Chemistry - Structure 1.3
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Pauli Exclusion principle
Only two electrons can occupy the same atomic orbital and those electrons must have opposite spins
Aufbau Principle
The lowest available energy orbitals fill before higher energy orbitals do
Hunds Rule
every degenerate orbital in a sublevel is singly occupied before any orbital is doubly occupied. All electrons in single occupied orbitals have the same spin
Exceptions to Aufbau Principle
Transition metals when forming ions lose their 4s electrons first. Copper and Chromium fill their 3d orbital before they fill their 4s orbital
Why do Copper and chromium not follow the aufbau principle
it helps them be more stable
Ionization Energy
The energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of an atom in its gaseous state
Why does the first ionization energy decrease down a group
The number of sublevels increases, which means there is a greater shielding effect and therefore less energy is required to remove electrons from the outermost sublevel
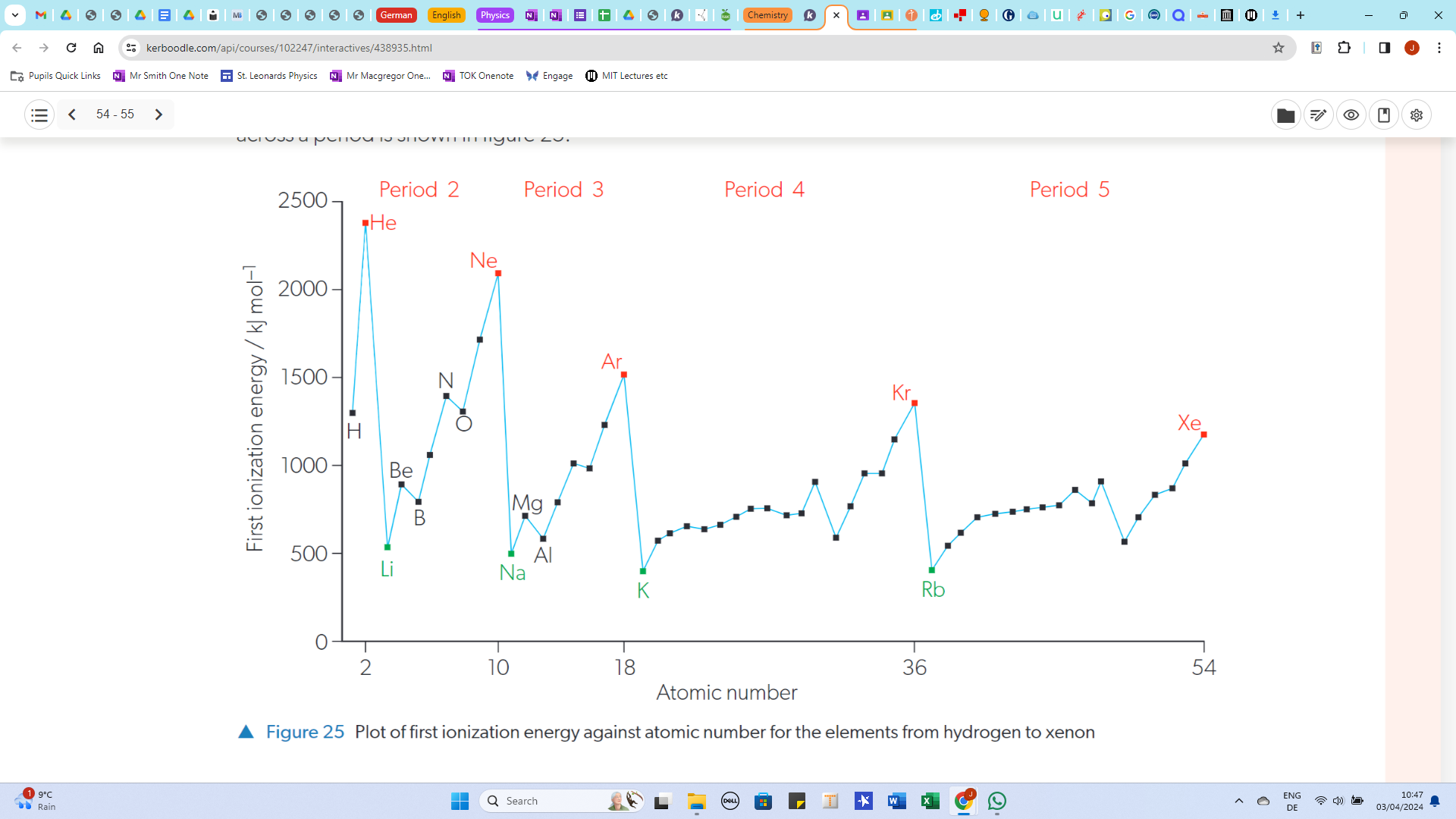
Why does the first ionization energy increase across a period
Number of protons increases, whichincreases the nuclear charge. Shielding effect remains constant because the number of inner electrons does not change. Therefore more energy is required to remove outermost electrons
General Trend of ionization energy
increases across a period, decreases down a group
Sucessive ionization energies
It requires more energy to remove the second and succesive electrons from an atom, because the number of protons exceeds the number of remaining electrons while electron-electron repulsion decreases
Why do gaseous atoms produce line spectra instead of continuous spectra?
Electrons in atoms occupy discrete energy levels, so electron transitions between these levels consume or emit specific quanta of energy. Each quantum of energy corresponds to a photon of specific wavelength
Atomic orbitals
s, p, d & f orbitals. They each have specific shapes and no. of electrons that can occupy them
s orbital
Spherical shape and can hold up to 2 electrons
p orbital
dumbbell shaped and can hold up to 6 electrons