Asthma and COPD drugs
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What are the main inhaled corticosteroids?
- Becomethasone
- Budsonide
- Ciclesonide
- Fluticasone
- Mometasone
Describe beclomethasone
- Available in two brands, Qvar and Clenil, not interchangable.
- Brands have different particle size and Qvar is more fine so more potent.
What dose is used for beclomethasone?
2-4 puffs BD
What are the side effects for inhaled corticosteroids?
- Hoarseness
- Throat irritation
- Candida
- Dysphonia
What are examples of SABAs?
Salbutamol
Terbutaline
What are examples of LABAs?
Salmeterol
Formoterol
Indacaterol
What is an example of a SAMA?
Ipratropium
Oxitropium
What is an example of a LAMA?
Tiotropium
glycopyrronium
What is drug classes make up Ultibro Breezehaler?
LABA (indacaterol)
LAMA (glycopyrronium)
What are side effects of muscarinic antagonists e.g., ipratropium?
-Dry mouth and skin.
- Palpitations, arrhythmias, tachycardia.
- Urinary urgency and retention.
When are SAMA and LAMAs used?
- More commonly used in COPD.
- Can be used in severe asthma
When should SAMA and LAMAs not be used?
- Patients with not sever asthma.
- Patients who suffer from BPH as can cause acute UR.
How log do SABA's work for?
4-6 hours
How long do LABA's work for?
12-24 hours
What are the side effects of beta agonists?
Most occur due to systemic absorption:
- Tremor
- Headache
- Hypokalaemia
What is MART therapy for asthma?
- Formeterol + steroid combination.
- Formoterol has short and long acting components.
- Usually taken BD as a preventer.
What is seretide?
An inhaler which contains Salmeterol (LABA) and Fluticasone (ICS)
Describe leukotriene receptor antagonists (LTRA).
- Only used in asthma
- They have a bronchodilatory and inflammatory effect
- Long term preventer therapy.
What is an example of a LTRA?
Montelukast
How should montelukast be used?
OD in the evenings
What are side effects of LTRAs?
- Neuropsychiatric reactions e.g., Speech impairment, OCD.
- Churg-Stauss syndrome.
Describe Xanthines
- Have a bronchodilatory effect but not rapid.
- Can be used intravenously and orally.
- Have an effect on late phase inflammatory responses.
What are the types of xanthines?
Theophylline
Aminophylline
Give an example of a theophylline and what is the dosage?
Uniphyllin Continus, 200mg BD
What are the side effects of Xanthines?
- GI effects e.g., Nausea, Diarrhoea.
- CV effects e.g., Tachycardia, palpitations
What are issues with Xanthines?
- It is metabolised by CYP450 so it has interactions with many antibiotics.
- Lots of nausea could show toxicity of drug.
When are Xanthines used?
- Reserved for those with severe asthma.
- Used in COPD treatment if individual cannot use inhaled therapies.
- Aminonphylline is used in severe acute exacerbation of asthma and COPD.
What are mucolytics?
Drugs used to manage hypersecretion of mucus in COPD.
Not used in asthma.
Give an example of a mucolytic and its dosage.
Carbocisteine, 2.25 g daily
Describe mast cell stabilisers.
- Prevents histamine degranulation of mast cells.
- Has value for asthma of allergic nature.
- Can lead to bronchospasms, should be replaced with SABAs.
How can asthma that is triggered by an allergy be treated?
- Avoidance of allergy can prevent asthma symptoms.
- Use of anti0histamines to prevent allergy.
- Nasal corticosteroids to prevent allergy.
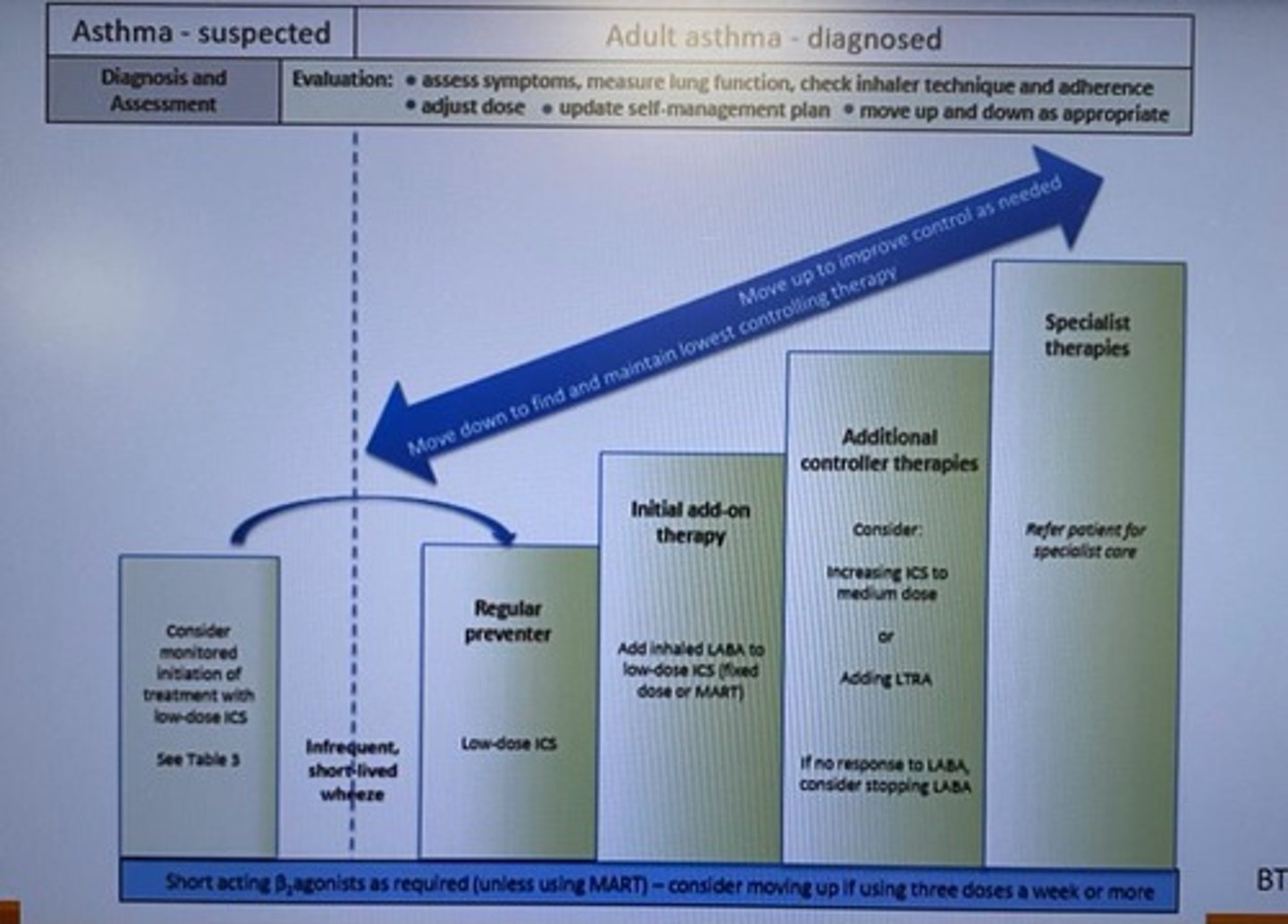
What is stage 1 of asthma treatment according to guidelines?
Use of a regular preventer - Low dose ICS (Beclomethasone)
What is stage 2 of asthma treatment according to guidelines?
Adding an inhaled LABA (Salmeterol) to the low dose ICS. Or MART therapy.
What is stage 3 of asthma treatment according to guidelines?
Increase the dose of the ICS or add an LTRA (Montelukast).
If there is no response to the LABA remove it.
What is stage 4 of asthma treatment according to the guidelines?
Refer to a specialist of the first 3 stages don't provide relief.
Describe the guidelines for asthma treatment?
What is the first stage of the COPD guidelines?
Offer a SABA or a SAMA to use as needed as reliever.
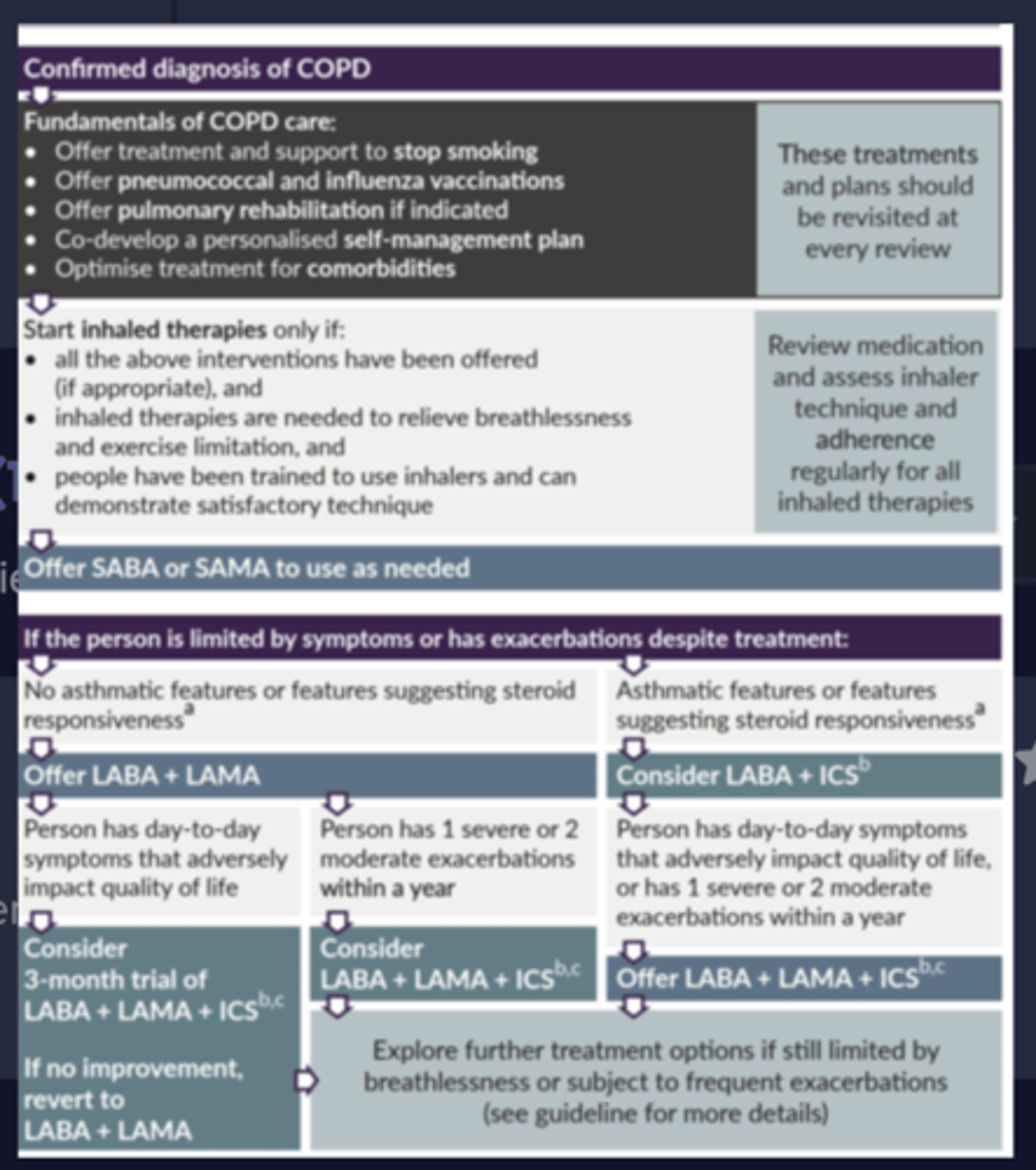
What is the second stage of COPD guidelines if patient is showing no asthmatic features or features suggesting steroid responsiveness?
Offer a LABA and a LAMA

What is the second stage of COPD guidelines if patient is showing asthmatic features or features suggesting steroid responsiveness?
Offer a LABA and an ICS

What is the third stage of COPD guidelines?
Offer a LABA, LAMA and ICS.

What colour inhaler are SABAs?
Blue
What colour inhaler are corticosteroids?
Brown
What colour inhaler are LABAs?
Green
What class of drugs are in relievers?
SABA
What class of drugs are in preventers?
ICS