Exam 2: Lec. 5 (Tooth Development)
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
What do trophoblasts become a portion of?
The Placenta
Put the following in order:
1) Morula
2) Zygote
3) Blastocyst
2>1>3
What does the Embryoblast give rise too?
Bilaminar Disc
Does the bilaminar disc have a one or two-layered stage of embryonic development?
Two-Layered
What layer of the bilaminar disc gives rise to all the cells, organs, and tissues of the embryo?
Epiblast
What layer of the bilaminar disc is a temporary structure that is displaced by epiblast cells?
Hypoblast
What layer of the bilaminar disc is the cuboidal ventral layer?
Hypoblast
What layer of the bilaminar disc is the columnar dorsal layer?
Epiblast
What three primary germ layers make up the Trilaminar disc?
1) Ectoderm (dorsal layer)
2) Mesoderm (middle layer)
3) Endoderm (ventral layer)
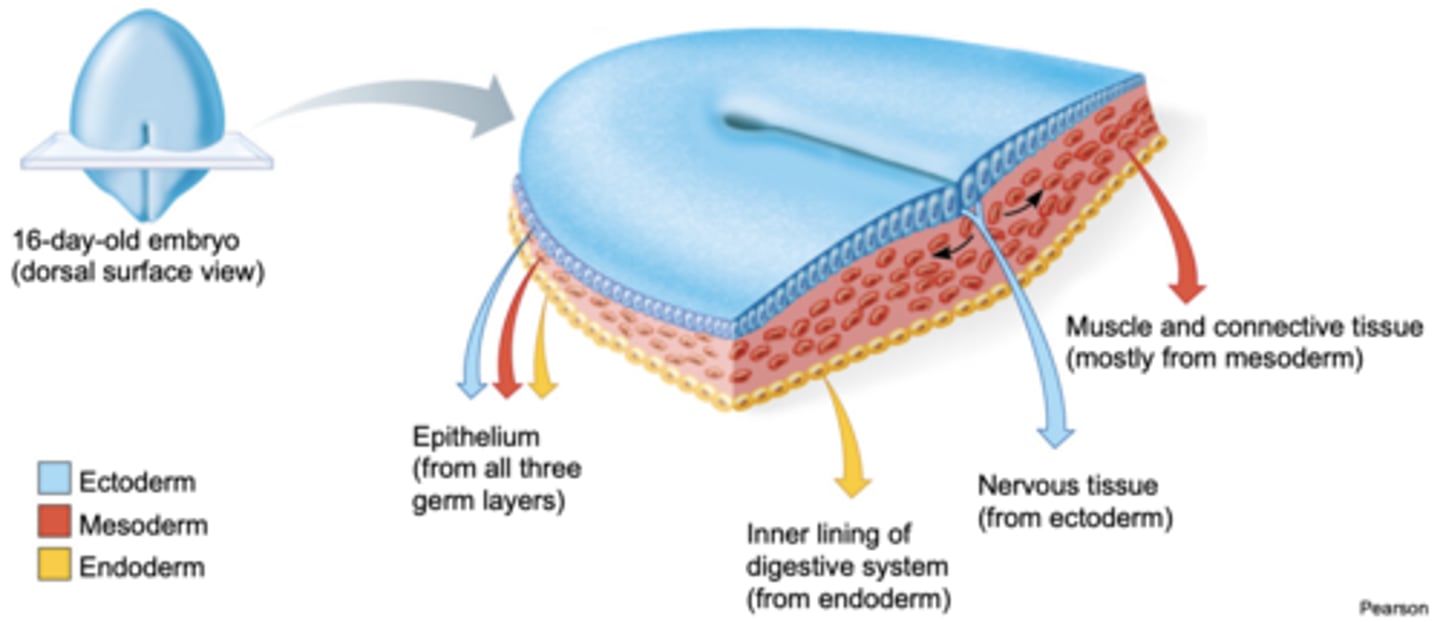
What primary germ layer gives rise to oral epithelium (enamel)?
Ectoderm
What primary germ layer are neural crest cells derived from?
Ectoderm
What cell type do neural epithelial cells transition to? (from ectoderm)
Neural Crest Cells
What is embryonic connective tissue?
Mesenchyme
What are neural crest cells that have migrated to the connective tissue compartment of the embryo?
Ectomesenchyme
What is an epitheliomesenchymal transformation?
Neural Crest Cells to Ectomesenchyme
What tooth structures do ectomesenchyme give rise to?
1) Dentin
2) Cementum
3) Periodontal Ligament
4) alveolar Bone
What is odontogenesis?
the process of tooth developement
What two types of epithelium are present in odontogenesis?
1) oral epithelium
2) odontogenic epithelium
T/F There is a basement membrane under oral and odontogenic epithelium.
True
Oral epithelium thickens to for what structure?
Primary Epithelial Band
What does the primary epithelial band give rise to?
Dental Lamina
What condenses under the dental lamina at 20 distinct locations to form the deciduous teeth?
Ectomesenchyme
How many locations are formed for the deciduous teeth?
20
What are the three stages of tooth development?
1) Bud Stage
2) Cap Stage
3) Bell Stage
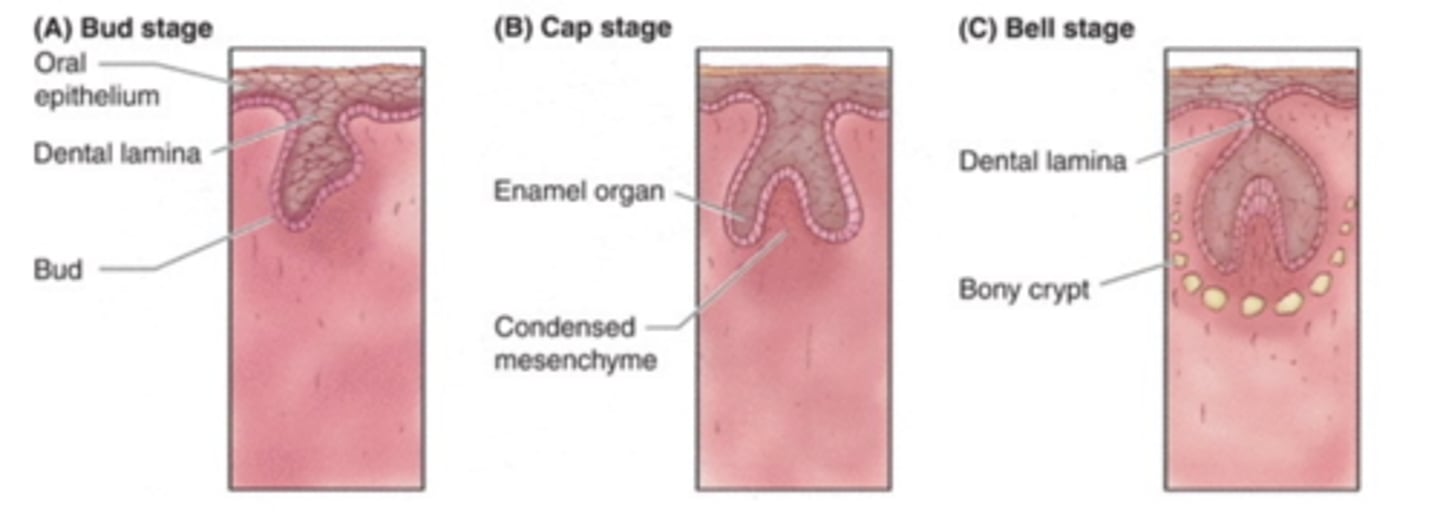
In what tooth development stage do cells proliferate?
Bud Stage
When does the dental lamina proliferate and the ectomesenchyme condense and proliferate?
Bud Stage
In what tooth development stage do enamel organs and dental papilla form?
Cap Stage
What is established during the cap stage?
Tooth germ
What does the enamel organ develop from?
tooth bud
What does the dental papilla form from?
ectomesenchyme
What is also formed from the ectomesenchyme besides the dental papilla?
Dental Follicle/Dental Sac
What are the tree parts of the tooth germ?
1) Enamel Organ
2) Dental Papilla
3) Dental Sac
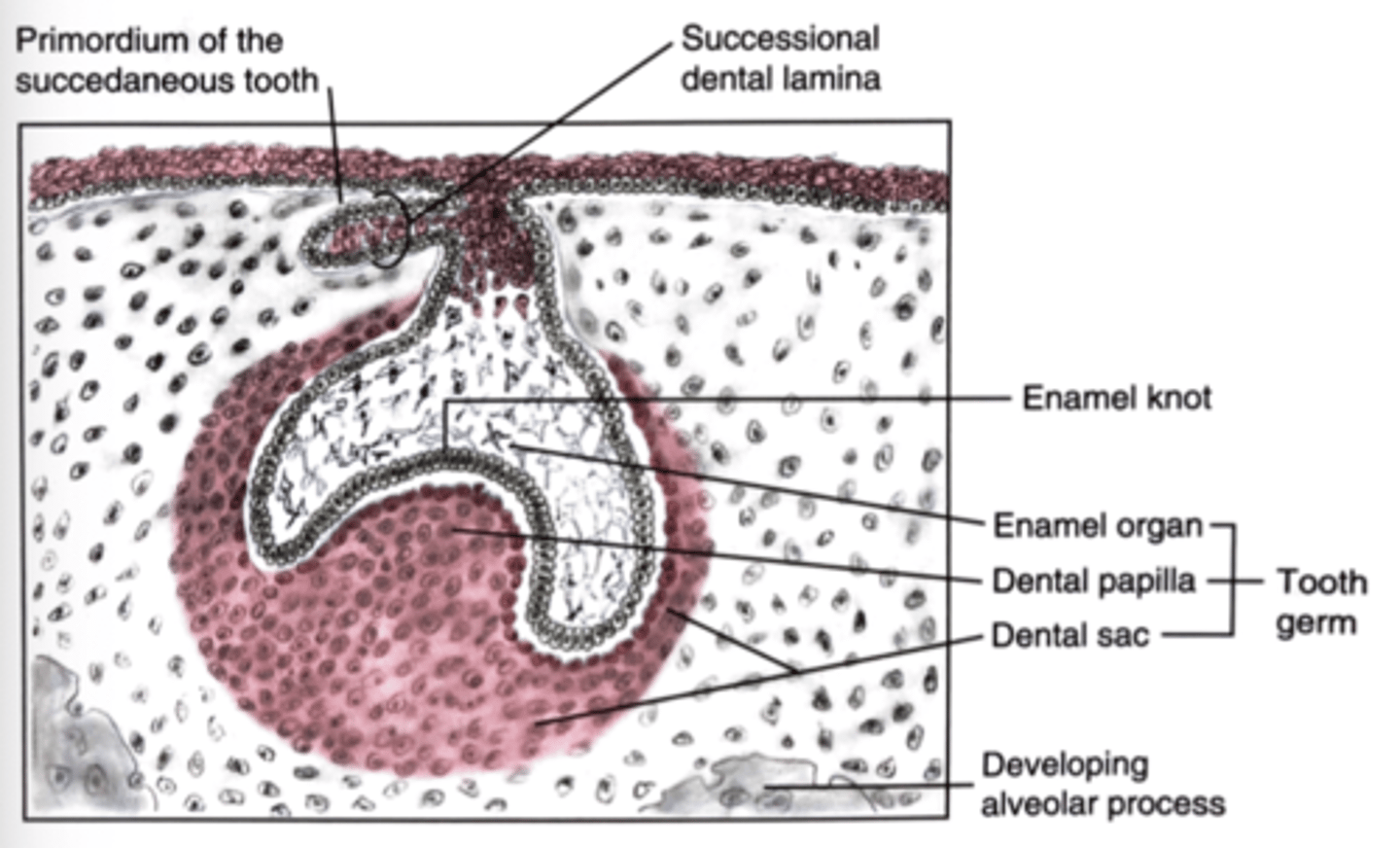
Why does the stellate reticulum form?
increase hydration (glycosaminoglycans)
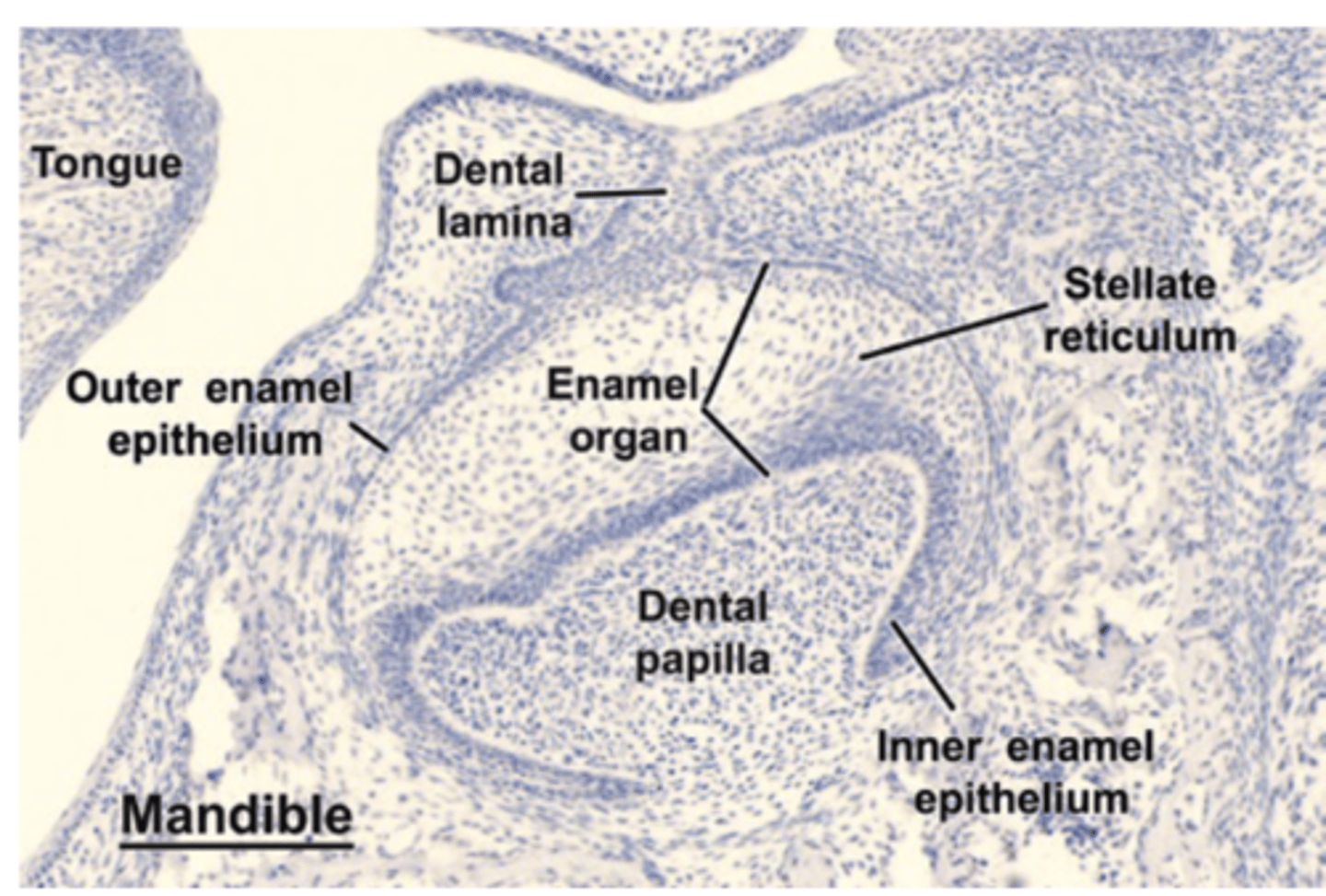
What does the dental papilla transition to when hard tissue is present?
Pulp Cavity
T/F The enamel knot is present in the bud stage.
False: The enamel knot is present in the Cap stage.
In what tooth development stage does cytodifferentiation and histodifferentiation occur?
Bell Stage
During the Bell Stage what disintegrates?
Dental Lamina
What four cell types does the enamel organ have during the bell stage
1) Outer enamel epithelium
2) Stellate reticulum
3) Stratum intermedium
4) Inner enamel epithelium
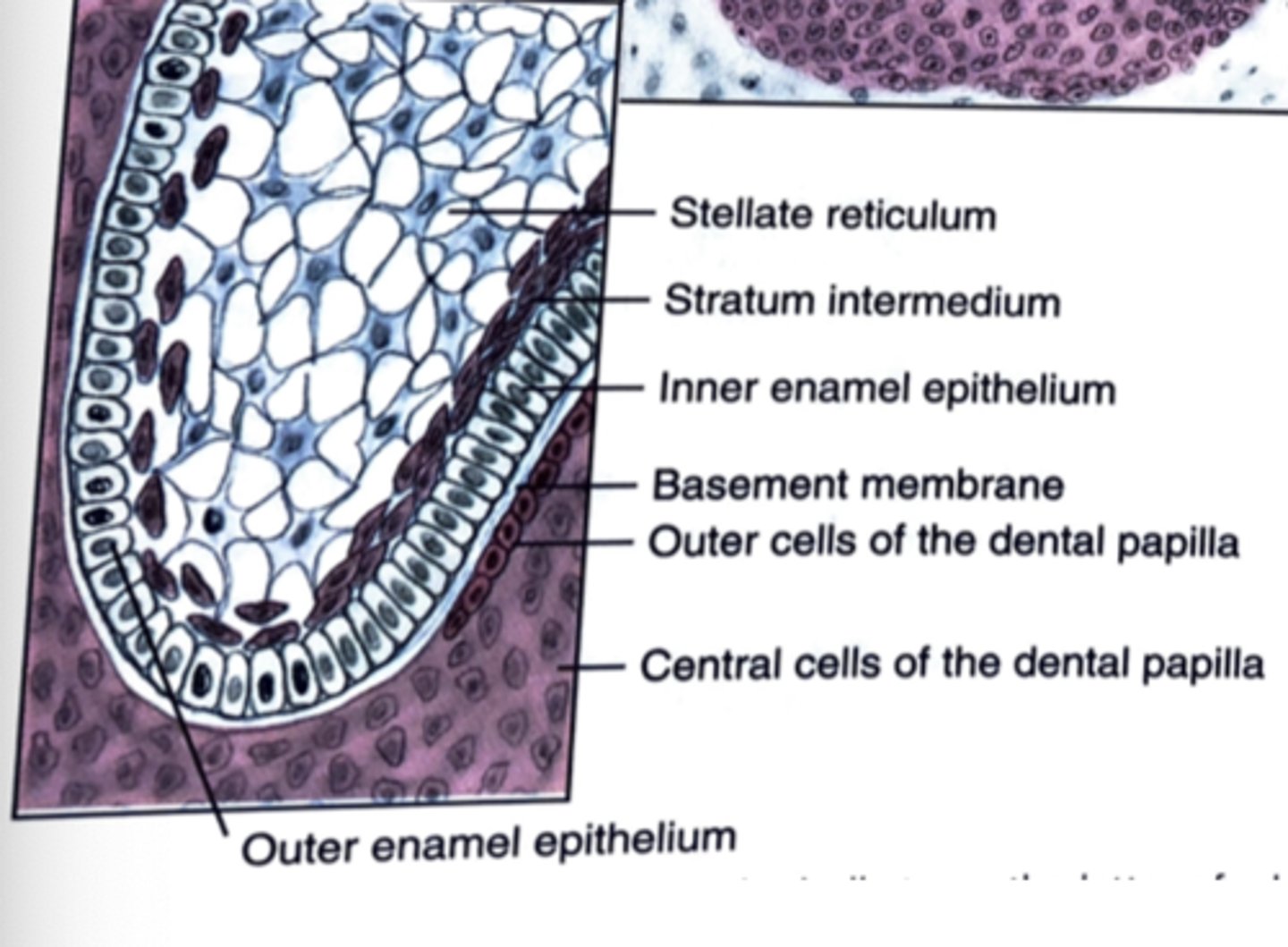
What enamel organ cell is star shaped?
Stellate reticulum
What type of epithelium is the outer enamel epithelium?
Cuboidal
What type of epithelium is the stratum intermedium?
squamous to cuboidal
What type of epithelium is the inner enamel epithelium?
Tall Columnar
What are the two layers of the dental papilla?
1) Outer cells
2) Central cells
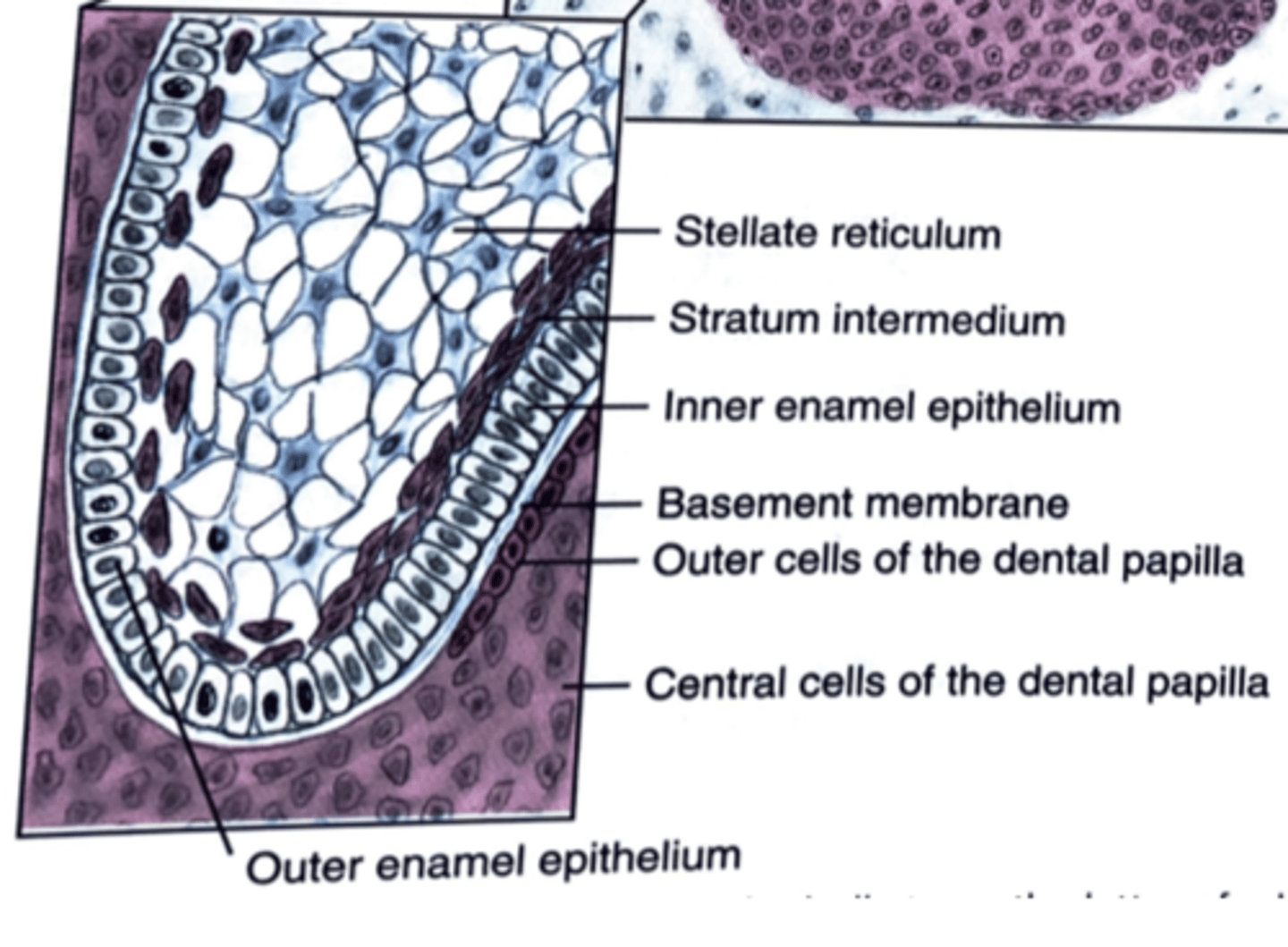
T/F The dental follicle/sac accumulated collagen fibers.
True
What occurs First and second in hard tissue formation?
1) Crown
2) Root
What does the dentin in the crown form from?
odontoblasts (NCC > ectomesenchyme > outer cells of dental papilla > odontoblasts)
What does the enamel in the crown form from?
inner enamel epithelium of enamel organ (originates from ectoderm)
What is root dentin derived from?
odontoblasts (NCC > ectomesenchyme > outer cells of dental papilla > odontoblasts)
What is the periodontium derived from?
dental sac (NCC)
What three structures make up the periodontium and are derived from the dental sac?
1) Cementum
2) Periodontal ligament
3) Alveolar bone
What "_______blast" forms each structure that make up the periodontium?
1) Cementoblasts form Cementum
2) Fibroblasts form Periodontal Ligament
3) Osteoblasts form Alveolar bone
What are the four things that occur during hard tissue formation in the crown?
1) Enamel organ collapses
2) Reciprocal induction
3) Basement membrane disintegrates
4) Dentinoenamel junction forms
During Reciprocal induction, IEE signals to odontoblasts to produce ___________, which triggers ___________ to produce enamel (ectodermal/mesenchymal interaction)
predentin, ameloblasts
What are the two stages of hard formation?
1) Appositional Stage
2) Maturation Stage
What occurs during the apposition stage
Hard tissue matrices of pre-dentin and pre-enamel are laid down
What occurs during the maturation stage
Matrices of hard tissue become fully mineralized into dentin and enamel
Put the following in order of occurrence for the reciprocal induction of hard tissue:
1) Neural crest cells of dental papilla differentiate into
odontoblasts
2) Pre-ameloblasts form from IEE (ectodermal origin)
3) Ameloblast contact with dentin initiates the production of enamel
4) Odontoblasts extend odontoblast processes and
produce pre-dentin
5) Pre-dentin mineralizes to become dentin (more acidophilic = darker pink staining)
2>1>4>5>3
1) Pre-ameloblasts form from IEE (ectodermal origin)
2) Neural crest cells of dental papilla differentiate into
odontoblasts (O)
3) Odontoblasts extend odontoblast processes and
produce pre-dentin (PD)
4) Pre-dentin mineralizes to become dentin (D) (more acidophilic = darker pink staining)
5) Ameloblast (A) contact with dentin initiates production of enamel (E)
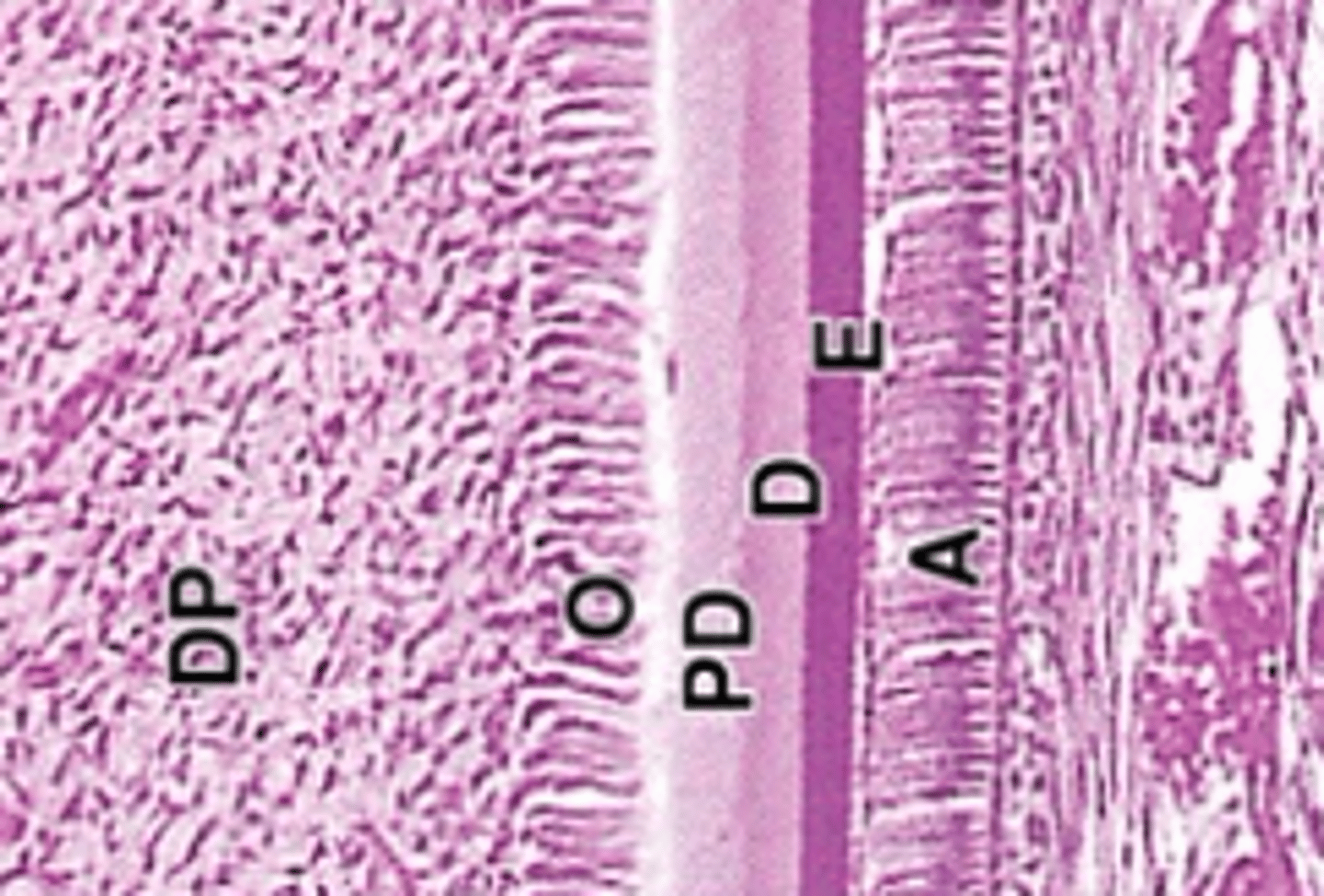
Put the following in order of occurrence for the hard tissue formation in the crown:
1) Ameloblasts form from pre- ameloblasts
2) Odontoblasts form from outer cells
3) Odontoblasts produce pre-dentin matrix (basement membrane begins to disintegrate)
4) Pre-ameloblasts form from IEE (cellular repolarization)
5) Ameloblasts produce enamel matrix
4>2>3>1>5
1) Pre-ameloblasts form from IEE (cellular repolarization)
2) Odontoblasts form from outer cells
3) Odontoblasts produce pre-dentin matrix (basement membrane begins to disintegrate)
4) Ameloblasts form from pre- ameloblasts
5) Ameloblasts produce enamel matrix
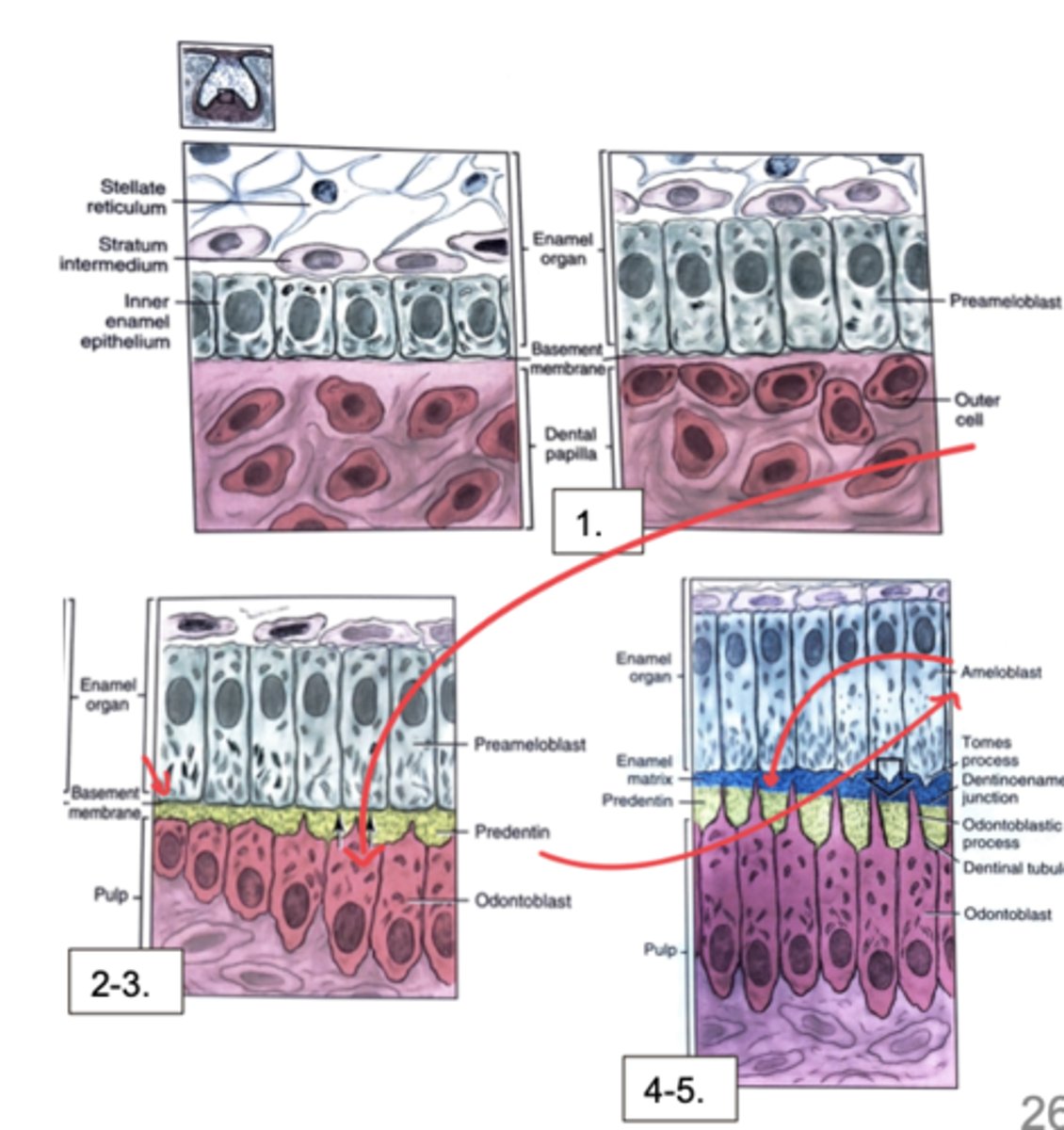
Put the following in order of occurrence for dentinogenesis:
1) Ectomesenchymal cells of the dental papilla are induced by IEE cells to differentiate into pre-odontoblasts and then odontoblasts
2) Once dentin begins to form, the dental papilla is named the
pulp cavity
3) Dentinogenesis (of the crown) begins at the tip (cusp) of the IEE and extends down to the cervical loop
4) Odontoblasts secrete predentin, which then mineralizes to form dentin
1>4>2>3
1) Ectomesenchymal cells of the dental papilla are induced by IEE cells to differentiate into pre-odontoblasts and then odontoblasts
2) Odontoblasts secrete predentin, which then mineralizes to form dentin
3) Once dentin begins to form, the dental papilla is named the
pulp cavity
4) Dentinogenesis (of the crown) begins at the tip (cusp) of the IEE and extends down to the cervical loop
Statement: Dentin formation continues throughout the life of the tooth, and gradually increases the size of the pulp cavity.
1) Both statements A and B are true
2) Both statements A and B are false
3) Statement A is true and B is false
4) Statement A is false and B is true
3) Statement A is true and B is false
(gradually decreases the size of the pulp cavity)
Dentinal tubules contain _______________ ______________ as odontoblasts move away from dentinoenamel junction
odontoblast processes
Put the following in order of occurrence for dentinogenesis:
1) As odontoblasts migrate away from dentin, each cell leaves behind an odontoblast process
2) Calcification (24 hours later) to form dentin (calcium phosphate)
3) Odontoblasts elongate
4) Pre-dentin – type I collagen fibers
5) Outer pulp cells differentiate
6) Odontoblast process forms at the future dentinoenamel junction
5>3>6>4>2>1
1) Outer pulp cells differentiate
2) Odontoblasts elongate
3) Odontoblast process forms at the future dentinoenamel junction
4) Pre-dentin – type I collagen fibers
5) Calcification (24 hours later) to form dentin (calcium phosphate)
6)As odontoblasts migrate away from dentin, each cell leaves behind an odontoblast process
Put the following in order of occurrence for amelogenesis:
1) Reduced enamel epithelium forms from collapsed enamel organ
2) Initial enamel deposition establishes the dentinoenamel junction
3) After a few micrometers of dentin are mineralized and the basement membrane is gone (apposition), ameloblasts secrete enamel (secretory phase)
4) Ameloblasts develop Tomes’ processes at apical ends
3>4>2>1
1) After a few micrometers of dentin are mineralized and the basement membrane is gone (apposition), ameloblasts secrete enamel (secretory phase)
2) Ameloblasts develop Tomes’ processes at apical ends
3) Initial enamel deposition establishes the dentinoenamel junction
4) Reduced enamel epithelium forms from collapsed enamel organ
Ameloblasts
Dentin Odontoblasts
When does reduced enamel epithelium (REE) form?
After enamel production is complete
All of the following are true EXCEPT:
1) Forms after enamel production is complete
2) All tissues of the enamel organ collapse and become indistinguishable
3) Stellate reticulum collapses
4) Ameloblasts become cuboidal
4) Ameloblasts become squamous
Put the following in order of occurrence for Tooth Eruption:
(reduced enamel epithelium = REE)
1) REE secretes enzymes
2) Junctional epithelium forms
3) REE enzymes degrade oral
epithelium
4) REE fuses with oral epithelium
1>4>3>2
1) REE secretes enzymes
2) REE fuses with oral epithelium
3) REE enzymes degrade oral
epithelium
4) Junctional epithelium forms
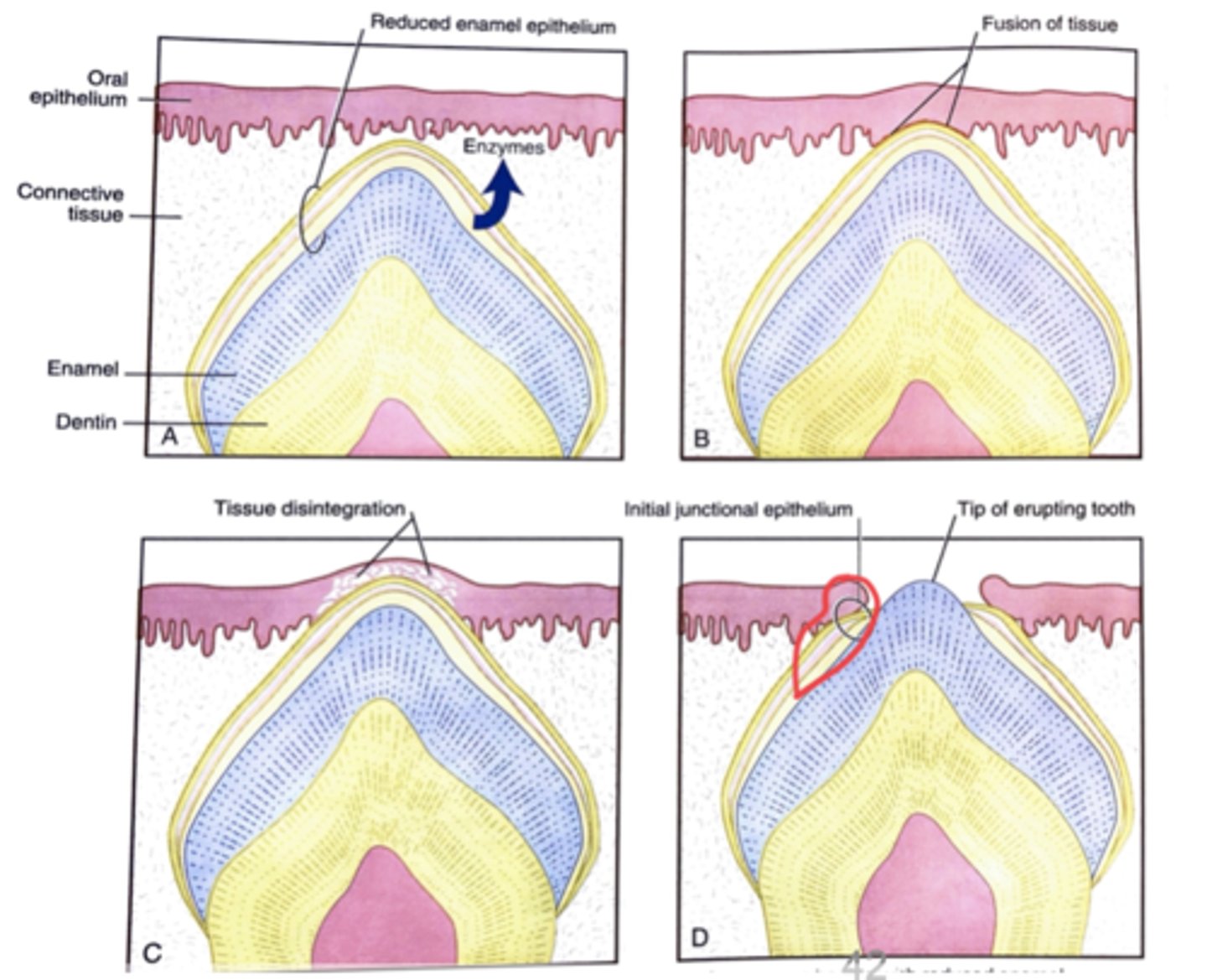
Once junctional epithelium forms the tooth can pass through an epithelial-lined "___________ ___________"
eruption tunnel
Put the following in order of occurrence for Root Development:
1) Cell proliferation where IEE & OEE meet - Hertwig's Epithelial Root Sheath (HERS)
2) IEE of root sheath induces odontoblasts to form (from pulp cavity) and produce root dentin
3) Elongation of the root sheath lengthens the root and dentin formation tapers
4) NCC cells of the dental follicle/sac are induced to form bone (osteoblasts), PDL (fibroblasts), and cementum (cementoblasts)
1>2>4>3
1) Cell proliferation where IEE & OEE meet - Hertwig’s Epithelial Root Sheath (HERS)
2) IEE of root sheath induces odontoblasts to form (from pulp cavity) and produce root dentin
3) NCC cells of the dental follicle/sac are induced to form bone (osteoblasts), PDL (fibroblasts), and cementum (cementoblasts)
4) Elongation of the root sheath lengthens the root and dentin formation tapers
HERS develops from proliferation of the _______ and ______ at the cervical loop
IEE, OEE
Put the following in order of occurrence for Root Hard Tissue Formation:
1) IEE and OEE proliferate at the cervical loop and form Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath (HERS)
2) Cells of the inner dental follicle form into cementoblasts, which secrete cementoid that mineralizes into cementum
3) Outer pulp cells (ectomesenchyme) are induced to become odontoblasts, which secrete root pre-dentin
4) The cementoenamel junction is located at the neck of the tooth (cervical margin)
5) HERS and basement membrane disintegrate
6) Cells of the outer dental follicle form the periodontal ligament and alveolar bone
1>3>5>2>4>6
1) IEE and OEE proliferate at the cervical loop and form Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath (HERS)
2) Outer pulp cells (ectomesenchyme) are induced to become odontoblasts, which secrete root pre-dentin
3) HERS and basement membrane disintegrate
4) Cells of the inner dental follicle form into cementoblasts, which secrete cementoid that mineralizes into cementum
5) The cementoenamel junction is located at the neck of the tooth (cervical margin)
6) Cells of the outer dental follicle form the periodontal ligament and alveolar bone
Statement: Cementum resembles bone, and is vascular.
1) Both statements A and B are true
2) Both statements A and B are false
3) Statement A is true and B is false
4) Statement A is false and B is true
3) Statement A is true and B is false (bone is avascular)
Which of the following statements is True?
1) cementum covers the crown of the tooth
2) cellular cementum cementocytes reside in lacunae but don't have canaliculi
3) Acellular cementum has cementocytes
4) cellular cementum cementocytes reside in lacunae and have canaliculi
4 is True
1) cementum covers the ROOT of the tooth
2) cellular cementum cementocytes reside in lacunae AND have canaliculi
3) Acellular cementum LACK cementocytes