The General and Special Senses
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
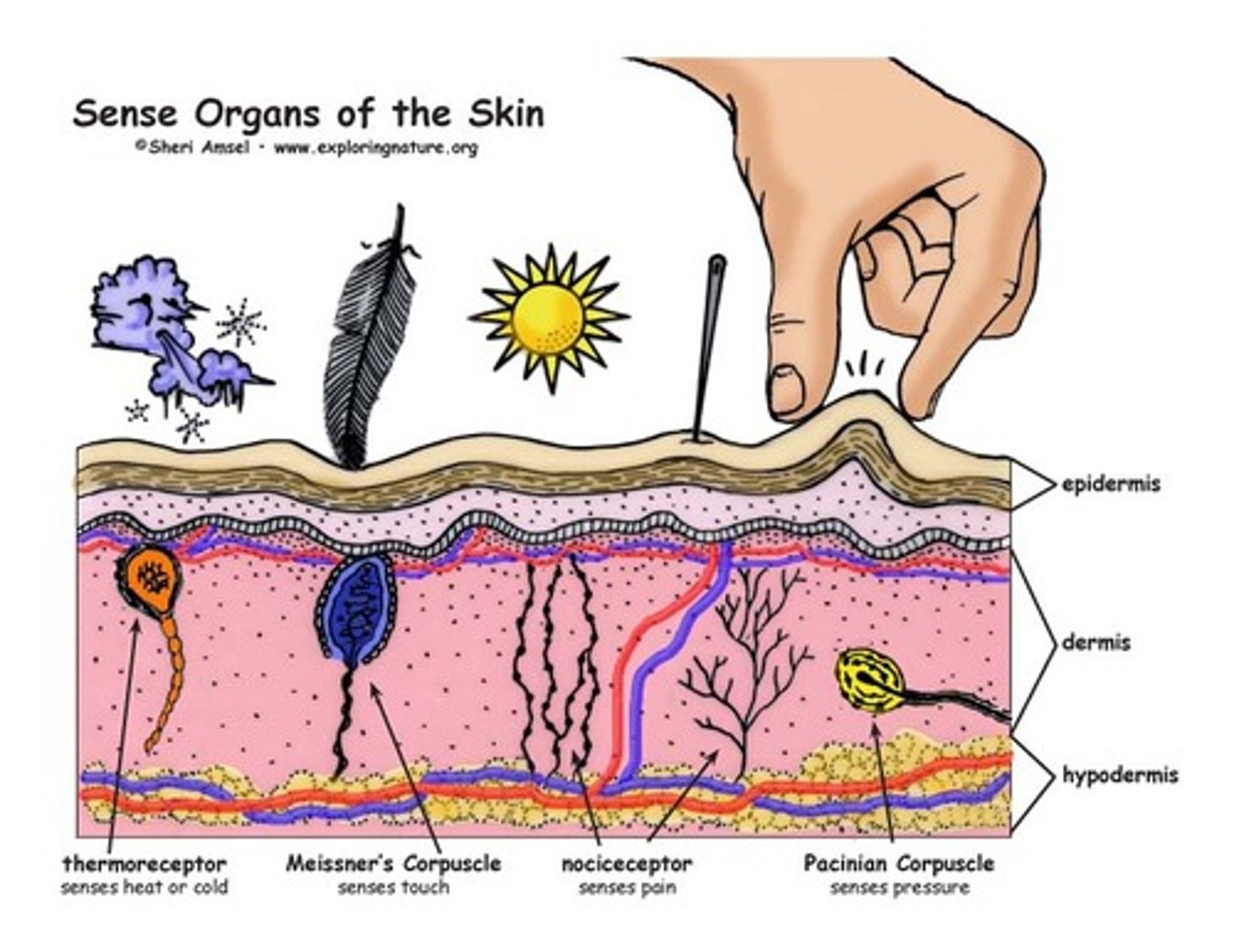
General Sensory Receptors
Detect touch, pressure, temperature, pain, stretch, and vibration
Special Sensory Receptors
Detect vision, hearing, equilibrium, smell and taste

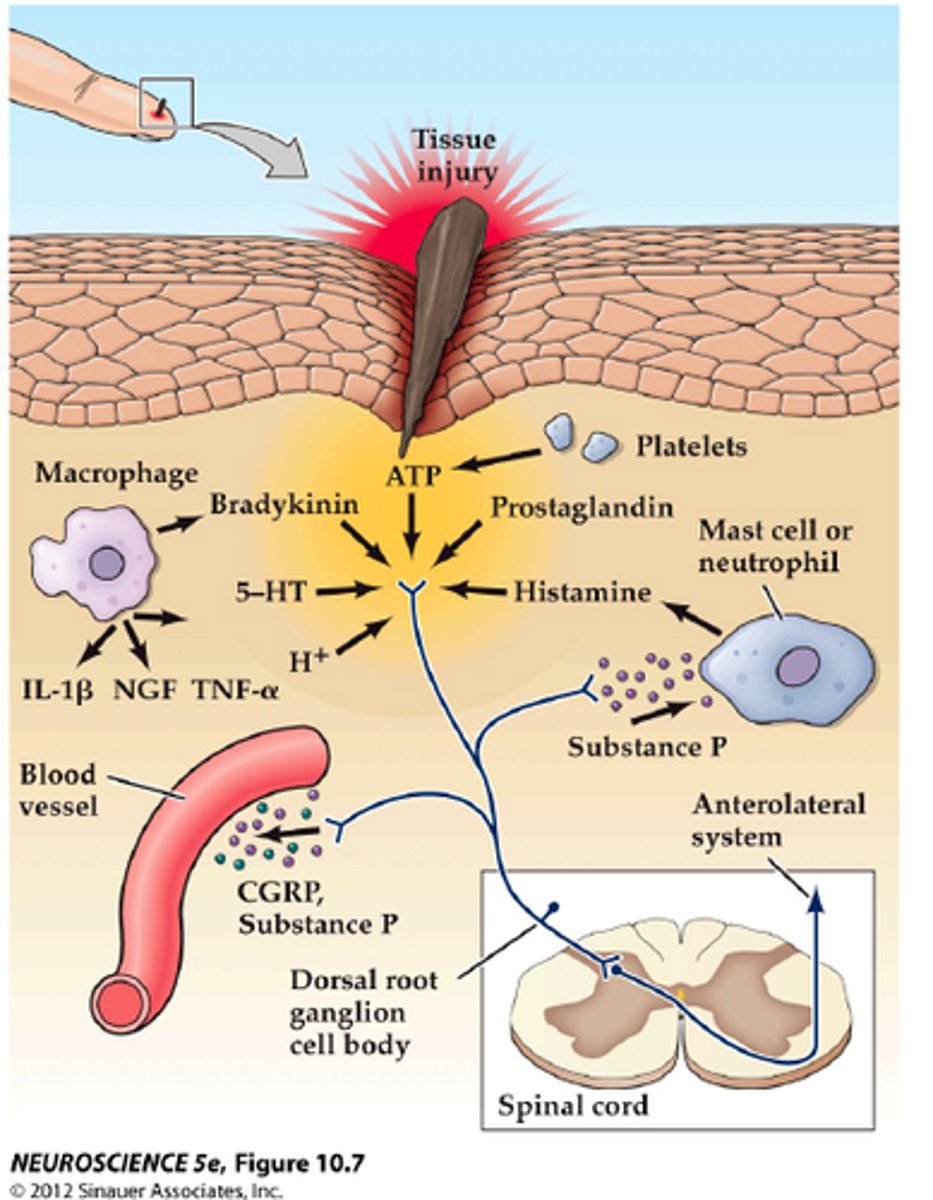
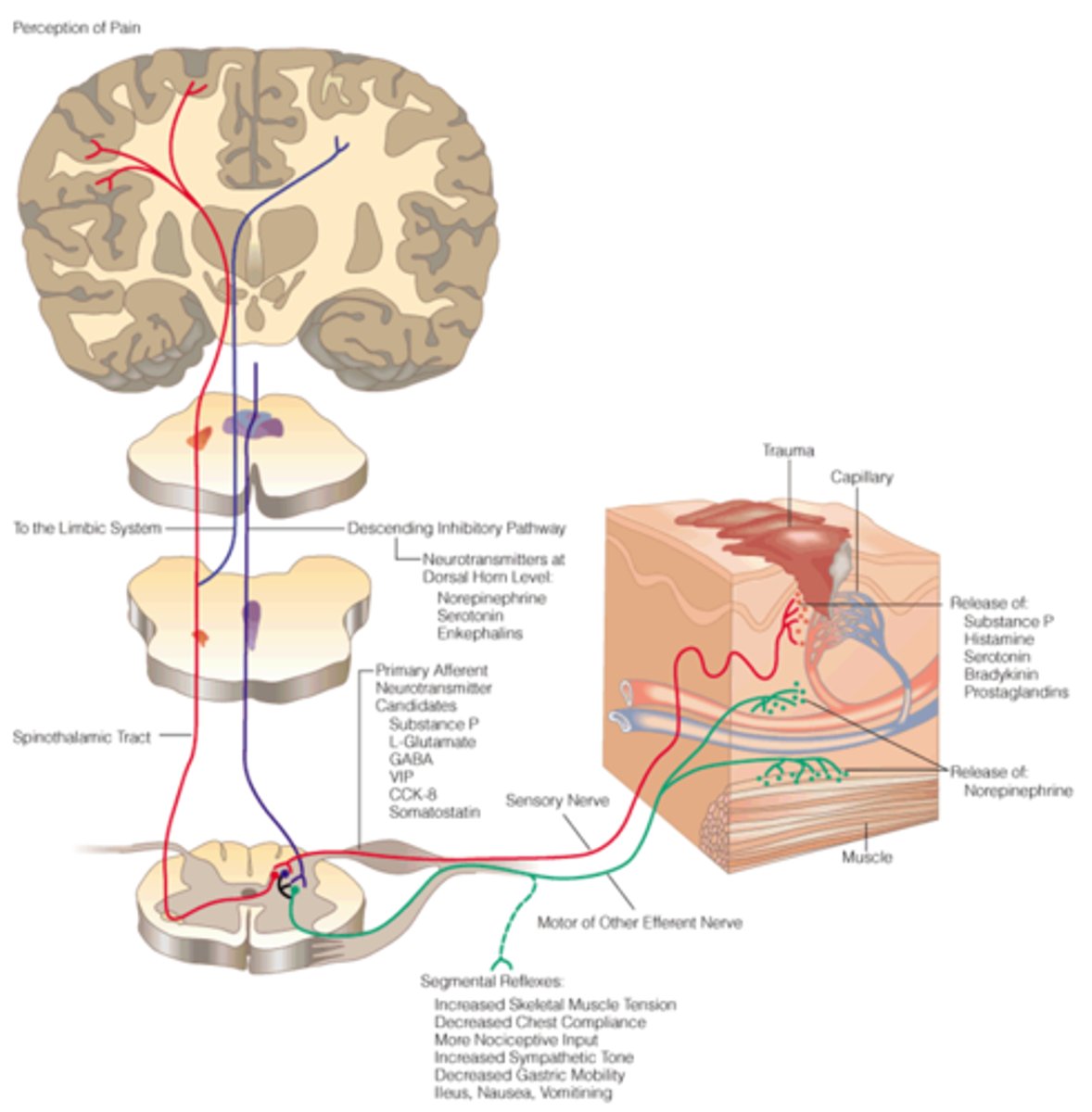
Nociceptors
Pain receptors. Nociceptors are found everywhere in the body except for the brain.
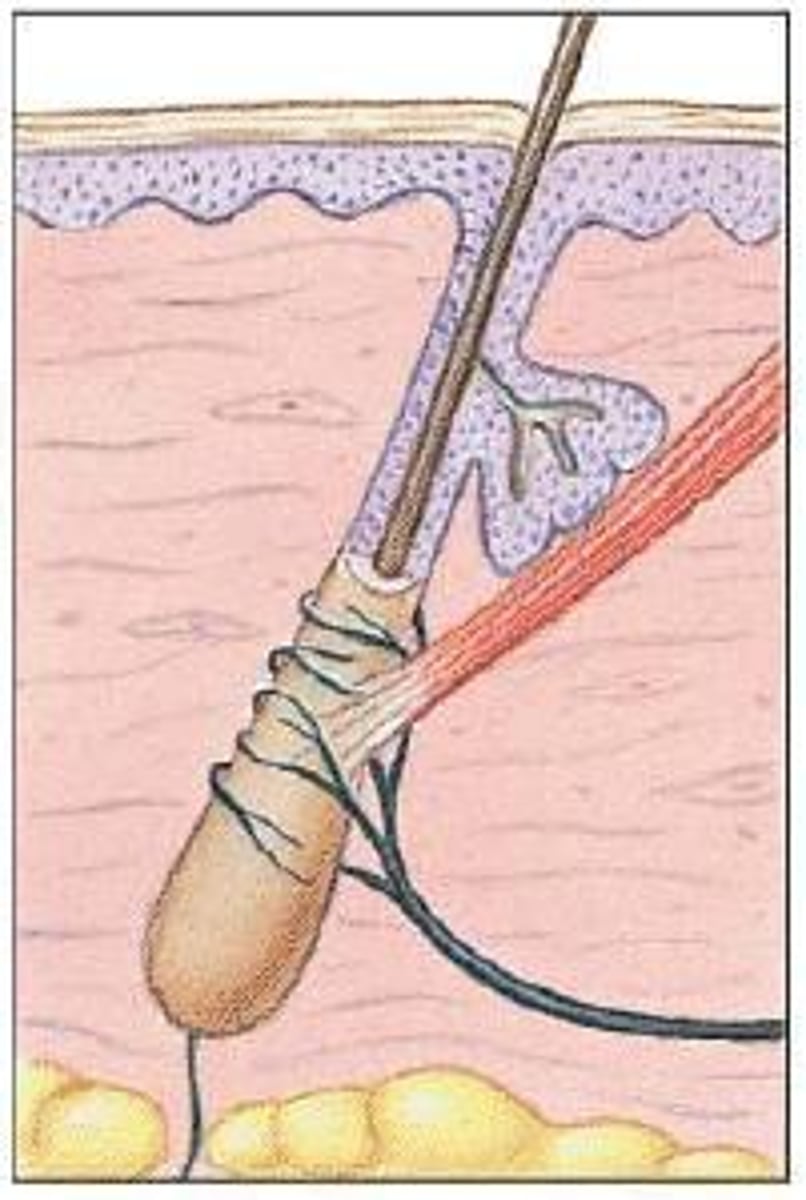
Root Hair Plexus
free nerve ending wrapped around hair root detects hair movements or distortion
Proprioception
The cumulative sensory input to the central nervous system from all mechanoreceptors that sense body position and limb movement.

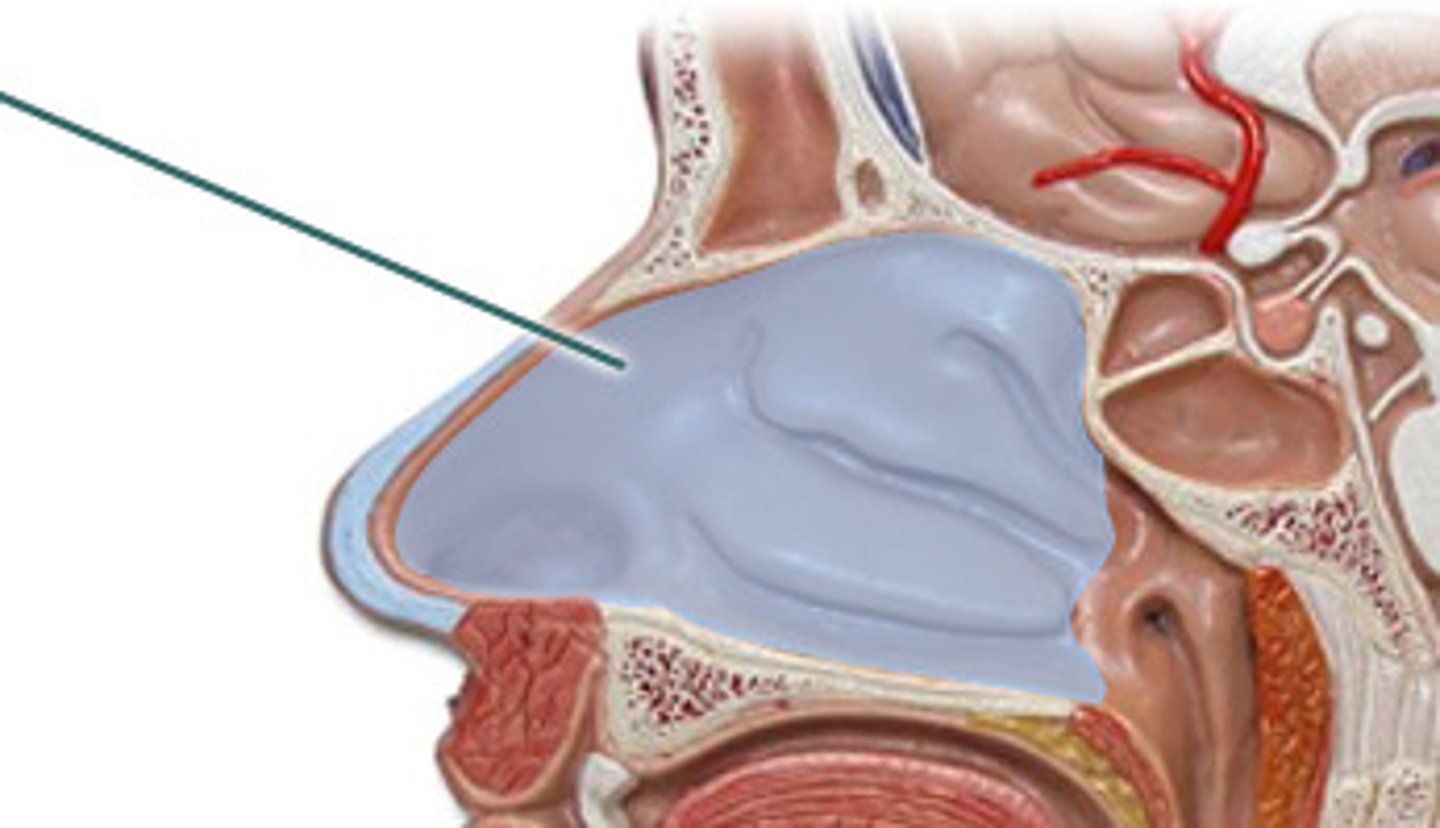
Nasal Cavity
the interior portion of the nose
Oral Cavity
contains the lips, hard and soft palates, salivary glands, tongue, teeth, and the periodontium
Tongue
manipulates food for chewing and swallowing; a taste organ
Optic Nerve
the nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
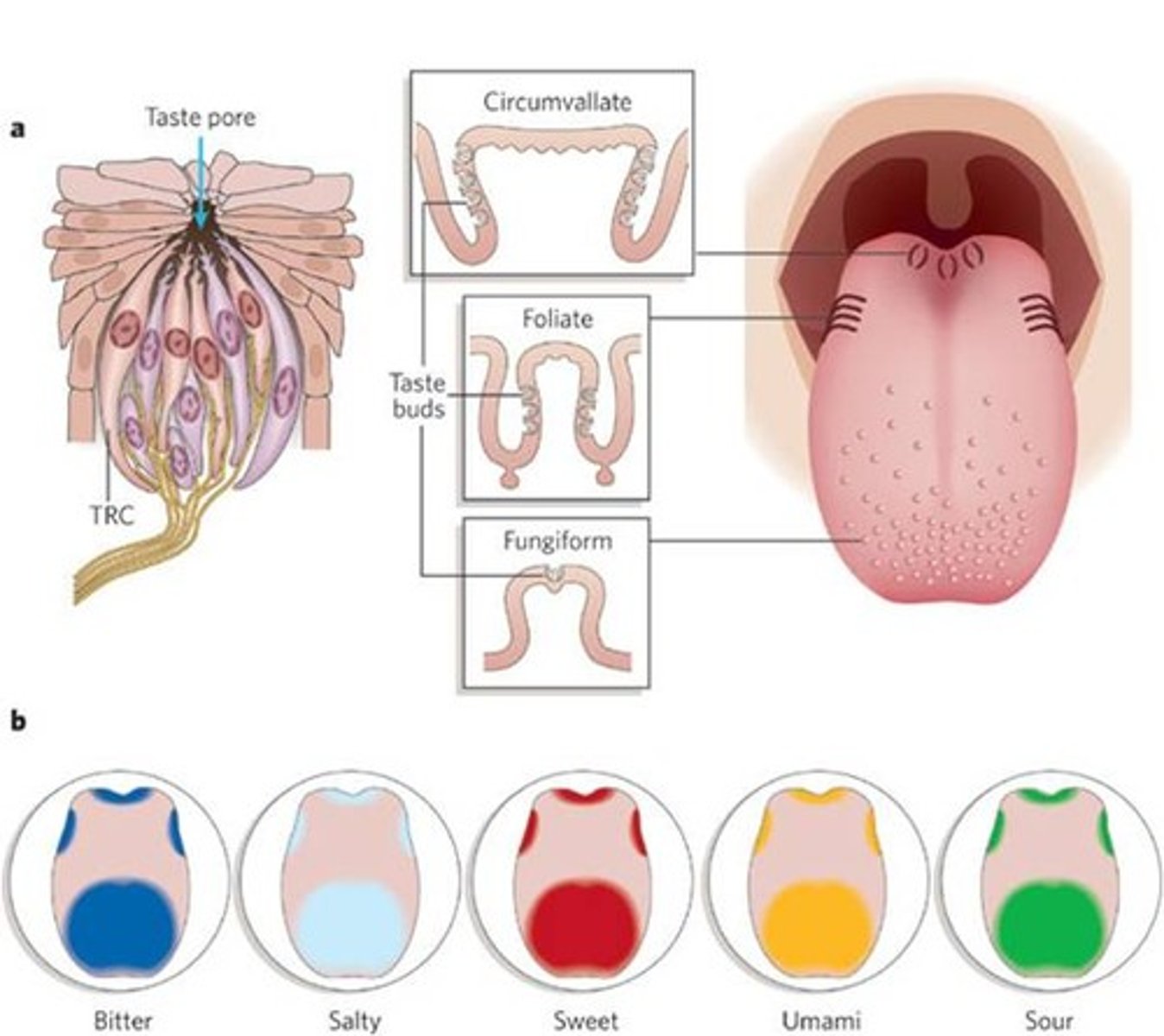
Five Tastes
1. Sweet
2. Sour
3. Bitter
4. Umami
5. Salty
5 Types of Receptors
1. mechanoreceptors
2. thermoreceptors
3. proprioceptors
4. pain receptors
5. chemoreceptors
Pain Receptors
Nociceptors that only respond to intense stimulation either by chemical, mechanical, or thermo stimulation.
there are 3 types located throughout the body
1. Cutaneous (skin)
2. somatic (joints & bones)
3. visceral (body organs)
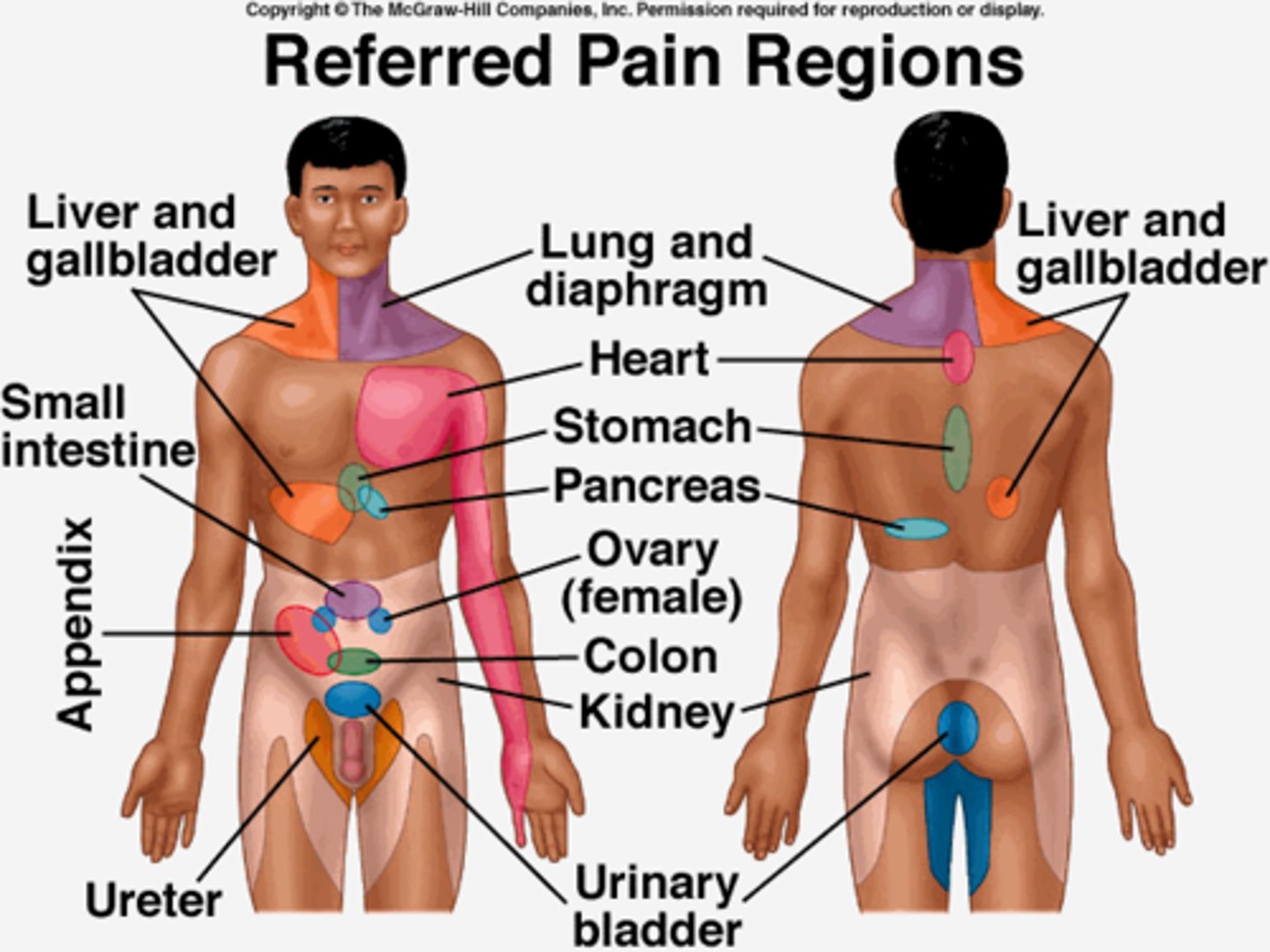
Referred Pain
pain felt in a part of the body other than its actual source.
Adaptation vs. Projection
-Projected Pain is pain that has been localized incorrectly due to the ascending pain pathway
-Pain Adaptation is your body builds up tolerance for a consistent pain stimuli
Special Senses vs. General Senses
Special sense receptors are structurally more complex than general sense receptors and localized in special sense organs.
Examples of Special Senses:
Smell (olfaction)
taste (gustation)
balance (equilibrium)
hearing
vision
General sense receptors are scattered throughout the body.
Examples of General sensations of:
temperature
pain
touch
pressure
vibration
proprioception (body position)