Water and osmosis
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
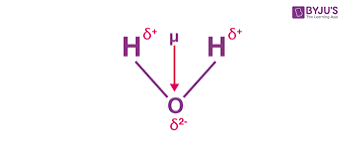
What is water made of
Water is a medium for metabolic reactions and is an important component of cells making up 65-95% mass of plants and animals. Humans are made of 70% water.
Water is dipole which is a polar molecule with a positively charged end (hydrogen) and negatively charged end (oxygen) separated by a very small distance. The signs are in the picture above. This means it they have no overall charge.
Hydrogen bonds are a weak attractive force between a hydrogen atom with a partial positive charge and an atom with a partial negative charge eg. Nitrogen or oxygen. In water they are weak but because there are so many of them the molecules are difficult to separate.
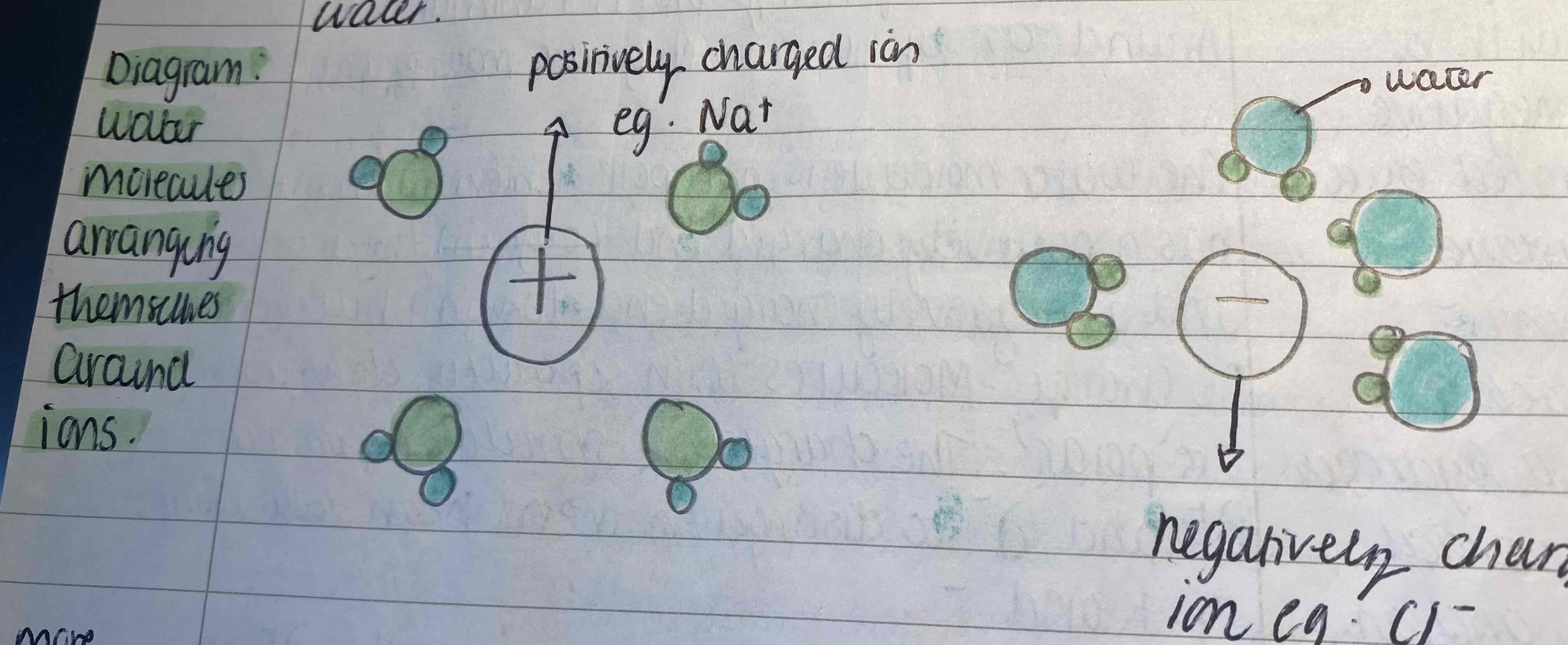
What is the first property of water
Water can be used as a solvent
Living organisms obtain their key elements from aqueous solution. Water is an excellent solvent because they are dipoles and polar so they can attract charged particles like ions and polar molecules eg. Glucose. These dissolve in water so the chemical reactions take place in solution. This can be used as a transport mediums eg. In animals the plasma transports substances in the blood or in plants water transports minerals in the xylem and sucrose and amino acids in the phloem. Non polar cant dissolve in water
What is the second property of water
Water is a metabolic -
Water is used as a reactant in many reactions eg.photosynthesis or hydrolysis
Hydrolysis:
Water + maltose = glucose + glucose
And in condensation reactions water is a product - reverse of reaction above
What is the third property of water
High specific heat capacity
This means lots of heat energy - thermal is need to raise its temperature. This is because the hydrogen bond in water restrict their movement so they resist an increase in kinetic energy and hence resisting temperature increasing. This prevents large fluctuations in waters temp and so this is important in keeping aquatic habitats stable and enzymes in cells to work efficiently.
What is the fourth property of water
High latent heat of vapourisation
This means a lot of heat energy is required to change its state from a liquid to a Vapour. This is importantly in temperature control where heat is used to vaporise water from sweat on the skin and on a leads surface as as the water evaporates the body cools
Explain the fifth property of water
Cohension
Water molecules are attracted to each other forming hydrogen bonds and individually these are weak but together they are strong in a lattice shape. This is called cohesion and allows water molecules to travel up tbe xylem together
Explain the sixth property of water
High surface tension
at ordinary temperatures water has the highest surface tension of any liquid except mercury. In a pond cohesion between water at the surface means that the body of an insect is supported eg. A pond skater
Explain the seventh property of water
High density
Water is dense than air so the habitat of aquatic organisms is provided with support and buoyancy. Waters maximum density is at 4 degrees. Ice is less dense than liquid water because the hydrogen bonds hold the molecules further parts - ice explanation - so ice floats on water
It is a good insulator and prevents large bodies of water losing heat and freezing complete so the organism below can survive
What is the final property of water
Water is transparent
So light can pass through so aquatic organisms can photosynthesise
What is osmosis - key term
Most cell membranes are permeable to water and osmosis refers to the movement of this water across the membrane
Key term - osmosis -
The net movement of water from a region of high water potential to the area of low water potential through a selectively permeable membrane down the water potential and concentration gradient - passive
What is water potential
Water potential key definition is the measure of free energy of water molecules and the tendency for water to move from a less negative water potential area to a more negative water potential area. it’s measured in kPa
There is no tendency for water molecules in pure water to move as conc are the same so water potential of pure water is 0.
The addition of a solute to pure water brings the water molecules in because the water molecules become weekly bonded to the solute so fewer are free to move (wp is the tendency for water to move). Therefore here the system has less potential to move. As force pulls inwards - osmotic pull - it has a negative so and so it gives the water a negative sign. So the more solute the more negative the sign as more force is pulled in.
Water goes down the water potential gradient so it moves from the less negative wp to more negative wp

What is the water potential equation and explain it
Water potential = pressure potential + solute potential
What does hypotonic solution mean
A hypotonic solution is when the water potential of the extra cellular and external solution is higher less negative than the WP of inside the cell so the water moves down the water potential gradient via osmosis into the cell causing it to become turgid or burst
Hypo - hippo
What does hypertonic solution mean
Hypertonic solutions have an extra cellular fluid with a lower more negative WP and therefore the water moves from inside the cell with a higher less negative WP to outside the cell down the WP gradient via osmosis causing it to become plasmolysed.
Hyper - active so not fat
What is an isotonic solution
An isotonic solution is when the cell has the same water P as the extra cellular fluid so so the water molecules are still moving but they are at equilibrium so there is no 0 net movement.
What is solute potential
solute potential is how easily it is for water to move out of solution. The more solute present the tighter the water molecules are held together as more weak bonds so the lower the tendency for the water to move out of solution so the lower the concentration of solute the higher the solute potential.
What is pressure potential in plants
Because of the cell wall in plants they have a pressure potential on this cell wall that effects WP
It is when water entering the cell via osmosis expands the vacuole and pushes the cytoplasm against the cell wall which causes pressure to build up resisting the entry of more water making the cell TURGID. This pressure potential has a positive sign when it pushes out meanwhile there is a negative force pulling water in causing the water potential to increase due to positive PP
Explain the 2 forces that plant cells experience
The pulling in force comes from the Solute potential as lots of solutes in the vacuole and cytoplasm pull water in
The push out force from the pressure potential increases tendency of water to move out as more negative the outisde becomes
The balance of these determines whether water moves in or out - hydrostatic
Explain how the water potential of a plant cell can be 0 and
If a plant is in a hypotonic solution the water is taken in until prevented by opposing pressure of cell wall - PP increases. It rises until they are equal so if they are equal solute potential much be 0 so water potential is 0
Explain 3 states of a plant cell
Turgid, plasmolysed and incipient plasmolysis or flaccid
Explain osmosis in animal cells
An animal cell has no cell wall so there is no pressure potential so solute P is equal to WP so water potential is only increased by increasing solutes
Red blood cells
When In a hypertonic solution - the cell strinks as there is a highly concentrated solution so the water potential is more negative as there are more weak bonds to the solute so it has less tendency to move. This means the water from the less negative cell moves out causing strinkage down the WP gradient via osmosis - called CRENATED
when red blood cells in same conc of solute like blood stream isotonic - no burst as equal tendency to move so no net movement - equilibrium
In a hypotonic solution the cell bursts because the solution is less negative WP than the more negative WP of the cell so the water moves down the WP gradient via osmosis and so cell has too much water as no pressure potential to cancel out negative so bursts - HAEMOLOYSIS