1.8 Acids, Bases and Salts
1/89
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Hazard
A danger or risk.
Explosive
It is a chemical compound, mixture or device that explode

Oxidising
Provides oxygen to make other substances burn more fiercely

(Extremely) Flammable
Capable of burning with a flame and sets fire easily

Corrosive
These substances can burn through skin, clothing and other tough materials. When spilled tell teacher immediately and start washing off. Use goggles and a lab coat
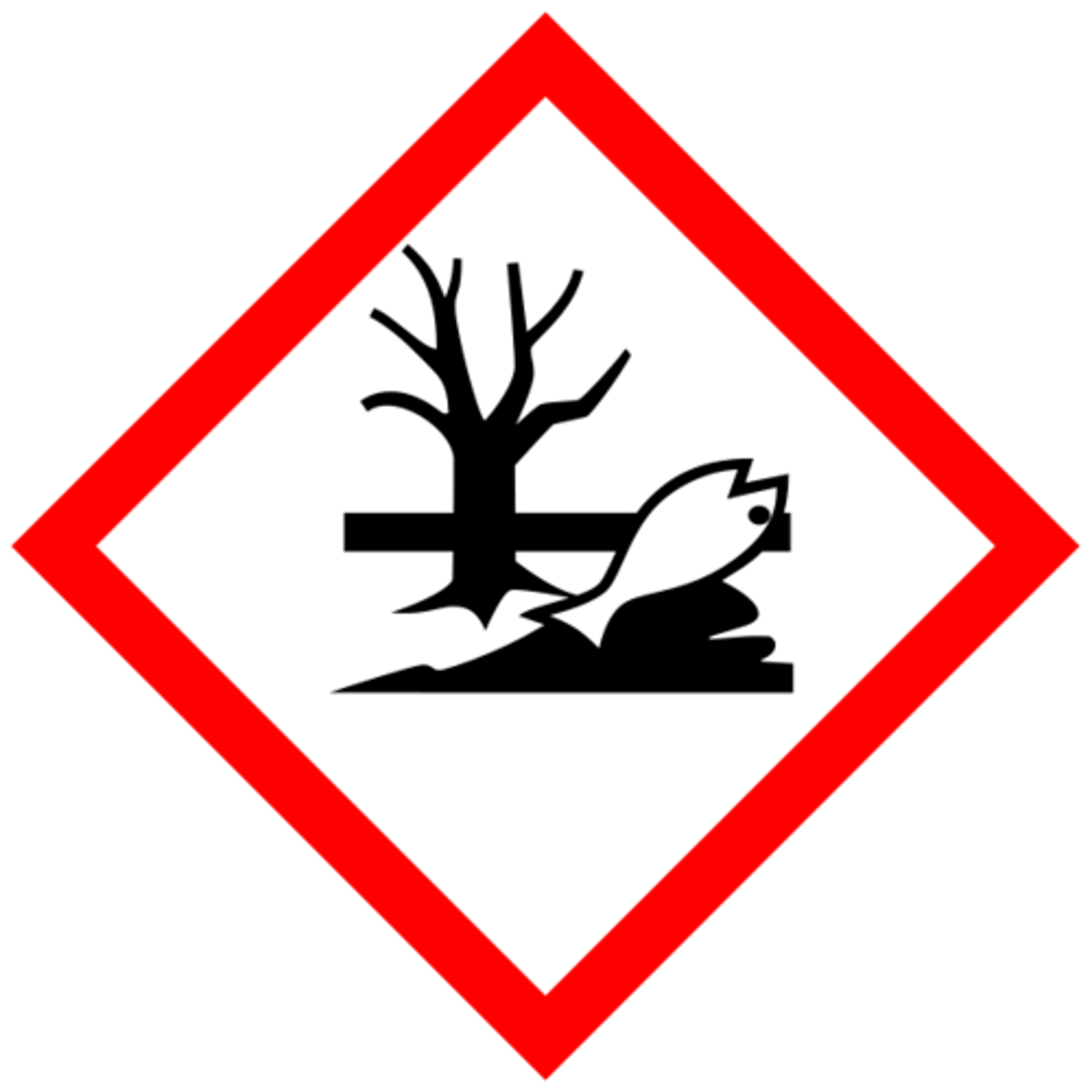
Environmental Hazard
Substances that can cause harm to the environment. Special disposal regulations

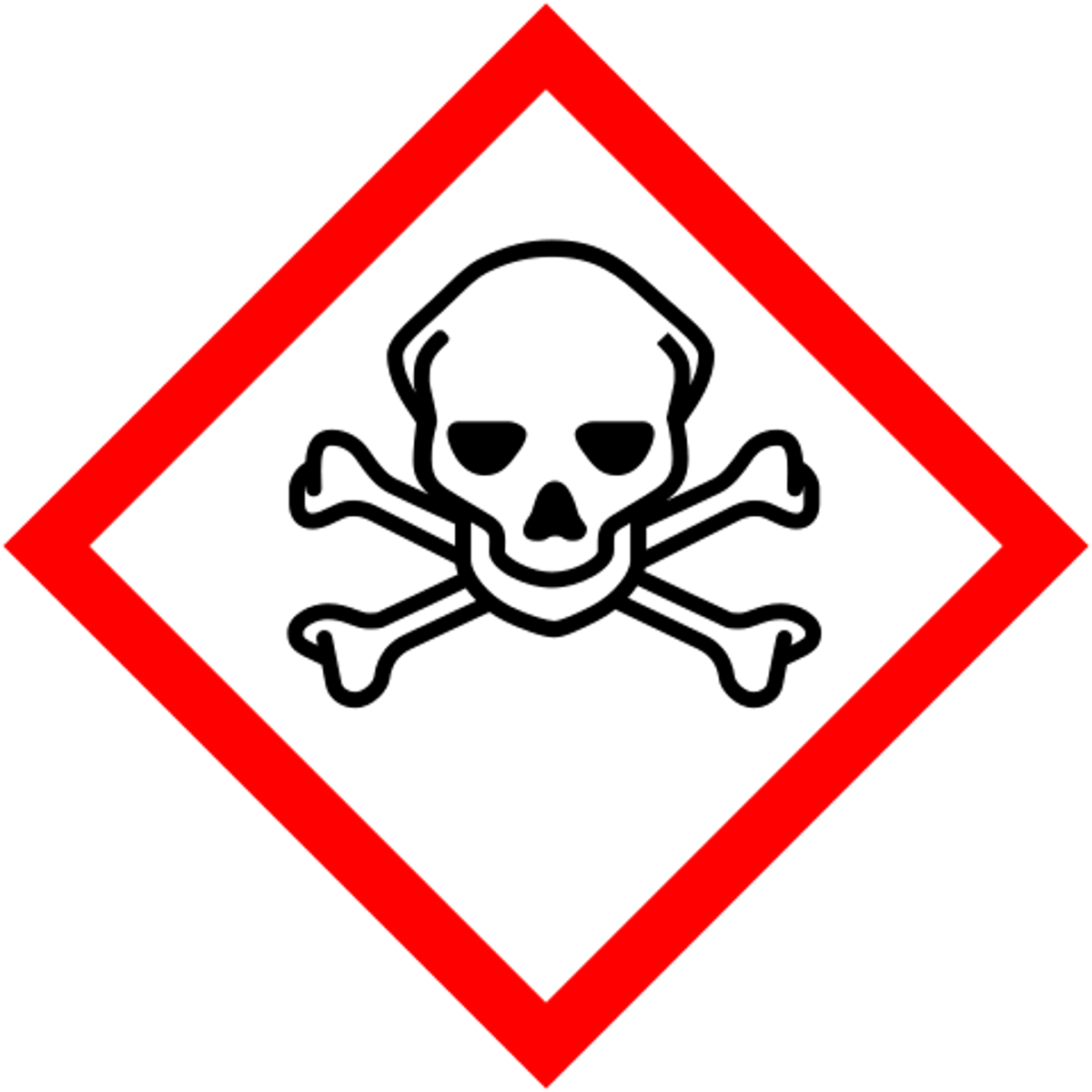
acute toxicity
These substances can cause death when breathed in, swallowed or absorbed by skin. We will not use these substances.

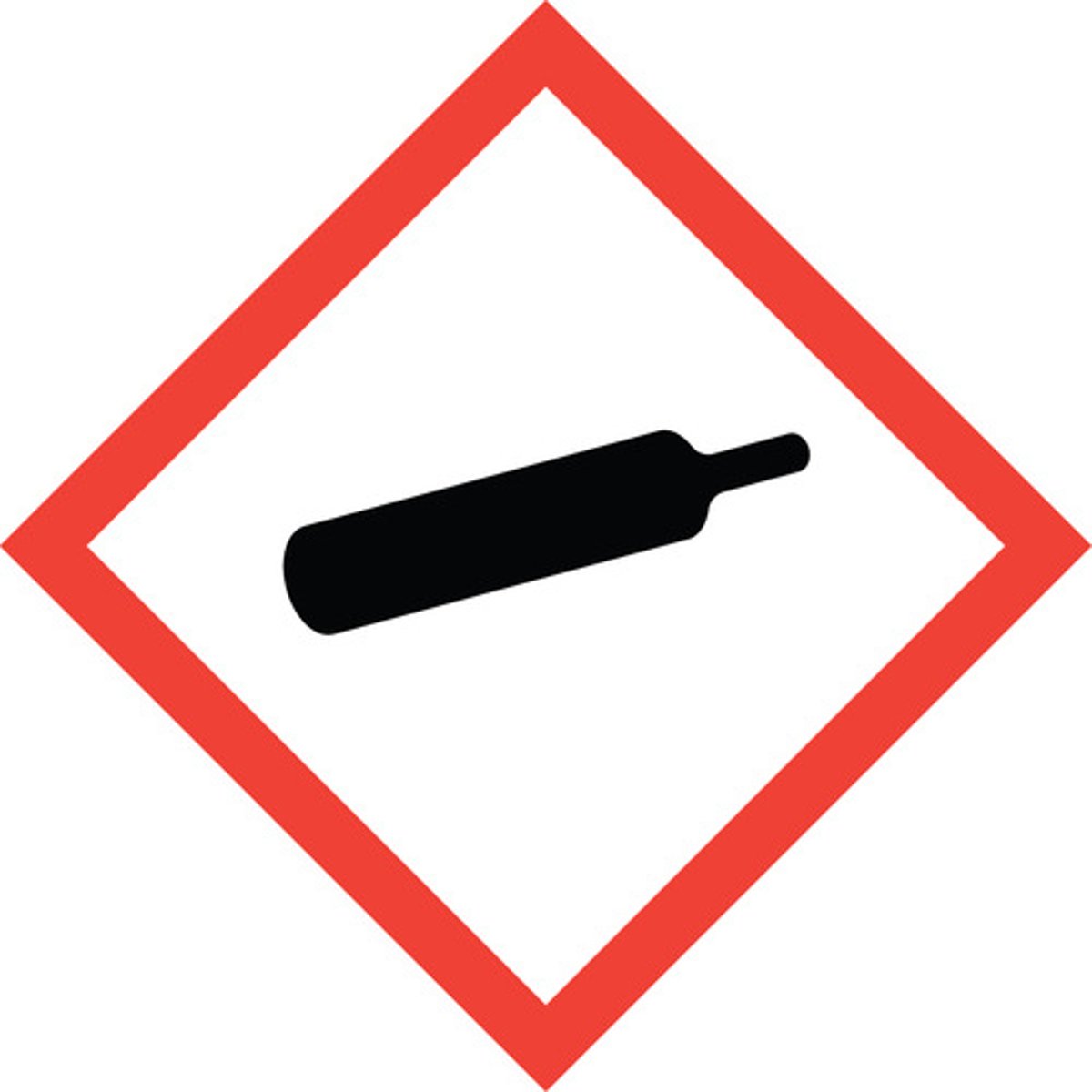
Gases under pressure
Gas released may be very cold. Gas container may explode if heated

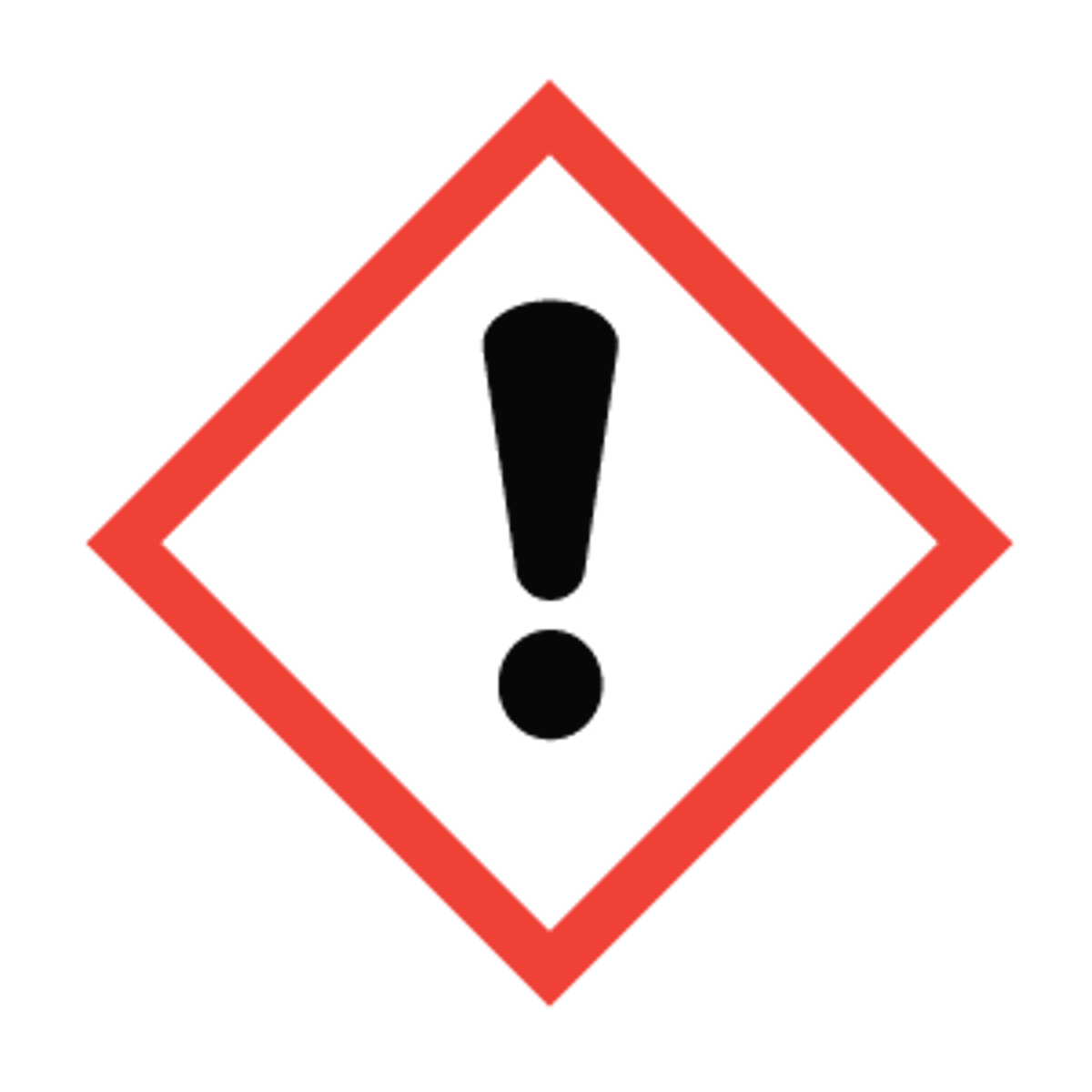
Moderate hazard
A substance that may cause irritation to the skin, eyes or inside your body.

Health hazard
may cause serious health effects, for example to the respiratory tract

Risk
How likely a hazard is to cause harm
Precaution
A measure taken in advance to prevent harm
Common laboratory precautions
Using less hazardous substances, wearing eye protection, using a waterbath
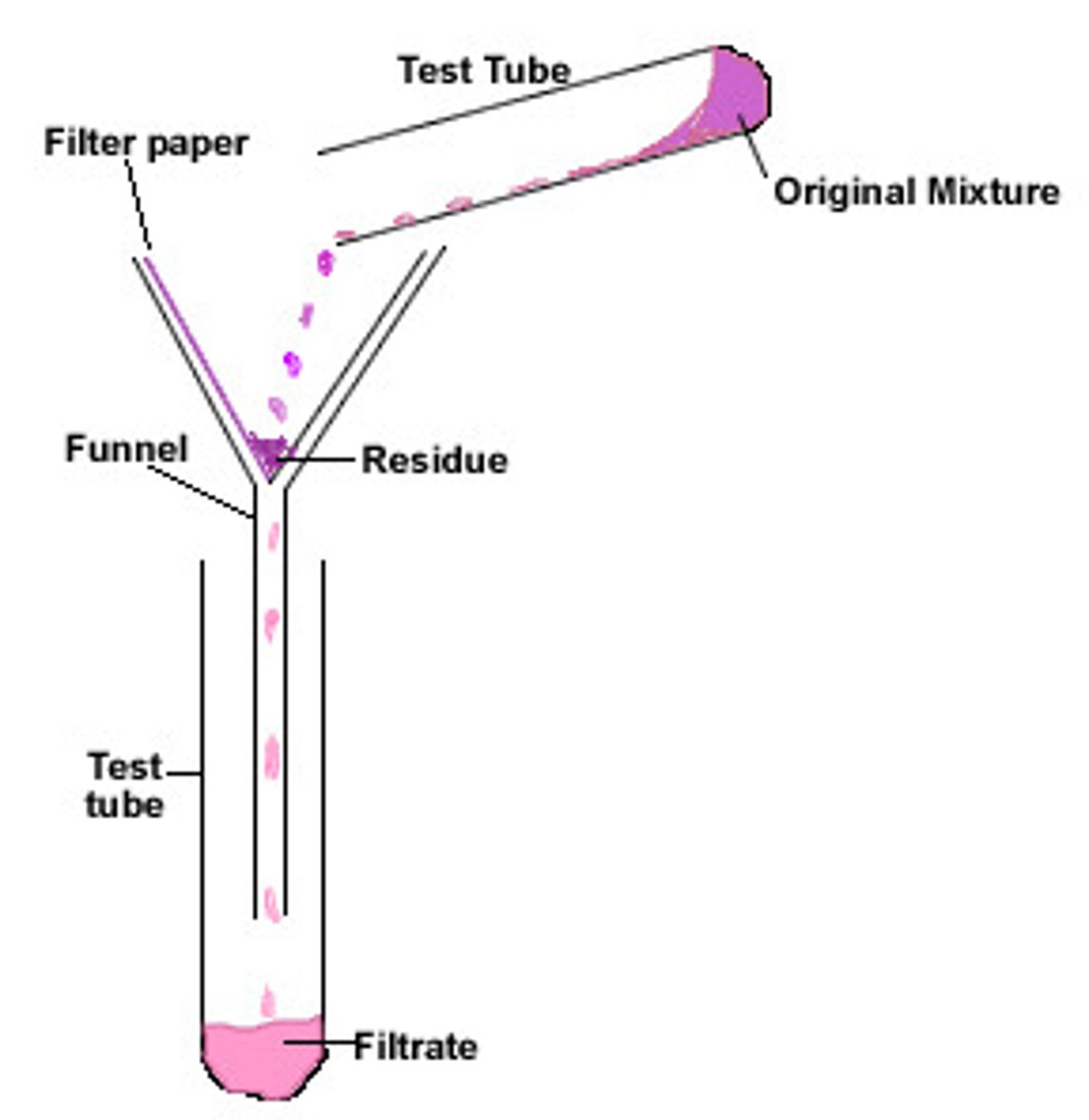
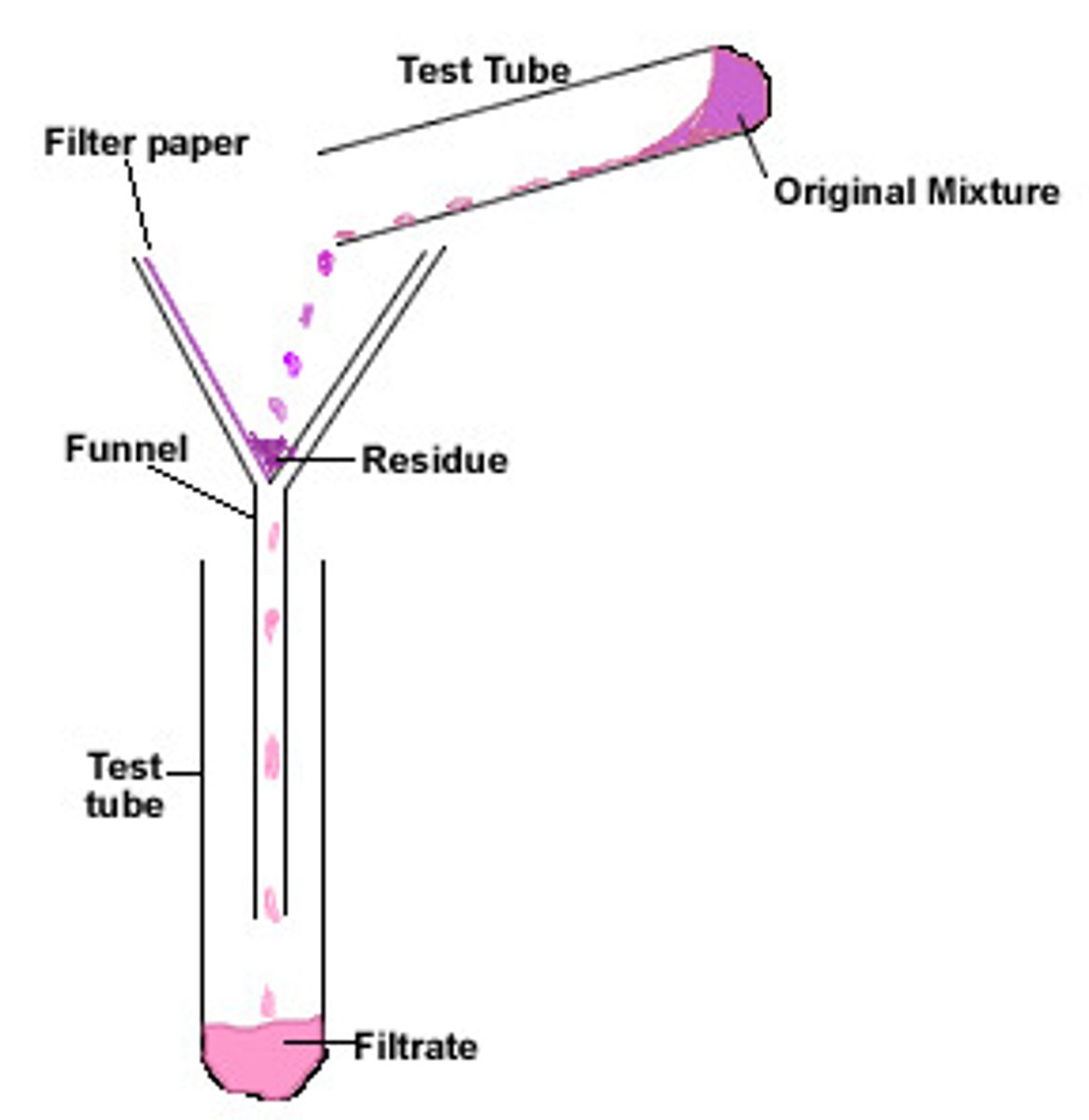
Filtration
Separates insoluble solid from a liquid
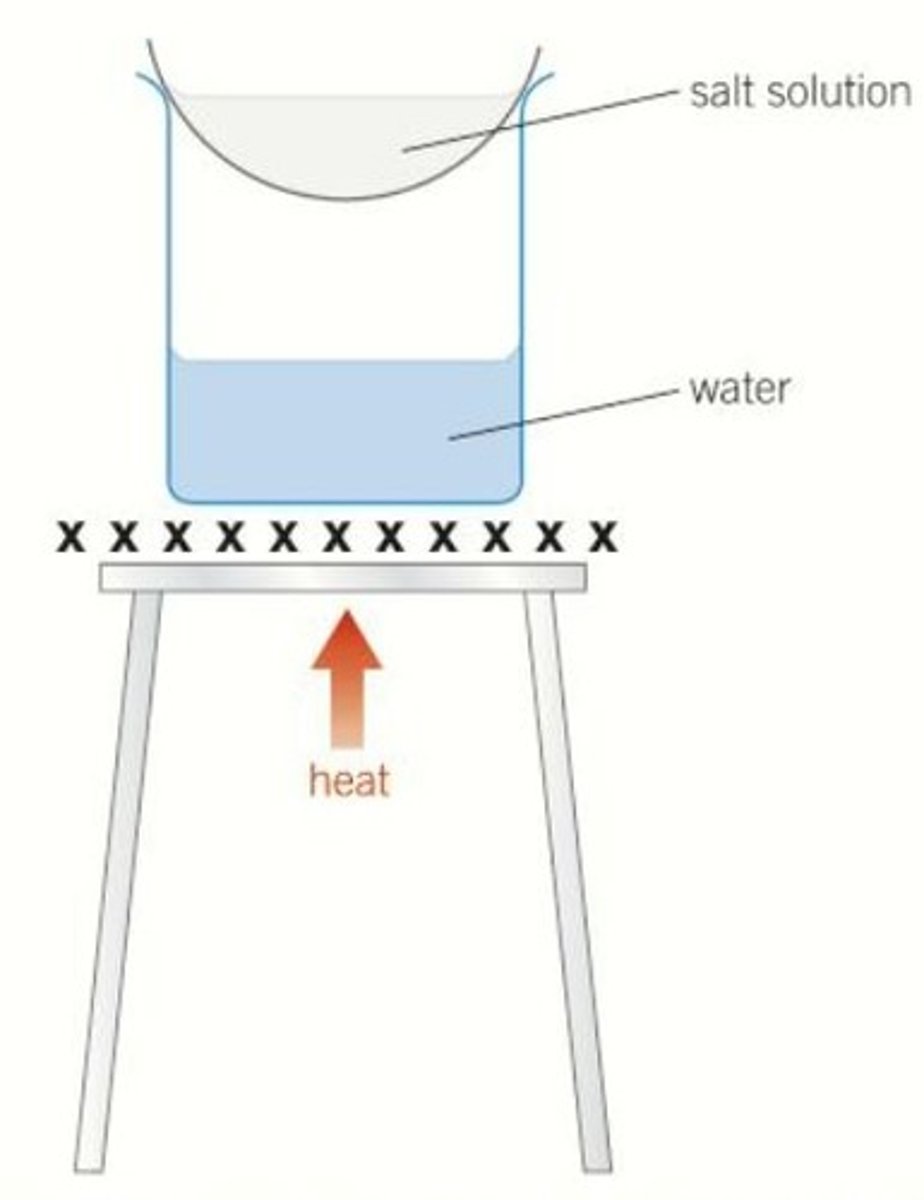
Crystallisation
The formation of crystals (as solvent evaporates from solution)
Filtrate
Liquid that has passed through a filter
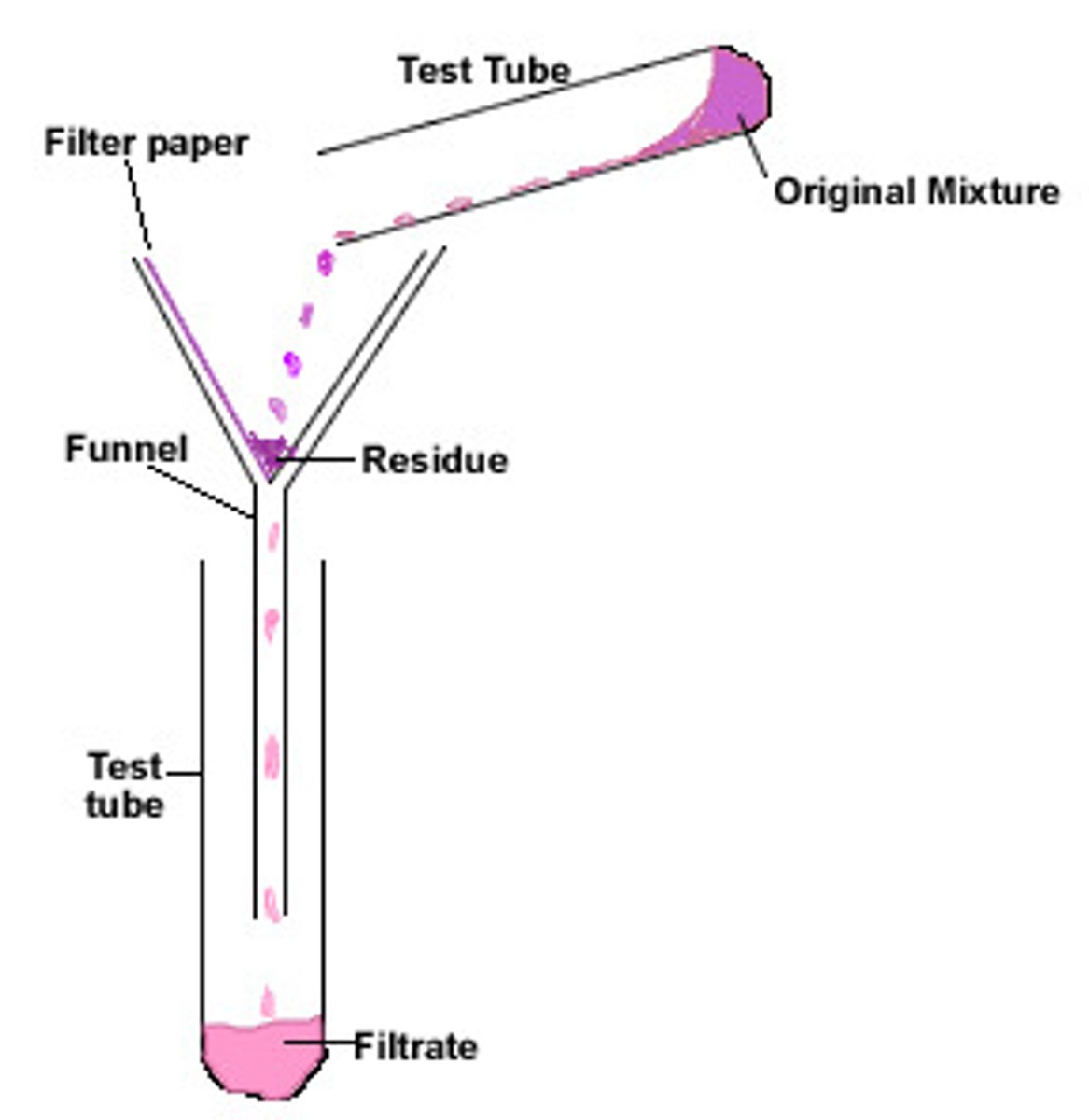
Residue
The insoluble solid left in the filter paper
Advantage of heating a reaction
Speeds the reaction up
Making salt from acid+base
Reacting an excess of insoluble base with an acid, filter off excess base
Making a salt from acid+metal
React an excess of metal with an acid, filter off excess metal
Making salt from acid+alkali
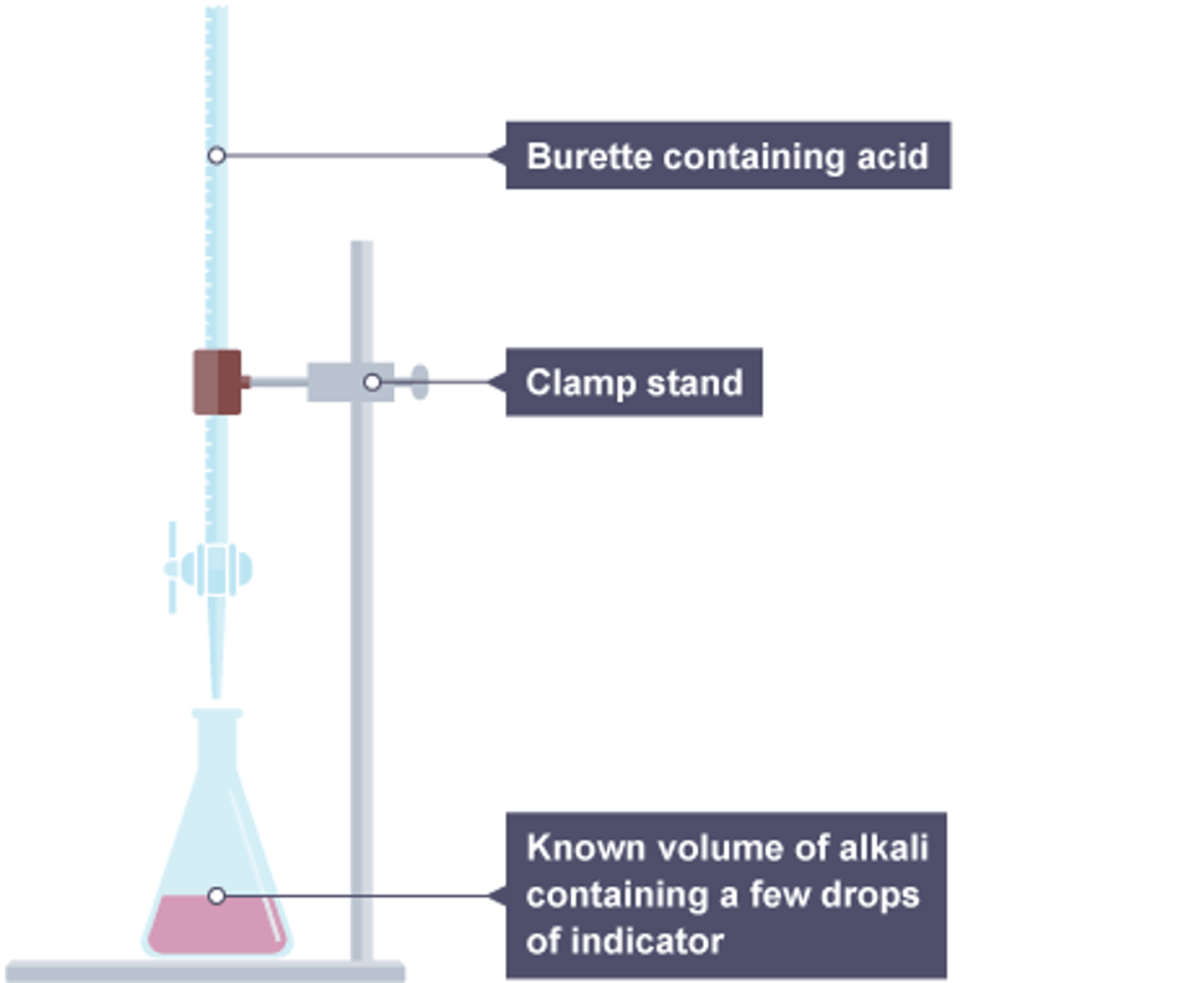
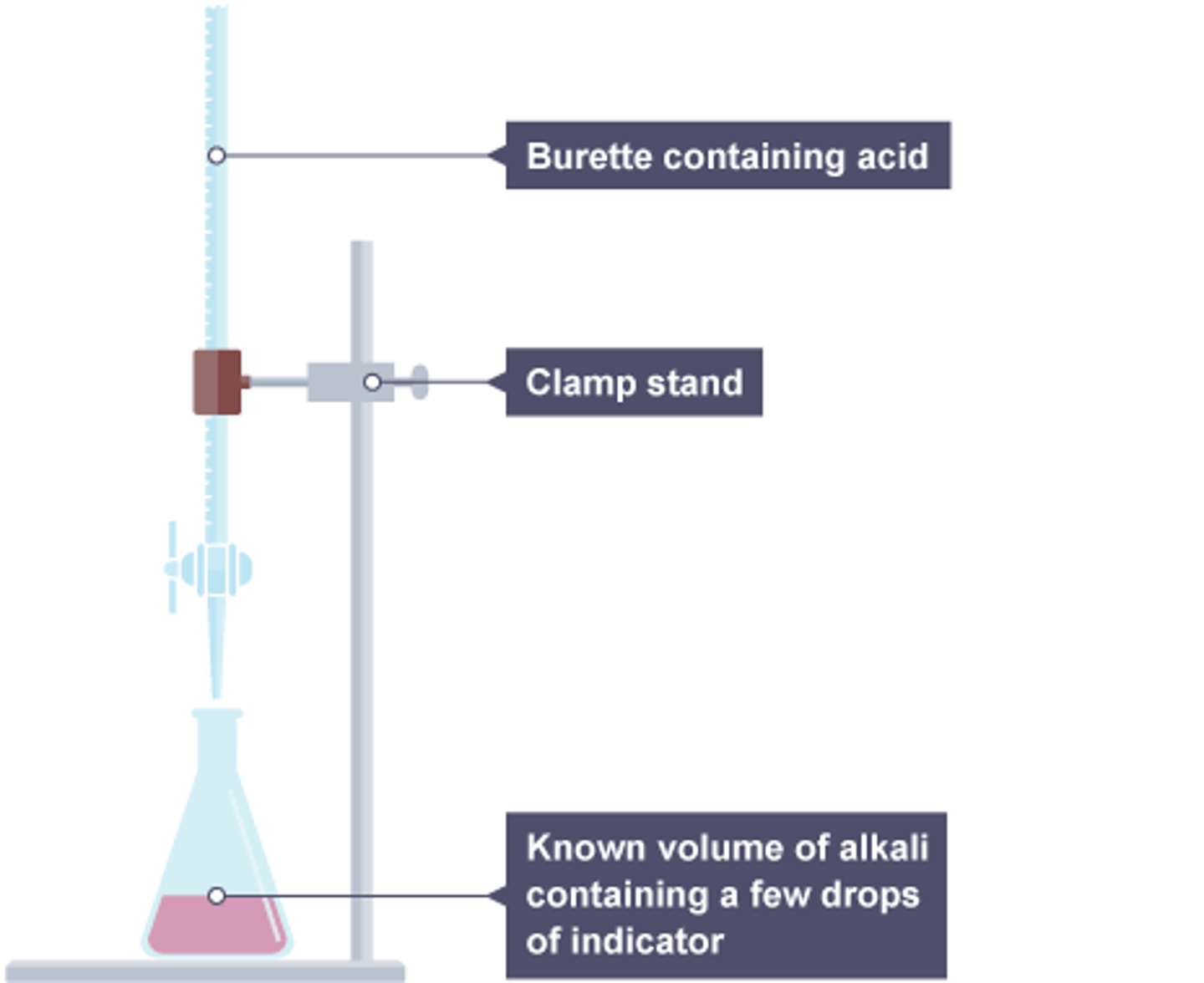
Use titration with an indicator to find the amount alkali to neutralise the acid, repeat without indicator to make a pure sample
Making pure dry crystals
Crystallisation then pat crystals dry between two pieces of filter paper
Advantage of a water bath
Heats gently, allowing water to evaporate slowly
Indicator
A compound that changes color in the presence of an acid or a base
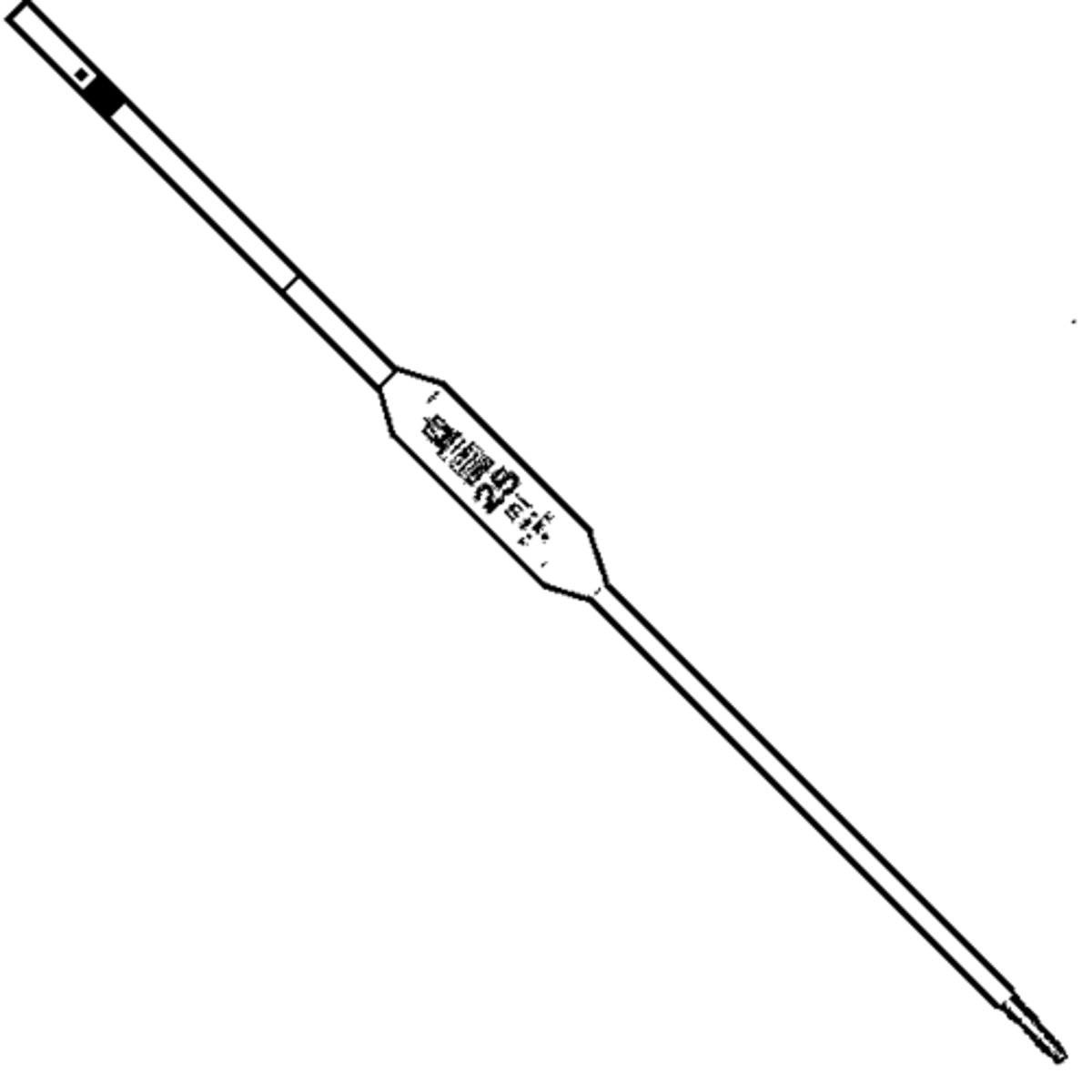
Pipette
A glass or plastic tube used to accurately measure liquid
Burette
A graduated glass tube with a tap at one end, for delivering known volumes of a liquid

Making salt from an acid and an alkali
Use a titration to find the amounts of acid and alkali, repeat without indicator, evaporate water
Acid
A substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution.
Base
A substance that reacts with an acid and neutralises it
Alkali
A soluble base, that produces OH- ions in solution
Types of chemicals that are bases
Metal oxides, metal hydroxides, metal carbonates, ammonia
Types of chemicals that are alkalis
Metal hydroxides, ammonia
Ions produced by acids
H+
Ions produced by alkalis
OH-
Neutralisation reaction
The reaction of an acid and a base forming a salt and water
Ionic equation for an acid and an alkali
H+(aq) + OH-(aq) --> H2O(l)
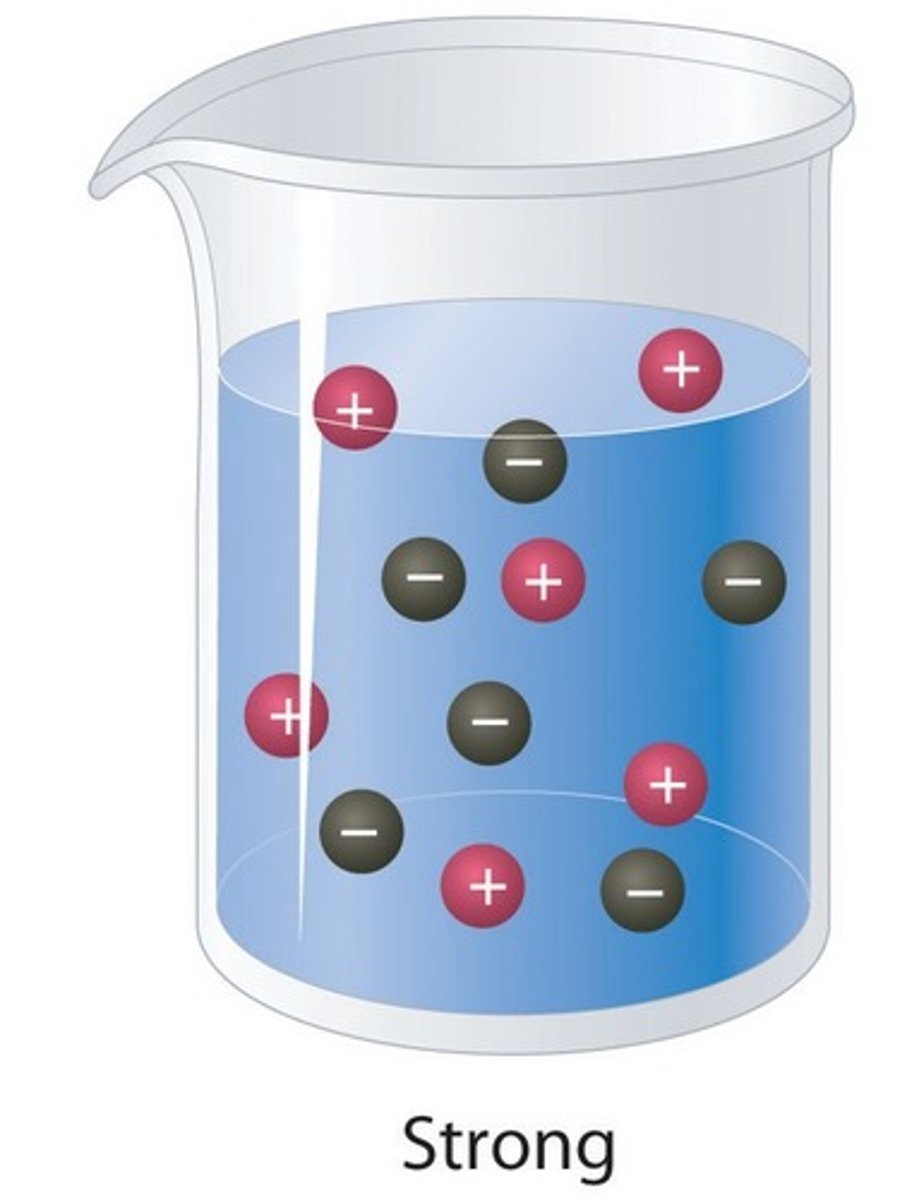
Strong acid
An acid that ionises completely in water
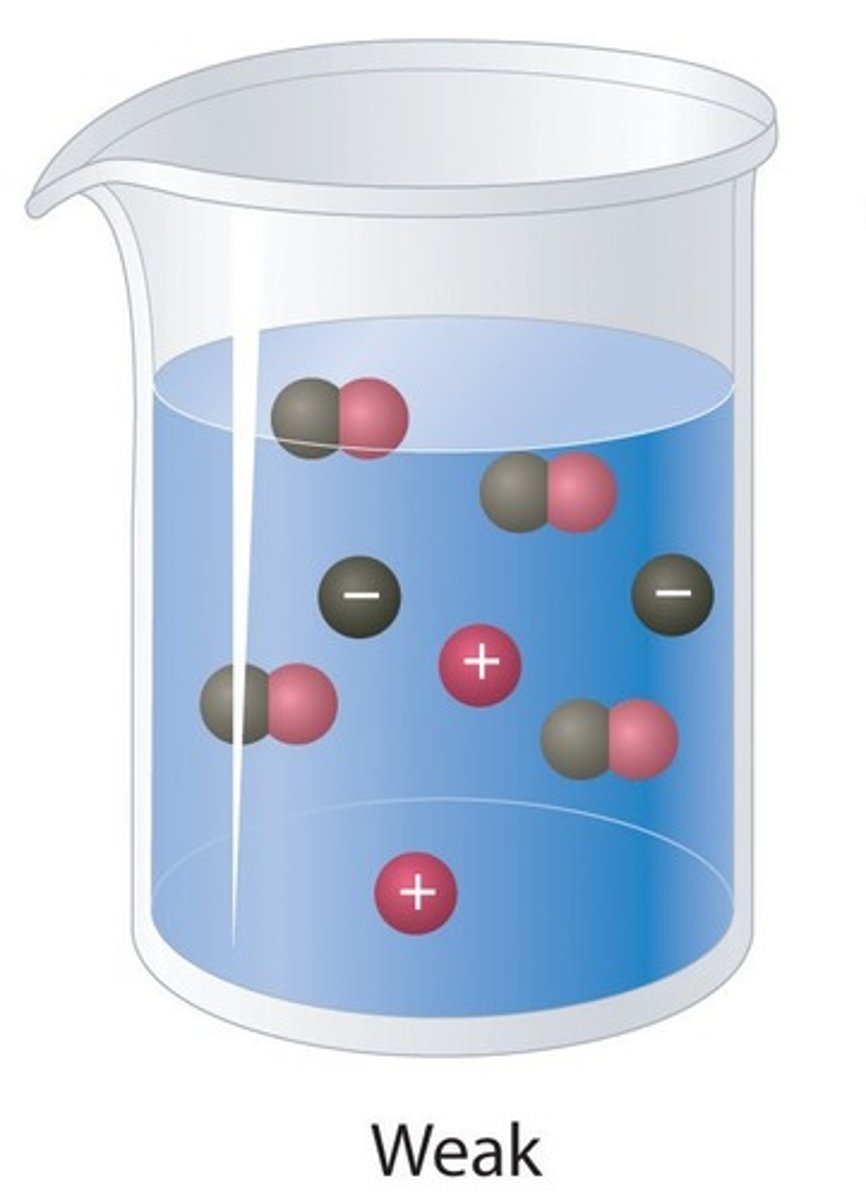
Weak acid
An acid that only partially ionises in water
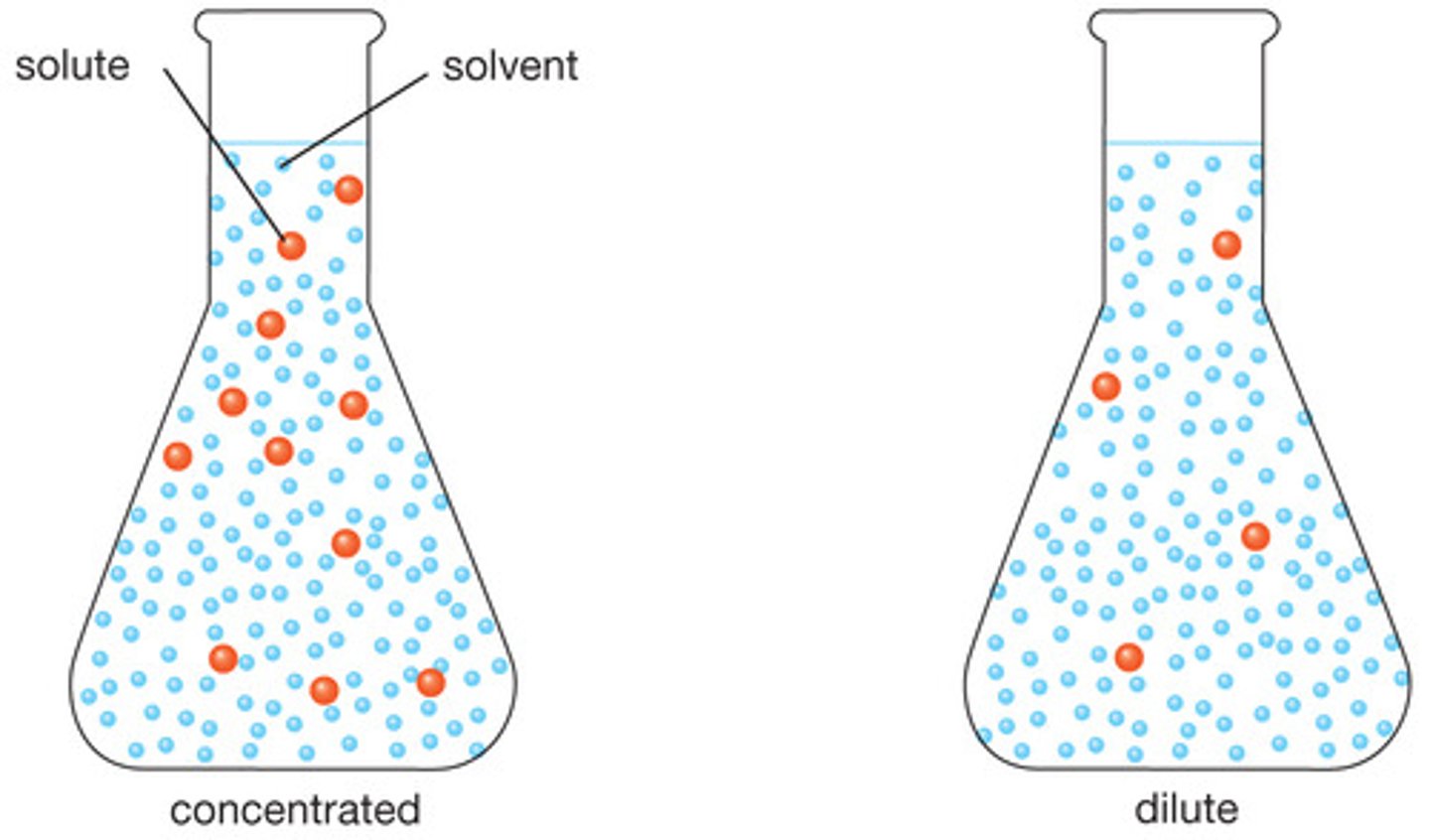
Dilute
a solution containing little solute
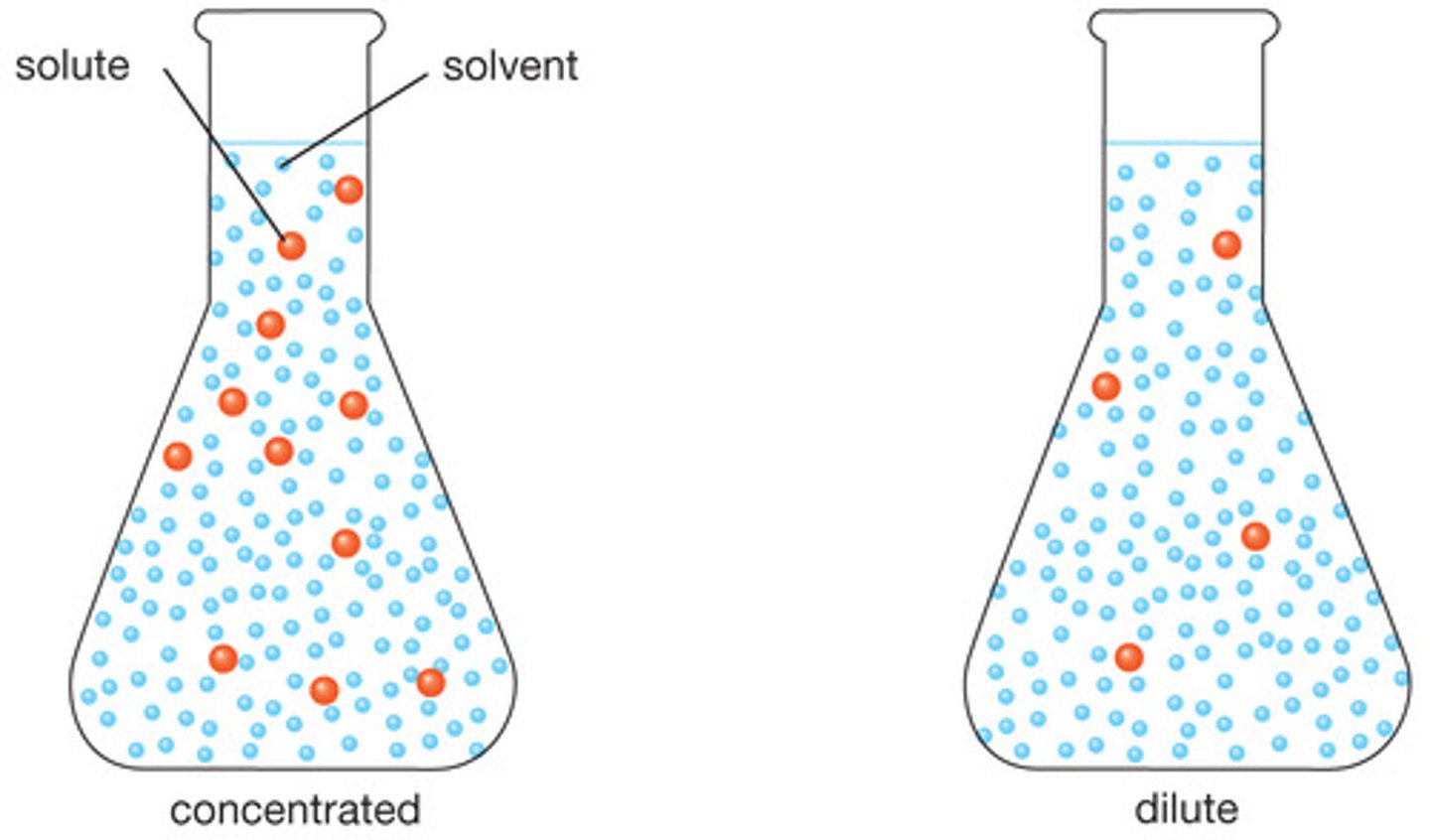
Concentrated
large amount of solute
Standard solution
A solution of known concentration
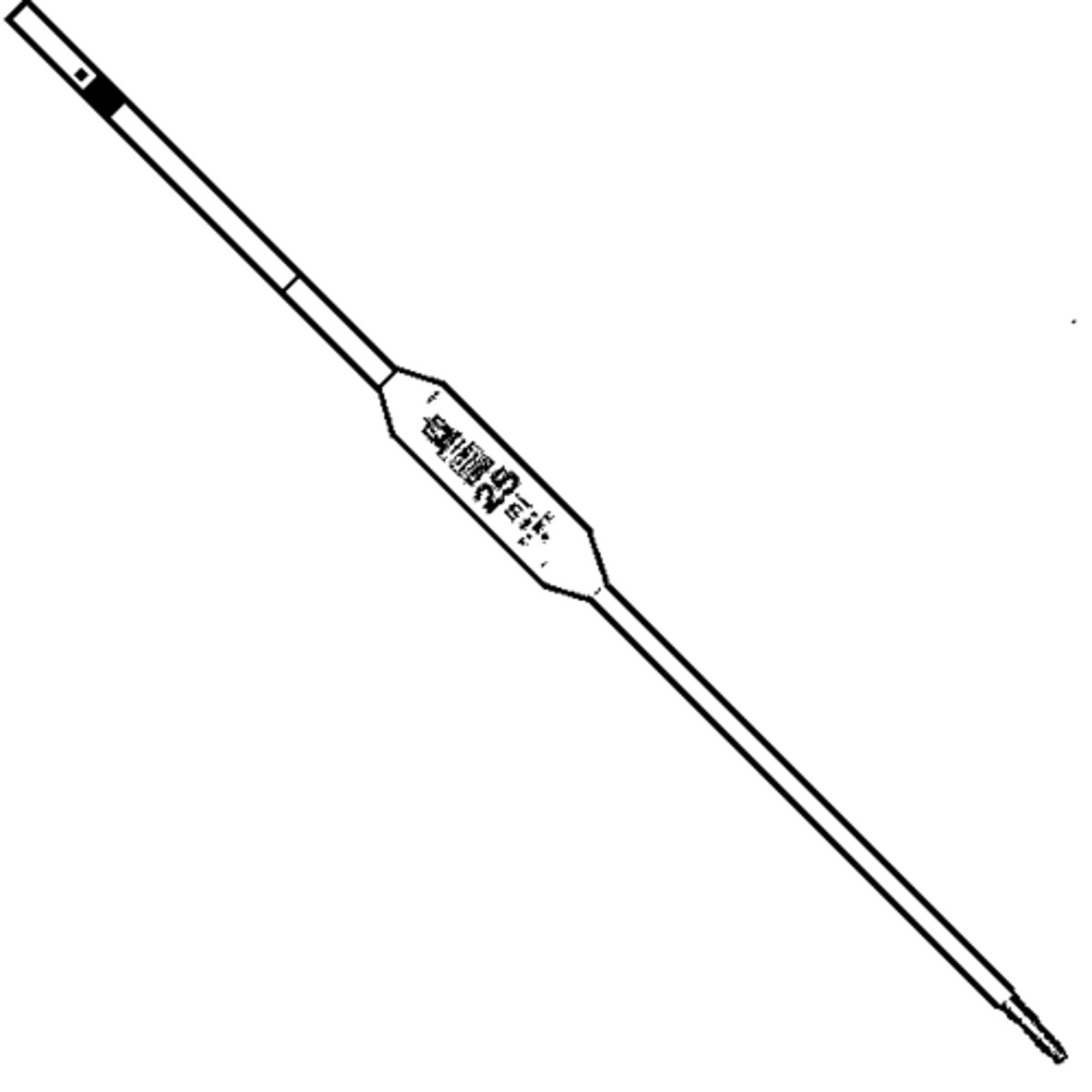
Burette
A graduated glass tube with a tap at one end, for delivering known volumes of a liquid

Pipette
A glass or plastic tube used to accurately measure liquid
Meniscus
Curved surface of liquid

End point of titration
the point at which the indicator changes color
Indicator
A compound that changes color in the presence of an acid or a base
Titre
The volume of liquid added at the end point
Rough titre
A quick titration 'test-run' which can tell us roughly what your titre would be.
Concordant results
Titres that are within 0.10cm3 of each other
Phenolphthalein
Indicator which is clear in acidic solution and pink in basic solution.
Pipette filler
Device used to safely fill a pipette
White tile
A white surface to clearly see the indicator changing colour
Conical flask
Used to hold liquids, narrow neck to prevent splashes

pH Strong acids
0-2
pH Weak acids
3-6
pH Strong alkalis
12-14
pH
A measure of H+ concentration
pH Weak Alkali
8-10
Neutral pH
7
pH of acids
less than 7
pH of alkalis
more than 7
Universal indicator
An indicator with a different colour for each pH value
If pH decreases by 1
hydrogen ion concentration increases x10
At pH 7
concentration of H+ = concentration of OH-
Strong acid
An acid that ionises completely in water
Weak acid
An acid that only partially ionises in water
Phenolphthalein
Indicator which is clear in acidic solution and pink in basic solution.
Litmus
Indicator that turns red in acid and blue in base
Methyl orange
Indicator that is red in acid, yellow in alkali
pH probe
An instrument which measures pH to 1 decimal place