Kinematics and Dynamics
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What are the major SI units?
"My Kind Teacher Always Keeps Moles Counted"
Meter (m)
Kilogram (kg)
Time: second (s)
Ampere (A)
Kelvin (K)
Mole (mol)
Candela (cd)
What are vectors in physics and math?
Vectors are quantities that have both magnitude (size) and direction.
They are often represented by arrows, where the length = magnitude and the arrow points in the direction.
What are the main vector quantities?
Displacement
Velocity
Force
Acceleration
What are scalars in physics and math?
Scalars are quantities that have magnitude only — no direction.
What kinds of quantities can scalars be?
They may be:
Magnitude of vectors — e.g., speed (magnitude of velocity)
Dimensionless numbers — e.g., coefficients of friction, refractive index
How can vectors be added?
Graphical methods:
Tip-to-tail method: Place the tail of the second vector at the tip of the first. The resultant vector goes from the tail of the first to the tip of the last.
Analytical methods:
Component method: Break vectors into x and y components, add all the x components and then add all the y components, then use Pythagoras’ theorem and trigonometry to find the resultant.
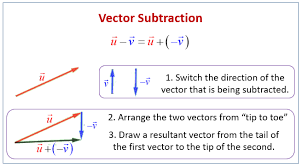
How do you subtract vectors?
Graphical methods:
Graphical method:
Reverse the direction of the vector and use tip-to-tail method.
Component method:
Subtract x and y components separately:
What happens when you multiply a vector by a scalar?
Magnitude changes: The vector gets longer or shorter depending on the scalar.
Direction may reverse: If the scalar is negative, the vector points in the opposite direction.
Direction unchanged if the scalar is positive.
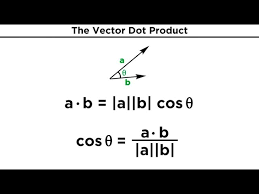
What is the dot product of two vectors?
The dot product is a way to multiply two vectors that gives a scalar (a number), not another vector.
Formula:
A⃗ ⋅ B⃗ =∣A⃗∣∣B⃗∣cosθ
∣A⃗∣| and ∣B⃗∣ are the magnitudes of the vectors
θ is the angle between them
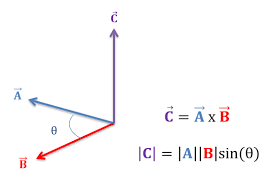
What happens when you multiply two vectors using the cross product?
The cross product (also called vector product) of two vectors results in a vector, not a scalar.
Formula:
A⃗ × B⃗ = ∣A⃗∣∣B⃗∣sinθn^
∣A⃗∣ and ∣B⃗∣| = magnitudes of the vectors
θ = angle between vectors
n^ = unit vector perpendicular to the plane formed by A and B (direction given by the right-hand rule)
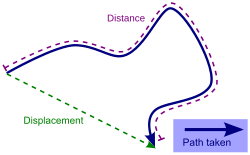
What is displacement in physics?
Displacement is a vector representing the change in position of an object.
Path-independent: Only depends on the starting and ending points, not the route taken.
Magnitude: Straight-line distance between start and end positions.
Direction: Points from start to end.
"Displacement = straight arrow from start to finish" — ignores the path traveled.
What is distance in physics?
Distance is a scalar quantity — it has magnitude only, no direction.
Reflects the total path traveled, not just the start and end points.
Always positive and path-dependent.
"Distance = all the steps you take" — counts the path, ignores direction.
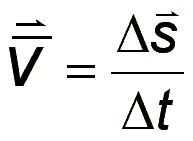
What is velocity in physics?
Velocity is a vector that represents the rate of change of displacement with respect to time.
Formula:
v⃗ = Δx⃗/Δt
Δx⃗ = displacement
Δt = time interval
Has both magnitude (speed) and direction.
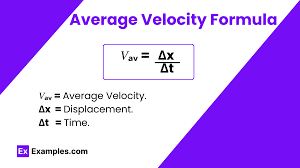
Average velocity:
Definition: A vector that is the total displacement divided by the total time.
v_avg = Δx_total/Δt_total
Average speed:
Definition: Total distance ÷ total time
speed_avg = distance_total/Δt_total
Scalar → has magnitude only.
Path dependent — cares about the full route taken.
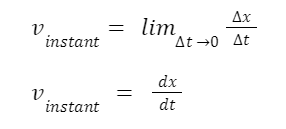
Instantaneous velocity:
The limit of the change in displacement over time as the change in time approaches zero.
Formula:
v = lim Δx/Δt
Δt→0
Represents the velocity at a specific instant.
Vector quantity — includes both magnitude and direction.
Instantaneous speed:
The magnitude of the instantaneous velocity vector.
Scalar quantity — has no direction.
Always non-negative.
Force:
Any push or pull that can cause an acceleration.
Vector quantity — has both magnitude and direction.
SI unit: newton (N), where 1 N = 1 kg·m/s².
Gravity:
Attractive force between two objects due to their masses.
Always acts along the line joining the centers of the objects.
Formula: Fg = Gm1m2/r2
G = gravitational constant 6.67×10−11 Nm2/kg2.
Friction:
Force that opposes motion between two surfaces in contact.
Caused by electrostatic interactions at the surfaces.
Can be static (no motion yet) or kinetic (sliding in progress).
Static Friction:
Exists between two objects not moving relative to each other.
Prevents motion from starting.
Magnitude ranges from 0 up to a maximum value fs ≤ μsN, where μs is the static friction coefficient and N is the normal force.
Kinetic Friction:
Exists between two objects sliding past each other.
Magnitude is fk = μkN, where μk is the kinetic friction coefficient and N is the normal force.
Value is constant for given surfaces and does not depend on speed.
Difference between static and kinetic friction:
Static friction: Varies from 0 up to a maximum depending on the applied force; prevents motion from starting.
Kinetic friction: Constant once objects are sliding; opposes motion.
Key idea: static adjusts, kinetic is fixed.
Coefficient of Friction:
Depends on the two materials in contact.
Static friction coefficient (μs) is always higher than kinetic friction coefficient (μk).
Explains why it’s harder to start moving an object than to keep it sliding.
Mass vs Weight:
Mass: Amount of matter in an object; scalar; constant; SI unit = kg.
Weight: Force due to gravity acting on mass; vector; changes with gravitational field; SI unit = N.
Relationship: W = mg, where g = acceleration due to gravity.
Mass
Measure of an object’s inertia — its resistance to changes in motion.
Represents the amount of material in the object.
Scalar quantity, SI unit = kg.
Weight:
The force experienced by a mass due to gravity.
Formula: W = mg
m = mass
g = acceleration due to gravity (~9.8 m/s² on Earth)
Vector quantity — points toward the center of the Earth.
SI unit = newton (N).
Acceleration:
Vector quantity representing the change in velocity over time.
Can be average or instantaneous:
Average: a⃗avg = Δv⃗/Δt
Instantaneous: a⃗ = dv⃗/dt
Has magnitude and direction.
Newton’s First Law (Law of Inertia)
An object remains at rest or moves with constant velocity if no net force acts on it.
Motion changes only when an unbalanced (net) force is applied.
Mathematically: ΣF⃗ = 0 ⟹ v⃗ is constant.
Newton’s Second Law
Acceleration is produced when a net force acts on a mass.
Formula: F⃗net = ma⃗
The direction of acceleration is the same as the net force.
Newton’s Third Law
When two objects interact, they exert equal and opposite forces on each other.
These forces are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction.
Formula: F⃗AB = −F⃗BA
Linear Motion
Motion in a straight line.
Includes free fall and any motion where velocity and acceleration are parallel or antiparallel.
Path is not curved.
Projectile Motion
Has both x- (horizontal) and y- (vertical) components.
With negligible air resistance, gravity is the only force acting.
Horizontal velocity is constant; vertical motion is affected by acceleration due to gravity.
Inclined Planes
Example of two-dimensional motion.
Best analyzed using axes parallel and perpendicular to the surface.
Parallel axis → motion due to component of gravity.
Perpendicular axis → normal force balances gravity’s perpendicular component.
Circular Motion
Has radial (inward) and tangential (along the path) components.
Uniform circular motion → only force is centripetal, pointing radially inward.
Instantaneous velocity is always tangential to the path.
Free Body Diagrams:
Show all forces acting on an object.
Useful for solving equilibrium and dynamics problems.
Translational Equilibrium
Occurs when no net force acts on an object.
Object moves with constant velocity.
May or may not also be in rotational equilibrium.
Rotational Equilibrium
No net torque on the object.
Pivot point can be anywhere (center of mass is most common).
Constant angular velocity (usually zero on the MCAT).