VM 534 Final Exam
1/170
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
171 Terms
You just received a biopsy report from a mast cell tumor you removed from a 14-year-old female spayed Chinese Shar pei. Which of the following is most worrisome regarding the dog’s prognosis?
A. The tumor was 2 cm in diameter
B. There was metastasis in the nearest lymph node (which you also removed)
C. The mitotic count was 9 per 10 hpf
D. The tumor was in the inguinal region
C.
Which of the following is a Primary cause of Otitis Externa?
A. Atopic Dermatitis
B. Bacteria
C. Swimming
D. Excessive Hair
A.
T/F: Underlying disease should be a minor consideration when managing Otitis Externa.
False
Which of the following medications would be MOST appropriate to treat a first time Otitis Externa only yeast identified on cytology?
A. Mometamax (gentamicin, clotrimazole, mometasone)
B. Animax (neomycin, nystatin, triamcinolone)
C. Miconazole
D. Silver Sulfadiazine
C.
T/F: From a pathophysiological standpoint Atopic Dermatitis in dogs is a multifaceted disease process. It is a vicious cycle of barrier defects of the skin, giving allergens and bacteria access to the immune system, subsequent reactions cause an inflammatory cascade and failure of tolerance.
True
T/F: Atopic Dermatitis in dogs can be cured in most cases with Allergen specific immunotherapy.
False
T/F: A dog with a food allergy may present with the history of a non-seasonal pruritus of 1 year's duration, which developed for the first time in the dog’s life at 11 years of age, as a food allergy may not clinically express this problem from an immunologic standpoint until late in life.
True
T/F: Atopic dermatitis can be diagnosed by intradermal testing or in-vitro testing (ELISA) alone?
False
What are the three most common cutaneous malignancies in dogs?
A. Squamous cell carcinoma, lymphoma, mast cell tumor
B. Mast cell tumor, lipoma, histiocytoma
C. Basal cell tumor, mast cell tumor, squamous cell carcinoma
D. Melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma, mast cell tumor
D.
What differentiates carcinoma from carcinoma in situ?
A. Carcinoma in situ is more locally aggressive than carcinoma
B. Carcinoma in situ is associated with FeLV while carcinoma is associated with PPV
C. Carcinoma in situ is an early stage of carcinoma
D. Carcinoma in situ lesions are often solitary while carcinoma lesions are often multifocal
C.
The most common malignant tumor of the ear canal in dogs is _______ and in cats is _______.
A. Ceruminous gland adenocarcinoma; ceruminous gland adenocarcinoma
B. Squamous cell carcinoma; squamous cell carcinoma
C. Ceruminous gland adenocarcinoma; squamous cell carcinoma
D. Squamous cell carcinoma; ceruminous gland adenocarcinoma
A.
What is the gold standard for determination of food allergies?
Compliant food elimination diet trail for a min of 10-12 weeks
What is the sequence of events in the immune response to an allergen in the skin?
A. Langerhans cells capture allergens, stimulate B cells directly to produce IgE, and activate T-helper cells to become Th1 phenotype.
B. Naive Langerhans cells capture allergens, process and present them to T-helper cells, which polarize towards Th2 phenotype, producing IL-4 and IL-13, ultimately leading to B cell activation and IgE production.
C. Allergens directly bind to T-helper cells, polarizing them towards Th2, and B cells respond by producing IgE without needing plasma cells.
D. B cells initially produce IgE, which then signals Langerhans cells to activate T-helper cells and trigger a Th1 response.
B.
How does a surface lipid barrier abnormality worsen the condition in atopic dermatitis?
Decreases lipid composition of stratum corneum, especially ceramides and may involve filagrin mutation
Allows for increased contact between allergens and antigen-presenting cells
Allows for over-colonization of bacteria and yeast
What is the chief compaint in Atopic Dermatitis?
Pruritus
What is the distribution pattern seen in atopic dermatitis?
Face, ears, feet, friction areas like inguinal and axillary regions, proximal anterior foreleg region, perianal region
What is the age predisposition for environmental allergies?
< 3 years and as early as 6 weeks
Name secondary lesions seen in atopic dermatitis
Post-traumatic alopecia
Salivary staining of hairs
Excoriations and hot spots
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation
Lichenification
What is the most common dermatological manifestation of food allergies?
Pruritic dermatitis
T/F: Atopic dermatitis due to food vs environmental allergies can be clinically distinguishable by assessing the distribution of lesions
False
When should you suspect food allergy induced atopic dermatitis?
Non-seasonal pruritus
Severe pruritus with no response to scabies treatment
Concurrent GI signs
Otitis externa without other areas of skin affected
Seizures
In cats - severe facial pruritus
What are some “stumble blocks” for clients who are wanting to start and stick to a food trial for their dog?
Flavored medication
Giving meds with food
Family members not compliant
Toddlers in house
Neighbors
Delivery service people
Multiple dogs in household
Which of the following is NOT a approved prescription diet for food trials?
A. Royal canin Ultamino
B. Hill’s Z/D
C. Purina Pro Plan Elemental
D. Hill’s d/d
D.
What is the gold standard for diagnosis of atopic dermatitis due to environmental allergies?
History then ruling out other causes of pruritus
T/F: Histopathology is useful in diagnosing environmental allergies
False - non-diagnostic and will only be helpful is not sure that it’s allergic dermatitis or something else
How should a patient prepare for intradermal allergy testing?
R/O other causes of pruritus
Assure appropriate drug withdrawals - antihistamines, EFA’s NSAIDS, steroids
What does the serology (ELISA) test for environmental allergies measure?
IgE circulating in the blood
T/F: Antihistamines, corticosteroids, cyclosporine, Apoquel and Cytopoint are all appropriate treatment options for atopic dermatitis
True
Name potential side effects of cyclosporine
Vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, gingival hyperplasia, verrucous skin lesions, hirsutism, lameness, hyperglycemia
What are the key contraindications for using Apoquel (Oclacitinib) in dogs?
Dogs <12 months of age and dogs with serious infectious,
How does Apoquel work?
Inhibits JAK-1 and -3 which signal pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-31
T/F: Cytopoint is a canine specific anti-IL-31 monoclonal antibody
True
What are some differences between ASIT and SLIT?
Allergen specific immunotherapy: if pruritus present more than 3 months, if unacceptable side effects to oral medications, need compliant owner, but 70-80% effective, in most cases lifelong treatment
Sublingual immunotherapy: for clients unwilling to give SQ injections, for patients with previous unacceptable adverse reactions to ASIT, less effective than ASIT, give 1-2x daily
T/F: Pemphigus Foliaceus in dogs is an autoimmune skin disease that involves destruction of the desmosomes of keratinocytes, most commonly specifically targeting desmocollin-1. This causes the development of acantholytic cells and the subsequent formation of subcorneal pustules.
True
T/F: Avoidance of direct exposure to UV light is important in the treatment of Discoid Lupus Erythematosus in dogs.
True
T/F: Erythema Multiforme (EM) is an acute reaction pattern representing different degrees in severity of common process which involves lesions produced by keratinocyte apoptosis throughout all layers of the epidermis and/or follicular epithelium. It can be associated with the use of drugs (so-called "Drug Reaction"), an infectious process, or a neoplastic process. It is considered to be "idiopathic" only by EXCLUSION!
True
T/F: Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN) is considered to be a severe form of Pemphigus Foliaceus with massive and sudden destruction of the desmosomes of keratinocytes.
False
T/F: Cutaneous Vasculitis can be induced by any foreign protein capable of inciting an Ag-Ab reaction including infections (bacterial, fungal, viral, or rickettsial), drugs, vaccines, foods, and neoplasias. However, the disease is idiopathic in > 50% of cases.
True
T/F: So-called "Alopecia-X" presents with clinical features including: bilaterally symmetrical alopecia with hyperpigmentation, a "fuzzy" hair coat, and changes in hair coat color. Alopecia can become wide spread but usually excludes the head and lower legs.
True
T/F: As the etiology of (Seasonal) Flank Alopecia is believed to be related to length of day light maybe resulting in melatonin hormone changes in which melatonin normally increases in the fall/early winter to begin the growth of the winter haircoat. Therefore, a common initial history of a dog with (Seasonal) Flank Alopecia is the development of a bilaterally symmetrical alopecia involving the flank regions that is first observed in the fall/early winter, and spontaneously resolves in the following spring/early summer months, but some dogs never cycle and hair loss is permanent, others may only have it happen one year and not again in following years.
True
T/F: The alopecia observed in dogs with Sebaceous Adenitis is due to the lack of sebum, and the weakened hair shaft simply breaks off at the level of the follicular ostia.
True
T/F: Diagnosing cataneous tumors starts with visual cues, including signalment, followed by incisional biopsy
False - Cytology most important, if inconclusive, then biopsy
What are the 3 most common skin tumors in cats?
Basal cell tumor, mast cell tumor, squamous cell carcinoma
What are mast cells?
Hematopoietic cells that develop in the bone marrow
What would you expect to find in a cytology of a MCT?
Round cells with variable metachromatic granules, eosinophils, fibroblasts
Which of the following is NOT a typical clinical sign or feature of mast cell tumors (MCT) in dogs?
A. The mass may wax and wane in size.
B. Mass may be present for years or newly noted.
C. All MCTs present as well-defined, firm masses.
D. Manipulation of the tumor can cause it to flare up (“Darier’s sign”).
C.
What are the most common distant metastasis sites of MCT?
Spleen and liver
T/F: Approximately 30% of dogs have nodal metastasis at diagnosis with spread via lymphatics and approximately 40% have a sentinel node that is NOT the closest node
True
High grade tumors are more likely to:
Recur, even with complete excision
Metastasize
Have median survival time that is <1 yr
Select all of the FAVORABLE MCT tumor locations
A. Subungual
B. Subcutaneous
C. Mucocutaneous
D. Muzzle
E. Pinna
F. Conjunctival
G. Bone marrow
H. Inguinal
B and F
What are the three proliferation markers of MCT?
Ki-67: protein expressed during proliferative phases of cell cycle
AgNOR: determines number of nucleoli per cell
Mitotic count: actively dividing cells per 10 high powered fields
Which of the following statements about c-kit mutations in MCT is correct?
A) c-kit mutations are present in nearly all low-grade MCTs.
B) KIT is expressed only on mutated mast cells.
C) c-kit mutations result in a receptor that is constantly active without ligand binding.
D) Tumors with c-kit mutations have a better prognosis compared to those without the mutation.
C. Leads to uncontrolled proliferation, expressed on nearly all mast cells, mutation in 25-30% of high grade MCT
Which of the following scenarios would NOT warrant submission of a MCT for an MSU VDL prognostic panel?
A) A low-grade tumor in a Shar-Pei.
B) A low-grade tumor with a history that conflicts with its grade.
C) A low-grade tumor located on the right flank
D) A low-grade tumor with a borderline mitotic count or marked nuclear atypia.
C. - submit if tumor is in a concerning anatomic location
T/F: Treatment of a local MCT includes surgical excision with wide margins, followed by RT to reduce recurrence rate
True - also intralesional injection of Traimcinolone or Stelfonta
Which of the following statements about the treatment options for mast cell tumors (MCTs) in dogs is correct?
A) Corticosteroids are primarily used as a standalone treatment for mast cell tumors.
B) Palladia, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), blocks KIT activation by turning the receptor off.
C) Vinblastine is rarely used in chemotherapy protocols for MCTs.
D) Gilvetmab is a monoclonal antibody used to treat mast cell tumors in cats.
B. - corticosteroids used as adjuvant therapy, vinblastine is chemo most commonly used, Gilvetmab is immunotherapy used for dogs only
Where do feline cutaneous MCT typically present?
Head and neck; pinnae/ear base
What is the most common form of cutaneous lymphoma in dogs?
Epitheliotropic - most often T-cell lymphoma, malignant T-cells infiltrate the epidermis, adnexal structures and mucocutaneous junctions
A 2-year-old dog presents with a solitary, raised, pink nodule on its skin. The lesion has been present for about 2 months and is not causing any discomfort to the dog. The owner reports that the tumor has shown slight reduction in size since the last visit. Based on these findings, which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A) Cutaneous histiocytoma
B) Mast cell tumor
C) Squamous cell carcinoma
D) Cutaneous lymphoma
A.
Why is there a decreased risk of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) seen in Siamese cats compared to other breeds?
Increased pigmentation provides protection from UV - SCC in cats most common on head, light haired areas and white cats
T/F: Squamous cell carcinoma is has a high risk of metastasizing to the lymph nodes
False - predominantly locally invasive
What’s the difference between SCC and SCC in-situ?
SCC in-situ is carcinoma before it has broken through the basement membrane.
In-situ in cats, often multifocal and can be anywhere on the body, sun exposed or non, surgery, RT or topical immunomodulator for tx
SCC - head and digits, surgery for tx
Name clinical signs associated with ceruminous gland adenocarcinoma
Deafness
Neurologic signs
Pain opening mouth
Which of the following tumors is most commonly found in the perianal region and is hormonally mediated, often stimulated by androgens, with a high cure rate following surgical removal?
A) Perianal lymphoma
B) Perianal papilloma
C) Perianal carcinoma
D) Perianal adenoma
D.
Which of the following tumors is virally mediated, typically affects young or immunocompromised animals, and is caused by the integration of viral DNA into the host genome, leading to rampant cellular growth and a predisposition for cancer development?
A) Fibropapillomas
B) Adenoma
C) Papilloma
D) Squamous cell carcinoma
C.
T/F: After surgical excision of an adenoma, there is a 30% chance it will regress
False - 90% cure with sx + castration
T/F: The most common malignancy of the digit is melanoma, followed by squamous cell carcinoma
False - other way around
This type of tumor presents mostly in dogs as a raised, darkly pigmented, usually small, most often benign and localized mass
Cutaneous melanoma
What is the most likely cause of Malassezia dermatitis?
Secondary to allergies (AD, FAD, food allergy)
Which of the following clinical features is commonly associated with Malassezia pachydermatis infections in dogs?
A) Painless swelling of the joints
B) Moist, greasy, and malodorous skin folds
C) Pruritic dry skin patches
D) Sudden hair loss with no other symptoms
B. - extremely variable clinical features but also usually pruritic
T/F: Malassezia dermatitis shows poor response to systemic steroids, antibiotics and antibacterial shampoos
True - antiseptic shampoos for treatment (selenium disulfide, chlorhex) and systemic antifungals if severe
Which of the following requires acid-fast stains for identification on cytology and/or histopathology?
a) Sporothrix
b) Sterile Nodular Panniculitis
c) Blastomyces
d) Atypical Mycobacteria
D.
Regarding nodular skin diseases, which of the following is in correct?
A. The head and lower extremities are common sites for lesions of feline progressive histiocytosis
B. Sporotrichosis commonly occurs through puncture wounds, e.g. thorns
C. Sterile nodular panniculitis cannot be diagnosed on histopathology alone
C.
Regarding reactive histiocytosis in dogs, which of the following is incorrect?
A. Cutaneous reactive histiocytosis represents a non-neoplastic proliferation of Langerhans cells
B. There are both cutaneous and systemic forms
C. Cutaneous nodules are typically not painful or pruritic
D. A macerated tissue culture should be performed to rule out infectious causes
A.
Regarding fungal infections, which of the following statements is incorrect?
A. Broad based budding of fungal organisms on cytology is characteristic of Blastomyces spp.
B. A Zielh-Neelson stain can be used to identify Blastomyces yeast forms in histopathologic sections
C. Cryptococcus is characterized by narrow based budding and prominent clear capsule
B.
Which best describes the behavior of soft tissue sarcomas?
A. Minimally locally aggressive, highly metastatic to lungs
B. High locally aggressive, minimally metastatic to lungs
C. Minimally locally aggressive, minimally metastatic to lungs
D. High locally aggressive, highly metastatic to lungs
B.
What is the most common location for intermuscular lipoma formation?
A. Within the semimembranosus or semitendinosus
B. Between the biceps and triceps
C. Between the semimembranosus or semitendinosus
D. Within the biceps or triceps
C.
T/F: Equine insect hypersensitivity is the most common cause of equine pruritus and is thought to be mostly a type I hypersensitivity, mediated by IgE antibodies
True
T/F: Atopic dermatitis can be diagnosed by intradermal testing or in-vitro testing (ELISA) alone?
False
T/F: Results of a skin biopsy for Histopathology will show specific changes with equine atopic dermatitis different from other allergic skin diseases
False
T/F: Only dermatophytes can cause a color change to red in dermatophyte test medium (DTM).
False
T/F: Chronically affected horses are the primary source for insects to transmit Dermatophylosis congolensis to other horses when the skin has been exposed to chronic moisture
True
T/F: Pastern dermatitis can be caused by primary or secondary photosensitization.
True
T/F: You can trust a tumor grade on incisional biopsy of soft tissue sarcoma
False - do NOT trust
Why would FISS have multinucleated giant cells on cytology?
Macrophages that fuse to form multinucleated giant cells that want to phagocytose adjuvants left behind by the vaccine
I just vaccinated my cat, is it FISS…. What is the 3-2-1 rule?
Is the mass present for 3 months after vaccination?
Is it ever larger than 2 cm?
Is it still increasing size at 1 month post-injection?
T/F: Secondary infection (deep pyoderma) very likely even with no bacteria seen on cytology
True
What are primary causes for otitis externa?
Atopic dermatitis
Food hypersensitivity
Mass
Parasites
FB
Endocrine
Autoimmune
Otitis media
What are predisposing causes for otitis externa?
Excessive moisture
Iatrogenic irritation
Conformation
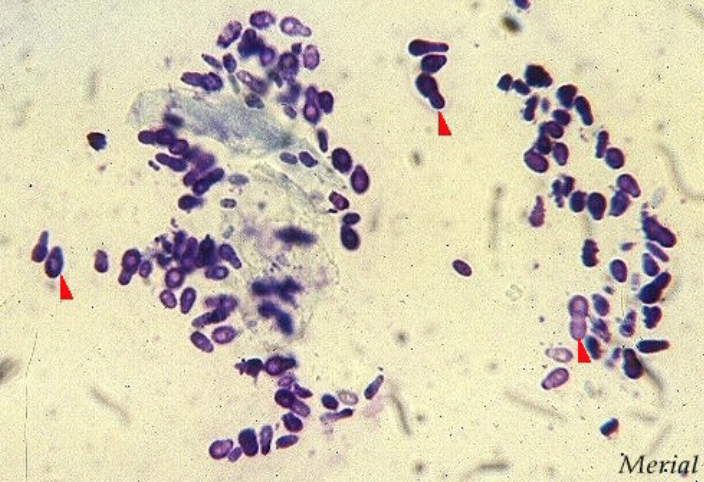
2 yr old FS lab scratching at ears, you see moderate erythema of the concave pinna at the entrance of the canal, you find this on cytology, how do you treat?
Clean ears in hospital
Miconazole for yeast infection
Add dexmethasone to solution
How do you assess treatment success in uncomplicated otitis externa?
Otoscopic exam AND ear cytology - treat until no more bacteria on cytology
1 yr old MN shih tzu comes back 3 months after initial visit where one ear was affected with otitis externa due to cocci bacteria. He was treated with neomycin and infection resolved. This visit, both ears are affected and cytology reveals cocci again. How would you treat this time and what would be your advise?
Use the same topical regimen as previous because it cleared up infection and advise that allergies are likely cause of recurrence, recommend further work-up for allergies
T/F: Bacteria and yeast are primary factors for otitis externa
False - perpetuating
T/F: Bacterial culture/susceptibility is useful when you find rods only on ear cytology
False - Pseudomonas develop rapid resistance to abx, faster than culture results
What is the risk of flushing the ear if the tympanic membrane is ruptured?
Flush can reach lungs via eustachian tube
What is the most common cause of otitis in dogs?
Allergies
T/F: A otoscopic exam should be performed BEFORE obtaining a cytology from an ear
True
Which one of the following statements regarding bacterial culture in otitis is FALSE?
A. Bacterial culture and susceptibility testing are generally not recommended because they are often unrewarding, misleading, and slow.
B. Susceptibility results are based on the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) required in blood or tissues to kill bacteria, not concentrations achieved topically.
C. Topical antibiotics achieve much lower concentrations in the ear canal compared to systemic antibiotics.
D. Resistant bacteria may still respond to higher topical doses of the same drug.
C. - higher concentrations
What ear medication should you not use on cats as it can cause major neurological problems?
A. Claro (Florfenocol)
B. Sorulan (Polymyxin B)
C. Amikacin
D. Tobrex (Tobramycin)
A.
When would you want to use Sorulan (Polymyxin B) to treat otitis?
Use for Pseudomonas resistant to gentamicin (it has stopped working)
When would you want to use silver sulfadiazine to treat otitis and how do you prepare it for the client?
With resistant rods, dilute with water 1:3, often use it with 2nd antimicrobial like Amikacin