SCM 4003 exam 4 review
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
offshoring
is the transfer of specific processes to lower-cost locations in other countries
- different from outsourcing because with offshoring the company may still own and control the process itself in the lower-cost location
Nearshoring
the practice of transferring a business operation to a nearby country, often to reduce costs and improve supply chain efficiency.
-Where companies move their offshored activities to countries closer to their home market as a result of the potential risks, delays, and extra costs associated with moving product from a distant location
what is rightshoring
seeking to locate an activity at the 'right' location
Omnishoring
Having a rich portfolio of sourcing destinations (close and far) and of institutional models (a firm’s own facilities and subcontracted ones) that allow firms to manage different products, seasons, stages of product innovation and so forth
what is reshoring (aka reverseshoring or backshoring)
where a company abandons offshoring and moves the activities back to the original home market
What is outsourcing?
defined as the transfer(from the outsourcer) to a third party of the management and delivery of a process previously performed by the company itself
- different from offshoring because outsourcing involves handing process ownership over to a third-party
what is the environmental separation index (ESI)?
an index that measures the difference between the working environments of outsourcer and outsourcee companies
-a metric used to quantify the differences in environmental practices and policies between the outsourcing company and the company receiving the outsourced services. It assesses potential impacts on sustainability and compliance.
what is a master-servent stage of the relationship between the outsourcer and the outsourcee?
in this conventional relationship, the outsourcer sets the expectations and rules and the outsourcee delivers as per the stipulated norms.. low cost is the main driver of the outsourcing arrangements
good and bad things about outsouring
good: sometimes is the best thing to do for a business, can save money
good: improved focus on core competencies, access to specialized expertise, potential for innovation.
bad: a lot of opportunities for outsourcing arrangements to fail
- erosion of standards over time
- 'hidden' costs not originally envisaged begin to surface
- communication delays and breakdown
- differences in culture and understanding between the parties
- outsourcee becomes less dependent upon the outsourcer
bad: an increased risk of losing control over processes, potential data security issues, and challenges in maintaining quality standards.
What are landed costs?
landed costs incorporate the various costs associated with sourcing and receiving products from suppliers - as well as vendor(i.e. material) costs.
- other costs such as working capital, transport, insurance, and so forth are also included
-in the total cost of obtaining products. This ensures that the final price reflects all expenses incurred until the goods reach their destination.
-Landed costs refer to the total expenses involved in acquiring products from suppliers, which include not only the purchase price but also additional costs such as transportation, insurance, duties, and handling until the goods reach their final destination. This comprehensive understanding of costs ensures that businesses accurately reflect all expenses in their pricing strategy.
what are costing material on an ex works basis
literally not defined in the book but this is the only time it is mentioned
- costing materials on an 'ex-works' basis is not adequate to make a purchasing decision and so it is important that all related costs are considered and compared
- Google AI definition: calculating the cost of a product based solely on the materials used to produce it, with no additional costs like transportation, customs clearance, or any other shipping expenses included, as the buyer is responsible for all aspects of delivery once the goods are ready at the seller's factory under the "Ex Works" (EXW) Incoterm.
-costing materials based solely on seller's prices without factoring in delivery expenses
-Costing materials on an 'ex-works' basis refers to calculating product costs focusing only on material expenses at the seller's location, excluding additional costs like delivery, shipping, or customs. This method does not provide a complete picture for purchasing decisions.
what is backwards intergation
integration with selected first-tier and increasingly second-tier suppliers to gain more control over the supply chain and reduce costs.
-This strategy involves acquiring control over the suppliers that provide raw materials and components to improve efficiency and lower expenses.
-Backwards integration is a strategy where a company merges or acquires its suppliers to enhance control over the supply chain, streamline operations, and decrease production costs.
in general, what is procurement?
procurement is an 'umbrella term' that includes sourcing and purchasing and incorporates the activities involved in specifying requirements, identifying appropriate sources, evaluating options, and then arranging the purchase of products and/or services from those sources that are fit for purpose, cost-effective and sustainable
what is the largest estimated component of logistics costs
transportation
what is activity based costing
apportioning costs to a particular actvity and calculating costs per unit, for example cost to pick an item from the warehouse
-Activity-based costing (ABC) is a managerial accounting method that assigns costs to products and services based on the resources they consume, allowing for more precise cost management and pricing strategies.
It helps identify inefficient processes and optimize resource allocation.
what are, in terms of green issues, some key concerns around the world and what are some of the big ones you have to be worried about
- the use of fossil fuels for power generation and the resultant carbon emissions
-These concerns include sustainability in sourcing materials, reducing carbon footprint during transportation, and ensuring that packaging and disposal practices are eco-friendly.
water scarcity, deforestation, and climate change. - Addressing these issues involves adopting sustainable practices and technologies.
what are the 4 main drivers behind the increase emphasis on our green issues
1. legislation
2. cost reduction
3. social responsibility (environmental impact)
4. market pressure
what is the kyoto protocol?
A binding agreement between the world's industrialized nations to reduce greenhouse gases
- called for a 60% reduction in carbon emissions by 2050
carbon footprint of the real life container movements from the middle east to the UK
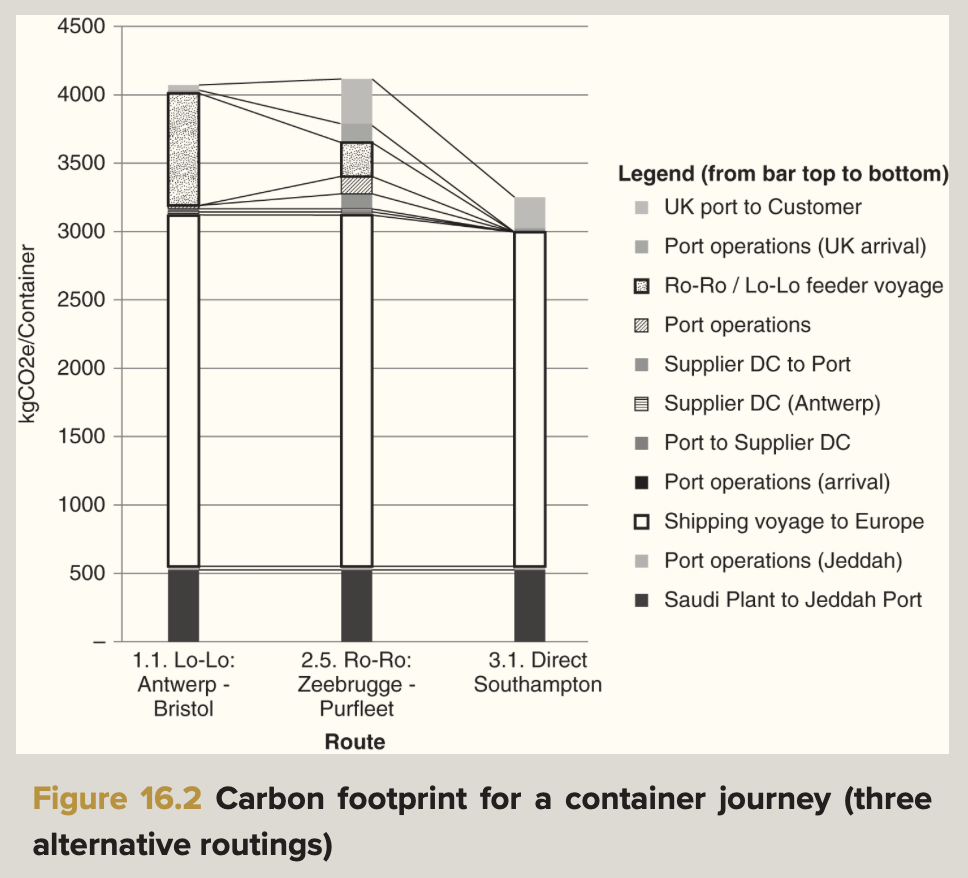
-the total amount of greenhouse gases emitted directly and indirectly through the transportation and handling of containers, including factors like fuel consumption and logistics management.
what are the important ways to green a supply chain?
supply chain design decisions have the greatest impact on the total carbon footprint.
Implementing energy-efficient practices, optimizing transportation, using sustainable materials, and reducing waste.
These strategies can significantly lower emissions and enhance sustainability throughout the supply chain.
a lot of the carbon savings start at what stage in the supply chain
the design stage
what are the three ways to improve sustainability of logistics
1. redesigning supply chains
2. using scale to reduce the negative environmental effects of logistics activities
3. similarly promoting various efficiency solutions
what are the ways to improve road haulage logisitics
- reducing empty running, pooling, and sharing capacity, obtaining 'backhaul' loads
- increasing vehicle payload capacity - double deck and higher trailers, single tractor unit, multiple combinations, etc.
- improved vehicle routing using GPS and other systems
- more efficient use of packaging and loading of containers
- improved vehicle operating efficiency
triangular recovery options hierarchy
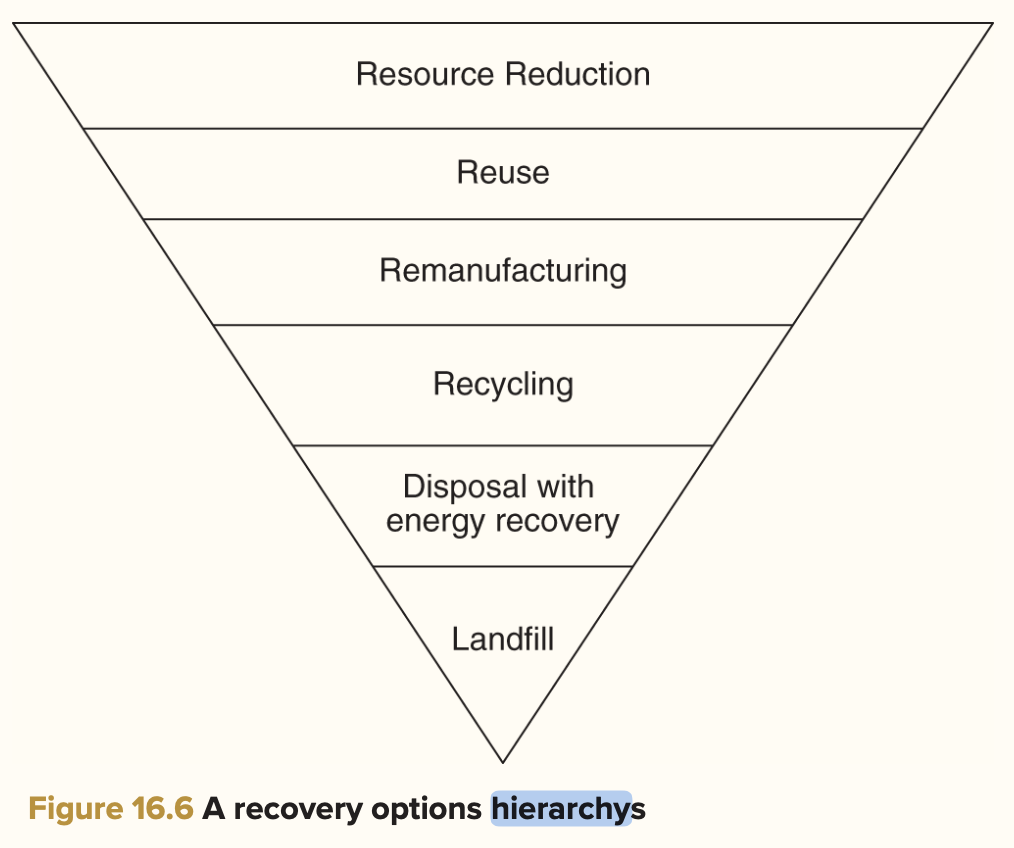
- a hierarchy among recovery options can be obtain by looking at the value they add to the supply chain
what is the circular economy
- aims to eliminate waste by designing and optimizing products for a cycle of disassembly and reuse
- characterized by the '3Rs'
- reduce the use of resources
- reuse products and components
- recycle products and components
fostering sustainable production and consumption patterns, aiming for a closed-loop system that minimizes resource extraction and waste.
Circular economy- for LSCM
For LSCM, the circular economy means that a holistic management approach is needed for materials and products, ensuring that the use of raw materials is minimized, products are designed to be durable and have a long lifespan, and reverse logistics processes are in place. In the circular economy, the whole supply chain endeavors to be fueled by renewable energy, thereby reducing its environmental impact. The overarching aim then is to reduce adverse impoacts of resource on the world's 'natural capital'.
-Circular economy in LSCM focuses on managing resources sustainably, designing durable products, and implementing reverse logistics to minimize environmental impacts and resource use.
We talked about initially focusing on a lean supply chain, and it was really nice because we had a cost reduction. But what do we need to go do going forward?
while the cost reduction is good, it is not enough to survive and prosper today. For many organizations, responsiveness is now a key capability that they wish to enhance
-that enhances customer satisfaction and enables businesses to adapt to market changes rapidly. Therefore, organizations must focus on developing agility alongside lean practices to remain competitive.
instead of producer push, what are we leaning towards
consumer pull, personalized & localized
What are humanitarianism logistics?
encapsulates capabilities for providing logistics services in austere environments, contingency planning for emergencies, and also affords an opportunity for organizations across both the public and private sectors to share expertise
Even if we have a great, great supply chain, it can't compensate for what?
Poor products
What kind of planning do we have to do for greening our supply chain?
forward planning
- it is noted that over 80% of carbon savings are only achievable at the supply chain design stage
What are the three main flows for supply chain?
material, data, & resources
So in order to achieve any measure of success, there's three critical elements that we have to balance, what are they?
people, process, and technology
What is the criteria for performance expectations to meet customer demand (aka to be a supplier)
The criteria for performance expectations include quality, delivery, flexibility, and cost, ensuring that suppliers can consistently meet customer requirements.
-There are a number of issues to be considered in outsourcing: first, how to go about selecting an outsource partner, and then how to effectively manage the chosen partner. In order to effectively manage the outsource arrangement, companies generally put in place a service‐level agreement (SLA) and set various performance metrics.
-An SLA is a key part of a contractual agreement between a customer and a supplier to identify upfront the performance (i.e. service) levels expected. Potential suppliers will have to first qualify by meeting those criteria and/or performance expectations defined in the SLA before they are given proper consideration.
Name a few issues that cause outsourcing to fail
-lack of clear communication,
-cultural differences,
-insufficient quality control,
-and misalignment of goals between the outsourcing company and the provider.
-inadequate monitoring of performance metrics.
-poorly defined expectations.
-and lack of trust between partners.
What are the outsourcer/outsourcee stages
The stages of outsourcing include planning and evaluation, vendor selection, contract negotiation, implementation, and ongoing management and review, ensuring successful partnerships and goal alignment.
Master–servant stage
Consultative stage
Peer‐to‐peer relationship stage
Competitive stage
Master–servant stage
in this conventional relationship, the outsourcer sets the expectations and the rules and the outsourcee delivers as per the stipulated norms. Low cost is the main driver of the outsourcing arrangement.
Consultative stage
this stage is a type of a ‘consultant–client’ relationship. The outsourcer consults with the outsourcee on a regular basis. In addition to the cost, other factors such as quality, reliability and responsiveness are important for sustaining the outsourcing arrangement.
Peer‐to‐peer relationship stage
this is considered to be the ideal stage where the outsourcer and the outsourcee share a peer‐to‐peer relationship. This stage of collaboration results in a more synergistic long‐term relationship creating ‘win–win’ situations for both parties.
Competitive stage
in this stage, the original outsourcee company takes the lead role and starts to compete with the outsourcing company in global markets.
What is a push vs a pull
Push refers to a supply chain strategy where products are manufactured in anticipation of demand,
-Push: Materials are produced according to a planned forecast (which may or may not be accurate) and moved to the next stage of the supply chain
while pull refers to a strategy driven by actual customer demand, with products produced as needed.
-Pull: Materials are only produced and moved when they are required
What do we mean by greening the supply chain
Refers to the integration of environmentally sustainable practices into supply chain management, aiming to reduce waste, emissions, and resource consumption while promoting eco-friendly initiatives. FORWARD PLANNING!
What are some critical elements to keep a supply chain in balance
These include effective communication, inventory management, demand forecasting, supplier relationships, and adaptability to changes in market conditions.
-PEOPLE, PROCESS, and TECHNOLOGY!!)
One way for an outsourcer to look for alternative outsourcees if the qualifier conditions are met, is to look at the level of difference between the working enivornment or the:
Environmental separation index (ESI)
External integration can take on what forms?
Backward, forward, or even a combo
Many companies will procure all the share of a product from one supplier to enjoy the procurment economies of scale.
False
What is minimum wage?
Minimum wage refers to the lowest legal hourly wage that employers can pay their workers, aimed at ensuring a basic standard of living for employees.
What happens when the minimum wage is raised?
Raising the minimum wage can lead to increased earnings for low-income workers, potential job losses or reduced hiring from employers, and adjustments in pricing by businesses to maintain profit margins.
What are the benefits and detriments to raising the minimum wage?
Benefits include higher earnings for workers and reduced poverty,
while detriments may involve increased unemployment rates and potential inflation.
What is the border economy?
The border economy refers to the economic activities and interactions that take place between neighboring countries along their shared borders, often involving trade, labor, and cross-border investments.
What is the on-demand economy?
The on-demand economy is a digital economy that enables consumers to access goods and services whenever they need them, often facilitated through mobile applications and platforms that connect providers with consumers.