1 Ortho (Midterm): Intro + Andrew's 6 Keys
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Palmar numbering system
What tooth numbering system is used in orthodontics?
hairline
the outline of hair growth on the head or face:
glabella
A single bony prominence of the frontal bone located between the superciliary arches, Smooth area between the eyes:
subnasale
the point at which the nasal septum merges with the upper lip in the midsagittal plane:
pogonion
the most anterior point on the contour of the chin:
menton
the most inferior point of contour of the chin:
positive
patients with class II occlusal relationships normally will have a ____ angle of convexity
negative
patients with class III occlusal relationships normally will have a ____ angle of convexity
orthognatic
In terms of facial profile, a Class I occlusion would present with a ______ profile
retrognathic
In terms of facial profile, a Class II occlusion would present with a ______ profile
backwards
In Class II occlusions, the mandible is said to have a ______ rotation
forwards
In Class III occlusions, the mandible is said to have a ______ rotation
prognathic
In terms of facial profile, a Class III occlusion would present with a ______ profile
3rds
vertically, the entire face can be broken down into____
- nasion
- subnasale
- pogonion
For a class I relationship, what 3 points would you like to be in a straight line ( and also divide the face into equal 3rds)?
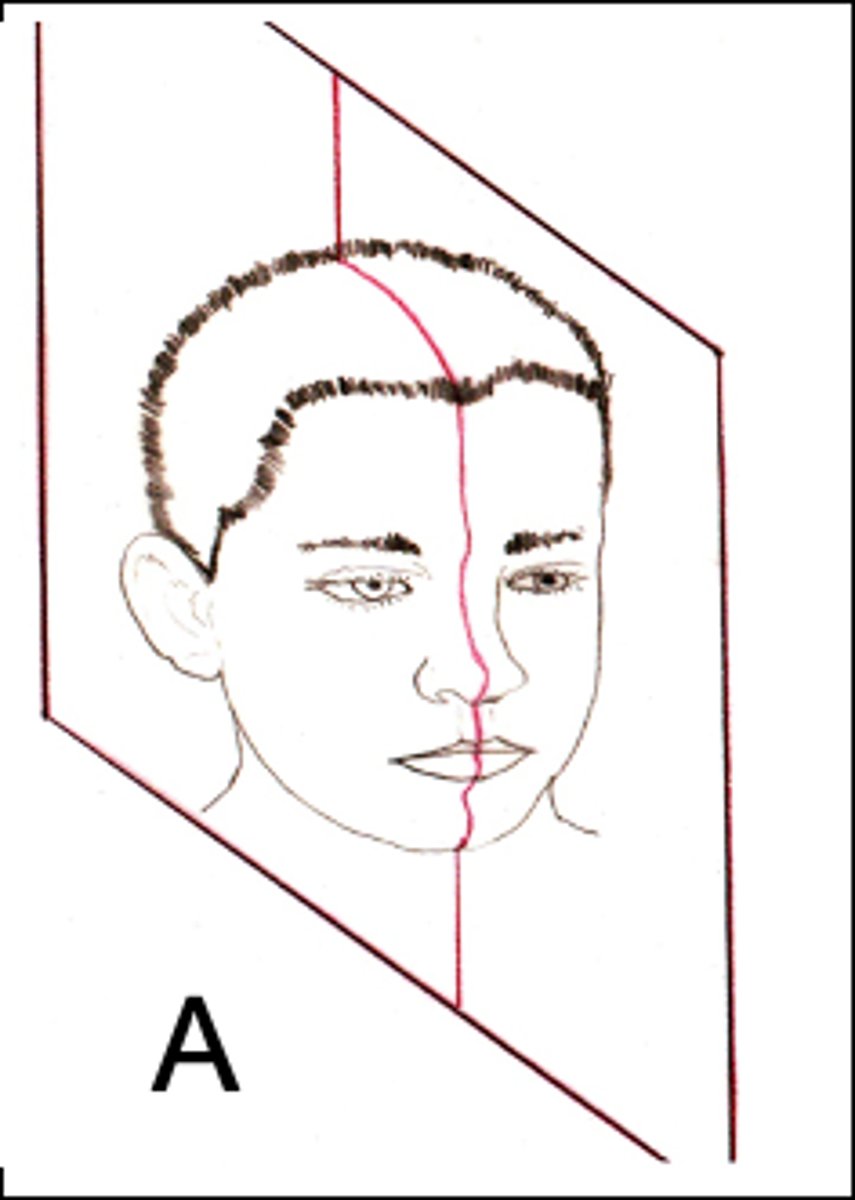
sagittal plane
ID the plane of orientation:
frontal/coronal plane
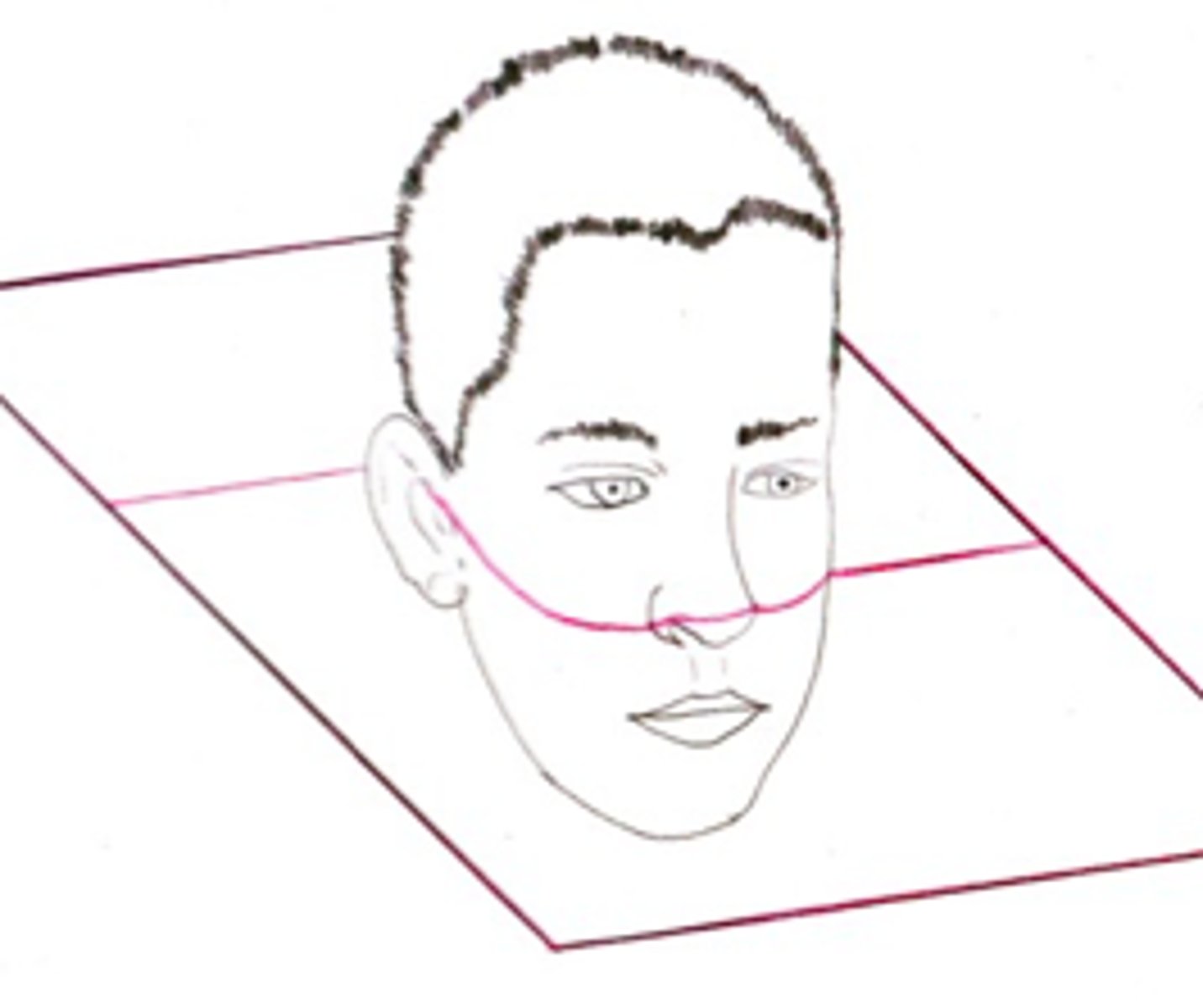
ID the plane of orientation:
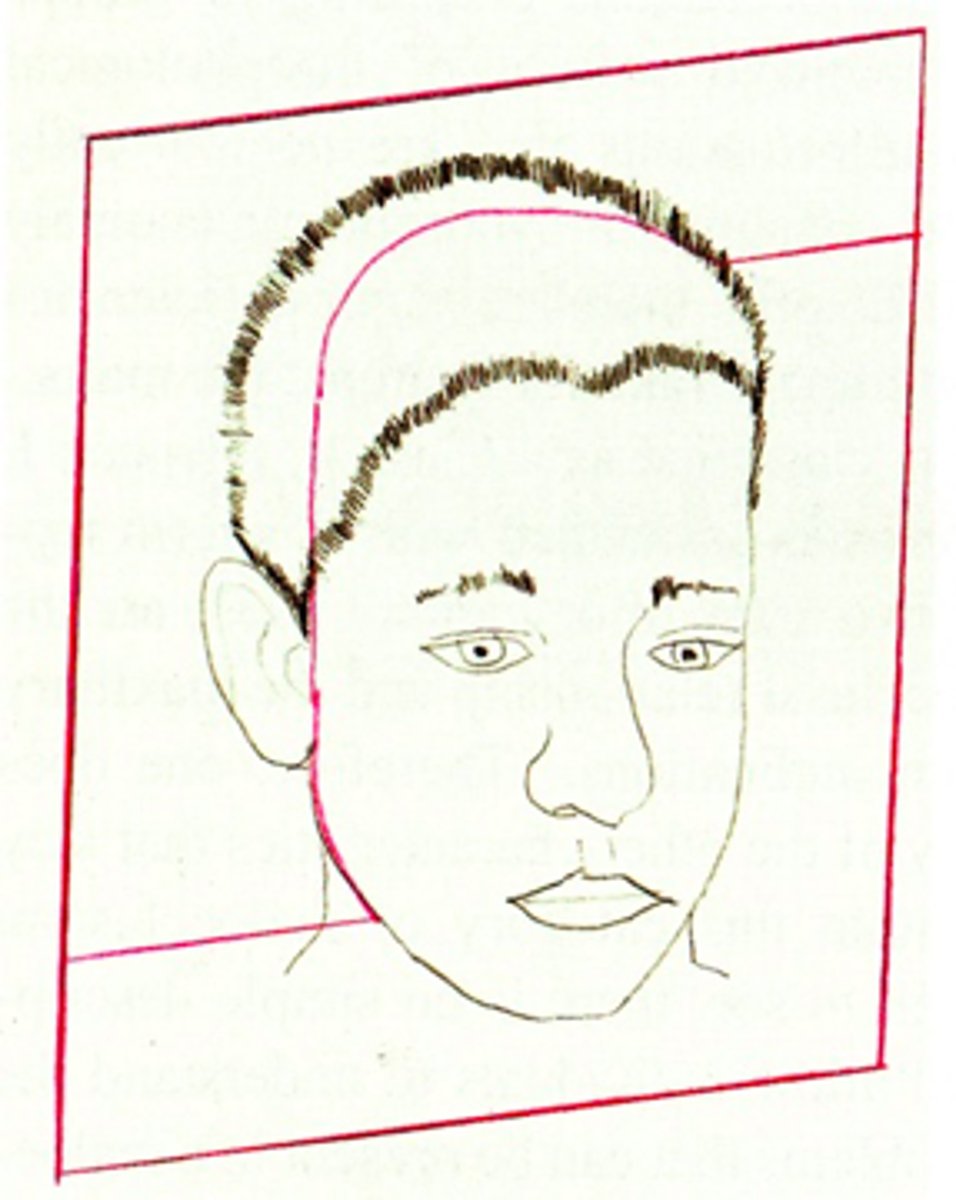

transverse plane
ID the plane of orientation:
max head width x 100/ max head length
how do find the facial/cephalic index?
79-81
What is the CI (cephalic index) for a patient that is Mesocephalic / Mesoprosopic / Normocephalic?
>81
What is the CI (cephalic index) for a patient that is Brachycephalic/Euryprosopic?
<79
What is the CI (cephalic index) for a patient that is Dolichocephalic/ Leptoprosopic?
- glabela
- subnasale
When determining symmetry a line from what two points on a face determines the reverence line?
pogonion
When determining symmetry, a line from the glabella to the subnasale is the reference line, what do you evaluate the position of?
occlusion
_______ is the static and dynamic relationship of the teeth and is basic to all aspects of dentistry
a line the follows the central grooves of the posterior teeth and the incisal edges of the anterior teeth
Describe the ideal line of occlusion for the maxillary teeth:
a line that follows the buccal cusps of the posterior teeth ad the cuspal inclines of the anterior teeth
Describe the ideal line of occlusion for the mandibular teeth:
maxillary 1st molar
Which tooth is the most important tooth in determining the occlusal scheme for a patient (according to Edward Angle)?
maxillary canines
Which tooth is the most important tooth in determining the occlusal scheme for a patient (according to Simon)?
sagittal plane
Occlusal classes I, II and III are evaluated in what plane?
transverse plane
Crossbites and midline deviations are classified and evaluated in what plane?
vertical plane
Deep bites and Open bites are are classified and evaluated in what plane?
- its direct(ly below) relationship with the zygomatic buttress of the zygomatic process
- 1st perm tooth to erupt
Why does Edward Angle claim that the Key tooth in the mouth is the maxillary 1st molar?
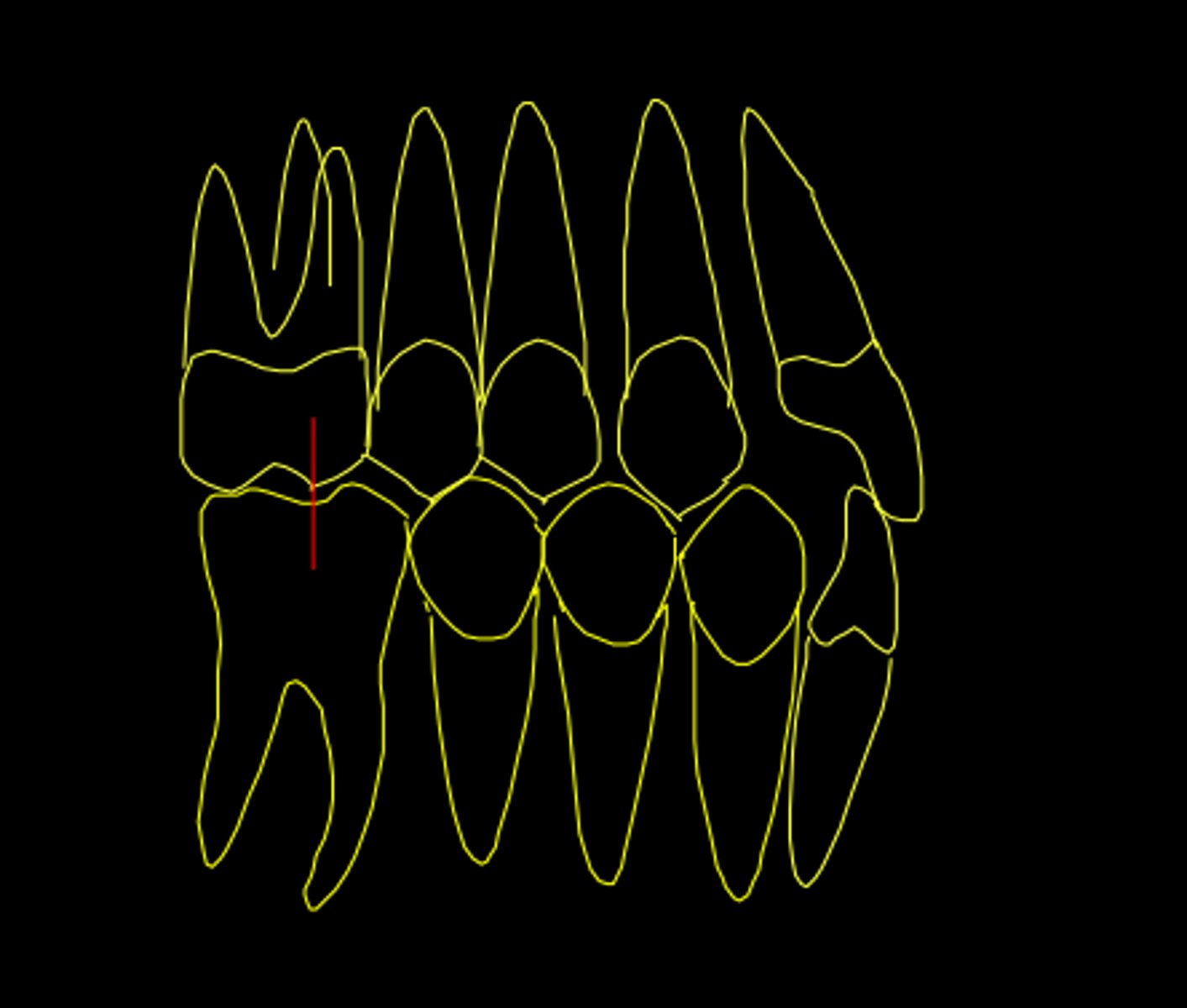
when the MB cusp of the maxillary 1st molar falls into the buccal developmental groove of the 1st mandibular molar
describe the ideal intercuspation for a Class I occlusion:
when the mandibular 1st molar is positioned further distal to the maxillary 1st molar
describe the intercuspation of a Class II occlusion:
when the mandibular 1st molar is positioned further mesial to the maxillary 1st molar
describe the intercuspation of a Class III occlusion:
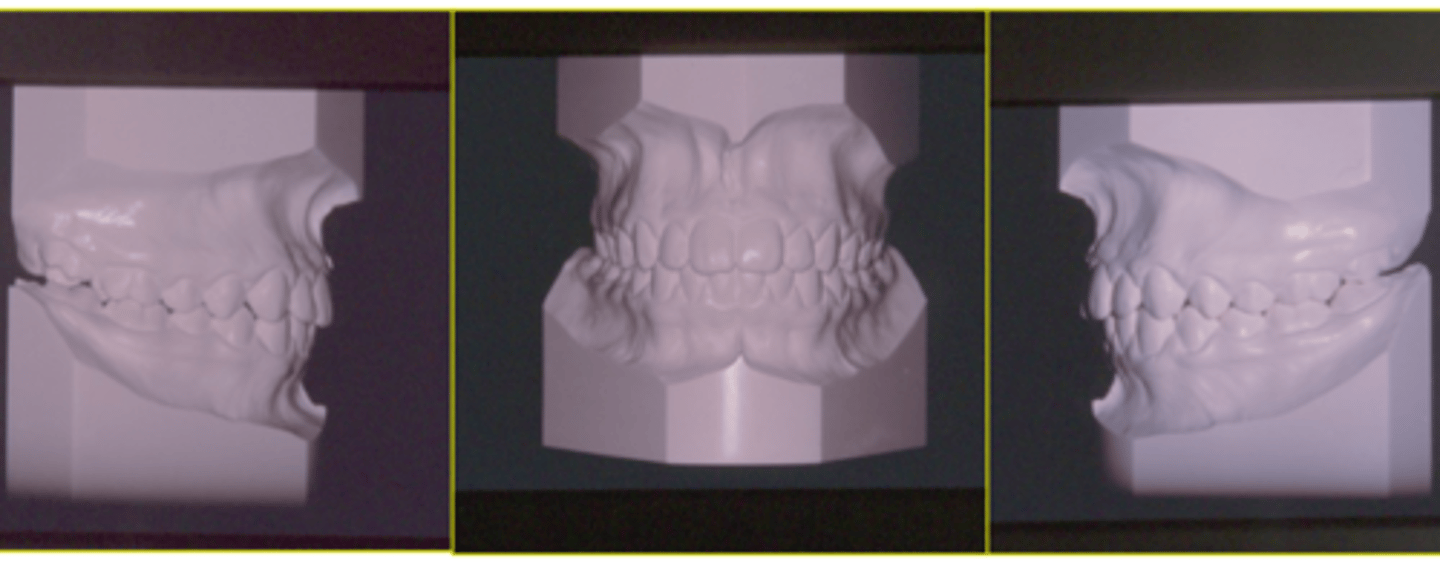
Class I
ID the class of occlusion:
Class I
ID the class of occlusion:
Class II, division 1
ID the class of occlusion:
maxillary incisors are protrusive are procumnent (proclined)
describe the incisors in a Class II, division 1 relationship:
-maxillary centrals are recumbent ( retrusive + retroclined)
-maxillary laterals are procumbent ( proclined)
describe the incisors in a Class II, division 2 relationship:
protrusive
definition: linear more forward of its normal position
proclined
definition: anglularly more inclined forward
Class II, division 1
This occlusal class presents with Maxillary incisors that are BOTH protrusive and proclined:
Class II, division 2
This occlusal class presents with Maxillary central incisors that are retrusive and retroclines, lateral incisors are proclined, patients present with deep bite
Class II, division 2
Which Class II division is considered more esthetically pleasing?
Class II, division 1
ID the class of occlusion:
Class II, division 1
ID the class of occlusion:
Class II, division 2
ID the class of occlusion:
Class II, division 2
ID the class of occlusion:
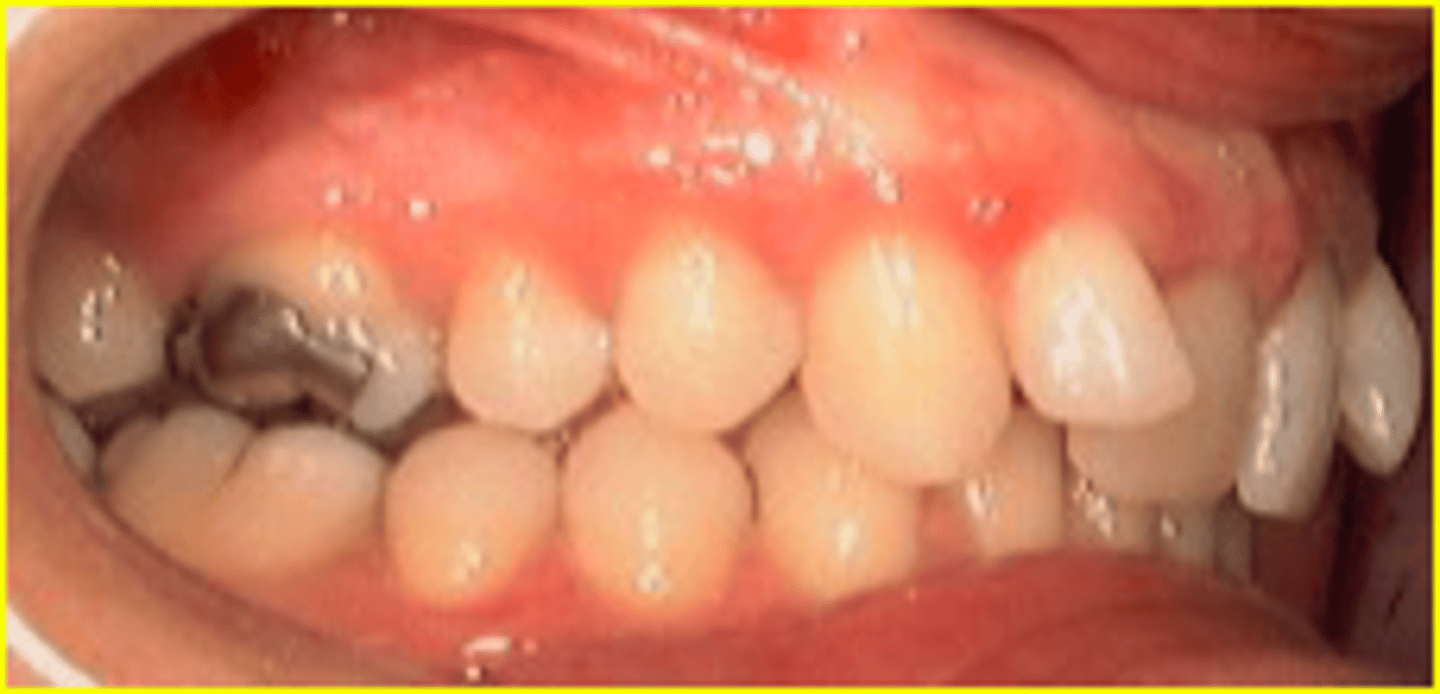
Class II, division 2
ID the class of occlusion:
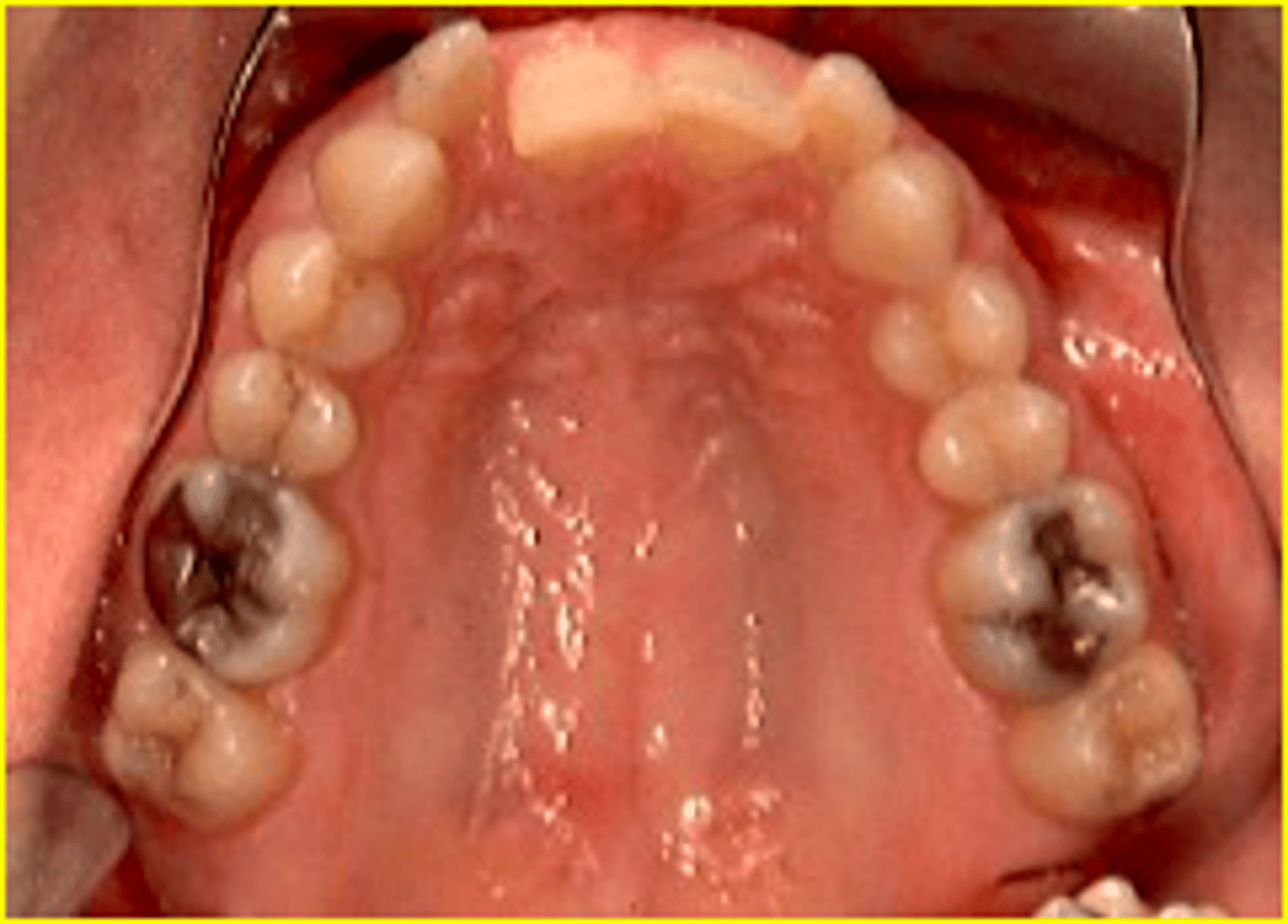
Class III
ID the class of occlusion:
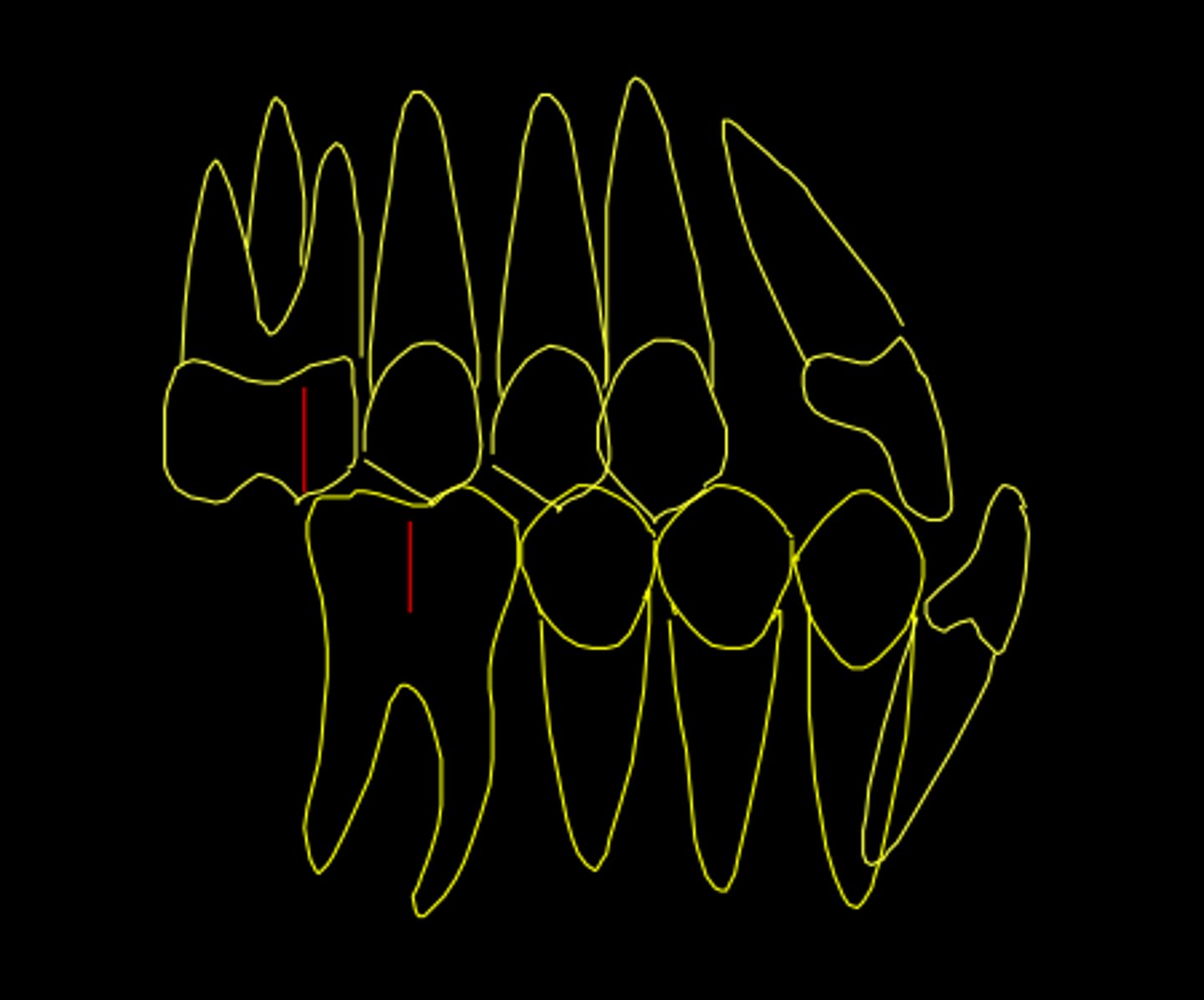
Class III
ID the class of occlusion:
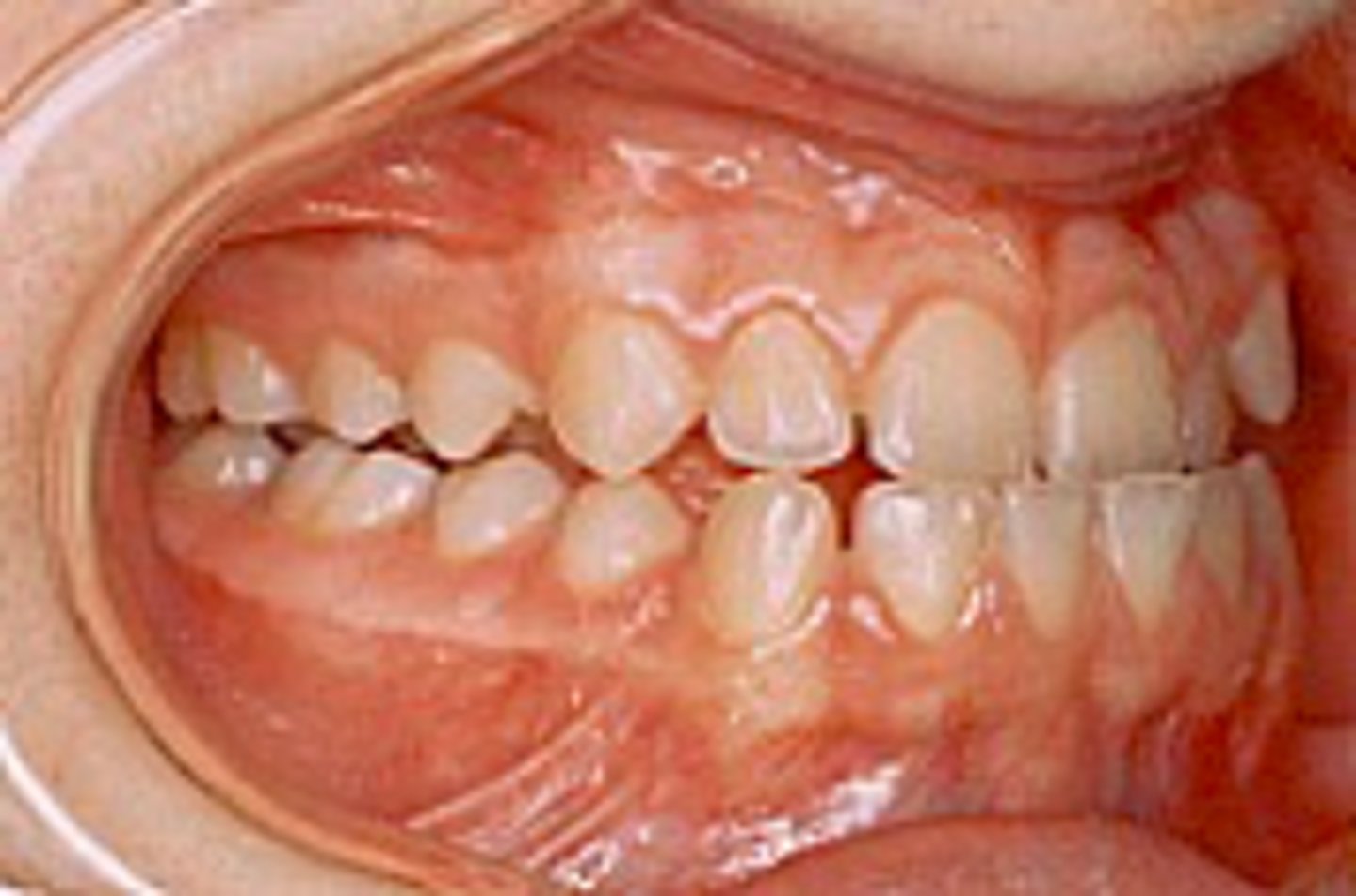
sub-division
If a patient has a unilateral class I occlusion and a class II on the other side, what is that considered?
pseudo class III
if a patient CAN occlude in class I occlusion, but because of either habit, incisor guidance or muscular pattern, the patient prefers a class III occlusion
- can do edge-to-edge
- can be guided into Class I
- does not have retroclined lower incisors
What are 3 clinical ways you can tell if a patient is a pseudo class III?
- normal molar relationship
- mesio-distal crown angulation
- bucco-linqual crown inclination
- no rotations
- no spaces
- flat occlusal planes
What are Andrew's 6 Keys to Normal Occlusion?
- MB cusp of the max 1st molar fits in the buccal groove of the mandibular 1st molar
- DB cusp articulates w/ distal cusp of lower molar
According to Andrew's 6 Keys to Normal Occlusion, describe the ideal molar relationship:
distal
Andrew's 6 Keys to Normal Occlusion, the teeth should have a slight _____ tip
- curve of Spee
- curve of Wilson
What curves allow for flat curves in Andrew's 6 Keys to Normal Occlusion?