CHEM 1601 Functional Groups
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Alkane
saturated C; maximum number of single bonds, not typically considered a functional group
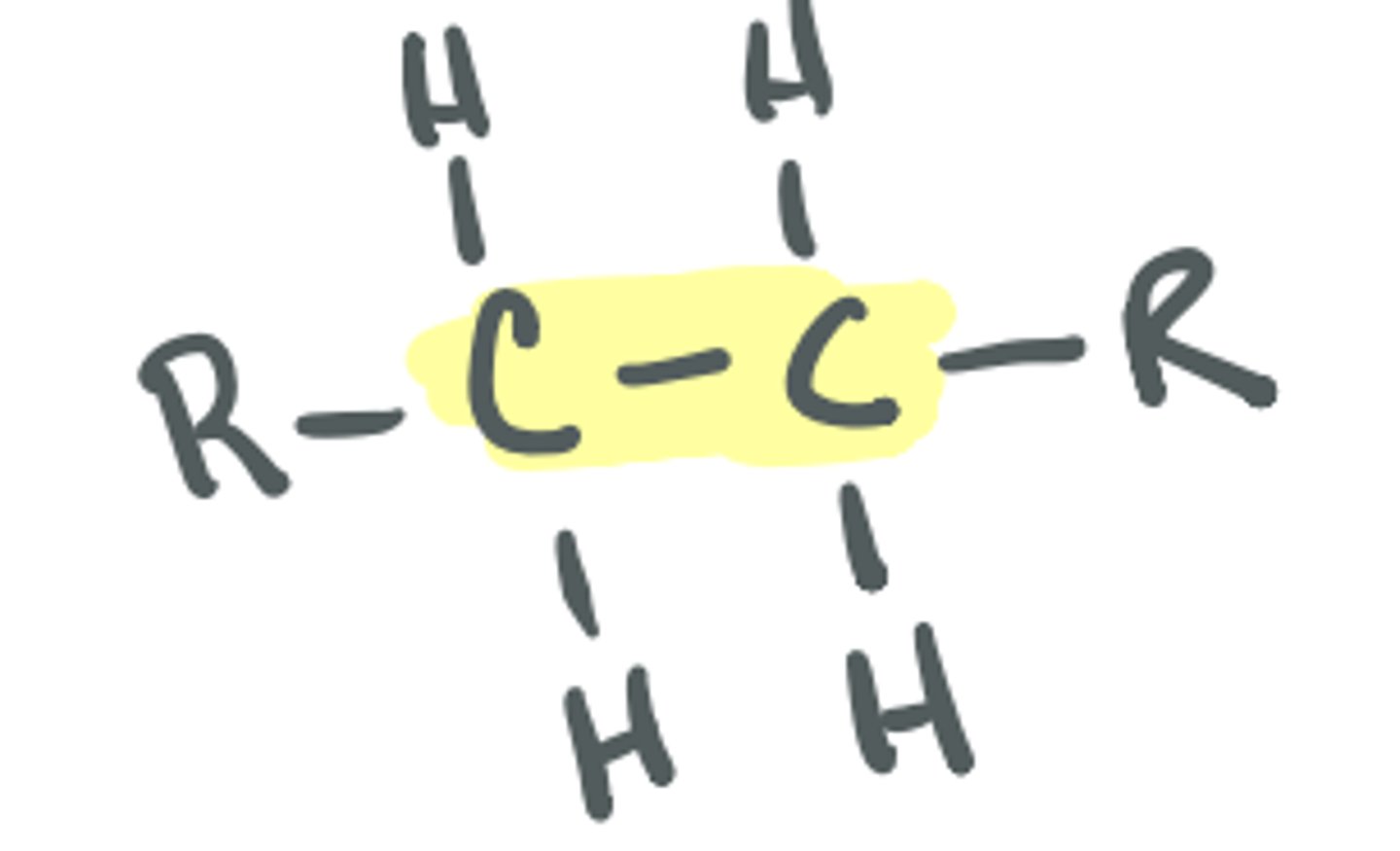
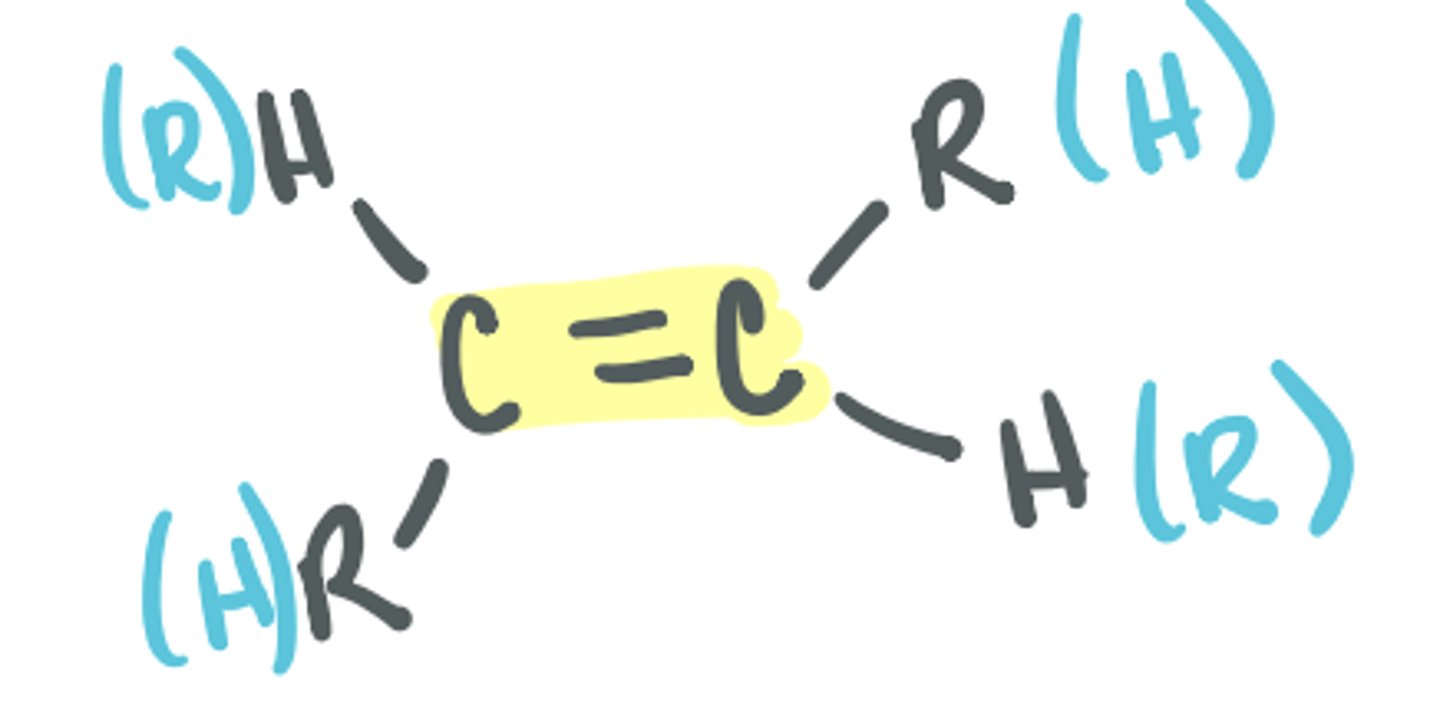
Alkene
C=C double bond; can be bonded to H, C, other heteroatoms as long as it's not aromatic (aryl)
Alkyne
carbon-carbon triple bond; can also be bonded to H, C, other heteroatoms
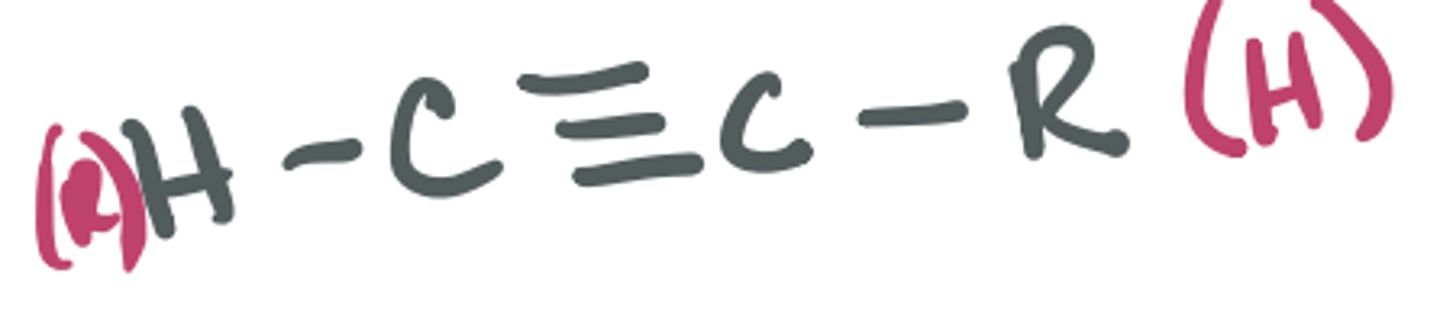
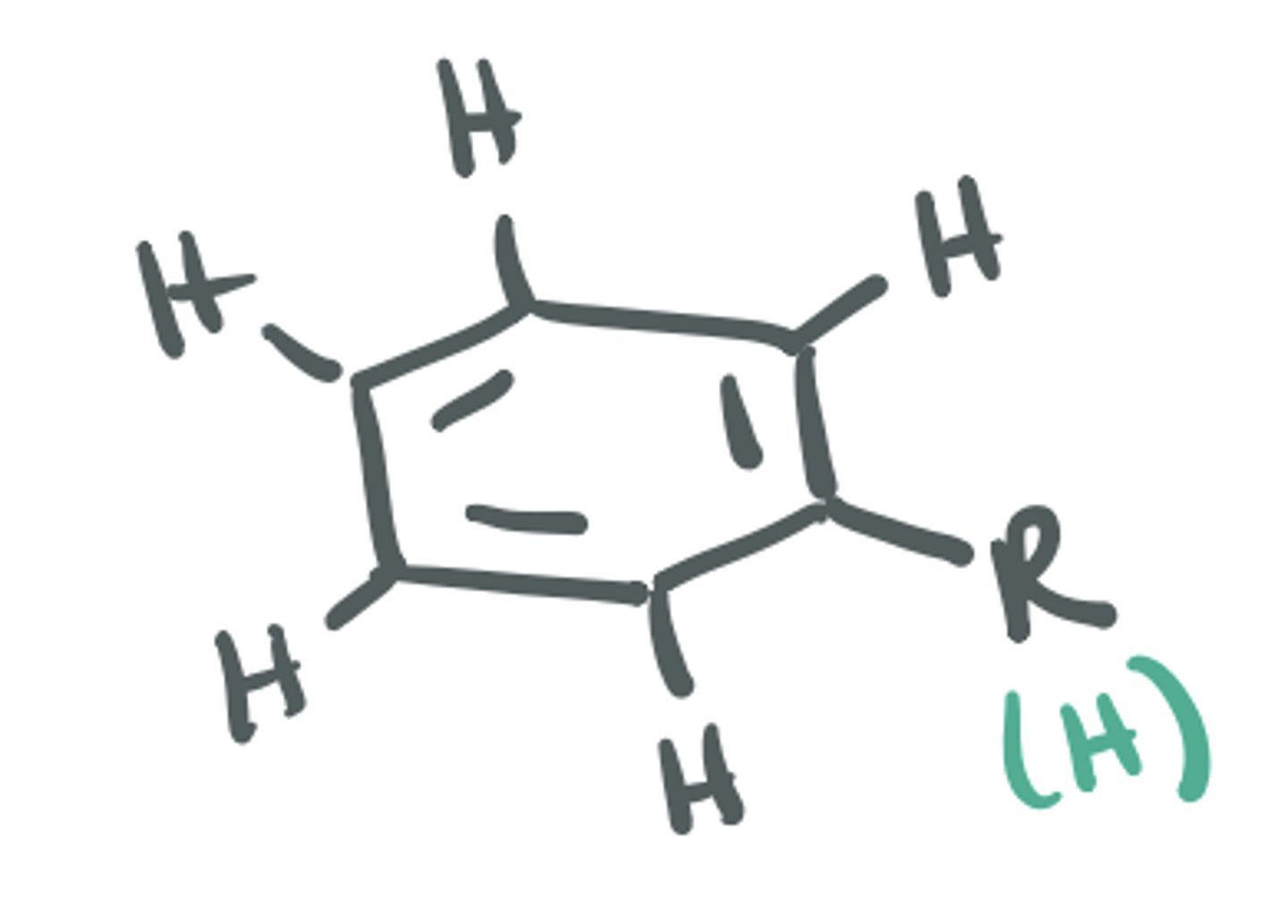
Aryl (aromatic ring)
characteristic ring of 6 C atoms w alternating double bonds (can be substituted at each C atom)
Alcohol
(OH) group attached to a C atom; as long as its not on a carboxylic acid
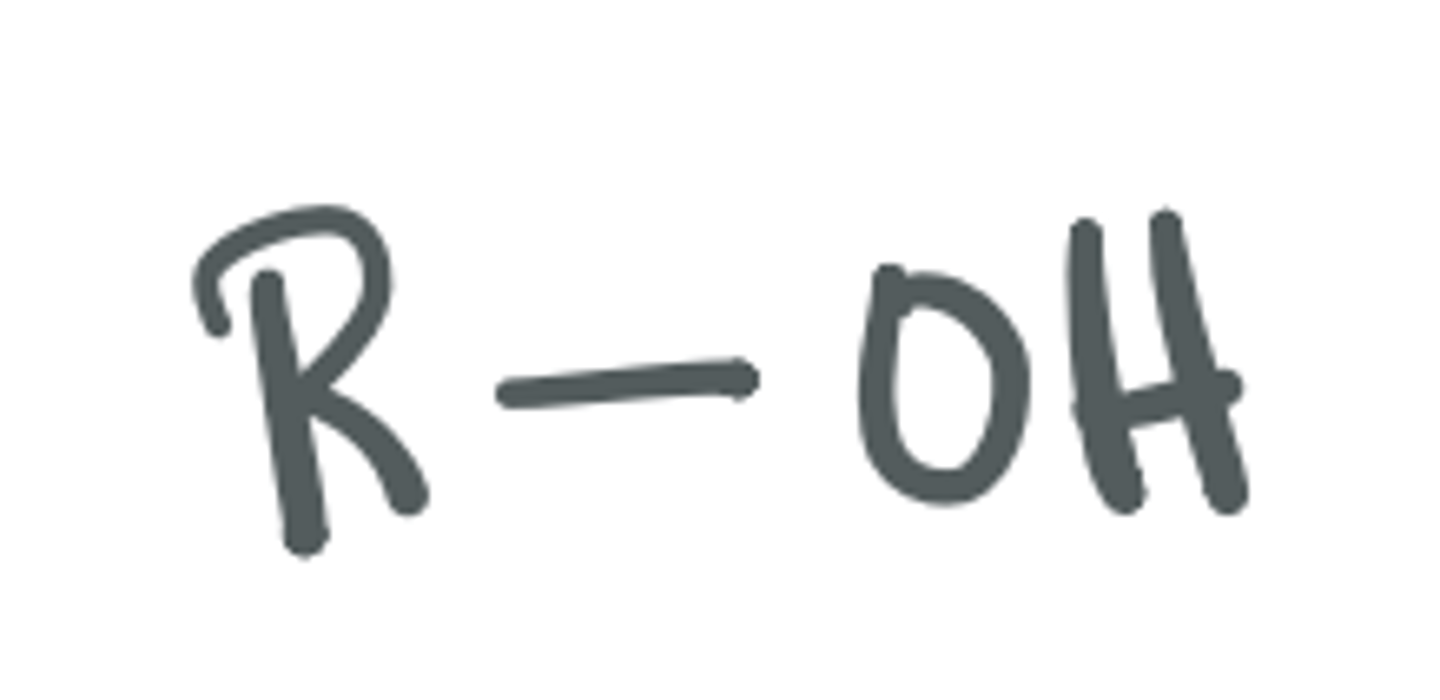
Ether
the two R groups are two alkyl or two hydrocarbon groups
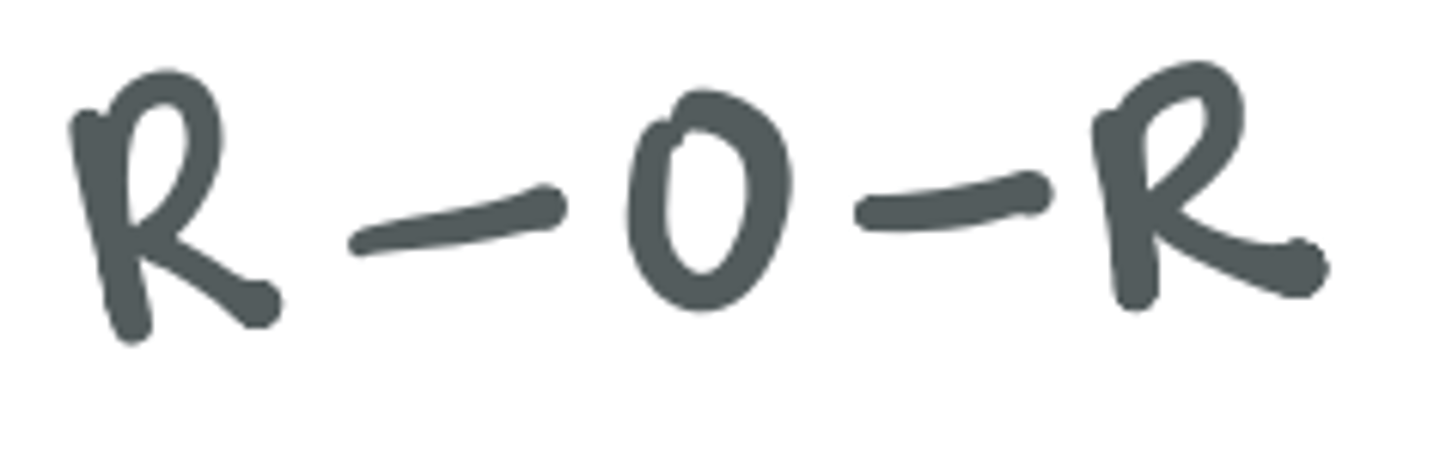
Aldehyde
The C=O is called a carbonyl; there MUST be at least one H bonded to the C of the C=O
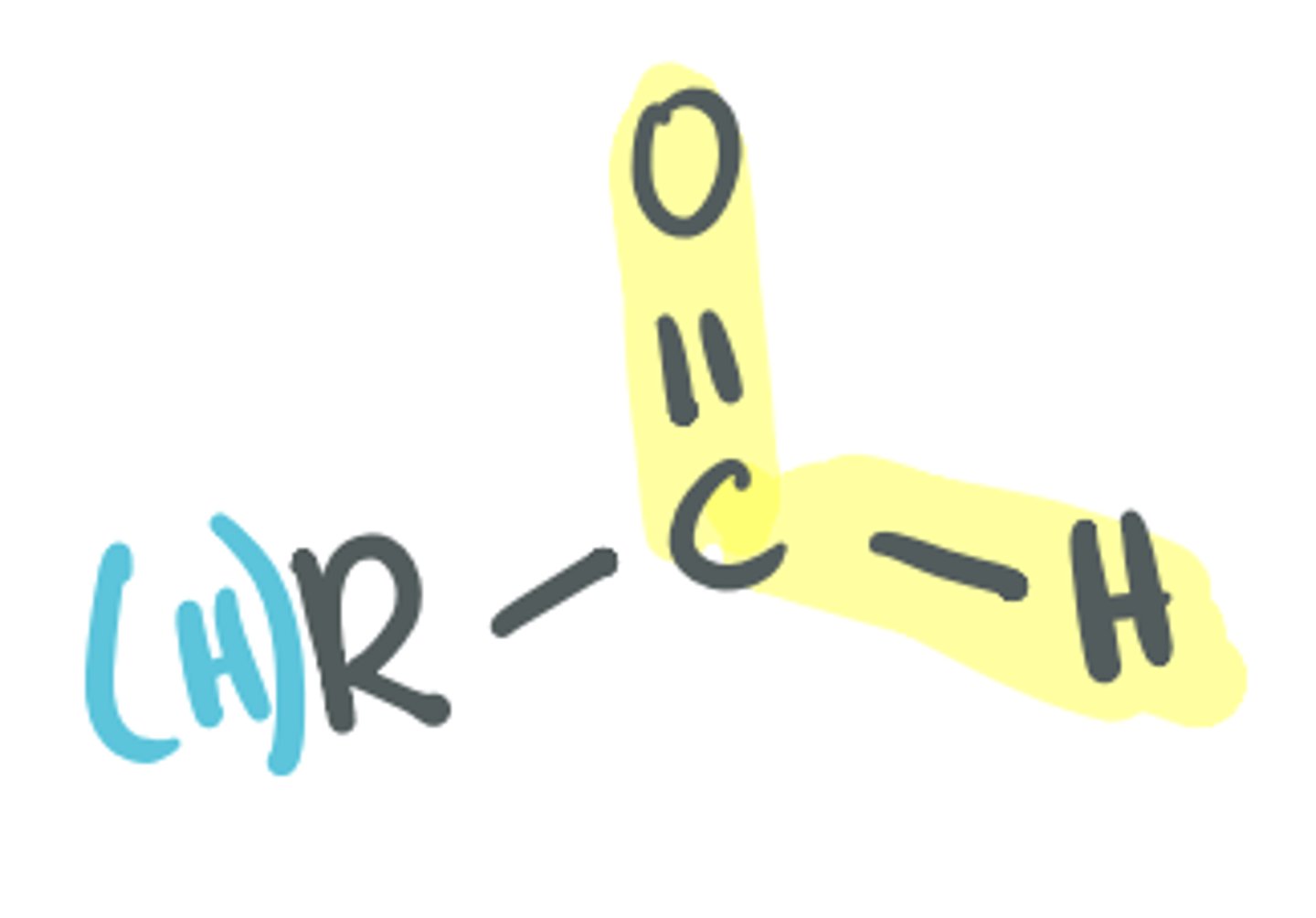
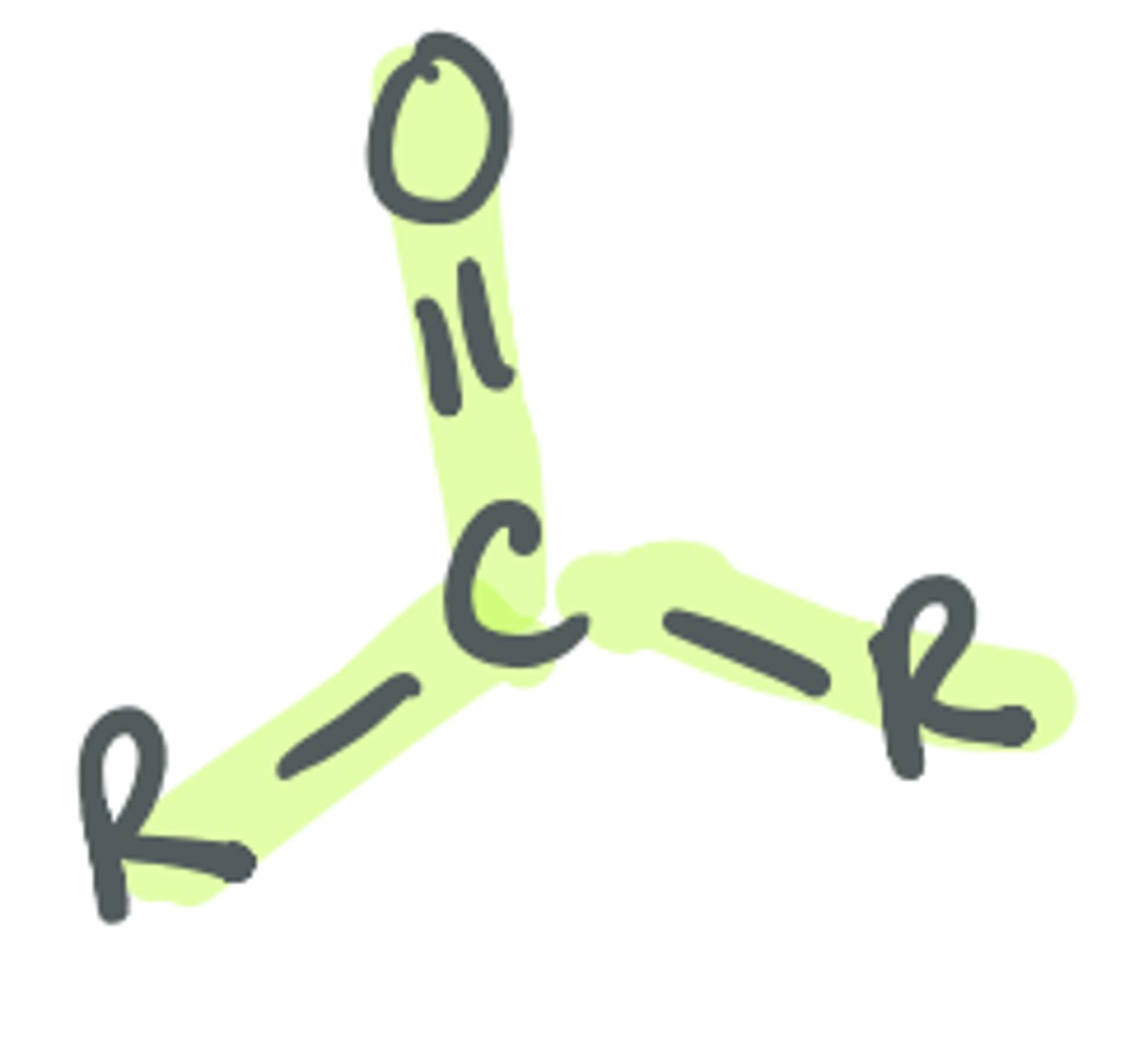
Ketone
the carbonyl C is bonded to 2 other C groups that do not change the identity of the functional group
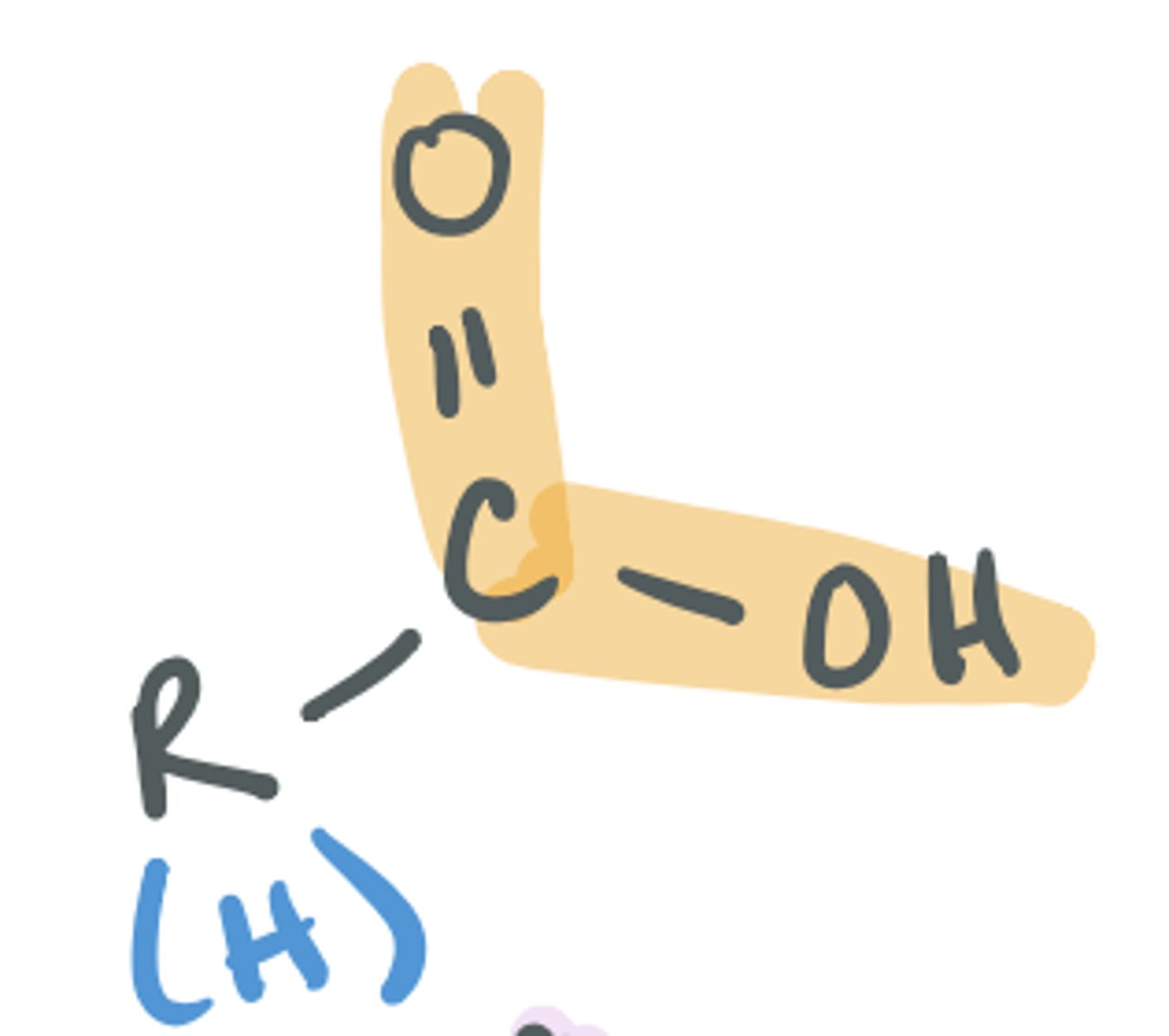
Carboxylic acid
COOH, CO2H are two common ways of representing the functional group
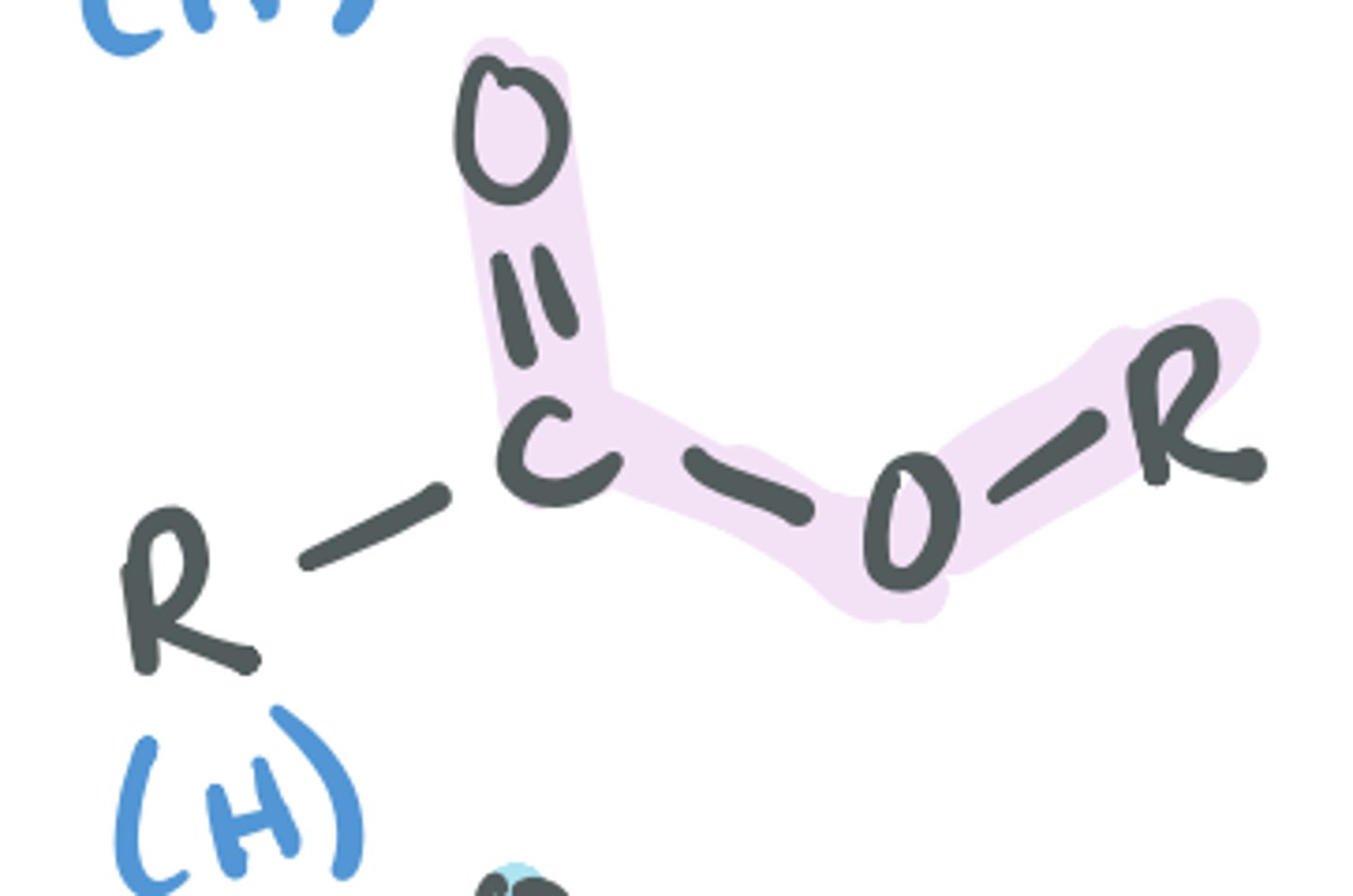
Ester
Looks similar to carboxylic acids, but the H (acidic H) is replaced by another C group
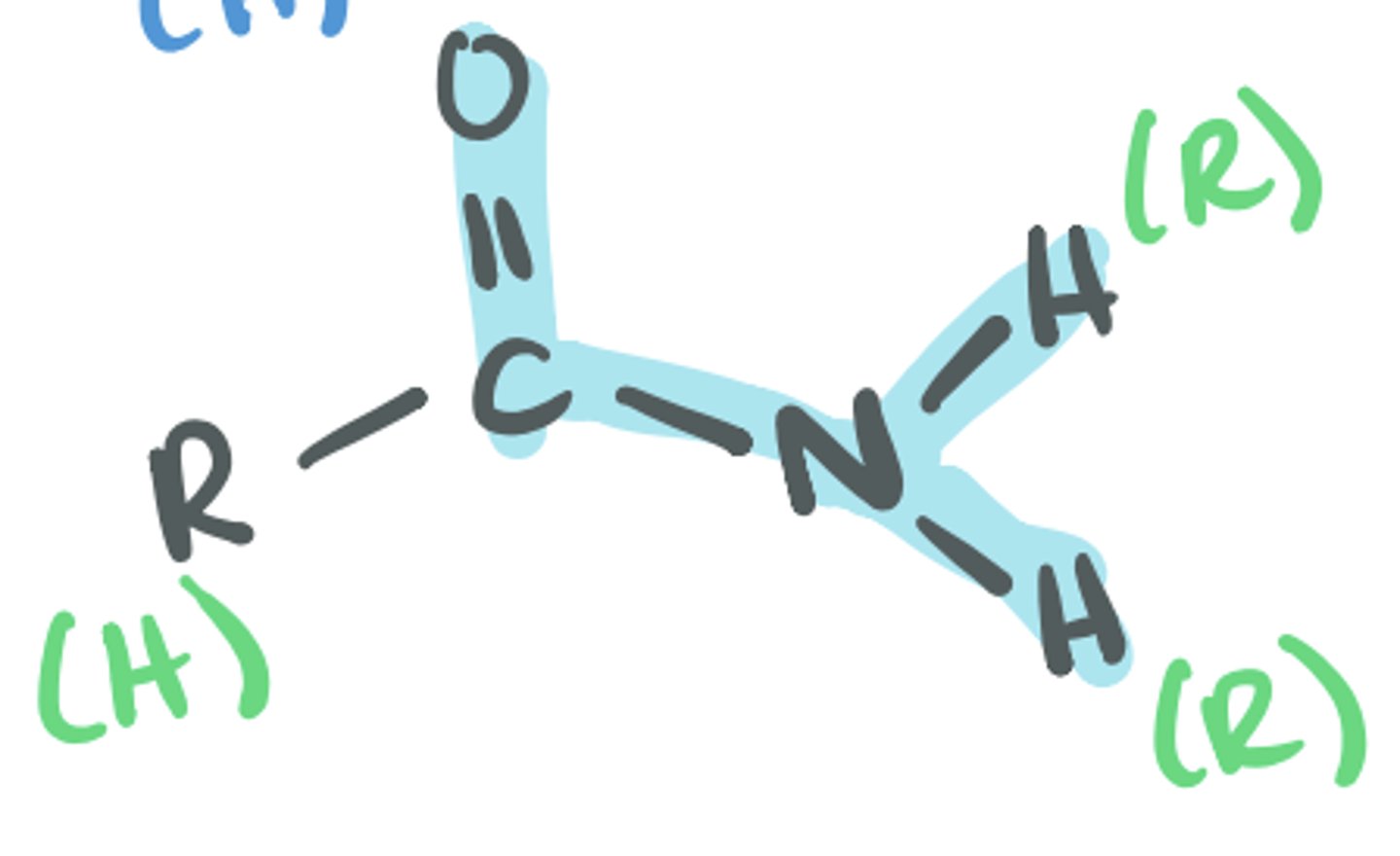
Amide
Has the C=O then a bond to an N, the N can be bonded to 2 Hs, 1 H, 1 R, or 2 R groups
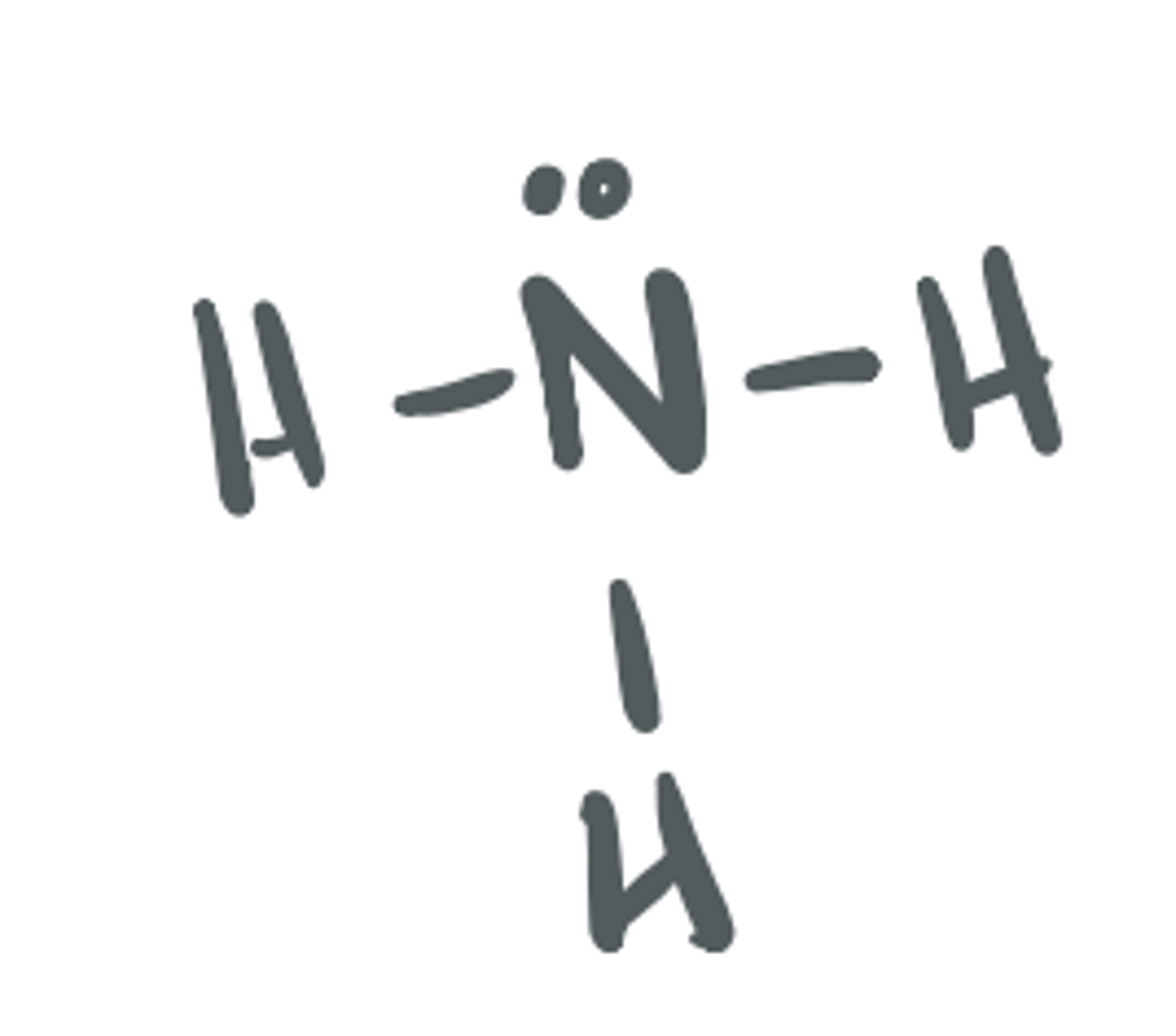
Ammonia
NH3
Amine (primary)
based on the structure of ammonia, where 1 of the H atoms is replaced with a C group
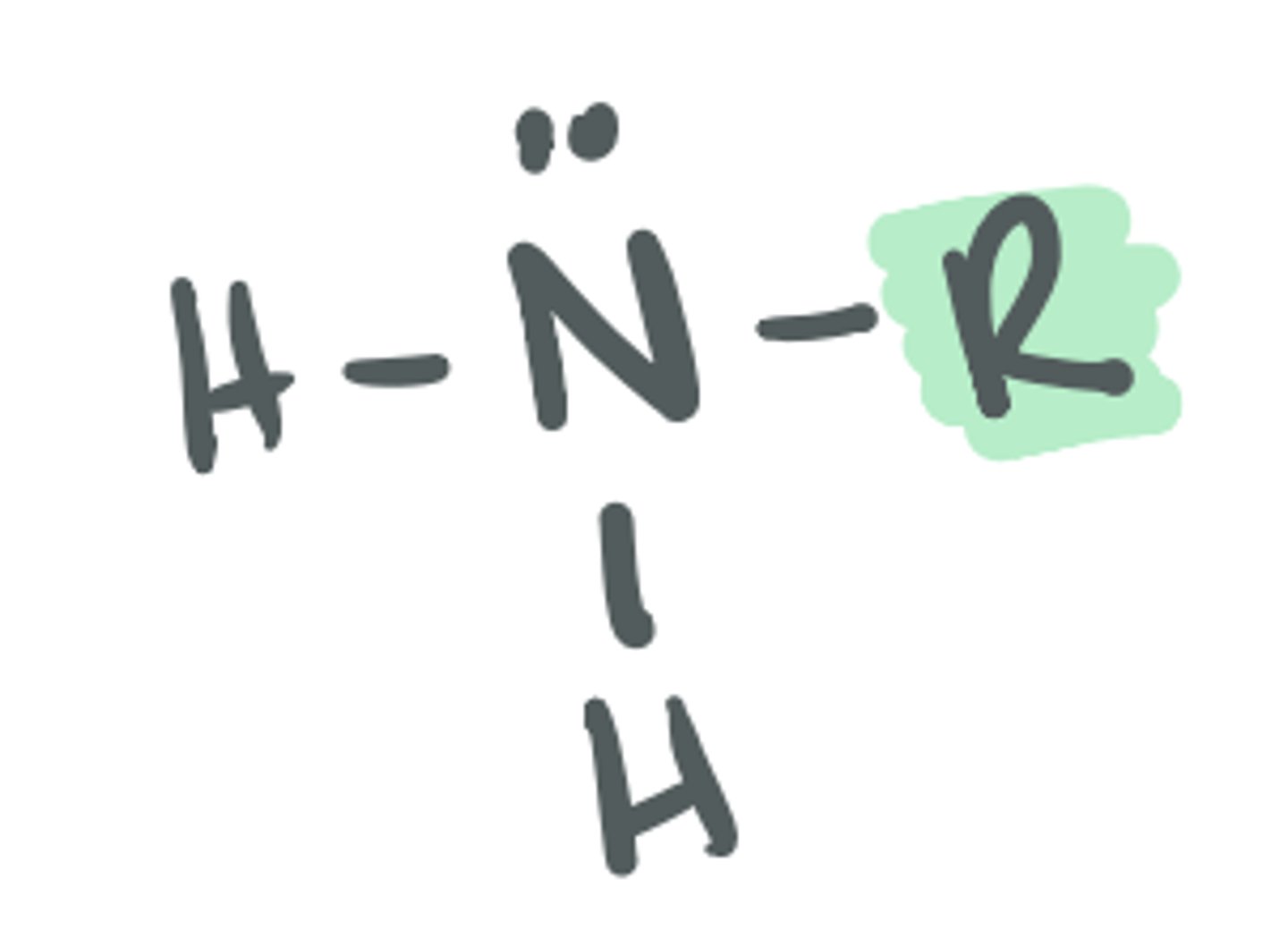
Amine (secondary)
based on the structure of ammonia, where 2 of the H atoms are replaced with a C group
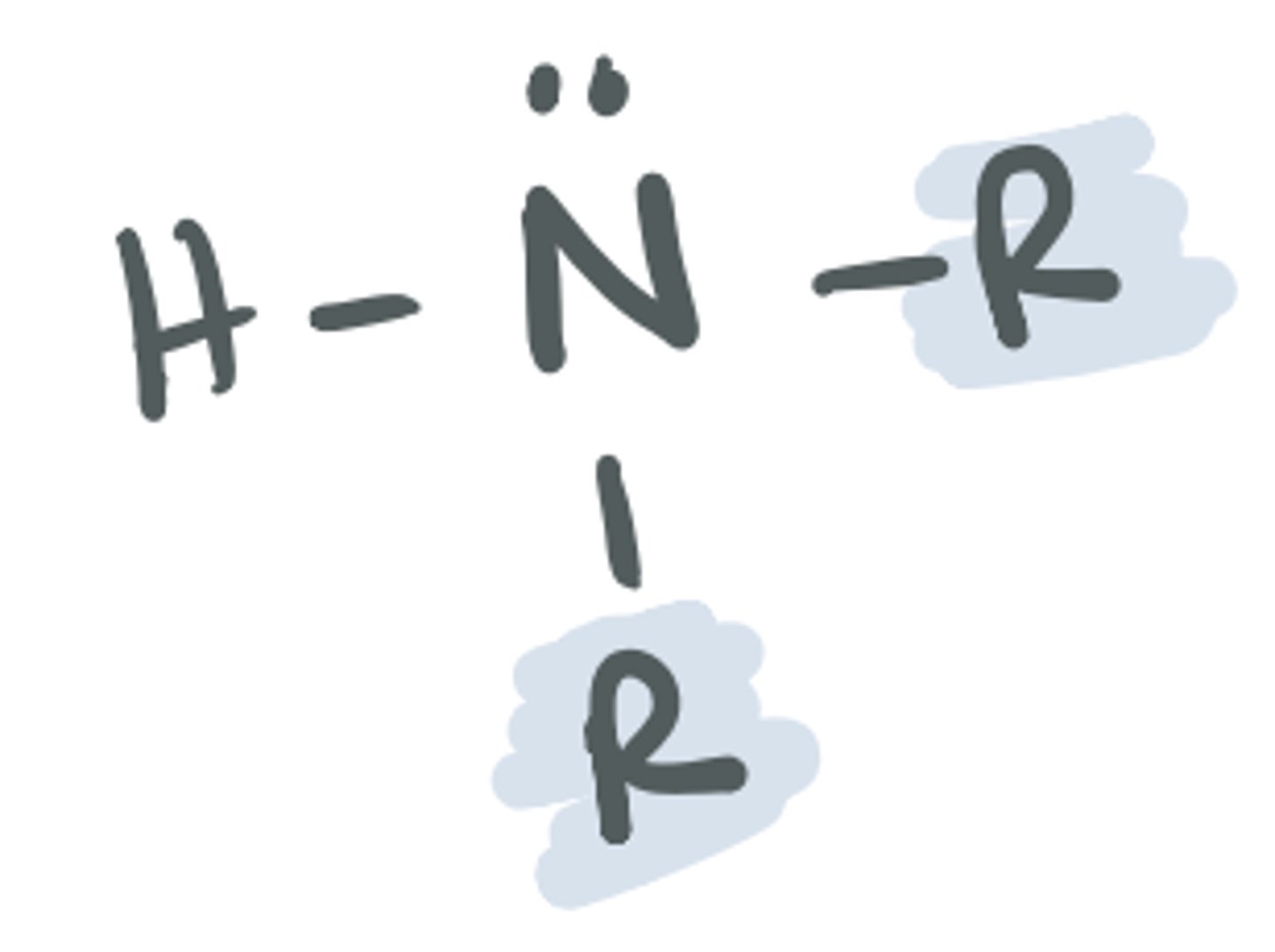
Amine (tertiary)
based on the structure of ammonia, where 3 of the H atoms are replaced with a C group
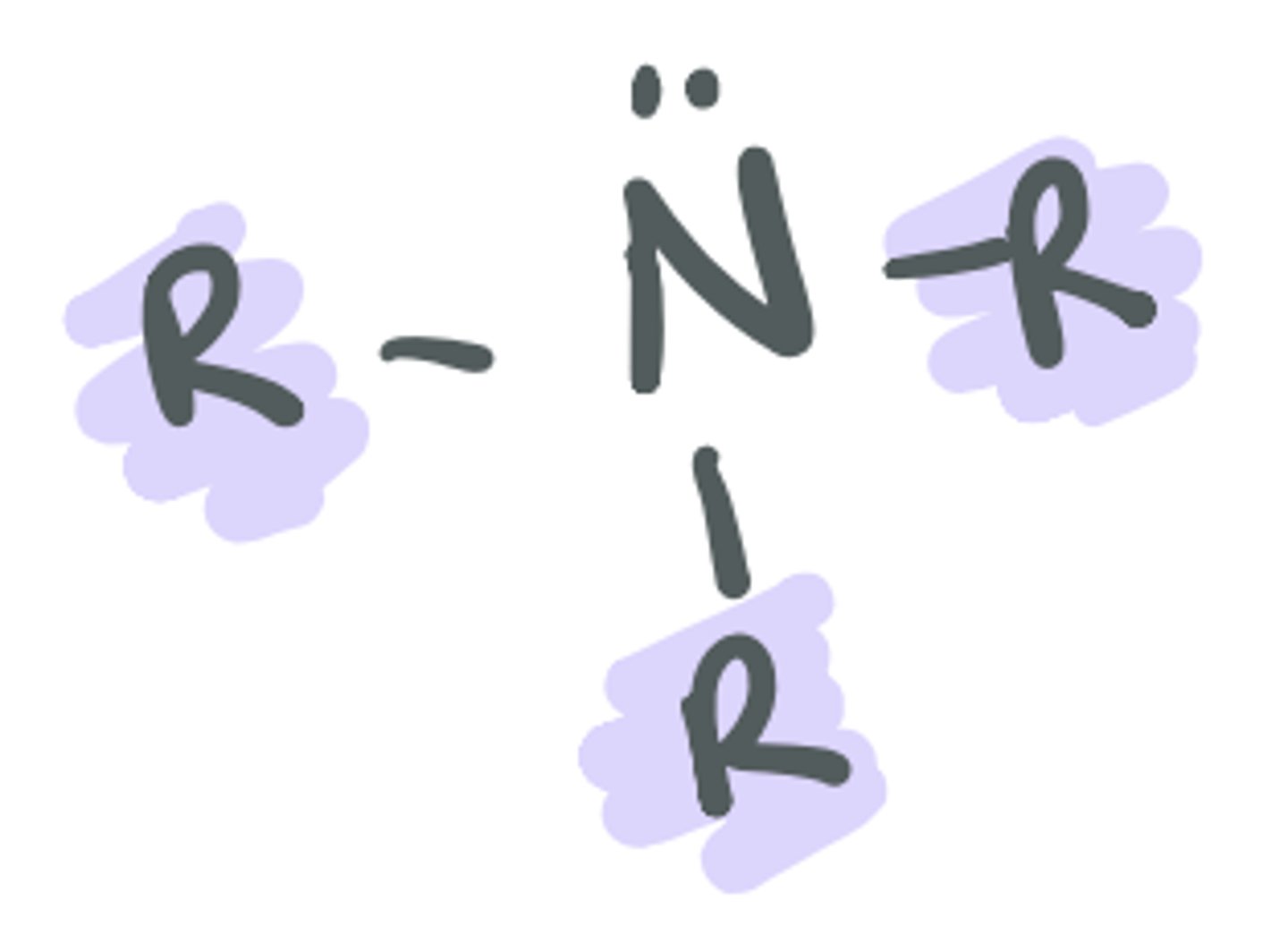
R
alkyl or a carbon-containing portion of the molecule that does not change the identity of the functional group