Topic 5 - Synaptic Signaling
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Central Nervous System (CNS)
includes the brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the CNS to the rest of the body
sensory neurons (afferent)
neurons that carry incoming info from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
motor neurons (efferent)
neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
Interneurons (association neurons)
found in neural pathways in the CNS, connect sensory and motor neurons
glial cells
cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons
schwaan cells
glial cells in the PNS that form myelin sheaths around axons
Dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
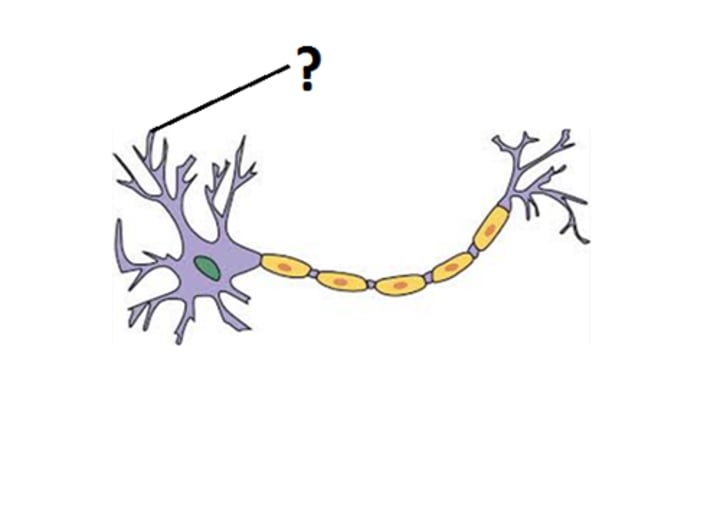
axon hillock
the cone-shaped area on the cell body from which the axon originates
Axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath to which voltage-gated sodium channels are confined.
myelin sheath
A layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the fibers of many neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node to the next.
synaptic bouton
end of the axon from which neurotransmitters are released
terminal branches
Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to other neurons
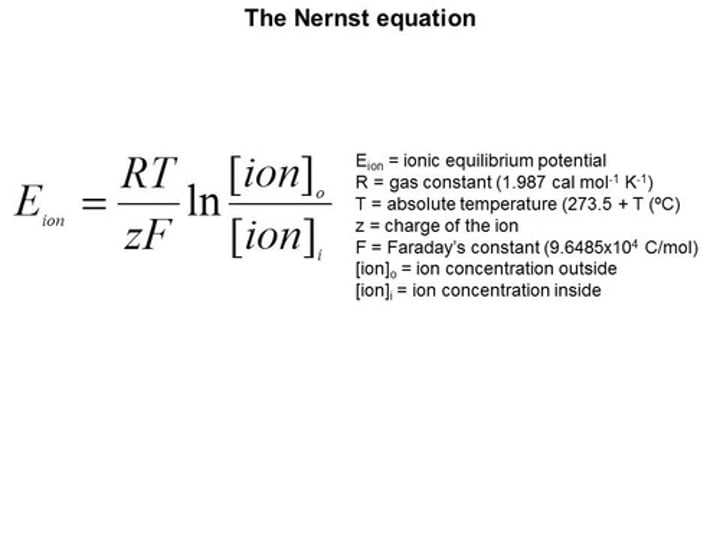
Nernst equation
a mathematical relationship used to calculate an ionic equilibrium potential
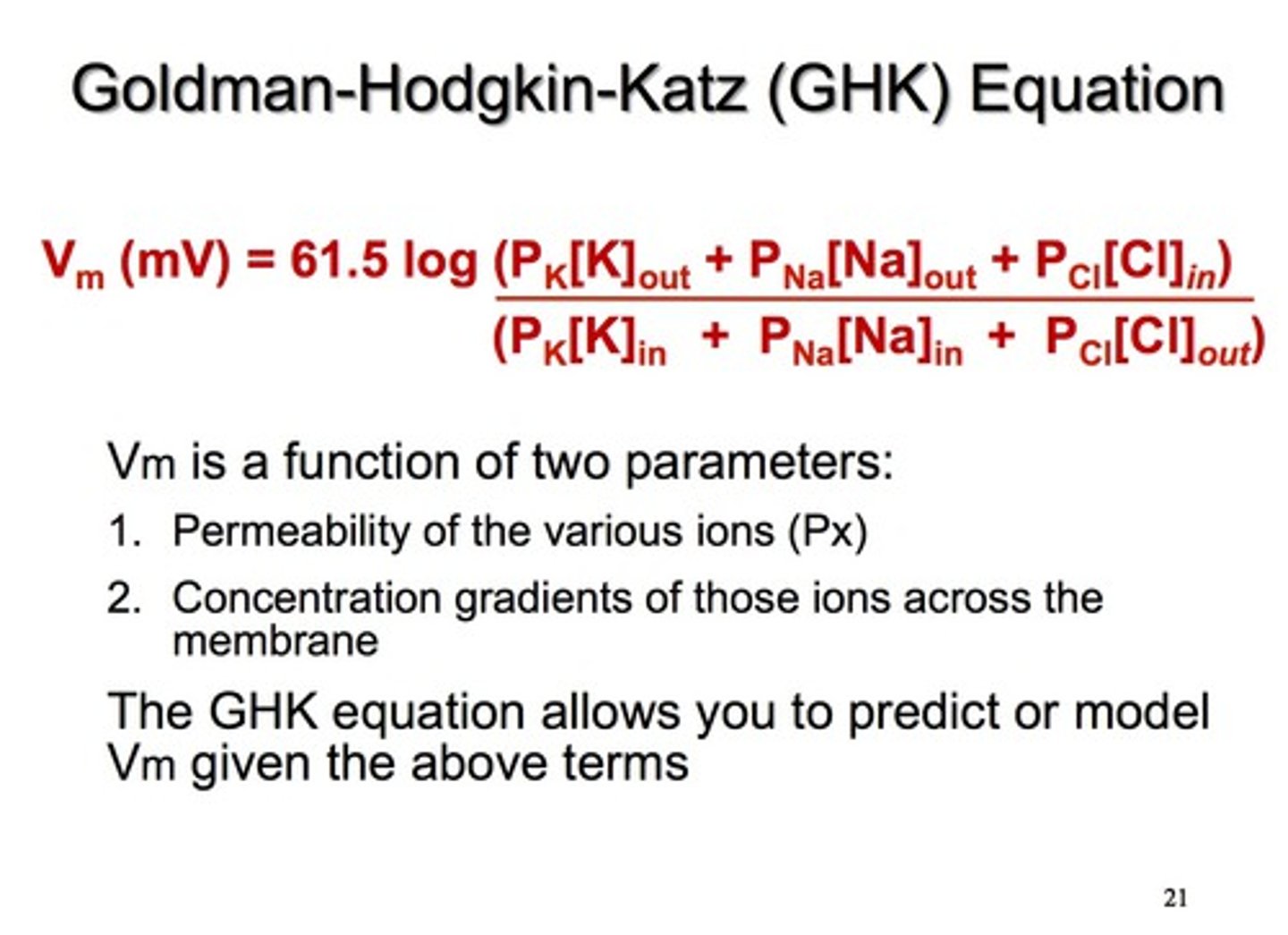
Goldman equation
a mathematical formula that takes into consideration the relative permeability of the membrane to different ions.
voltage-gated ion channels
A specialized ion channel that opens or closes in response to changes in membrane potential
passive spread of depolarization
process in which cations (mostly K+) move away from the site of membrane depolarization to regions of membrane where the potential is more negative
transmission of action potential
Nerve impulse occurs, impulse reach voltage gated
ca+ channels causing influx of Ca+, this allows synaptic vessels to fuse with the presynaptic membrane, these are then released into the synaptic cleft, and will bind with the post synaptic receptors
myelination of axons
the process of insulating axons in myelin, which speeds their conductivity and allows information to move more rapidly through the brain and body