AQA GCSE Computer Science : Systems Architecture
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
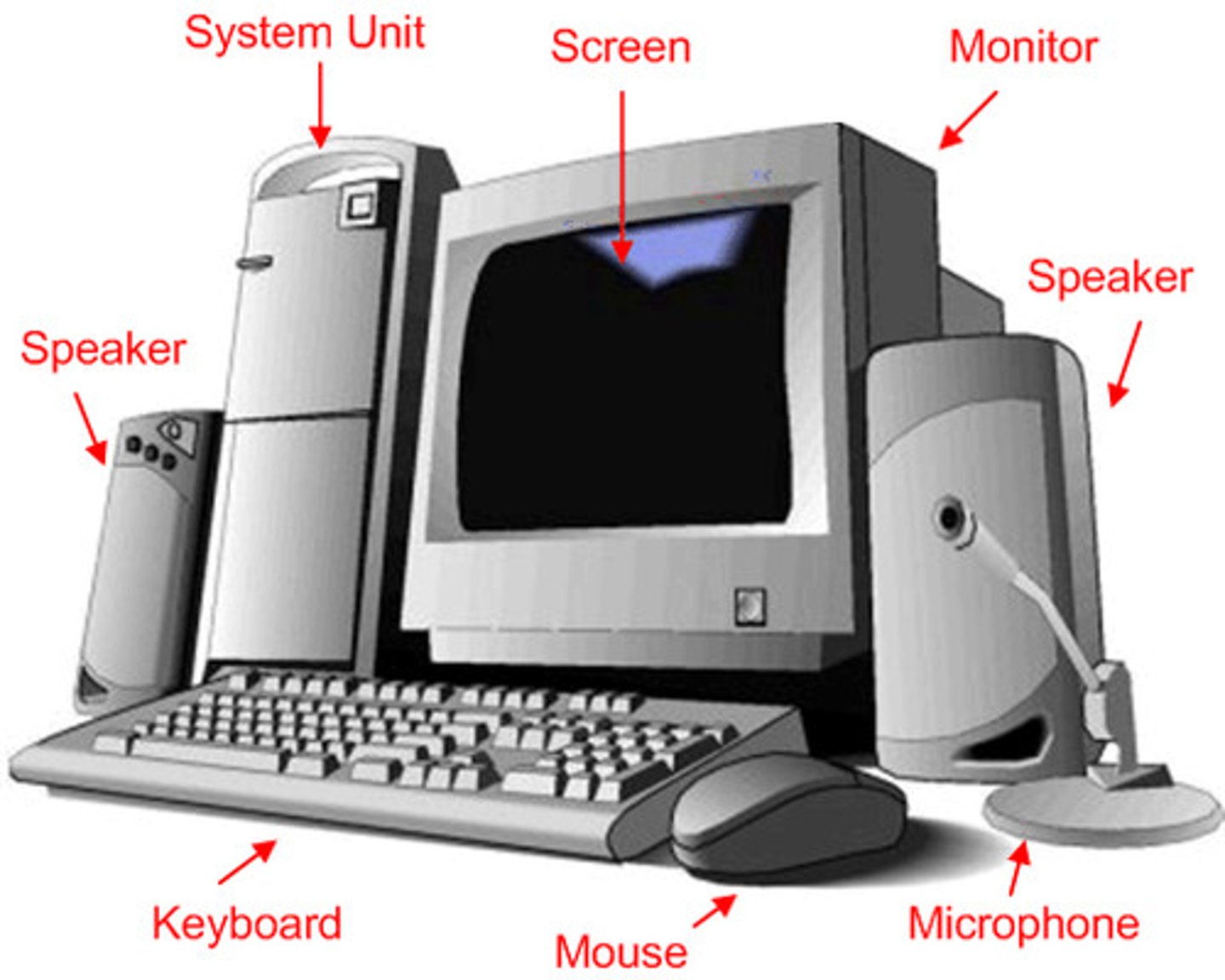
Hardware
The physical elements of a computer system
Embedded system
A system developed for a single, or set purpose. E.g. A washing machine, microwave, digital watch
General Purpose System
A computer system that can change its purpose by adding more software
Volatile Memory
Memory which is only saved whilst the power is on. E.g. RAM
Non-Volatile Memory
Memory which is saved even when the power is switched off. Eg. ROM
ROM
Non Volatile. Small area of memory which holds the boot up program.

RAM
Volatile memory. Very fast. Holds the currently running programs & files.

Device Driver
A program stored on the hard drive that tells the computer how to communicate with a hardware device such as a printer, mouse, or keyboard.
Scheduler
System software which establishes the order in which instructions are executed by the processor
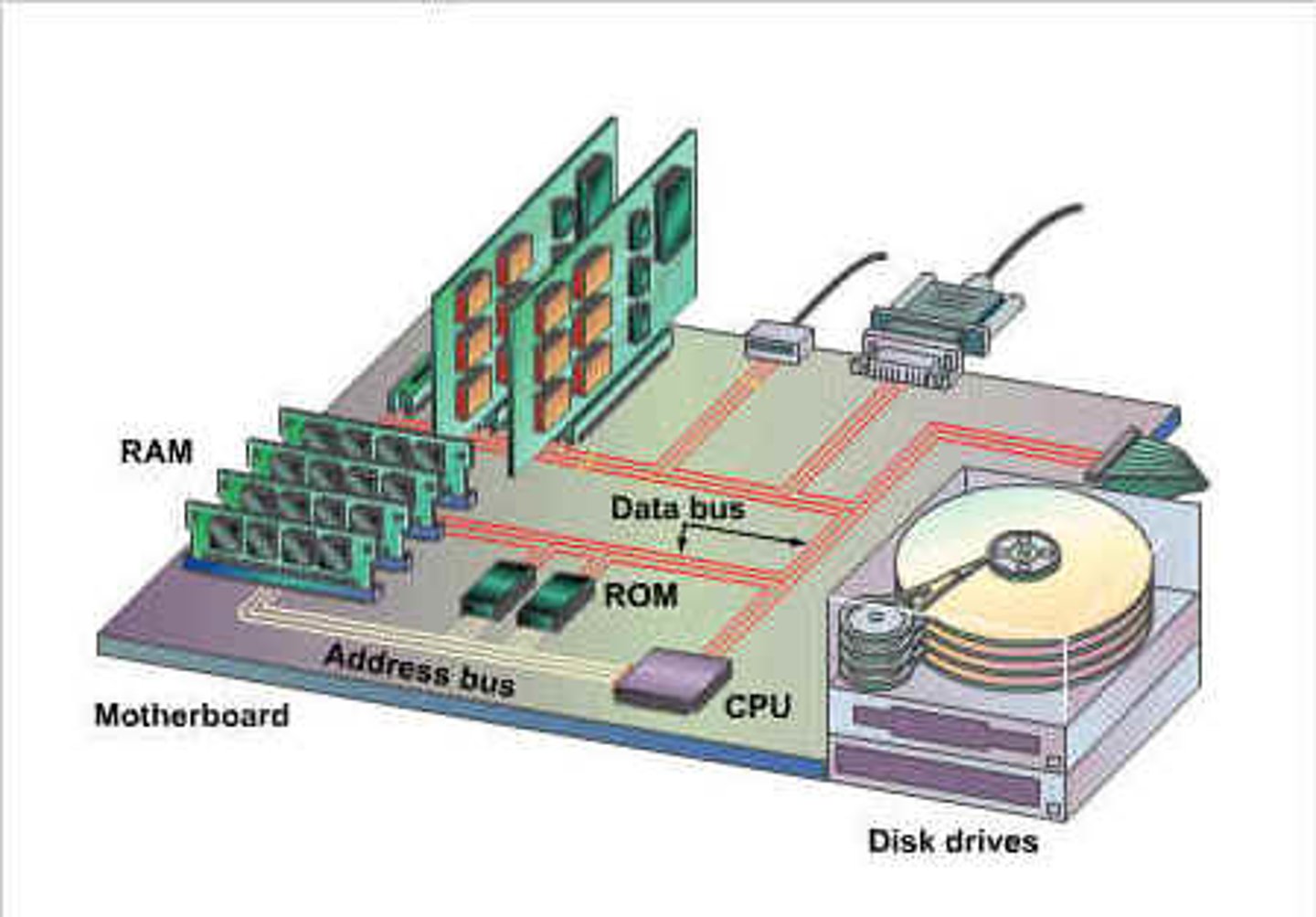
Address Bus
A physical wire which transmits memory addresses between the CPU and the RAM
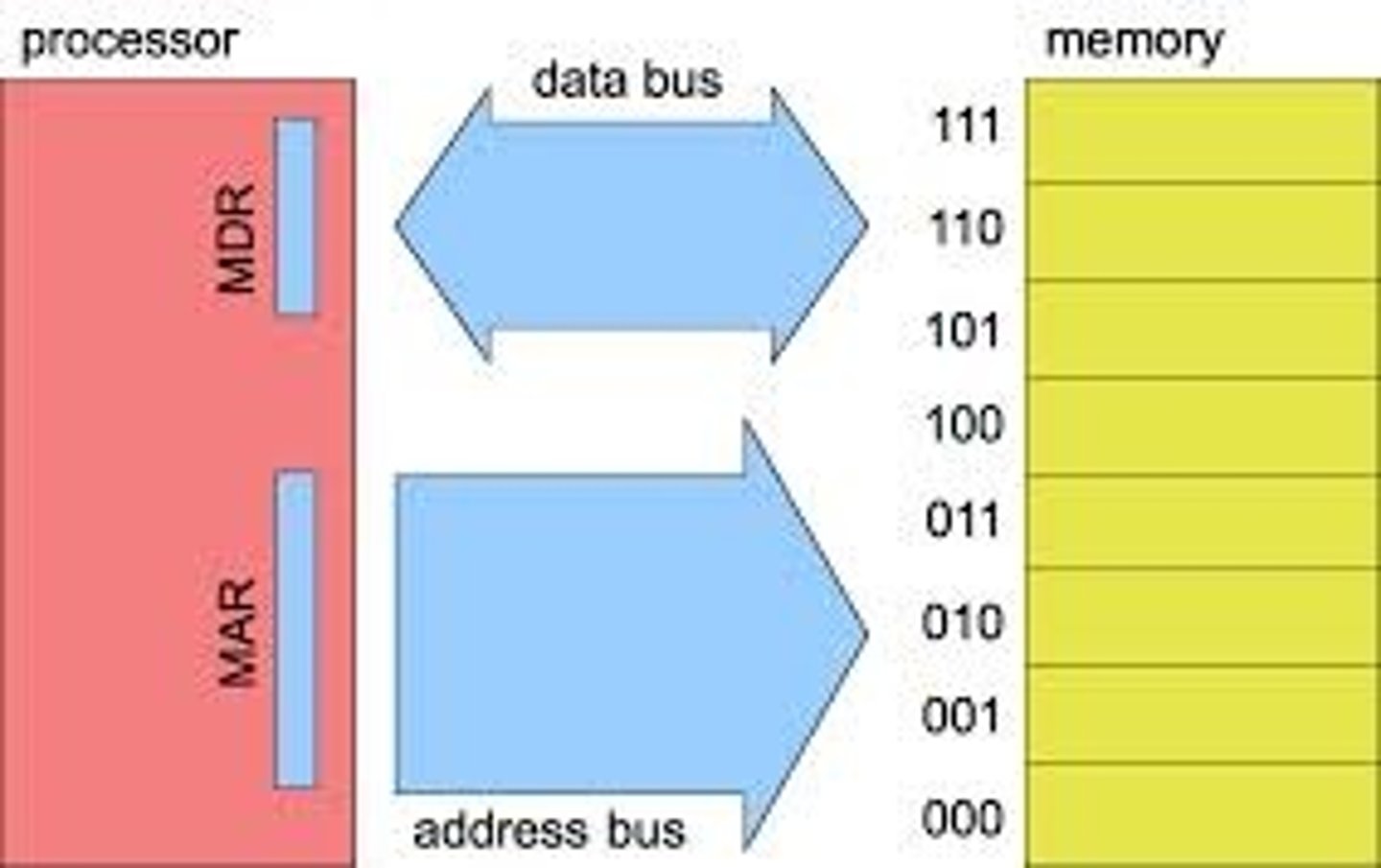
Von Neumann architecture
Instructions (programs) and data are stored in the same memory.
Bus
A collection of parallel wires which transmits data between components
Fetch
Fetches the next instruction and data into the CPU from main memory.
Decode
Decodes the instruction so it can carry it out
Execute
Carries out the instruction
CPU
Central Processing Unit. Responsible for all of a computers processing.
Control Unit
Part of the CPU responsible for coordinating and controlling all computer operations
ALU
Arithmetic and Logic Unit. Carries out arithmetic operations (+, -, *, /) and Logic operations - comparing two pieces of data (e.g. is A

System clock
controls the timing of all computer operations - measured in GHz (3 GHz == 3 billion cycles per second)
System performance
CPU performance affected by clock speed, number of cores, cache size
Number of cores
The number of processors linked together on a single chip. Dual core - 2 / Quad core - 4 cores
Cache
Superfast memory in the CPU used to store common instructions / data
Clock speed
Cycles per second - measured in Hertz.
Virtual memory
When RAM is full the operating system uses storage on the hard disk drive as an extension to RAM. Very slow to read / write data.