Business Operations Management
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Operations Management
Operations management is concerned with the strategies that are used to create, operate and control the transformation of inputs from a variety of resources into outputs, or goods and services to satisfy the demands of customers
The operations manager aims to maximise the levels of productivity and quality through the operational process
Role of operations management
1.Describe the responsibilities for this position.
2.Describe the skills required for this position.
3.Write one sentence providing an overview of the role of an Operations Manager.
-Conduct roundtables, interviews, focus groups, surveys, and other qualitative research to answer regional insight questions. Represent the voice of our customers in strategy setting and tactical planning.
-Research: Lead end-to-end qualitative, quantitative, and data analytics research projects for the Australia & New Zealand Regional Operations Team.
- Share Customer Insights. Synthesize and communicate findings from both your own research and that of HQ teams to drive action.
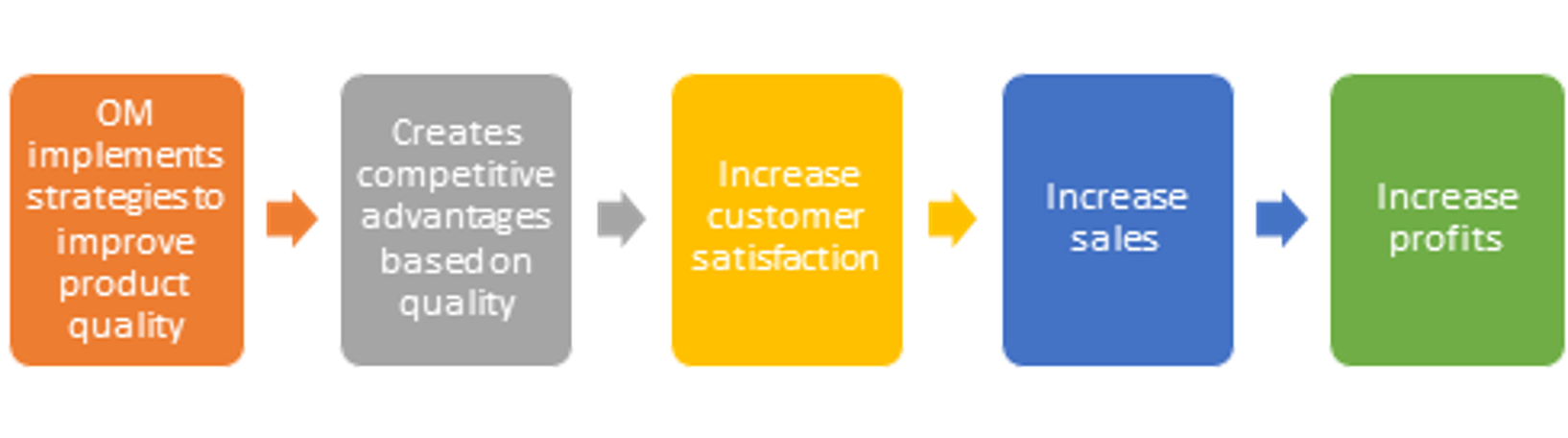
How can om can achieve business objectives
MANUFACTURING business
Tangible: Can be seen and touched and productivity.
Quality and productivity is therefore easy to measure
Products can be stored
very little customer involved in the production. Customer Involvement.
Other characteristics available on handout SR
Service Business
Intangible outputs Quality difficult to measure cannot be stored
Efficiency and effectiveness productive
Efficiency: how well a business uses resources to achieve objectives
Effectiveness: the degree to which a business has achieved its stated objectives
Productivity: a measure that indicates how many inputs (resources) it takes to produce an output (goods or services)
Automated production lines
Comprises machinery and equipment arranged in a sequence with components added to a good as it proceeds through each step, with the process controlled by computers
•Manufacturing industries involving mass production.
•Series of workstations that perform a specific operation and the product is processed step by step as it moves along the line in a sequence.
•Each workstation linked by an automated transfer system which moves products between stations.
• Timing and sequencing of equipment controlled by computers.
• Human role reduced to: system design, making adjustments to equipment, supervision and monitoring.
AUTOMATED PRODUCTION LINES
•Improved productivity through lower labour costs, reduced production time, lower unit costs of production
• Faster production
• Workplace safety as dangerous tasks performed by technology rather than humans
• Repetitive, boring and difficult jobs replaced by automation
•Minimises waste
Automated production advantages
•Improved productivity through lower labour costs, reduced production time, lower unit costs of production
• Faster production
• Workplace safety as dangerous tasks performed by technology rather than humans
• Repetitive, boring and difficult jobs replaced by automation
•Minimises waste
Automated production lines disadvantages
•huge initial costs in purchasing systems that can be unaffordable for small and medium scale manufacturers
• Ongoing maintenance expensive because involves employment of highly skilled maintenance workers
• Reduce available employment opportunities
•Production lines can break down halting production
Robotics
Highly specialized form of technology capable of complex tasks
Robots are used in engineering and specialised areas of research as well as on automated production lines, where a programmable machine capable of doing several different tasks is required
Computer-aided design
A computerized design tool that allows a business to create product possibilities from a series of input parameters.
• Standard in most manufacturing and design businesses.
• Creates three-dimensional diagrams, allowing for accurate predictions of what final product will look like from all angles and how it will function.
•Used to draw and adjust three-dimensional designs based on client requirements – allows for differentiation and specific modification which can be made to the design
•From the design, material use can be calculated, as can time for the task to be completed
•Normal drafting processes would cost much more, take longer and be less accurate
Computer aided design advantages
• Speeds up process of product design, without the need for erasing and redrawing
•The designer can produce a two or three dimensional computerized version of a product. Changes can be made to this before a prototype is made. Material choices and associated costs can be explored at this stage
•Allows a business to view a design from multiple angles, assisting both the designer and the end user to visualize what will be produced
computer aided design disadvantages
•Software can crash, resulting in a loss of work
•Costly to introduce & expensive to purchase
•Employees need to be trained to use CAD – can slow productivity while they gain experience and familiarity with the system
COMPUTER-AIDED MANUFACTURING (CAM)
CAM is the use of software to direct and control manufacturing processes.
•Machines are fed programmed instructions from a central computer.
•Aim is to create a faster and more efficient production process
•CAM is often more precise, which results in less wastage and improves productivity
•Allows for products to be more consistent
•CAM often combines with CAD to produce products with CAD design implemented into CAM software to manufacture product
COMPUTER-AIDED MANUFACTURING (CAM) Advanatges

Computer aided manufacturing disadvantages
•Software can crash, resulting in a loss of work
•Costly to introduce & expensive to purchase
•Employees need to be trained to use CAD – can slow productivity while they gain experience and familiarity with the system
articial intelligence
The ability of a computer or a robot controlled by a computer to do tasks that are usually done by humans because they require human intelligence and discernment
Online services
Establishing and maintaining an accessible and easily locatable business website to enable customers to purchase products online or communicate with the business.
Online services advantages
•Can be used to deliver consistent messages to customers and suppliers, and can also be used to gain customer feedback
•A website means that a business is online 24hours a day, 7 days a week
•Reduces the costs of labour and of leasing or purchasing physical space
Online services Disadvanatges
• Designing, registering and publishing a website may initially be expensive and time-consuming
•Crashes occur-If a business website is constantly crashing, this could impact on potential sales, or the business reputation
•Operating websites and applications can require highly skilled staff who may be expensive to employ or train
•Risk of data/security breaches
Fore casting materials management strategies
Relies on data from the past and present and analysis of trends to attempt to determine future events
vEnsures operations system is prepared with enough materials on hand to meet demand
vA business may forecast the costs of materials and transportation
vCan be qualitative or quantitative
vHow does it improve effectiveness?
- Allows operations system to continue without stops or slowdowns due to insufficient materials on hand
vHow does it improve efficiency?
- Helps prevent overstocking and understocking of materials. Prevents the operations system slowing due to not enough materials, as well as reduces wastage from having idle stock for long periods.

Master production schedule
A statement of what the business intends to produce, in what quantities over a set time frame, taking into accountcustomer demand and production costs.
vOutlines the types and amount of employees required
vAllows operations to manage the logistics of the supply chain to ensure orders can be transported to customers
vHow does it improve effectiveness?
- enables the business to ensure it has enough materials to meet demand
vHow does it improve efficiency?
- Enables production to flow continuously, improving productivity along with reducing waste
Materials requirement schedule
Is completed after the business has a clear understanding of the quantities to be produced and the time frame involved. It is an itemised list all the material involved in the production to meet the specified orders.

Just in time
JIT IS A MATERIALS MANAGEMENT STRATEGY THAT ENSURES THAT THE EXACT AMOUNT OF MATERIAL INPUTS ARRIVE ONLY AS THEY ARE NEEDED IN THE PRODUCTION PROCESS.

Just in time advantages

Just in times disadvantages

seven wastes
1.Transportation – Reduce unnecessary movement of machines and products among the processes
2.Inventory – Minimise storage required
3.Motion – Reduce unnecessary movement of workers and products within the process
4.Waiting time – Eliminating any idle time waiting between stages and processes
5.Overprocessing – Not adding more value to a product than customers want
6.Overproduction – Not making more than is required or making it earlier than required
7.Defects – Reducing errors that take time to fix
waste minimisation strategies
¡Reduce involves identifying any waste occurring (using employee input) in the production of goods and services and eliminating the cause. Policies such as reducing photocopying and encouraging non-paper data storage, turning off power or using power reduction devices on technology will reduce waste.
¡Reuse involves identifying any waste occurring (using employee input) in the production of goods and services and finding ways to use it to benefit the business or society. Examples are reclaiming waste water (or capturing rain water from rooftops) and using it to water gardens, donating left over food to charity, refilling printer cartridges
¡Recycle involves identifying ways that waste from production of goods or services can be effectively recycled so that they do not end up in landfill or polluting the environment. Examples include a business organising for its waste paper to be collected by a recycling business in order for new paper products to be created from the waste.
¡Recovery involves taking materials that would otherwise be sent to waste and using them for another purpose Examples could be using the services of a business that collects hazardous waste, oils or chemicals in order to create a supplementary fuel or providing incentives for customers to return batteries, phones or computers so that they can be repurposed or disposed of correctly.
Waste minimisation advantages

Waste minimisation disadvantages
¡-Can involve high implementation costs. Implementation of technology and training and maintenance and wages costs for waste minimisation based activities
¡-Businesses can lose focus on core business due to focus on waste reduction. Resources and time can be wasted on meetings.
¡-Assumes all employees want responsibility and are motivated towards business goals.
¡-Can result in increased workplace stress as a result of the constant pressure.
¡-Requires good relationships between managers and employees, that could be damaged
¡-Requires good relationships and communication with suppliers, again that maybe impacted
Lean management
Lean Management is an approach that improves the efficiency and effectiveness of operations by eliminating waste and improving quality
•According to the principles of lean management, waste is anything that reduces the speed of production or stops production occurring at the lowest possible cost. As waste is reduced, production times and costs are cut
Pull focused (key principle lean management)
1.The amount that is produced is determined by the demand from customers. Rather than a business stockpiling large quantities, then trying to sell them, the pull concept is where the business only produces the amount that the market is demanding. This allows the business to stop over producing so that the waste is greatly reduced.
One piece flow (lean management key principle)
1.One piece flow involves a piece of production moving through the operations process in once continuous flow - one at a time. All steps in the operations process must be focused and aligned to adding value, one piece at a time, removing all wasteful and unnecessary activities.
Takt
3.is known as the heart beat of the operations system. It outlines how fast a business needs to produce a good or service to meet demand. This allows a business to have a continuous flow and adapt quickly to any rises or falls in demand. It is better to have a continuous flow of production rather than having various starts and stops. Having a continuous flow allows the business to synchronise processes which reduce waiting times throughout the production.
Zero defects
striving to have defects. Defects cause waste and a lean business will aim to have zero defect. Although errors will always occur in operations, a lean business will aim to not pass on defects to the next area of production. Defects are rectified before they move on to the next stage of the operations system
summary of four principles of lean
Pull – Customer demand determines the rate products are produced
One piece flow – Operations are conducted one step at a time in a continuous flow minimizing waiting time
Takt – The average time that passes between production starting on one unit and the start of production of the next unit
Zero defects – Errors or defects need to be identified as closely as possible to where they occur and corrected
strengths of lean manage,ent
-reduced energy and resource consumption
-reduced delays
-increased worker productivity
-reduced uncertainty
-increased customer satisfaction
Weaknesses of lean management
-requires committed and experienced employees
-employees may resent the change to lean or may prefer to not provide any input
-the constant focus on improvement and elimination of waste can result in workplace stress
-requires good relationship with suppliers
-can involve high implementation costs