Kinesiology anatomy exam
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
Cervical Atlas
C1 vertebra; supports the skull.
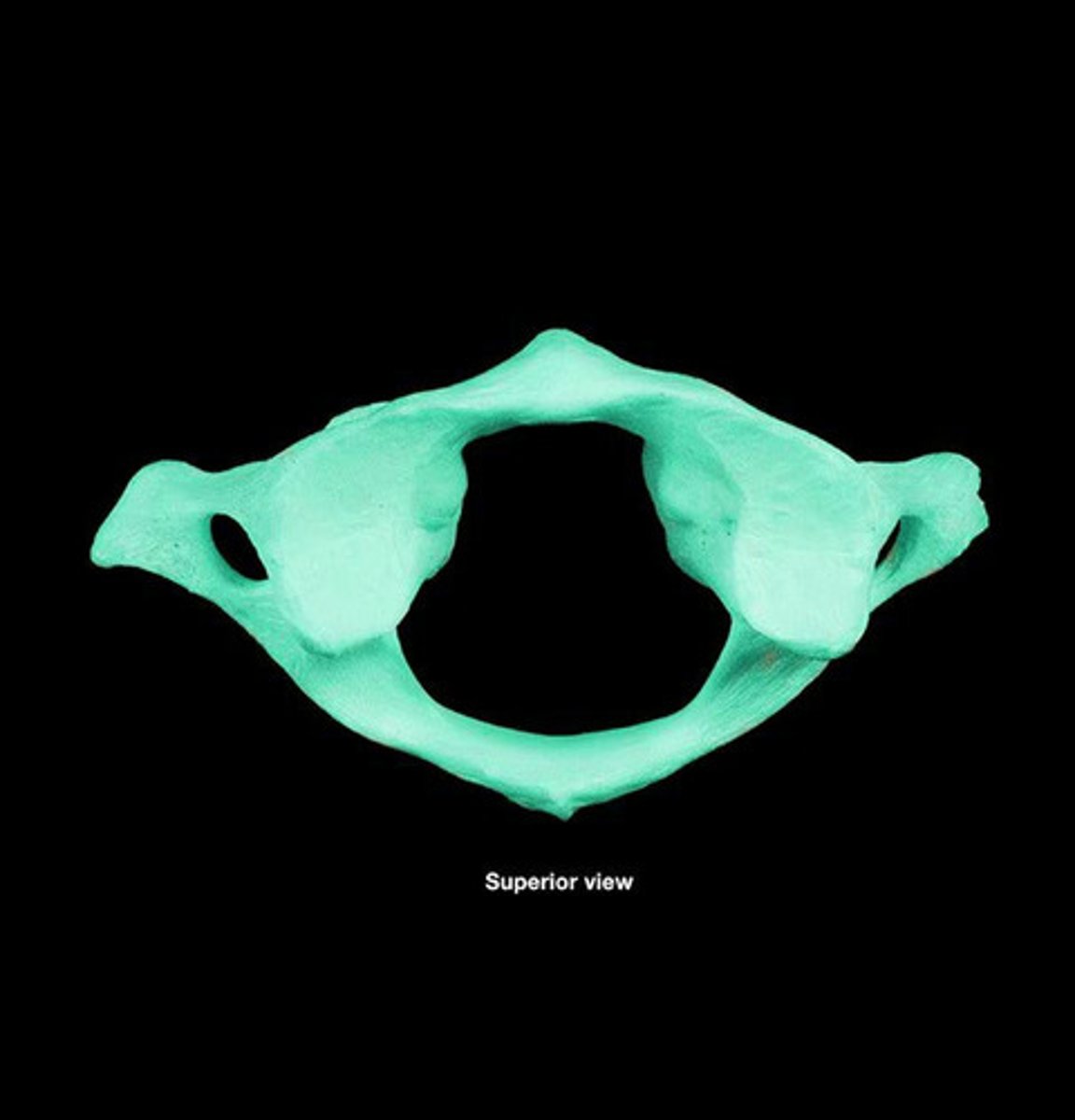
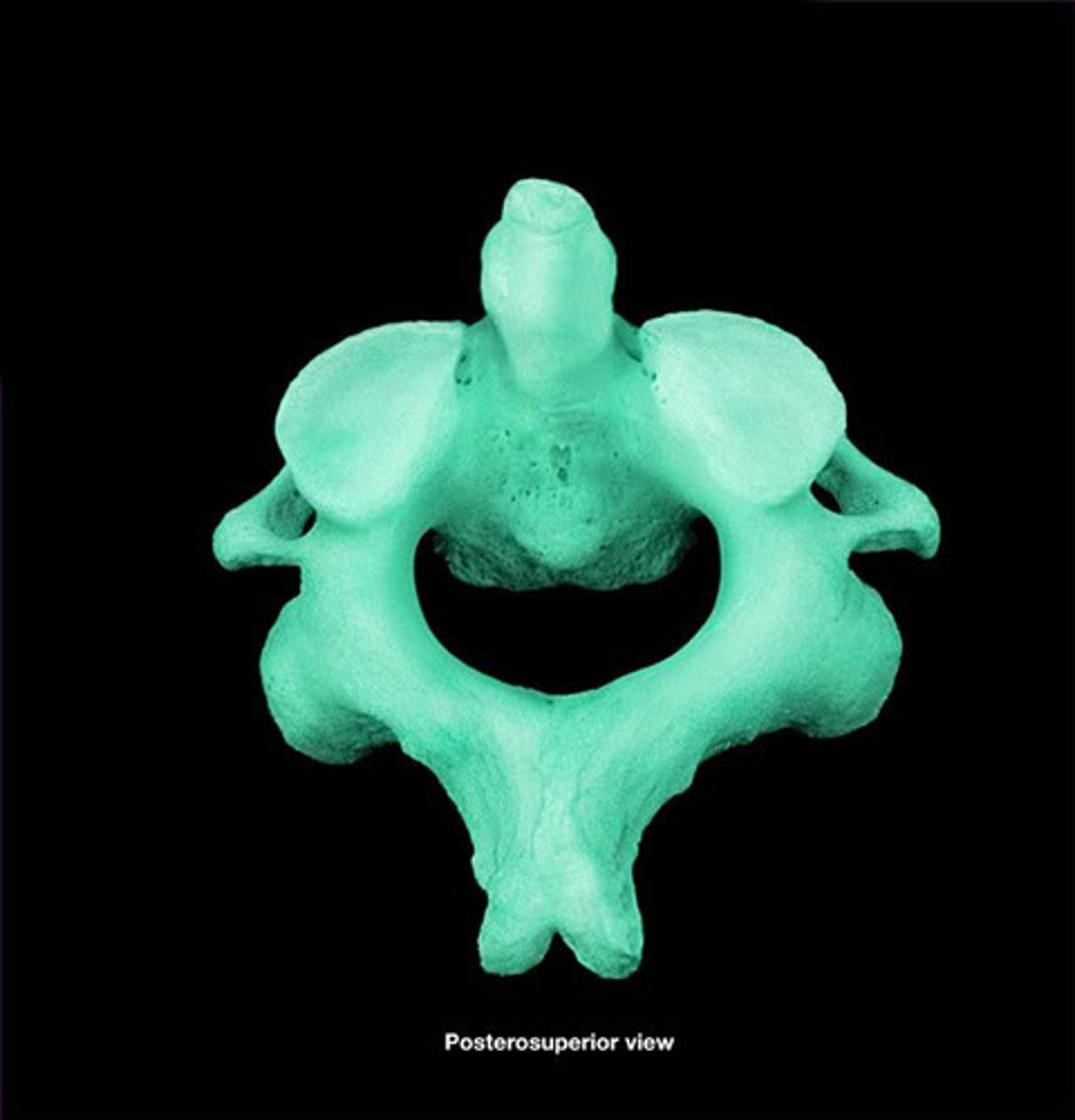
Cervical Axis
C2 vertebra; allows for head rotation.
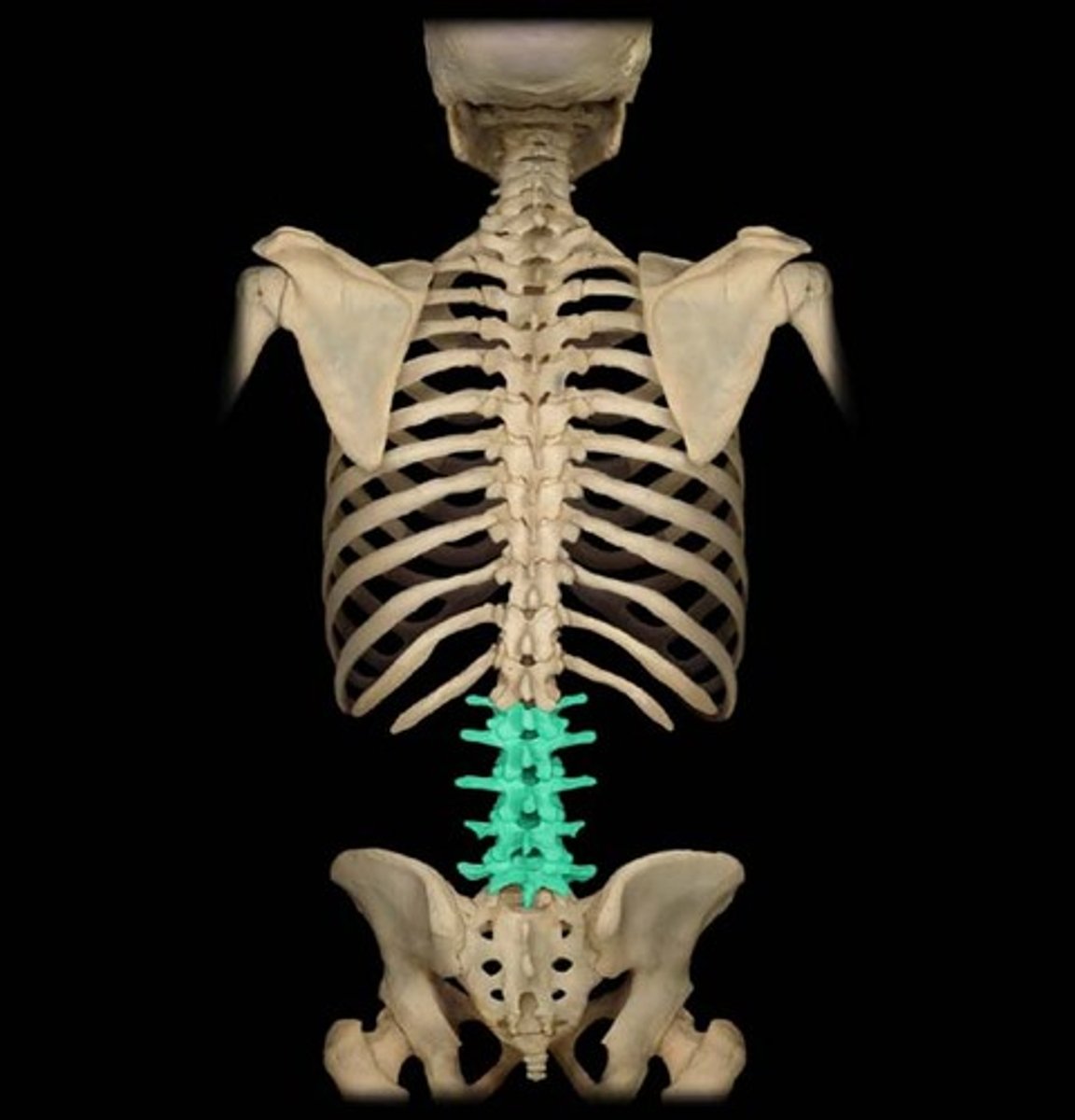
Lumbar Vertebrae
Five large vertebrae (L1-L5) in the lower back, designed for weight bearing.
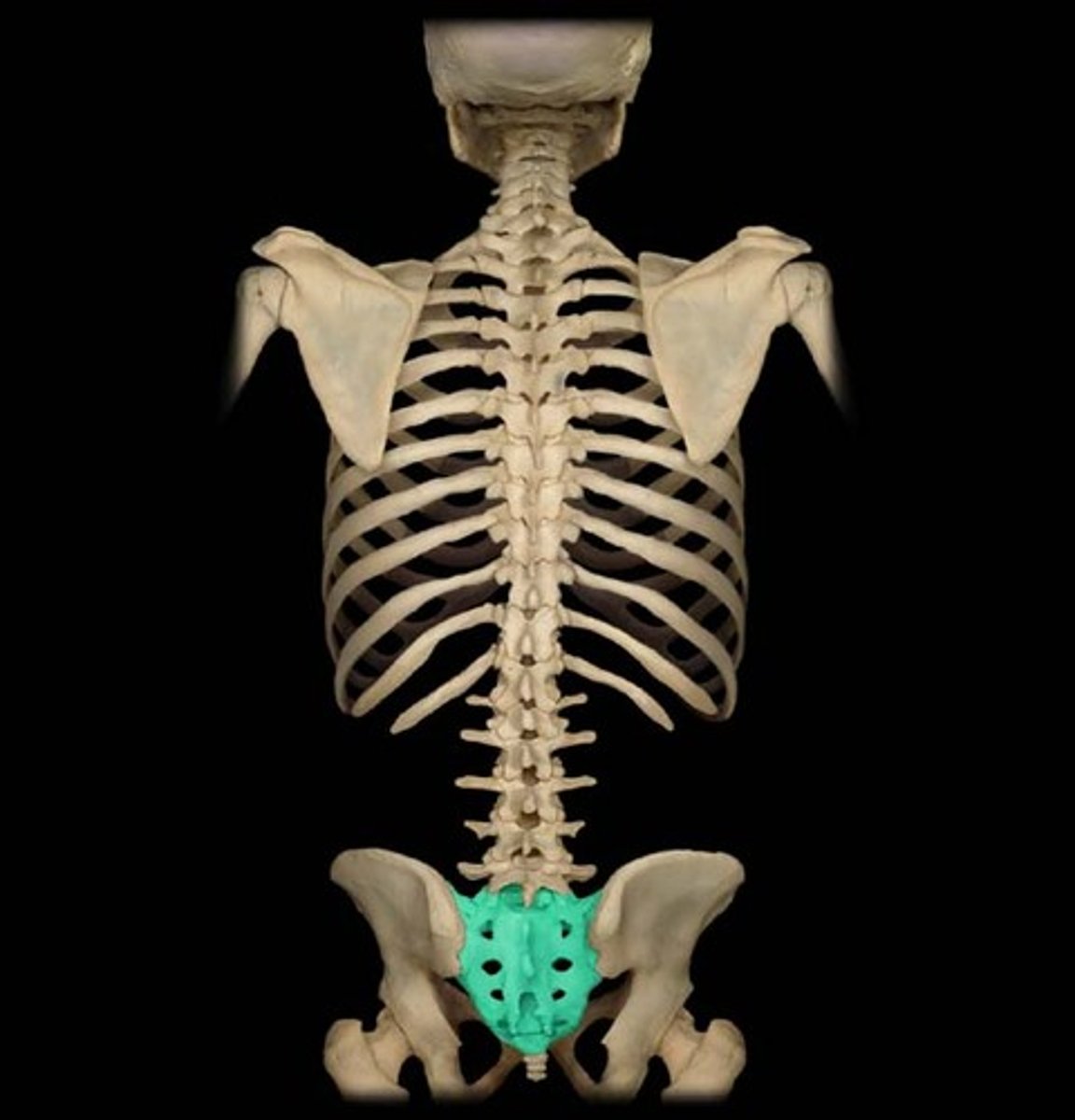
Sacrum
Large, triangular bone at the base of the spine, formed by 5 fused vertebrae (S1-S5).
Flexion
Movement that decreases the angle between two body parts or bones at a joint.
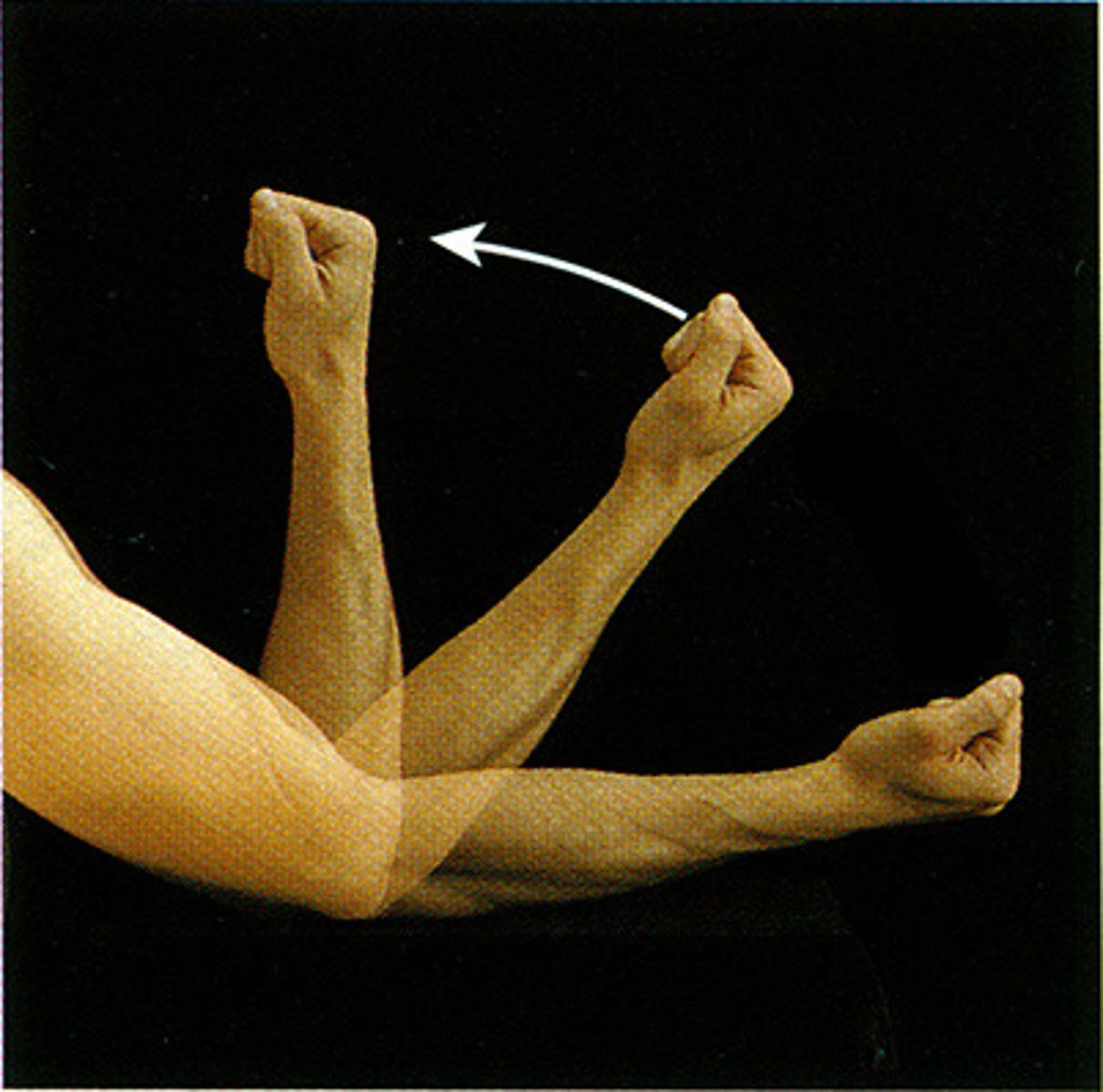
Abduction
Movement of a limb or body part away from the midline of the body.
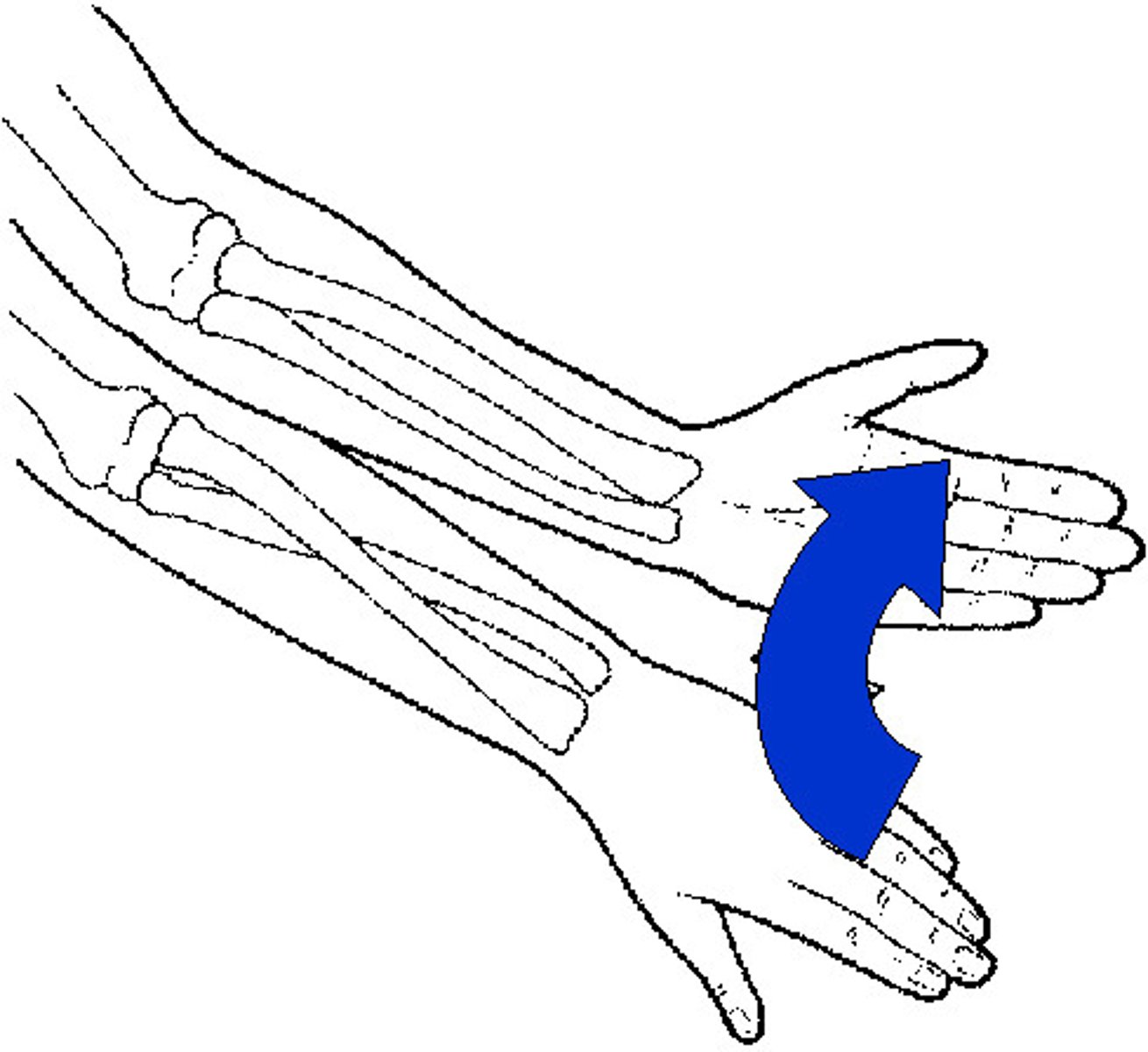
Supination
Rotational movement of the forearm and hand in which the palm faces anteriorly (upward).
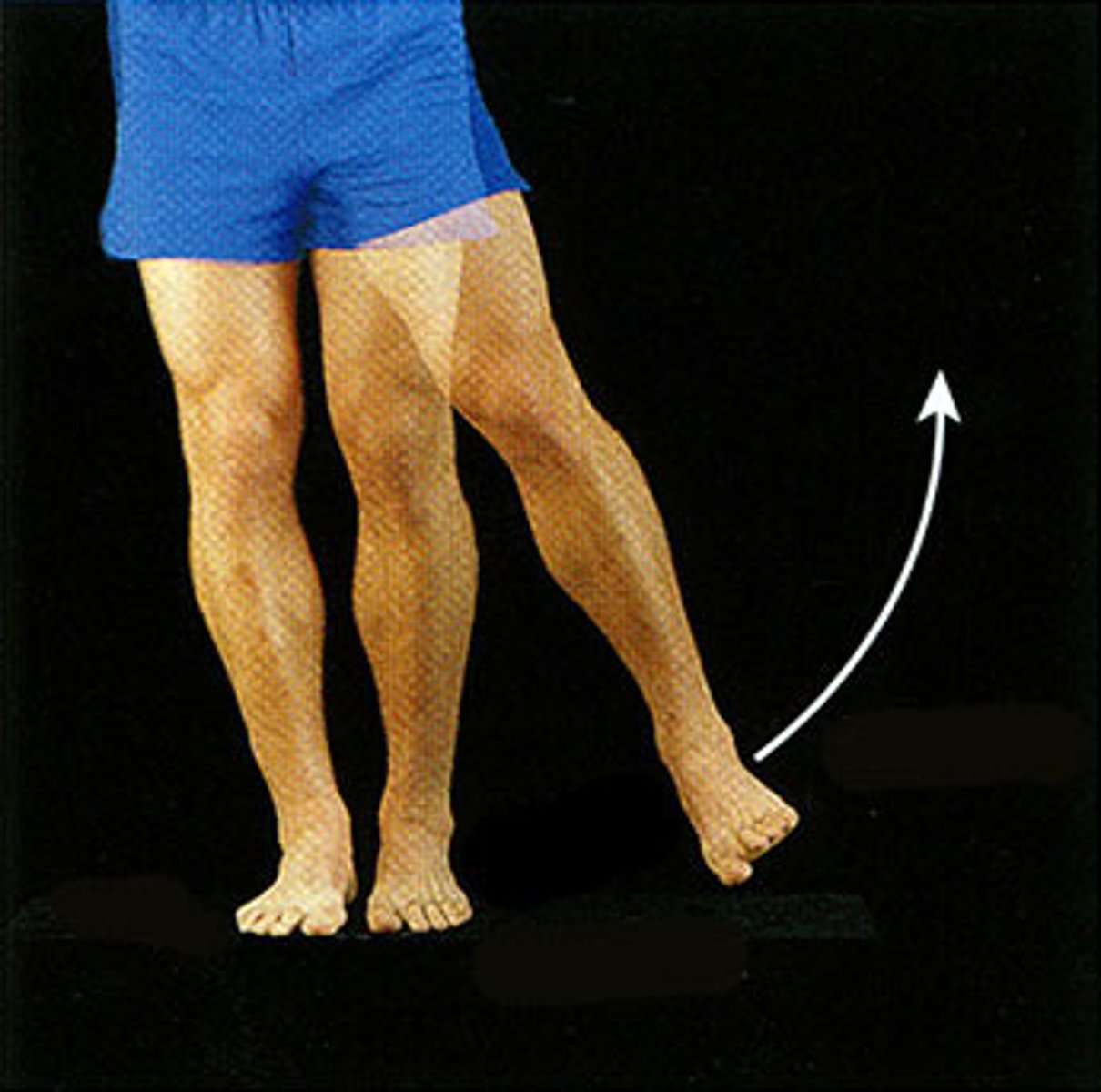
Plantar Flexion
Movement of the foot that extends the foot downwards, pointing the toes.
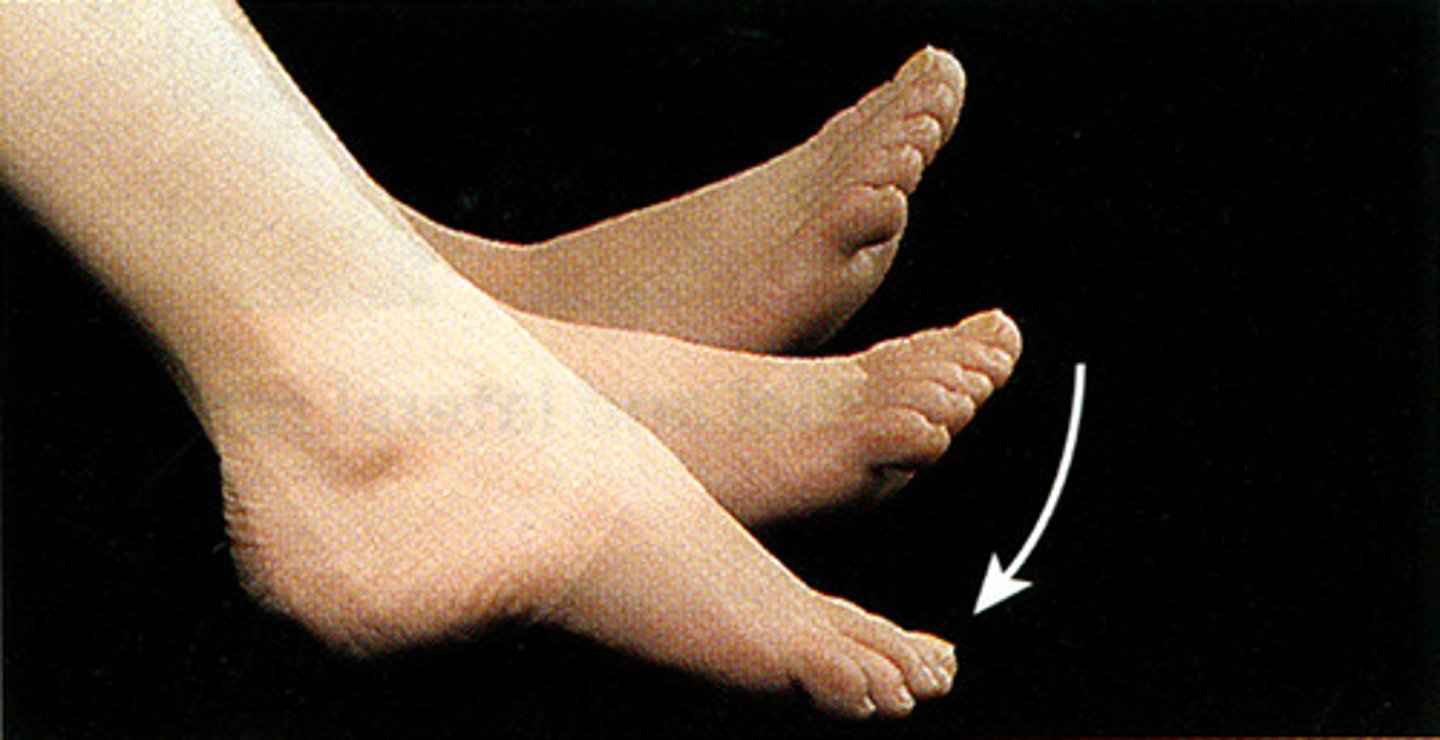
Dorsiflexion
Movement of the foot that flexes the foot upward towards the shin.
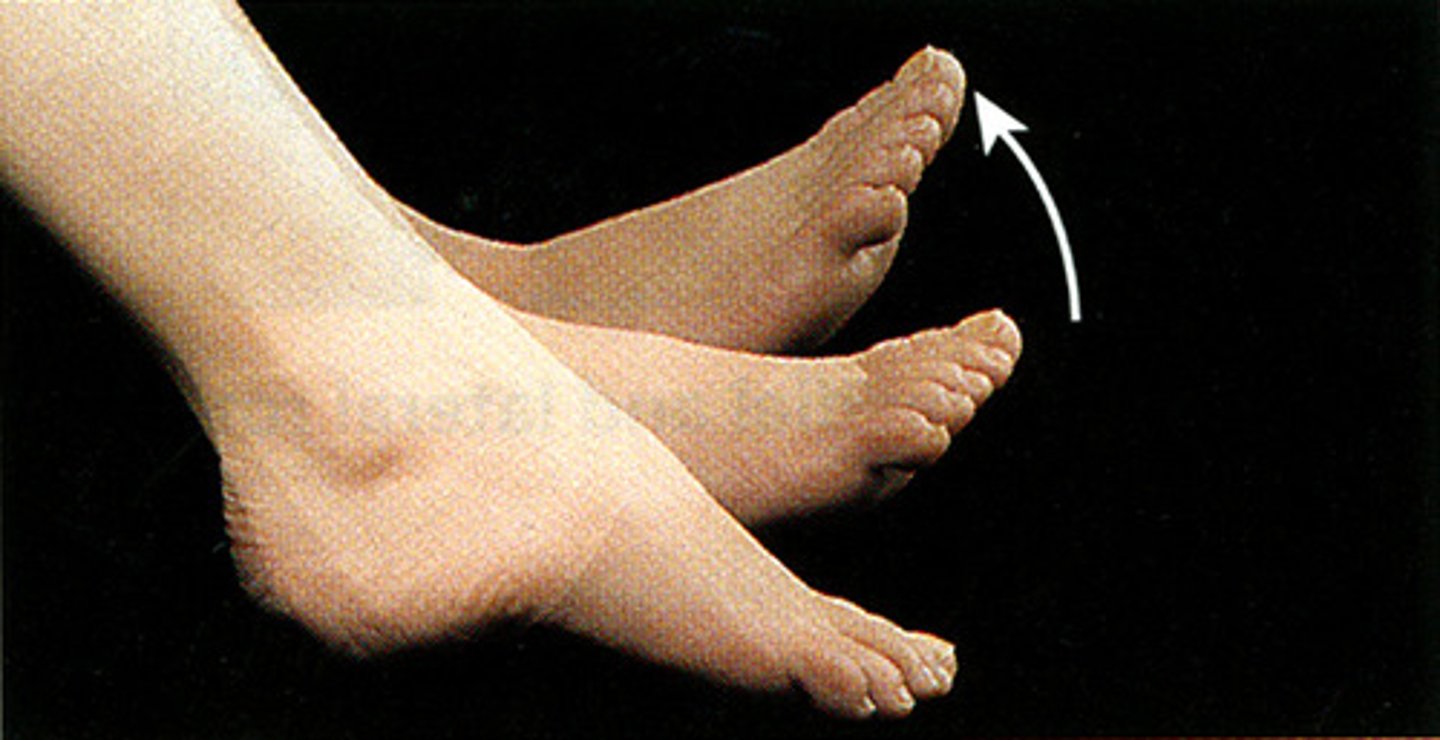
Inversion (Foot)
Movement of the sole of the foot inward towards the midline.
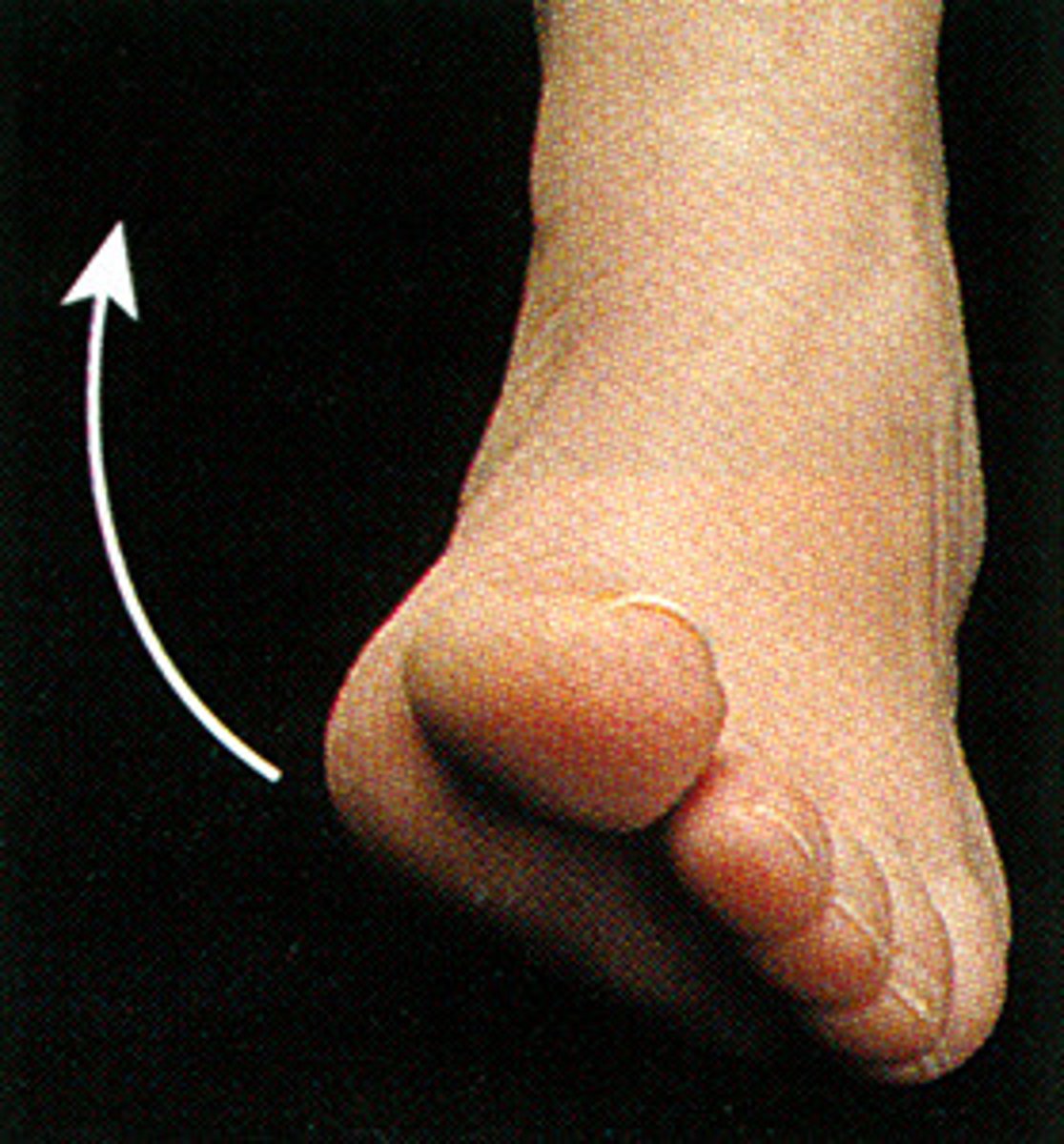
Eversion (Foot)
Movement of the sole of the foot outward away from the midline.
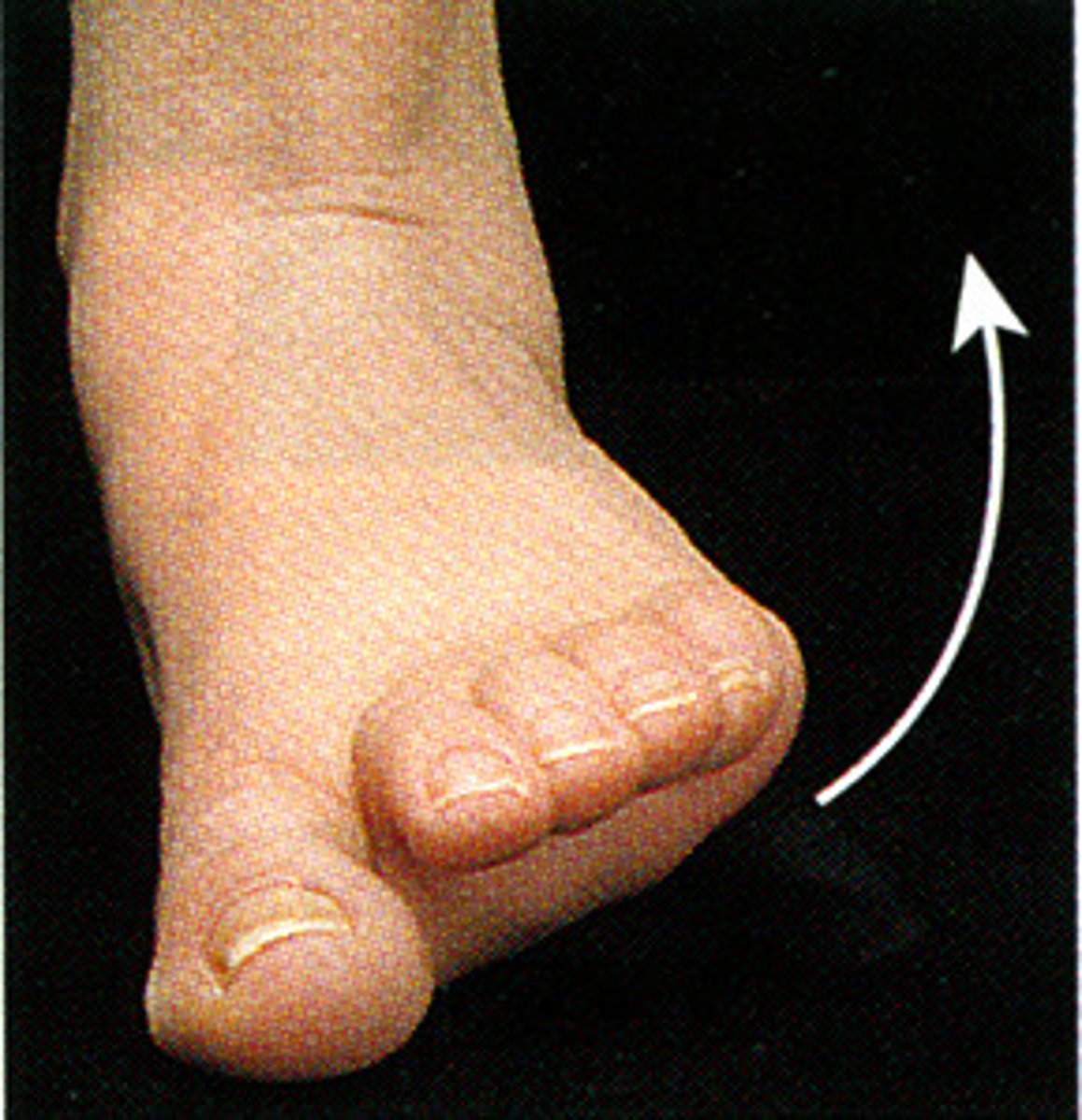
Internal (Medial) Rotation
Rotational movement of a limb around its longitudinal axis toward the midline of the body.
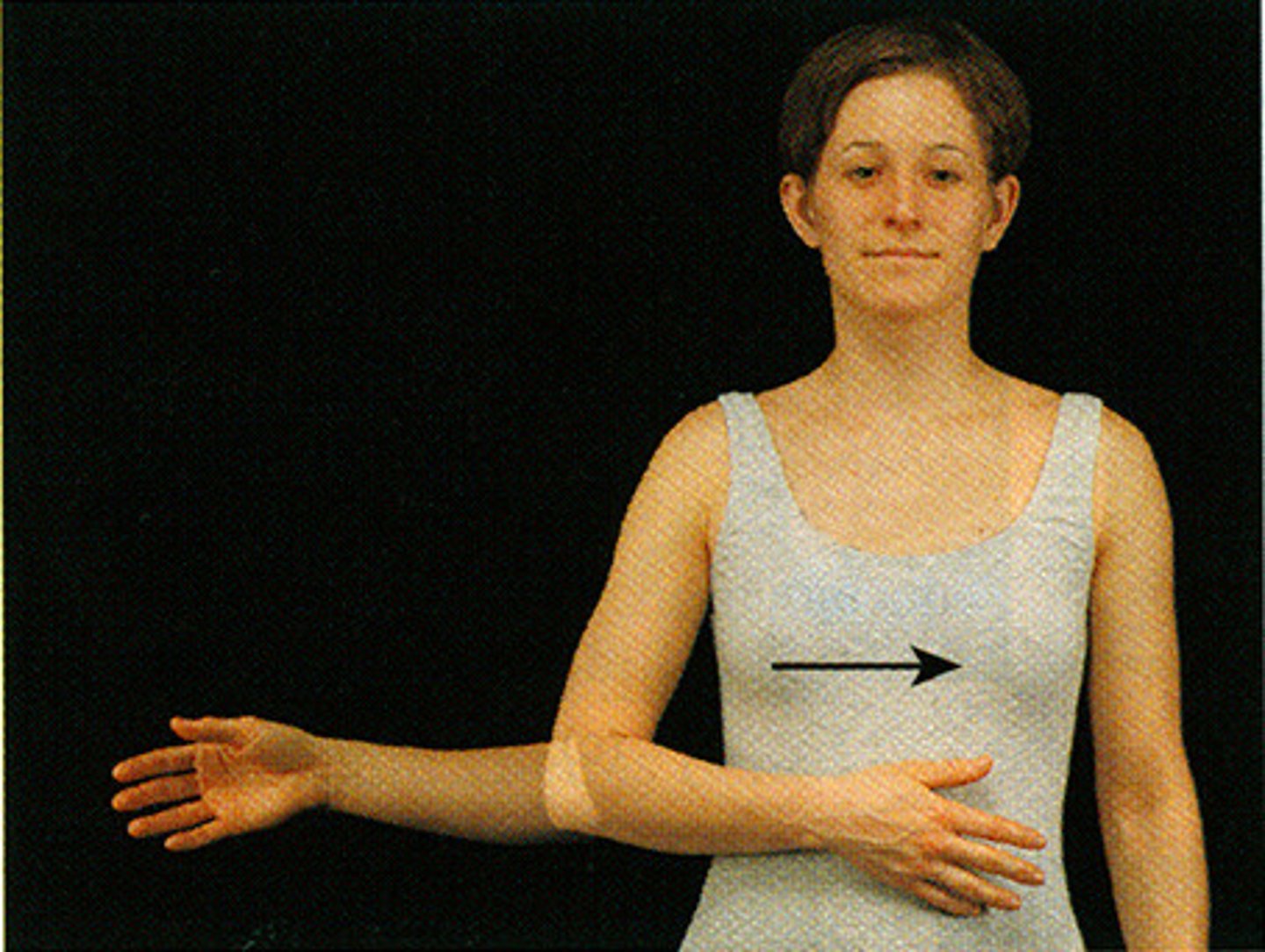
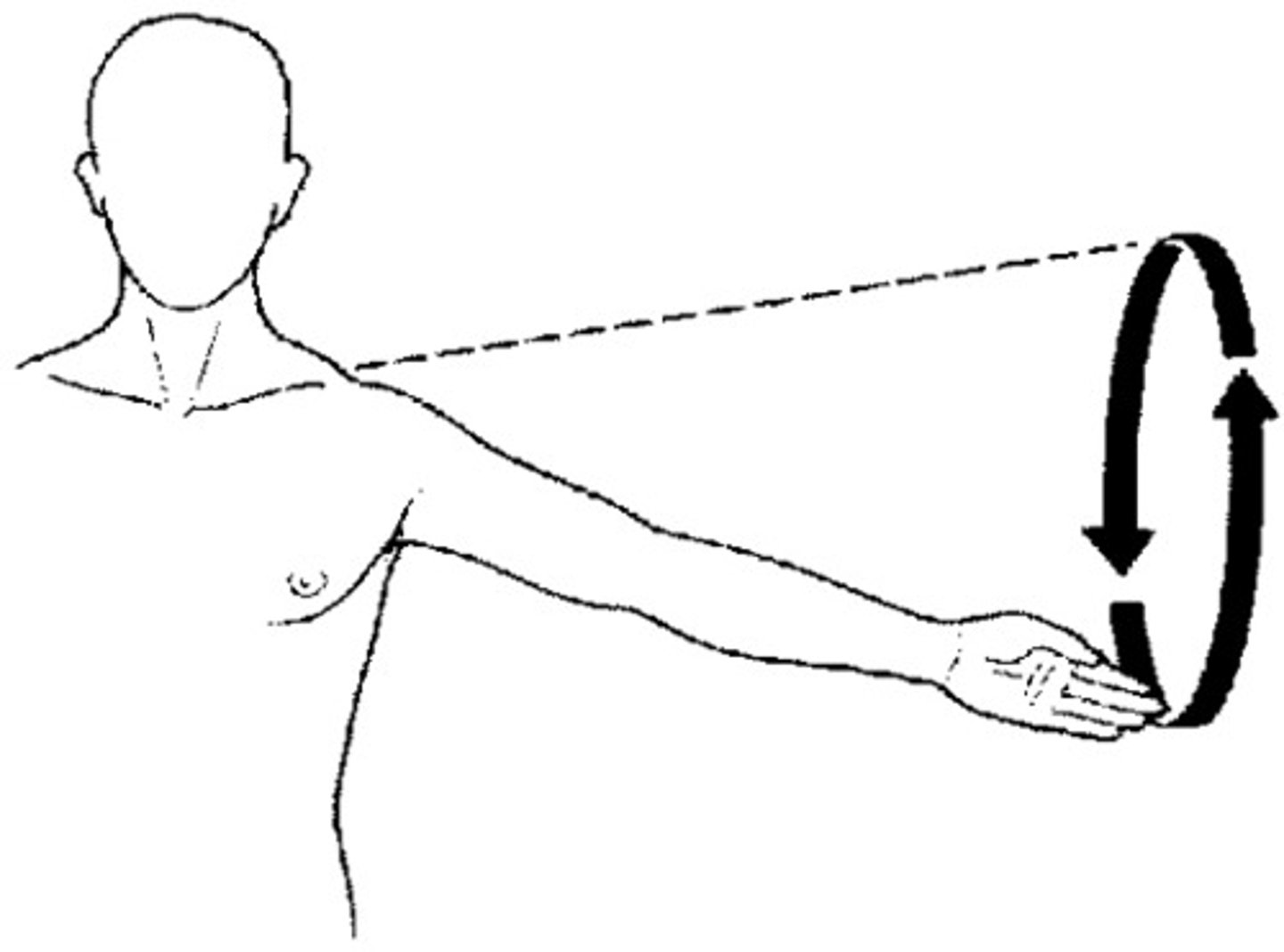
Circumduction
Circular movement of a limb, combining flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction.
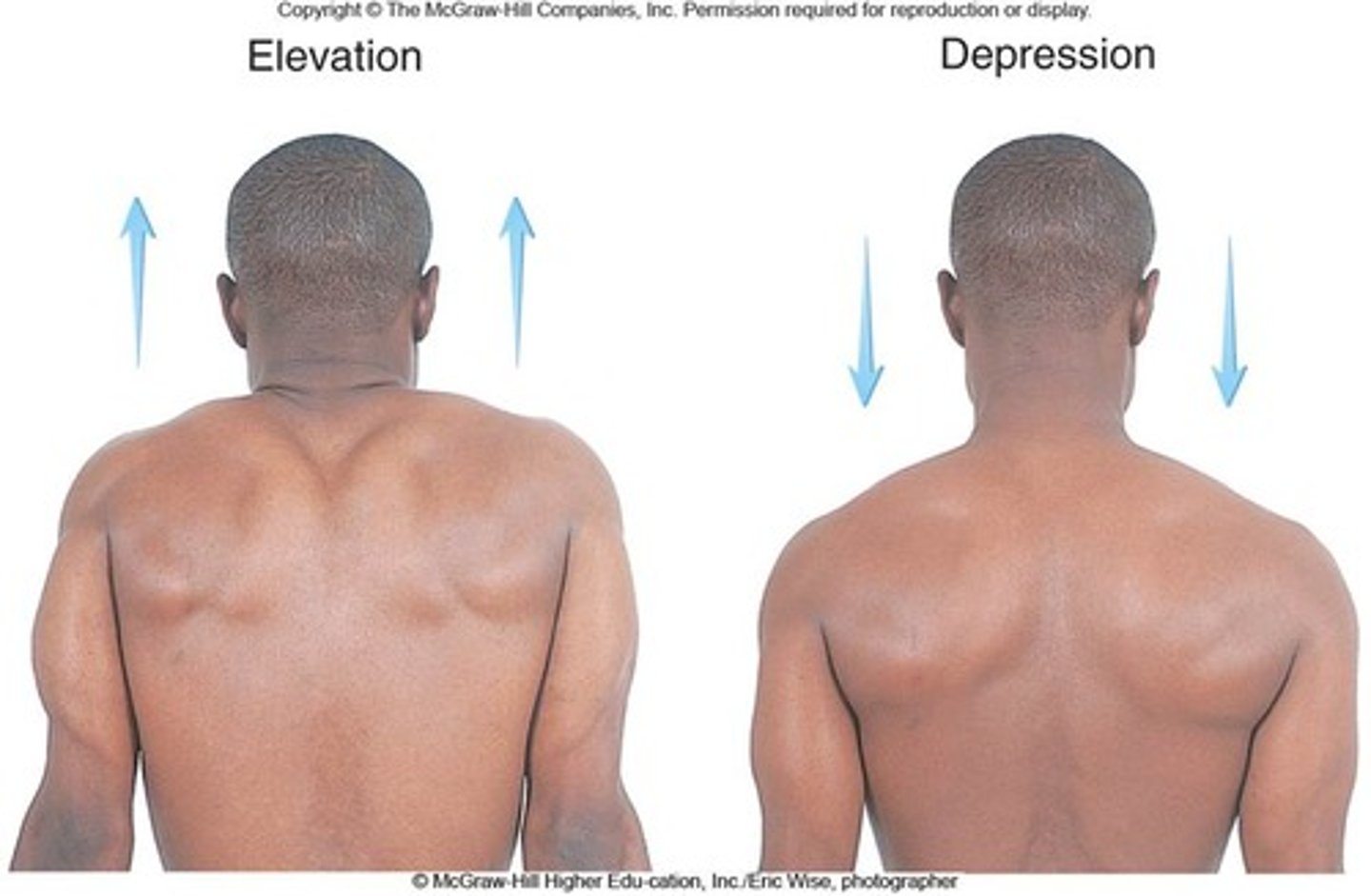
Depression
Movement that lowers a body part, such as the scapula or mandible.
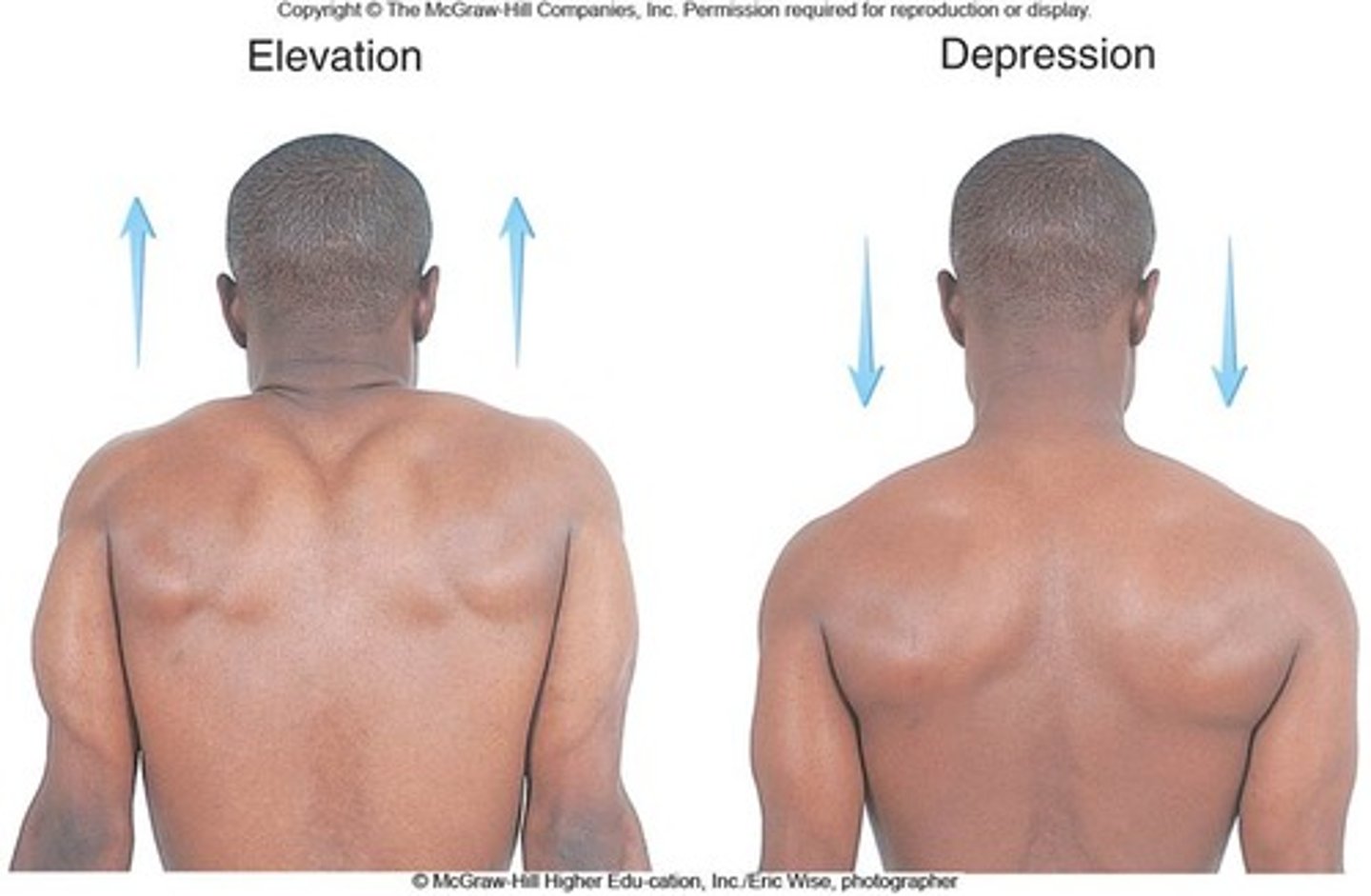
Elevation
Movement that raises a body part, such as the scapula or mandible.
Protraction
Movement of a body part forward on a horizontal plane, such as the mandible or scapula.
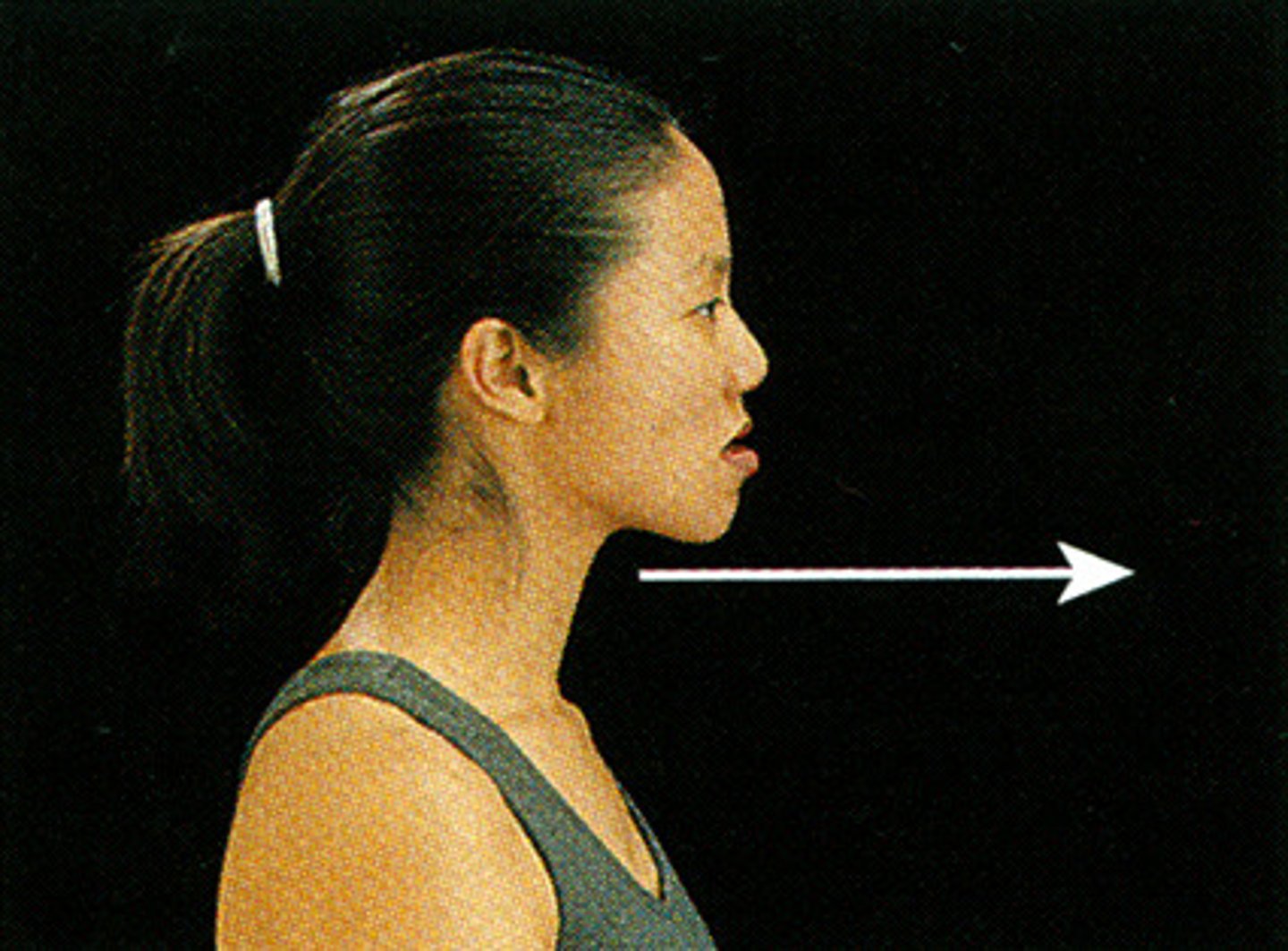
Retraction
Movement of a body part backward on a horizontal plane, such as the mandible or scapula.
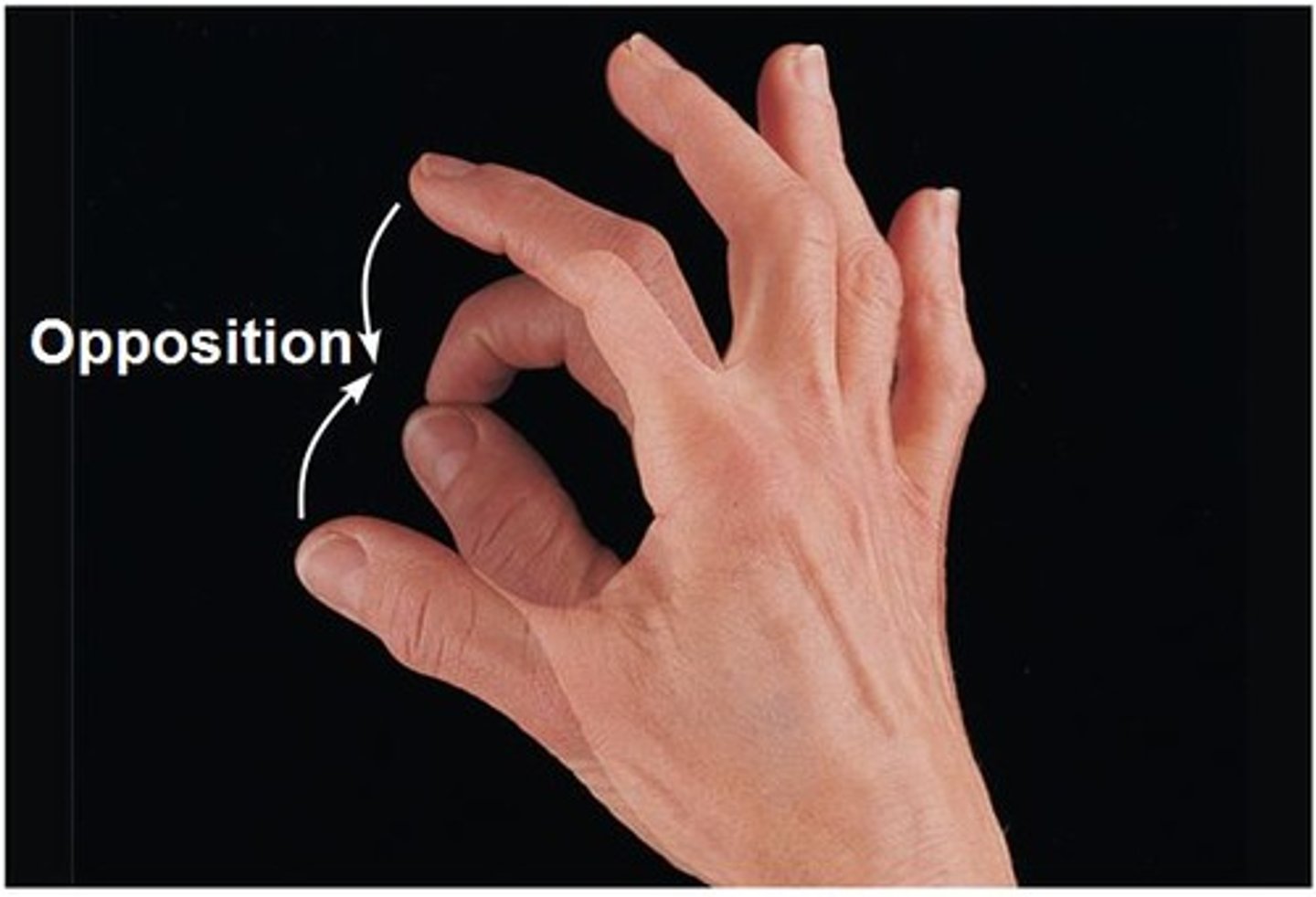
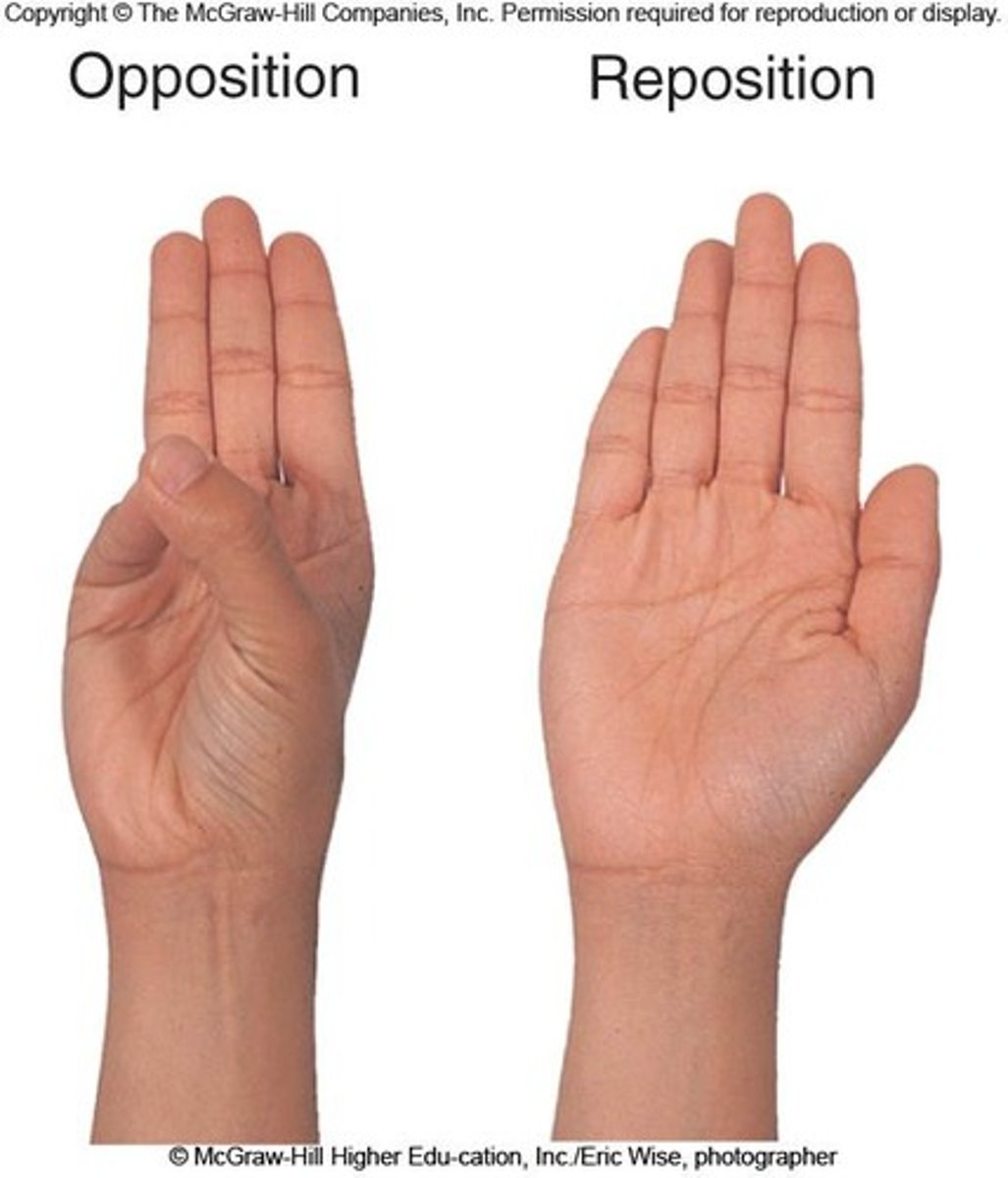
Opposition
Movement of the thumb across the palm to touch the fingertips of the same hand.
Reposition
Movement of the thumb from opposition back to its anatomical position.
Functions of the Skeletal System
Support, protection of organs, movement (with muscles), mineral storage (calcium, phosphorus), and blood cell production (hematopoiesis).
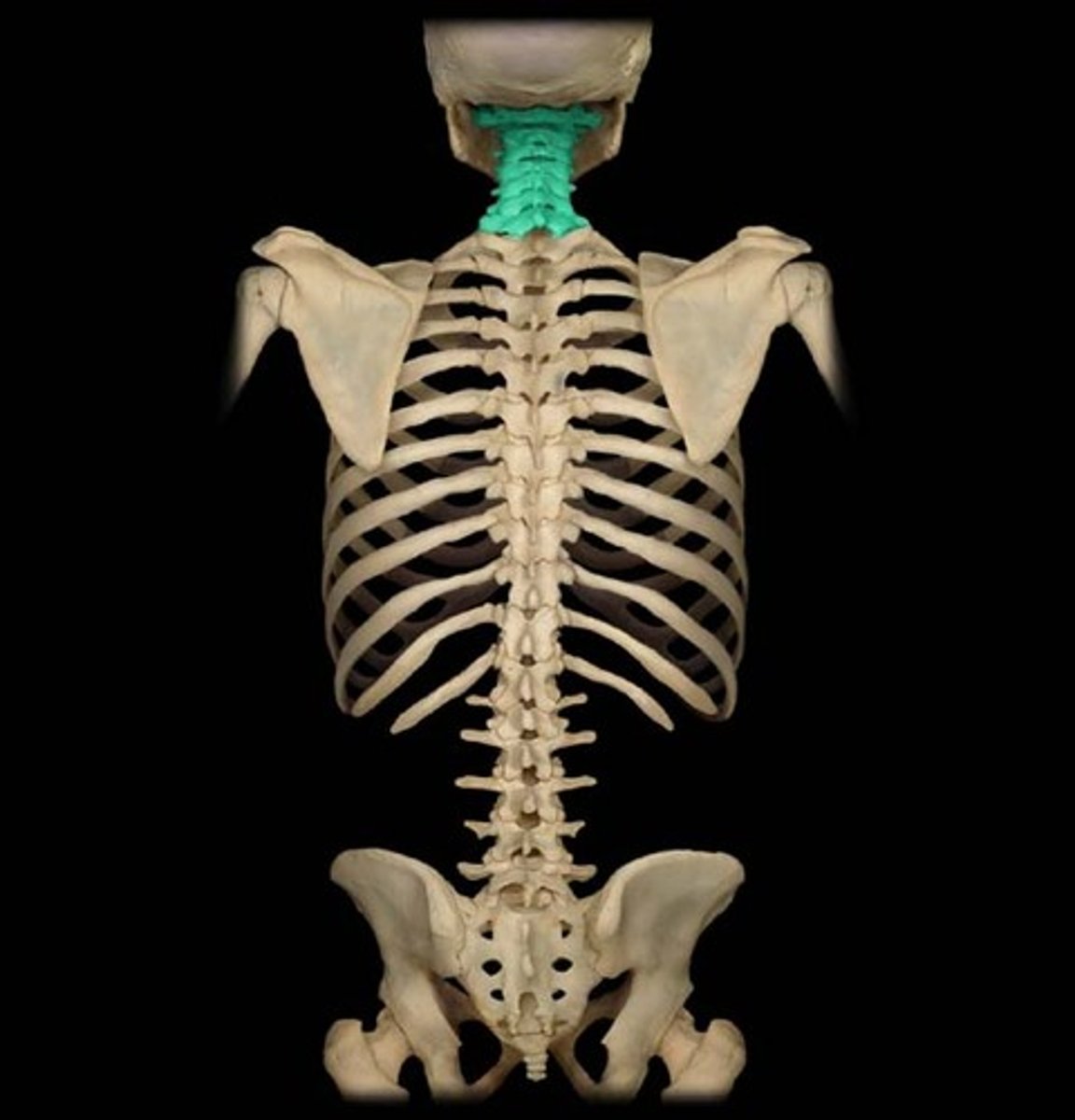
Cervical Vertebrae
Seven vertebrae (C1-C7) forming the neck region.
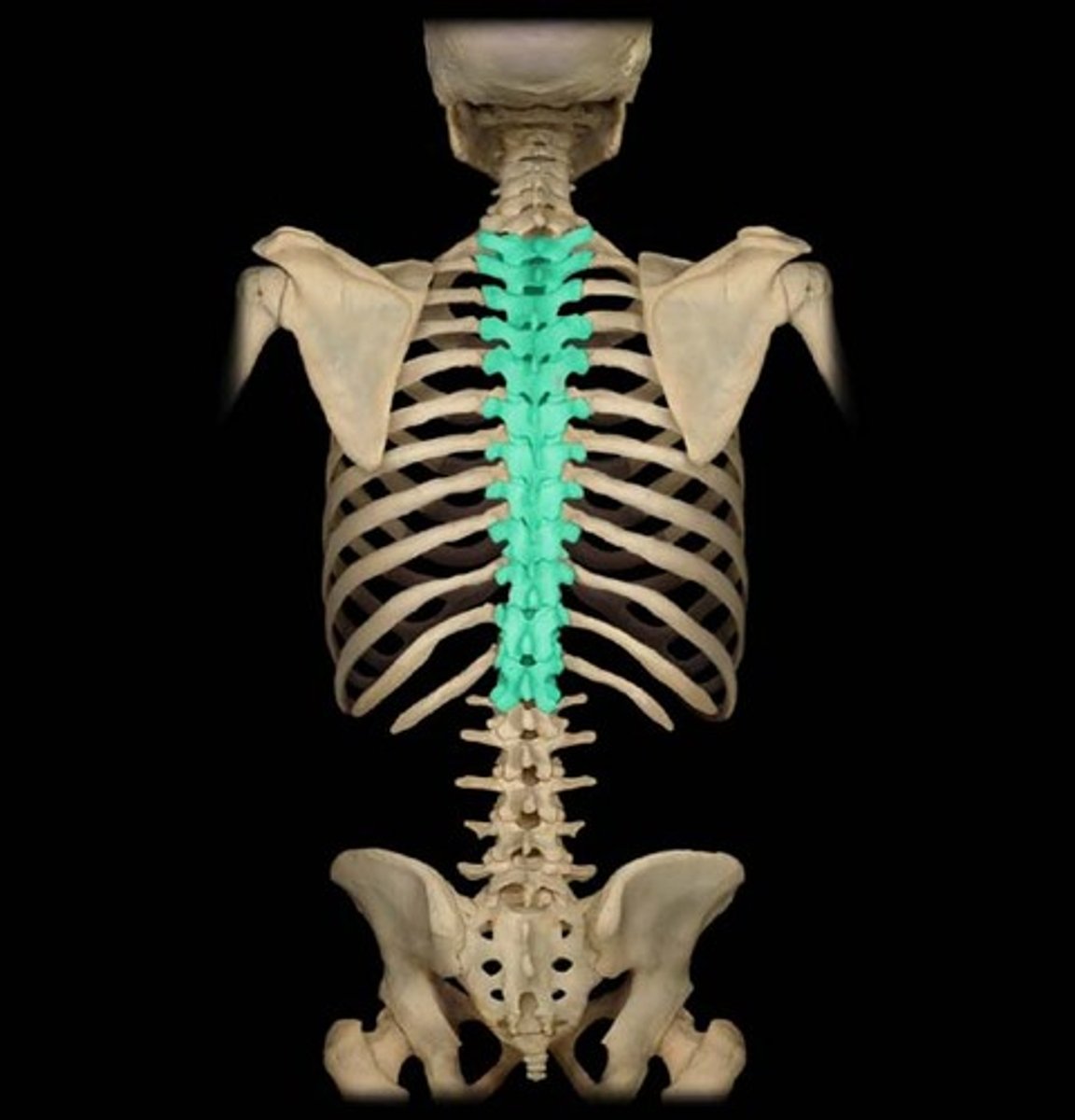
Thoracic Vertebrae
Twelve vertebrae (T1-T12) located in the mid-back, articulating with the ribs.
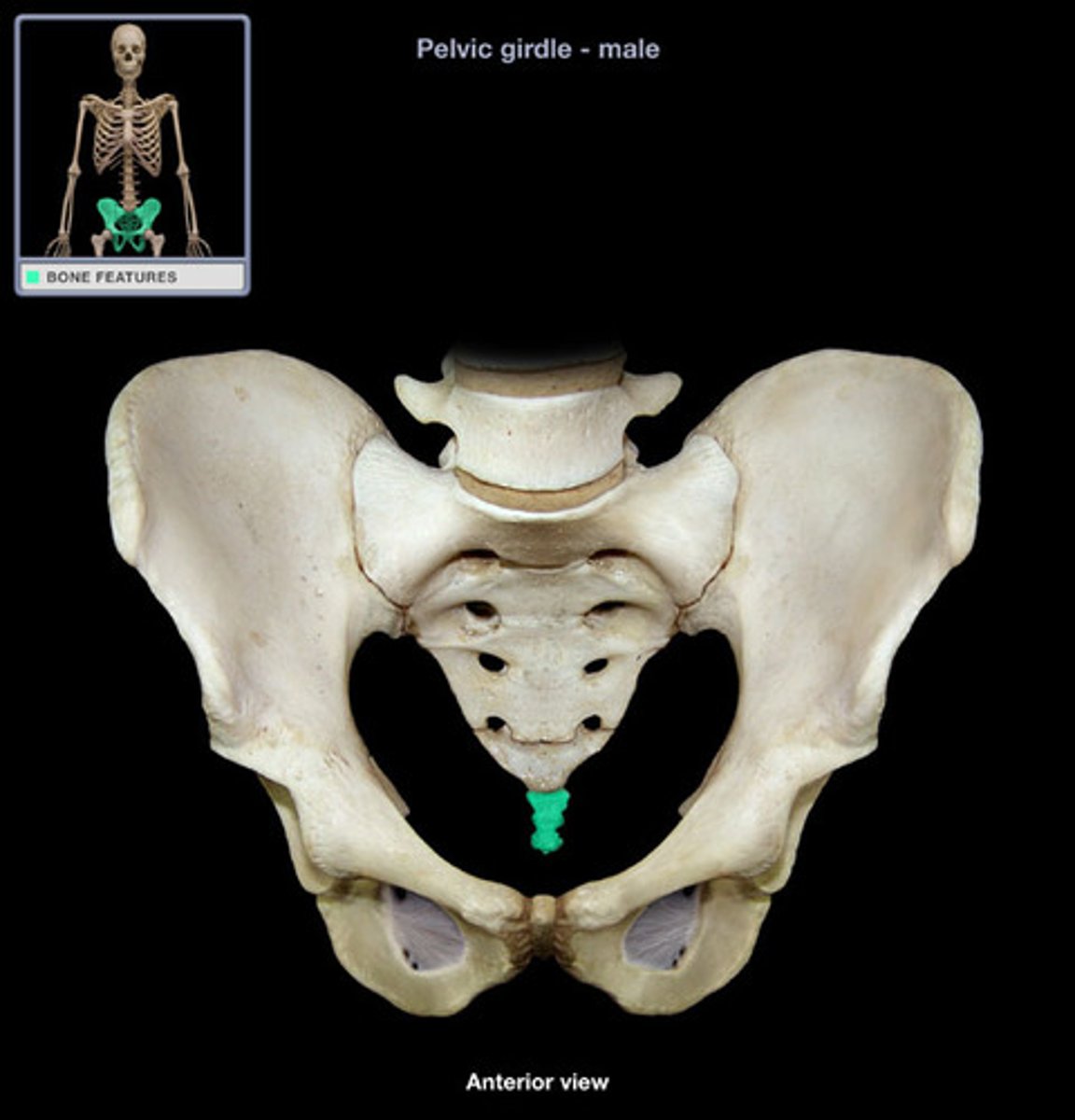
Coccyx
Small, triangular bone at the very end of the spine, commonly known as the tailbone.
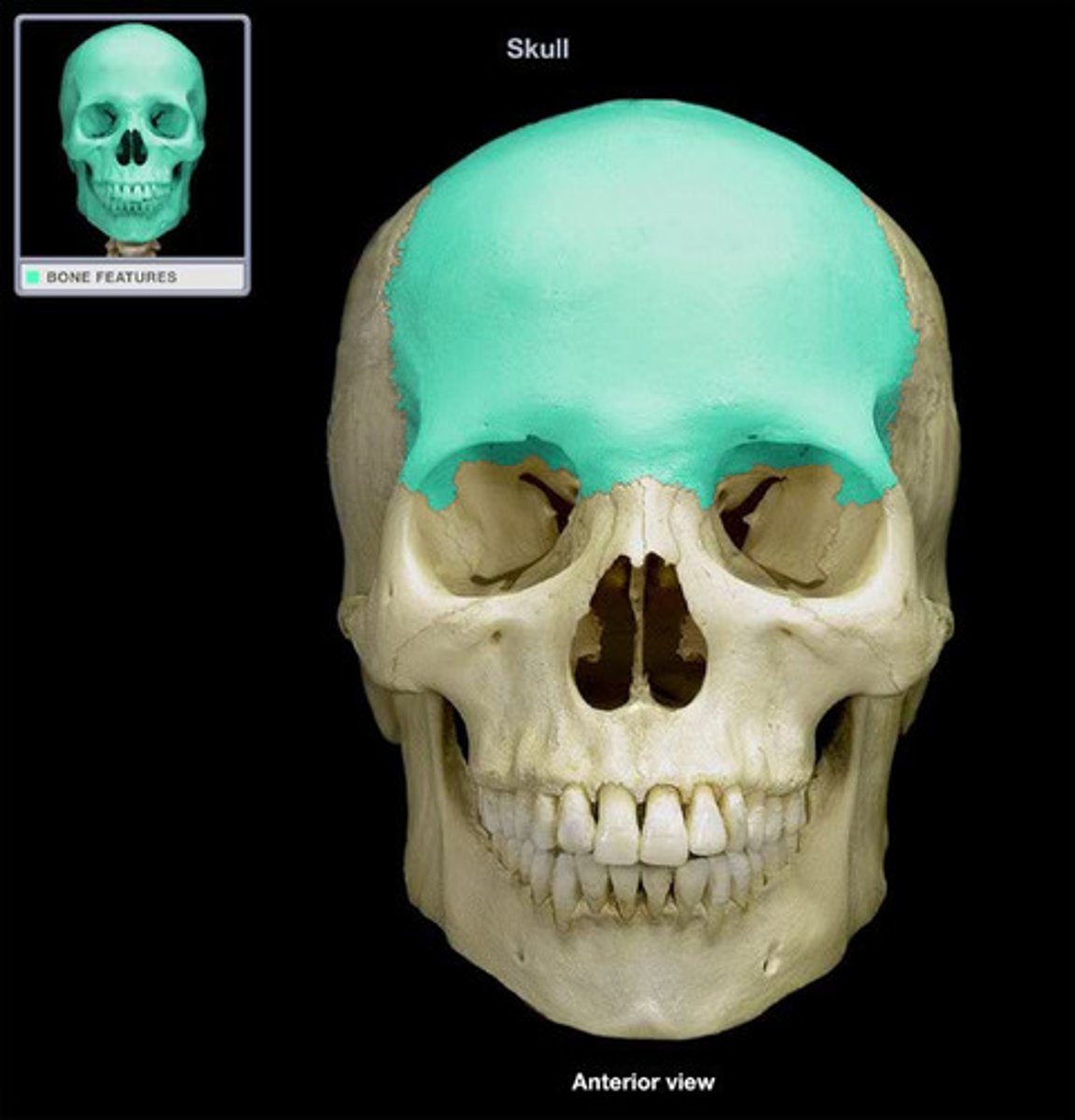
Frontal Bone
Bone forming the forehead.
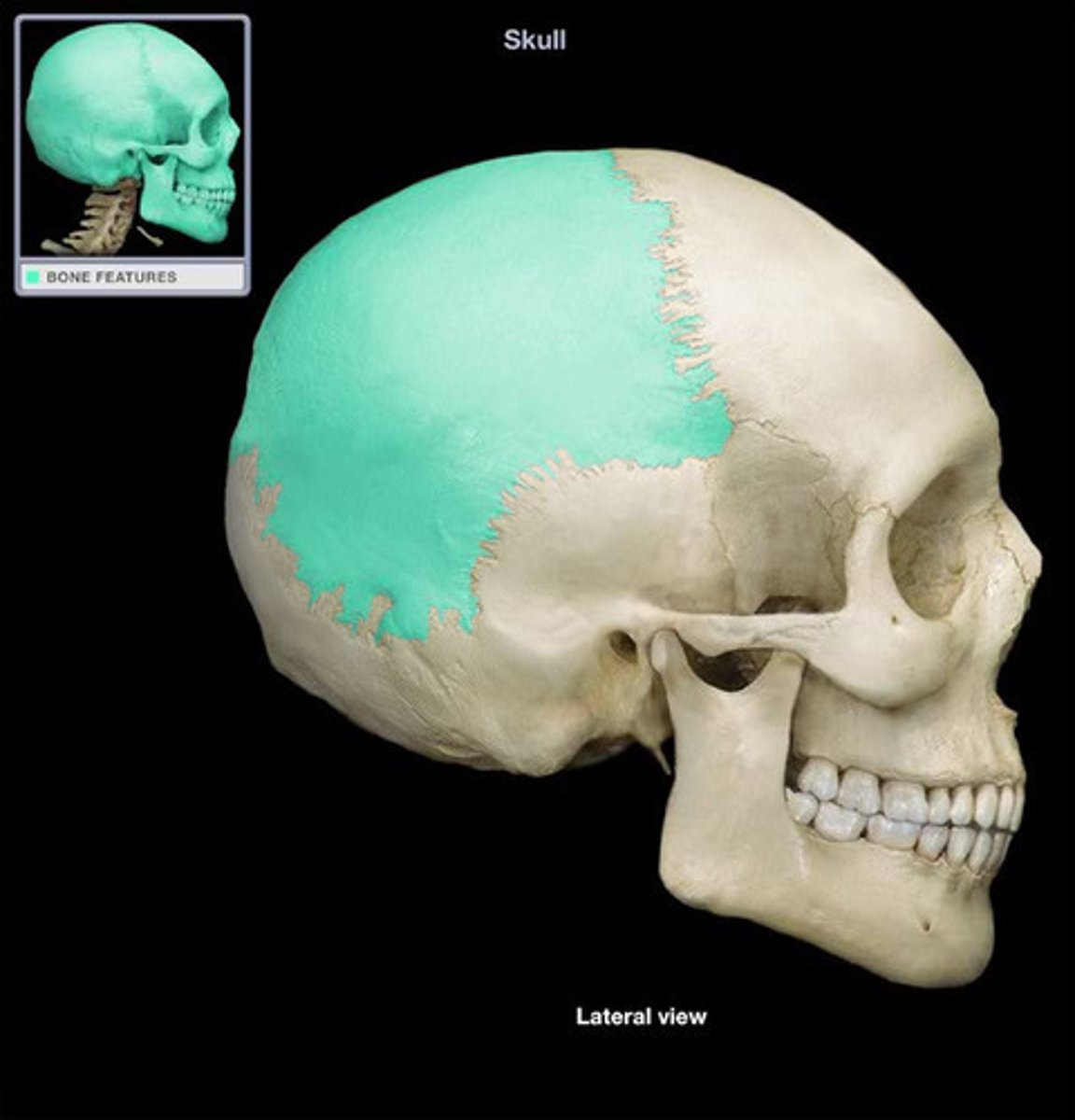
Parietal Bone
Either of two skull bones between the frontal and occipital bones, forming the top and sides of the cranium.
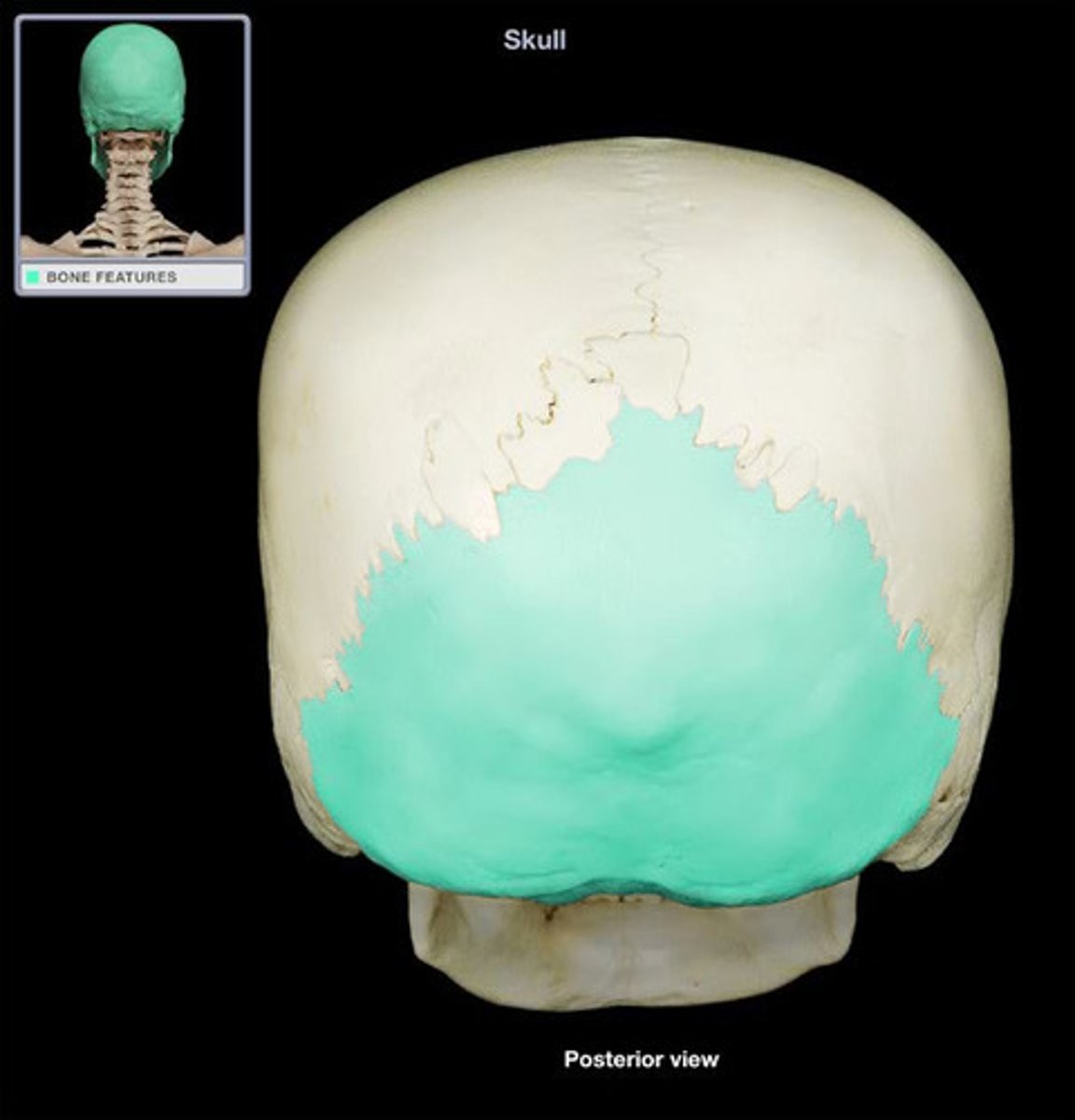
Occipital Bone
Bone forming the back of the head.
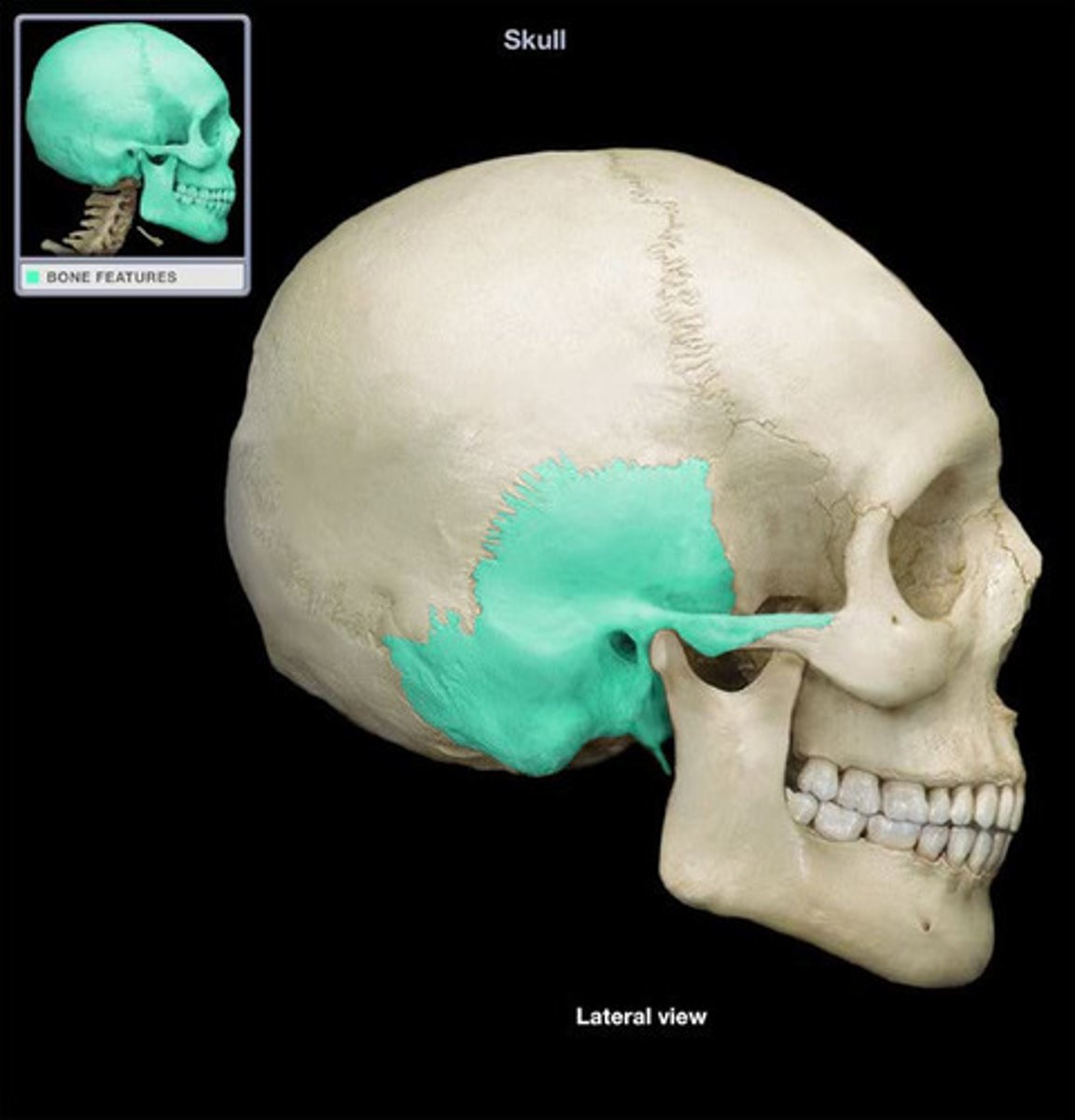
Temporal Bone
Bone located on the sides and base of the skull, near the temples.
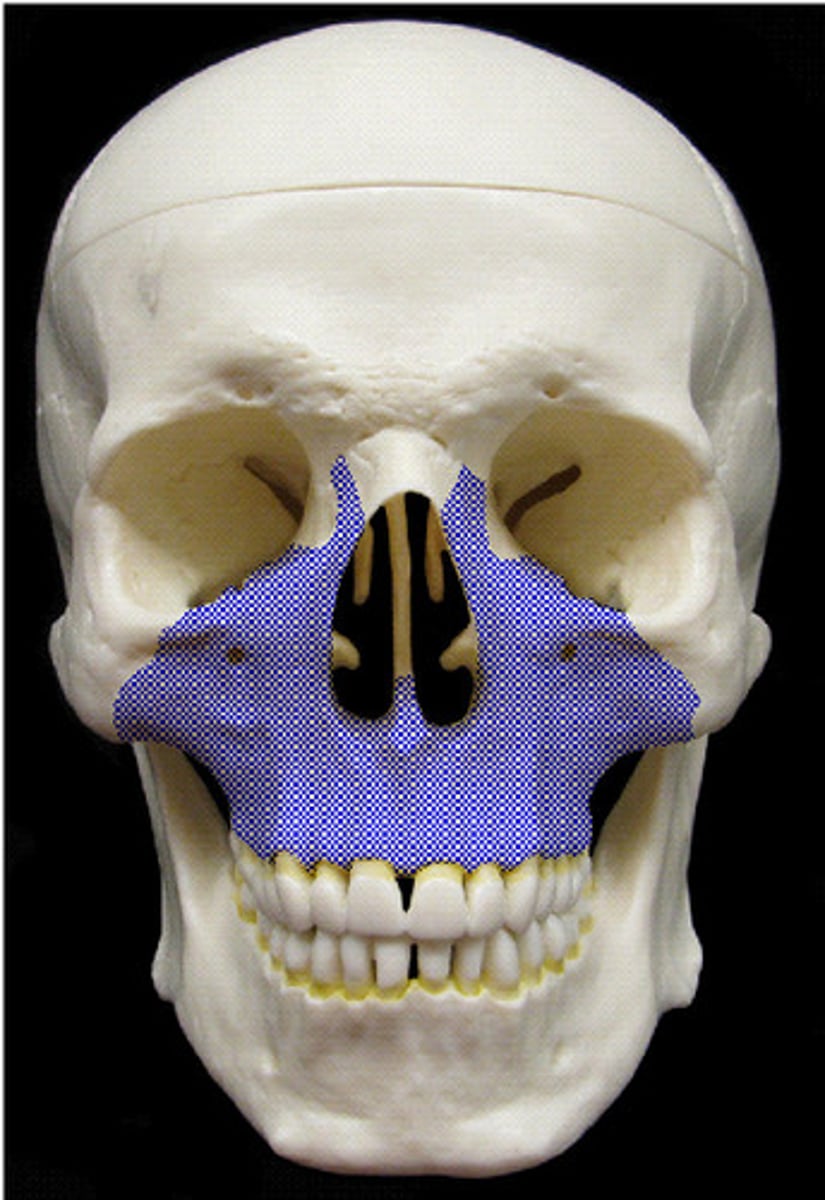
Maxilla
Bone forming the upper jaw.
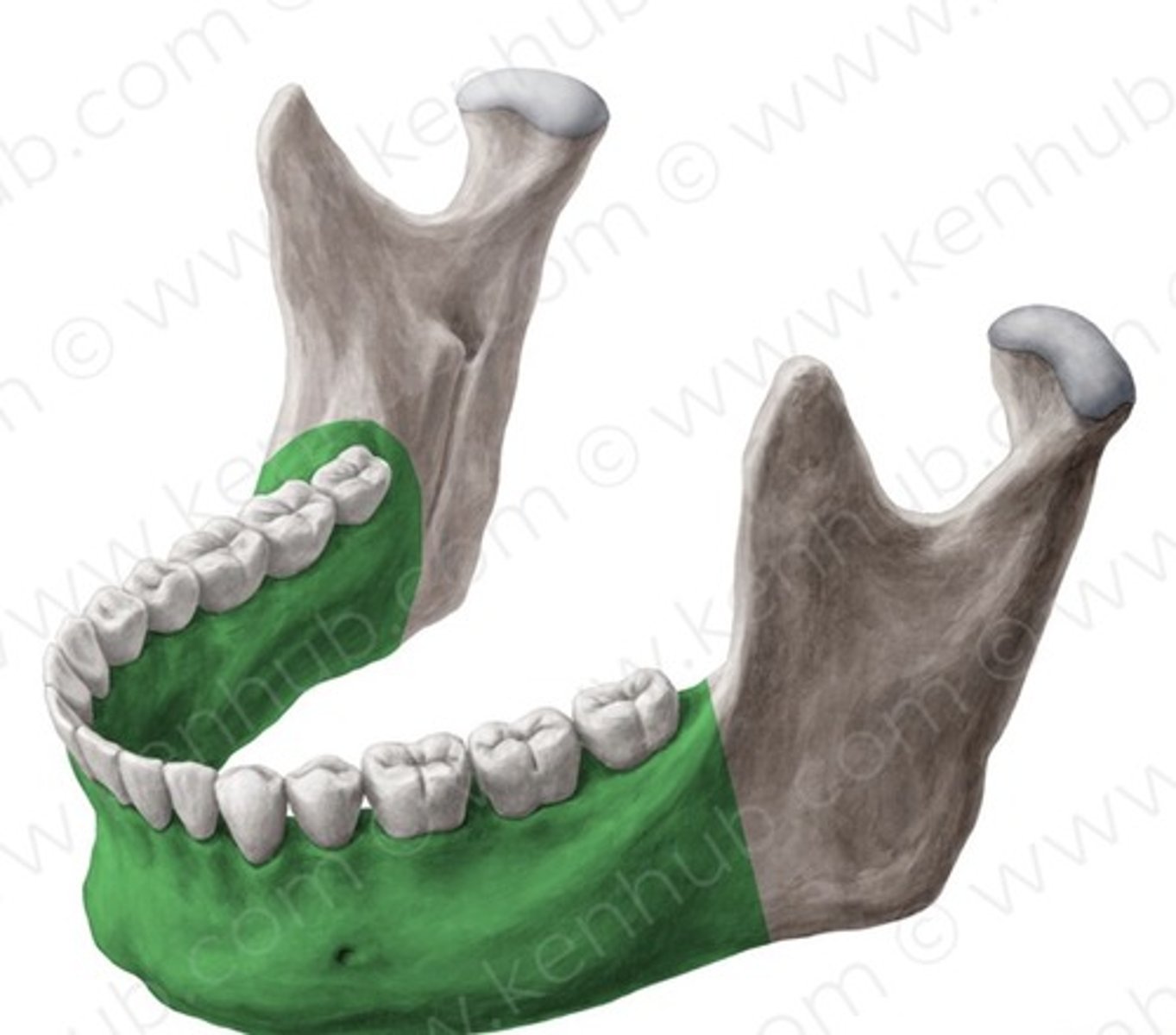
Mandible
The U-shaped bone forming the lower jaw, holding the lower teeth, and capable of movement.
Extension
Movement that increases the angle between two body parts or bones at a joint, straightening a limb.
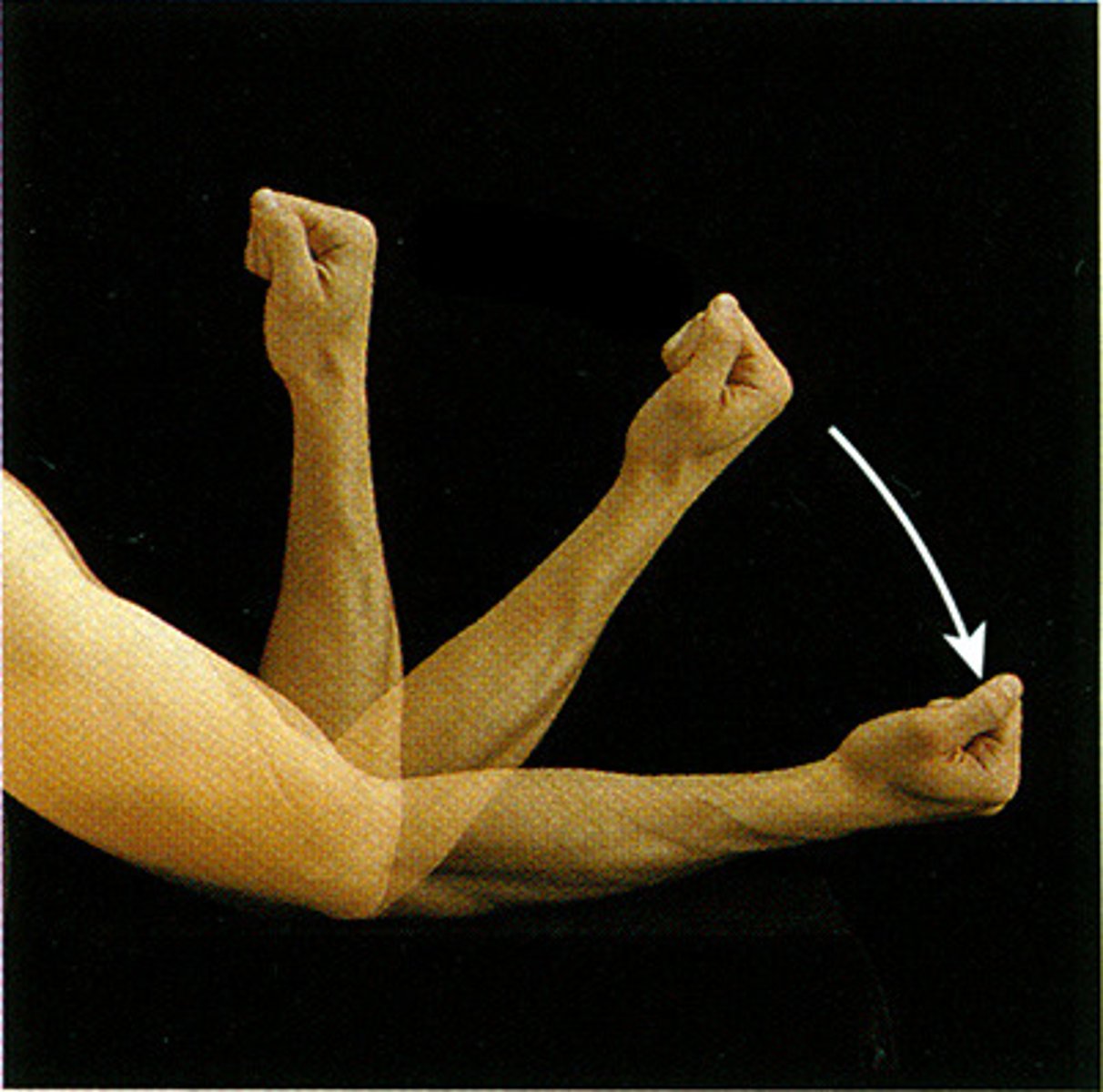
Adduction
Movement of a limb or body part toward the midline of the body.
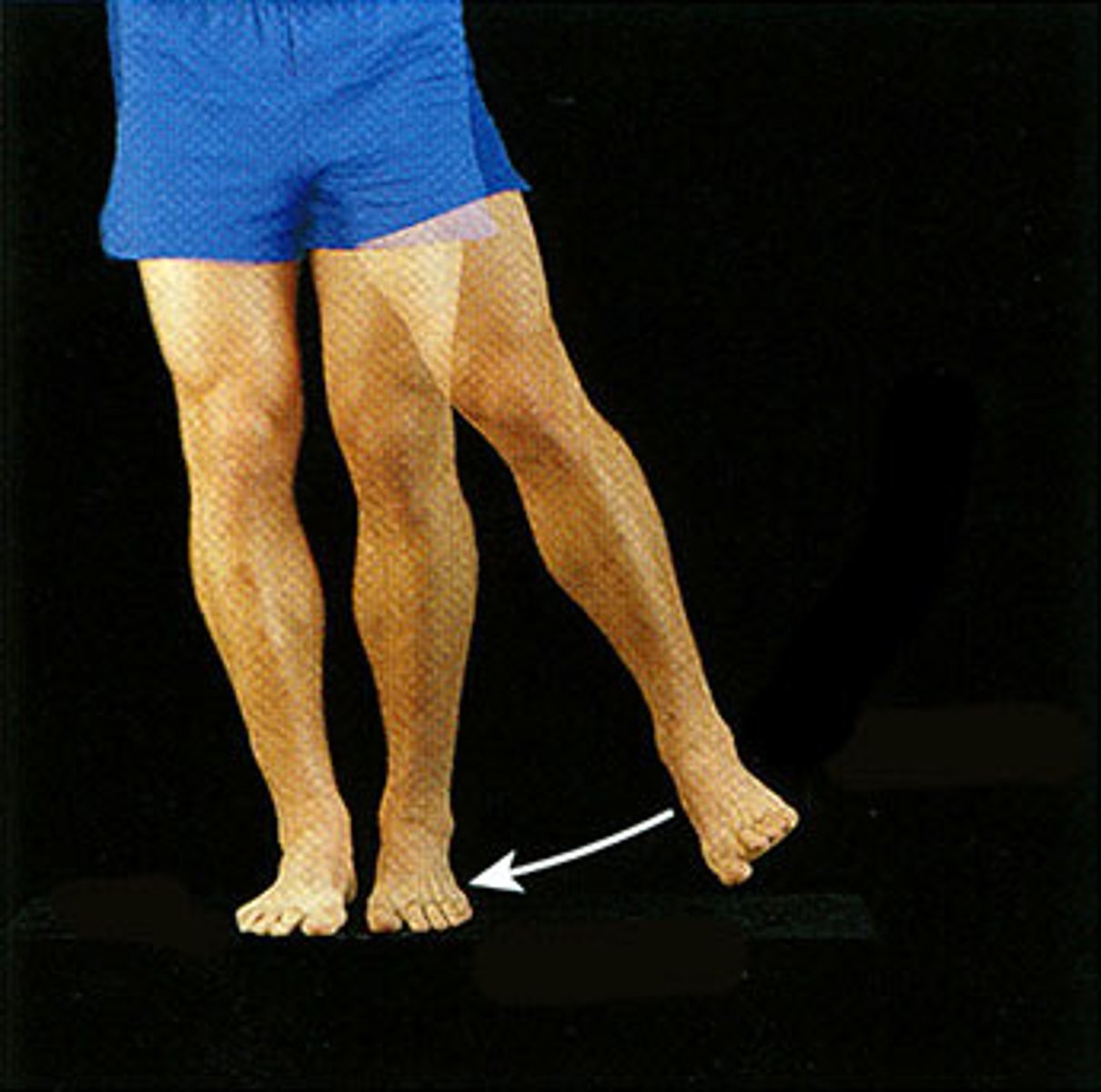
External (Lateral) Rotation
Rotational movement of a limb around its longitudinal axis away from the midline of the body.
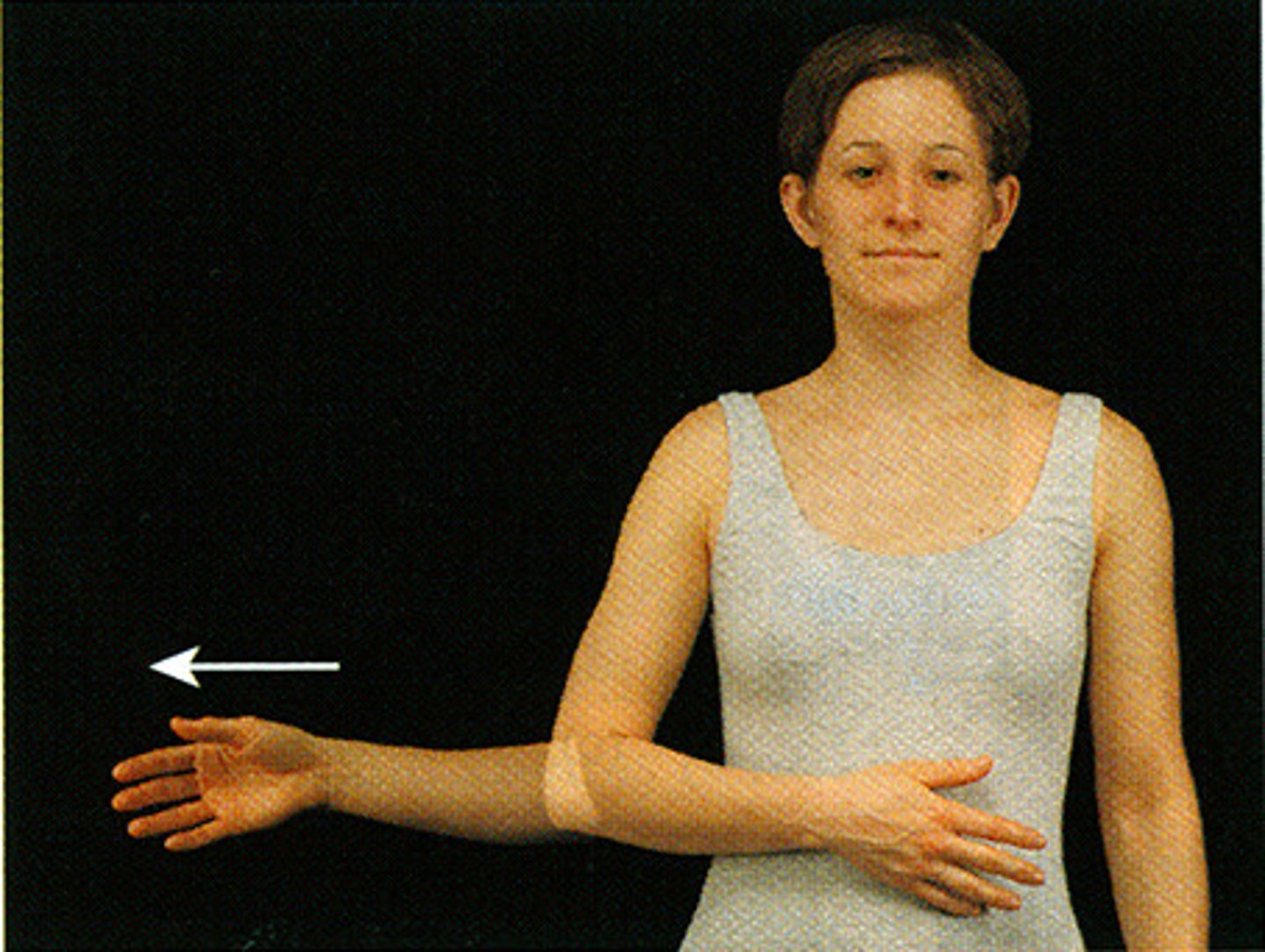
Zygomatic Bone
Facial bone that forms the prominence of the cheek and part of the orbit; commonly known as the cheekbone.
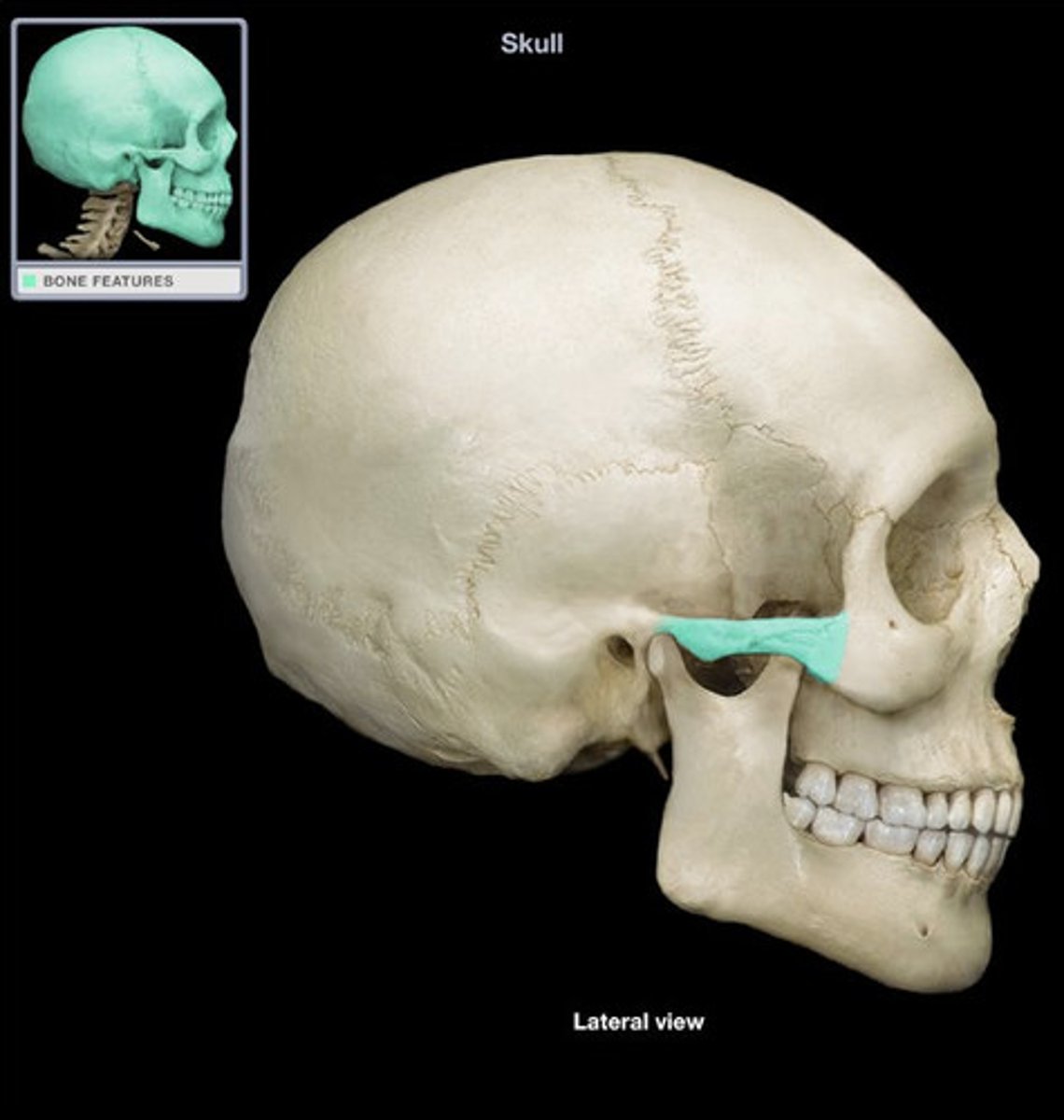
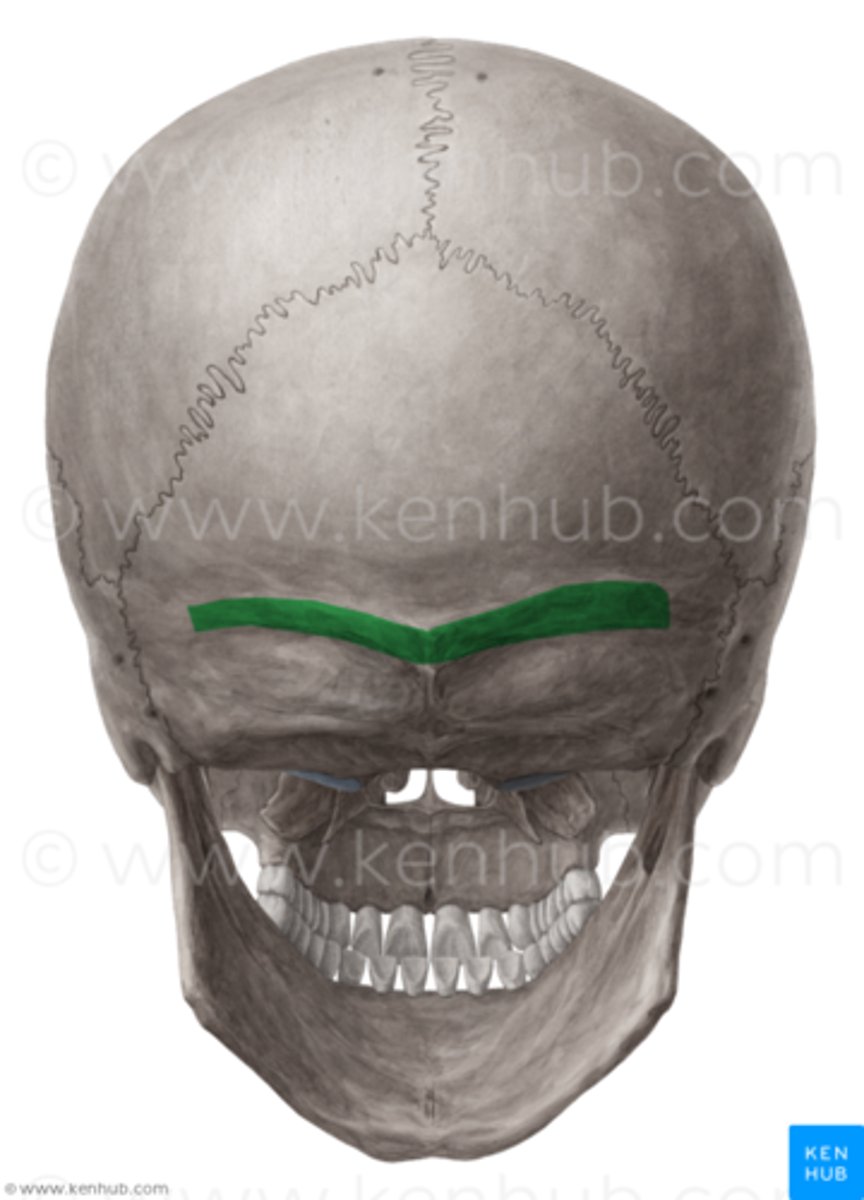
Nuchal Line
Ridge on the external surface of the occipital bone, serving as an attachment point for neck muscles.
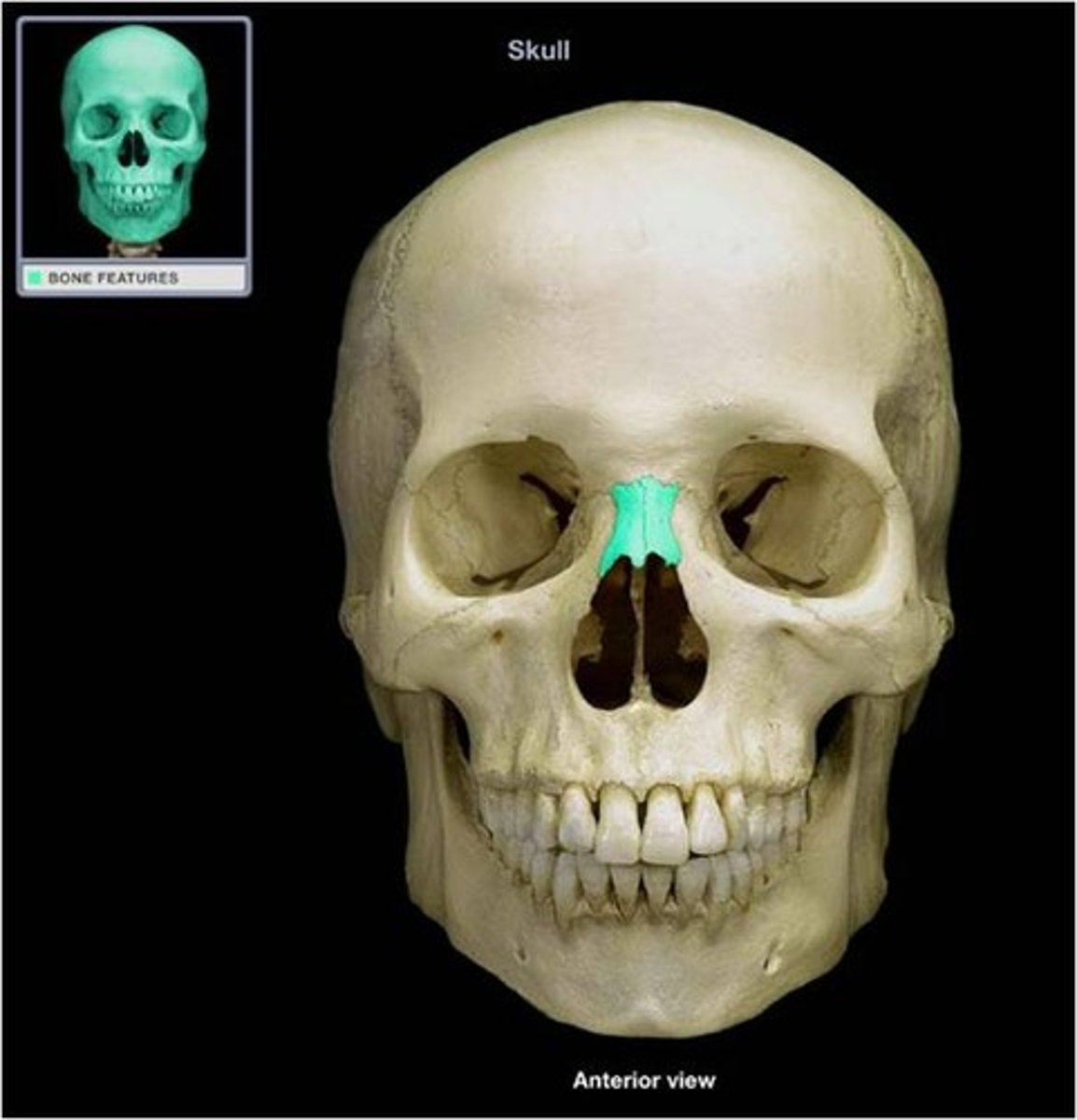
Nasal Bone
Bone forming the bridge of the nose.
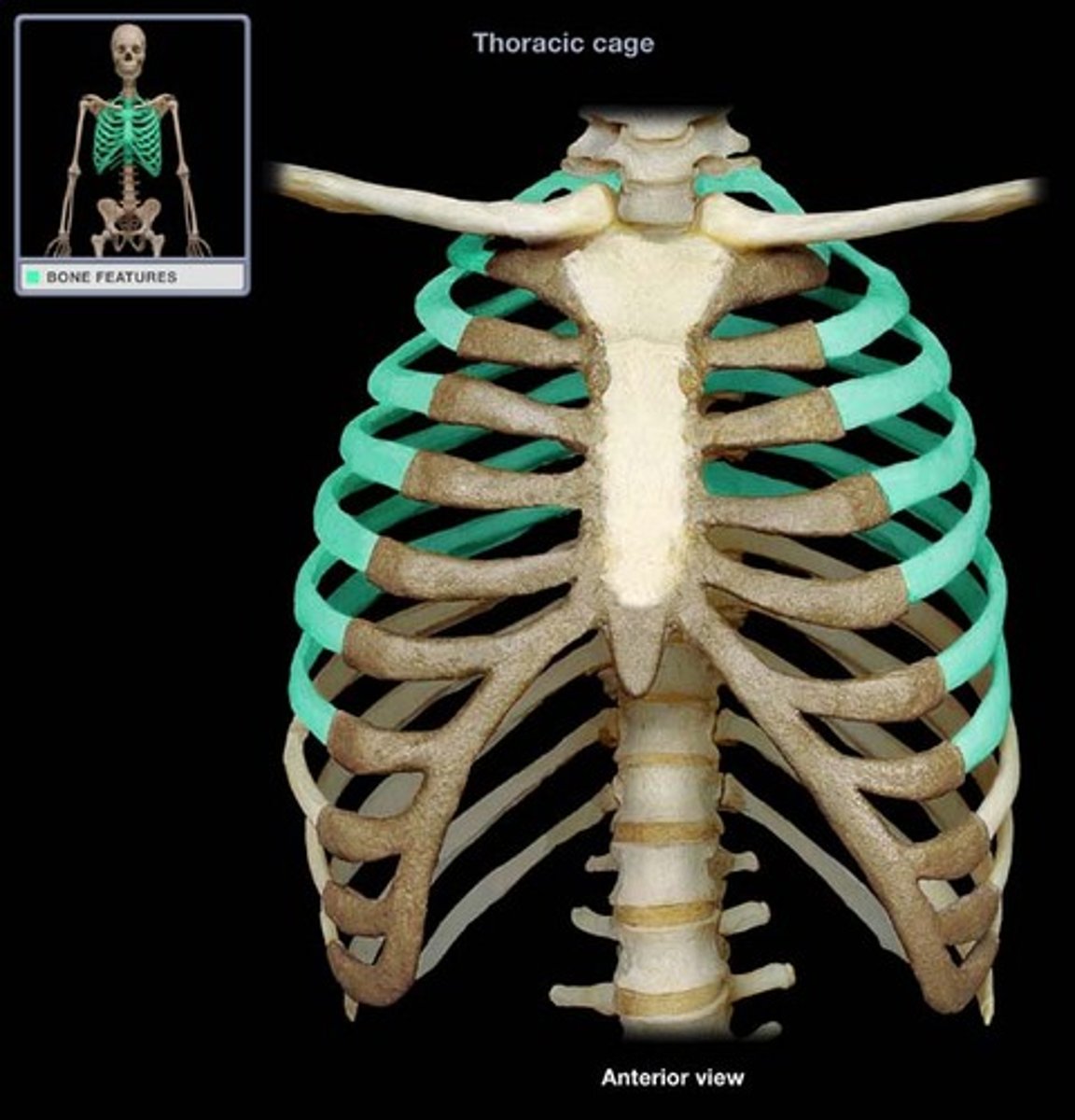
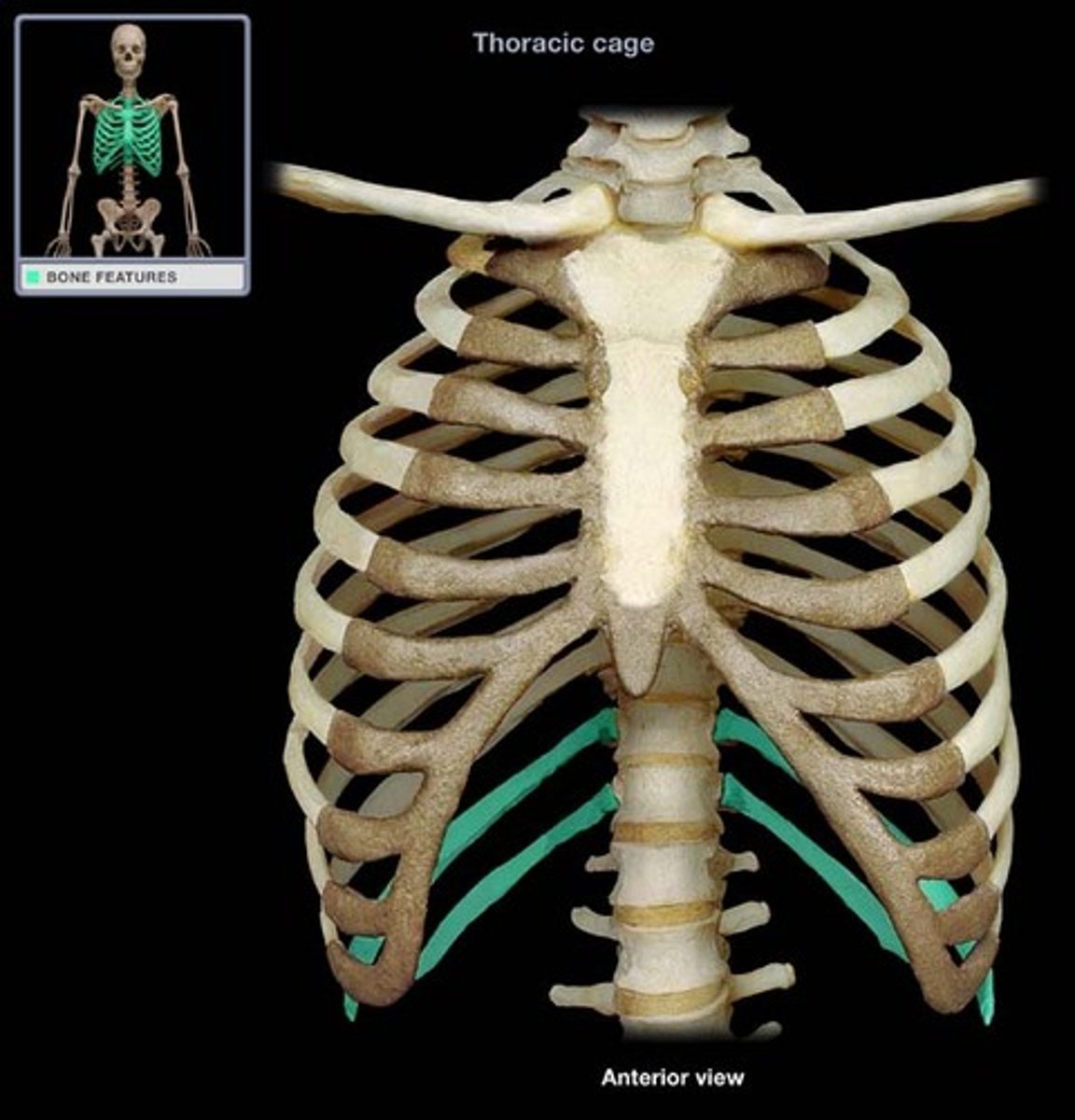
True Ribs (1-7)
Ribs (1-7) that have a direct attachment to the sternum via cartilage.
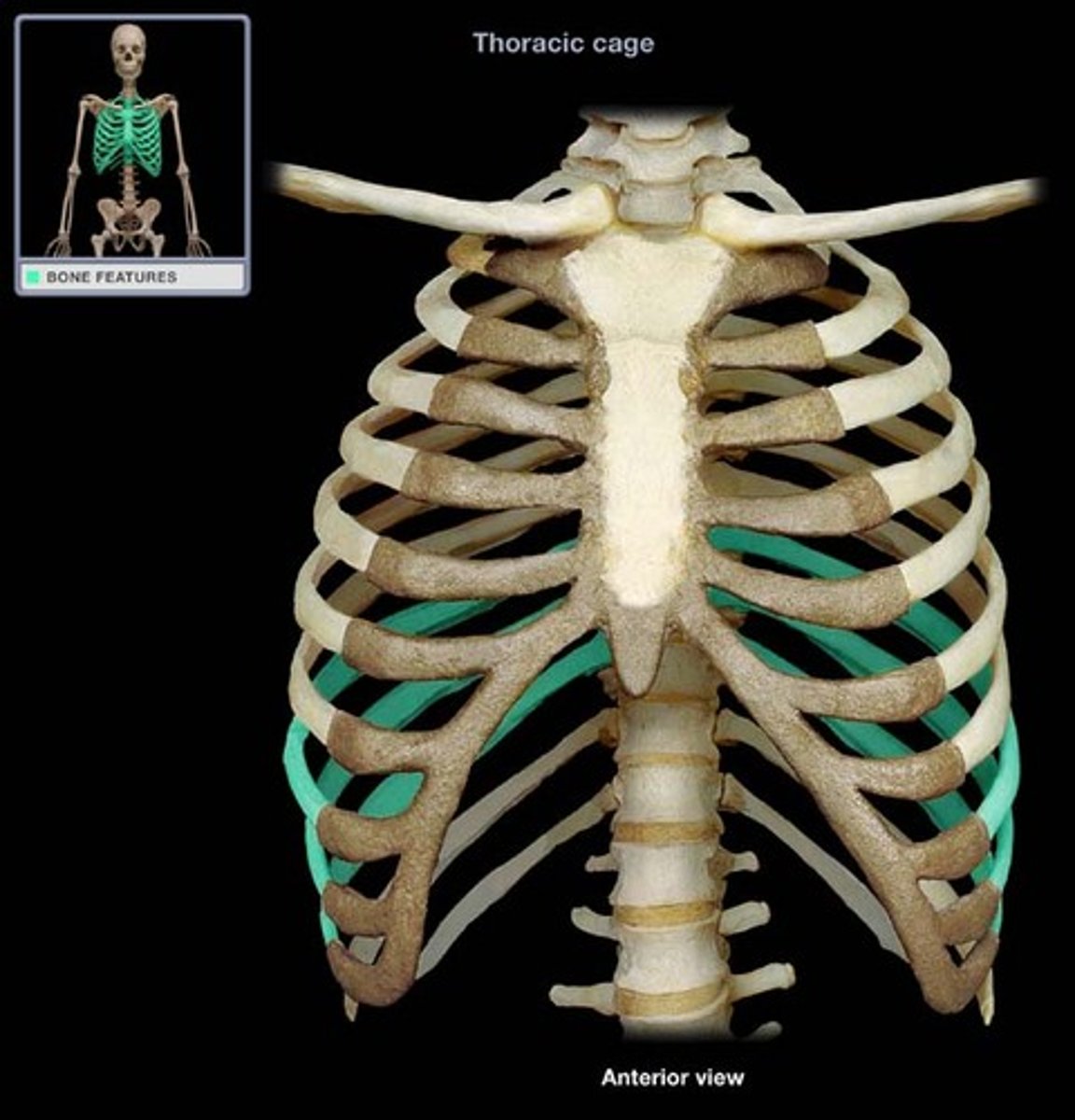
False Ribs (8-12)
Ribs (8-12) that do not have a direct attachment to the sternum (either indirectly attached or not at all).
Floating Ribs
Last two pairs of ribs (11-12) that do not attach to the sternum or other ribs.
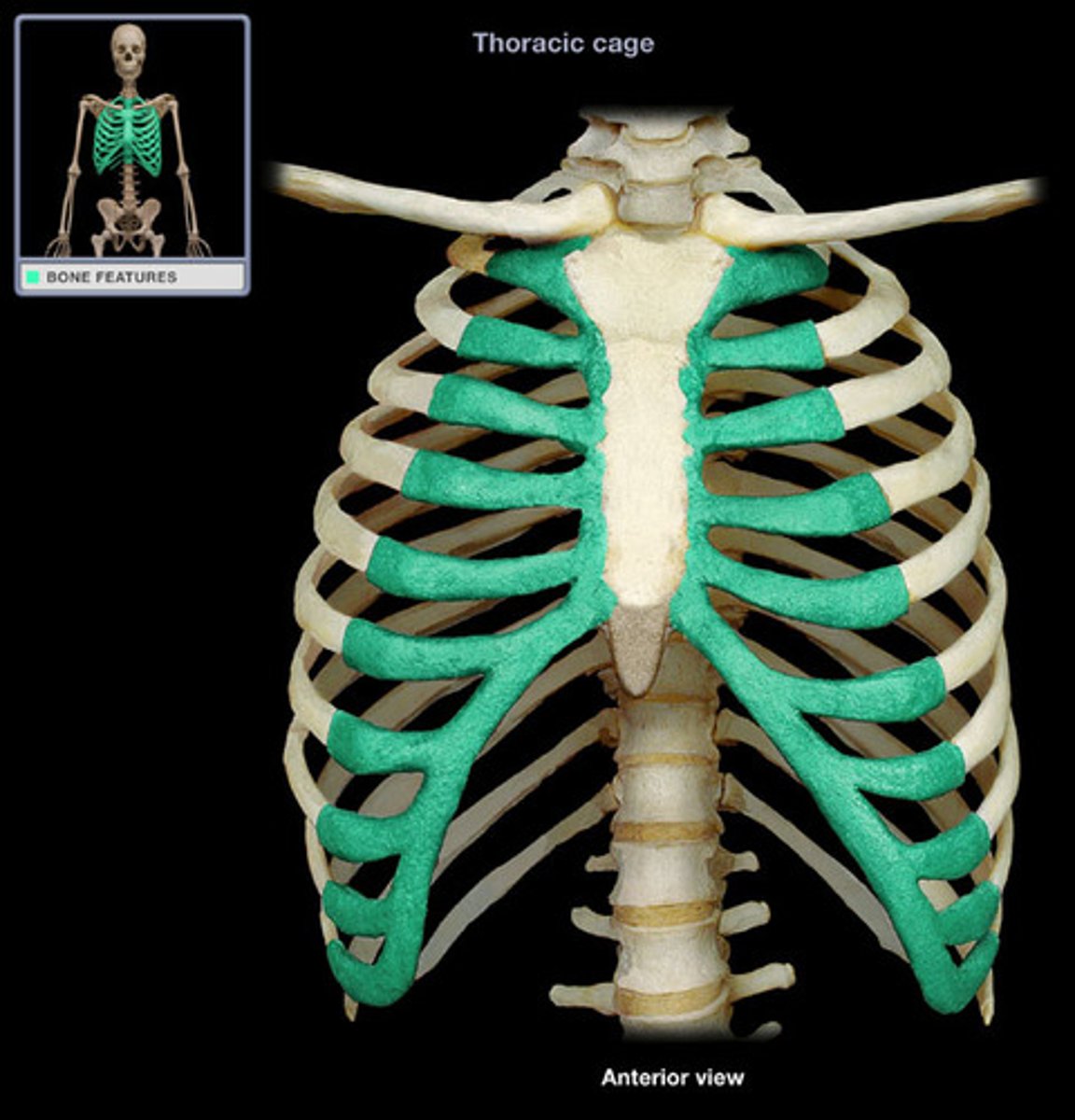
Costal Cartilage
Cartilage that connects the ribs to the sternum.
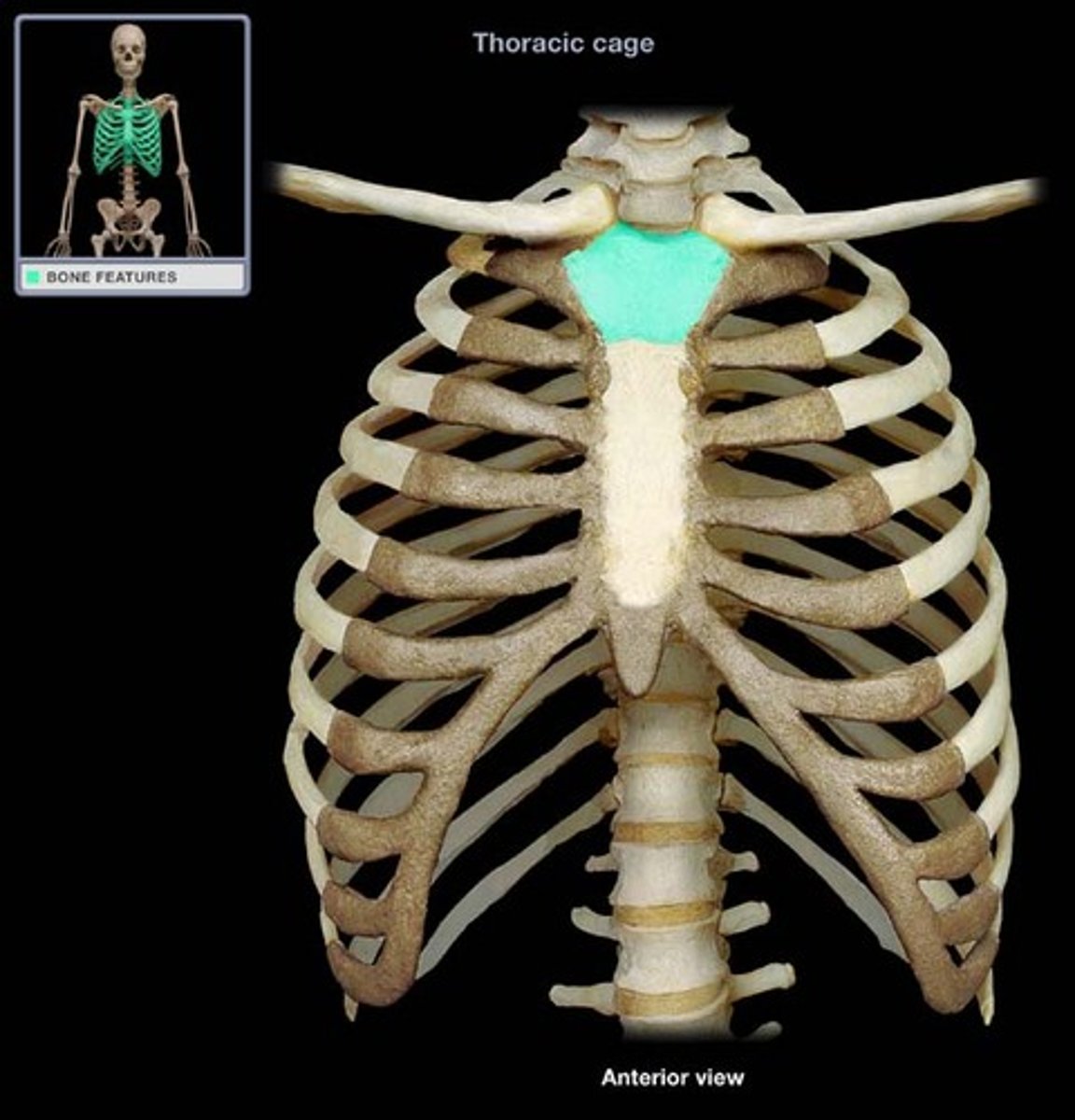
Manubrium
Upper portion of the sternum.
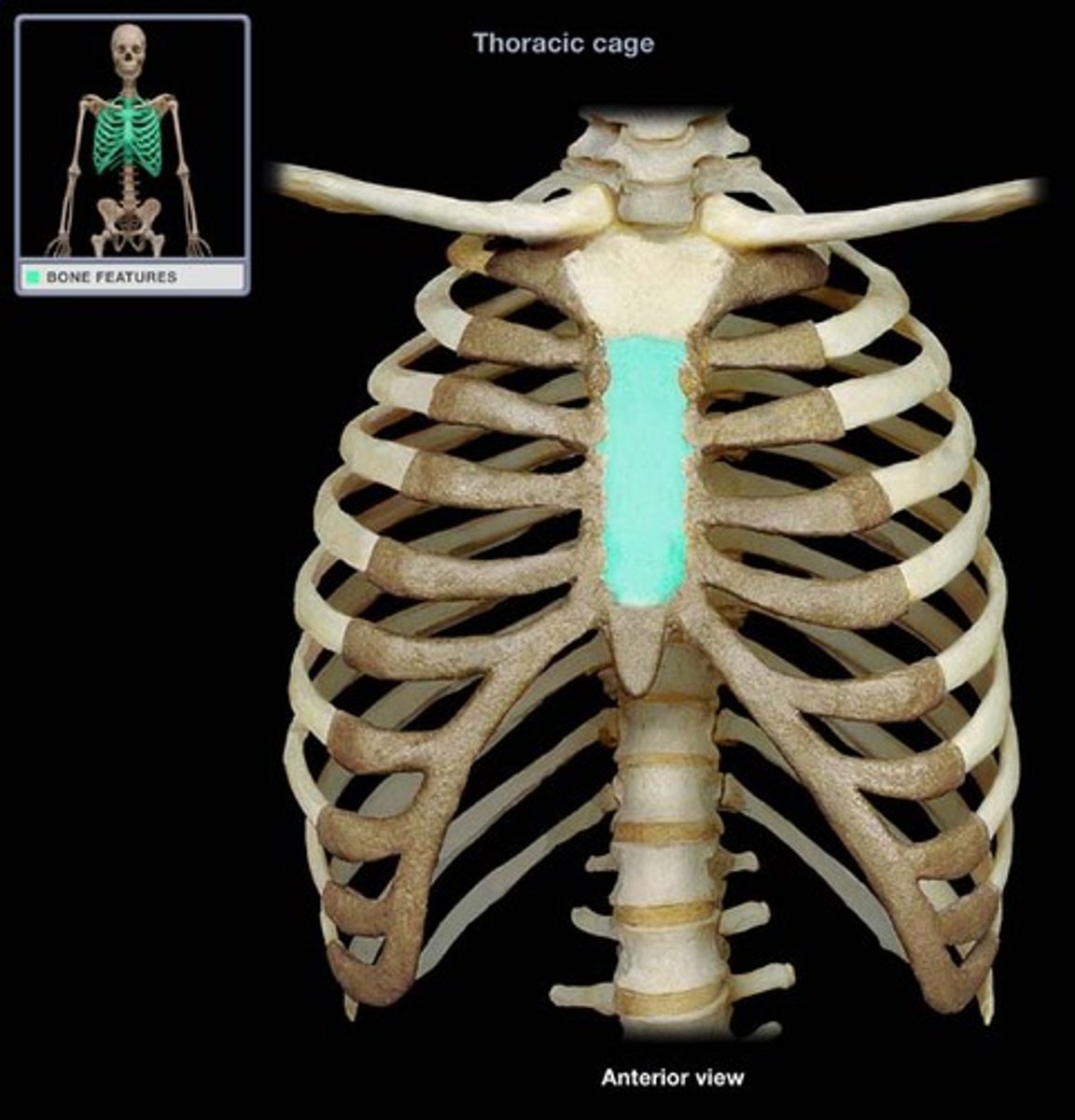
Sternum Body
Main long part of the sternum.
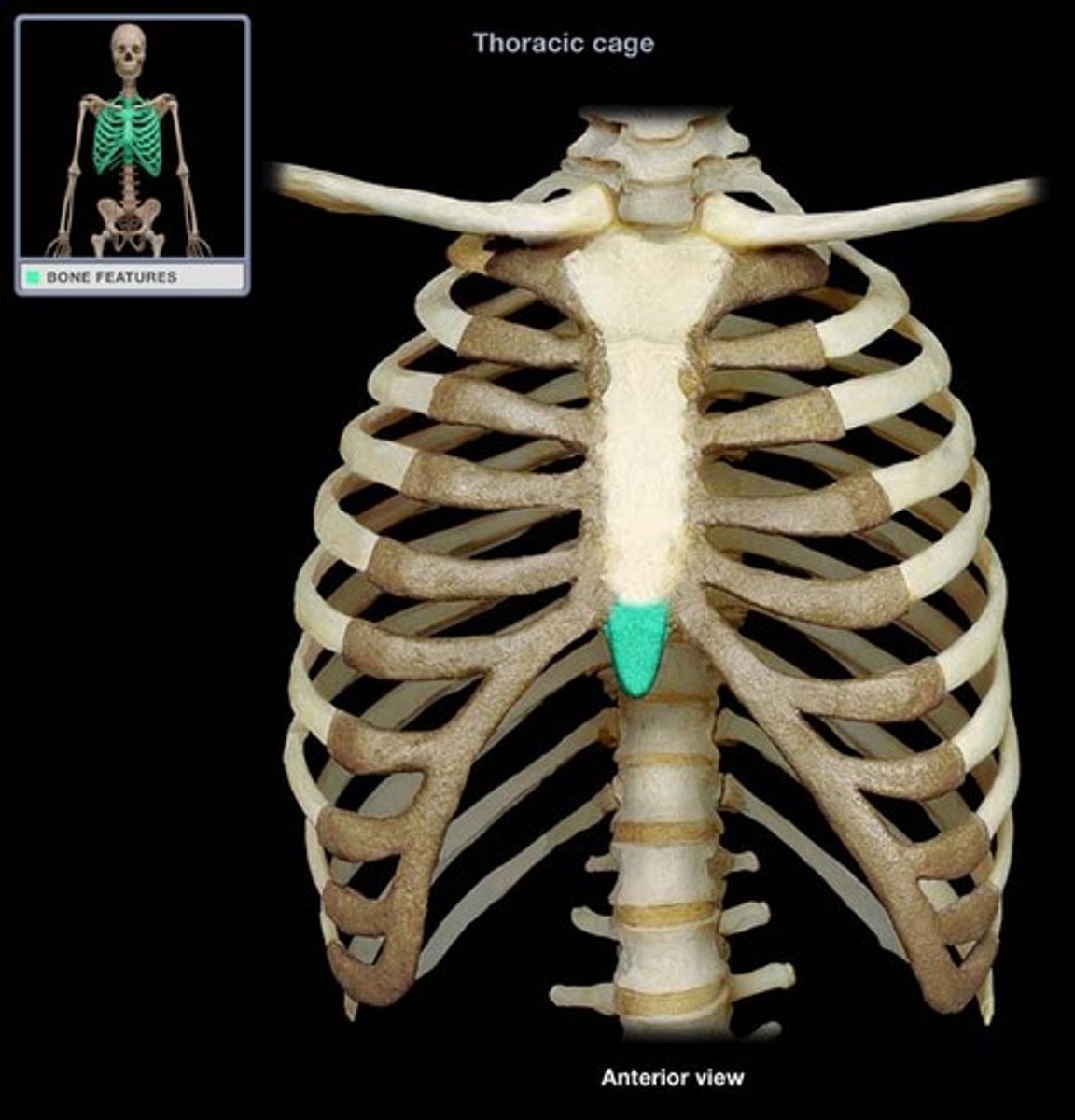
Xiphoid Process
Lower, narrow portion of the sternum.
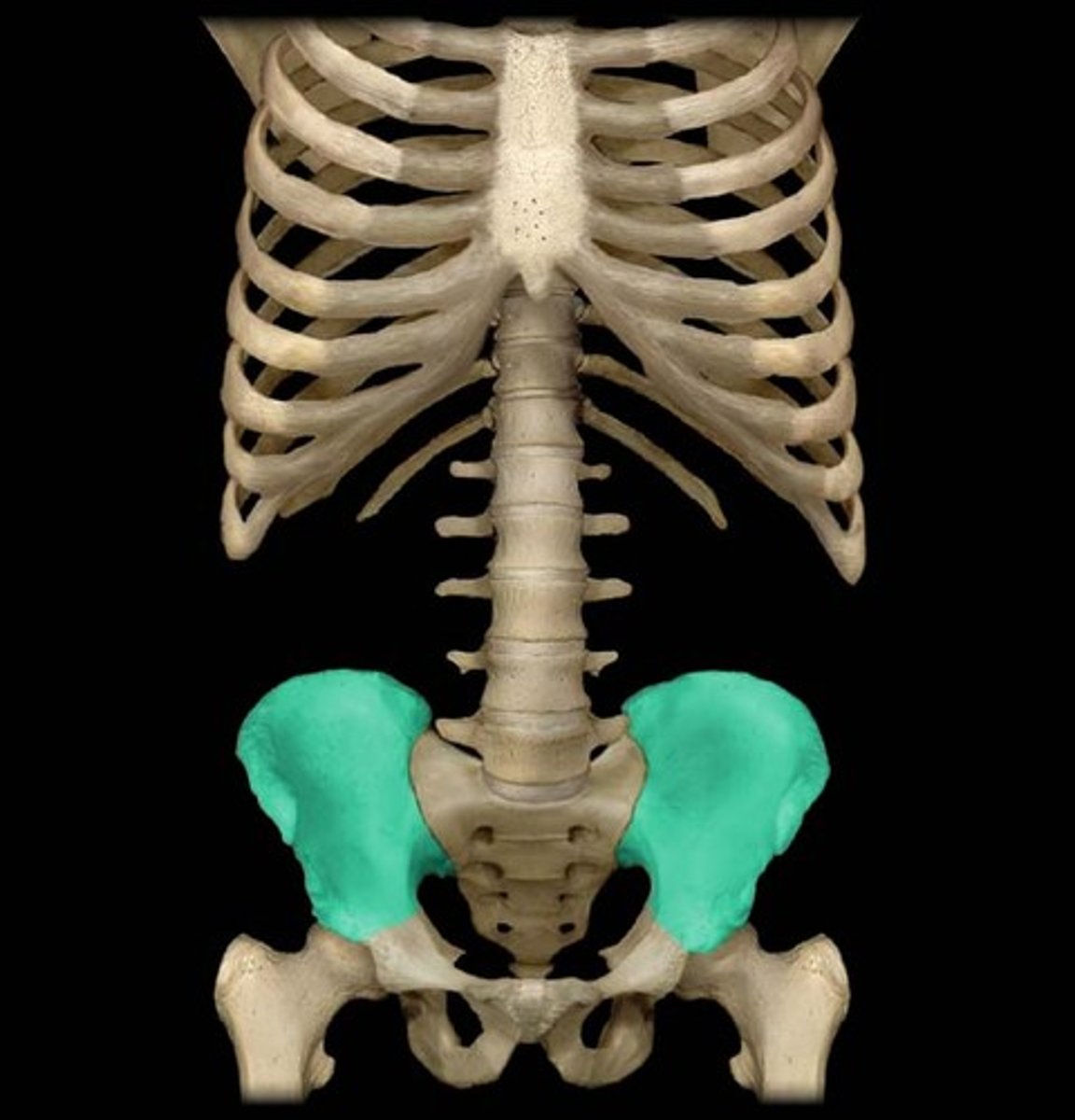
Ilium
The largest and uppermost part of the hip bone.
Ischium
The lower, posterior portions of the pelvis, forming the 'sitting bones'.
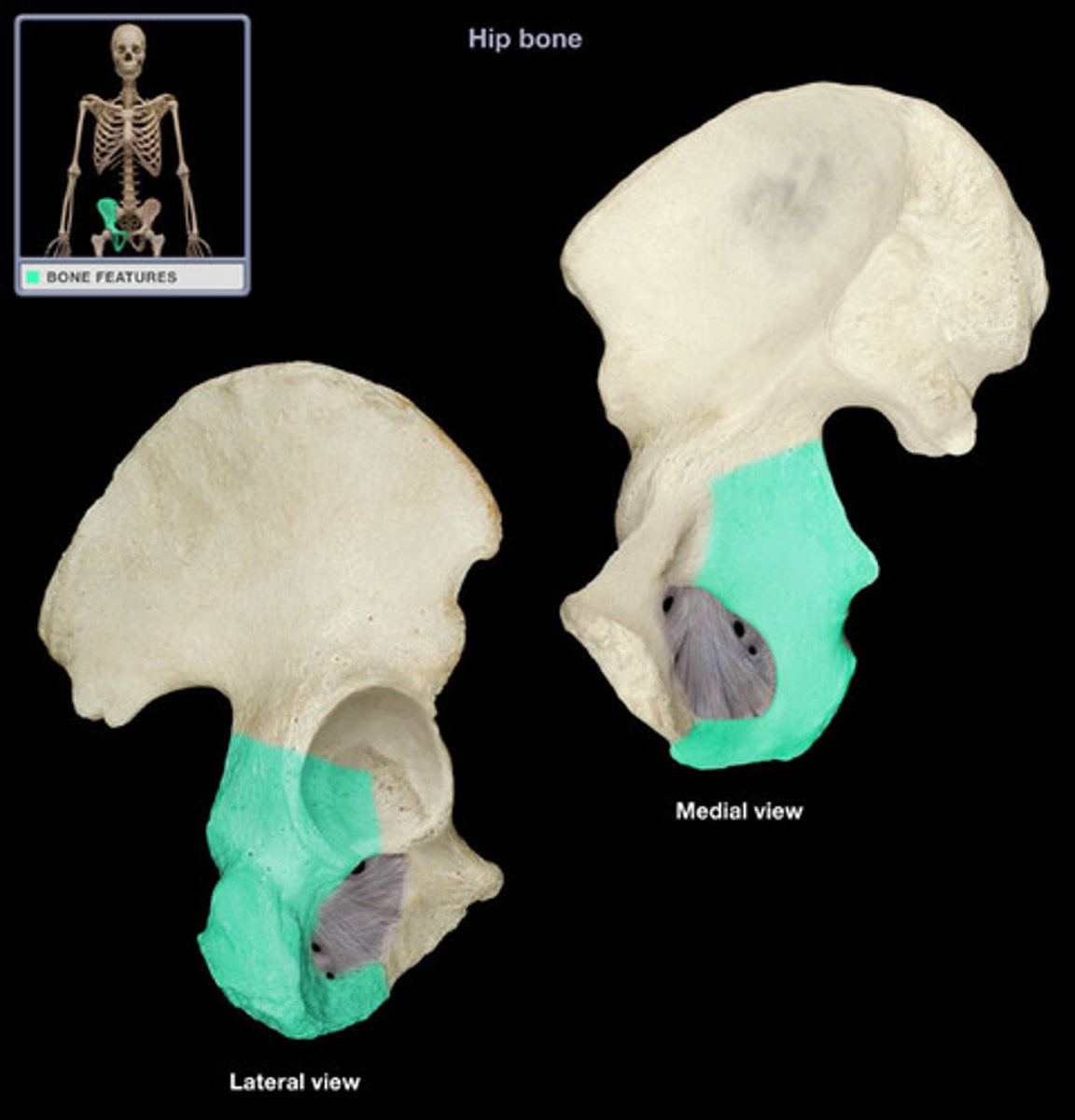
Pubis
The medial anterior portion of the pelvis.
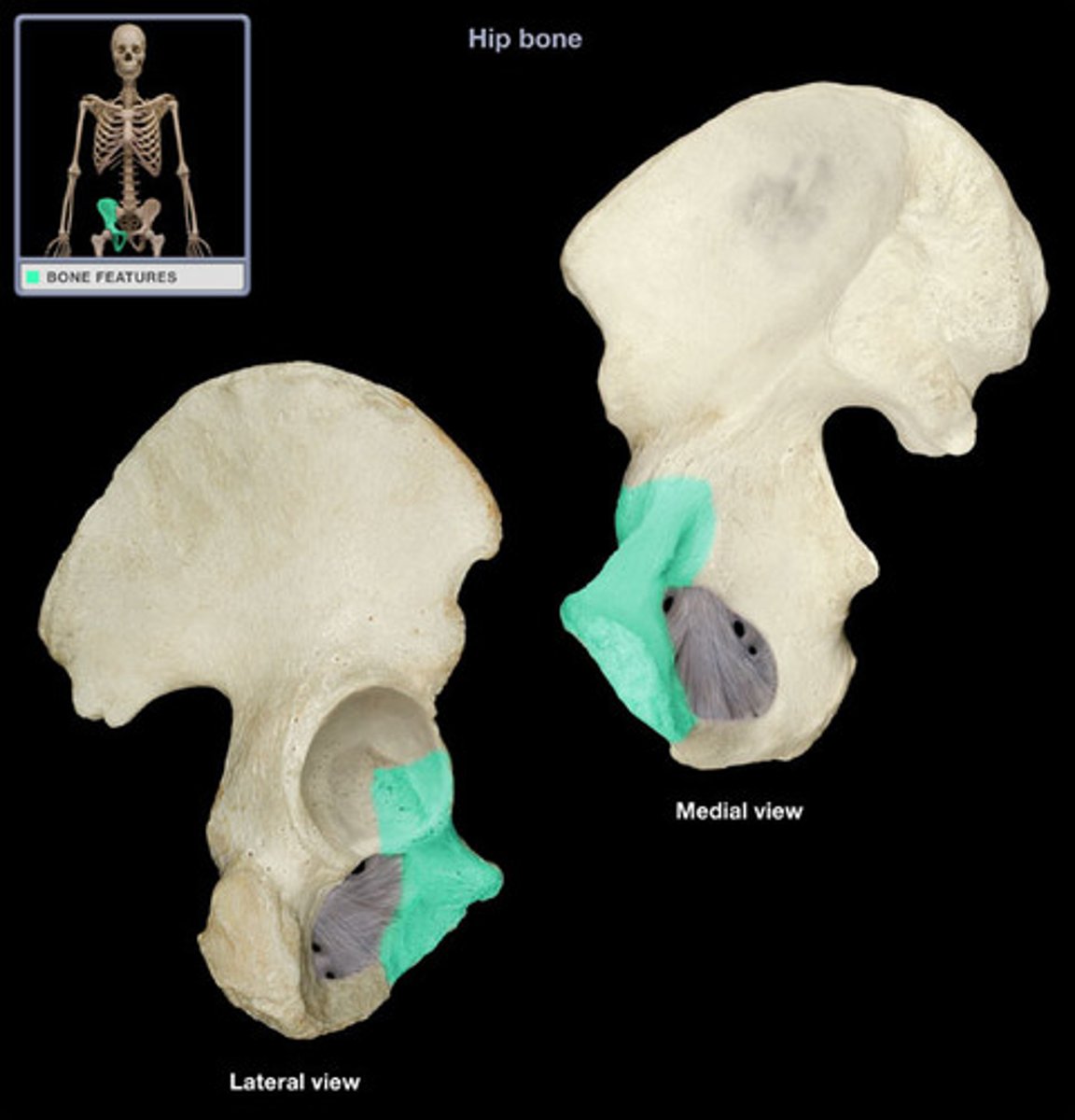
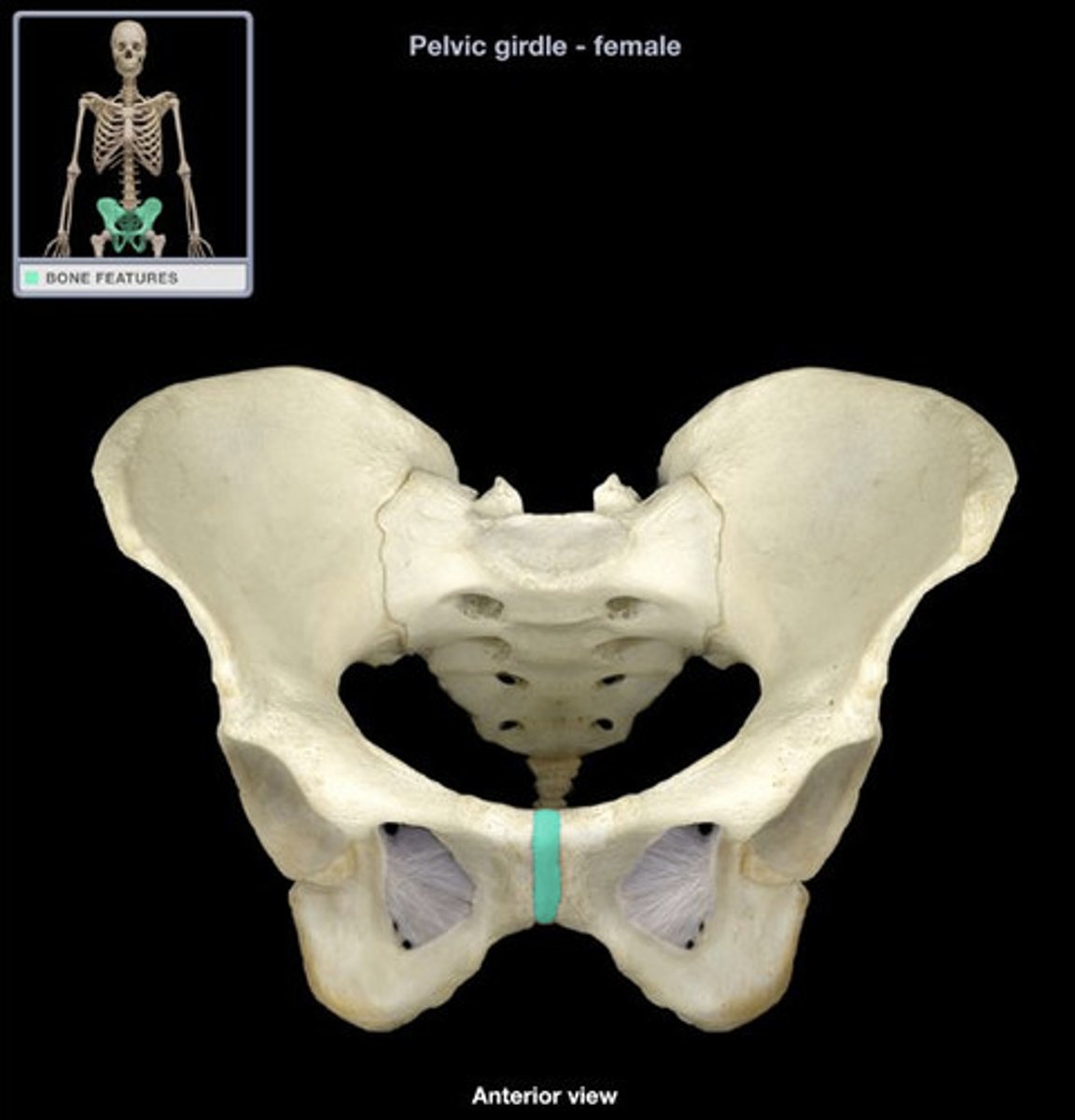
Symphysis Pubis
A cartilaginous joint that is the point of fusion for the two pubic bones, located anteriorly.
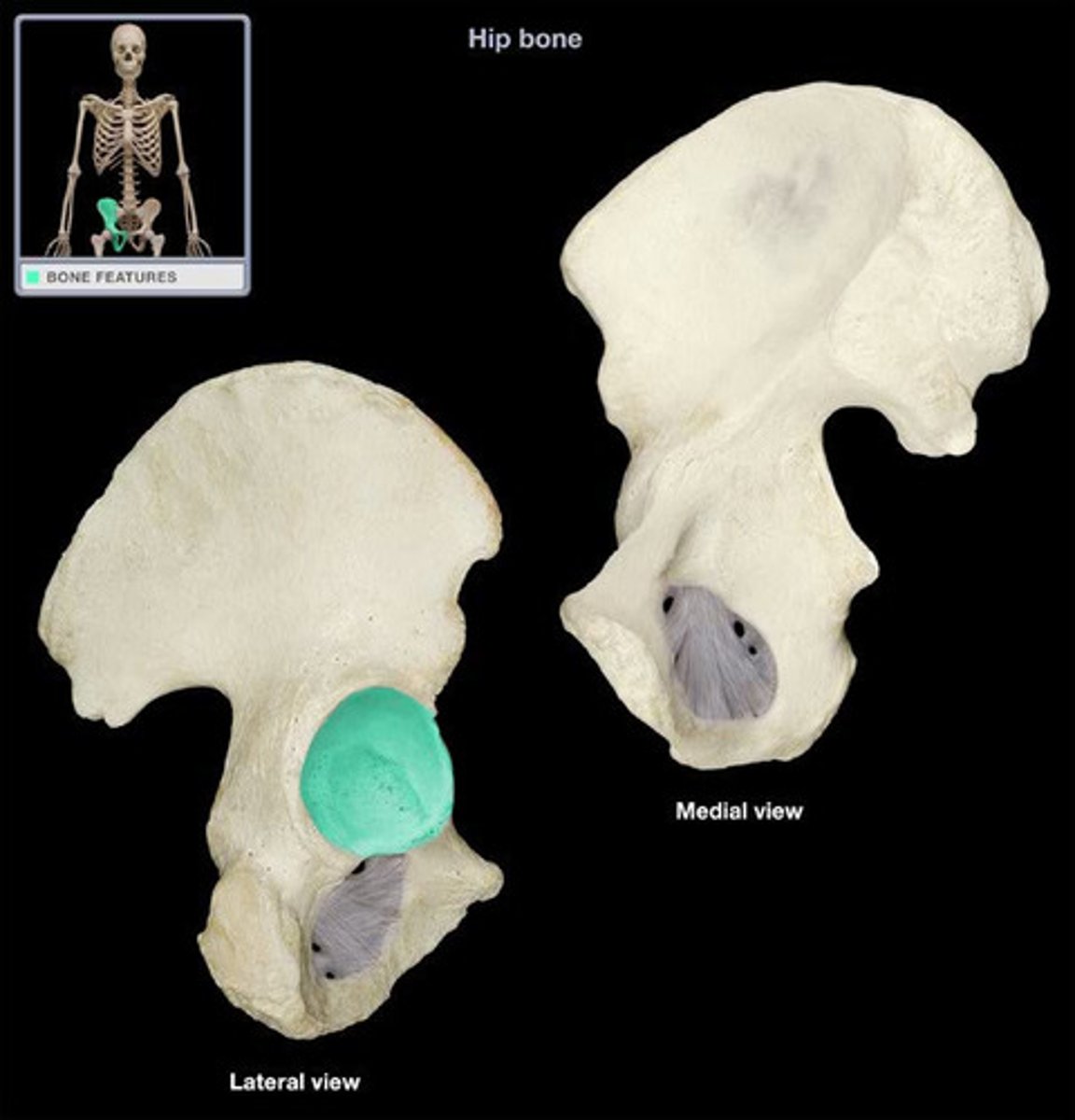
Acetabulum
The hip socket, a cup-shaped depression on the lateral surface of the hip bone, articulating with the head of the femur.
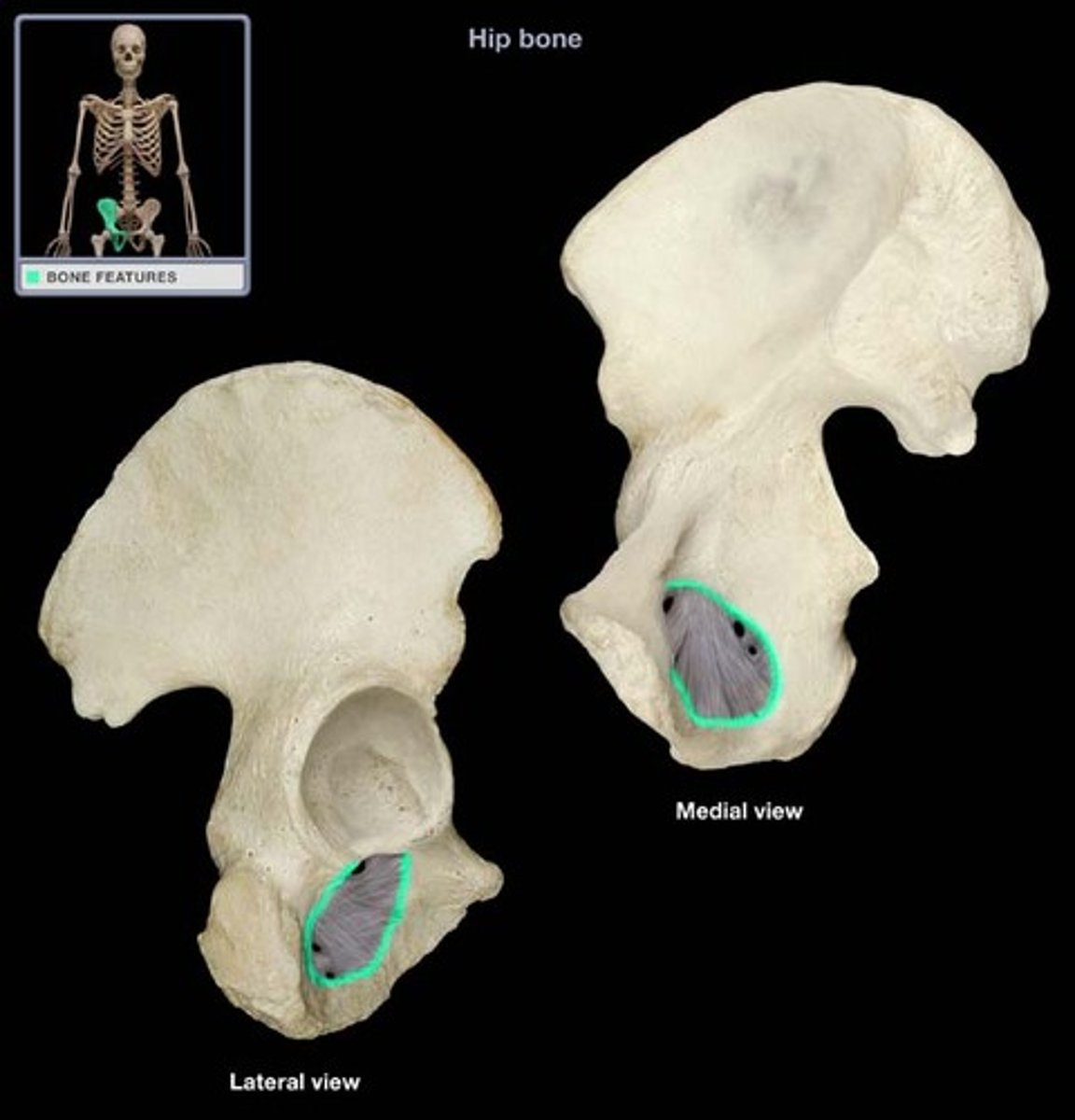
Obturator Foramen
Large opening in the hip bone formed by the pubic and ischial rami.
Scapular Spine
Prominent ridge running horizontally along the posterior aspect of the scapula, dividing it into supraspinatus and infraspinatus fossae.
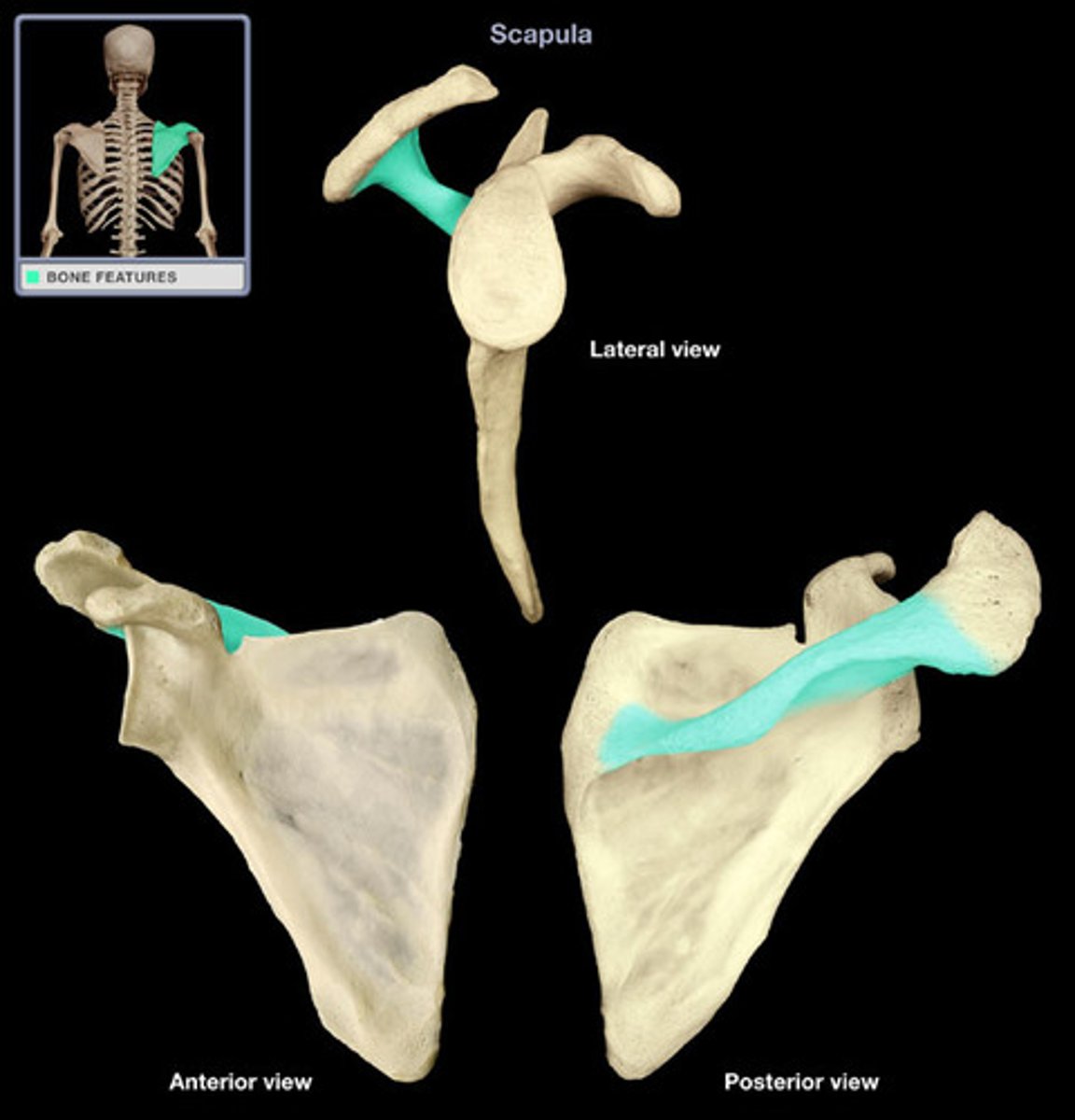
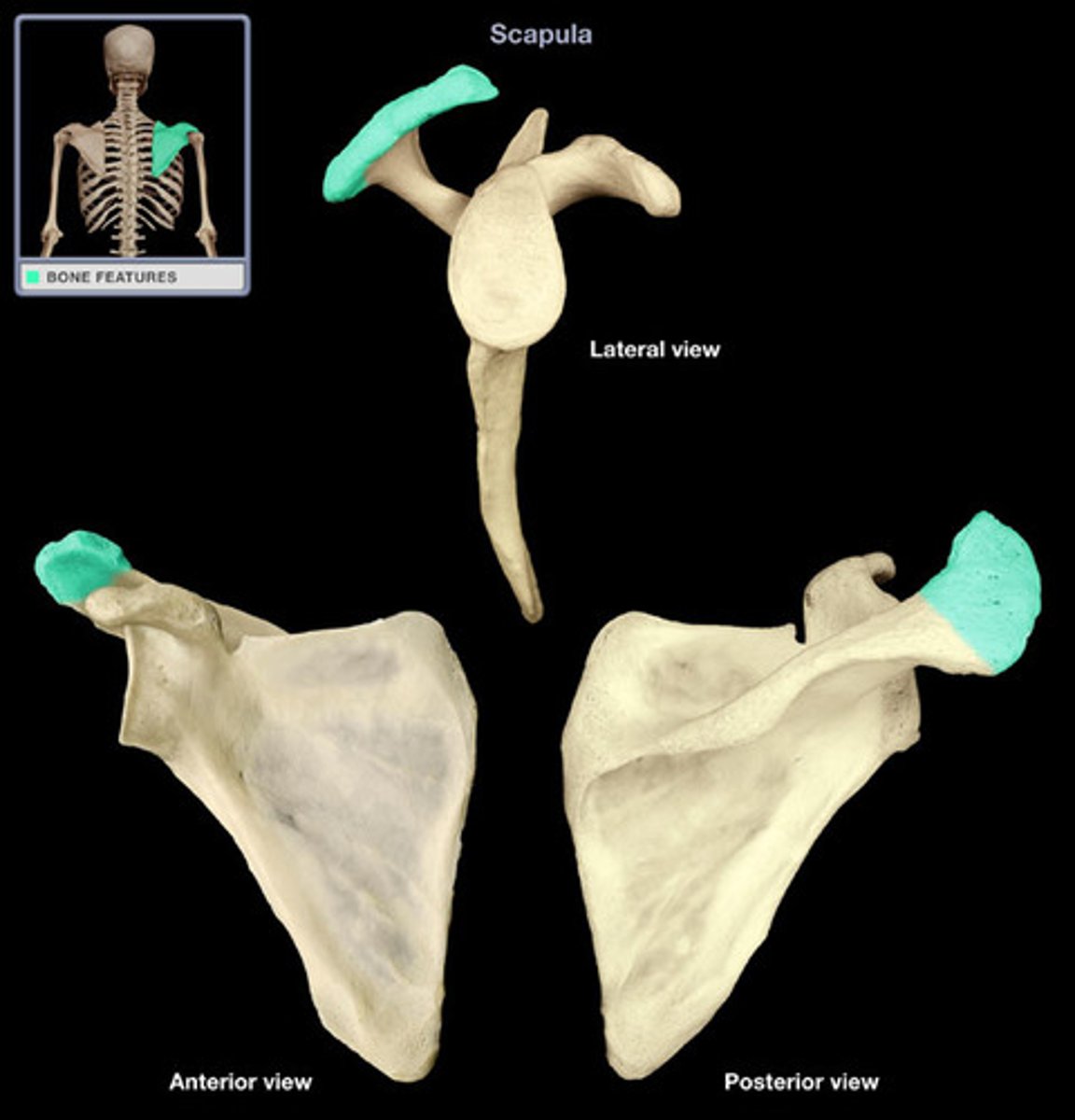
Acromion Process
The highest portion of the shoulder, forming the lateral part of the scapular spine and articulating with the clavicle.
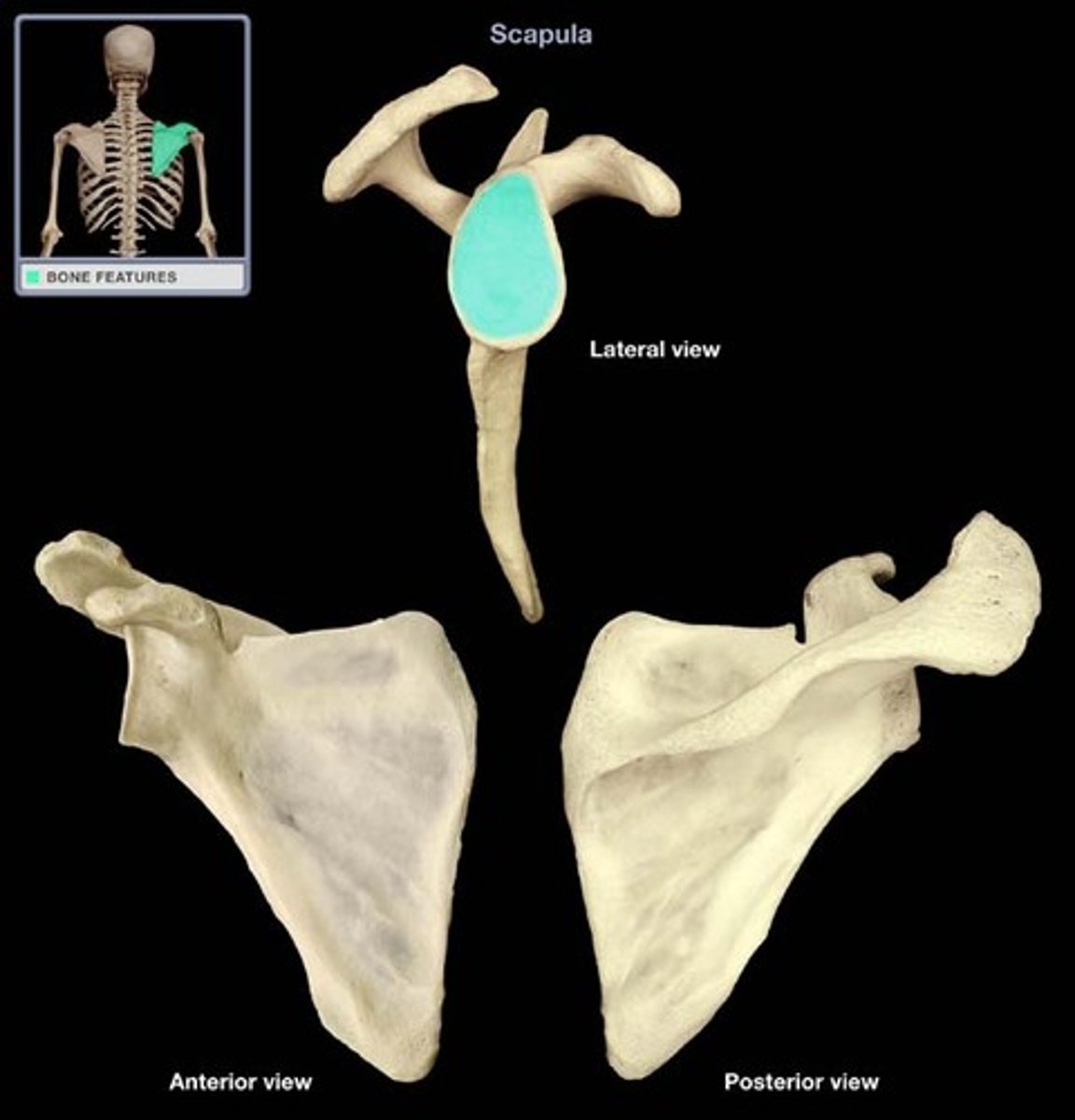
Glenoid Fossa (Cavity)
Shallow articular surface (cavity) on the lateral aspect of the scapula that articulates with the head of the humerus.
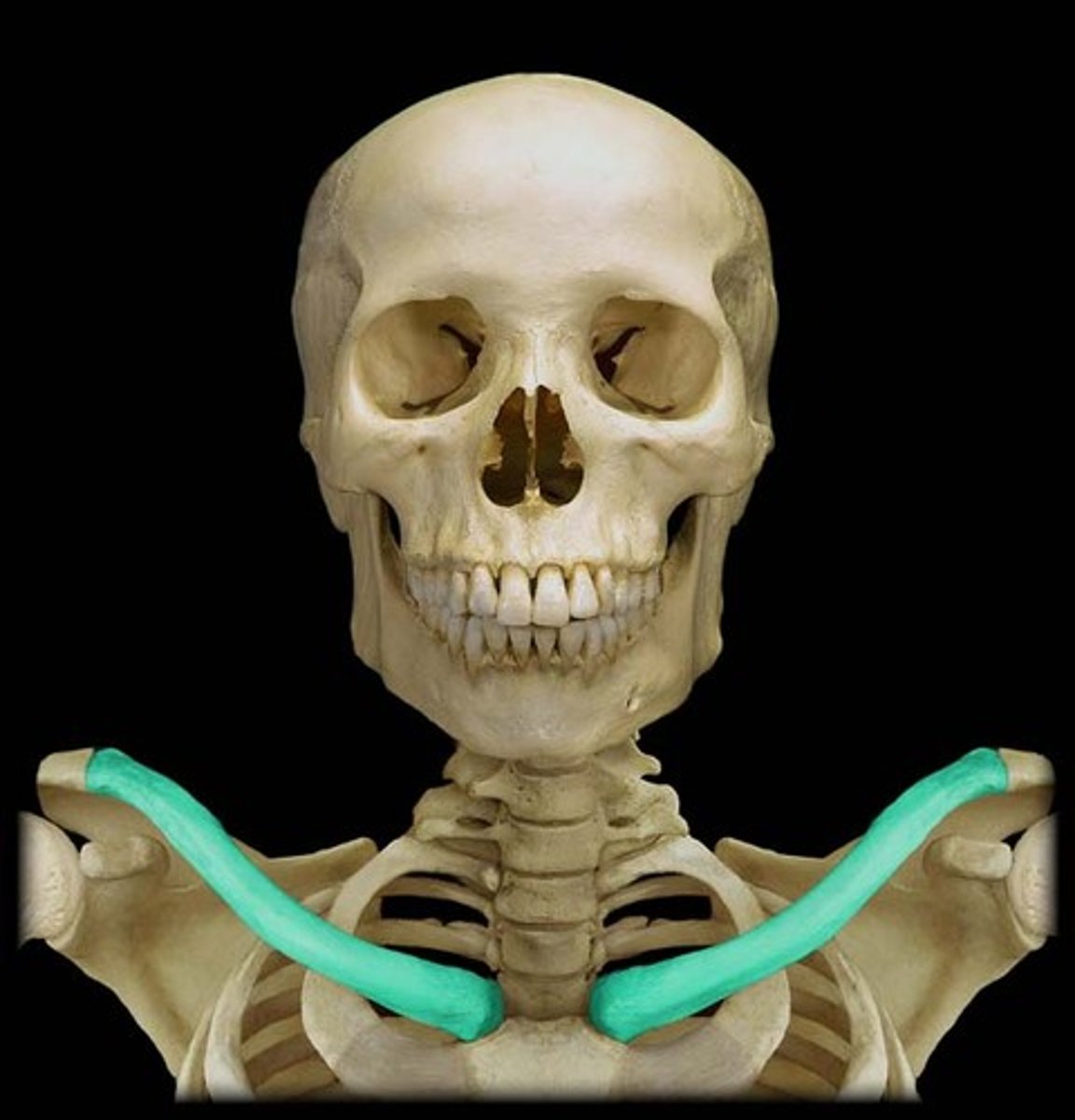
Clavicle
The collar bone, a slender, curved bone extending between the sternum and the acromion.
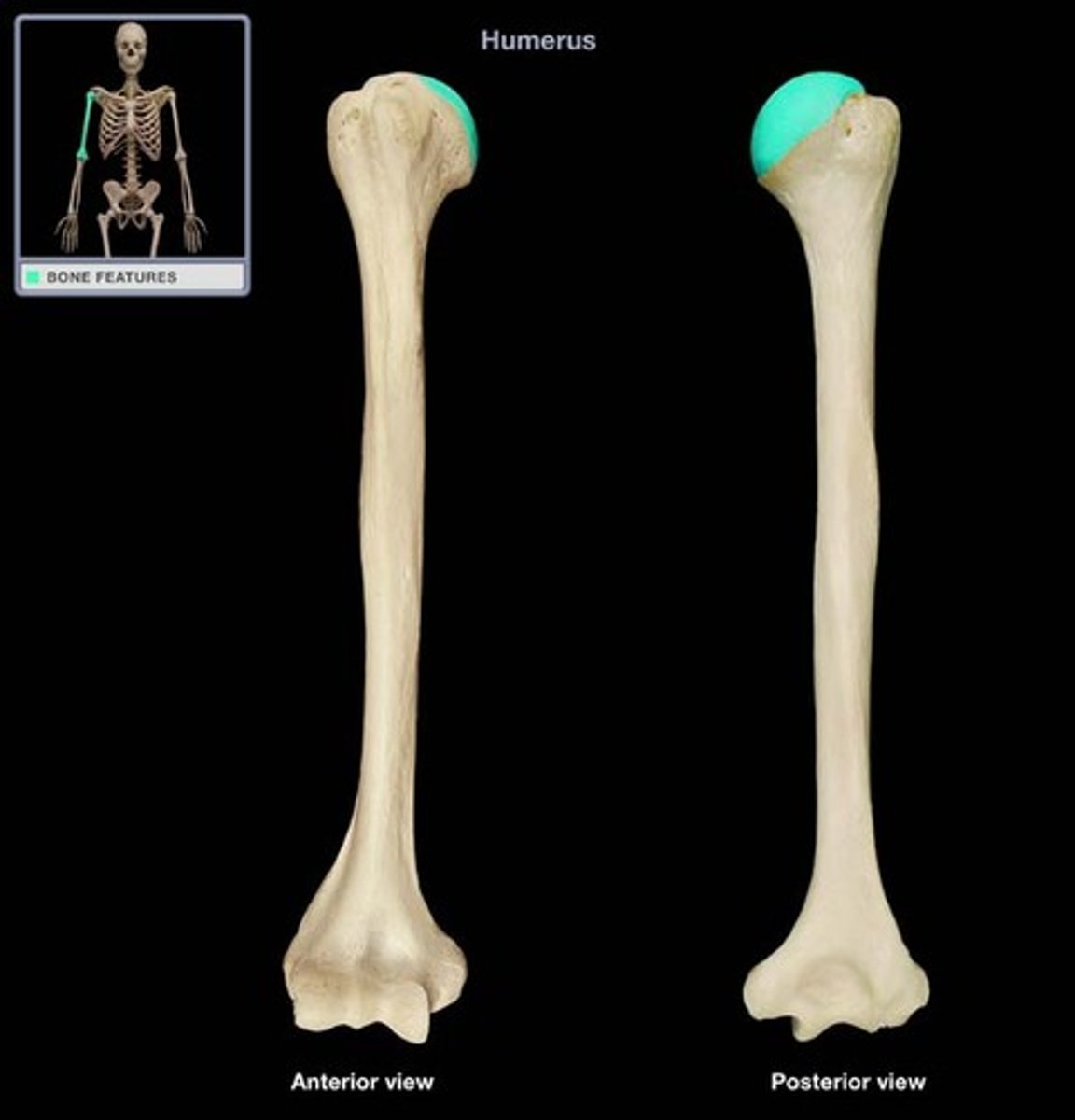
Head of Humerus
The rounded proximal end of the humerus that articulates with the glenoid cavity of the scapula.
Deltoid Tuberosity
Rough, triangular elevation on the lateral surface of the humerus where the deltoid muscle attaches.
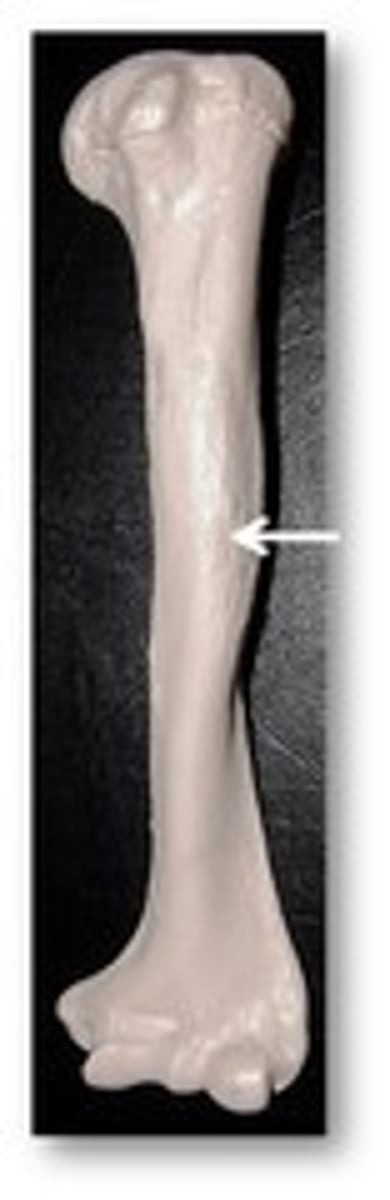
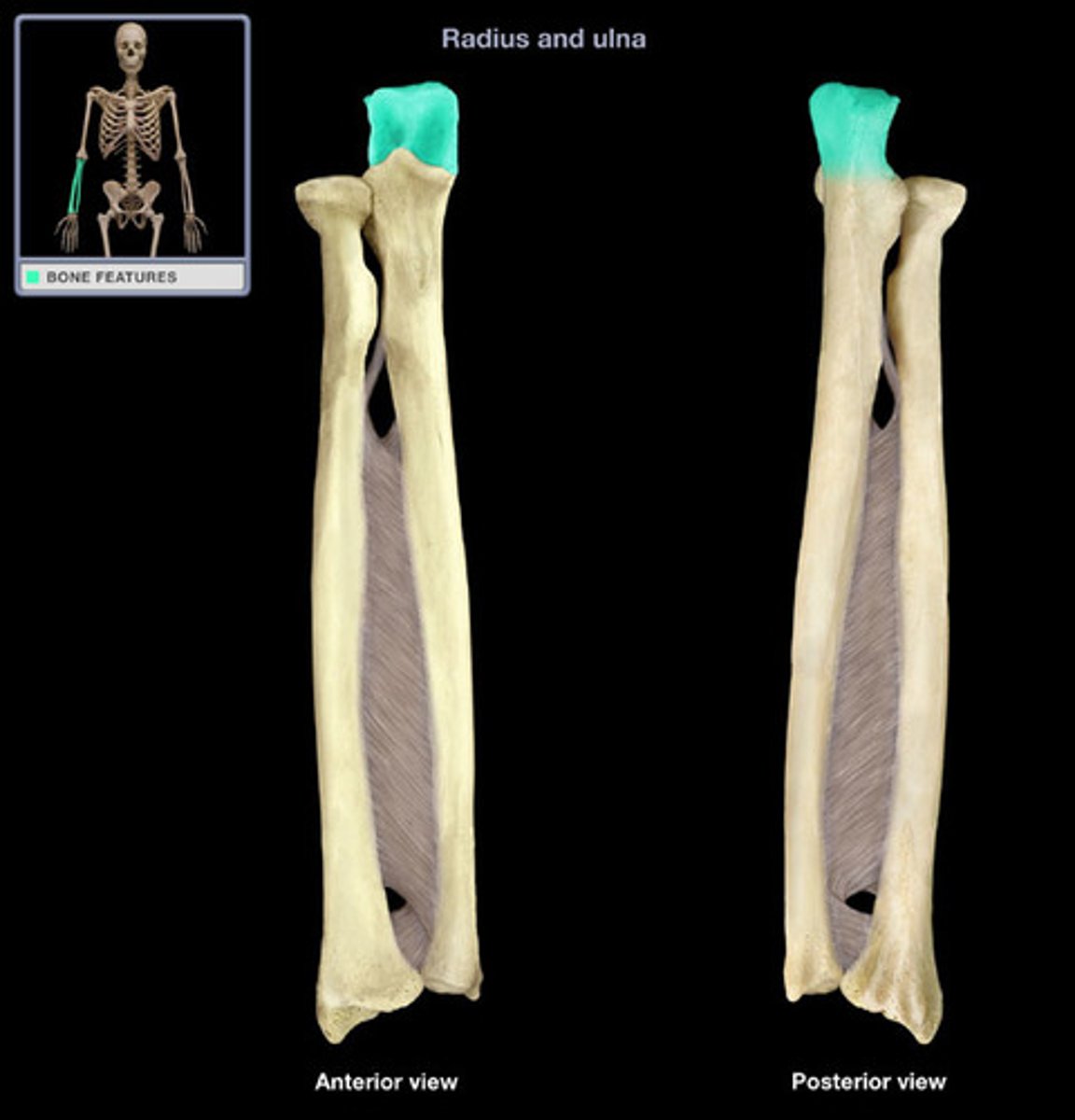
Radius
The lateral bone of the forearm, articulating with the humerus and carpals, allowing for rotation.
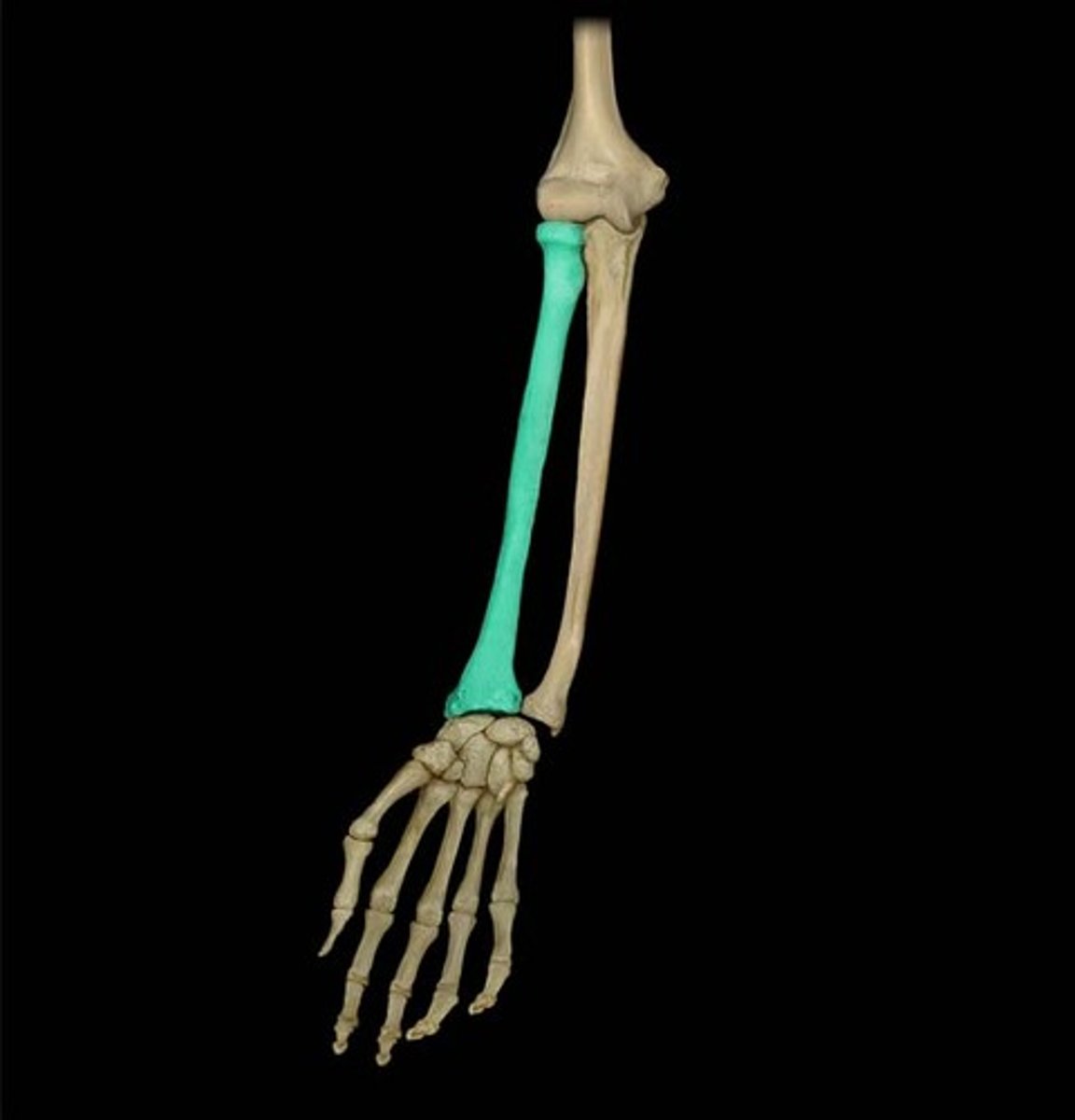
Ulna
The medial bone of the forearm, forming the elbow joint with the humerus.
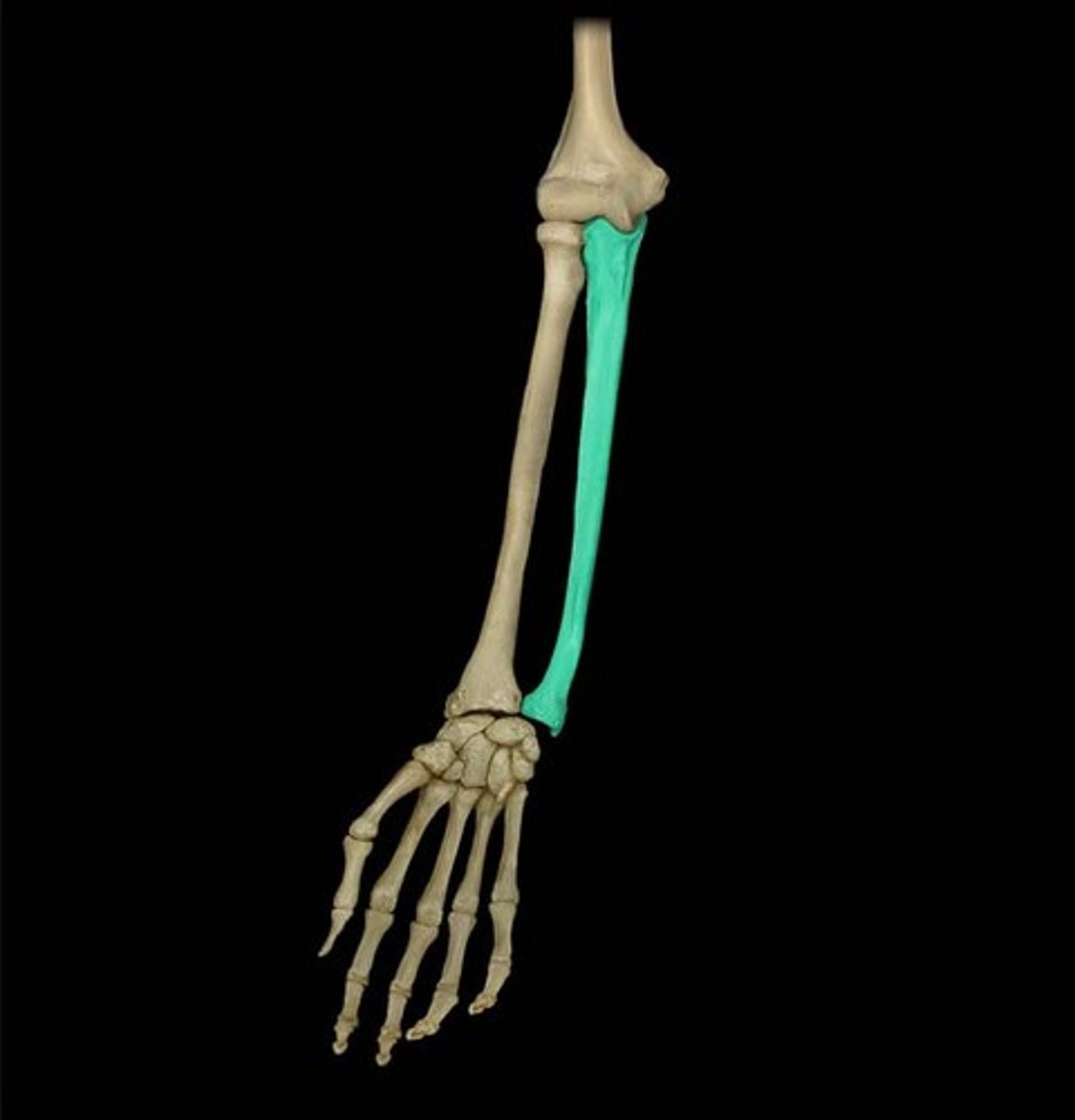
Olecranon Process
Large, bony projection on the proximal end of the ulna, forming the prominent bone of the elbow.
Carpals
Eight small bones that form the wrist (carpus), arranged in two rows.
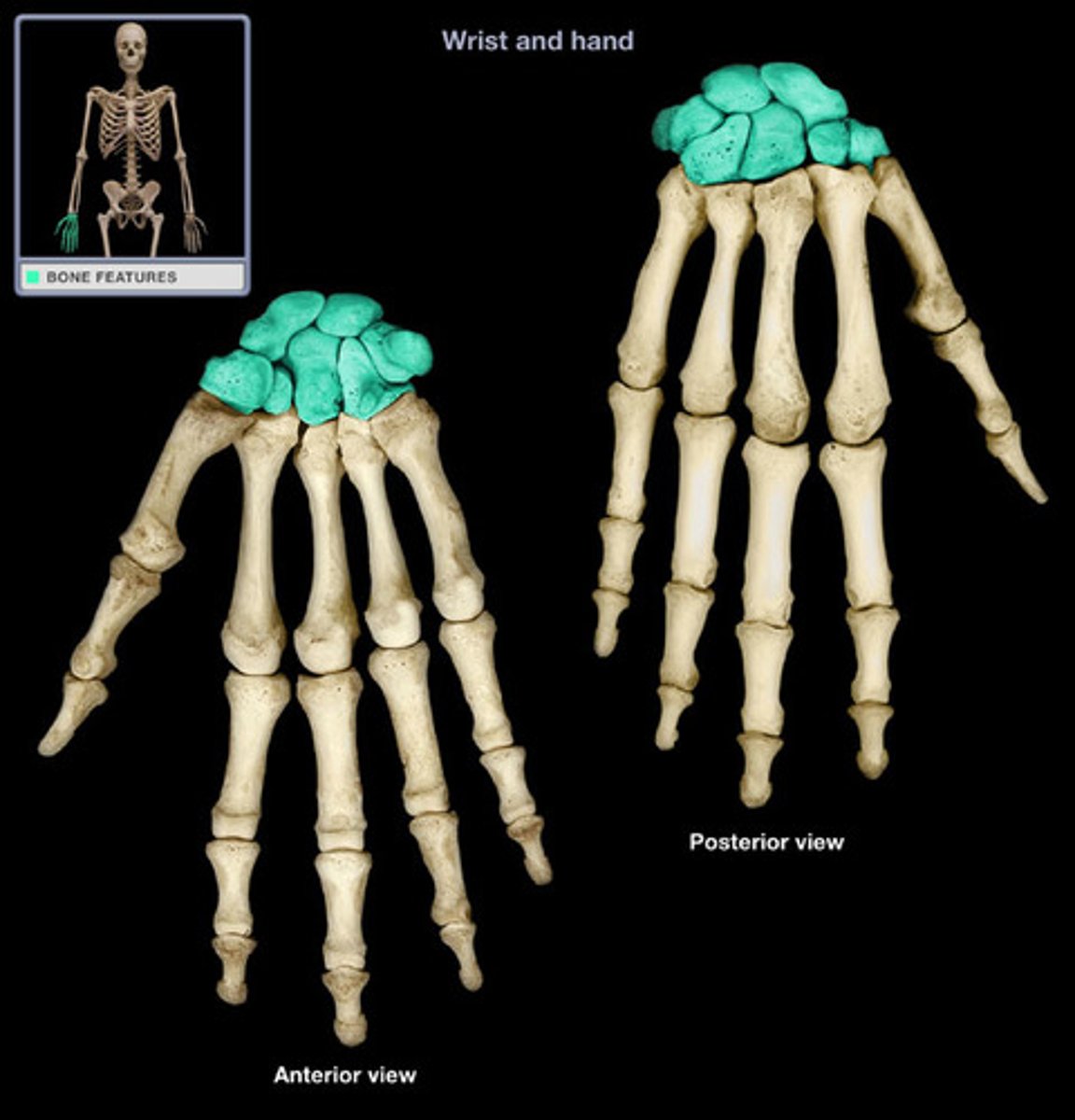
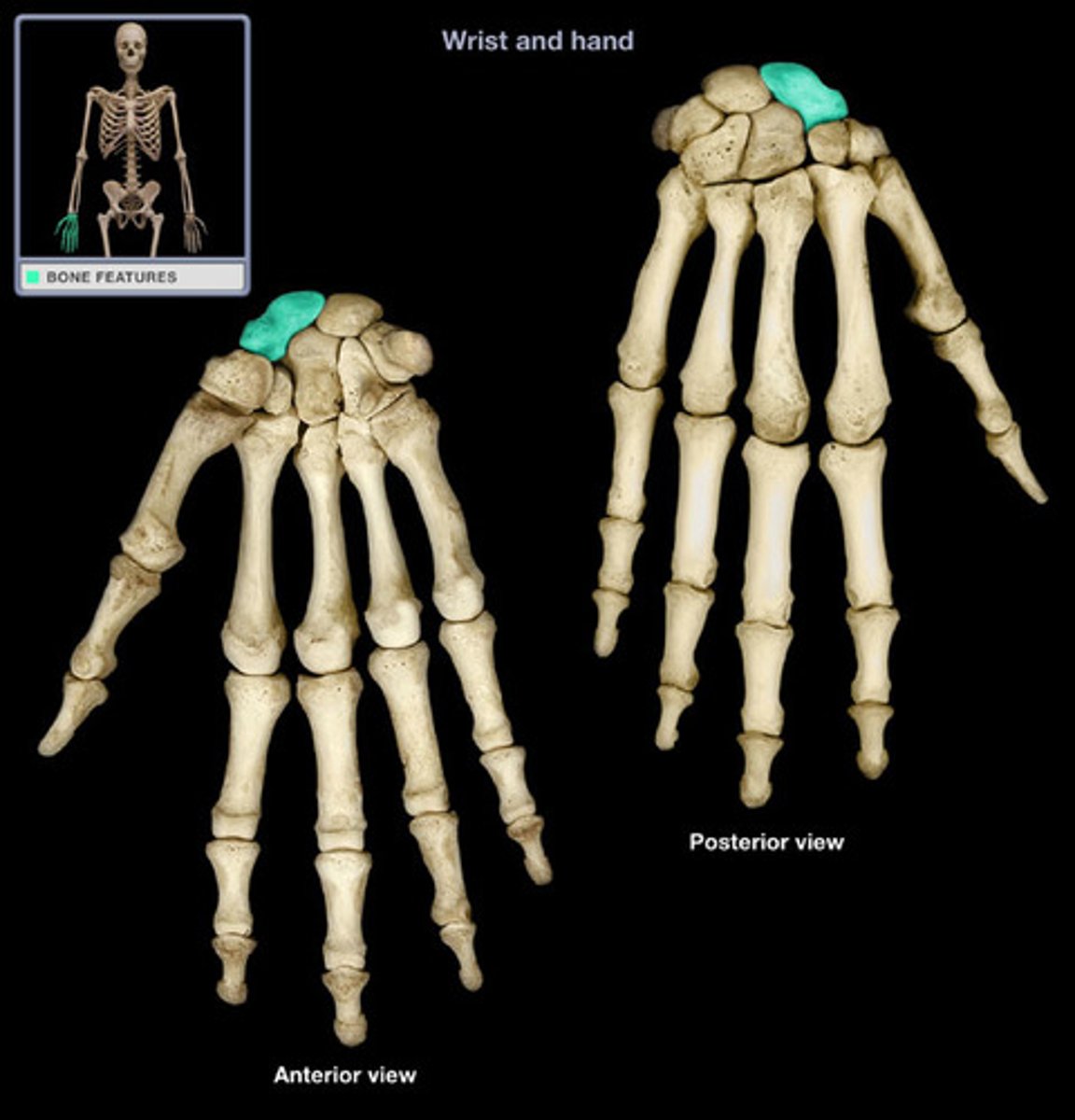
Scaphoid
Largest carpal bone in the wrist, located on the thumb side, commonly fractured.
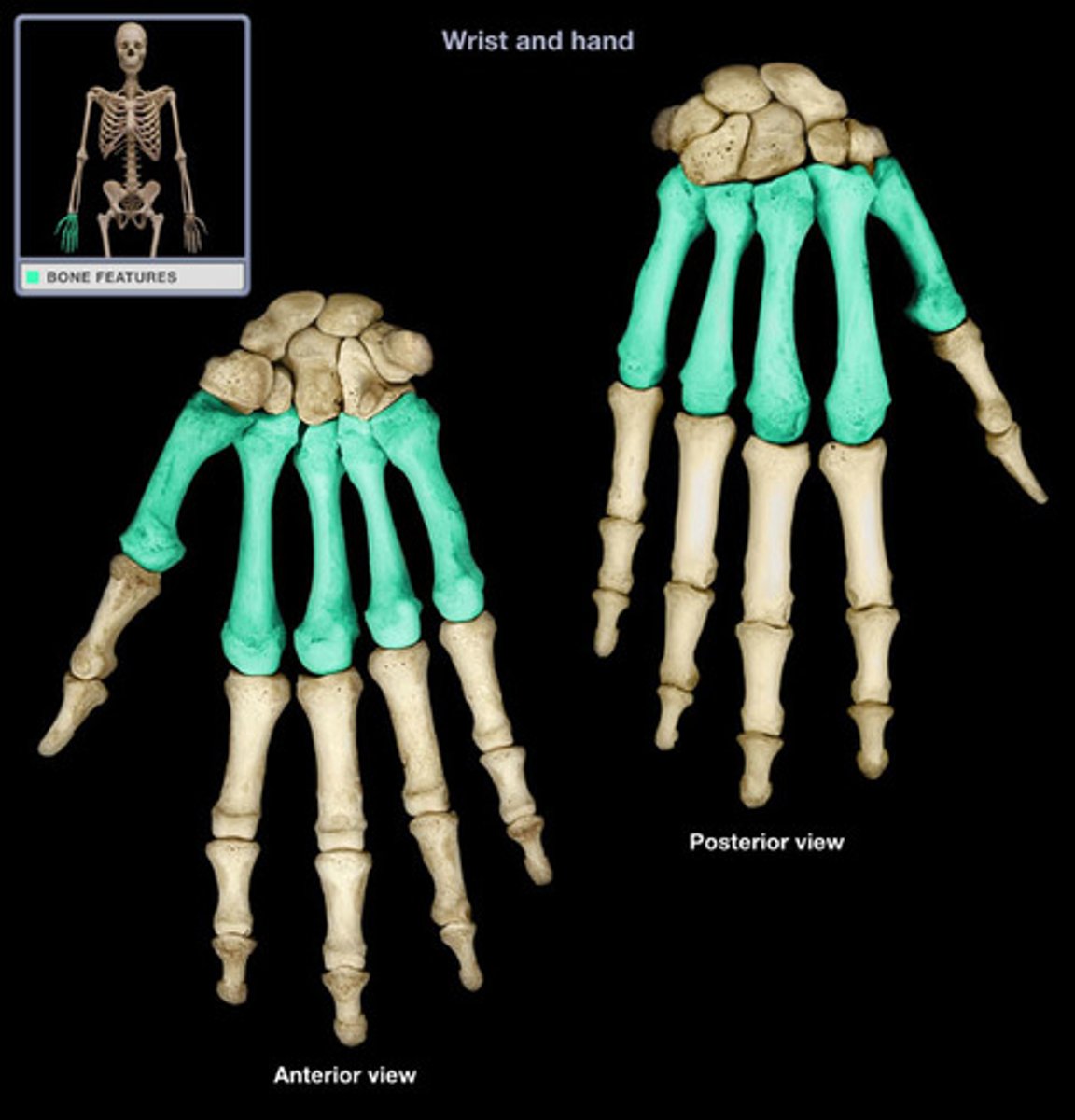
Metacarpals
Five long bones that form the palm of the hand, connecting the carpals to the phalanges.
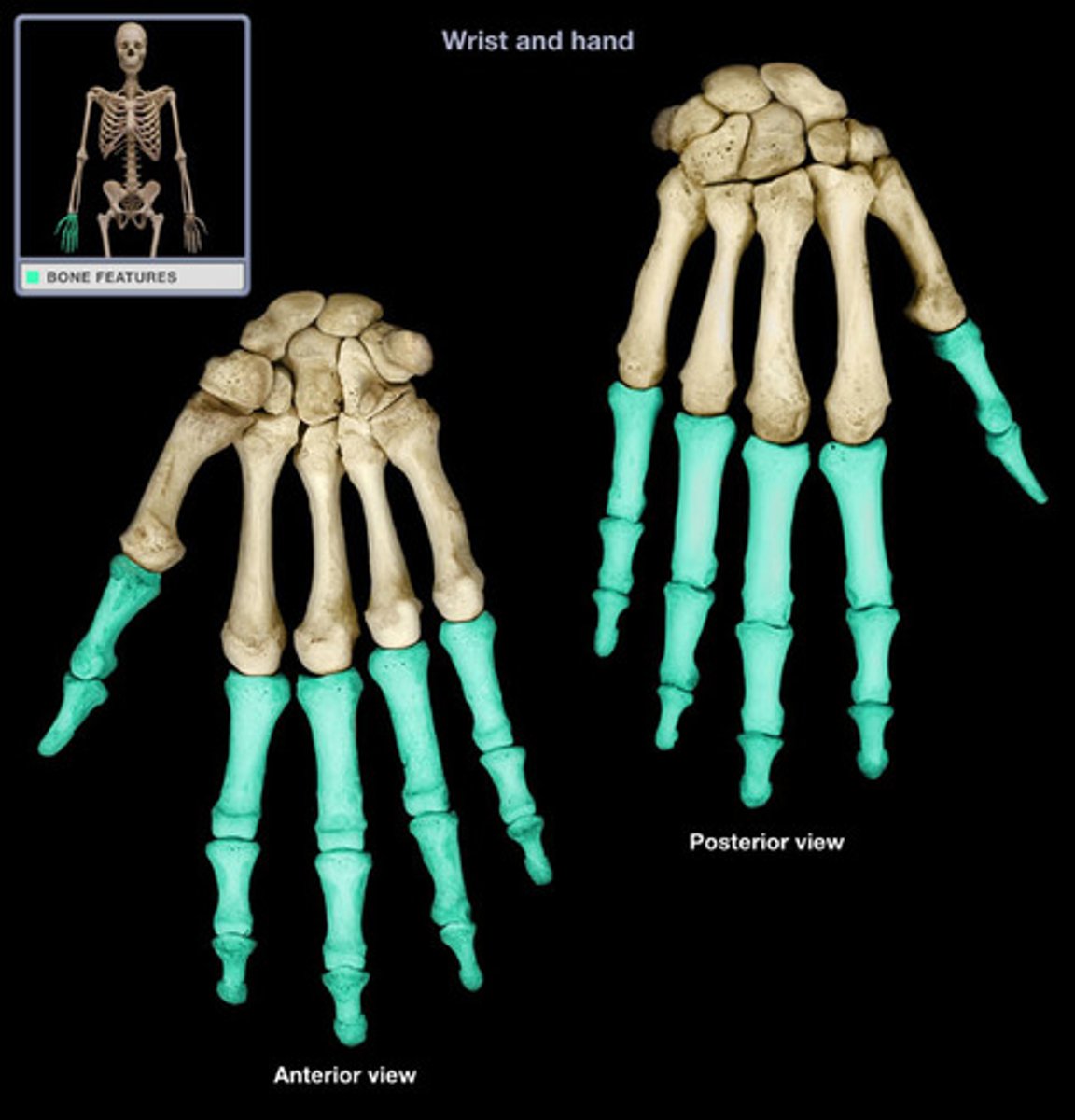
Phalanges
Bones of the fingers and toes; each digit typically has three (proximal, middle, distal), except the thumb/great toe (two).
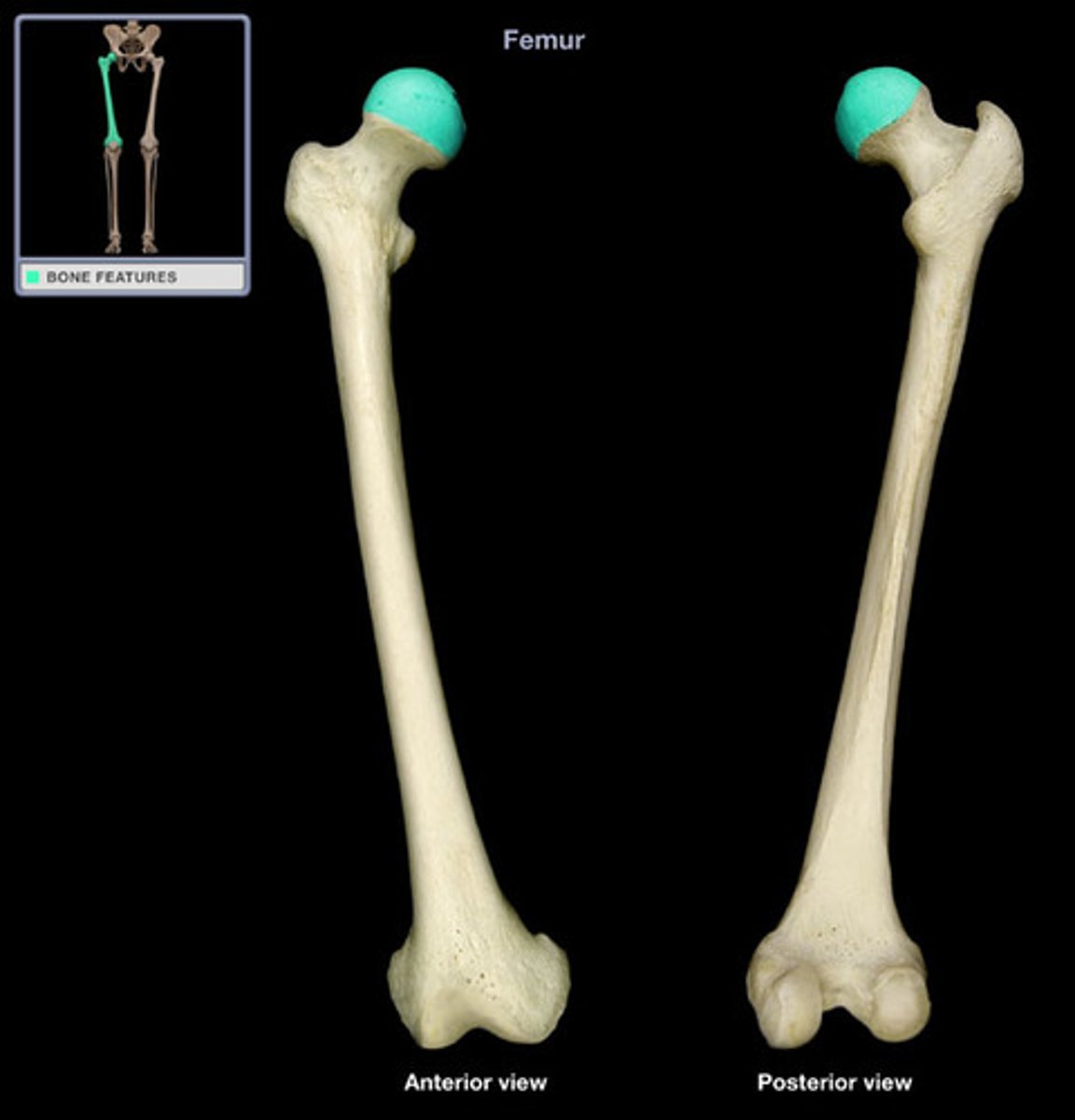
Femur
The longest and strongest bone in the human body, forming the upper leg (thigh bone).
Head of Femur
The rounded proximal end of the femur that articulates with the acetabulum of the pelvis.
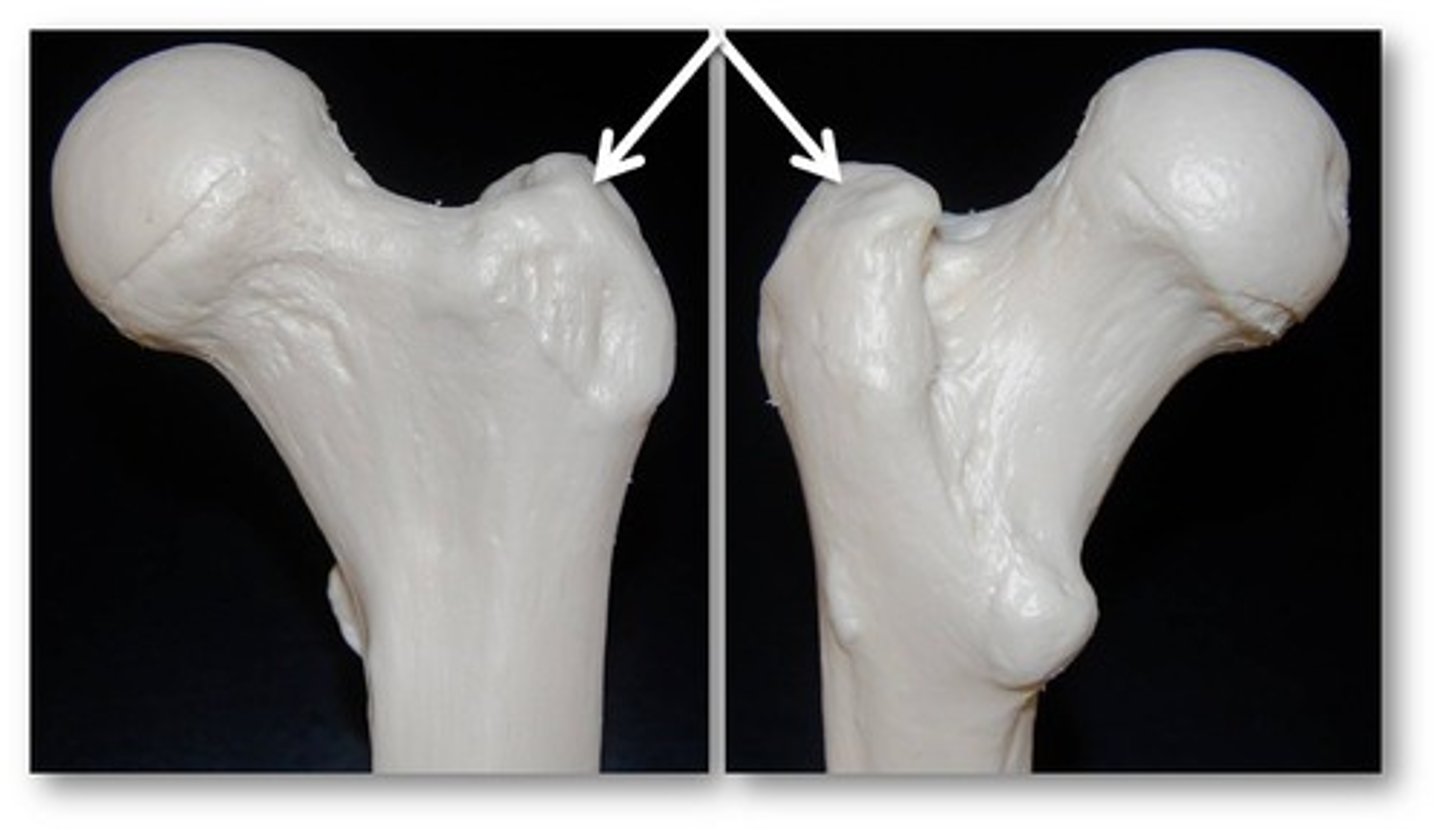
Greater Trochanter
Large, irregular bony prominence located on the proximal lateral aspect of the femur, serving as a muscle attachment site.
Tibia
The larger of the two bones in the lower leg, commonly known as the shin bone, supporting most of the body's weight.
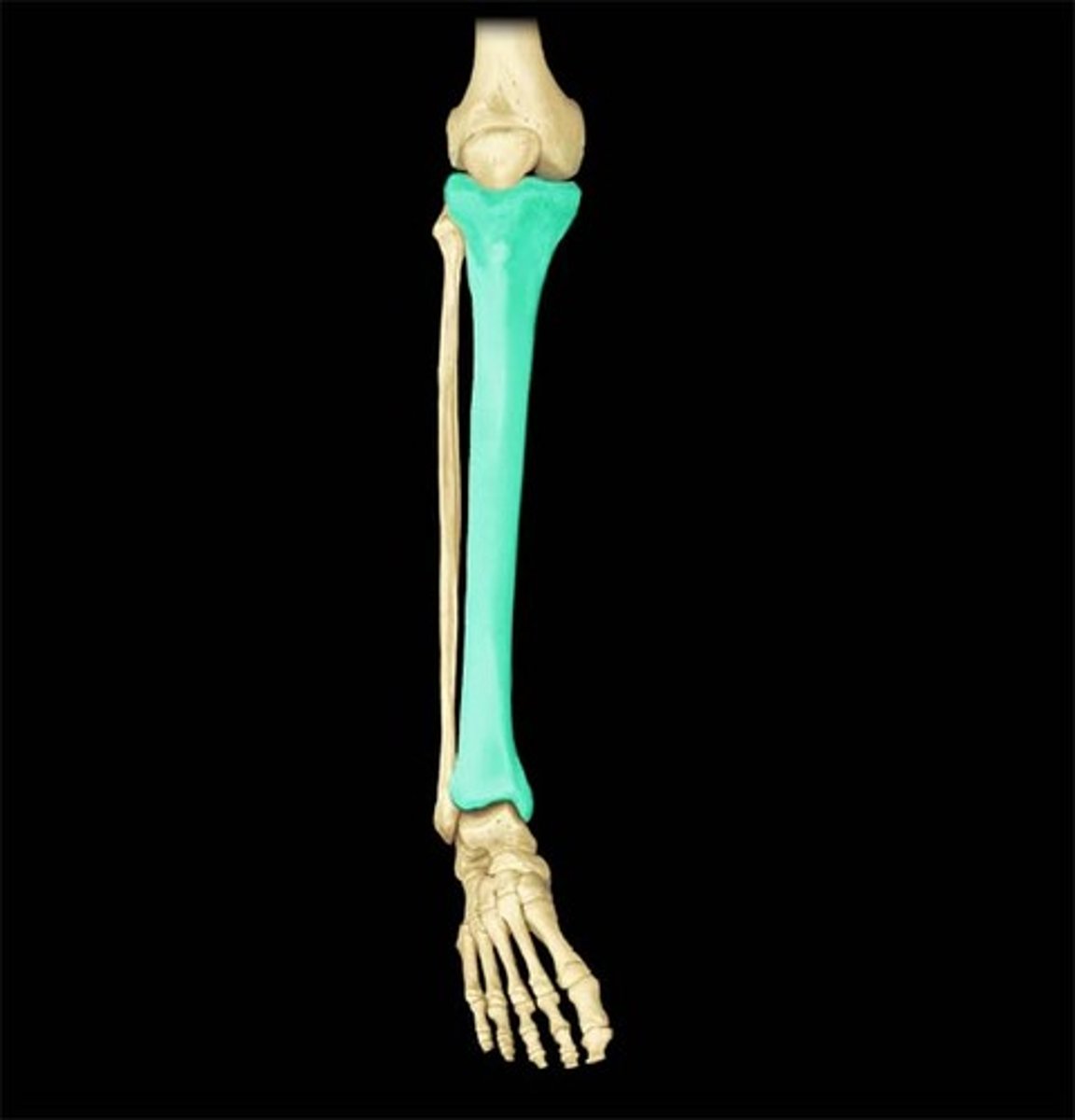
Medial Malleolus
Bony prominence on the medial side of the ankle, formed by the distal end of the tibia.
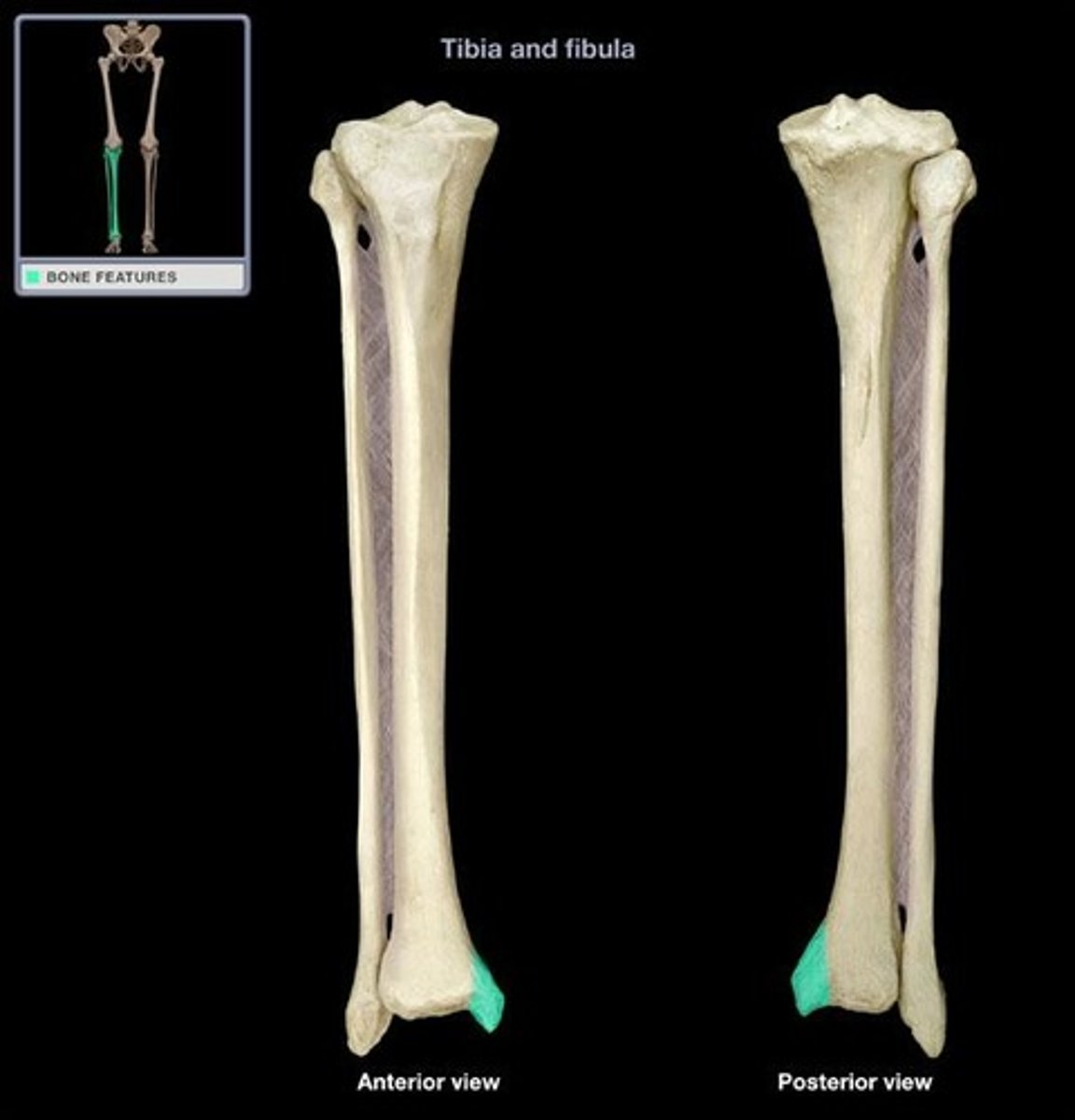
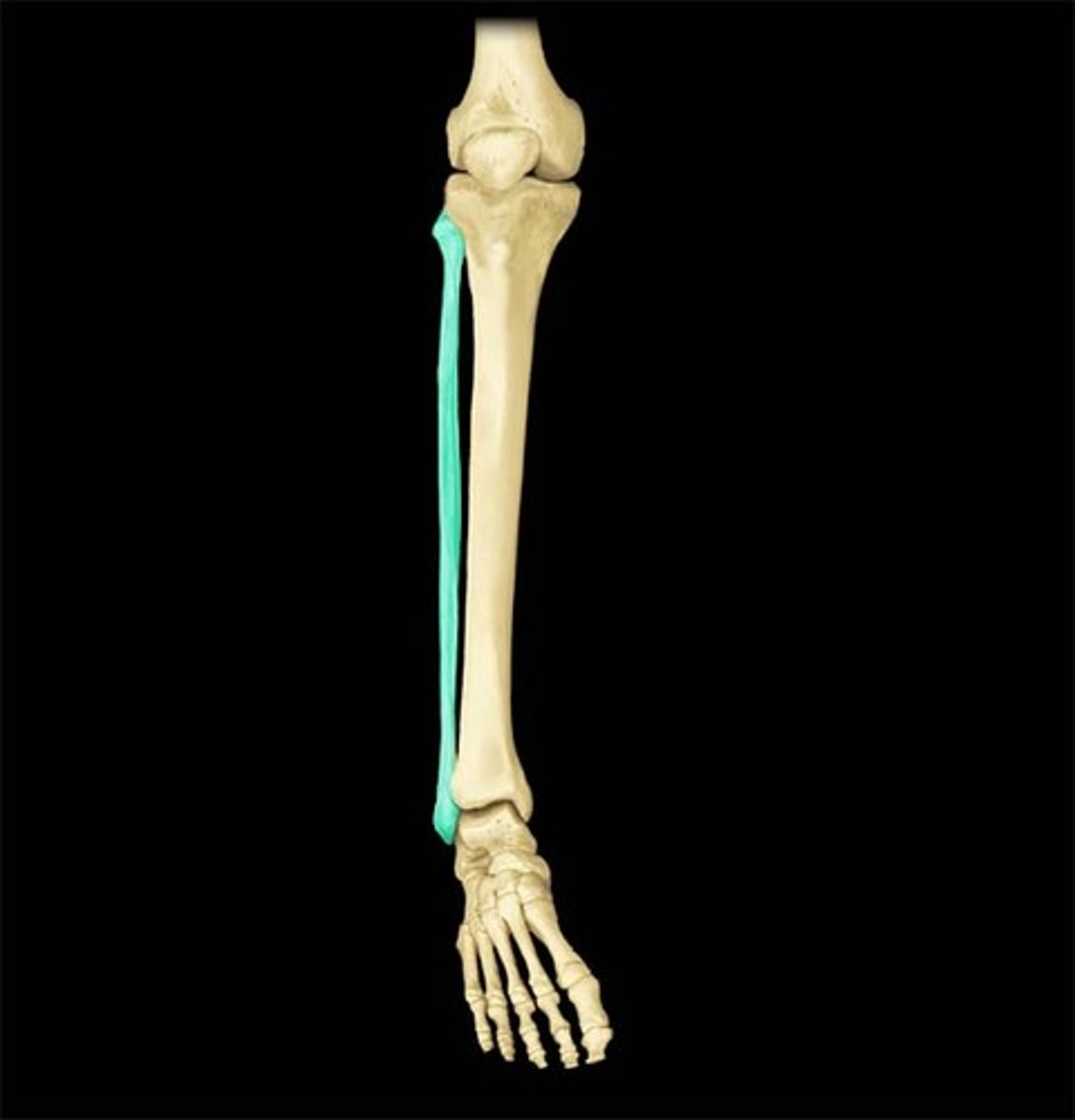
Fibula
The lateral and smaller of the two bones in the lower leg, also known as the calf bone.
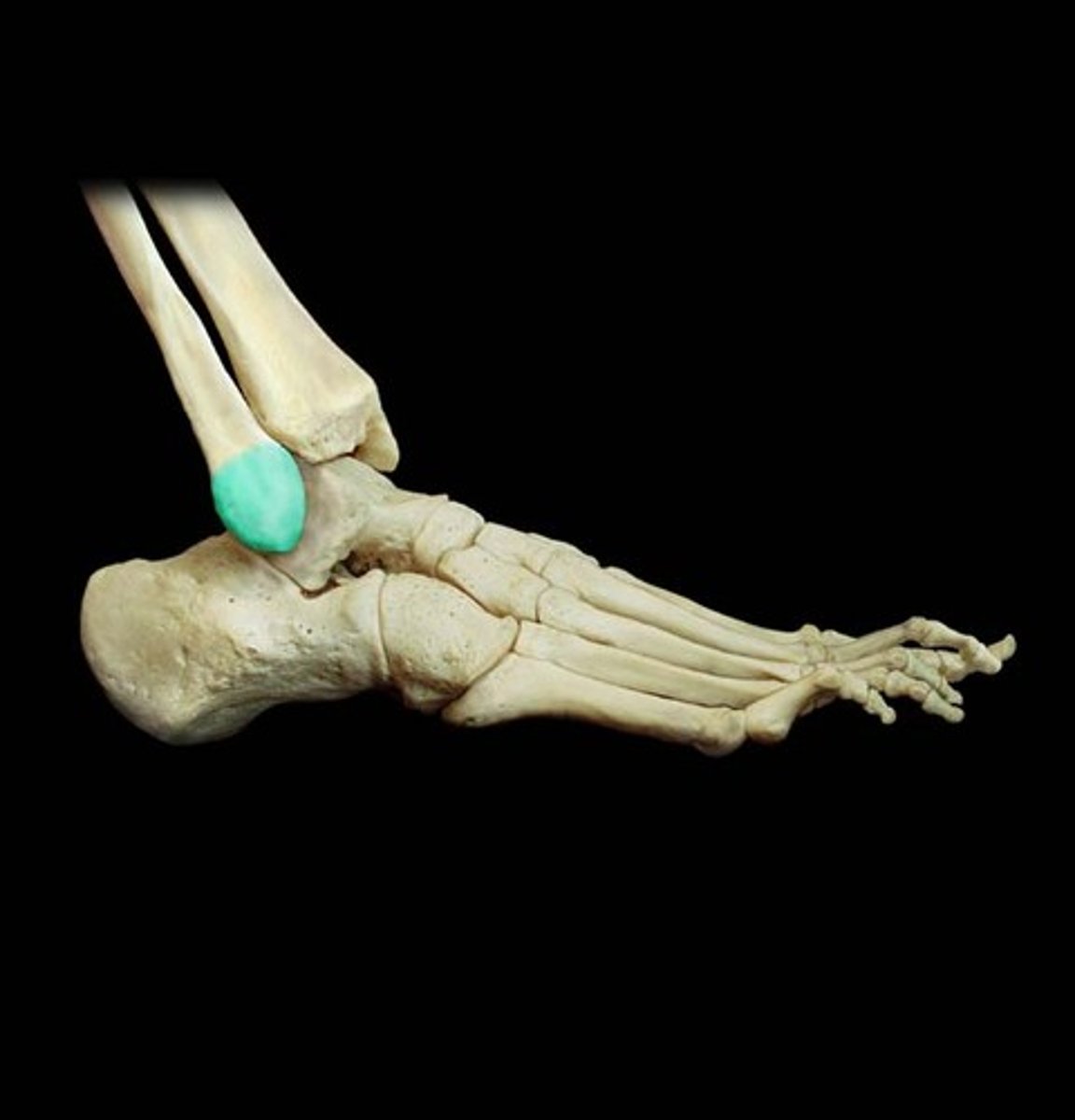
Lateral Malleolus
Bony prominence on the lateral side of the ankle, formed by the distal end of the fibula.
Tarsals
Seven irregularly shaped bones that form the ankle (tarsus) and upper part of the foot.
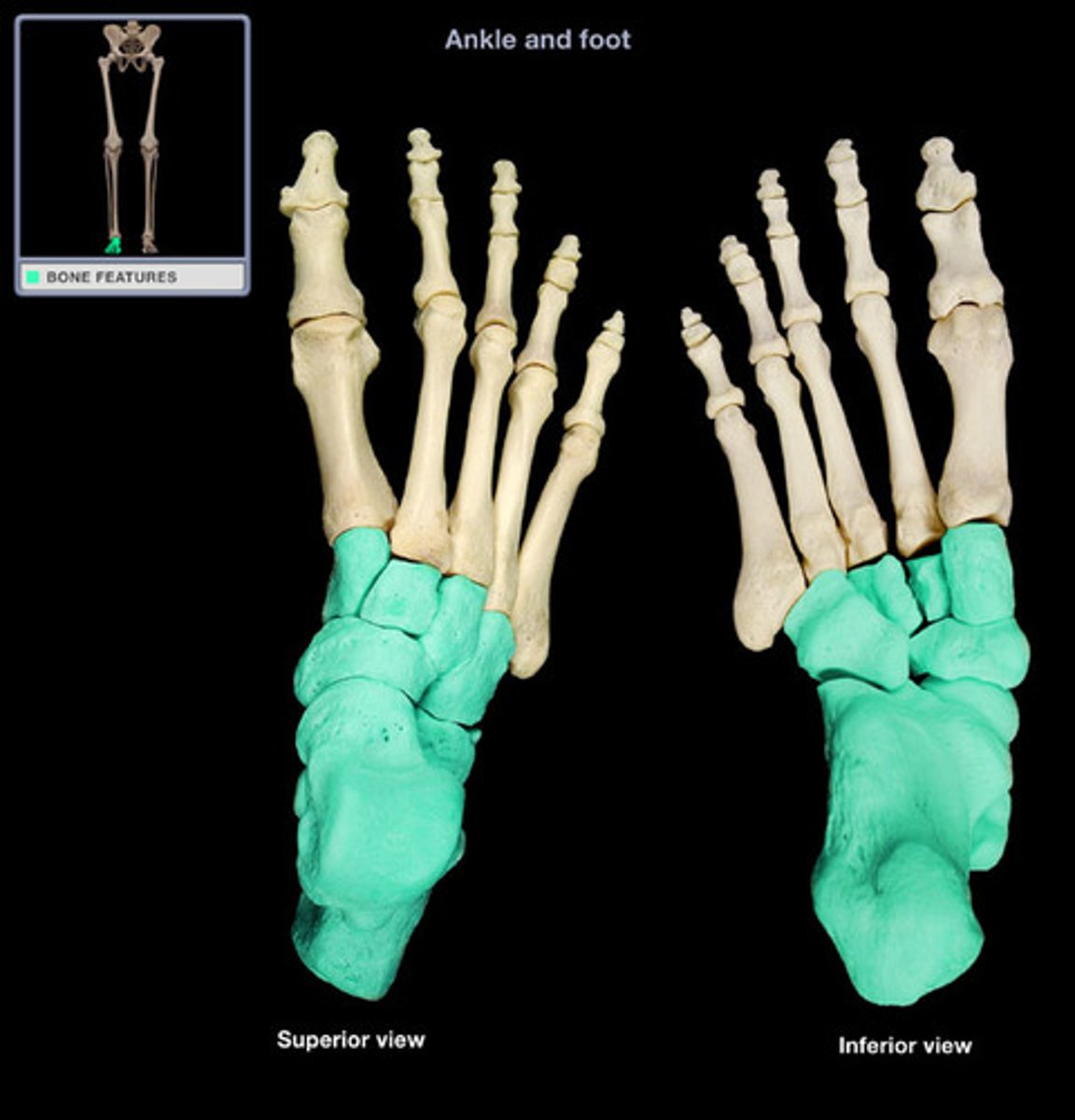
Talus
Second largest tarsal bone, forming the upper part of the ankle joint, articulating with the tibia and fibula.
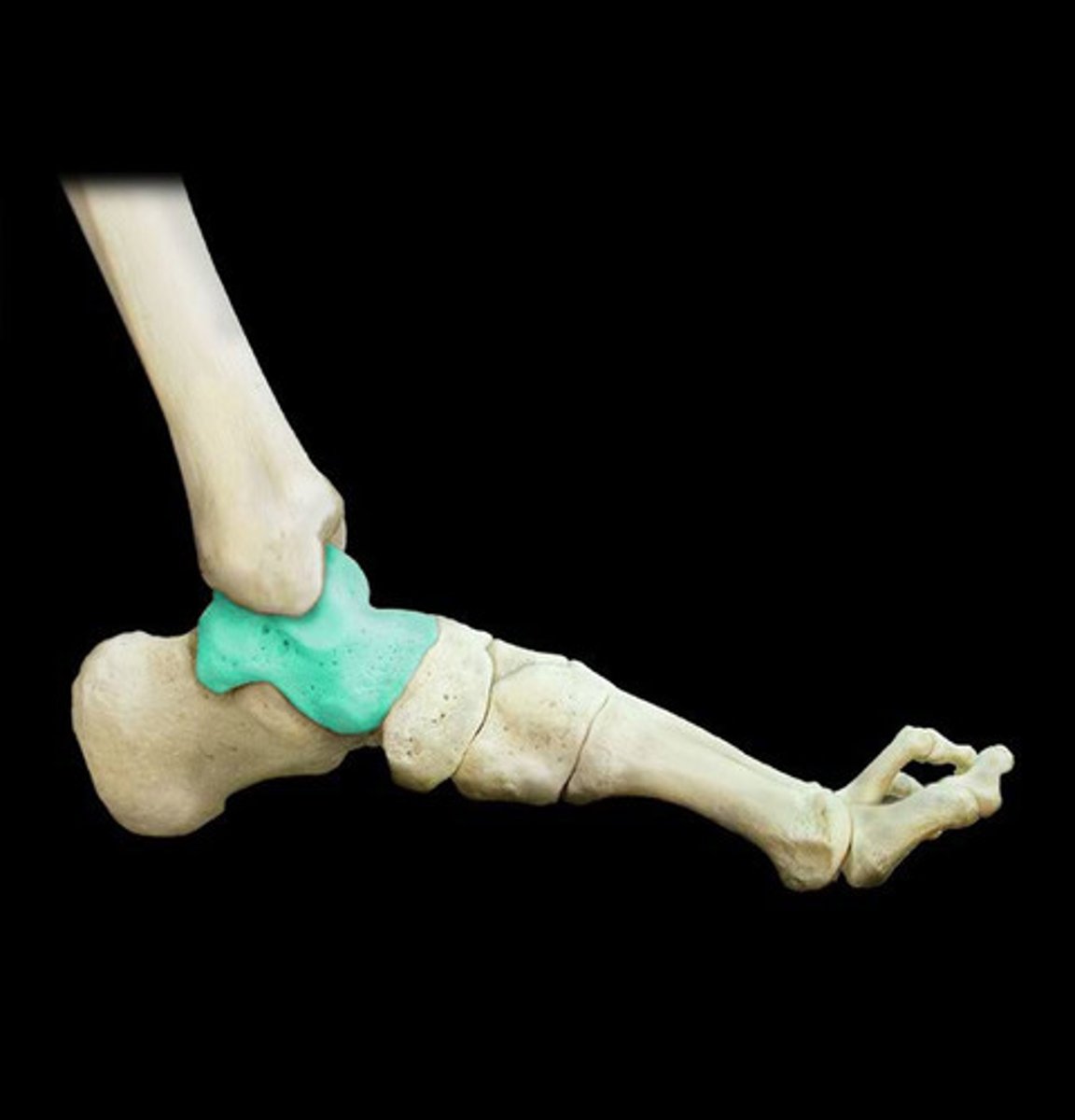
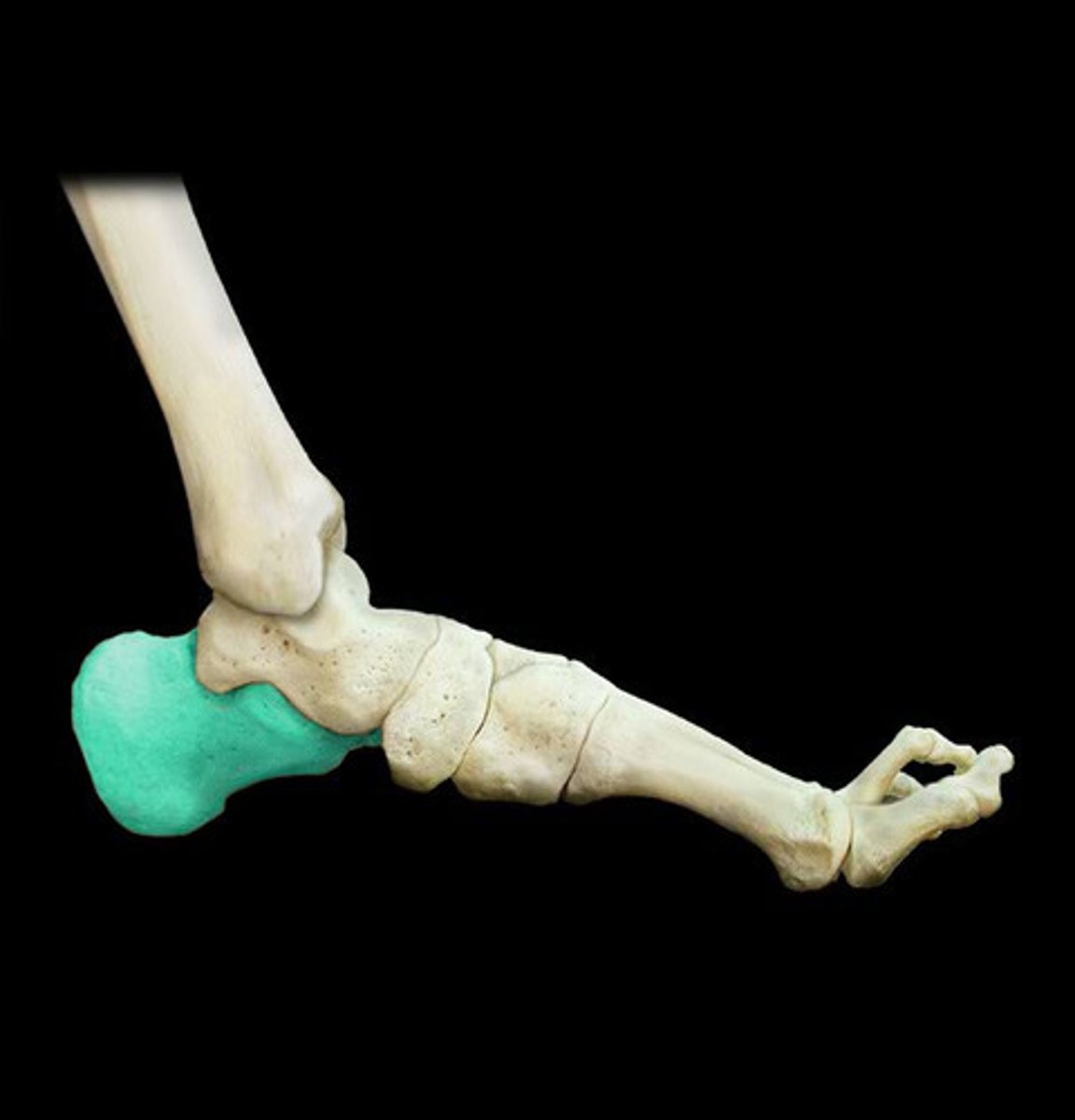
Calcaneus
The largest tarsal bone, forming the heel of the foot; commonly known as the heel bone.
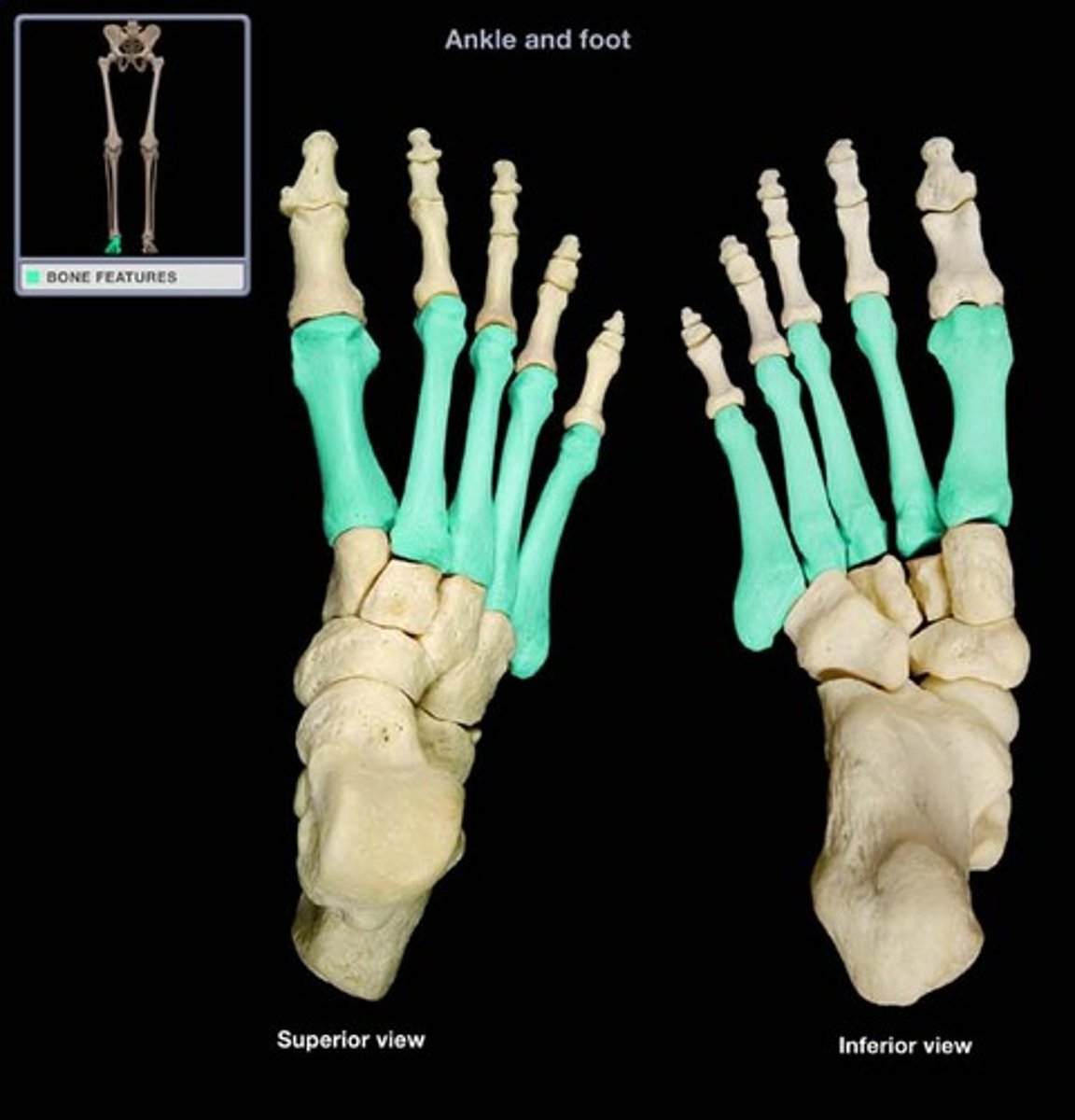
Metatarsals
Five long bones that form the sole of the foot, connecting the tarsals to the phalanges.
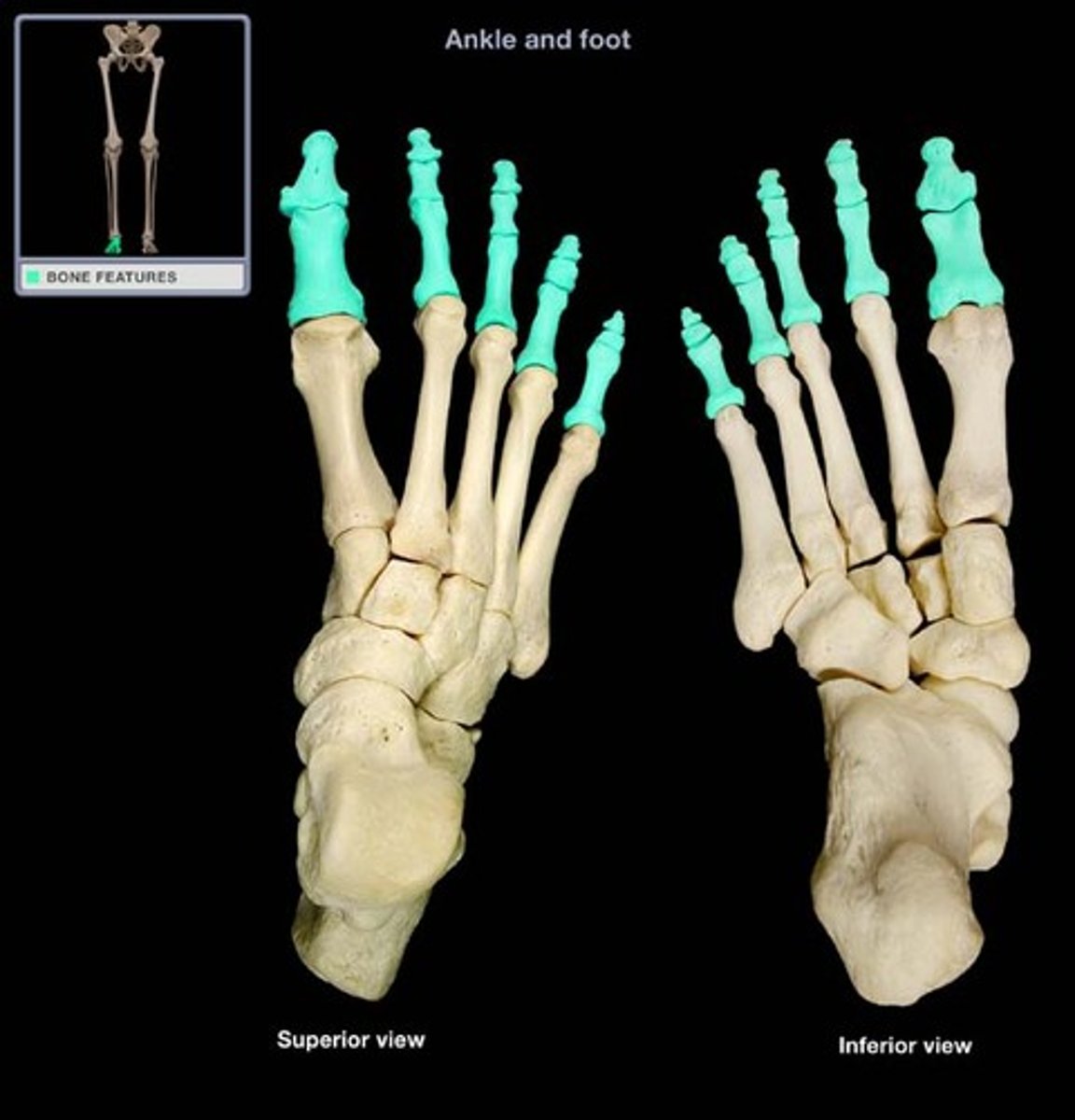
Phalanges
Bones of the fingers and toes; each digit typically has three (proximal, middle, distal), except the thumb/great toe (two).
Deltoid
Large, triangular muscle forming the rounded contour of the shoulder.
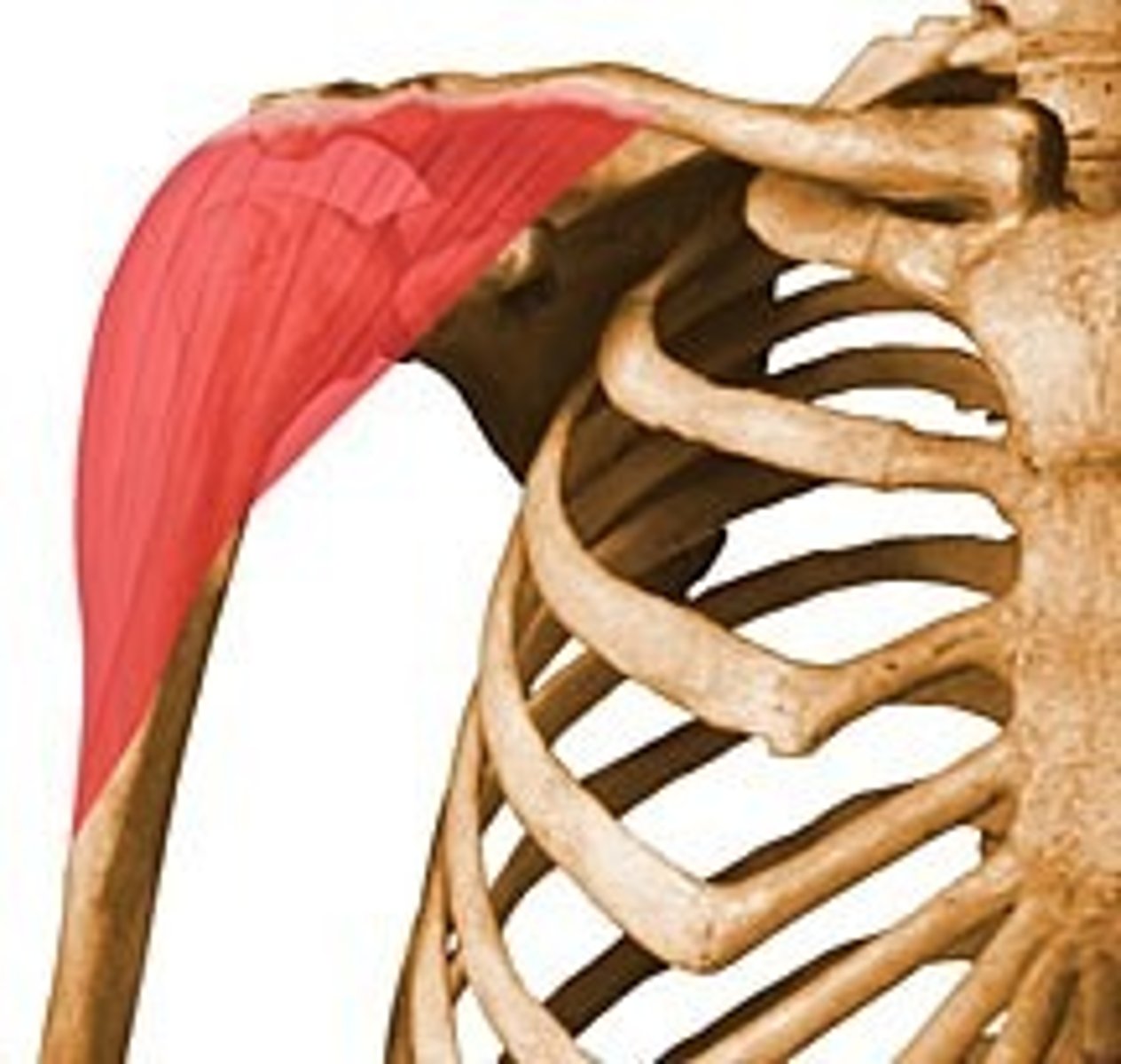
Pectoralis Major
Large, fan-shaped muscle covering the upper part of the chest.
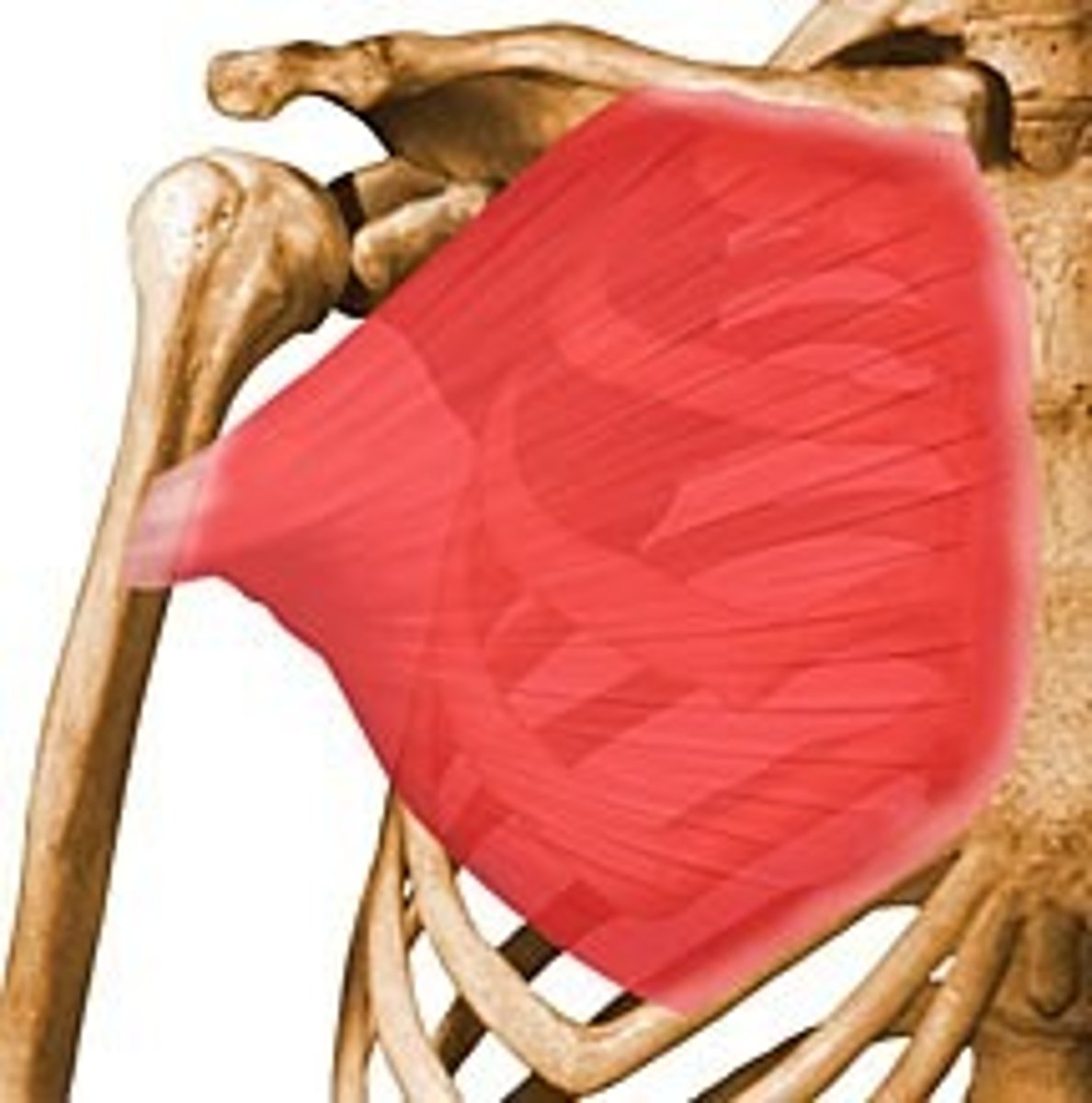
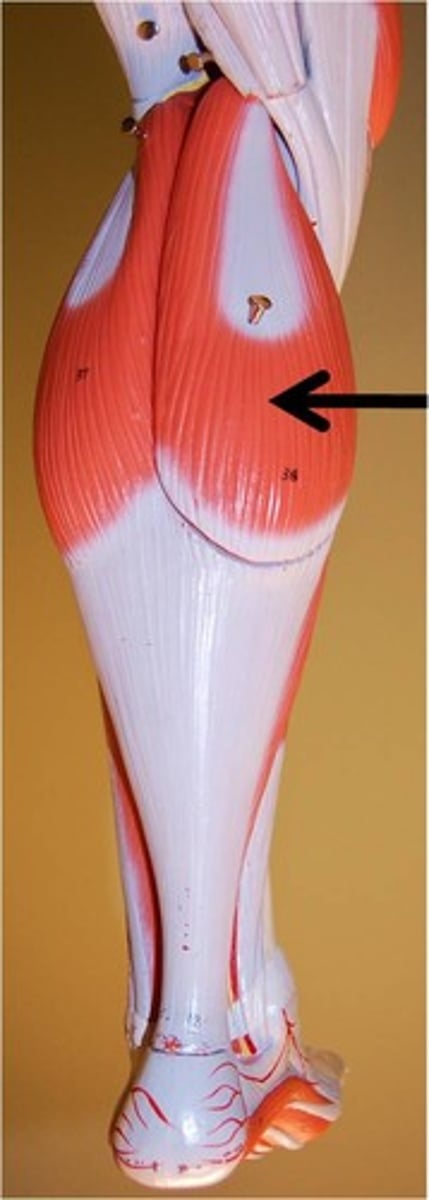
Gluteus Maximus
Largest and most superficial of the three gluteal muscles, forming the prominence of the buttocks.
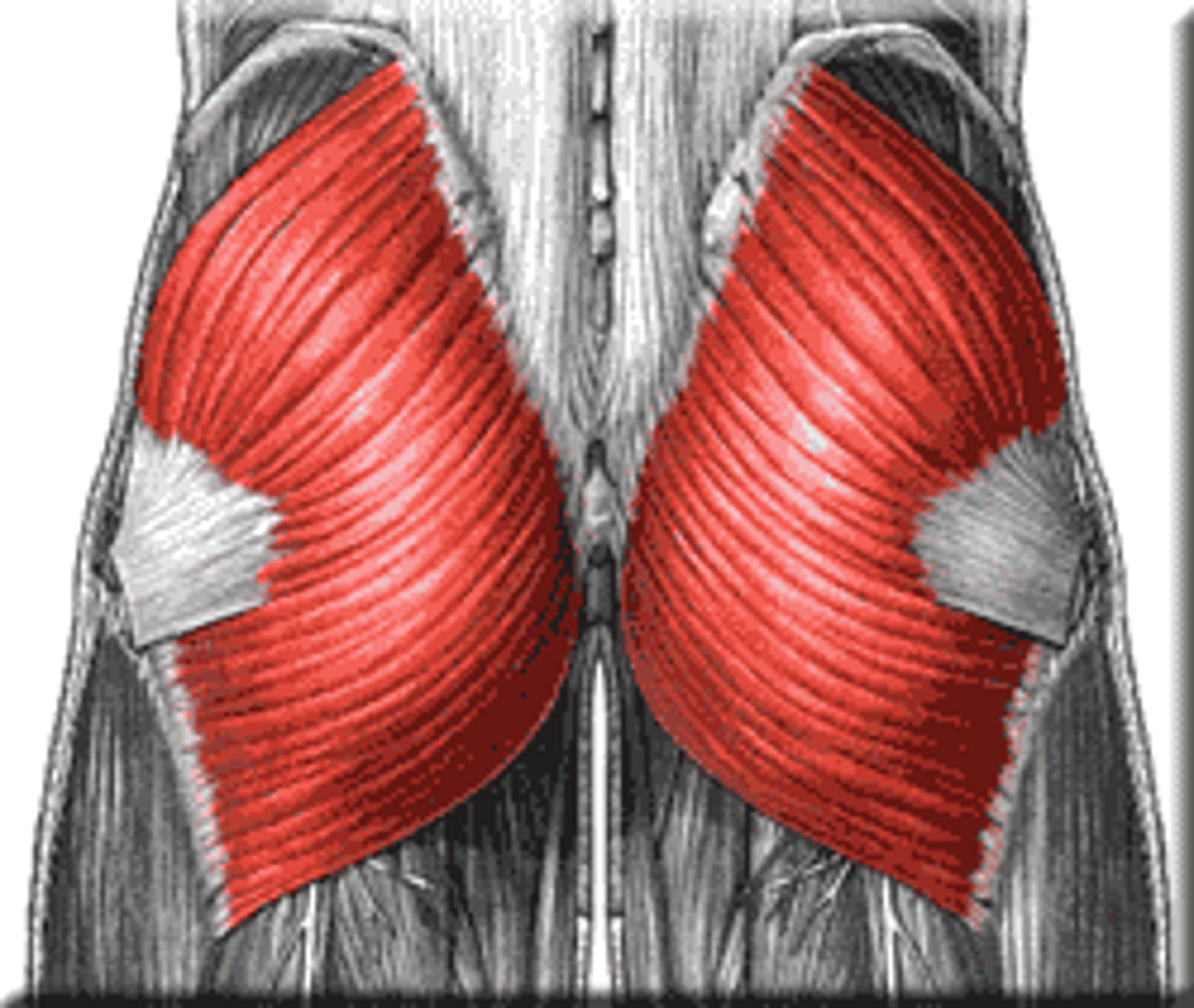
Triceps Brachii
Large muscle on the posterior aspect of the upper arm, responsible for elbow extension.
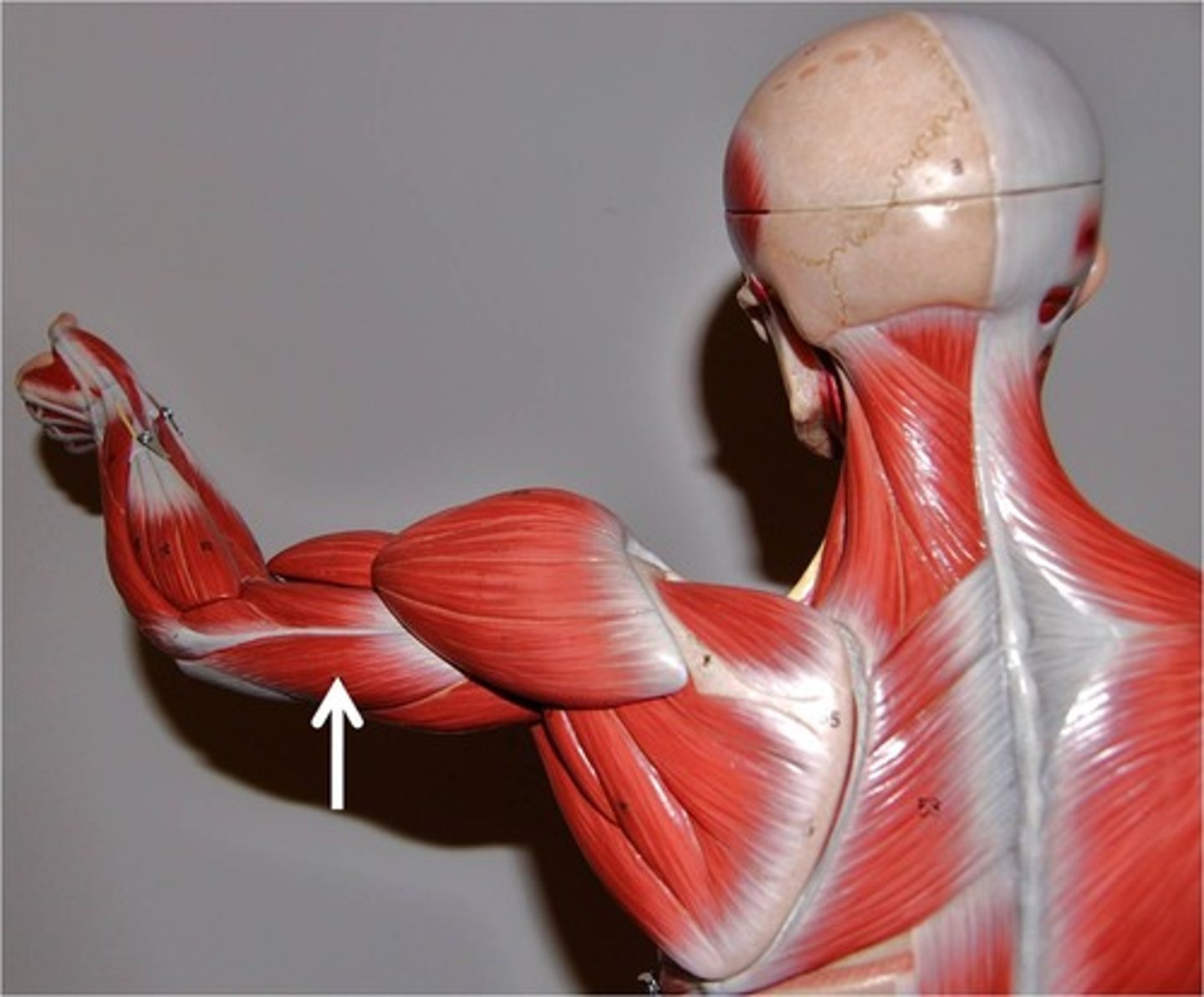
Biceps Brachii
Two-headed muscle on the anterior aspect of the upper arm, responsible for elbow flexion.
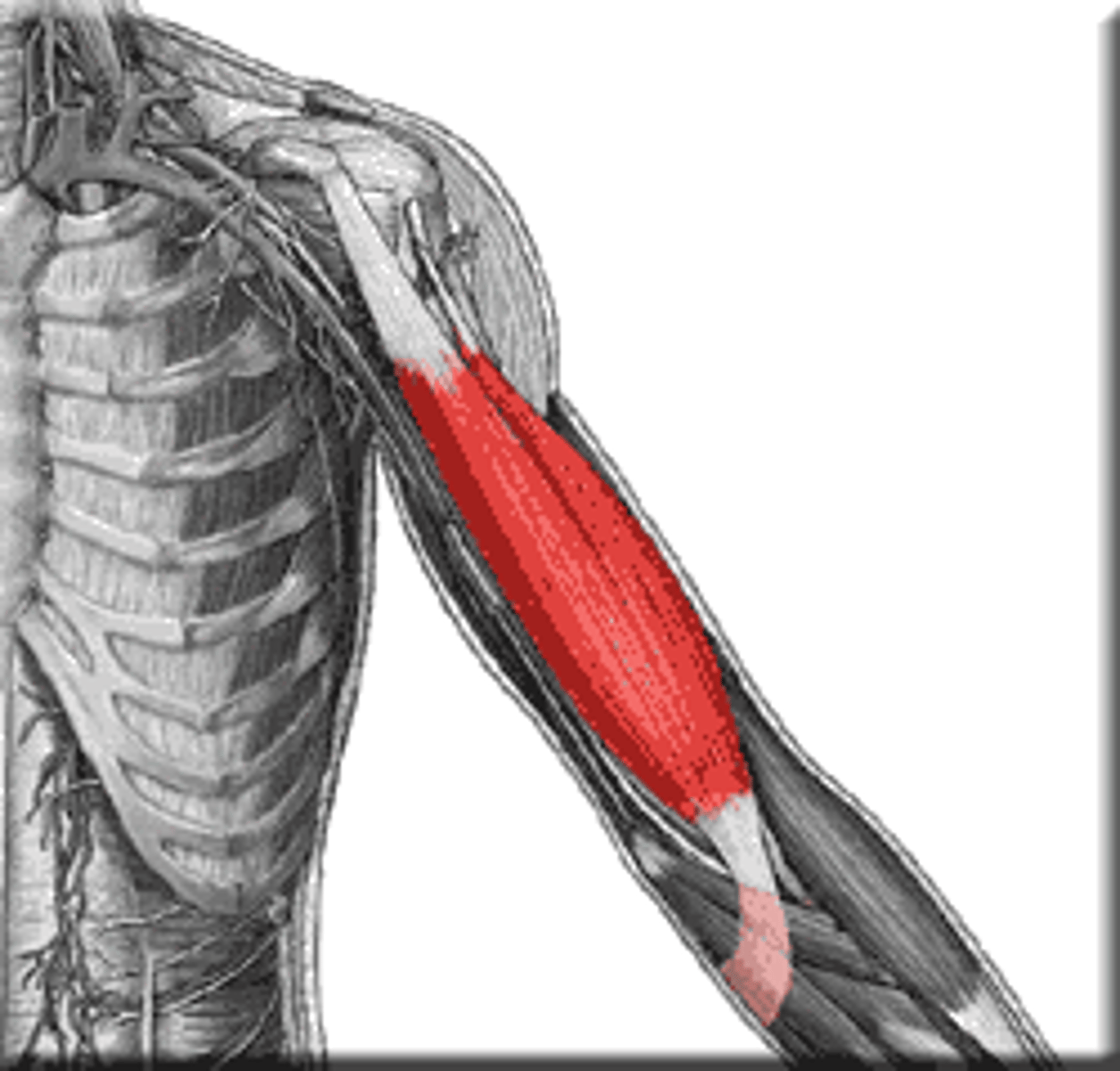
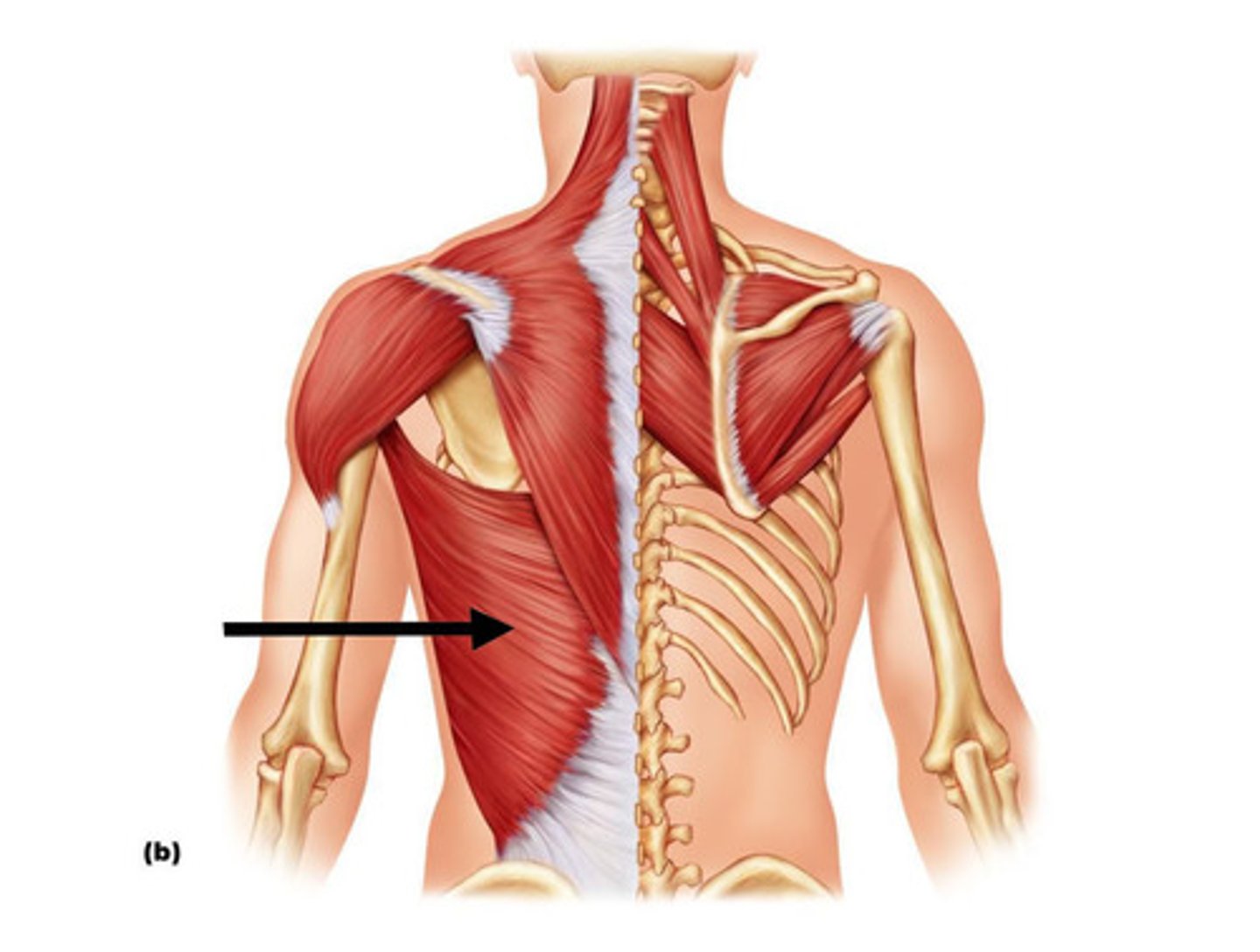
Latissimus Dorsi
Large, flat muscle of the lower back, extending to the upper arm.
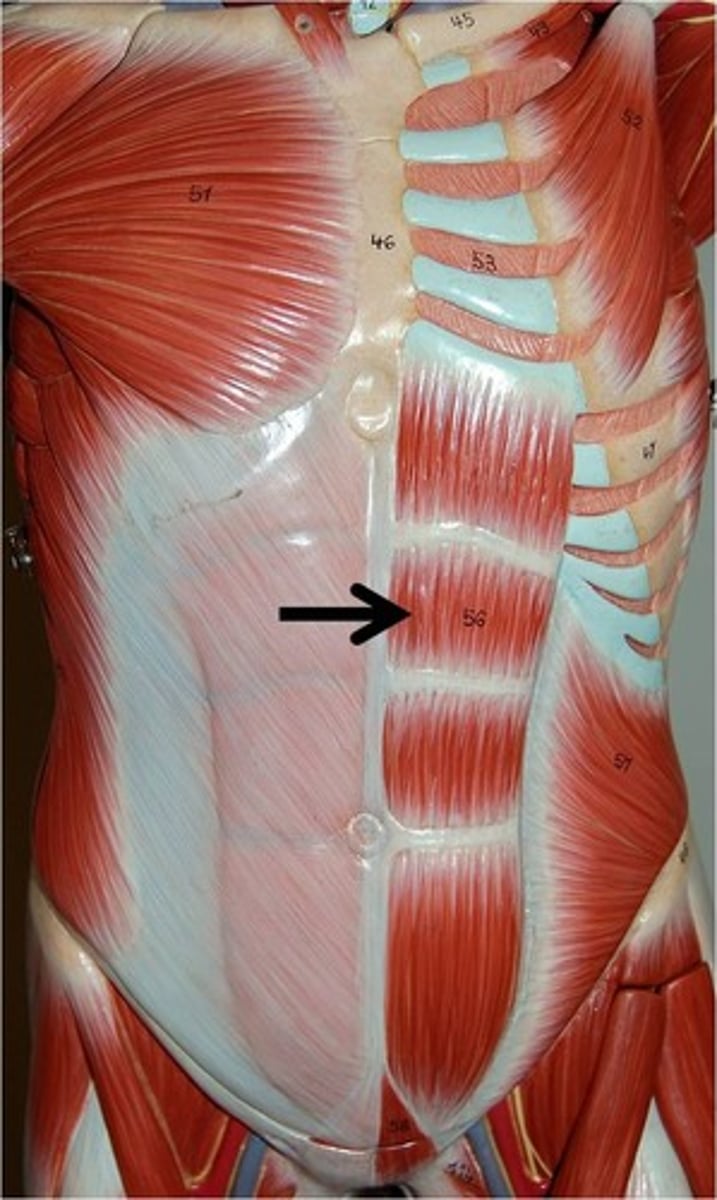
Rectus Abdominis
Paired muscle running vertically on each side of the anterior abdominal wall; commonly known as 'abs'.
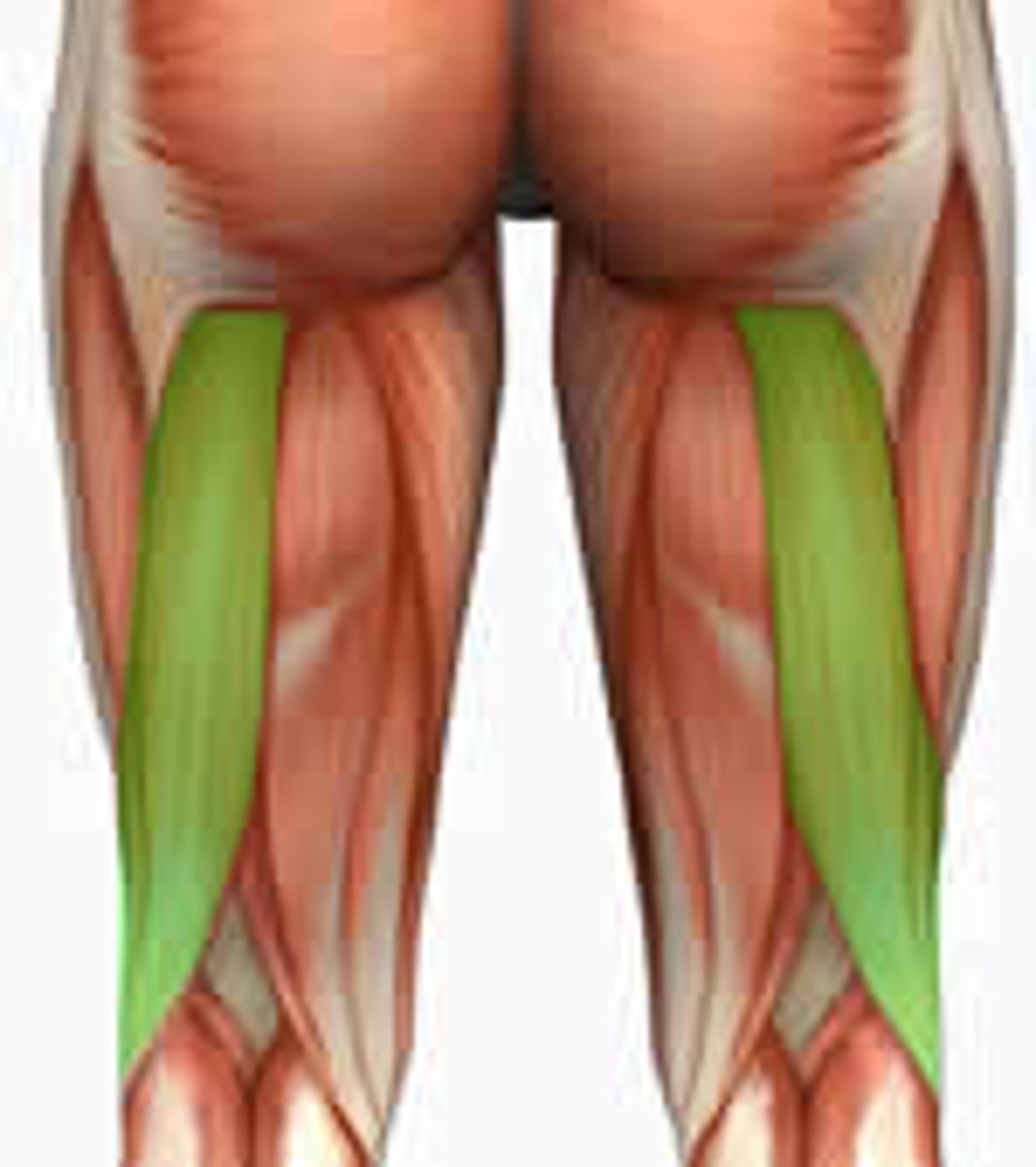
Biceps Femoris
One of the three hamstring muscles, located on the posterior thigh.
Rectus Femoris
One of the four quadriceps muscles, located centrally on the anterior thigh.
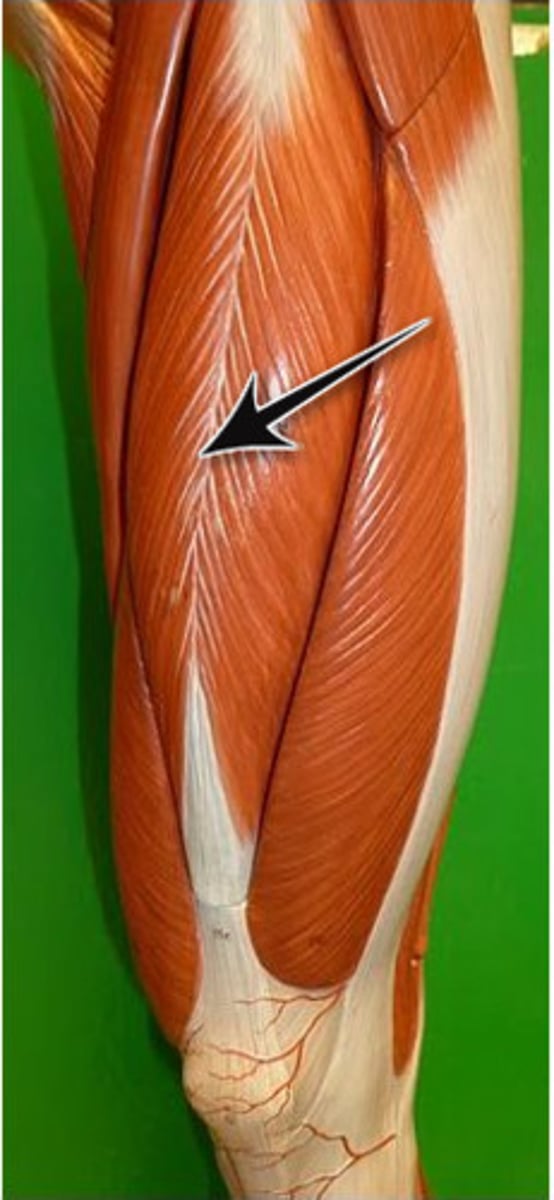
Gastrocnemius
Large, superficial muscle at the posterior leg, forming part of the calf.
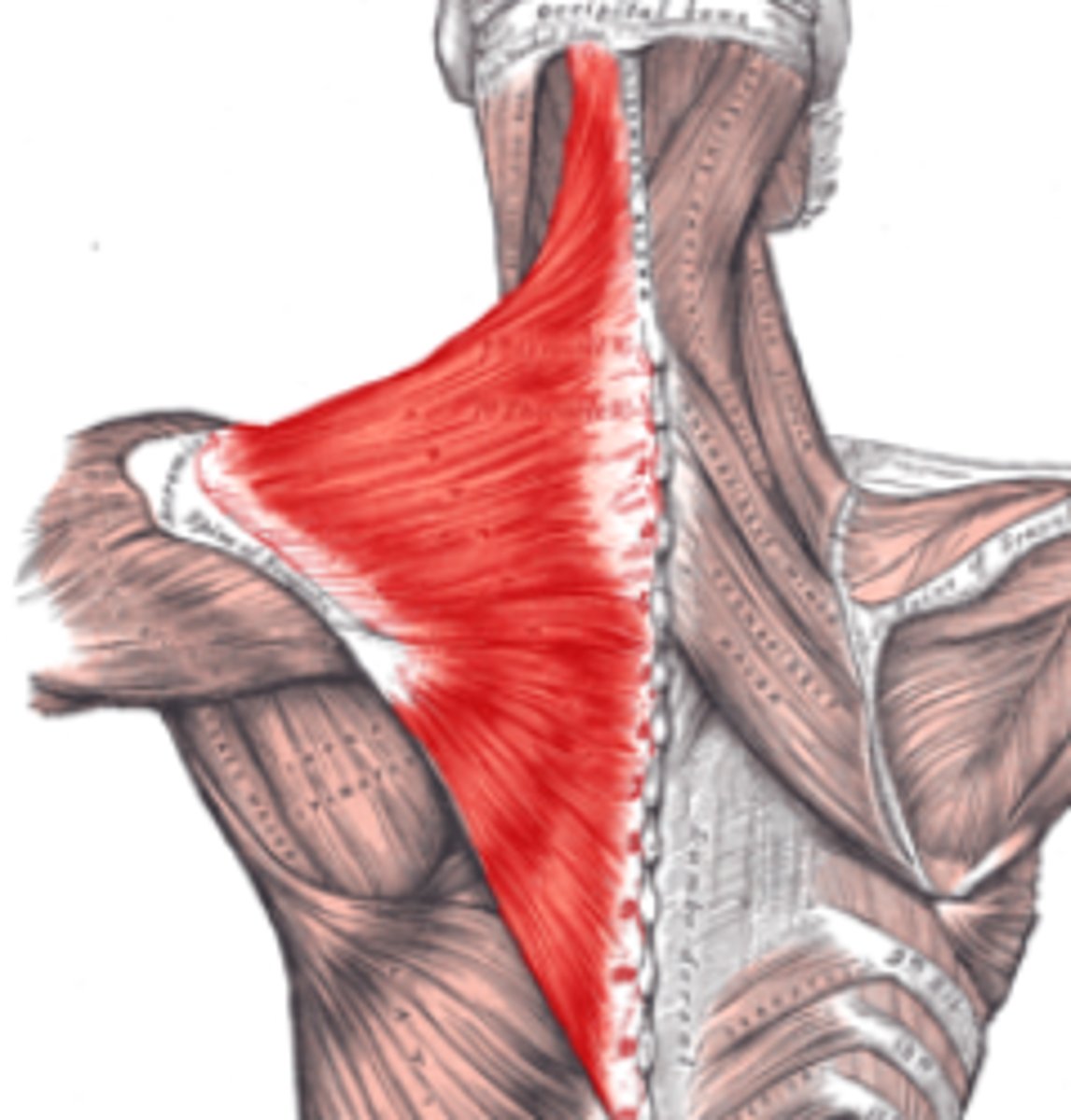
Trapezius
Large, superficial muscle extending from the neck to the mid-back and shoulders.
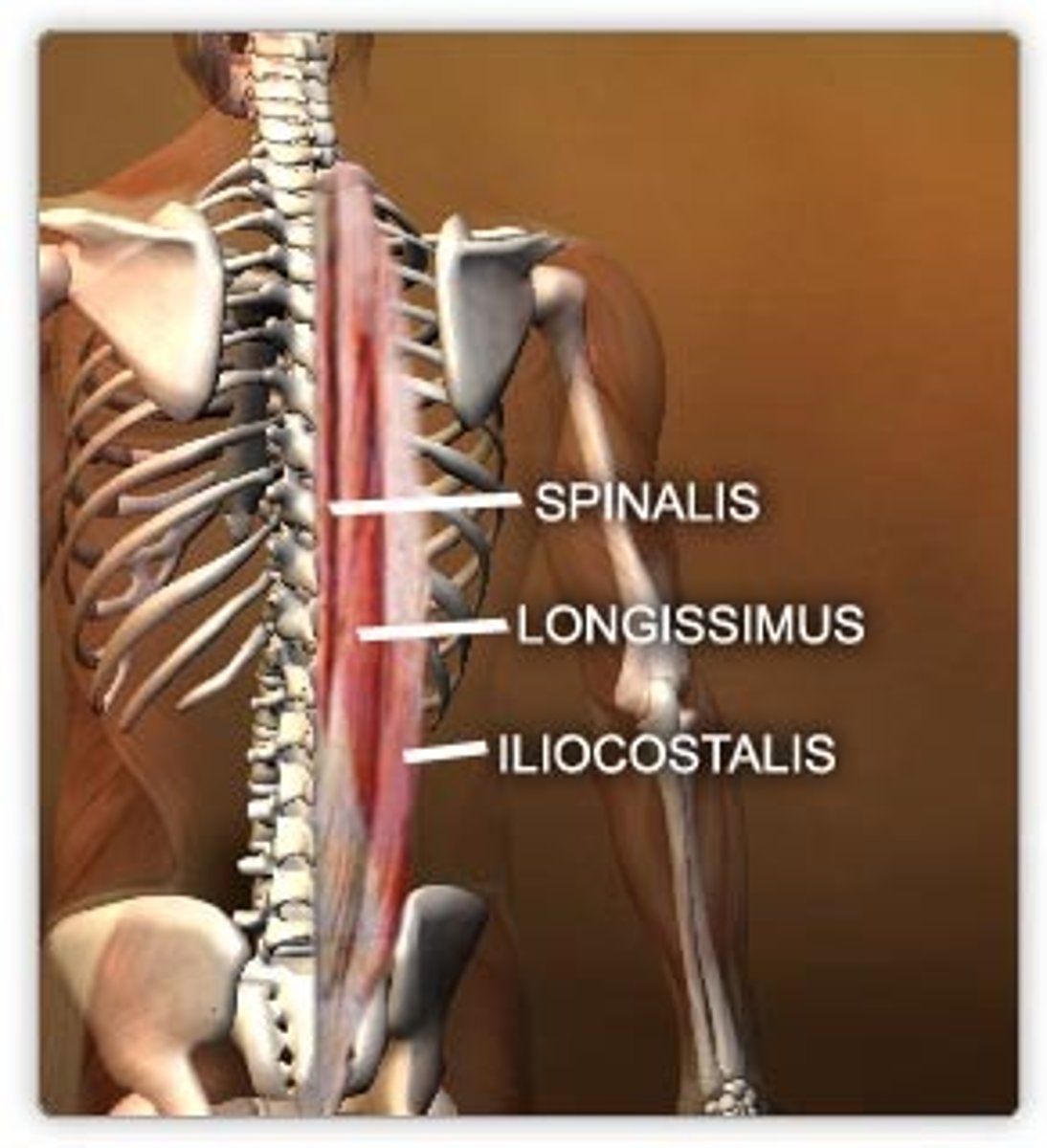
Erector Spinae Group
Group of muscles that run along the vertebral column, primarily responsible for extending and straightening the back.
Tibialis Anterior
Muscle located on the anterior lower leg, primarily responsible for dorsiflexion and inversion of the foot.
Anterior
Front or toward the front.
Posterior
Back or toward the back.
Superior
Above or higher than another body part.
Inferior
Below or lower than another body part.
Medial
Toward the midline of the body.
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body.
Proximal
Closer to the point of attachment or origin of a limb to the body trunk.
Distal
Farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk.
Function of Deltoid
Shoulder abduction.
Function of Trapezius
Elevation, retraction, and rotation of the scapula.
Function of Pectoralis Major
Flexes, adducts, and medially rotates the humerus.
Function of Latissimus Dorsi
Extends, adducts, and medially rotates the humerus.
Function of Biceps Brachii
Flexes the elbow and supinates the forearm.
Function of Triceps Brachii
Extends the elbow.