Bio Exam 3 Material
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
ETC (Electron Transport Chain)
• Consist of protein complexes in the inner mitochondrial membrane
• Energy from transferring electrons is used to pump H+ from the matrix to the
inter membrane space creating a H+ gradient = proton motive force
Loss of Electrons is
Oxidation
1,3, and 4 are pumps
They pump hydrogen ions across the membrane
1,3 and 4 get energy from
Electrons
Nadh gets droppef off at 1 and gets shudled to 3 by
Q
With each transfer of electrons
Energy is decreased
FADH 2
Is more electronegative than complex 1
Complex 2 is able to get
Electrons from FADH
The whole purpose of the ETC
Form a hydrogen ion gradient
02 Is the final electron acceptor in the
ETC
ETC forms
Hydrogen ion gradient but no ATP
ATP Synthase (think of a windmill)
• H+ flows down its gradient through ATP synthase.
“Chemiosmosis”
• Energy from release of gradient is used to make ATP.
Most of the ATP in cellular respiration are generated through
electron transport & oxidative phosphorylation
You breath oxygen to…
Serve as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain
ETC Blockers
– Inhibit flow of electrons & pumping of H+ by ETC
– Prevent formation of H+ gradient
Rotenone
• Disrupts electron transport in metabolism
Block electron transport
Cyanide or CO (Block at 4)
Uncouplers
– Allow pumping of H+, but disconnect it from ATP synthesis
– Let H+ sneak back into matrix without using ATP synthase
Uncoupling protein
• Allow formation of H+
• Disconnect gradient from ATP synthesis - H+ move back into matrix
without using ATP synthase (generate heat instead of ATP)
Cyanide and carbon monoxide block the protein that donates the
electrons to oxygen, thus forming water. Cyanide and carbon
monoxide block ATP synthesis by
preventing the formation of an H+ ion concentration
gradient.
Drugs known as uncouplers facilitate diffusion of protons across the
membrane. With an uncoupler, what will happen to ATP synthesis and
oxygen consumption?
ATP synthesis will decrease; oxygen consumption will greatly
increase.
ATP Synthase inhibitors
– Allow electron flow & creation of H+ gradient
– Directly inhibit activity of ATP synthase
Carbohydrates are
Polar
We tend to burn
Carbs and Fats first
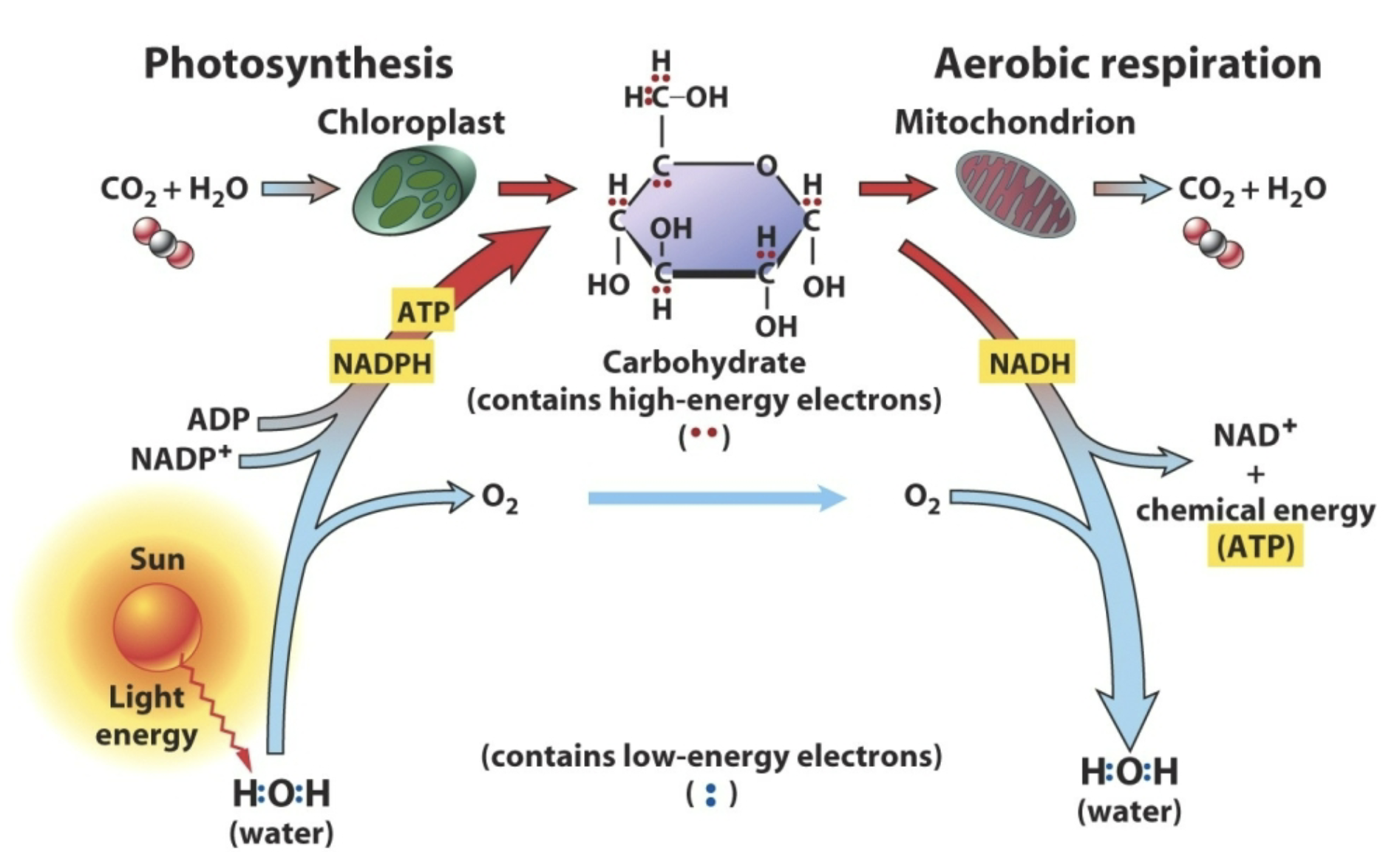
Relationship between photosynthesis & aerobic
respiration
NADPH
Electron Carryier
How does Respiration relate to Photosynthesis?
• Respiration – oxidation of sugars to generate ATP.
What does it use? What does it produce?
• Photosynthesis – reduction of CO2 and water to
build sugar. What does it use? What does it
produce?
Autotroph
produce complex
organic molecules (e.g., glucose,
starch) from simple inorganic
molecules (e.g., CO2, H2O)
Photoautotroph
transform
radiant energy (sunlight) into
chemical energy (ATP) to produce
complex organic molecules (e.g.,
glucose, starch) from simple
inorganic molecules (e.g., CO2,
H2O)
What is a photoautotrophs
Plants, protists and prokaryotes can all be
photosynthetic
Anoxygenic Photosynthesis:
no O2 produced; purple & green bacteria
Oxygenic Photosynthesis:
O2 produced; cyanobacteria, many protists, most green plants.
Producers store potential energy in
covalent bonds of the sugars, starch, etc
Why do apple trees (autotrophs) produce starch?
- Starch is used to fuel respiration
Stomata can be opened and closed to exchange
gases and to regulate H2O loss
Photosynthesis consists of two sets of reactions
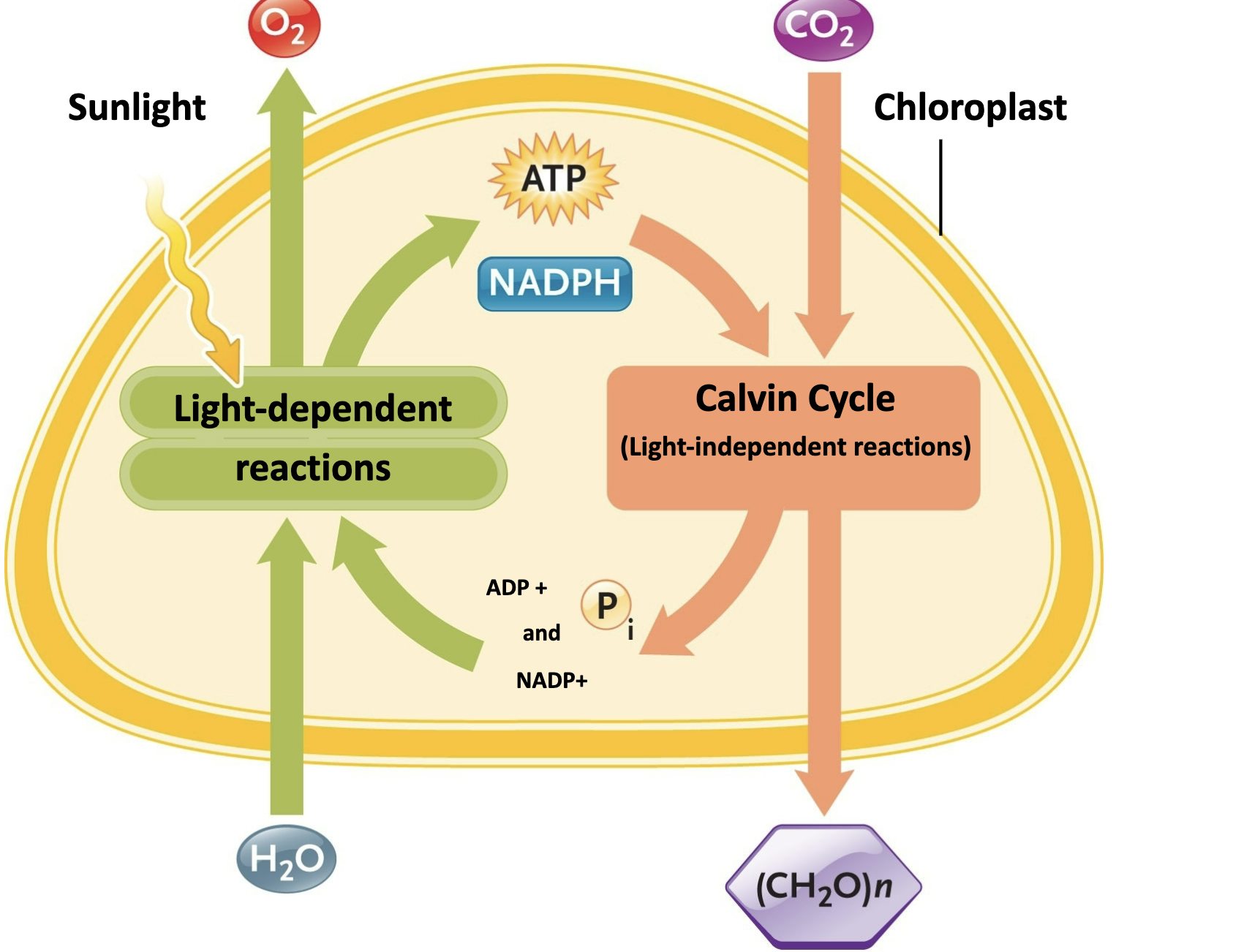
Photosynthesis Inside a Leaf
Photosynthesis starts in the photosystems of a thylakoid – Photosystems contain pigment molecules
Light
• Light is a form of energy
• Different wavelengths contain different amounts of energy
• Pigment molecules in chloroplasts absorb light energy
• The pigment in human eyes is retina
Pigments in plants
Pigments (mostly chlorophyll) give leaves their characteristic green color
Chlorophyll is
The main pigment in plants
Carotenoids are accessory
pigments
They capture wavelengths
not efficiently absorbed
by chlorophyll
Carotenoids
are accessory pigments, they capture wavelengths not efficiently absorbed by chlorophyll
Chlorophyll absorbs light energy
Multiple chlorophyll molecules
function together with thylakoid
membranes
Chlorophyll molecules and
accessory pigments are assembled
into…
antennas
About ___ chlorophyll molecules
per antenna
300
Photosystem I
Absorbs longer wavelength
light and funnels energy to a
special chlorophyll a molecule
called P700
Photosystem II
Absorbs shorter wavelength
light and funnels energy to a
special chlorophyll a molecule
called P680
What is the ultimate purpose of exciting an
electron from chlorophyll?
The excited electron is donated to an electron acceptor.
If one molecule is being ____ (NADP+ to
NADPH, another molecule is being ____
Reduced, Oxidized
WATER gets ____ and serves as the electron
donor
Oxidized
Thylakoid membranes are packed with photosystems
and ATP synthase
Which of the following are produced
during the Calvin cycle?
glucose, ADP, NADP+
Dna is held in
Nucleus
Transcription
The process copying DNA into mRNA
Translation
Process of protein synthesis from mRNA sequence
Step 1 to make a protein
Identify and copy the gene. (Transcription)
Step 2 to make a protein
Send the information to the cytoplasm
Step 3 to make a protien
Translate the genetic information in the primary amino acid sequence (Translation)
A gene is
a section of DNA that encodes a specific protein
Nucleic acid (DNA)
deoxyribonucleic acid
Nucleic acid (RNA)
ribonucleic acid
DNA and RNA are both
Nucleic acids
DNA is a polymer of
nucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds
DNA is made up of two __________ strands of nucleic acids
Antiparallel
The strands are held
together by __bonds
H
Adenine pairs with
Thymine
Guanine pairs with
Cytosine
Transcription
Synthesis of RNA from DNA, Produces mRNA
Translation
Synthesis of a polypeptide from mRNA, uses tRNA
Ribosomes-
Site of translation
Transcription =
DNA to RNA
Transcription from DNA to RNA
1. Identify the gene
2. Single strand the DNA
3. Polymerize RNA
4. Process pre-mRNA to make mRNA
Promoter
Series of base pairs where RNA polymerase attaches (Includes start site)
Transcription factors
Proteins that turn genes on and off by alowing or blocking the binding of RNA polymerase
RNA polymerase
Enzme that brings in new RNA nucleotides to synthesize mRNA
Enyzme is
RNA polymeraze
RNA polymerase
Binds to specific DNA
sequence found near all
genes called a promoter
What happens after the motification of RNA
Add a cap and a tail
Why add guanylated cap and tail
protect from degradation, increase the stability of the mRNA in cytoplasm, aid in its transport from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, indication to protein machinery that transcript is complete and intact
Introns
In eukaryotes, genes have extra bases
Exons
middle of their coding regions
____MUST BE REMOVED (by a process called RNA splicing) before the RNA is made into protein.
Introns___
The portion of a gene that ecodes protein is found on the
Exon
Ribosome consists of
Protein and rRNA
tRNAs
Bring in the right amino acids to the ribosome
Translation requires
Ribosome, mRNA, tRNA
In translation _____ is used as a template
to form ____
RNA, Protein