Diffusion & Osmosis (2B)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Diffusion
The spontaneous movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration until equilibrium is reached.
Dynamic equilibrium
A state where there is a uniform distribution of particles and net diffusion stops.
Passive Transport
The movement of molecules across cell membranes without energy input, driven by diffusion.
Simple Diffusion
A type of passive transport that allows some (determined by size, charge, and polarity) particles to cross the phospholipid bilayer.
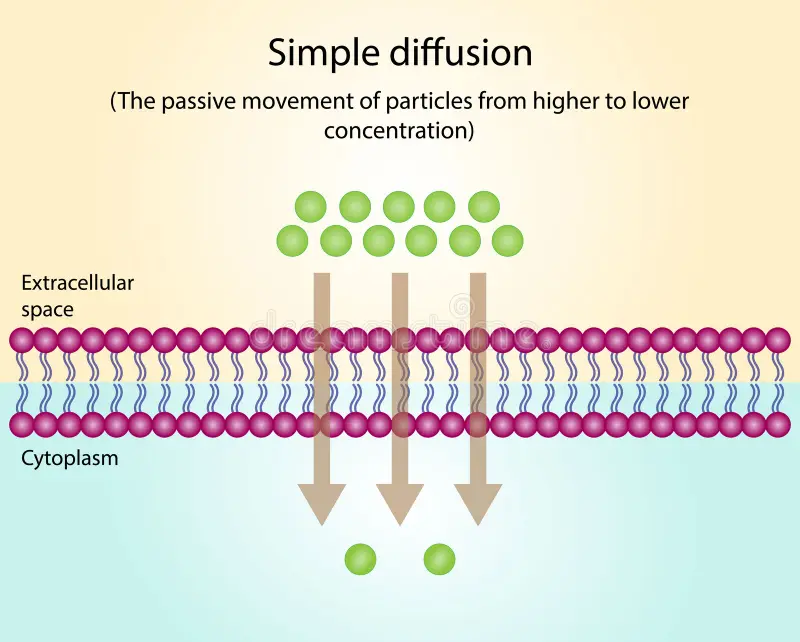
Simple Diffusion - “Some” Substances
small, uncharged, nonpolar molecules (oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen + water (polar))
water molecules can diffuse directly but the rate of transport may be slower
Osmosis
The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane.
moves slowly (polar) from a solution where its concentration is higher (dilute) towards the solution where its concentration is lower (more concentrated solution)
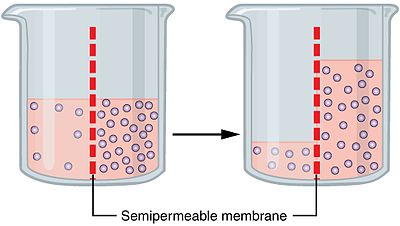
Tonicity
The ability of a solution surrounding cells to change the volume of the cells by changing their water content.
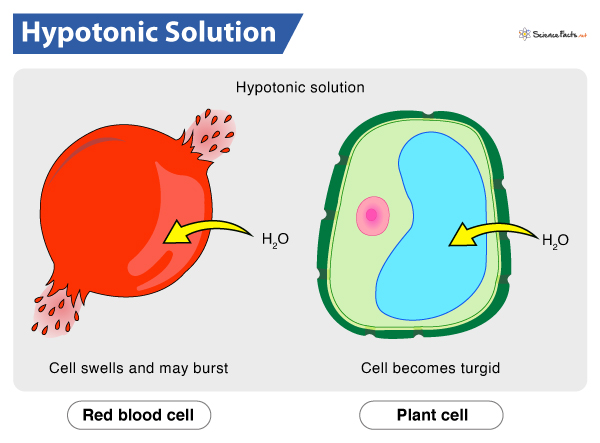
Hypotonic solution
A solution with a lower solute concentration than the cell.This causes water to enter the cell, potentially leading to swelling or bursting.
(cytolysis - the process of a cell bursting due to excessive water intake.)
(turgid = 😁)
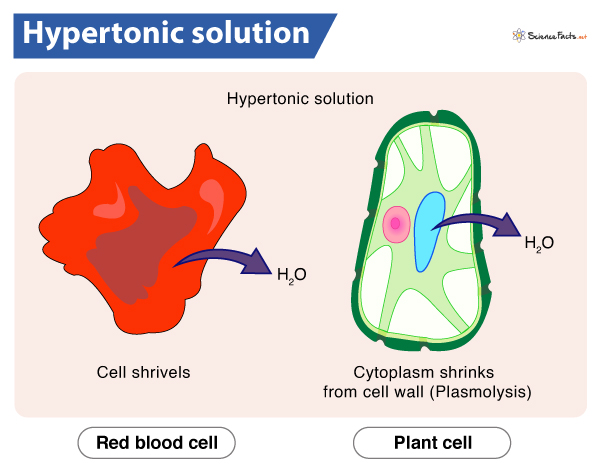
Hypertonic solution
A solution with a higher solute concentration than the cell. This causes water to exit the cell, leading to shrinkage or crenation.
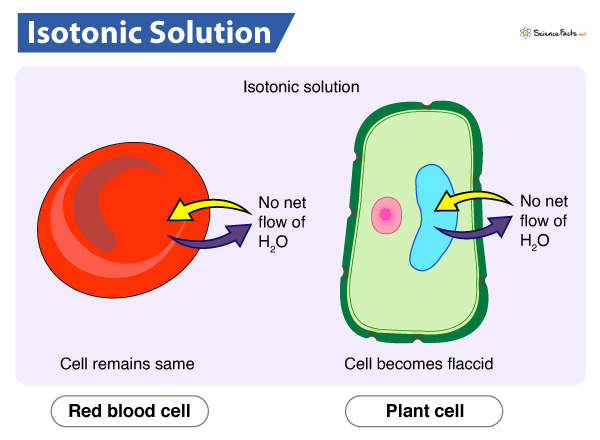
Isotonic solution
A solution with the same solute concentration as the cell. This results in no net movement of water into or out of the cell, maintaining cell size and shape.
3 Types of Passive Transport
Simple Diffusion, Facilitated Diffusion, Osmosis.
Movement of Substances
Substances move down their concentration gradient, from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Solution
A mixture of two or more substances with evenly distributed particles.
Concentration
Of a solution; the mass of a solute in a given volume of solution
Dilute vs Concentrated
Dilute - less solute, more solvent
Concentrated - more solute, less solvent
Solutes
Substances that get dissolved in a solvent to form a solution.
Solvents
Substances, commonly water, that dissolve other substances (solutes) to create a solution.