Final Test - Digestive and Senses
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
175 Terms
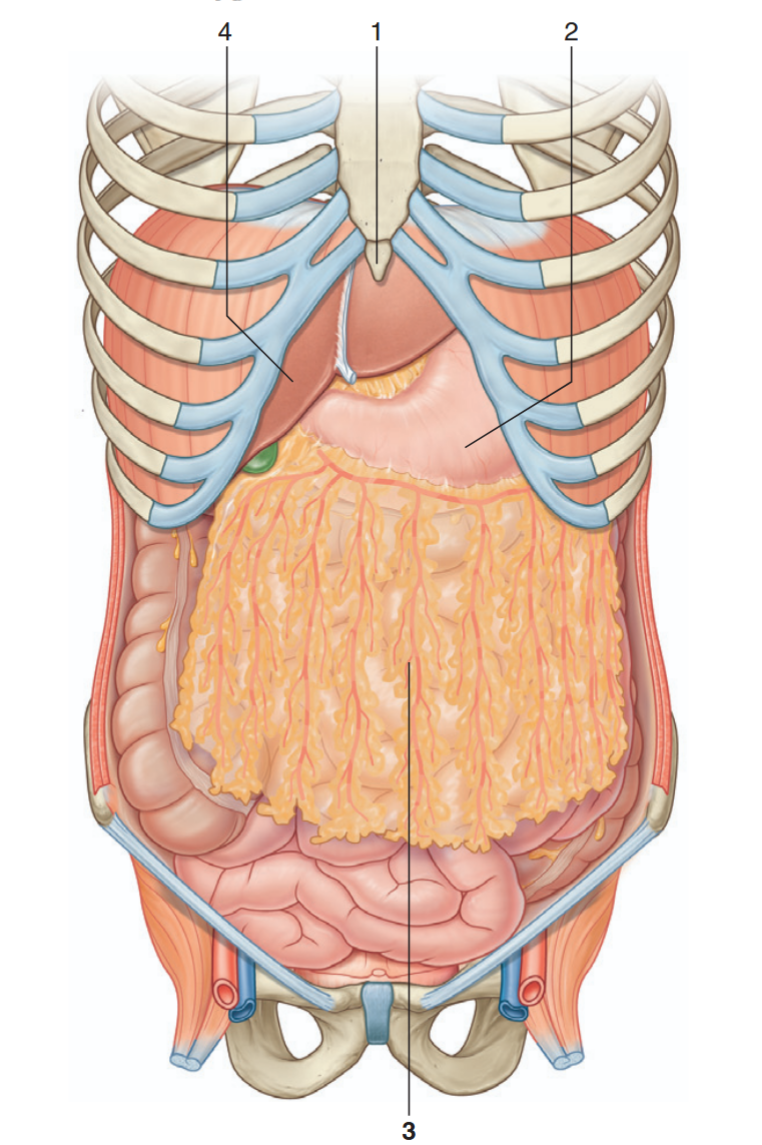
Identify the indicated structures
xiphoid process
stomach
greater omentum
liver
What are the two main anatomical divisions of the digestive system?
The gastrointestinal (GI) tract/alimentary canal and the accessory organs.
What is the primary function of the organs in the gastrointestinal tract?
To form a continuous tube through which ingested food material passes.
List three examples of accessory digestive organs.
Salivary glands, gallbladder, and pancreas.
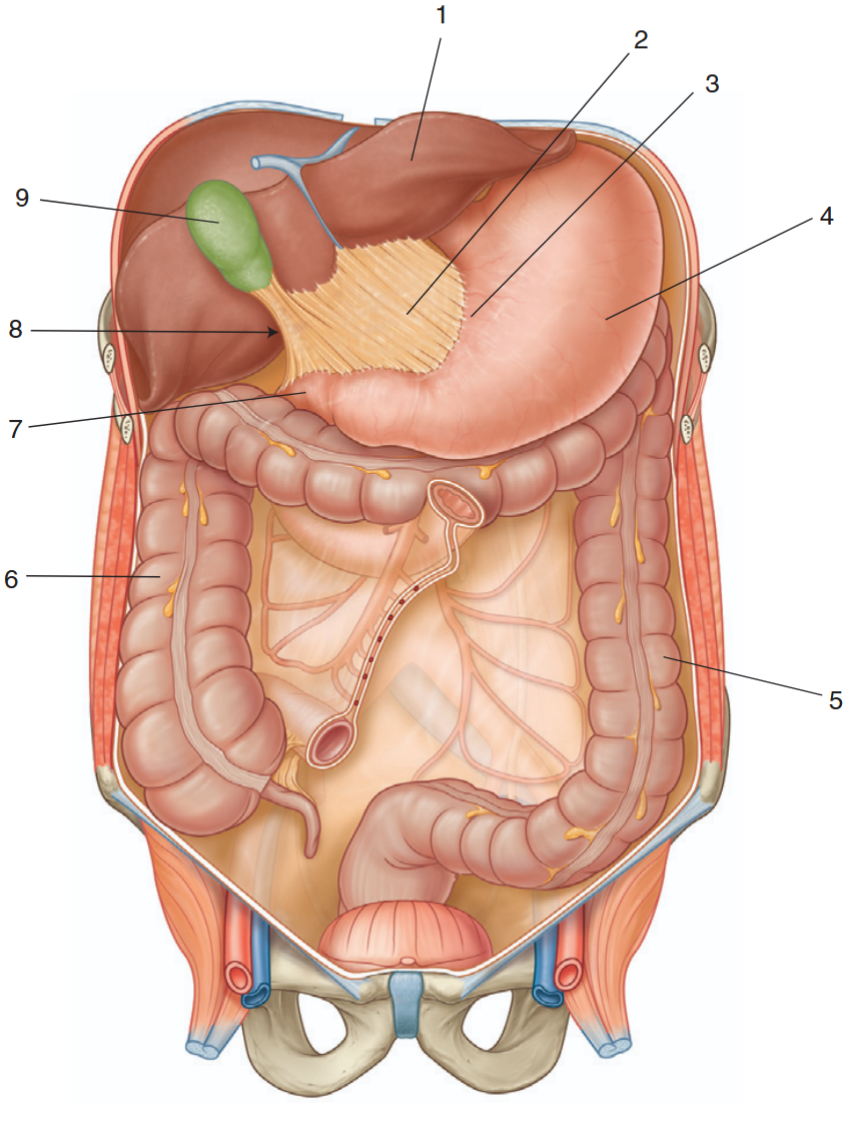
Identify the indicated structures
liver
lesser omentum
lesser curvature of the stomach
stomach
descending colon
ascending colon
duodenum
omental foramen
gallbladder
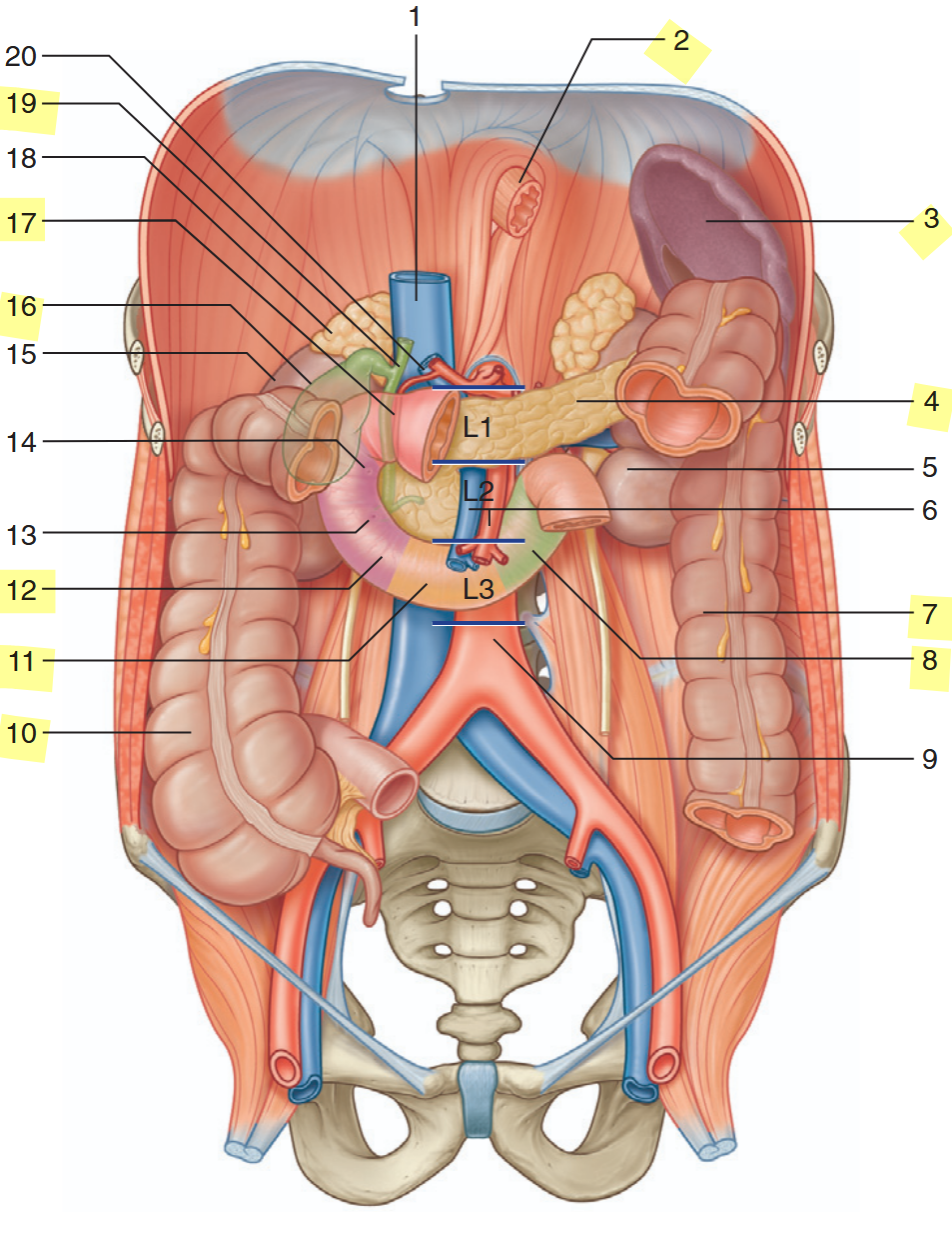
identify the highlighted structures
esophagus
spleen
pancreas
descending colon
duodenum (ascending)
ascending colon
duodenum (inferior)
duodenum (descending)
gallbladder
duodenum (superior)
bile duct
In what fundamental way is material within the lumen of the GI tract considered to be "outside" the body?
It is outside the internal environment; it is exocrine.
What is the core process of digestion?
Breaking down food into smaller, absorbable molecules.
What are the four primary tissue layers (tunics) of the GI tract, from innermost to outermost?
Mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, serosa.
Which layer of the GI tract contains the epithelial lining, lamina propria, and muscularis mucosae?
The mucosa.
Which layer of the GI tract contains blood vessels, glands, and the submucosal nerve plexus?
The submucosa.
What is the primary function of the muscularis layer in the GI tract?
To provide motility (movement) via smooth muscle contractions.
What is the outermost layer of the GI tract, often continuous with the mesentery?
The serosa.
What is the function of the mesentery?
To support and anchor the intestines, allowing free movement and preventing strangulation.
What forms the anterior boundary of the oral cavity?
The lips.
What muscle forms a large part of the structure of the cheeks?
The buccinator muscle.
What two structures form the roof of the mouth?
The hard palate (anterior) and the soft palate (posterior).
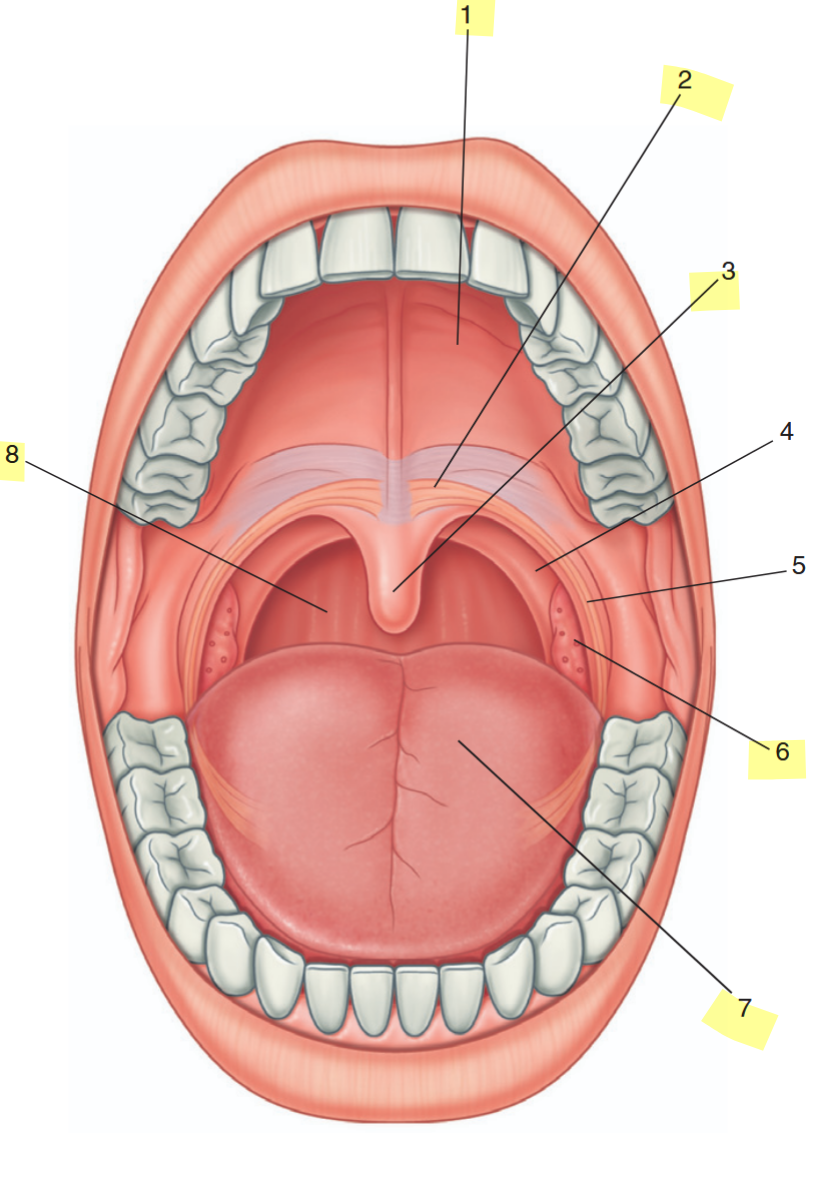
identify the highlighted features
hard palate
soft palate
uvula
palatine tonsil
oral part of tongue
posterior wall of oropharynx
What is the function of the soft palate and uvula during swallowing?
They elevate to prevent food from entering the nasal cavity.
Where are the palatine tonsils located?
Between the muscular arches (faucial pillars) in the oropharynx.
What type of muscle comprises the bulk of the tongue?
Skeletal muscle.
What structure anchors the tongue to the floor of the mouth?
The lingual frenulum.
What is the term for an abnormally short lingual frenulum that restricts tongue movement?
Ankyloglossia (tongue-tie).
What are the three major pairs of salivary glands?
Parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands.
Which salivary gland is the largest and produces a watery, enzyme-rich saliva?
The parotid gland.
Which salivary glands produce a mixed serous and mucous secretion?
The submandibular glands.
What are the three main anatomical parts of a typical tooth?
Crown, neck, and root.
What is the hardest substance in the human body, covering the tooth crown?
Enamel.
What tissue comprises the majority of the tooth's structure, underlying both enamel and cementum?
Dentin.
How many deciduous (baby) teeth are there?
20.
How many permanent teeth are there, including wisdom teeth?
32.
What type of epithelium lines the esophagus for protection against abrasion?
Stratified squamous epithelium.
What are the two sphincters of the esophagus?
The upper esophageal sphincter (UES) and the lower esophageal sphincter (LES).

Identify the indicated parts of the stomach
cardiac notch
fundus
body
greater curvature
pyloric antrum
pyloric canal
angular incisure
lesser curvature
cardia
What are the four main anatomical regions of the stomach?
Cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus.
What are the folds of the stomach's inner mucosal lining called?
Rugae.
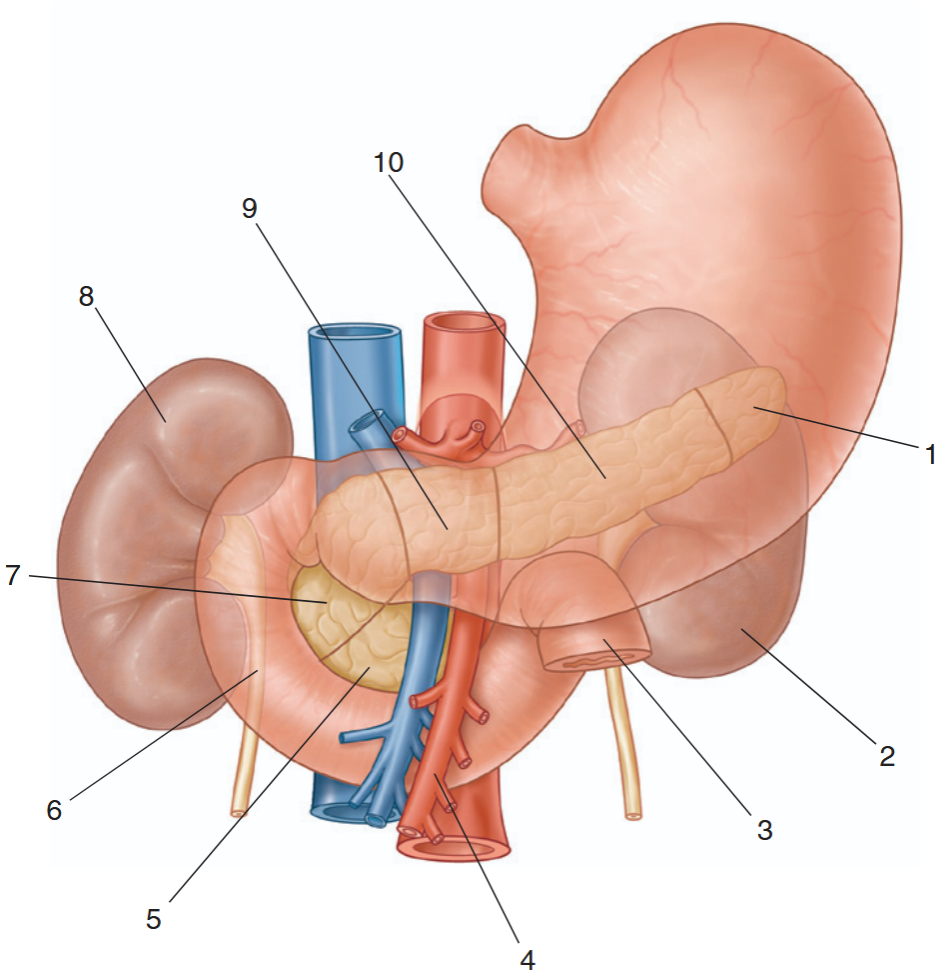
identify the indicated structures
tail of pancreas
left kidney
jejunum
superior mesenteric artery
uncinate process
duodenum
head of pancreas
right kidney
neck of pancreas
body of pancreas
What sphincter controls the passage of food from the stomach into the duodenum?
The pyloric sphincter.
What do chief cells in the gastric glands secrete?
Digestive enzymes (e.g., pepsinogen).
What do parietal cells in the gastric glands secrete?
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) and intrinsic factor.
What is the function of intrinsic factor secreted by parietal cells?
It is essential for the absorption of vitamin B12 in the small intestine.
What are the three divisions of the small intestine, in order?
Duodenum, jejunum, ileum.
What microscopic structures in the small intestine greatly increase its surface area for absorption?
Villi and microvilli (brush border).
What is the function of the lacteal vessel within each intestinal villus?
To absorb dietary fats (as chylomicrons) into the lymphatic system.
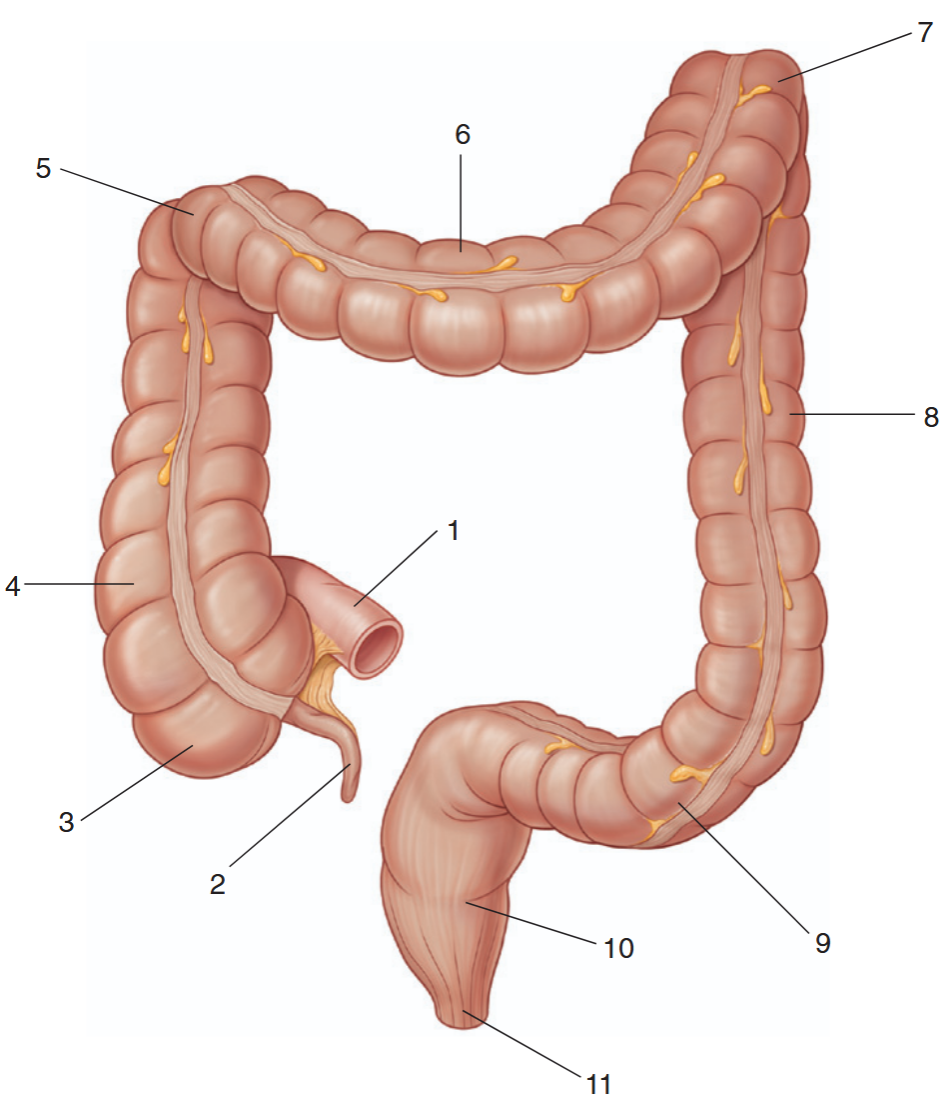
identify the indicated parts of the large intestine
ileum
appendix
cecum
ascending colon
right colic flexure
transverse colon
left colic flexure
descending colon
sigmoid colon
rectum
anal canal
What are the four main anatomical divisions of the large intestine?
Cecum, colon, rectum, anal canal.
What is the name of the small, worm-like appendage attached to the cecum?
The vermiform appendix.
What valve prevents material from flowing back from the large intestine into the ileum?
The ileocecal valve.
What are the four segments of the colon, in order from the cecum?
Ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon.
What is the primary secretory cell type in the mucosa of the large intestine?
Goblet cells (secreting mucus).
What is the large, continuous sheet of serous membrane that lines the abdominopelvic cavity and covers its organs?
The peritoneum.
What is the name for the peritoneum that lines the cavity wall?
Parietal peritoneum.
What is the name for the peritoneum that covers the organs?
Visceral peritoneum.
What is the term for organs located outside the parietal peritoneum, against the posterior body wall?
Retroperitoneal.
What is the fatty, apron-like extension of the peritoneum that hangs over the intestines?
The greater omentum.
What structure attaches the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach and the duodenum?
The lesser omentum.
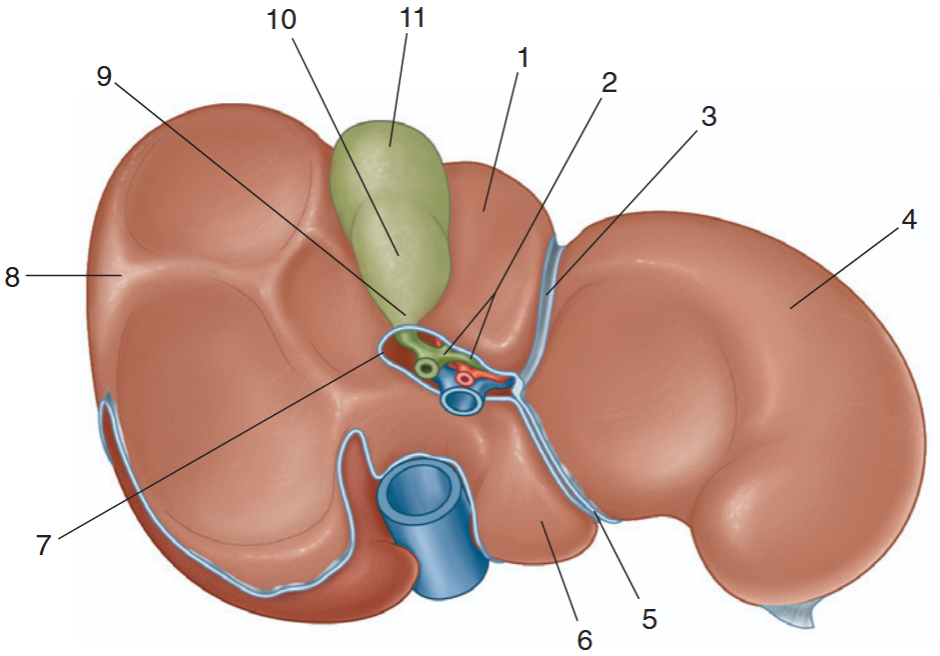
identify the indicated parts of the liver and gallbladder
quadrate lobe
hepatic ducts
fissure for ligamentum teres
left lob of liver
fissure for ligamentum venosum
caudate love
porta hepatis
right lobe of liver
neck of gallbladder
body of gallbladder
fundus of gallbladder
What is the largest gland in the human body?
The liver.
What are the functional, microscopic units of the liver?
Hepatic lobules.
What are the phagocytic cells lining the liver sinusoids that remove pathogens and debris?
Kupffer cells.
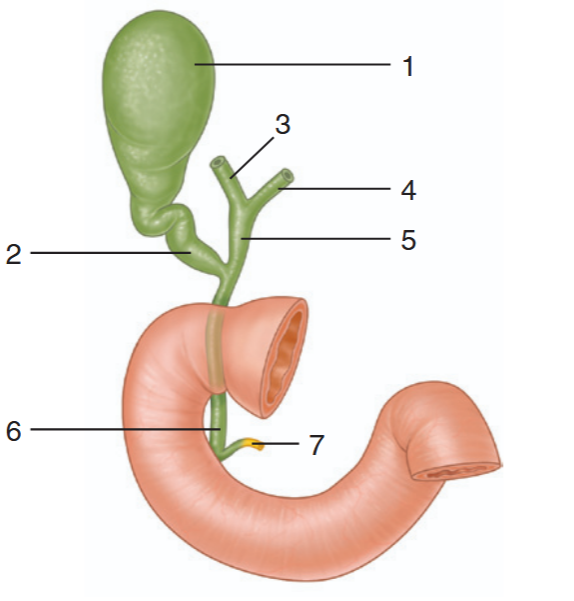
identify the indicated parts of the bile drainage system
gallbladder
cystic duct
right hepatic duct
left hepatic duct
common hepatic duct
bile duct
main pancreatic duct
What is the name of the duct system that transports bile from the liver and gallbladder to the duodenum?
The biliary tract (or biliary tree).
Trace the flow of bile: Liver produces bile -> hepatic ducts -> ? -> common bile duct -> ? -> duodenum.
Liver produces bile -> hepatic ducts -> common hepatic duct -> (joins with cystic duct from gallbladder) -> common bile duct -> (joins with pancreatic duct at hepatopancreatic ampulla) -> duodenum via major duodenal papilla.
What is the primary function of bile?
To emulsify fats, increasing their surface area for enzymatic digestion.
Where is bile produced, and where is it stored and concentrated?
Produced in the liver; stored and concentrated in the gallbladder.
What are the two main functional components of the pancreas?
The exocrine acinar tissue (secretes digestive enzymes) and the endocrine islets of Langerhans (secrete hormones).
What pancreatic cells secrete insulin?
Beta cells (β-cells).
What pancreatic cells secrete glucagon?
Alpha cells (α-cells).
What age-related change in the digestive system can allow intact proteins to trigger allergic responses in infants?
Immature intestinal mucosa with higher permeability.
What is a common age-related digestive change in older adults that can lead to constipation?
Decreased digestive fluids, slowed peristalsis, and reduced physical activity.
What is diverticulosis?
The presence of abnormal sac-like out-pouchings (diverticula) in the intestinal wall.
What is the primary difference between diverticulosis and diverticulitis?
Diverticulosis is the presence of diverticula (often asymptomatic). Diverticulitis is the inflammation of those diverticula, causing pain and infection.
What is the classic early symptom progression of acute appendicitis?
Dull periumbilical pain that migrates to sharp pain in the right lower quadrant over a few hours.
What is rebound tenderness, and what does it often indicate?
Pain that is worse when pressure is suddenly released from the abdomen. It often indicates peritoneal inflammation, as in appendicitis.
What are hemorrhoids?
Dilated (varicose) veins of the rectum and anus.
What is the primary function of the digestive system?
To bring essential nutrients into the internal environment for use by the body's cells.
What are the five main mechanisms used by the digestive system to accomplish its primary function?
Ingestion, digestion, absorption, elimination, and regulation.
What is ingestion?
The process of taking food into the mouth.
What is the difference between mechanical and chemical digestion?
Mechanical digestion physically breaks food into smaller pieces. Chemical digestion uses enzymes to break complex molecules into simple ones.
What is the process of moving nutrients from the GI tract into the internal environment called?
Absorption.
What is peristalsis?
A progressive, wavelike muscular contraction that propels food along the GI tract.
What is segmentation?
A back-and-forth mixing movement within a single segment of the GI tract that breaks apart food and mixes it with digestive juices.
Where does carbohydrate digestion begin, and what enzyme is responsible?
It begins in the mouth with salivary amylase.
What are the final digestive enzymes for carbohydrates, and where are they located?
Sucrase, lactase, and maltase; they are located in the brush border of the small intestine.
What causes lactose intolerance?
A deficiency in the brush-border enzyme lactase.
What is the optimal pH for pepsin, and where is it active?
Approximately pH 2-3; it is active in the stomach.
What is the optimal pH for trypsin, and where is it active?
Approximately pH 6; it is active in the small intestine.
What is the main function of bile in fat digestion?
To emulsify fats, breaking large droplets into smaller ones to increase surface area for lipase action.
What are micelles, and what is their role?
Tiny spheres formed by bile salts and lecithin that transport lipid digestion products to the intestinal mucosa for absorption.
What is the main fat-digesting enzyme, and where is it secreted from?
Pancreatic lipase, secreted by the pancreas.
What is the role of colipase?
It anchors lipase to the surface of a micelle, positioning it for optimal fat digestion.
What enzyme in saliva begins starch digestion, and what component optimizes its pH?
Salivary amylase; sodium bicarbonate increases pH for optimal function.
What is the inactive precursor of pepsin called, and why is it secreted in this form?
Pepsinogen; to prevent the enzyme from digesting the proteins of the stomach wall.
What cells secrete hydrochloric acid (HCl) in the stomach?
Parietal cells.
What are the two primary functions of HCl in the stomach?
Activates pepsinogen to pepsin. 2. Denatures proteins to make them easier to digest.
What is the function of intrinsic factor, and what cells secrete it?
It binds to vitamin B12 to facilitate its absorption in the ileum; secreted by parietal cells.
What deficiency results from a lack of intrinsic factor?
Pernicious anemia (due to impaired B12 absorption).
What are the three phases of gastric secretion control?
Cephalic phase, gastric phase, intestinal phase.
What stimulates gastric secretion during the cephalic phase?
The sight, smell, taste, or thought of food (via vagus nerve stimulation).
What stimulates gastric secretion during the gastric phase?
Distention of the stomach by food and the presence of peptides/amino acids.