Gen Psych Exam #1
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam date: Friday September 29, 2023
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
psychology
the scientific study of thought, behavior, and emotion
hindsight bias
overestimation of the ability to have predicted an outcome
scientific method
tests ideas with the use of data- evidence (empiricism)
formulate the research question
formulate the hypothesis
design the study to test the hypothesis
perform the study (test the hypothesis)
interpret the data (draw conclusions)
communicate the findings
hypothesis
testable prediction
operational definition
statement about the procedures the researcher used to measure a variable
case study
in depth analysis of one subject (or more)
advantages and disadvantages of a case study
advantages: in depth knowledge and insights, understanding the cause and effect relationship between different variables
disadvantages: cannot be generalized to all subjects or cases, may be biased by the researcher, participants, or sources
observational method
Describe and measure people and/or animals' behavior systematically (observe behavior of parents dropping off kids at day care)
advantages and disadvantages of the observational method
advantages: easiest method, helpful for framing hypothesis, enhanced accuracy, global method
disadvantages: lack of clarity, subject to bias, lack of reliability, improper perception, expensive
survey method
Asking people questions about their thoughts, feelings, desires, and actions and recording their answers
advantages and disadvantages of the survey method
advantages: low cost, simplicity, ease of creation, quick feedback, high representativeness of large population
disadvantages: survey bias/response bias, survey fatigue, sampling errors, wording
wording effects
refers to the possible effects on participants caused by the order of presented words or even the choice of the words themselves. Wording effect can influence how people perceive and respond to different situations, such as gains and losses or emotional distress. Wording effect can also affect the expression of genes that regulate physical and emotional stress.
response bias
pattern of responses to questions that does not accurately reflect the content of the question
random sampling (aka random selection)
everyone in the population has an equal chance of being in the sample (being studied)
correlation (correlational method)
measures strength and direction of relationship between two variables
positive correlation
variables change in the same direction
negative correlation
variables change in opposite directions
correlation coefficients (rs)
indicator of the strength of the relationship between two variables (ranges from -1.00 to+1.00)
third variable
correlation does not indicate causation!!
instead of A causing B, B could cause A
OR there could be a third variable C that causes both A and B
experiment
researcher changes (manipulates) one variable and measures the effects of that change on another variable
the only research design in which cause and effect can be inferred
purpose: to test the effects of the IV on the DV, does the IV cause the DV?
independent variable (IV)
manipulated by the experimenter
dependent variable (DV)
outcome variable
experimental (treatment) condition (group)
receives treatment/stimulus
control condition (group)
does not receive treatment/stimulus (comparison group)
confounding variable
variable that is potentially responsible for the results, but is not the variable of interest (the IV)
random assignment
method used to place participants into experimental condition in which participants have an equal chance of being in every condition
experimental control
researcher makes sure that no factors other than the IV are changing and thus could affect the DV
placebo effect
observed improvement following an inert treatment
placebo control group
participants who receive placebo rather than actual treatment or nothing
expectancy effect (type of experimenter bias)
results when the experimenter's hypothesis(expectation) leads unintentionally to behavior toward the participants that then increases the likelihood that the participants' behavior will confirm the hypothesis (e.g., Rosenthal & Jacobson,1968)
single-blind procedure
the participants do not know if they have been assigned to the experimental or control group
double-blind procedure
neither the participants nor the researchers know who has been assigned to the experimental or control group
generalizability
the extent to which we can claim our findings inform us about a group larger than the one we studied (issue in research) (Can the results apply to other situations?)
replication
repetition of a study (important issue in research)
informed consent
permission based on researchers giving people enough information about a study to enable them to decide whether they wish to participate
debriefing
after an experiment ends, explaining to participants the study's purpose and any deceptions researchers used
biological/neuroscientific perspective
how physical systems (e.g., the brain) affect behavior, feelings, and thoughts
evolutionary perspective
how the natural selection of traits has promoted the survival of genes
behavioral genetic perspective
how our genes and our environment influence our behaviors
psychoanalytic/psychodynamic perspective
emphasizes the role of unconscious conflicts in determining behavior and personality, unconscious dynamics within the individual
behavioral perspective
learning via reinforcements and punishments
cognitive persepective
how people reason, remember, and interpret
social/cultural perspective
how social and cultural forces shape individuals' behavior
neurons
specialized cells that transmit neural messages to other neurons, glands, and muscles
dendrites
receives neural messages from other neurons
cell body (soma)
houses DNA
axons
thin tubes that transmit messages
glial cells (glia)
provide structure for neurons
blood-brain barrier
prevents some toxins from entering the brain, formed by some glial cells
myelin sheath
specialized cells that are wrapped around the axon to help transmit messages, formed by some glial cells
action potential
electrical signal within a neuron, electrical impulse that travels from the cell body down to the end of the axon (neural firing)
threshold
the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse, level of electric charge needed to stimulate action potential
all or none response
a neuron's reaction of either firing (with a full-strength response) or not firing.
once the electric charge of the neuron reaches a certain threshold, it fires an action potential
synapse
junction between two neurons, messages are transmitted across synapse via neurotransmitters
neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that travel across synapse form sending neuron to receptors on receiving neuron
reuptake
sending neuron reabsorbs excess neurotransmitters
inhibitory signals
decrease likelihood that neuron will fire
excitatory signals
increase likelihood that neuron will fire
acetylcholine (ACh)
involved in muscle action, learning, memory
endorphins
reduce pain and promote pleasure
dopamine
involved in voluntary movement, reward, learning, memory
serotonin
involved in sleep, appetite, mood
glutamate
excitatory- learning, memory, enhancement
GABA
inhibitory- calms
epinephrine and norepinephrine
adrenaline and noradrenaline
involved in stress response/fight or flight response
agonists
increase normal activity of a neurotransmitter
antagonists
decrease activity of a neurotransmitter
motor neurons
carry signals from brain or spinal cord to muscles, skin, and glands
sensory neurons
carry messages from receptors to spinal cord and brain
central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
responds to sensory information, sends messages to muscles, glands, organs
spinal reflexes
automatic responses that occur without any brain involvement
peripheral nervous system
all of the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord. allows communication between CNS and sensory systems. contains somatic and autonomic nervous systems
somatic nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's skeletal muscles
voluntary, sensory and motor pathways
autonomic nervous system
peripheral nervous system division that the glands and the muscles of the internal organs such as the heart and digestive system
contains sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems
sympathetic nervous system
arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations. increase heartbeat, blood pressure, and blood sugar levels. also slows down digestion and cools you with perspiration
parasympathetic nervous system
calms the body, conserving its energy. decreases heart beat, lowers blood sugar, enables you to rest and digest
endocrine system
Consists of glands that control many of the body's activities by producing hormones.
hormones
chemicals secreted by endocrine glands into bloodstream
hypothalamus
(brain structure) controls pituitary gland
pituitary gland
"master gland" endocrine glands' control center. a pea sized structure located in the brains core that is controlled by the hypothalamus and releases lots of hormones (growth hormone, oxytocin)
adrenal glands
a pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) that help arouse the body in times of stress.
important in mood, energy level, stress response
electroencephalogram (EEG)
Detect electrical activity of neurons in particular regions of brain
Does not produce image of the brain but can be used to asses function
PET scan (positron emission tomography)
Records biochemical changes in brain as they are happening in different locations
CAT scan (computerized axial tomography)
X-ray beams sent through head
Picture of brain tissues
spinal cord
extension of the brain. handles both incoming and outgoing messages, acts as a bridge between brain and body below neck
pineal gland
secretes melatonin, regulates sleep and circadian rhythm
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
Uses magnetic field to measure activity of various brain areas
fMRI (funcitonal magnetic resonance imaging)
uses MRI to measure relative activity of various brain areas during tasks (MRI with stimulus)
brainstem
medulla and pons
medulla
controls life sustaining bodily functions (breathing, gagging)
Regulates heartbeat and breathing, essential for survival
pons
involved in sleep; connects cortex to lower brain regions (bridge between lower centers and higher centers like the cortex)
reticular formation
controls alertness, attention
thalamus
relay station
Directs incoming information from sensory receptors to cerebral cortex
All senses but smell
cerebellum
coordination of movement, Balance, muscle coordination, Memory of simple skills
Habitual, things we do all the time so we don’t need to think about it (walking, typing, playing an instrument)
As we get older, the cerebellum doesn’t work as well. This, in part, explains why the risk of falling increases as we get older
amygdala
emotions
Aggression, fear
Can be damaged due to natural causes like a stroke or other injury to the brain
hypothalamus
regulates endocrine activity
Controls hormone release
reward/pleasure
hippocampus
gateway to memory
Enables formation of new conscious memories
cerebral cortex
Higher forms of thinking
2 hemispheres of cerebral cortex- left and right
4 lobes on each hemisphere – and their locations
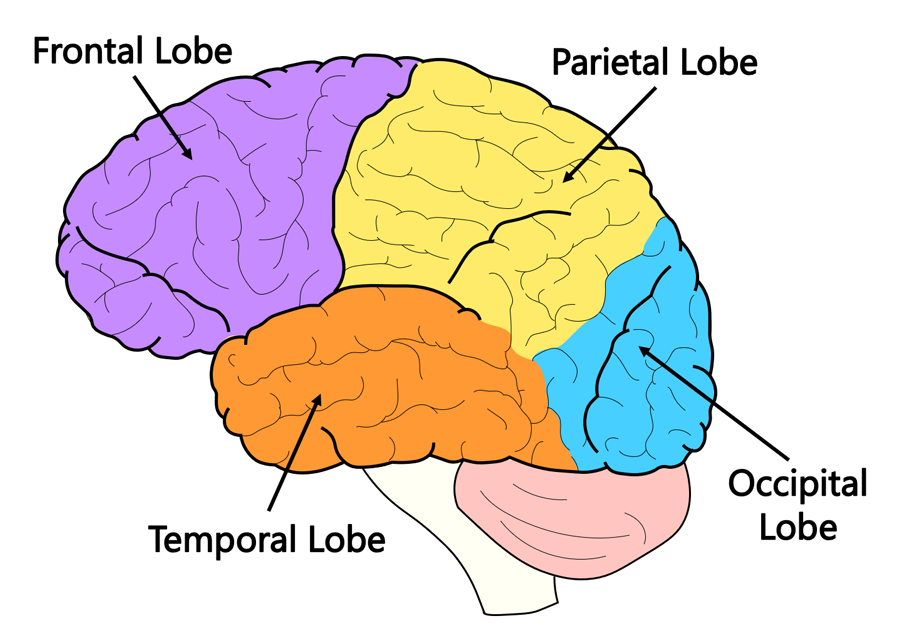
Frontal lobes
Parietal lobes
Occipital lobes
Temporal lobes
location of the 4 lobes
frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, temporal lobe