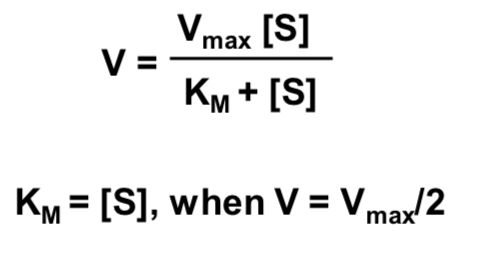Enzymes
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What is an apo-enzyme?
A protein molecule which has its own primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure
What is an enzyme?
Enzymes are specific proteins that catalyse biochemical reactions.
Biological catalysts
What is a coenzyme?
Prosthetic group of enzyme which can covalently and non-covalently associate with an apo-enzyme
What is a whole enzyme?
Consists of an apo-enzyme and co-enzyme
What is an enzyme’s active site?
Part of the enzyme which recognises the substrate and performs a catalytic reaction
What is the recognition site?
Part of the active site that recognises the substrate
What is the catalytic site?
Part of the active site that peforms catalysis
How do you name enzymes?
Add -ase to the substrate that the enzyme converts
How many classes are enzymes split into?
6
Name all the classes that enzymes are split into
Oxidoreductases
Transferases
Hydrolases
Liases
Isomerases
Ligases
Oxidoreductases
Catalyses oxidation and reduction reactions
Transferases
Transfers groups of atoms from one molecule to another
Hydrolases
Catalyses reactions involved in hydrolysis
Liases
Attaches functional groups to pi-bonds
Isomerases
Catalyses reactions of isomerisation
Ligases
Catalyses biosynthesis reactions
What does an enzyme’s EC number mean?
Four digits which mean:
Class of the enzyme
Subclass
Sub-subclass
Exact enzyme
Describe the enzymatic reaction
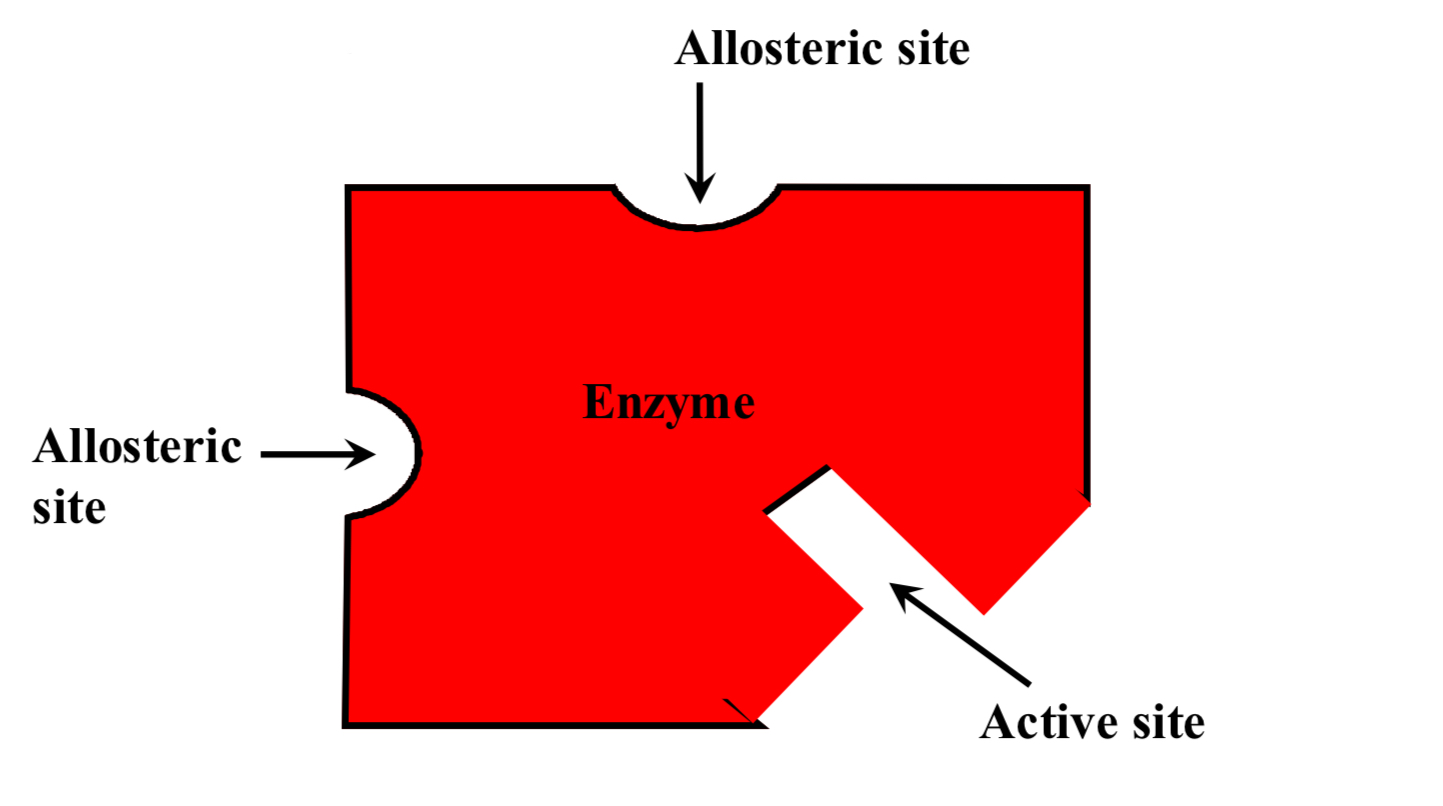
What is the allosteric site of an enzyme?
The amino acid sequence recognising and binding to the allosteric modulator (or allosteric inhibitor)
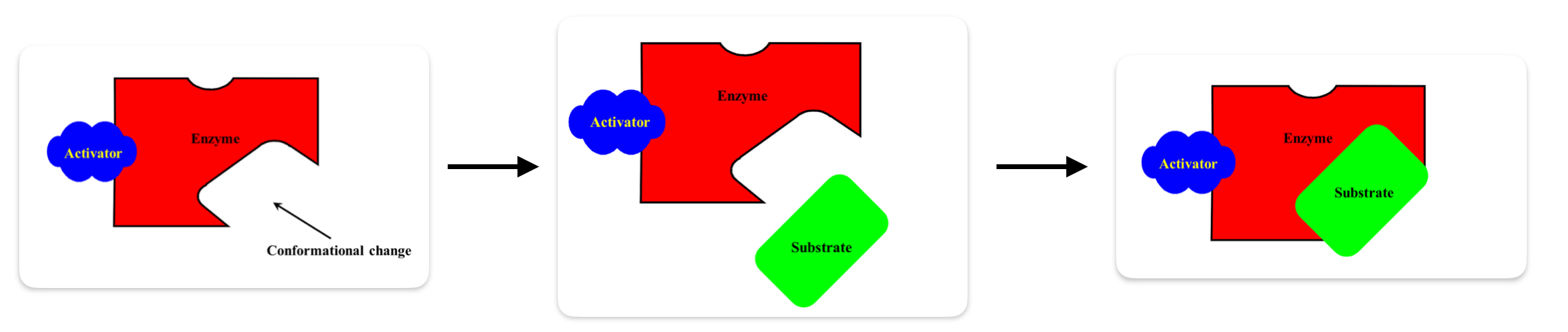
What is allosteric activation?
The allosteric modulator interacts with the allosteric site of the enzyme causing conformational change and activation
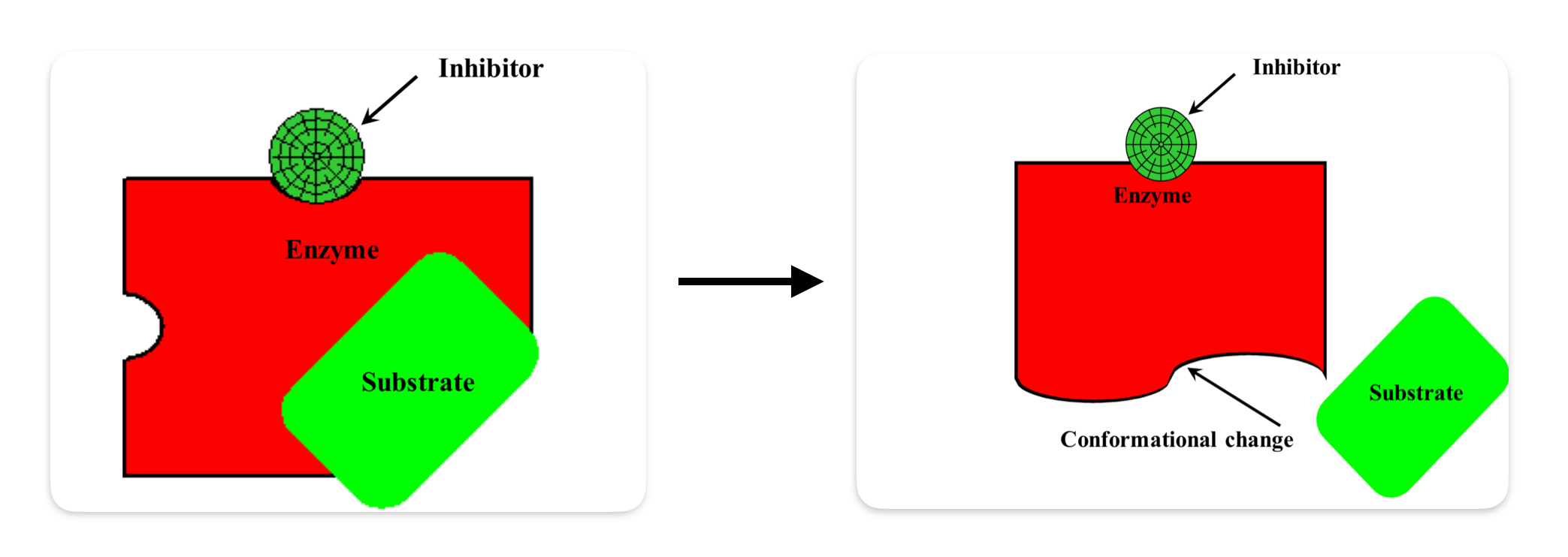
What is allosteric inhibition?
The allosteric inhibitor reacts with the allosteric site of the enzyme causing conformational change and inhibition
What is isosteric inhibition?
Inhibitor competes with the substrate for interaction with the active site of the enzyme.
This is normally reversible
What is absolute substrate specificity?
The case when the enzyme could convert only one substrate
What is temperature optimum?
The temperatures at which the enzyme displays maximal activity
What is pH optimum?
The pH value at which the enzyme displays maximal activity
What are iso-enzymes?
Enzymes of different sturctures (but normally similar) which perform the same reactions
What are multi-enzyme systems?
Systems containing several enzymes which catalyse consequent conversions of the same substrate
What does the equation of Michelins-Menthen describe?
The speed of enzyme reaction
What is the Michelin-Menthen equation?