Exam 01 Review: Management Information Systems
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
MIS
Management of information systems for organizational strategies.
Data
Raw facts and figures about something.
Information
Data processed with context to provide meaning.
Data Characteristics
Accuracy, timeliness, relevance, sufficiency, cost-effectiveness.
Computer-Based IS
Components interacting to produce information.
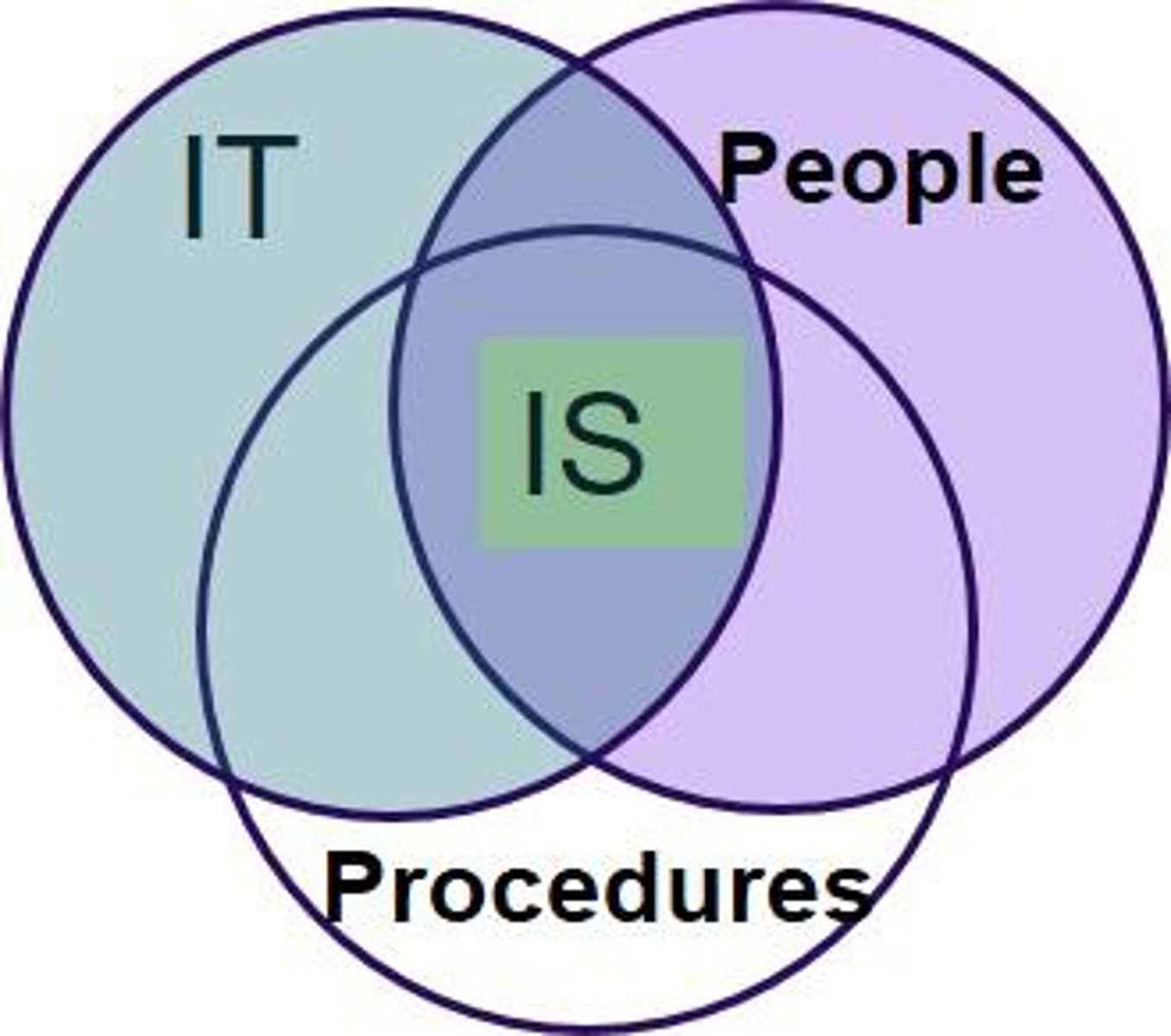
IT Components
Hardware, software, and data in information technology.
IS Components
IT plus procedures and people in information systems.
Abstract Reasoning
Ability to create and manipulate models.
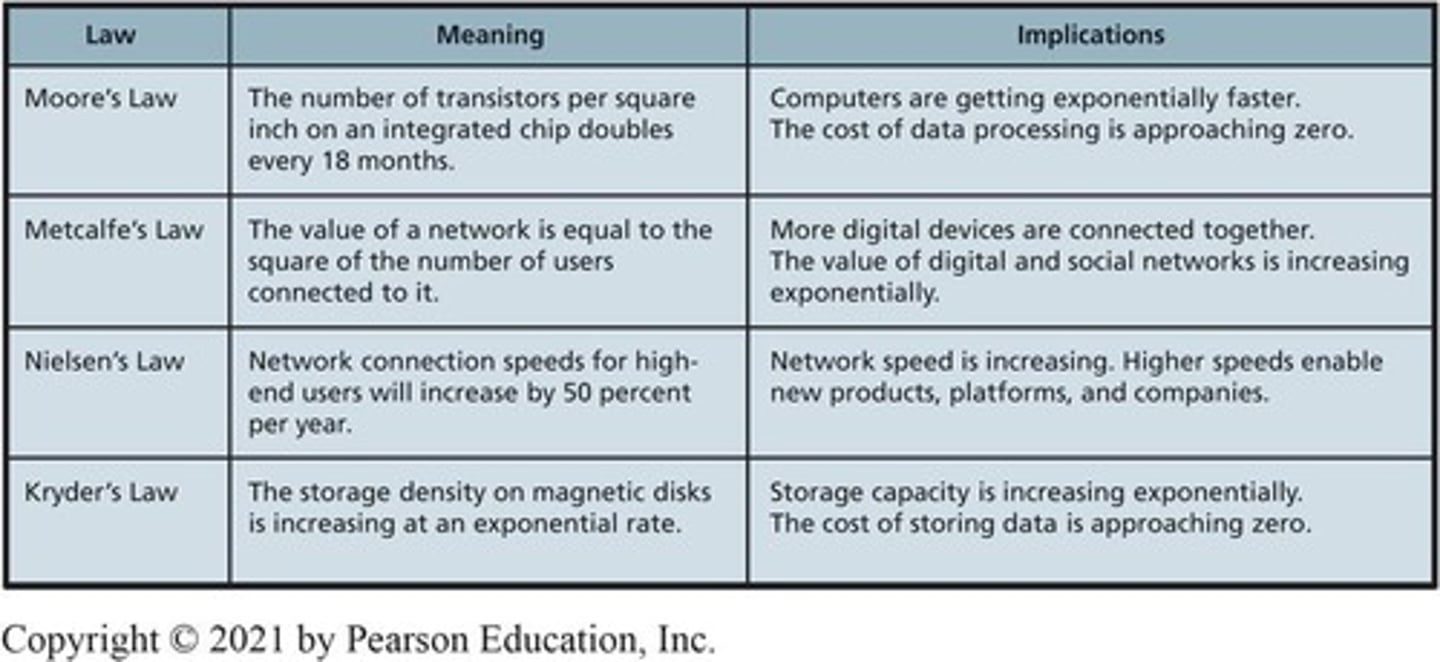
Moore's Law
Transistors double every 18 months, impacting computing.
Competitive Strategy
Organization's response to industry structure.
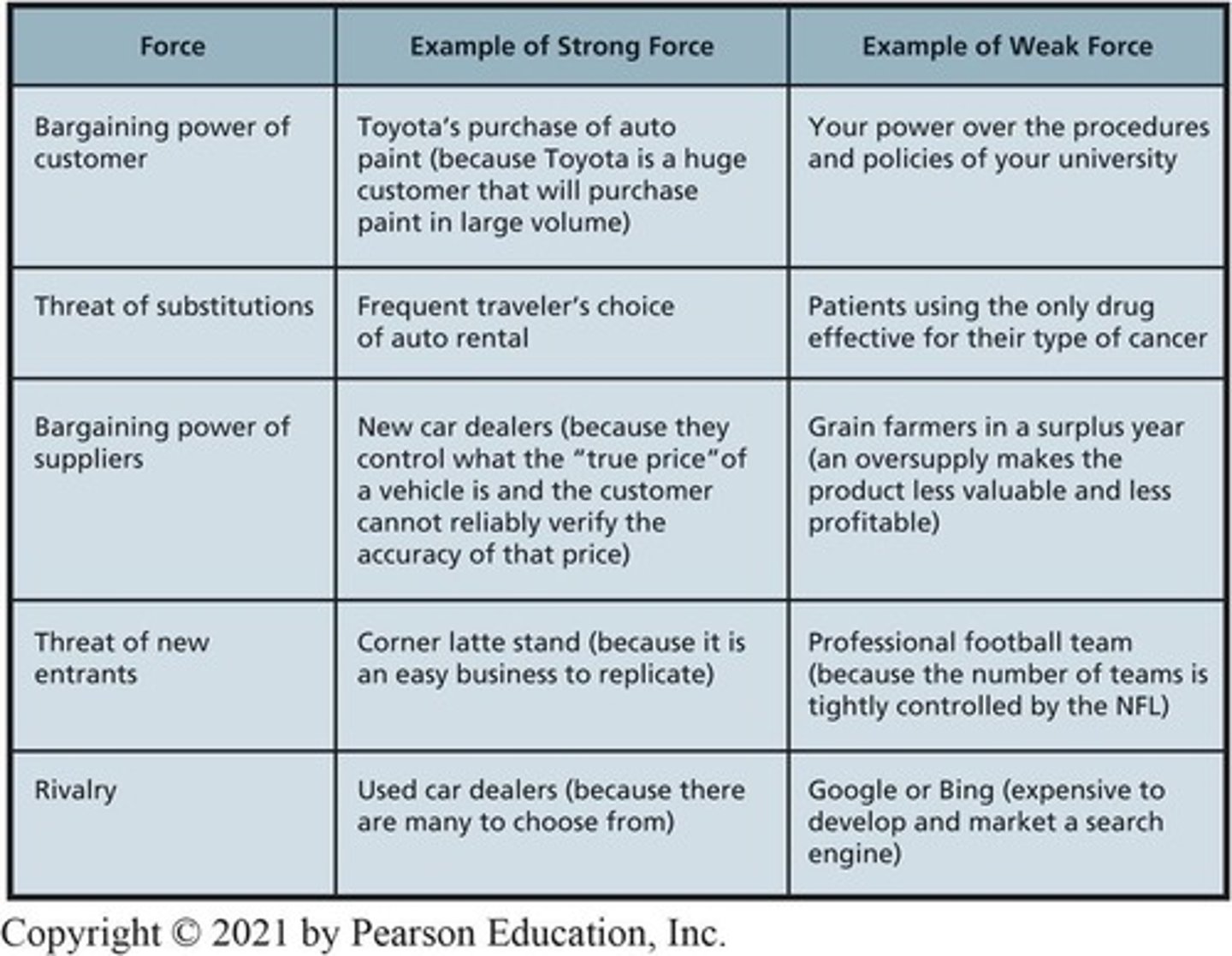
Example of bargaining power of cusotmers
Your power over the procedures and policies of ECU.
Porter's Five Forces
Framework for analyzing competitive environment.
Cost Leadership
Being the lowest cost provider in an industry.
Differentiation
Offering unique products/services for premium pricing.
Focus Strategy
Targeting a narrow market segment.
Switching Costs
Costs incurred when changing products or services.
High Switching Costs
Difficulties in switching products to retain customers.
Business Process
Set of activities to achieve a specific goal.
Procedures
Instructions for completing tasks within an IS.
People in IS
Users and stakeholders involved in information systems.
Quality Information
Information that meets data characteristics for decision-making.
Competitive Advantage
Edge gained through effective use of IS.
Product implementations
Create new product or service; enhance products or services; differentiate products or services
Process implementations
Lock in customers/buyers, lock in suppliers, raise barriers to entry, establish alliances, reduce costs
Organizational Strategy
Long-term plan to achieve goals and objectives.
Business Process
Network of activities transforming inputs into outputs.
Structured Processes
Standardized, formally defined, day-to-day operations.
Dynamic Processes
Flexible, informal, adaptive, strategic decision-making.
Workgroup Processes
Enable groups to achieve specific departmental goals.
Enterprise Processes
Span organization, supporting multiple departments' activities.
Information Silo
Data isolated in separate information systems.
Problems of Information Silos
Data duplication, inconsistency, integrity issues, inefficiency.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Suite managing customer interactions across life cycle phases.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Suite integrating applications for real-time updates.
Enterprise Application Integration (EAI)
Software connecting applications, enabling data sharing.
Intranet
Private internet used exclusively within an organization.
LAN Protocols
Standards for local area network communication.
Bluetooth
Wireless technology for short-distance data transmission.
Domain Name System (DNS)
Maps domain names to public IP addresses.
URL (Uniform Resource Locator)
Internet address protocol for accessing resources.
Private IP Addresses
Used within a network, not routable on internet.
Public IP Addresses
Globally unique addresses routable on the internet.
Integrated Information
Unified data accessible across different organizational systems.
Data Integrity Problem
Issues caused by data inconsistency and duplication.
Public IP addresses
Identifies a device on the Internet.
Private IP addresses
Identifies a device on a private network.
Net Neutrality
Regulations preventing ISPs from discriminating traffic.
HTTPS
Protocol for secure data transmission online.
The Cloud
Elastic leasing of pooled computer resources.
In-House Hosting
Local management of computing resources.
The cloud is preffered to in-house hosting because
Small capital requirements
When does the cloud not make sense?
- When law or standard industry practice require physical control or
possession of the data
- Financial institution might be legally required to maintain physical
control over its data
Resource Elasticity
Dynamic adjustment of server capacity based on demand.
SaaS
Software as a Service, provides applications online.
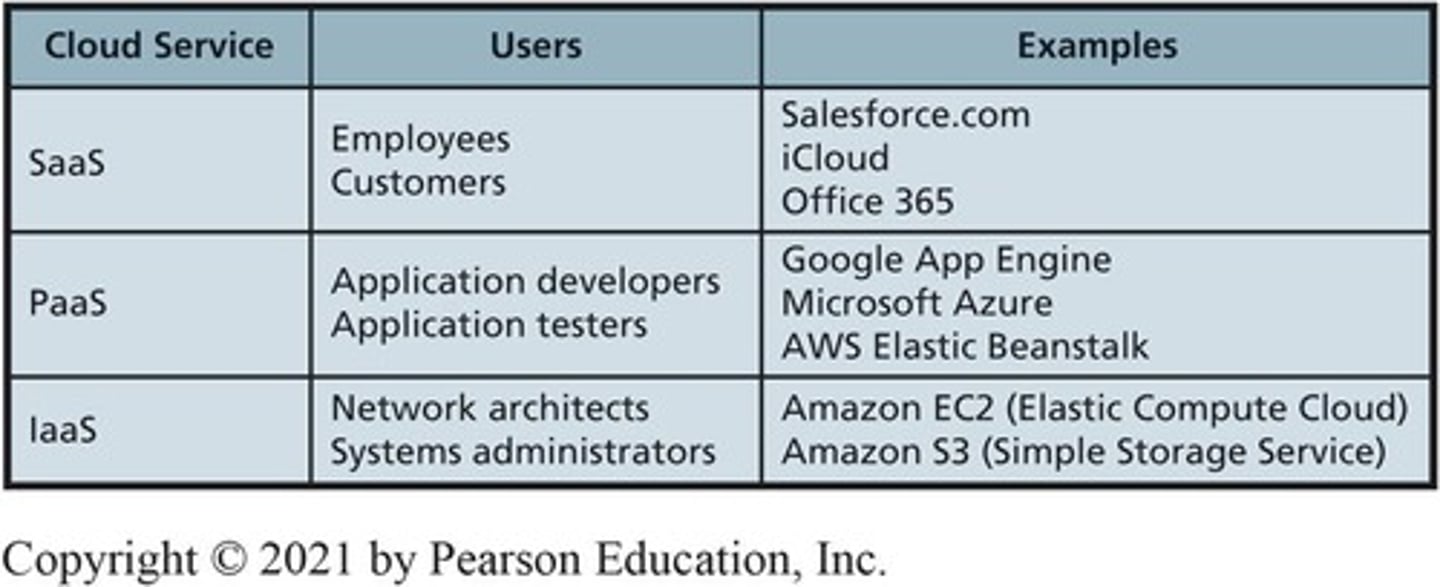
PaaS
Platform as a Service, offers hosted environments.
IaaS
Infrastructure as a Service, barebones cloud hosting.
Future of Cloud
Faster, cheaper, and more secure cloud services.
Mobile Systems
Information systems supporting users in motion.
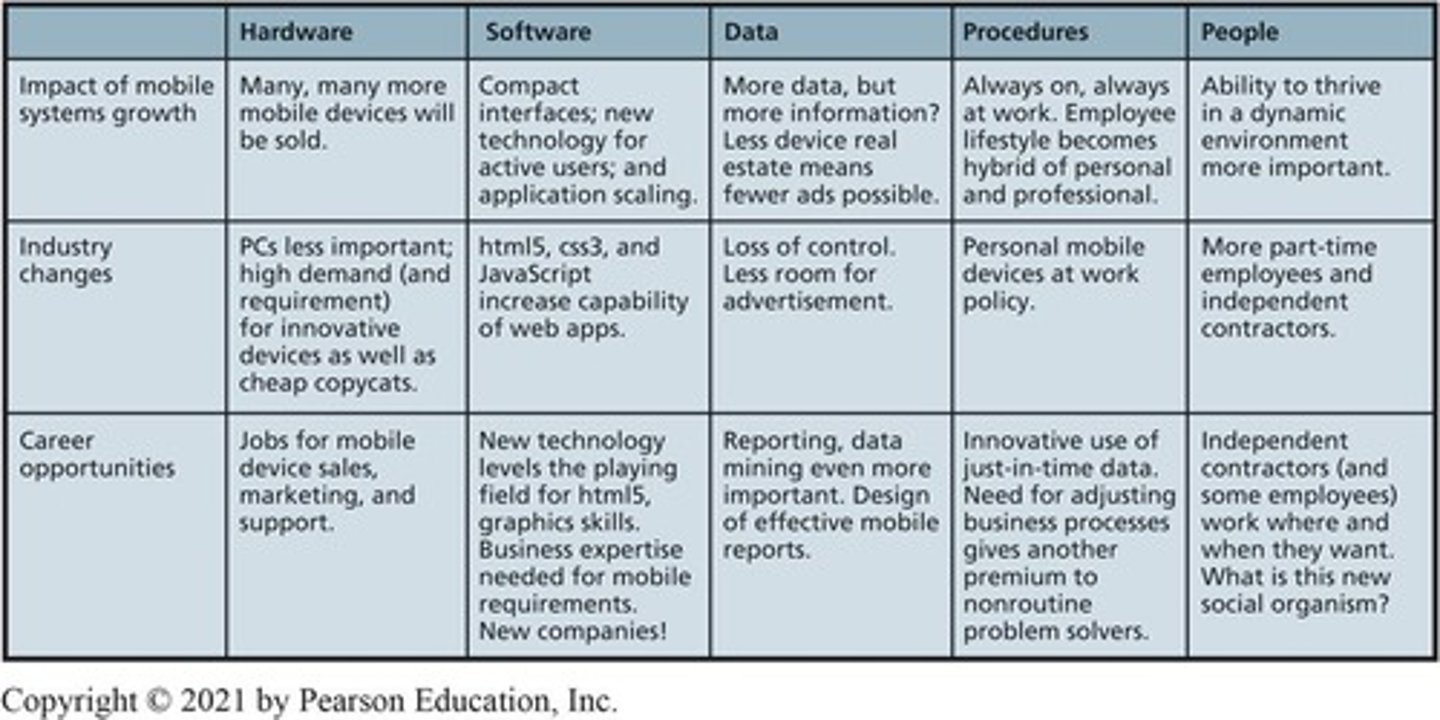
Mobile Devices
Small, lightweight, power-conserving communication tools.
Wireless Connectivity
Connection without physical cables.
Native Applications
Designed for specific devices and operating systems.
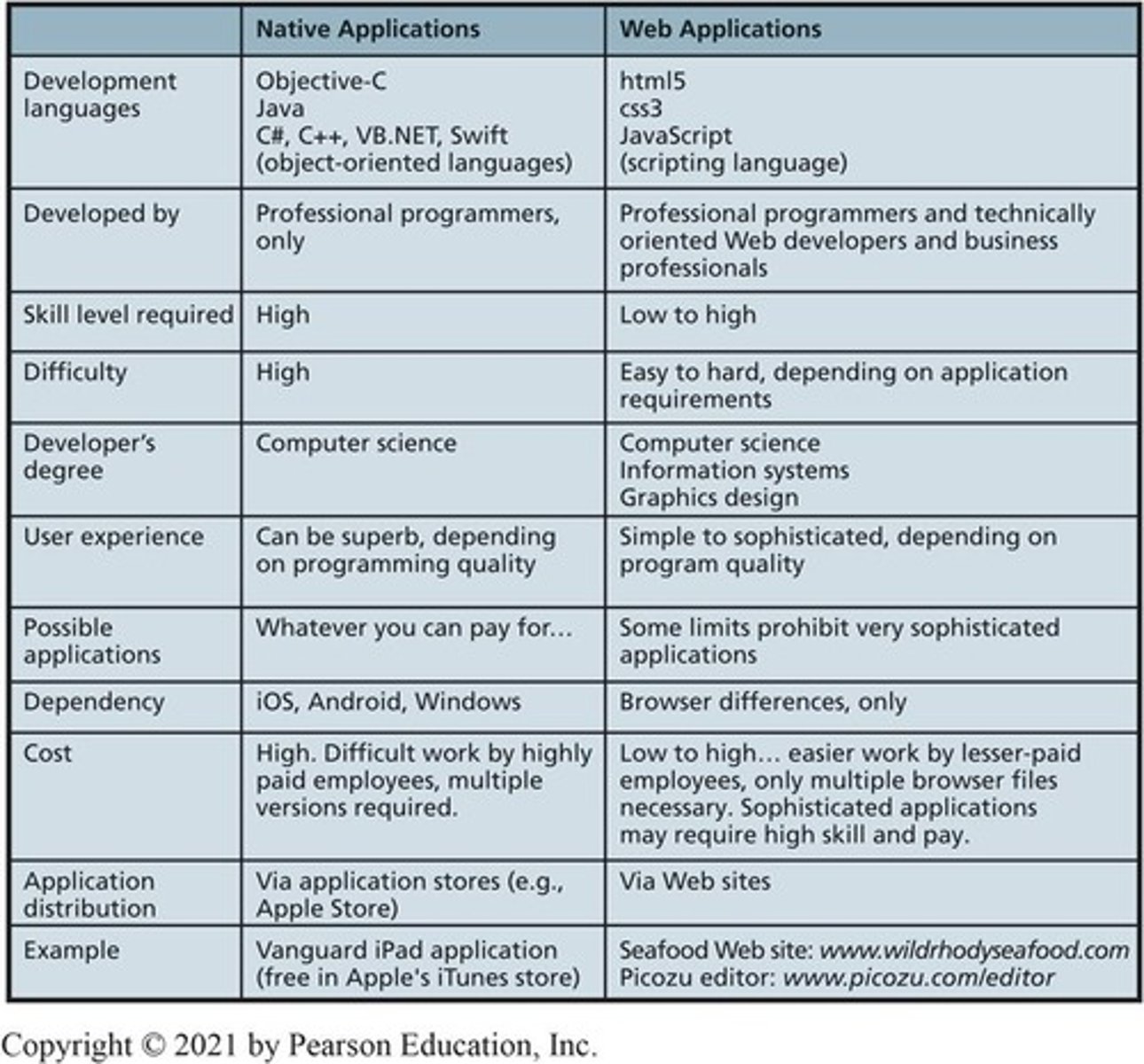
Browser-Based Applications
Run in web browsers, platform-independent.
Roaming
Moving activities across different devices.
BYOD
Bring Your Own Device policy at workplaces.
CIO
Principal manager of the IS department
Technology Group Manager (CTO)
Principal manager overseeing technology infrastructure.
Computing Infrastructure Group
Manages the physical and virtual computing resources.
The group managing the computing infrastructure
Operations
Manager for the orgainzation's IS security
CISO
Who manages the organization's asset security?
CSO
Systems analysts
Work with users to determien system requirements, design & develop job descriptions/procedures, and help determine system test plans.
Business analyst, IT
Work with business leaders and planners to develop processes and systems that implement business strategy and goals.
Organizations plan the use of IS by
Aligning information systems with organizational strategy.
Outsourcing
Hiring another organization to perform services

Popular reasons for outsourcing include
Management advantages
Cost reduction
Risk reduction
User Rights
Computer hardware and programs that allow you to perform your job proficiently
Reliable network and Internet connections
A secure computing environment
Protection from viruses, worms, and other threats
Contribute to requirements for new system features and functions
Reliable systems development and maintenance
Prompt attention to problems, concerns, and complaints
Properly prioritized problem fixes and resolutions
Effective training
User Responsibilities
Learn basic computer skills
Learn standard techniques and procedures for the applications you use
Follow security and backup procedures
Protect your password(s)
Use computers and mobile devices according to your employer's computer-use policy
Make no unauthorized hardware modifications
Install only authorized programs
Apply software patches and fixes when directed to do so
When asked, devote the time required to respond carefully and completely to requests for requirements for new system feature and functions
Avoid reporting trivial problems
Systems Development
Creating and maintaining information systems.
Major challenges of systems development
Difficulty of determining requirements
Changes in requirements
Difficulties involving scheduling and budgeting
Changing technology
Diseconomies of scale
Brooks' Law
Adding more people to a late project makes the project later.
Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
Framework for developing information systems.
Cost Feasibility
Evaluating if benefits justify costs.
Tangible Benefits
Measurable advantages from a system.
Intangible Benefits
Non-measurable advantages from a system.
Technical Feasibility
Can we make it?
Do we have the hardware/software, expertise, infrastructure to make it work?
Is there existing IT to be able to meet the needs of the new system?
Organizational Feasibility
Will people use it?
How much training is needed?
Will it require operational changes?
Are there any legal or ethical issues?
Will it interfere with the way we conduct business?
Does it fit our customs and culture?
Requirements Analysis Phase
Determining the system's requirements is most important making the Requirements Analysis phase the most important phase of the SDLC!
Implementation Approaches
Methods for introducing a new system.
Parallel Implementation
Running old and new systems simultaneously.
Plunge Implementation
Discard the old system completely and use the new
Pilot Implementation
Start with small groups of people on the new system and gradually add more users (limited portion of the business, entire system)
Phased Implementation
Implement the new system in phases, piece by piece (everyone, parts of the system)