Cell Structure and Function
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Cell Theory
all living things are made of cells
cells are the basic unit of life
all cells come from prexisitng cells
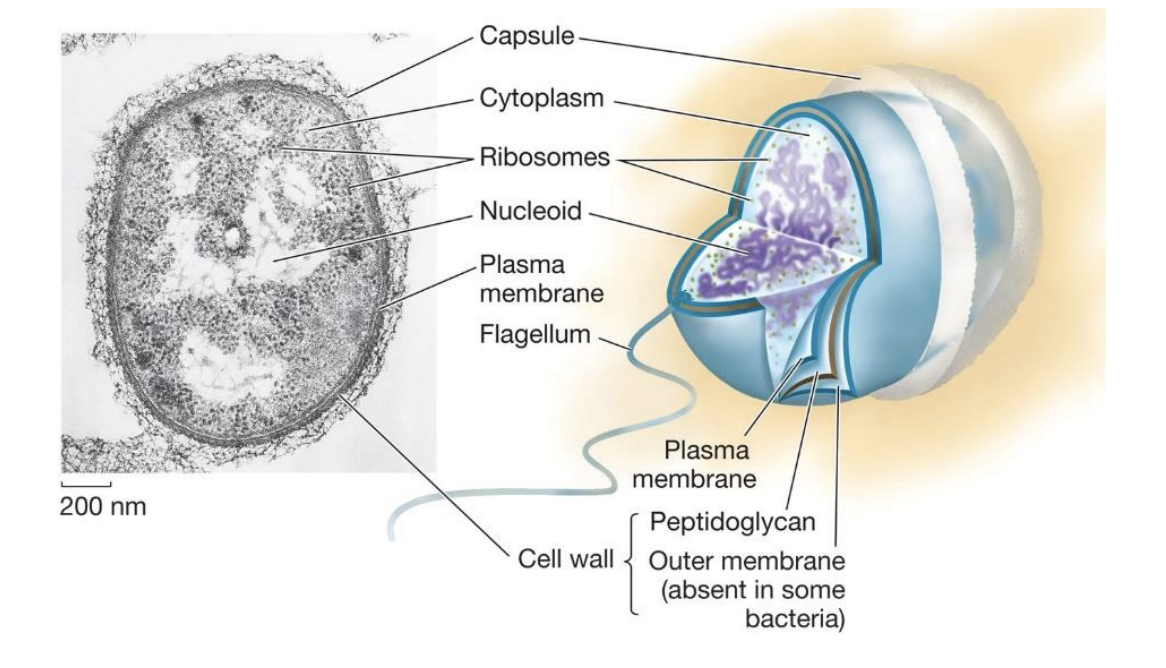
Prokaryotic cells
Small cells with no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles (DNA floats in cytoplasm)
Eukaryotic cells
Larger cells with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles

Peptidoglycan
A rigid structural molecule found in bacterial cell walls
What do prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have in common?
Cytoplasm
DNA
Ribosomes
Cell membrane of phospholipids and proteins
Semipermeable
Allows some substances to pass but blocks others
Diffusion
The movement of molecules from high concentration to low concentration without energy
Simple Diffusion
Small, uncharged molecules (like gases) moving directly across the cell membrane (no energy required)
Osmosis
Diffusion of a water across a semipermeable membrane
Isotonic
Solute concentration is the same inside and outside the cell (water flows in and out of the membrane at the same rate)
Hypotonic
Solution outside the cell had fewer solutes —> water enters the cell and it swells up (more solutes inside)
Hypertonic
Solution outside the cell has more solutes —> water leaves the cell and it shrinks shrink (less solutes inside)
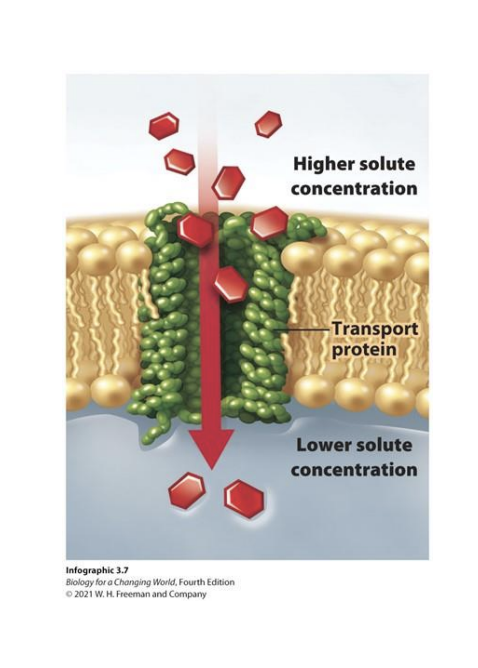
Transport Proteins
Proteins that help substances move across the cell membrane
Facilitated Diffusion
Passive transport (no energy) using channels or carriers to move substances across the membrane (high to low)
Active Transport
Movement of substances against the concentration gradient (low to hight) using energy (ATP) and pumps
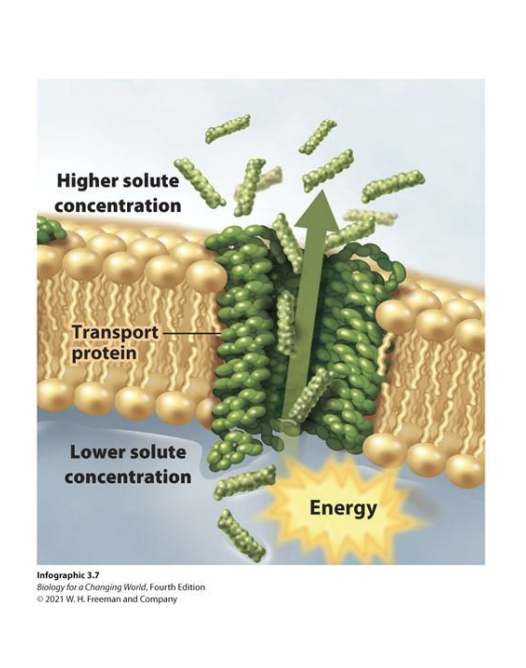
Whats the difference between channels, carriers, and pumps?
channels and carriers = passive (no energy)
pumps = active (need energy)
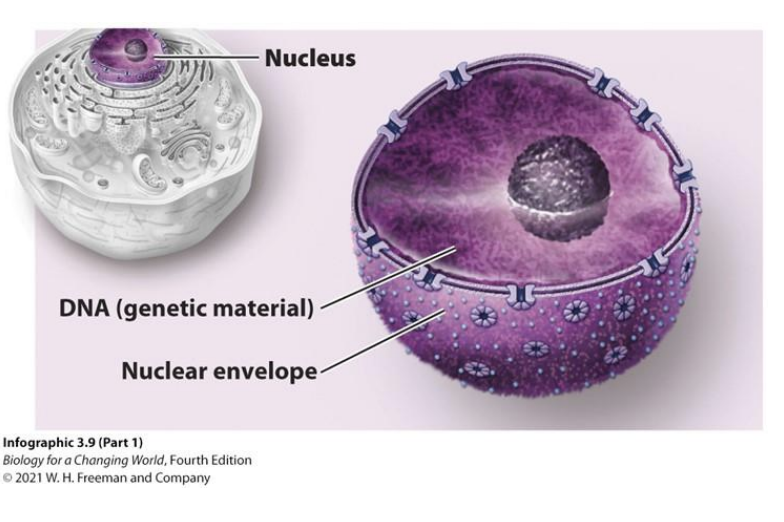
Nucleus
Organelle containing DNA,
transcription occurs here
surrounded by a double membrane
pores for transport
Transcription
The process of makeing RNA from DNA
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Organelle near the neucleus
makes proteins and anything that need to be exported from the cell
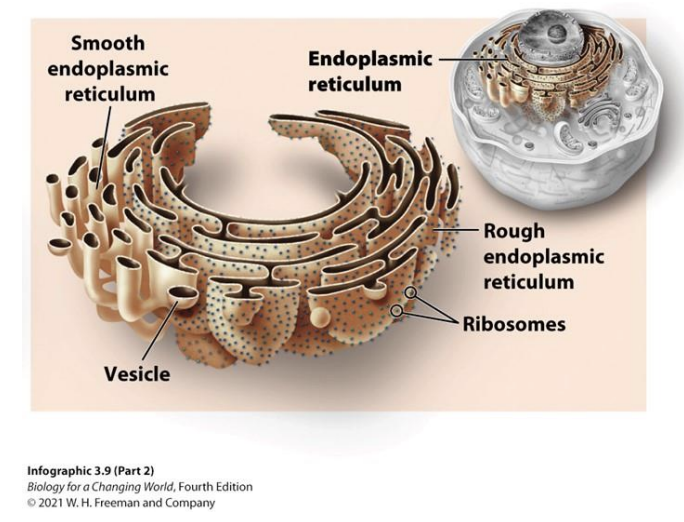
Rough ER
Ribosomes that make proteins
Smoother ER
Makes lipids, detoxifies cells
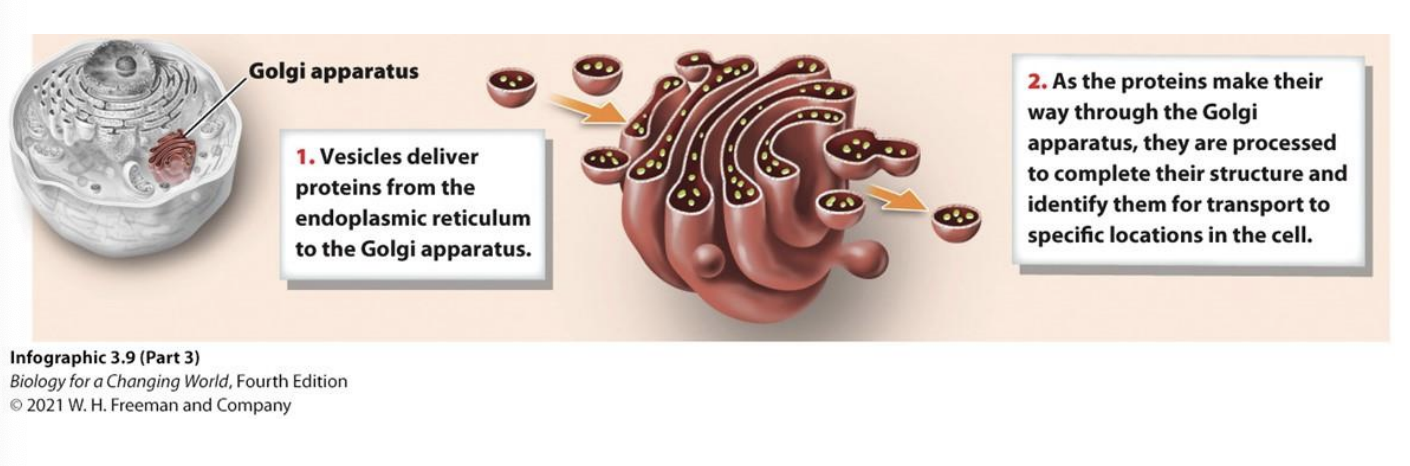
Golgi Apparatus
A stack of membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins received from the ER for transport to specific locations
Lysosomes
Organelles full of digestive enzymes that break down worn out parts of the cell and materials from the environment
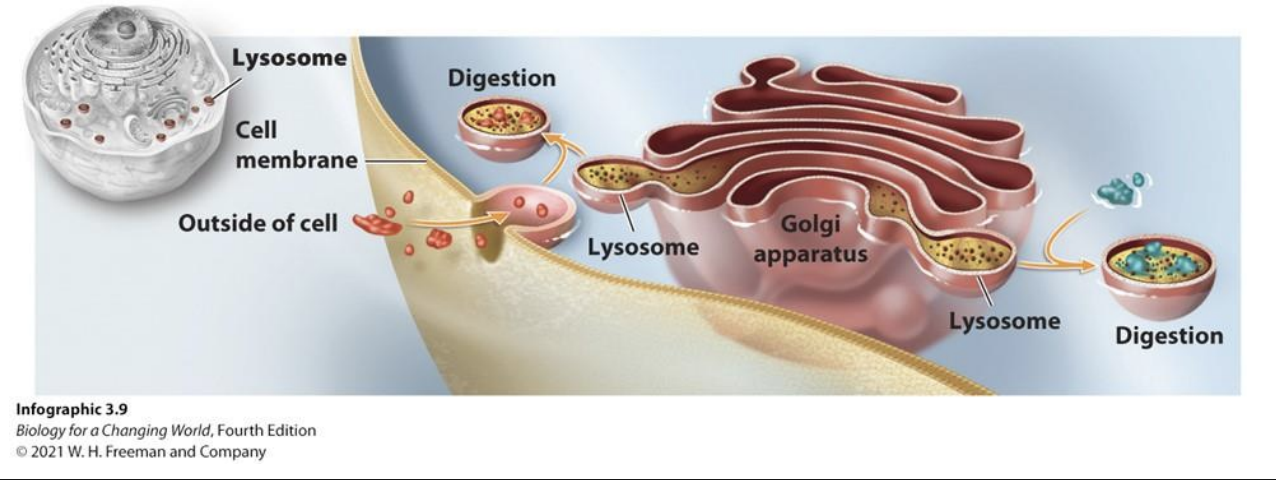
Vesicles
Small membrane-bound sacs that transport and store substances within a cell
Endomembrane System
Cell organelles that make, package, and transport proteins and lipids
Rough ER → makes proteins
Smooth ER → makes lipids
Golgi apparatus → modifies, sorts, and packages
Vesicles → transport materials
Lysosomes → break down waste
Cytoplasm
Gelatinous aqueous interior
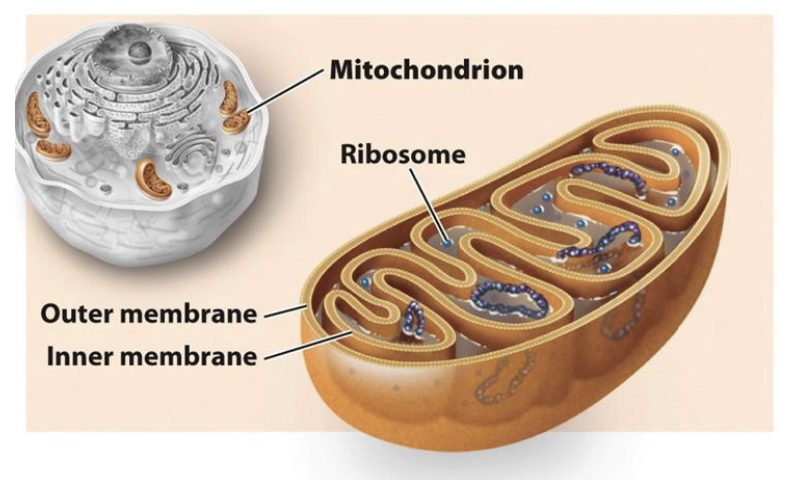
Ribosomes
A complex of RNA and protein that carry out protein synthesis (look like tiny dots: found on rough ER and scattered in the cytoplasm)
Mitochondria
extract energy from food
double membrane
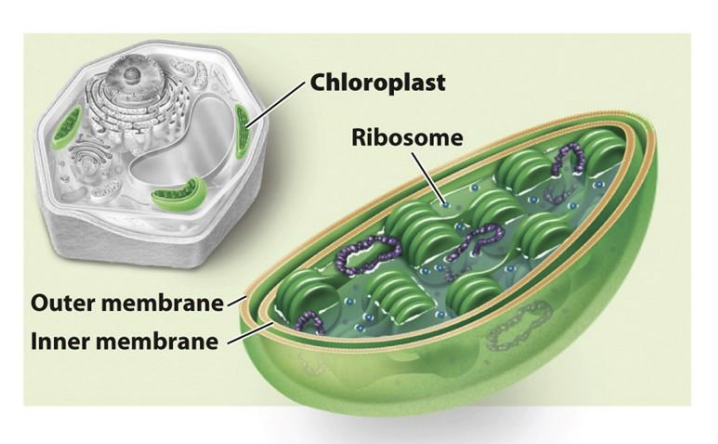
Chloroplasts
sunlight to energy
double membrane
specific to photosynthetic eukaryotes
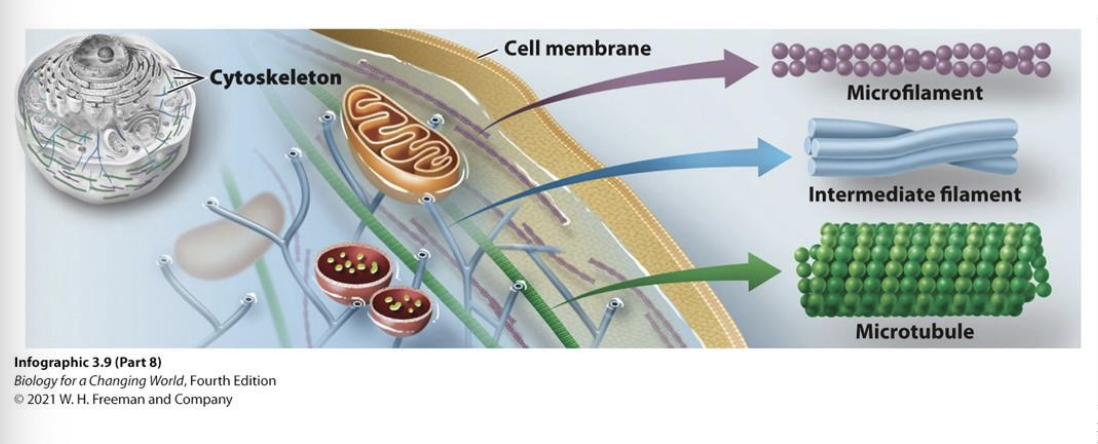
Cytoskeleton
Network of protein fibers that help with:
cell support
cell movement
movement of structures within cells
Endosymbiosis Theory
The idea that organelles formed by a eukaryotic cell eating another
How does penicillin function?
Blocks cell wall synthesis, creaking a holey cell wall (can’t make peptidoglycan)
Competitive Inhibition
The mechanism for blocked the normal function of a protein
Gram-Positive
Peptidoglycan in cell wall retains the Gram stain
Gram-Negative
Lipid outer layer of cell wall doesn’t have gram
Penicillin can’t reach the peptidoglycan
What cell components contain DNA?
mitochondria
nucleus
What things are shared by all organisms?
DNA
Cytoplasm
What cell components are present in both plant and animal cells?
mitochondria
ER
ribosomes
Golgi
mitochondrion
lysosome
Why can oxygen diffuse across biological membranes?
Oxygen can diffuse across biological membranes because they are small and non-polar