Lecture 62: Diseases of Ruminants, Dogs, and Cats
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What are the cause and features of listeriosis in ruminants?
listeria monocytogenes ingestion of contaminated silage → invades oral mucosa → trigeminal nerve → brainstem → leptomeningeal opacity, yellow discoloration, brain stem hemorrhage → circling, head tilt, facial paralysis, dysphagia, dullness, drooling
What are the cause and features of thrombotic meningoencephalitis (TME) in ruminants?
histophilus somni respiratory infection → bacteremia → endothelial damage → thrombosis and infarction → multifocal hemorrhage and necrosis at cortical gray-white junction → meningoencephalitis, vasculitis, vascular necrosis, 4ataxia, blindness, circling, head pressing
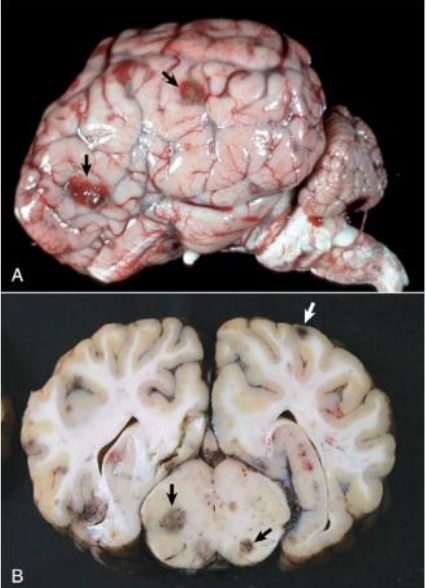
What is wrong with this steer brain?
TME
What are the cause and features of malignant catarrhal fever in ruminants?
gammaherpesvirus targets vasculature, lymphoid tissue, epithelia, and CNS → nonsuppurative meningoencephalomyelitis, vasculitis, perivascular lymphocytic cuffs → neurologic dysfunciton
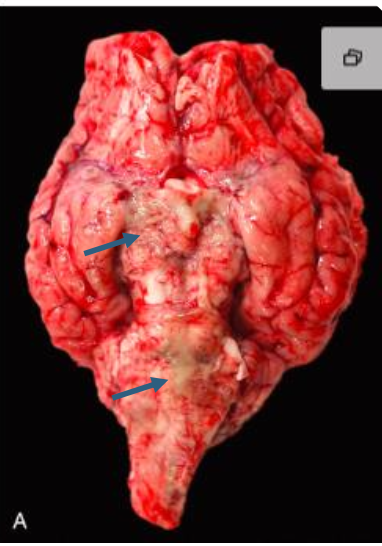
What is wrong with this bovine brain? note the blood vessels of the cerebral arterial circle and along the ventral aspect of the brain contain a white-gray exudate.
malignant catarrhal fever
What are the cause and features of CAE in ruminants?
lentivirus transmitted through colostrum, milk, or direct contact → lymphoproliferative or macrophage-trophic infection → tan foci in the white matter of brain and spinal cord, granulomatous inflammation with lymphocytes and plasma cells → hindlimb weakness progressing to quadriplegia in kids and arthritis, mastitis, and pneumonia in adults
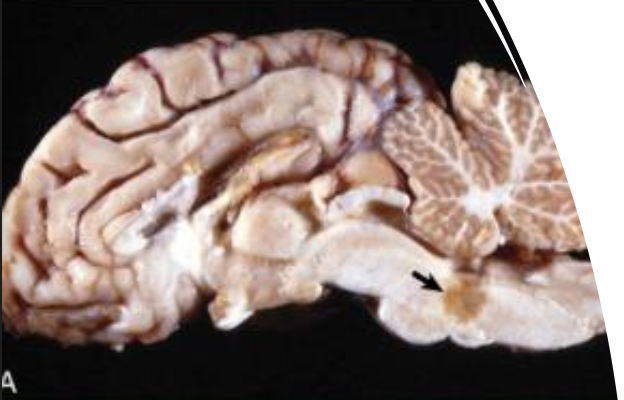
What is affecting the brainstem of this goat?
CAE
What are the cause and features of thiamine deficiency (polioencephalomalacia) in ruminants?
high-carb diets, ruminal acidosis, thiaminase-producing bacteria, or plant thiaminases → yellow softening of gray matter, edema (autofluorescence under UV) → ataxia, cortical blindness, head pressing, recumbency, opisthotonus
Other than thiamine deficiency, what are other causes of polioencephalomalacia?
sulfur toxicity, lead toxicity, salt poisoning
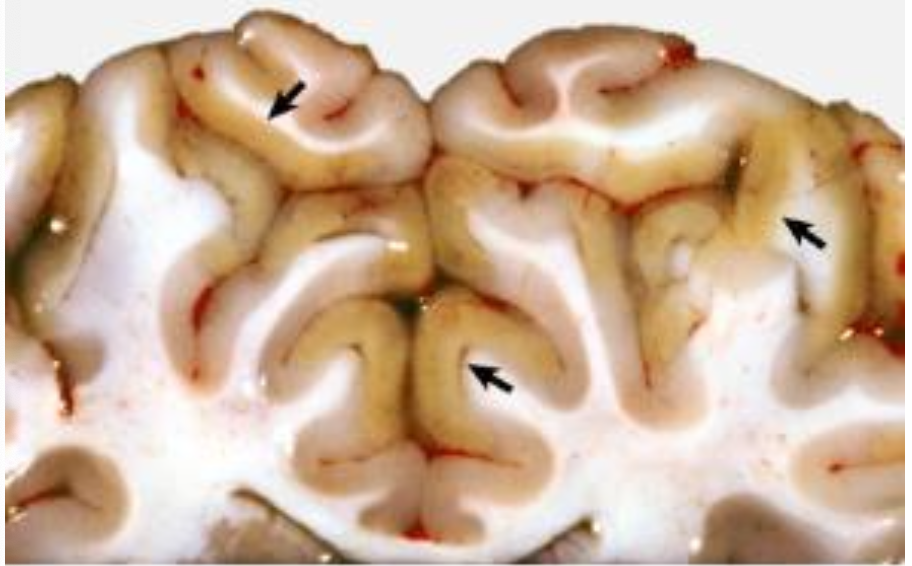
What is wrong with this bovine brain?
polioencephalomalacia
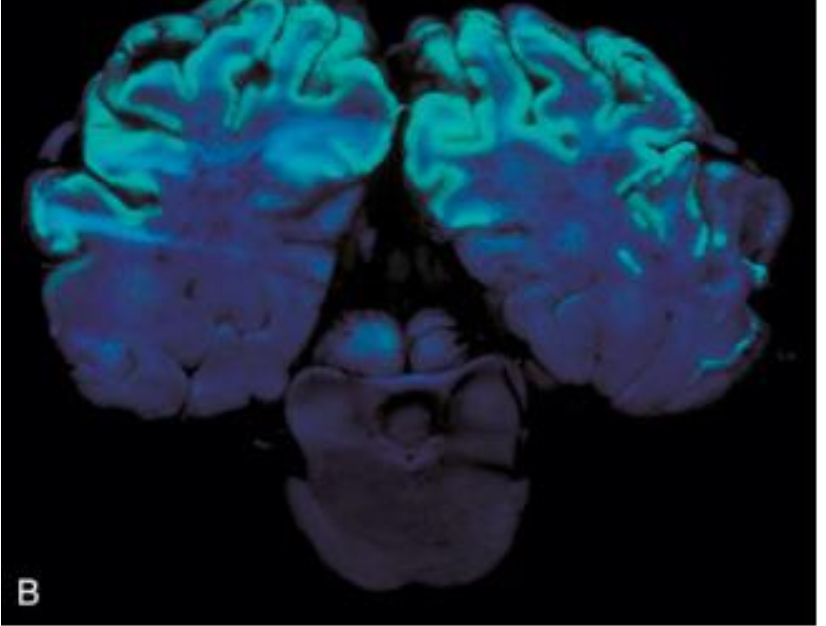
What is wrong with this brain?
acute polioencephalomalacia
What are the cause and features of copper deficiency in small ruminants?
copper-deficient soil or mineral imbalance causing two forms:
sway back (congenital): cerebral cortex lesions, cavitation
enzootic ataxia (delayed): brainstem and spinal cord degeneration
What are the cause and features of clostridium perfringens type D (enterotoxemia) in ruminants?
(“overeating disease” in lambs and kids) enterotoxin → vascular injury → BBB breakdown → bilaterally symmetric foci of malacia and cavitation in white matter (“focal symmetric encephalomalacia”)
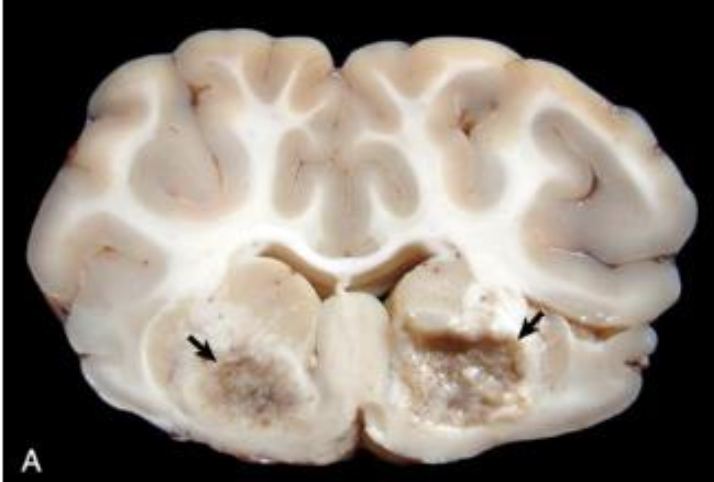
What is affecting this sheep brain?
focal symmetric encephalomalacia
What are the cause and features of canine distemper virus?
distemper virus (morbillivirus) spread through aerosol → lymphoid tissue → CNS via leukocytes → demyelination, encephalomyelitis, necrosis of gray and white matter → seizures, ataxia, myoclonus, paralysis
What are the cause and features of canine herpesvirus-1?
neonatal puppies infected with virus → multifocal necrotizing encephalitis (brainstem, cerebellum)
What are the cause and features of degenerative myelopathy in dogs?
mutation in SOD1 gene in German Shepherds → axonal degeneration of thoracic spinal cord → progressive hindlimb ataxia → paraplegia
What are the cause and features of Chiari-like malformations in dogs?
(commonly seen in cavalier king charles spaniels) mismatch between caudal fossa of skull and brain → cerebellar herniation through foramen magnum → syringomyelia
What are the cause and features of granulomatous meningoencephalitis (GME) in dogs?
immune mediated (T cell) → white matter inflammation most severe in brainstem → circling, seizures, paresis, behavioral changes
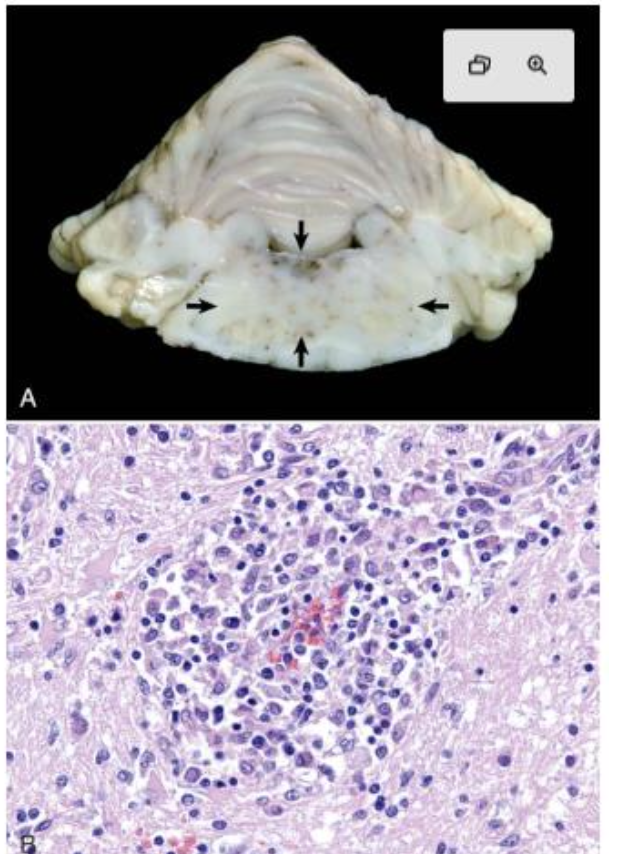
What is wrong with this canine brain?
granulomatous meningoencephalitis
What is the difference between the two necrotizing encephalitides in dogs?
Necrotizing meningoencephalitis (NME): pugs, chihuahuas, maltese; swelling of cerebral gyri with loss of distinction between white and gray matter → cortical necrosis, cavitation hydrcephalus
Necrotizing leukoencephalitis (NLE): yorkies; cerebral white matter and brainstem necrosis
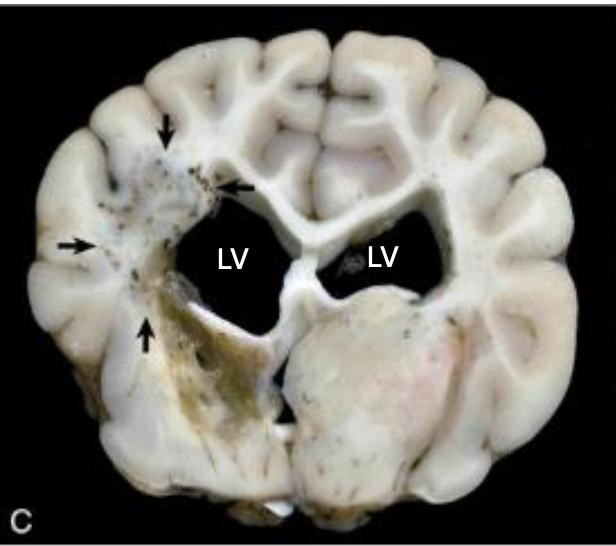
What is wrong with this yorkie brain?
NLE
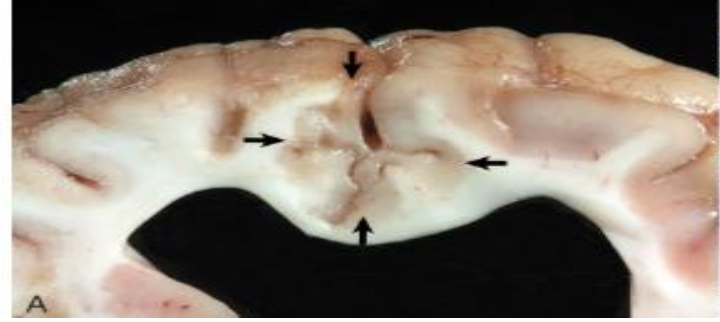
What is wrong with this maltese brain?
NME
What are the cause and features of steroid-responsive meningitis-arteritis in dogs?
immune mediated polyarteritis → fibrinoid necrosis of meningeal arteries with inflammation → neck pain, fever, neutrophilia on CSF, hunched posture
What are the cause and features of IVDD in dogs?
Degeneration of nucleus pulposus → disc material can protrude into still covered by annulus fibrosis (larger breed dogs – type II) or herniate through annulus fibrosis (chondrodystrophic dogs – type I) into the vertebral canal → spinal cord compression, wallerian degeneration, myelomalacia
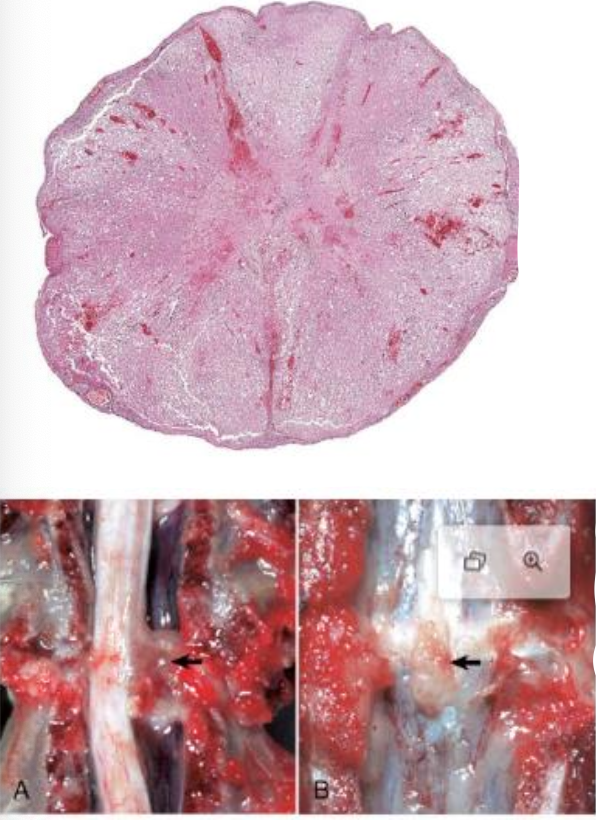
What is affecting this canine spinal cord?
IVDD
What are the cause and features of cognitive dysfunction in dogs?
amyloid deposition → senile plaques, cerebrovascular amyloidosis → cognitive decline
Where does leptomeningeal fibrosis most commonly occur?
in the sulci
What are the cause and features of FIP?
mutated feline coronavirus → pyogranulomatous meningitis and ventriculitis, yellow exudate obscuring meninges and vessels, white to tan plaques along the sulci or around the circle of Willis → hydrocephalus or cerebellar herniation can occur, coma, paresis ataxia, paralysis, seizures, behavioral changes
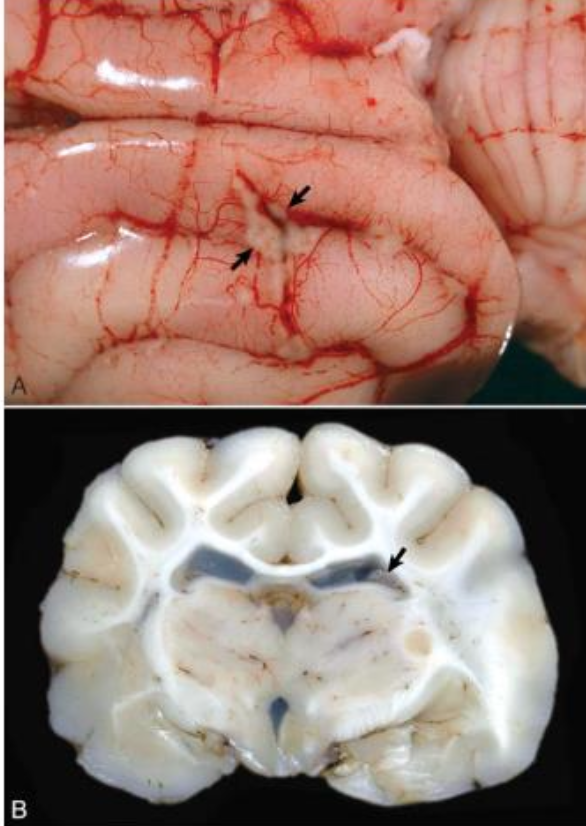
What is affecting this feline brain?
FIP
What are the cause and features of feline ischemic encephalopathy (FIE)?
migration of Cuterebra larvae through nasal cavity to brain → unilateral necrosis in the cerebral hemispheres, hemorrhage, cyst formation → depression, ataxia, seizures, blindness
What are the cause and features of feline thiamine deficiency?
thiaminase containing fish ingestion or deficient diets → bilaterally symmetric cavitating foci in the brainstem → ataxia, circling, seizures, opisthotonus, coma
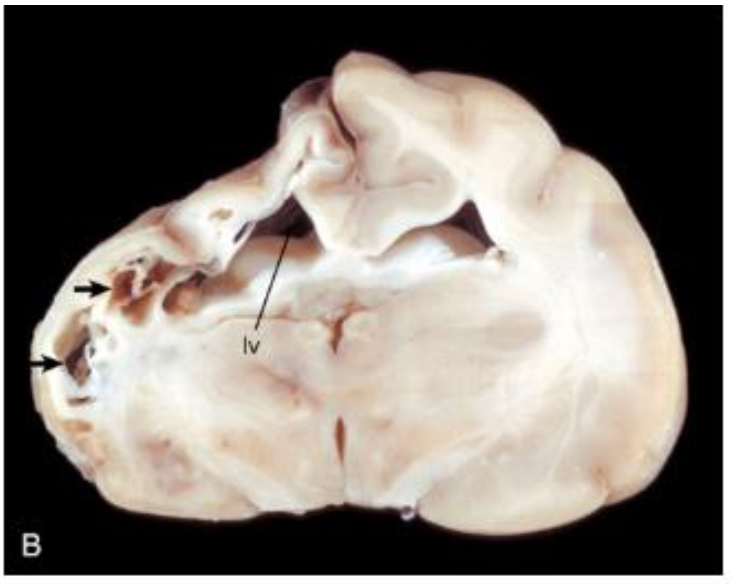
What is wrong with this feline brain?
feline ischemic encephalopathy
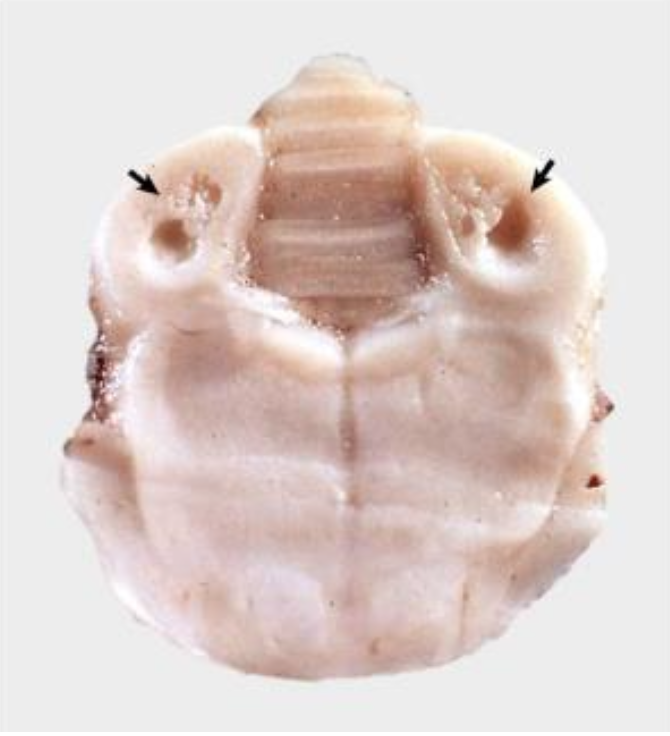

What is affecting this feline brain?
thiamine deficiency (vitamine B1)