MOD 6 - Intro to QA/QC Tests
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Quality Control in Imaging
the monitoring, testing and maintenance of the x-ray equipment to ensure it's working optimally to minimize patient dose and ensure high quality images
Total Quality Management (TQM)
all members of an organization participate in improving processes, products, services and the culture in which they work
everyone in the medical imaging department is involved in one way or another with QA and QC
Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI)
focusses on improving processes or systems in place
Quality Assurance (QA)
what
features
the planned and systematic actions for personnel that provide confidence that a diagnostic x-ray facility will produce high-quality images with minimum exposure of patients and it's personnel
Features Include:
Information Quality = provides diagnostic images and info
Clinical Efficiency = provides diagnostic images quickly and efficiently
Patient Dose = ALARA
Requirements to achieve a QA goal
working equipment
all staff understands the goal of the program
all staff is fully committed to the program
Equipment Testing Step Process
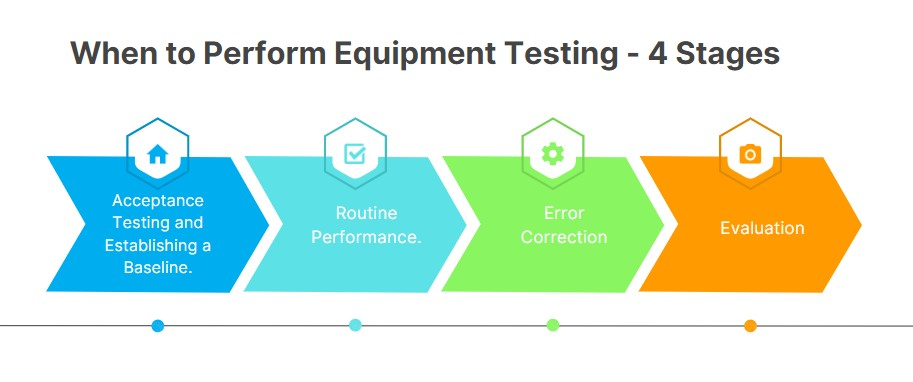
Acceptance Testing and Establishing a Baseline
done before the equipment is put to use (eg. new equipment)
conducted by a medical physicist (who has no relation/bias towards the equipment)
calibrated and a reference image is stored
takes around 8-10 hrs
Routine Performance
daily inspections of equipment to weekly, monthly and annual testing and inspections
done by medical physicists, biomed, QC team, techs
Error Correction
a decision tree that answers the following
done by biomed, vendor service
A repeat of the test to confirm
What to do if repeated test confirms performance failure
what to do if test fails only marginally
what to do if the test shows a history of failure
what to do if the test fails substantially

Evaluation
if an equipment has a +/- 10% acceptable test limit in place, the equipment is deemed unsafe for patient use, if repaired it needs to be tested again before use
done by med physicists, rads, chief tech
Implementation of a QA Program
list of personnel and their duties
policies to minimize dose to personnel
policies to minimize dose to patients
Guidelines to QC Tests
Policies to acquire new X-ray equipment
Policies for Record Keeping
QC Team
owner of the facility = primarily responsible
plan and managing = department supervisor, QC coordinator, physicist
sets litmits, evaluates QC = physicist
performs annual testing = physicist, biomed
repairing equipment = biomed
performs rest of QC tests = techs
Documentation
documented in the QC logbook
Format of a QC Test
Aim = overall goals of the test
Equipment = test tools/equipment needed for this test
Method = specific steps to conduct this test
Frequency = how often is the test completed
Data Record Keeping = QC log
Tolerances = setting max/min limits
Action = what to do after the results show equipment issues
1-6 is set by the med physicist, so we just have to follow
5 and 7 are our responsibility to record in the QC logbook
Determination of Testing Frequency
If equipment is showing significant signs of wear and tear between testing, then testing frequency may need to increase.
QC tests should NOT be less frequent if the QC tests always show stable results
Diagnostic Accreditation Program (DAP)
a governing body assigned to monitor for upkeep and adherence to a Quality Standard
regulated by College of Physicians and Surgeons of British Columbia