Biodiversity - Week 2
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What is biodiversity?
Biodiversity is the variety of life in all its forms, including species, genetic, and ecosystem diversity.
What are the three levels of biodiversity?
Species diversity, genetic diversity, and ecosystem diversity.
How is species richness defined?
Species richness is the number of different species in a given area.
What is species evenness?
Species evenness describes how evenly individuals are distributed among the species in a community.
What is a biodiversity index?
A mathematical measure that combines species richness and evenness to assess biodiversity.
What is the Shannon Index?
A biodiversity index that considers both abundance and evenness of species present.
What is Simpson's Index?
A measure of diversity that accounts for both richness and the proportion of each species.
What does a high biodiversity index indicate?
High biodiversity and a more stable, resilient ecosystem.
What is genetic biodiversity?
The variation of genes within a species.
provides lifeforms with a library of options under evolutionary timescales
Why is genetic diversity important?
It helps populations adapt to changes and resist diseases.
it is built up over a long time
How can low genetic diversity affect a population?
It can lead to inbreeding and reduced adaptability.
What are the major threats to biodiversity?
Habitat loss, climate change, pollution, invasive species, and overexploitation.
How does habitat fragmentation affect biodiversity?
It isolates populations and reduces gene flow.
What is an invasive species?
A non-native species that spreads and disrupts local ecosystems.
How does pollution threaten biodiversity?
It alters habitats and can poison species.
What is the island theory of biodiversity?
It explains species richness based on island size and distance from the mainland.
How does island size influence biodiversity?
Larger islands tend to support more species.
How does distance from mainland affect biodiversity?
Closer islands receive more immigrants and thus have higher species diversity.
What shape is the species–area relationship on a log-log plot?
A straight line, indicating a power-law relationship.
What does a steeper slope on a species–area curve indicate?
A stronger relationship between area and species richness.
How do you calculate a biodiversity index?
By applying formulas that combine species counts and proportions.
How do you interpret a biodiversity index value?
Higher values mean more diversity and greater ecosystem health.
What does it mean if one species dominates a community?
Low evenness and potentially lower biodiversity index.
Why might species diversity be high in recently deforested areas?
Temporary coexistence of pioneer and remaining native species.
What is the intermediate disturbance hypothesis?
Moderate disturbance can increase species diversity by allowing coexistence.
Why should we care about biodiversity?
It provides ecosystem services, supports resilience, and has ethical, economic, and cultural importance.
What are ecosystem services?
Benefits provided by ecosystems, like clean water, pollination, and climate regulation.
What is a utilitarian argument for conserving biodiversity?
Biodiversity provides resources and services humans depend on.
What is an intrinsic argument for conserving biodiversity?
Species have a right to exist regardless of human benefit.
What is an endemic species?
A species that exists only in one geographic location.
Why are islands often home to endemic species?
Isolation leads to unique evolutionary paths.
What is ecological resilience?
The ability of an ecosystem to recover from disturbance.
What are the species classification categories?
Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
What is alpha diversity
Count of species number within a community
useful to assess impact of small-scale human activities
What is beta diversity?
rate of change in species composition along a gradient
comparing two areas
What is Y diversity
total number of species within a region
Why is biodiversity important?
economics: ecosystem services
organisms have co-evolved to make maxiumum utility of local abiotic conditions
genetic diversity gives rise to more diversity
ethical: do we have the right to wipe out other species?
resilience against change
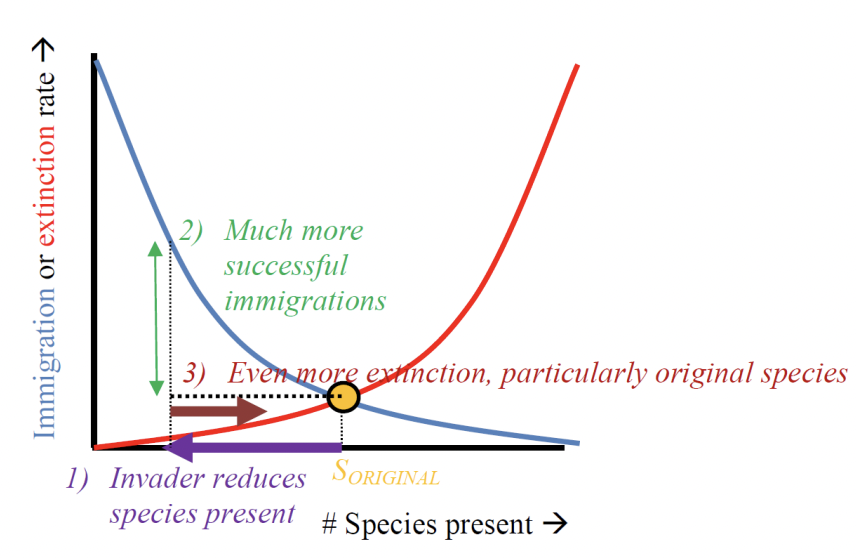
Explain the island biogeography theory
successful immigration rate decline w/ the number of species that is already present on the island
higher competition w/ more species
extinction rate increases with species number
small island = higher extinction rate
applies to fragmented habitats
Why are coastal ecosystems under particular threat?
rising sea levels, more frequent and intense storms, and ocean acidification, as well as habitat destruction from coastal development, pollution, and invasive species
erosion, dredging, development
coastal zones are particularly biodiverse
food, spanning, protection
Give an example of invasive species
american cherry
brown tree snake in Guam - consuming bird eggs - affecting bird populaition - lack of local predator
What does an invasion graph look like?
yellow dot = rate of invasion and extinction are in stable equilibrium
immigration rate becomes more succesful
higher extinction rate
What should be the focus of conservation?
biodiversity hotspots
endemic species in one region
relict species of previously larger range
isolated species