BJU World Studies Chapter 4, 4th Edition
4.0(4)Studied by 43 people
Card Sorting
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:23 PM on 10/11/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
1
New cards
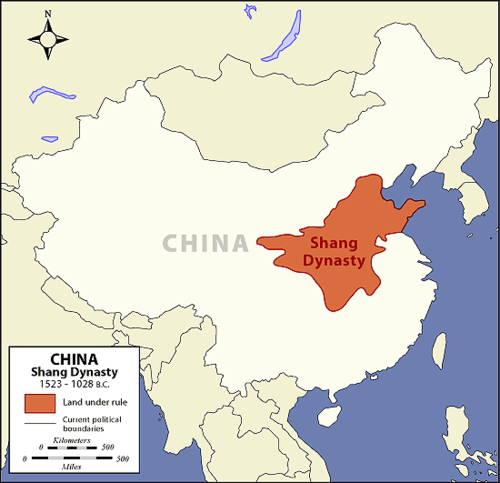
Shang
First Dynasty in Chinese History. Ruled for 2,00 years, beginning around 1500 BC
2
New cards
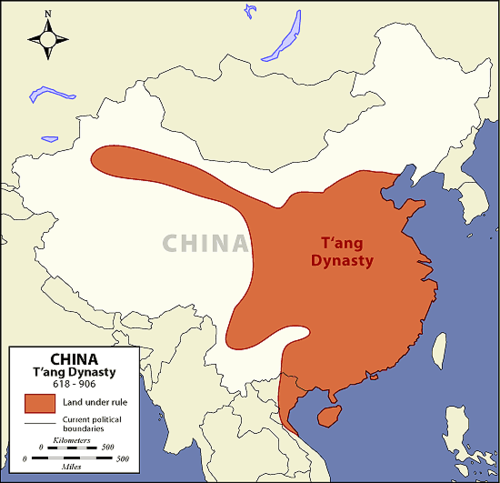
Tang
T'ANG: last dynasty to reign in China (7th Century)
3
New cards
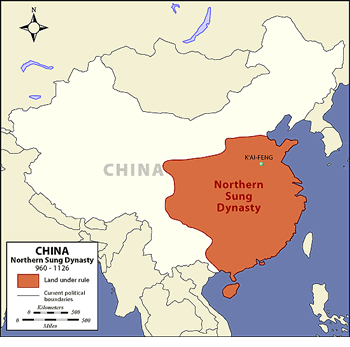
Song dynasty
dynasty divided into 2 parts; Southern Song & Northern Song; both fell to Mongols. Ruled during a time of strong economic growth
4
New cards
technology
putting knowledge to effective use
5
New cards
Chinese compass
the Chinese probably first used the compass to align buildings
6
New cards
saltpeter
used to make gunpowder
7
New cards
cast iron
formed when iron ore and small amounts of carbon and silicon are heated to about 1200 C.
Poured molten iron into a mold/cast
Poured molten iron into a mold/cast
8
New cards
ancestor worship
A religious practice based on the belief that deceased family members have a continued existence, take an interest in the affairs of the world, and possess the ability to influence the fortune of the living.
9
New cards
Confucius
Chinese teacher that developed a philosophy based on relationships
10
New cards
Buddhism
the teaching of Buddha that life is permeated with suffering caused by desire, that suffering ceases when desire ceases, and that enlightenment obtained through right conduct and wisdom and meditation releases one from desire and suffering and rebirth
11
New cards
Taoism
A Chinese philosophy in which people live a simple life in harmony with nature.
12
New cards
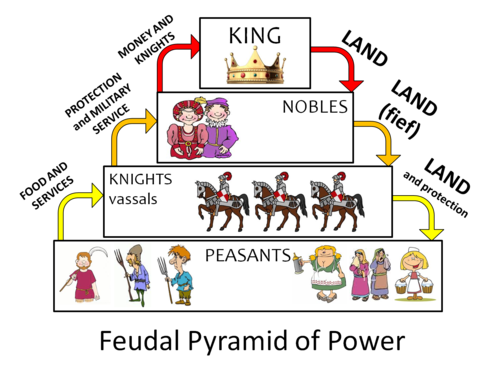
feudalism
A political system in which Nobles are granted land in exchange for their loyalty, military service and protection of the people who live on the land (like serfs).
13
New cards
shogun
A general who ruled Japan in the emperor's name. means "great general"

14
New cards
samurai
A Japanese warrior who lived by the code of bushido.

15
New cards
Bushido
"the way of the warrior" Samurai military code which required the warrior to display loyalty, honor, duty, and courage.

16
New cards
hara-kiri
a ritual of suicide associated with warriors in traditional Japan

17
New cards
Shintoism
A religion based in Japan, marked by worship of nature and reverence for ancestors

18
New cards
Zen Buddhism
A Japanese form of Buddhism, which focuses on meditation to reach Enlightenment. It's focus on intense mental concentration enabled samurai to endure hardships of battle.

19
New cards
Angkor Wat
An extensive city-and-temple complex built by the Khmer and dedicated to the Hindu god Vishnu.--Cambodia
20
New cards
yurts
movable tents Mongols lived in
21
New cards
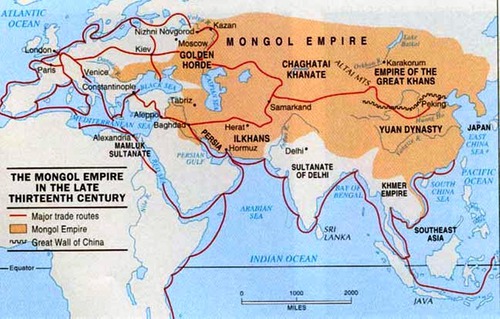
Chinggis Khan
Also known as Genghis Khan, in 1206 he became the supreme leader over all the Mongal tribes. "Great Ruler." United the Mongol people

22
New cards
Great Yasa
Chinggis Khan's written law code

23
New cards
siege warfare
an effective method in which Mongol soldiers fired arrows and flaming objects into the cities for weeks. They also kept food from going into the city until the people were starving. They borrowed rocket technology from the Chinese and fired gunpowder-filled bamboo rockets into the towns.

24
New cards
pretend retreat
a tactic used by Genghis Khan where they would pretend to be beaten, left their camps empty and when the towns people came to plunder the camp, the men would attack.

25
New cards
kamikaze
a "divine wind" that protected Japan from Mongol invastion

26
New cards
Batu Khan
another grandson of Chinggis, led Mongol forces (known as Tarters in Europe) through Russian defenses into Europe

27
New cards
Battle of Liegnitz
A combined army of Poles, Czechs, and Germans tried to stop the Mongols. Accounts vary, but the Mongol forces seem to have destroyed this army.
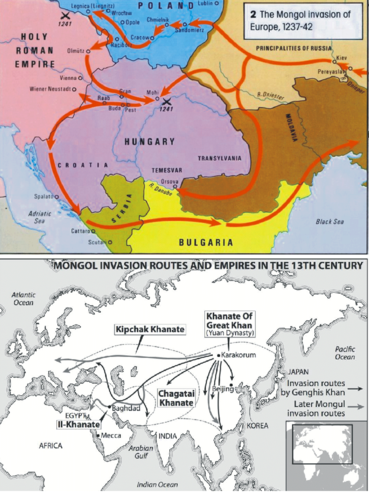
28
New cards
tengri
The Mongols supreme god who rulesd all the spirits. Means, "the great god of heaven."
29
New cards
shamans
Religious leaders, were believed to be able to speak to spirits and heal the sick. Priests of the Mongol religion.

30
New cards
Ming Dynasty, "Brilliant"
dynasty established after the overthrow of the Mongols and returned to old traditions (Confucianism, centralized rule); sought to remove all traces of Mongol rule in China
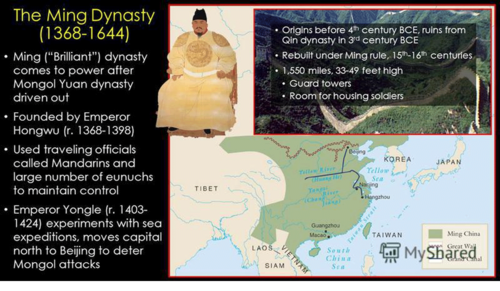
31
New cards
Tamerlane
Another name for Timur the Lame; a powerful Mongol ruler; Led his armies into the Middle East (from Turkey to India); was a Muslim; concentrated on collecting treasures taken in battle; DID NOT convert to Christianity
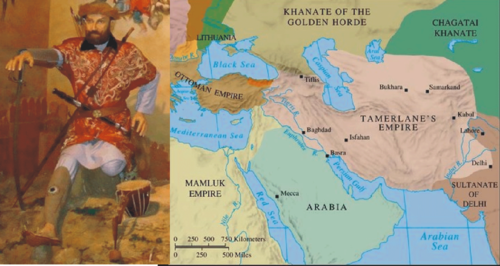
32
New cards
Taj Mahal
A beautiful tomb built by the Mughal ruler Shah Jahan to honor his wife. It is located in India.

33
New cards
the Mongolian Plateau
is located NORTH of China
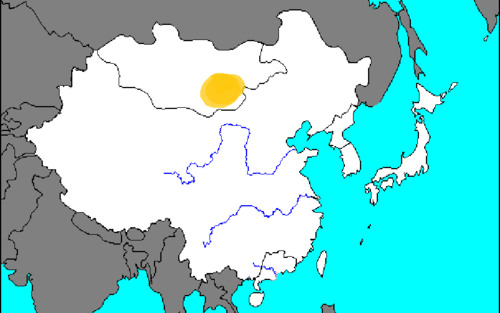
34
New cards
paper
first developed in China,
Formed from mixture of fiber, rags, and water
Formed from mixture of fiber, rags, and water
35
New cards
gunpowder
Invented within China during the 9th century, created by accident
36
New cards
printing
develobed in 1041 by the Chinese using wood blocks and later moveable type
37
New cards
merchants
regarded as the lowest members of society for over 2,000 years
38
New cards
Chinese society
officeholders, farmers, artisans, merchants
39
New cards
Four Nobel Truths of Buddhism
1) Suffering is part of all existence
2) Suffering has a cause-selfish desires
3) Suffering can be overcome by destroying selfish desires
4) 8-Fold Path will destroy selfish desires and suffering
2) Suffering has a cause-selfish desires
3) Suffering can be overcome by destroying selfish desires
4) 8-Fold Path will destroy selfish desires and suffering
40
New cards
because of merchant class growth
1) more wealth
2) factories
3) employment
4) towns
5) improved living
2) factories
3) employment
4) towns
5) improved living
41
New cards
population doubled
prior to and during the Song Dynasty (11th century)
42
New cards
Lao-Tzu
developed the teachings of Taoism
43
New cards
iron
a major export item for the Chinese
44
New cards
Fujiwara Clan (Japan)
the first dominant clan in Japan during the 8th century
45
New cards
Taiki Reforms
"Great Change". Attempt to remake Japanese monarch into an absolute Chinese-style emperor; included attempts to create professional bureaucracy and peasant conscript army.
46
New cards
Mongol unification
developed a government, created a common law, organized military
47
New cards
Yuan Dynasty (Mongols)
China's first foreign dynasty, promoted Chinese culture, very little change
48
New cards
1367
Mongol rule of China ended
49
New cards
Mongol invasion of Japan
2 attempts (1274 and 1281) were made by the mongols to invade Japan. Both times a storm destroyed Mongol fleet, Japan thought they had been saved by God.
50
New cards
Mughal Empire (Mongols)
last mongol empire; (1526-1857) located in India
51
New cards
Akbar the Great
The most famous Mughal leader, known for religious tolerance and building the Taj Mahal.
52
New cards
Tokugawa Clan (Japan)
clan that became the dominant clan by 1600 & brought about the FINAL period of Japanese feudalism. Moved capital to Edo(Tokyo)