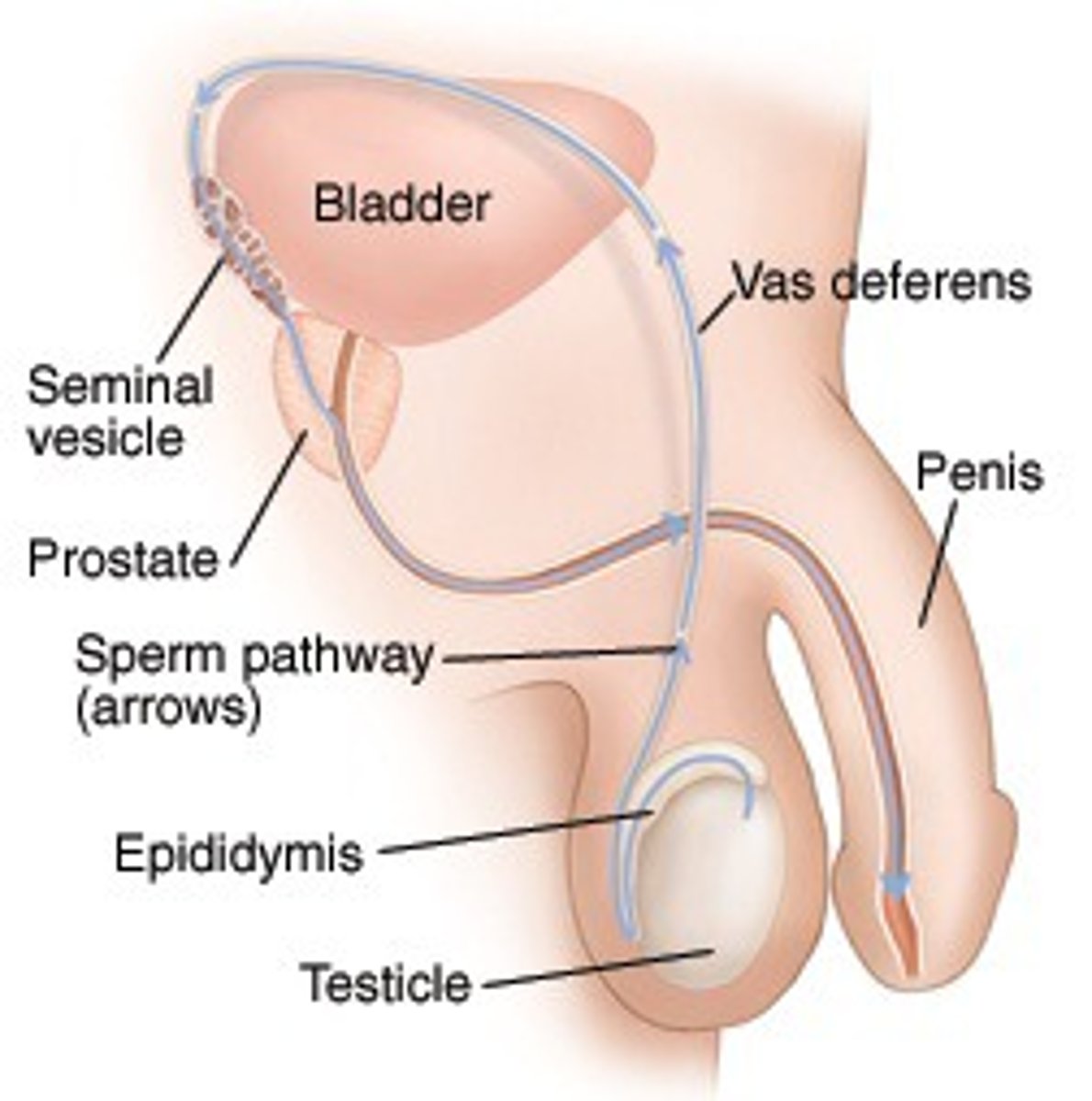
Male reproductive tract
epididymis:
capacitation
ductus deferens (vas deferens)
urethra
epididymis
monitor composition of fluid produced by seminiferous tubules
- recycling center for damages spermatozoa
- stores spermatozoa (sperm) for maturation
how long does it take spermatozoa to pass epididymis
2 weeks
sperm present in male body
- not present from birth
- process takes few weeks
- starts after puberty
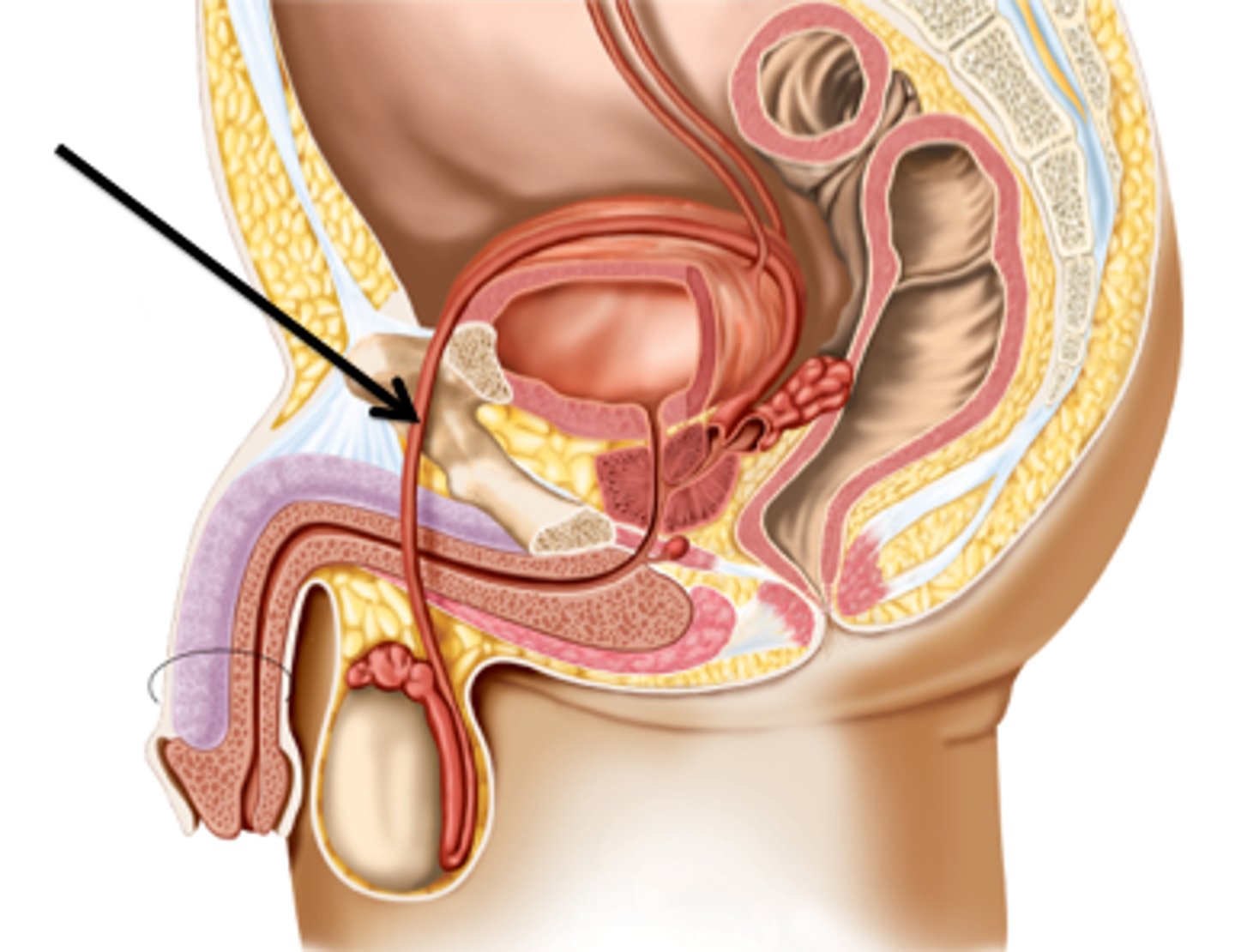
ductus deferens
- sperm and hormones pass through
- curves around urinary bladder and ureter then descends back toward prostate gland
ampulla
joins excretory duct of seminal gland to become ejaculatory duct
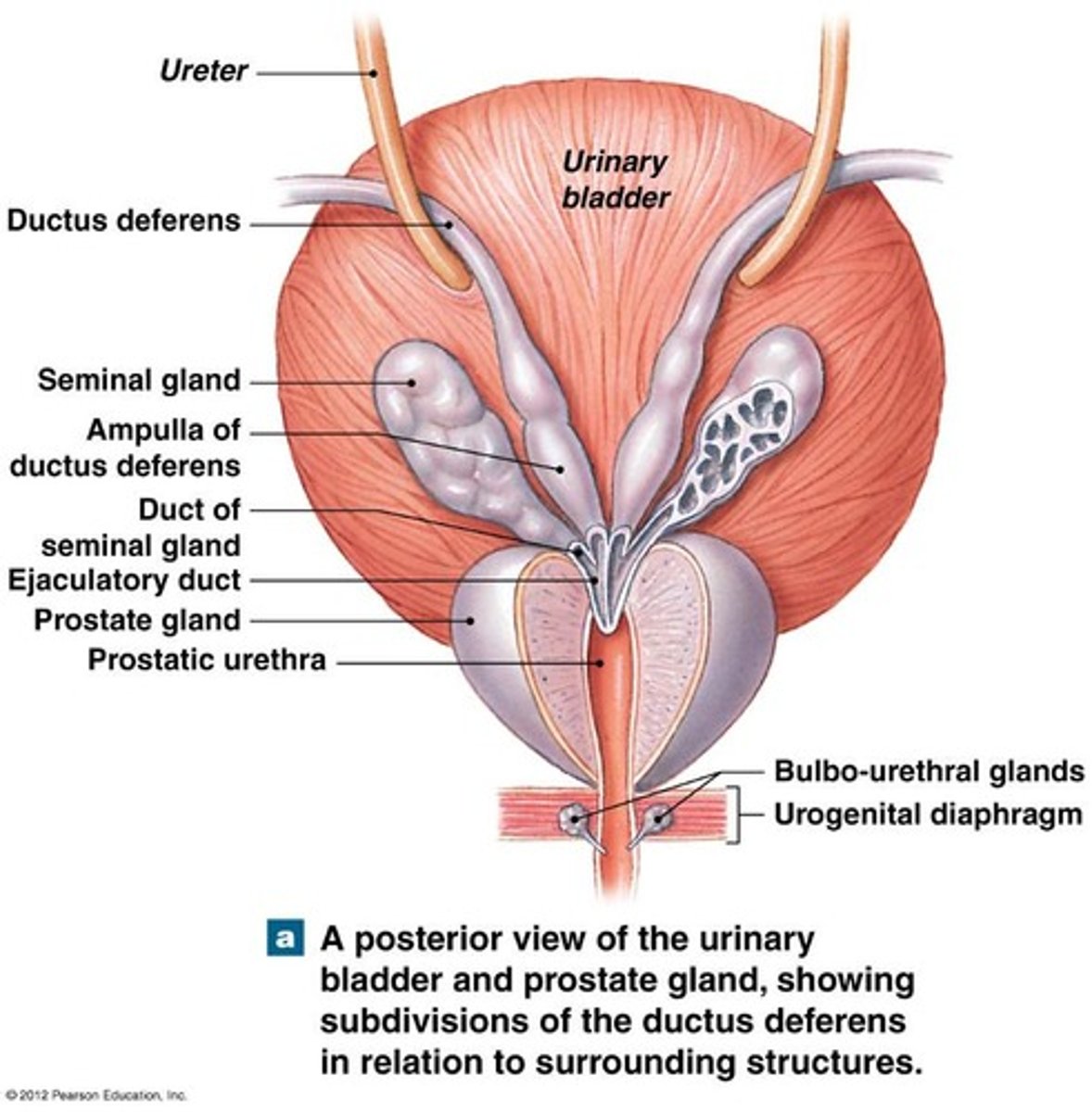
ejaculatory duct empties
to prostatic urethra
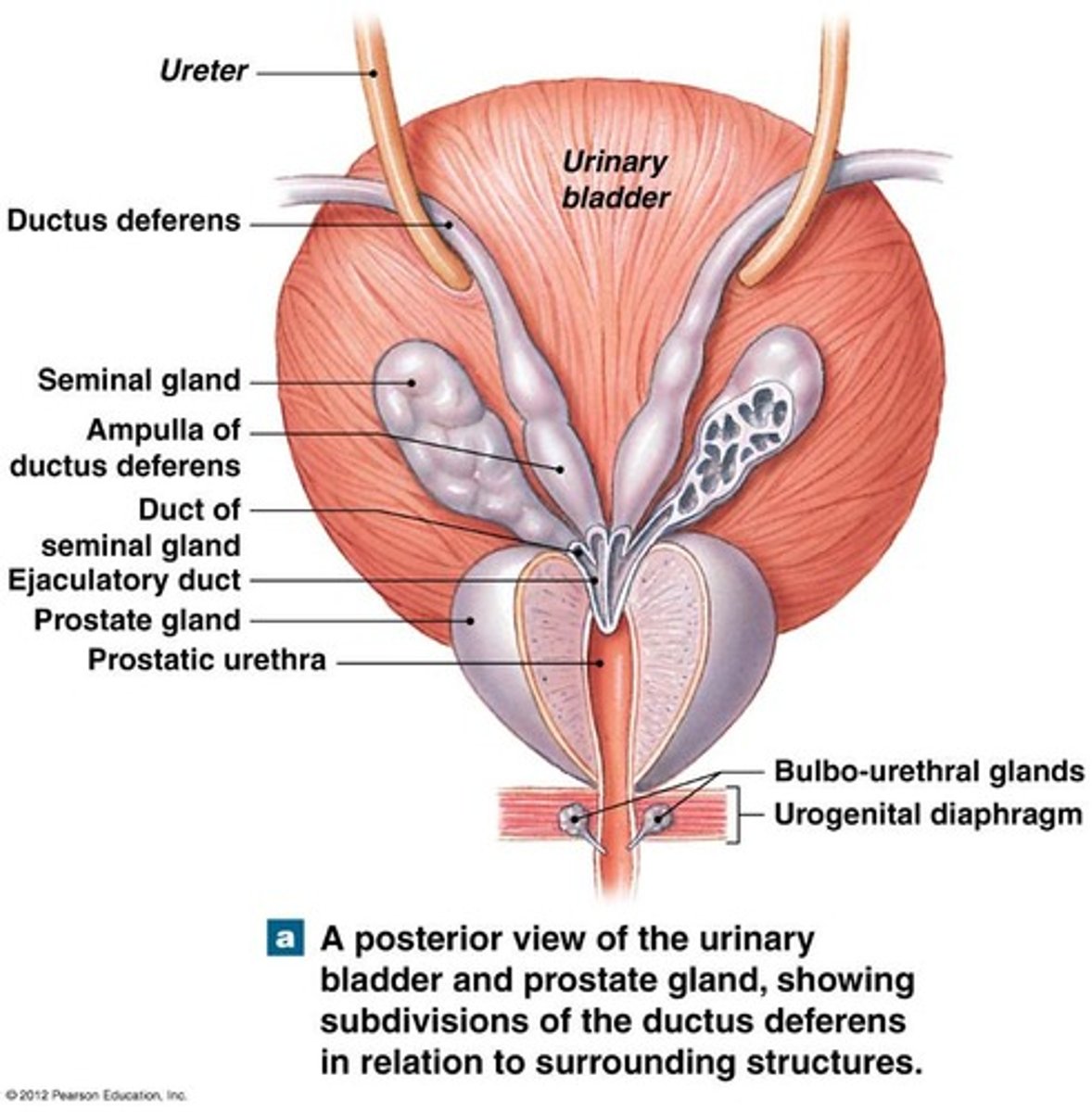
urethra (3)
prostatic
membranous
spongy/penile
seminal fluid
- 60% produced by seminal gland/vessels
- 30% from prostate
- 5% from bulbo-urethral glands
- 5% from epididymis
normal sperm count
- 20-300 million per milliliter of semen
- each ejaculation releases 2-5 milliliters of semen
enzymes in semen
- help dissolve vaginal mucus
- antibiotic
- prevent sperm coagulation in vagina
Capacitation of sperm
- biochemical process
- sperm is mobile & ready to fertilize an oocyte when exposed to female reproductive tract
- happens after ejaculation, inside the female body
sperm become motile when
mix w/ secretions of seminal glands
semen
= product of ejaculation
contains:
- sperm cells
- seminal fluid
- enzymes
how long does it take sperm to develop in testicles
50-60 days
how long does it take sperm to mature and move through epididymis
14 days
during spermatogenesis the testicles make _________ sperm a day
-several million
(15-hundred per second)
body maintains surplus of semen
- to ensure fresh supply for conception
seminal vesicles are producing & secreting
- alkaline viscous fluid high in and fructose and nutrients for sperm to help w/ motility
- coagulants
- prostaglandins
- to clot sperm and lubricant
Bulbo-Urethral Glands (Cowper's Glands)
releases fluid to clean acidic urine
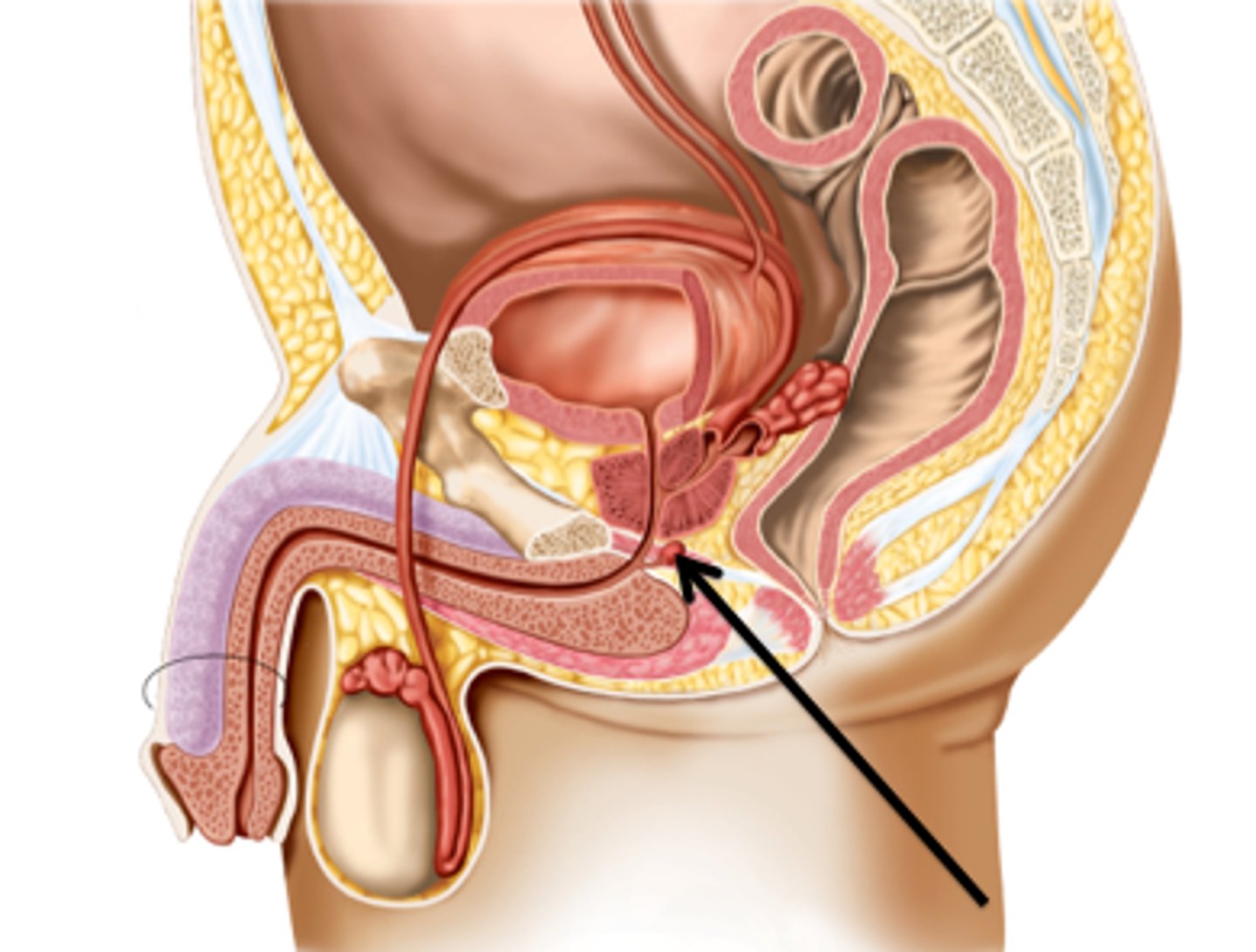
anatomy of male reproductive system
root (to pelvic bone)
body (shaft, where erectile tissue is found)
glans penis (distal end, surround external urethral orifice)
erectile tissue & blood vessels:
- 2 posterior corpora cavernosa
- 1 anterior (underside of penis) corpus spongiosum
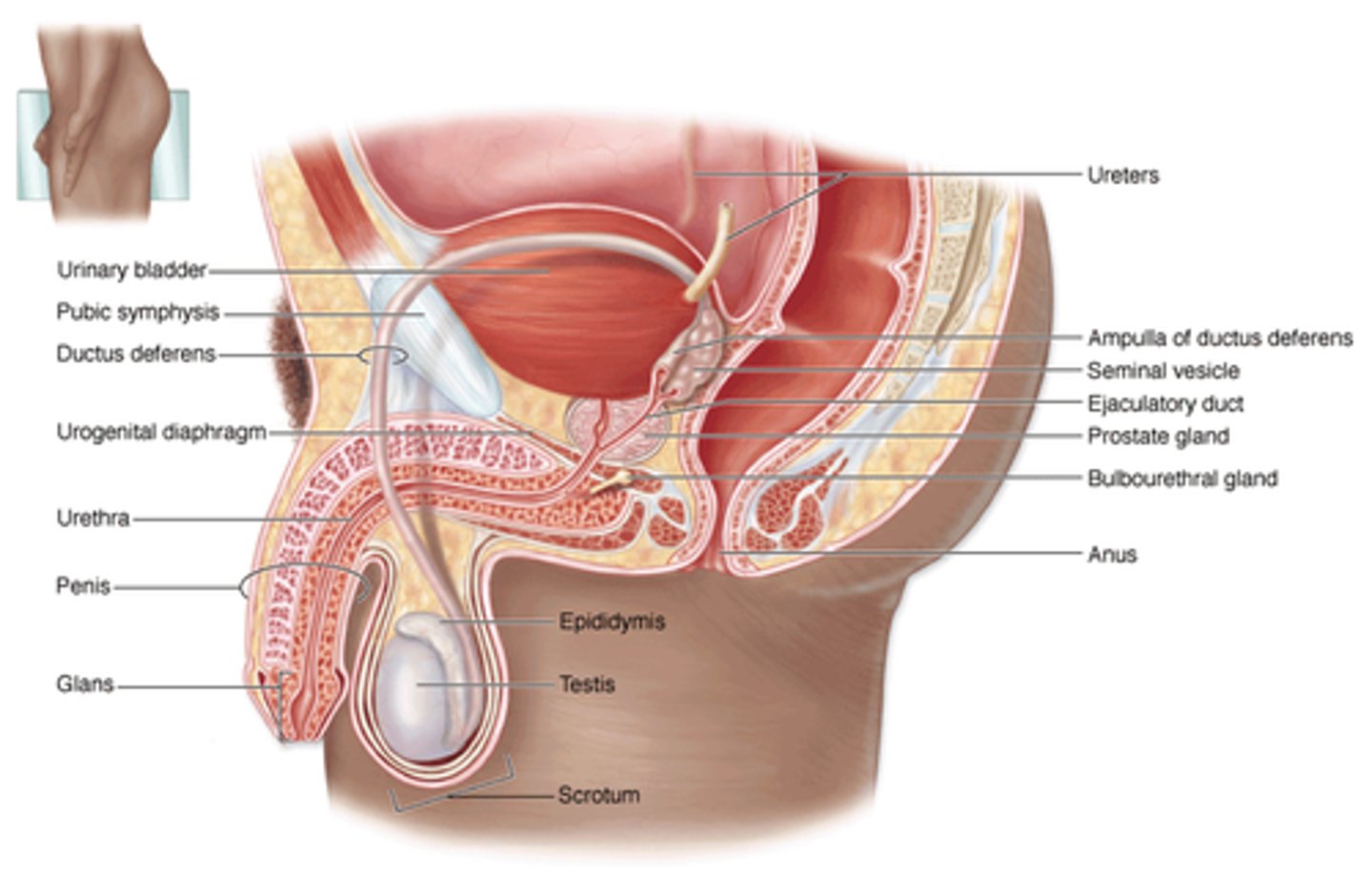
prepuce
foreskin
circumcision
removal of foreskin
erectile tissues of penis
posterior:
two corpora cavernosa
(deep artery)
anterior:
one spongiosum (spongnyurethra in center)
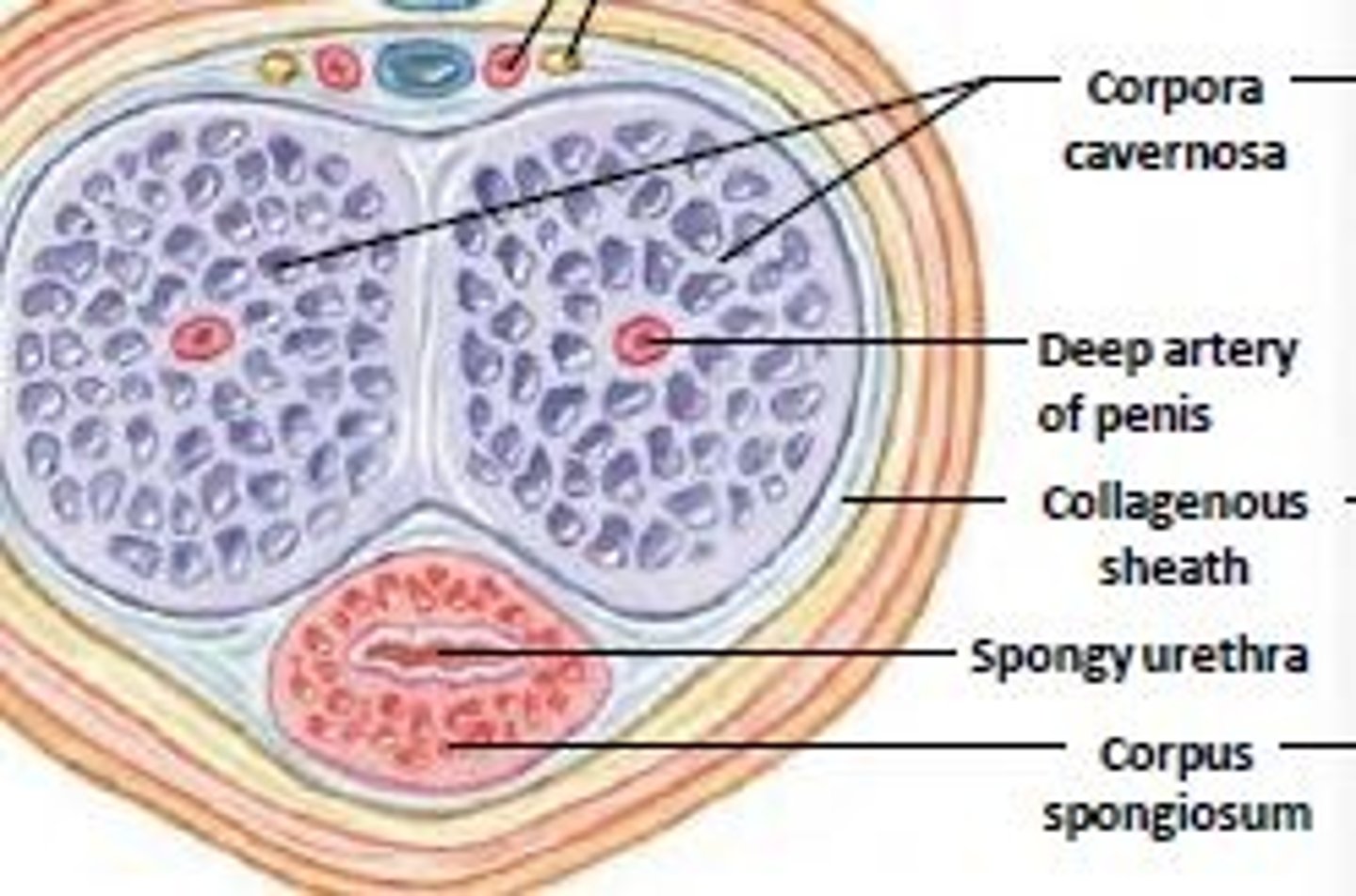
erection of penis (activation)
parasympathetic nerve activation
- smooth muscles in arterial walls relax
- arteriole muscles dilate and expand
- vascular channels in corpus cavernosa and spongiosum becomes engorged w/ blood
parasympathic and sympathetic for erection
parasympathetic
- smooth muscle relaxation
- increased blood flow to the penis
sympathetic
- controls ejaculation by stimulating contraction of smooth muscles
ejeculation activation
sympathetic activation
- sperm & semen pushed through by peristaltic actions of smooth muscle in ductus deferens
- ischiocavernosus: compresses base of penis to maintain erection
- bulbospongiosus: rhythmic contractions to eject semen
muslces both men and women have
Ischiocavernosus and bulbo-spongiosis
sensory innervation (penis)
in skin and area around penis
female reproductive system contains
ovaries
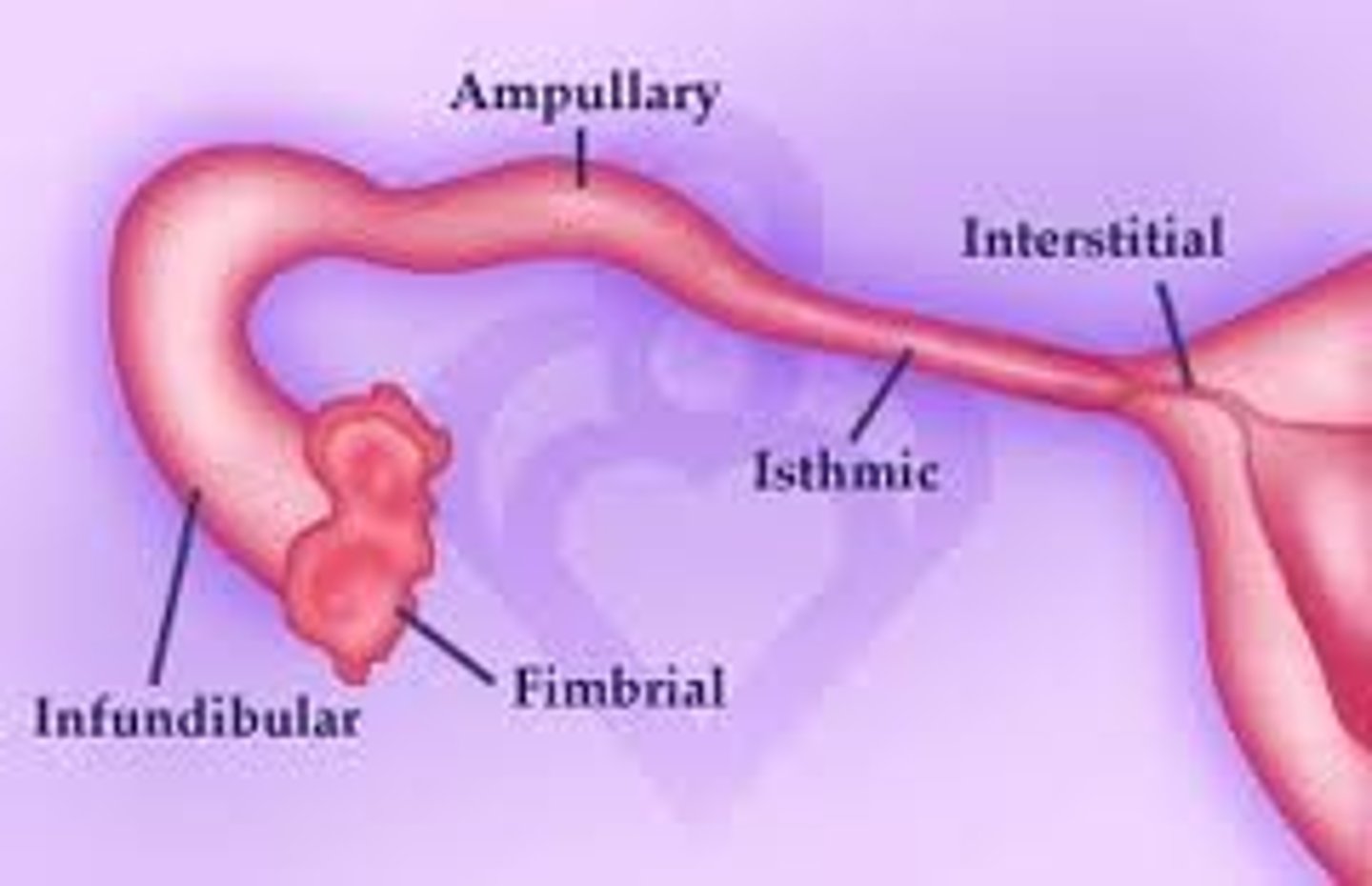
uterine tubes (fallopian tubes)
- fimbriae
uterus:
- cervix
vagina
external genitalis:
- labia minora/majora, clitoris
breasts
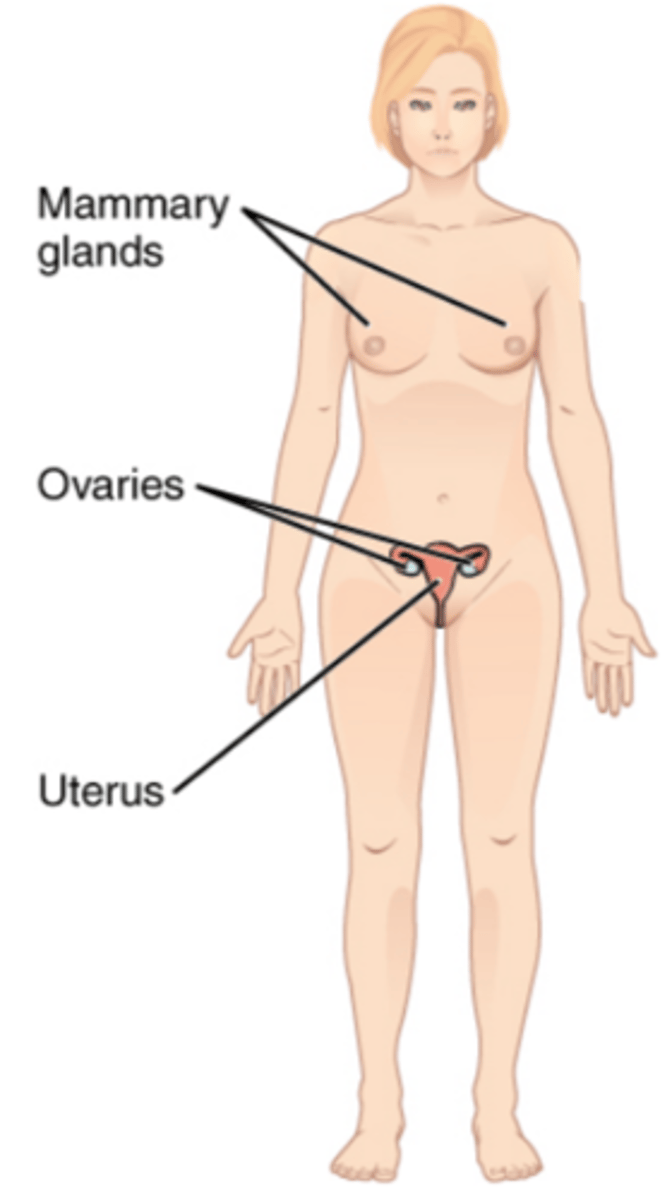
ovaries
- 2
- uterine tube attached by fimbriae (finger like projections)
- leads to uterus
uterus opening
cervix opens to vagina
infundibulum
curved area of uterine (fallopian) tube
ligaments of the uterus and ovaries
broad ligament:
- encloses ovaries, uterine tubes, and uterus
ovarian ligament:
- attaches ovary to uterus
mesovarium
round ligament
suspensory ligament:
- contains ovarian artery/vein
- connected to ovary by ovarian hilum
uteralsacral ligaments
broad ligament
- attaches to the lateral edges
- stabilizing structure for uterus, especially for expanding during pregnancy
processes of female reproductive system
oogenesis:
- production of female gametes (oocytes)
- initiated in embryonic stage of female
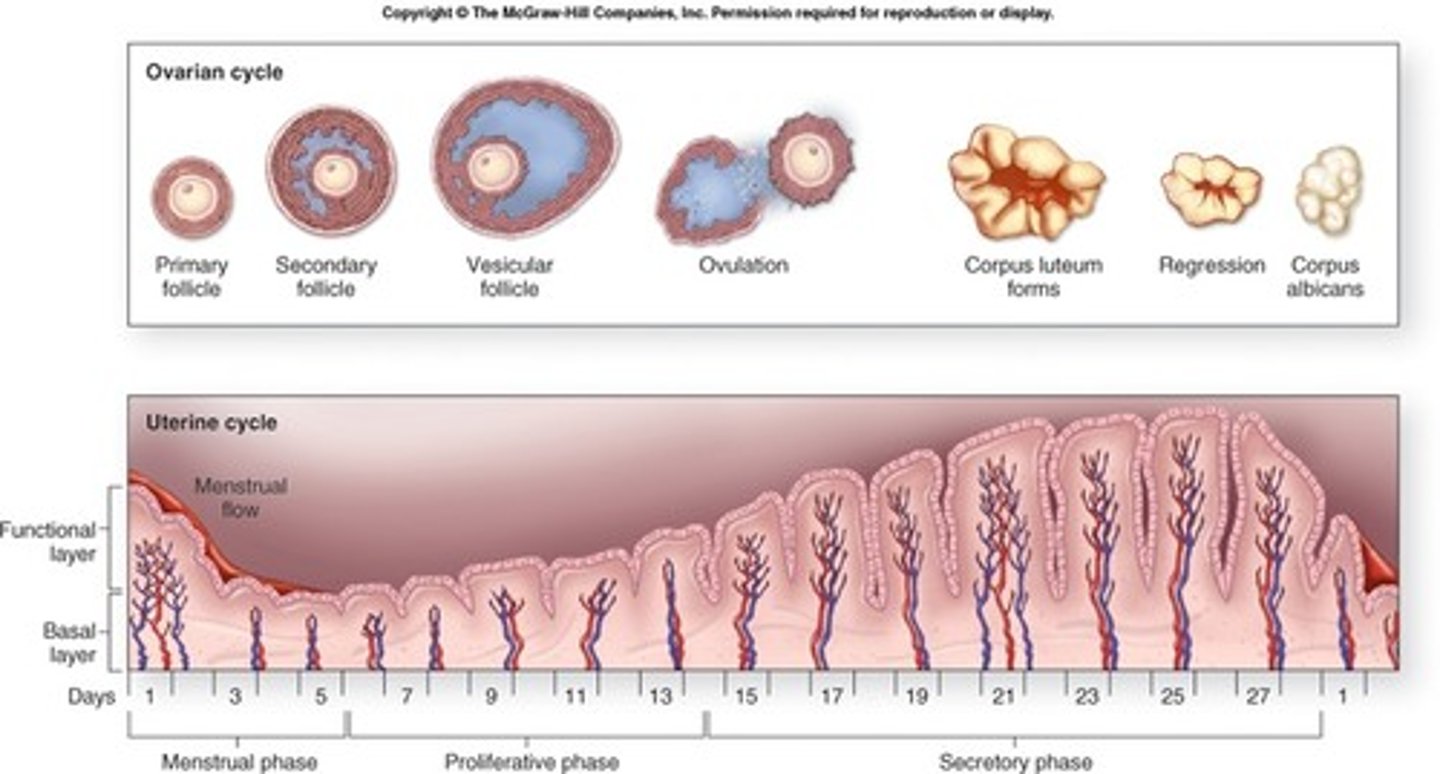
ovarian cycle:
- monthly
- development of ovarian follicles
- oocytes develop
unterine cycle:
- monthly
- prepare uterus for implantation of fertilized embyro
FSH and LH in females
- FSH and LH regulate the ovarian cycle
- FSH stimulating follicular growth
- LH triggering ovulation on day 14
- estrogen and progesterone prepare the uterus for implantation and regulate the menstrual cycle
ovarian cycle
primordial ovarian follicle:
- primordial oocyte
primary ovarian follicle:
- primordial oocyte
secondary ovarian follicle:
- primary oocyte
tertiary ovarian follicle:
- secondary oocyte
ovarian cycle hormones
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH):
- from pituitary gland
- initiate ovarian cycle
endocrine cells:
- estrogen
> stimulating bone and muscle growth
> female secondary sex characteristics (breast, pubic hair)
> sex drive
> maintain reproductive organs
> initiate repair and growth of uterine lining
lutinizing hormone (LH)
- weaken follicular wall to release secondary oocyte in corona radiata
once oocyte is released follicle becomes
corpus luteum:
- produce progesterone (prepare body for pregnancy)
- if no fertilization, corpus luteum decomposes, 12 days after ovulation into
corpus albicans:
- marks end of 1 ovarian cycle and start of next
start of ovarian cycle
decrease in:
- hormones
- progesteron
- estrogen
stimulate release of GnRH, LH, FSH:
- start new cycle
Mensturation
The shedding of the muscosal lining of uterus
path of oocyte
frimbriae > infundibulum > ampulla > isthmus > uterus
- smooth muscle
- 13 cm long
- 5 regions
ovum
mature reproductive cell
what helps move oocyte in its path (uterine tube)
cilia and smooth muscle
(peristaltic movement)
successful fertilization occurs in
- uterine tube (ampulla region)
- within 12 - 24 hrs after ovulation
ovulation
release of ovum from ovary into tube
fertilization of egg
diploid zygote then moves into uterus
ectopic pregnancy
- when fertilized zygote fails to move into the uterus
- very painful
- must be removed from tube or death can occur
anatomy of uterus
body (pear shaped)
fundus (superior)
uterine cavity (internal opening)
isthmus (narrowing of uterus)
internal os (opening into isthmus)
cervix (cervical canal)
external os (external orifice of cervix)
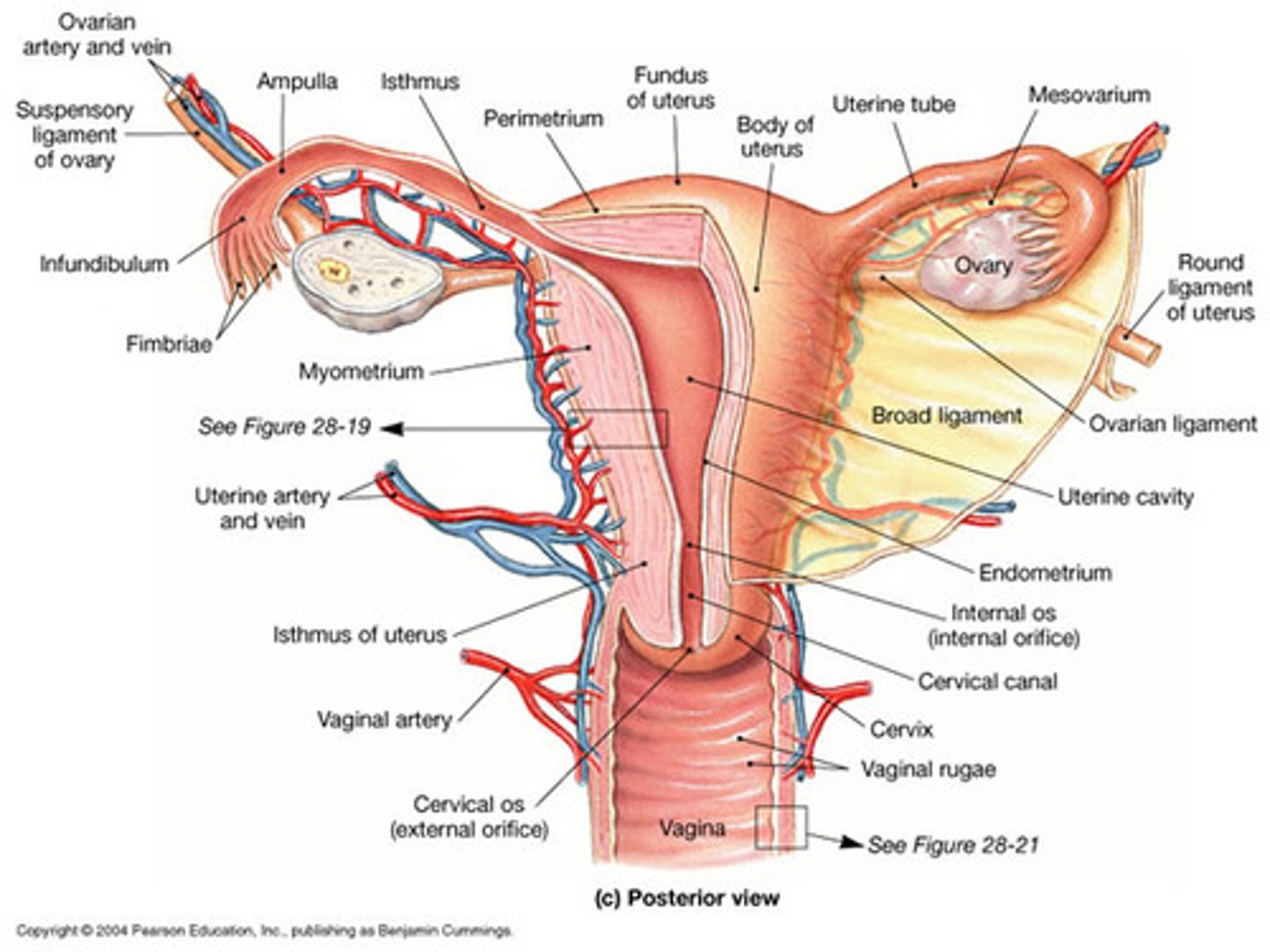
uterine wall layers
- 3 layers
endometrium (inner, glandular wall)
myometrium (muscles, important for child birth)
perimetrium (outer serousal layer)

uterine cycle
menstrual cycle 3 phases:
menstrual phase
proliferative phase
secretory phase
menarche - 1st uterine cycle at puberty
menopause - ending of cycle
menstruation phase
- from day 1-7
- destruction functional layer within uterus
- decrease in progesterone and estrogen cause menstruation
- constriction of arteries and decrease of blood flow to kill off layer
proliferative phase
- day 7-14
- repair and regeneration of layer
- from end of menstruation to ovulation
ovulation day
14
secretory phase
- day 14-28
- secretion by uterine gland ( progesterone & estrogen)
- functional layer ready for implantation
vagina
- elastic muscular tube
- smooth muscle
- from cervix to vaginal canal
- 7.5 to 9 cm long
rugae in vagina
- allow for expansion of surface (child birth)
hymen
separates vagina and vestibule
- usually broken by exercise and tampons
3 main functions of vagina
- passage way for elimination of menstrual fluid
- receive penis
- passage way for fetus
bacteria in vagina
- provide nutrients in cervical mucosa
- acidic environment to prevent pathogens
- reduces sperm mobility
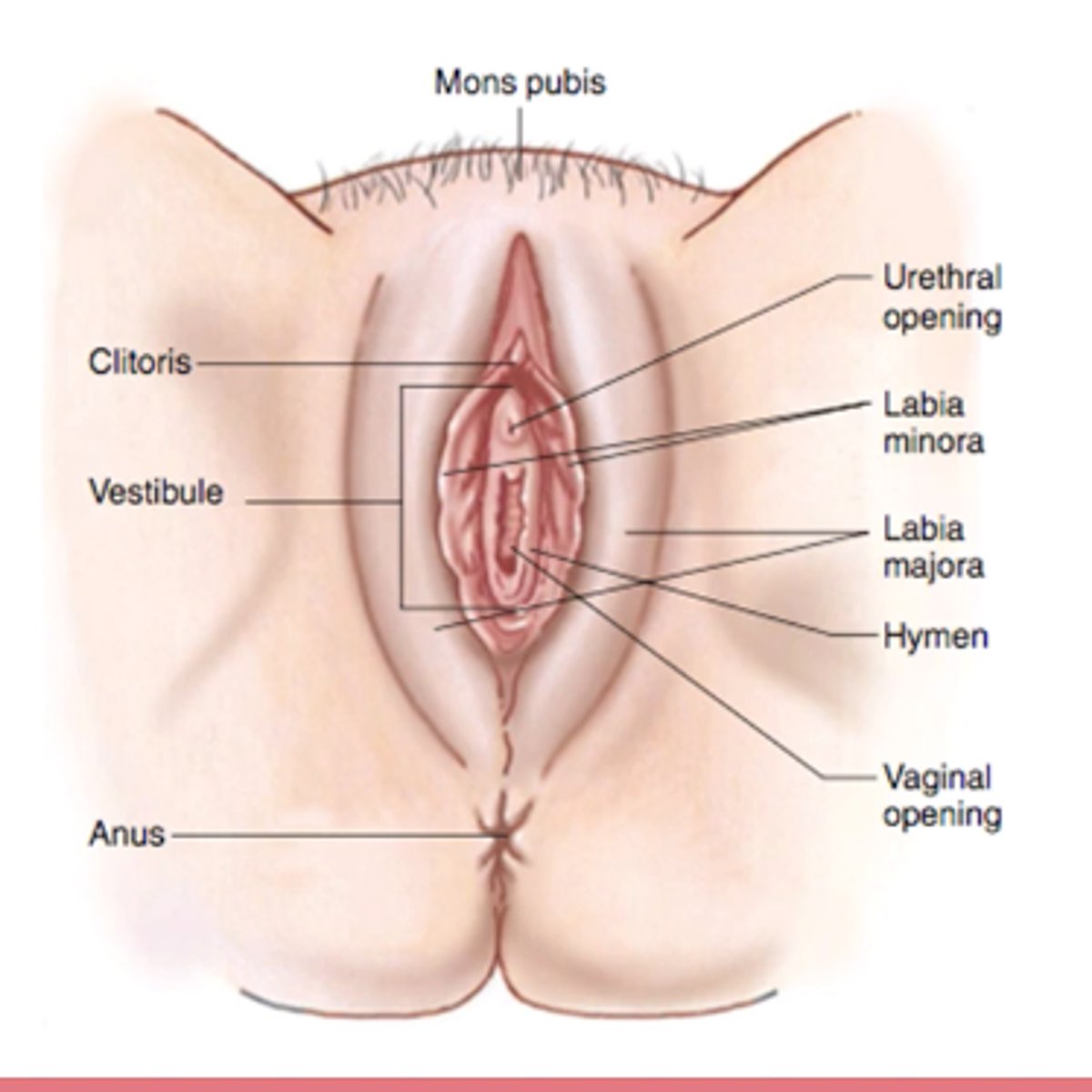
external gentalia of female
vulva:
- enclosing external genetila
vestibule:
- opening of vagina
- surrounded by labia minora
- moistened by greater & lesser vestibular gland
labia majora:
- surrounding labia minora
clitoris (prepuce):
- erectile tissue
urethral opening
anus
breast glands
Pressure → release of OXT from the pituitary gland → contraction of the lactiferous ducts → milk ejects
nipple
- surrounded by areola that contains large sebaceous glands
sebaceous glands
- exocrine gland
- release sebum, oily waxy substance for breastfeeding
lobules of mammary gland
- Lobules contain alveoli that produce breast milk.
- Milk flows: Lobules → ducts → lactiferous sinus → nipple.
- Prolactin makes milk, oxytocin releases it
suspensory ligament (breasts)
support:
ducts
lobes
lobules
mammary glands develop during
pregnancy
- fully develop in 6 months
- milk released when infant sucks on nipple
oxytocin release by nursing causes
- lactiferous ducts to release milk
- oxytocin from the pituitary gland stimulates milk ejection
colastrum
- first few days of nursing
- fluid filled with antibodies
- milk produced by 2-3 days
female climacteric (menopause)
decline estrogen:
- reduce size of uterus/ breast
- thinning of vaginal walls
- weakening supportive tissues of reproductive organs
- osteoporosis
- hot flashes
- typically between 45-55
male climacteric (andropause)
- testosterone levels decline ( not as rapidly as estrogen)
- avg 50-60
- reduction in sexual activity