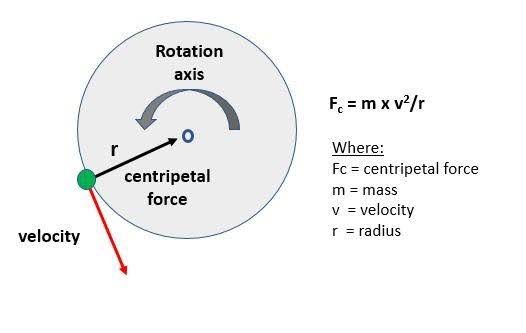
Uniform Circular Motion
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
uniform circular motion
Objects moving in a circle with constant speed (acceleration results in a change of direction) but no change in speed
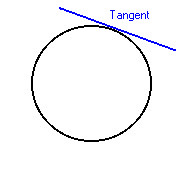
tangent
Constant velocity is _____ to the path
force
Constant ______ is towards the center
Centripetal force
Any force that causes an object to move in a circular path
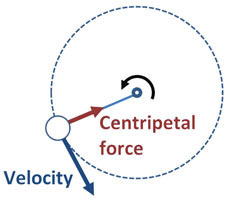
straight
When central forces are removed the object continues in a_____ line
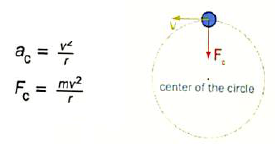
centripetal acceleration
acceleration toward the center of a curved or circular path
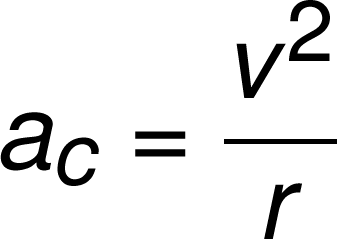
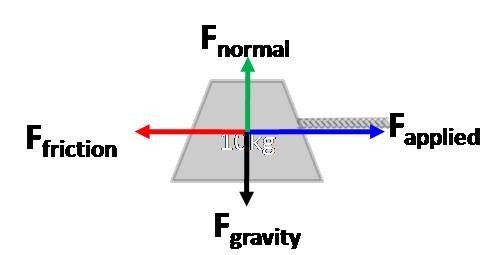
net
a body accelerates only in the presence of a ______ force
free body diagram
a diagram showing all the forces acting on an object
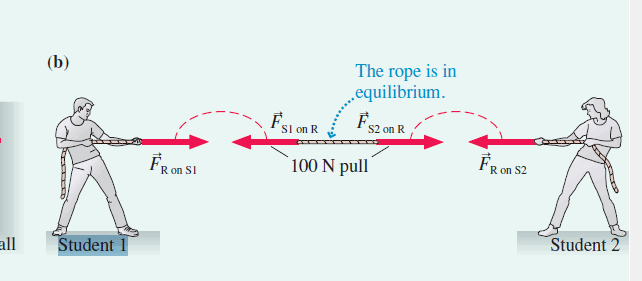
tension
force on a rope will put equal force at all points along that rope
weight
_____ is always directed towards the center or the earth
periodic motion
any motion that repeats at regular time intervals

Increases
the danger of breaking traction on a curve increases if the speed of the moving object ______

decreases
the danger of breaking traction on a curve increases if radius (sharper turn) of the curve ________
excessive
the danger of breaking traction on a curve increases if there is ______ wear (how used the rubber is) on the tires.
wetness
the danger of breaking traction on a curve increases if the _____ of the road increases
reduction
the danger of breaking traction on a curve increases if there has been ____ of the banking in the curve of the road
period
the time of one oscillation
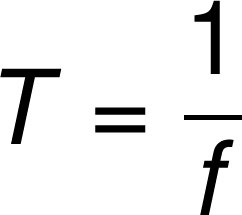
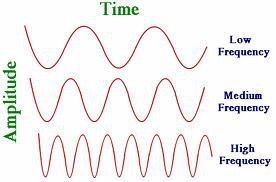
frequency
In any periodic motion, the number of complete oscillations measured in hertz.
newton
A unit of measure that equals the force required to accelerate 1 kilogram of mass at 1 meter per second
force in nature
A push or a pull
inversely
the centripetal force on an object is ____ proportional to the radius of path of the object
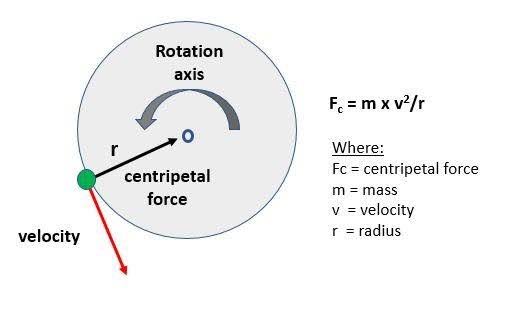
directly
the centripetal acceleration of an object in circular motion is ______ proportional to the velocity of the object squared