Cholinergic agonists
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
steps in cholinergic transmission
ACh synthesis by ChAT
vesicular packaging of ACh
release of ACh from vesicles
postsynaptic receptors
degradation by AChE
Re-uptake of choline
vesamicol
inhibits vesicular packaging
botulinum toxin
blocks release of ACh from vesicles
AChEIs
prevent degradation and indirectly simulate AChRs
hemicholinium
inhibits re-uptake of choline
M1 receptors
location: nerves
Postsynaptic receptor mechanism: IP3, DAG cascade to increase Ca2+
M2 receptors
“Cardiac M2”
location: heart
Postsynaptic receptor mechanism: inhibition of cAMP production, activation of K+ channels, inhibition of Ca2+ channels
M3 receptors
location: glands, smooth muscle, endothelium
Postsynaptic receptor mechanism: IP3, DAG cascade to increase Ca2+
NM
muscle type and plate receptor
location: skeletal muscle and NMJ
Postsynaptic receptor mechanism: Na+, K+ depolarizing ion channel
NN
neuronal type, ganglion receptor
location: postganglionic cell body, dendrites
Postsynaptic receptor mechanism: Na+, K+ depolarizing ion channel
muscarinic subtypes: M1
neural, located in the brain
involved in learning and memory, implicated in Alzheimer’s disease
muscarinic subtypes: M2
heart
decreased SA node firing rate and AV node conduction velocity
muscarinic subtypes: M3
smooth muscle (contraction) and glands (secretion)
selective M3 antagonists for Tx of OAB
synthesis of EDRF, involved in vascular relaxation
cholinergic
involving the synthesis, release, or action of ACh
cholinomimetic
a drug that results in the stimulation of ACh receptors, can be direct or indirect
parasympathomimetic
any agent mimicking ACh
parasympatholytic
any agent blocking the effects of ACh
Anticholinesterase
inhibits AChE (AChEI)
anticholinergic
a drug that blocks ACh receptors, either nicotinic or muscarinic receptors. most of the time it refers to muscarinic recptors
antimuscarinic
blocks muscarinic receptors
antinicotinic
blocks nicotinic receptors
miosis
small pupil (constriction of sphincter muscle)
mydriasis
large pupil (relaxation of sphincter muscle)
bradycardia
slow heart rate
tachycardia
rapid heart rate
direct acting cholinergic agonists: choline esters
ACh, methacholine, carbachol, bethanechol
direct acting cholinergic agonists: naturally occurring alkaloids
muscarine, pilocarpine, arecoline, nicotine
ACh can act at
muscarinic receptors (end organs of PSNS, sweat glands of SNS, certain brain synapses)
nicotinic receptors (ganglia of SNS and PSNS, adrenal medulla, NMJ, certain brain synapses)
why is ACh not used clinically?
it is not selective
it is rapidly hydrolyzed
naturally occurring muscarinic agonists
ACh, muscarine, pilocarpine
ACh structure
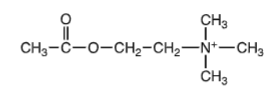
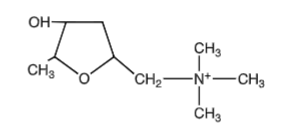
muscarine structure
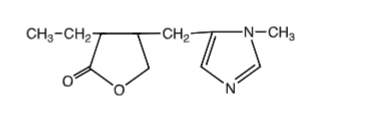
pilocarpine structure
AChEI
compete with ACh for the active site of AChE
- decrease in ACh degradation
- ACh in synaptic cleft increases
- ACh receptor binding increases
- PSNS: parasympathomimetic activity
Edrophonium
AChE-I
peripherally acting
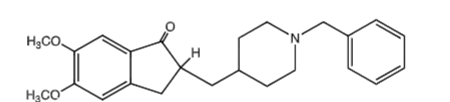
Donepezil
brand: Aricept
AChE-I
crosses BBB - Tx Alzheimer’s
non-competitive reversible inhibitors: MOA
bind to same active site as ACh (on AChE), the drug is hydrolyzed and leads to the formation of a carbamylated enzyme
the carbamylated form of AChE is less sensitive to a second hydrolysis reaction. takes 15-30 minutes to regenerate AChE
Carbamic acid derivatives
non-competitive reversible AChE inhibitors
pyridostigmine, neostigmine, physostigmine, demecarium, ambenoium
Irreversilble AChEIs: MOA
initial hydrolysis reaction leads to formation of phosphorylated enzyme (organophosphate binds at active site)
second hydrolysis rxn cannot happen - thus the inhibition is irreversible
takes days to weeks to make new enzymes
organphosphates
echothiopate, parathion, malathion
nerve gas poisons (sarin, soman, tabun)
2-PAM
organophosphate poisoning antidote
use before aging occurs - if you wait it will not work
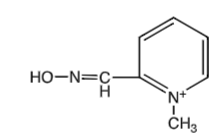
sarin
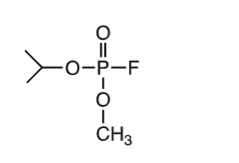
parathion

SLUDGE
Salivation
Lacrimation
Urination
Diarrhea
Gastric emptying
Emesis
parasympathomimetic effects
DUMBELS
Diarrhea/diaphoresis
Urination
Miosis
Bradycardia/bronchorrhea
Emesis/emptying
Lacrimation
Salivation
parasympathomimetic effects
MTWHFS
Mydriasis
Tachycardia
Weakness (muscle)
Hypertension
Fasciculations
Seizures
nicotinic agonist effects
eye - PSNS effects
miosis - constriction of pupils (sphincter muscle)
change shape of lens for near vision
increased aqueous humor outflow (helpful in glaucoma)
lacrimation
M2 effects on the heart
HR decreased
conduction velocity (dromotropy) decreased
contractile strength (inotropy) decreased
M3 effects on the blood vessels
PSNS fibers innervate muscarinic receptors only on blood vessels in the viscera
note: other vessels of the peripheral circulation have muscarinic receptors but are not innervated. They could, however, respond to circulating agonists
blood vessels: inner layer
endothelium, location of M3 receptors
blood vessels: middle layer
smooth muscle, location of adrenergic receptors
blood vessels: outer layer
collagen
endothelial regulation of nitric oxide-mediated vascular smooth muscle relaxation
- activation of M3 muscarinic receptors on the endothelial cells of blood vessels
- Gq activation increases Ca2+, which activates Ca2+ - calmodulin complex
- Endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) is stimulated to produce NO
- NO diffuses into vascular smooth muscle cells, where it activates guanylyl cyclase to produce cGMP, which causes relaxation of vascular smooth muscle
bronchomotor tone - agonist effects
major player in regulation - PSNS
contraction of bronchiolar smooth muscle and bronchoconstriction (via M3) (resistance to airflow)
pulmonary secretions - agonist effects
increased mucus secretions from epithelial cells lining the airways (via M3)
digestion - agonist effects
stimulation of salivary and gastric gland secretions
increased motility of the GI tract (increased peristalsis)
defecation - agonist effects
relaxation of sphincter muscles which line intestinal tract
detrusor muscle
forms the body of the bladder
contraction controlled by M3 receptors
relaxation controlled by beta 2 receptors
trigone sphincters
contraction controlled by alpha 1 receptors
relaxation controlled by M3 receptors
micturition
contraction of detrusor and relaxation of trigone sphincters
clinical uses - GI/GU surgical interventions
post-surgery, patients often experience atony of bladder, stomach, and/or intestines
agonists stimulate GI motility and emptying of bladder
bethanechol (urecholine)
direct cholinergic agonist
given orally or subcutaneously
induces peristaltic activity of the gut and stimulates bladder contraction
bethanechol: contraindication
peptic ulcer
urinary tract obstruction
systemic side effects are a concern
Myasthenia gravis
autoimmune disease
body produces antibodies against nicotinic receptors on skeletal muscle
muscles are unable to contract in response to the release of ACh from the motor neuron
symptoms: ptosis, diplopia, difficulty in swallowing and chewing, weakness in the extremities, breathing difficulties
edrophonium
IV administered AChE-I
very short acting
used for diagnosis of myasthenia gravis
Pyridostigmine (mestinon)
AChEI - reversible, indirect acting agonist
oral administration
slow onset of action (1-2 hours), DOA = 8-12h
useful for chronic treatment of MG
neostigmine (prostigmine)
AChEI - reversible, indirect acting agonist
oral admin
rapid onset (10-30 minutes), DOA = 2-4h
Tx MG
Presbyopia
age related blurry near vision
common, progressive condition that reduces the eyes ability to focus on near objects
Pilocarpine (Vuity)
ACh agonist
eye drops used once daily
recall PSNS actions of the eye
- contraction of the ciliary muscles - change shape of lens for near vision
- constriction of pupils (miosis)