Gen Chem 1 Exam Study Guide Topics / Questions (Ch. 1 & 2)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
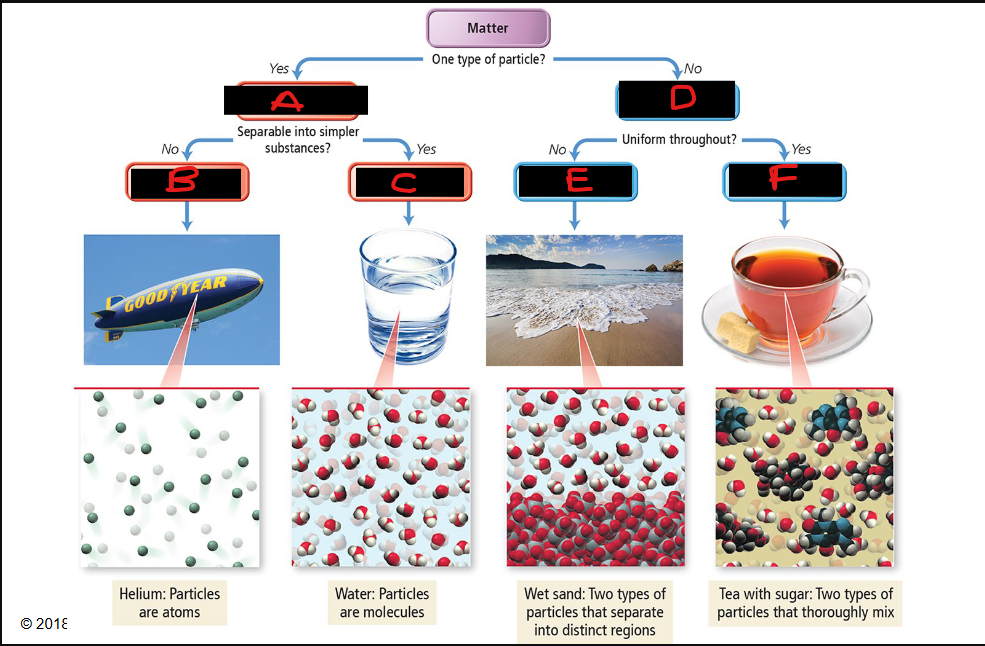
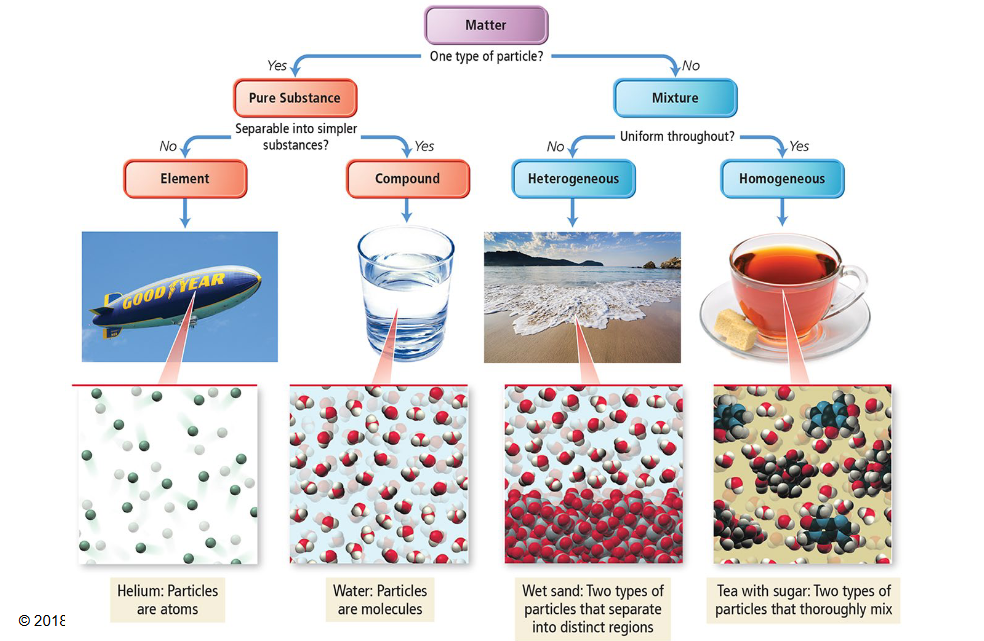
Label the diagram with its appropriate label from the choices below:
Mixture
Pure substance
Compound
Element
Heterogenous
Homogeneous
A → Pure substance
B → Element
C → Compound
D → Mixture
E → Heterogeneous
F → Homogeneous
Understand the structure of an atom – what are the three subatomic particles?
Proton, neutron, electron
What is the charge on each of the three subatomic particles, where each is located in the atom, and what are the relative masses of each?
Proton
Charge - Positive (+1)
Location - Nucleus
Mass - Relatively the same but slightly less dense than neutron (~1 amu)
Neutron
Charge - Neutral (0)
Location - Nucleus
Mass - Relatively the same but slightly more dense than proton (~1 amu)
Electron
Charge - Negative (-1)
Location - Electron cloud
Mass - the mass of an electron is so small that it is often considered insignificant for the purposes of this class (~0.00055 amu)
Which atomic particles are in the nucleus?
Answer: PROTONS AND NEUTRONS
Explanation: the electrons exist outside the nucleus
How does nuclear size of an atom compare to the atomic size?
The nucleus makes up an extremely small portion of the atom as a whole.
The ______ tells you the identity of the element.
atomic number / number of protons
How do you determine the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons for a given element?
The number of protons is given by the atomic number, the number of neutrons is the mass number minus the atomic number, the number of electrons is the same as the number of protons for a neutrally charged element.
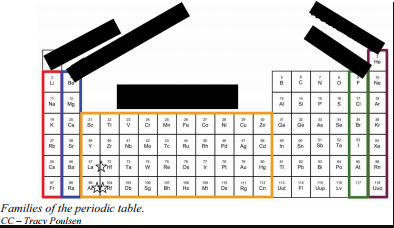
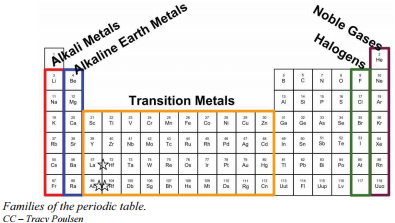
Label the following groups with their common names:
Red group = ?
Blue group = ?
Yellow Group = ?
Green Group = ?
Purple Group = ?
Red group = Alkali metals
Blue group = Alkaline Earth metals
Yellow Group = Transition Metals
Green Group = Halogens
Purple Group = Noble gases
Understand the definition of a mole as it relates to atoms and molecules.
What is a mole?
A mole represents 6.023*10^23 of any given particle, such as an atom, molecule, electron, photon, etc.
A mole is a conversion factor that can be used to covert from moles to particles.
A chemist’s “baker’s dozen”
The value of the mole is equal to the number of atoms in exactly 12 grams of pure C-12.
Be able to determine the number of moles given the number of atoms/molecules or the number of atoms/molecules given the number of moles.
Calculate the number of copper atoms in 2.45 mol of copper.
2.45 mol Cu * (6.022 × 1023 Cu atoms / 1 mol Cu) = 1.48 × 1024 Cu Atoms
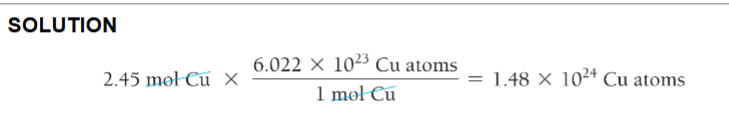
Be able to determine the number of moles given the number of atoms/molecules or the number of atoms/molecules given the number of moles.
A pure silver ring contains 2.80 × 1022 silver atoms. How many moles of silver atoms does it contain?
2.80×1022 Ag atoms * (1 mol / 6.022 × 1023 Ag atoms) = 0.465 mol Ag
How do you determine the molar mass of an element?
We locate the molar mass of that element on the periodic table. It is provided in units of g/mol.

How many moles of Kr are contained in 349 mg of Kr?
A) 4.75 × 10-3 moles Kr
B) 33.4 moles Kr
C) 2.11 × 10-4 moles Kr
D) 2.99 × 10-3 moles Kr
E) 1.19 × 10-4 moles Kr
Answer:
A) 4.75 × 10-3 moles Kr
Explanation:
convert to grams: 349mg = 349/1000 g = 0.349 g
Molar mass of Kr = 83.798 g / mol
Calculate moles of Kr:
0.349 g Kr / 83.797 g/mol Kr = 0.00475 mol Kr
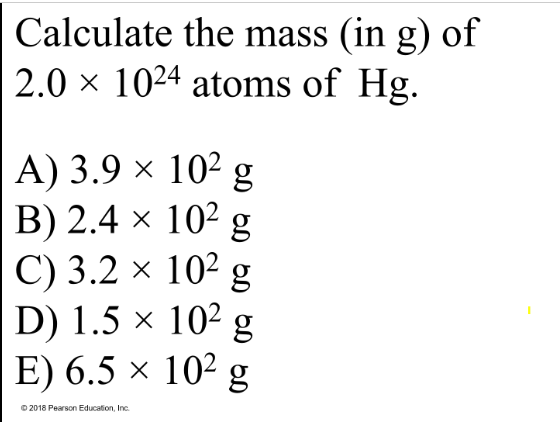
Also be able to combine these conversions
to convert to number of atoms/molecules given the molar mass of a substance and vice versa
Calculate the mass (in g) of 2.0 × 1024 atoms of Hg.
A) 3.9 × 102 g
B) 2.4 × 102 g
C) 3.2 × 102 g
D) 1.5 × 102 g
E) 6.5 × 102 g
Answer:
E) 6.5 × 102 g
Explanation:
First convert atoms to moles using Avogadro’s number.
2.0×1024 atoms / 6.022×1023 atoms/mol = 3.3 mol
Then convert moles to grams using molar mass
(200.59 g/mol) * (3.3 mol) = about 6.5 × 102 grams
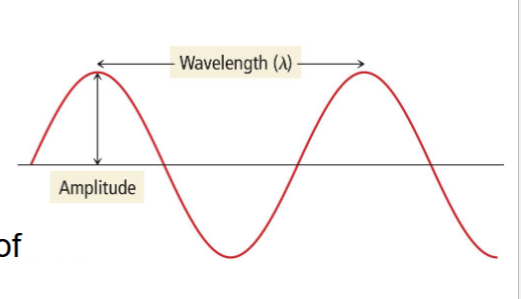
Match the following with the diagram and relate them to the properties of light.
Amplitude
Wavelength
A = Amplitude
The amplitude is a measure of light intensity
Larger amplitude = brighter light
B = Wavelength
The wavelength of light determines its color (intensive physical property).
Define the wavelength and frequency of a wave.
Wavelength:
A measure of the distance covered by the wave
The wavelength of light determines its color (intensive physical property).
Frequency:
The number of waves that pass a point in a given period of time
Define the wavelength and frequency of a wave.
The wavelength and frequency of
electromagnetic waves are _____ proportional.
• ____ wavelength → ____ frequency
• ____ wavelength → ____ frequency
The wavelength and frequency of
electromagnetic waves are inversely proportional.
• Long wavelength → low frequency
• Short wavelength → high frequency
v = c / lambda
How do the various regions of the electromagnetic
spectrum relate to each other?
Wavelength increases as frequency decreases, and vice versa.
ROYGBIV
Red = largest wavelength of visible light
→
Violet = smallest wavelength of visible light
Radio is lowest energy
gamma is highest energy
Einstein observed that when light is shined on a metal surface,
electrons are produced from the surface.
– The electrons emitted from the metal surface are photoelectrons.
– This phenomenon is called the ___________ effect.
photoelectric
A _________ is an electron that has been transferred energy via a photon.
This relates to the idea that “light is quantized”.
Meaning, light does not behave as a continuous entity but instead exists as discrete ______ of energy called photons.
Photons ≠ electrons
Photons are without _____, while electrons have it.
photoelectron, packets, mass
What does it mean for something (like mass, light, or energy) to be quantized?
To be quantized means that a property, such as energy, light, or electric charge, can only exist in discrete, indivisible units called "____". Instead of varying continuously, like a ramp, a quantized property exists in distinct steps, like a staircase.
quanta
“________“ means that the atom could have only very
specific amounts of energy
Quantized
What are the subshell shapes for each value of l (s, p, d, f)?
s: ?
p: ?
d: ?
f: ?
The subshell shape of:
s is spherical
p is like a dumbbell (two-lobed)
d is like a 4-leafed clover or a dumbbell with a donut in the middle
f is 8 lobed or two lobed orbital with a donut under each lobe
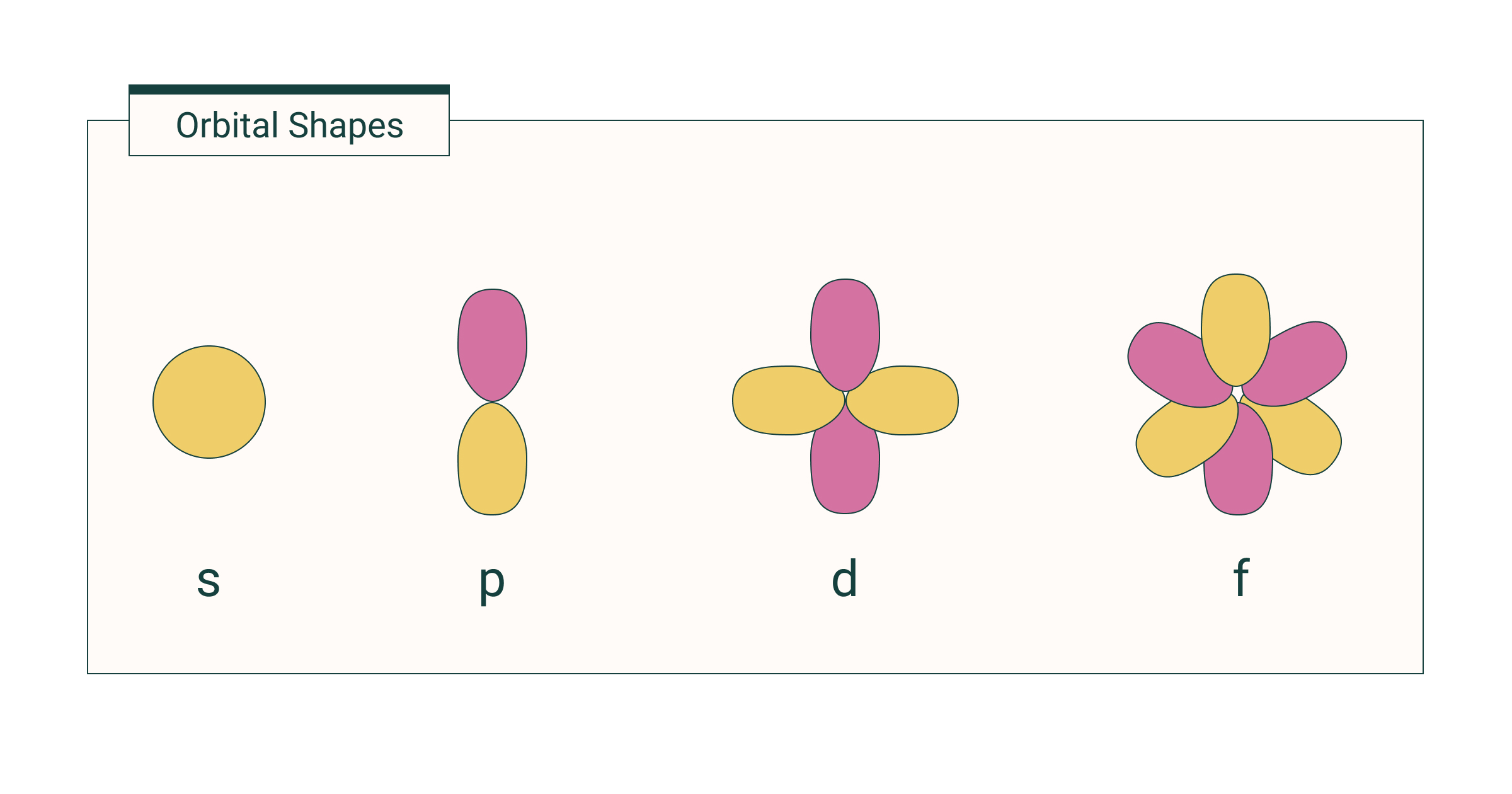
How many orbitals are in each of the following sublevels?
s: ?
p: ?
d: ?
f: ?
s has 1 orbital (boxes) 0
p has 3 orbitals (boxes) -1, 0, 1
d has 5 orbitals (boxes) -2, -1, 0, 1, 2
f has 7 orbitals (boxes) -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3
What is the difference between atomic mass and mass number?
The mass number is the count of protons and neutrons
The atomic mass is the weighted average of naturally occurring isotopes.