Complicated Pregnancy - Clin Med
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What does this refer to
before birth; during or relating to pregnancy
Prenatal/antenatal
What does this refer to
relating to the time, usually a number of weeks, immediately before and after birth
Perinatal/peripartum
What does this refer to
of, relating to, characteristic of, or denoting the period after childbirth
Postnatal
What does this refer to
Usually refers to the 6 weeks following birth
Postpartum
What does this refer to
Infants born very early are not considered to be viable until after 24 weeks gestation.
Viable pregnancy
What does this refer to
Transient increases in FHR
Fetal accelerations
What does this refer to
Temporary, but distinct, decreases in FHR
Fetal decelerations
What position is the fetus facing
toward the woman's back— face down when the woman lies on her back
Rearward
What position is the fetus facing
Face up
Forward
What does this refer to
_______ refers to the part of the fetus's body that leads the way out through the birth canal (called the presenting part).
Presentation
What does this refer to
Single egg cell is fertilized by a single sperm cell = zygote
Zygote splits into two = 2 separate embryos
Same gender
Most cases are not caused by genetic factors
Share the exact same DNA
Monozygotic (MZ) twins (identical twins)
What does this refer to
2 egg cells are each fertilized by a different sperm cell in the same menstrual cycle
twice as common as MZ twins
More likely to “run in families”
Genetic component is hyperovulation
Other influences
Mother’s age
Ethnic background
Diet
Body composition
Number of other children
Dizygotic (DZ) twins (fraternal twins)
What does this refer to
The average length of a pregnancy for triplets is 32 weeks.
For quadruplets, the average length is 30 weeks.
Continuing a multiple pregnancy past 36 weeks can be risky for you and your babies.
Multiple gestation
What does this refer to
Sign that the baby is not doing well
Baby isn't receiving enough O2 through the placenta.
Untreated —> baby breathing in amniotic fluid containing meconium (poo)
In utero
Decreased fetal movement
Decreased fetal heart rate
During labor
Tachycardia
Bradycardia
Variable decelerations
Late decelerations
Non-reassuring fetal status (NRFS)
What does this refer to
Biophysical profile
Type of US
Assesses
Fetal movement
Detal tone
Fetal breathing
Amniotic fluid volume
Non-stress test
Contraction stress test
NRFS detected prior to labor
What does this refer to
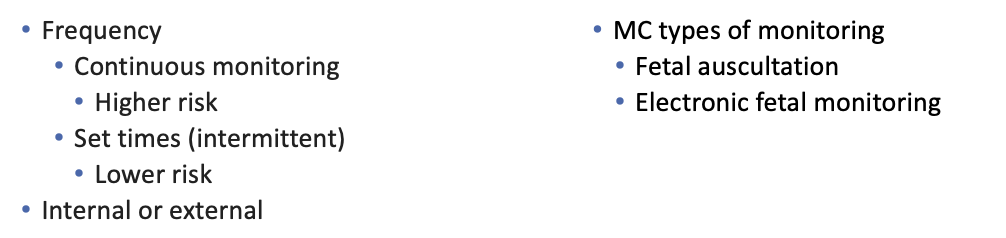
Fetal monitoring in labor
What does this refer to
Monitor identifies periods of fetal stress
Throughout the contraction
Recovering in the break periods
Only at the end of the contraction
Both during and after contractions
Fetal monitoring
What does this refer to
Unborn baby's umbilical cord slips through the cervix and into the vagina after a mother's water breaks and before the baby descends into the birth canal.
During delivery, the prolapsed cord can become compressed by baby's body.
Cord Prolapse
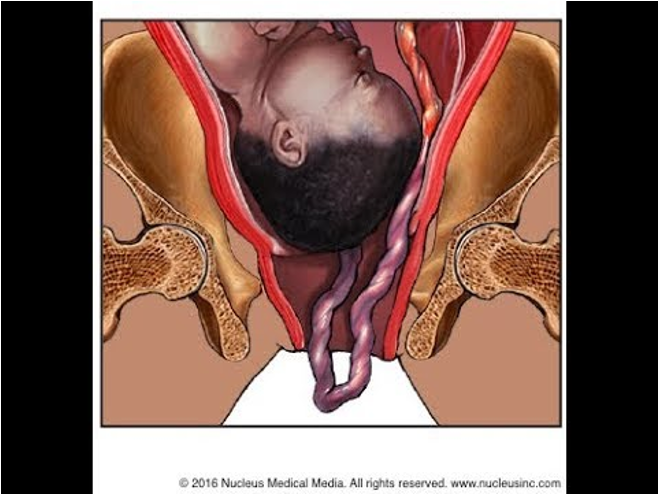
What does this refer to
both of the baby's knees are bent and the feet and bottom are closest to the birth canal.
Complete breech
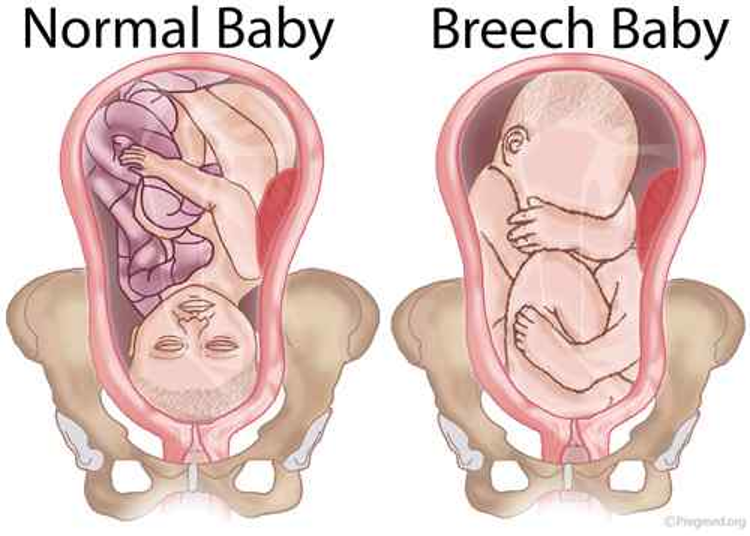
What does this refer to
one of the baby's knees is bent and the foot and bottom are closest to the birth canal.
Incomplete breech
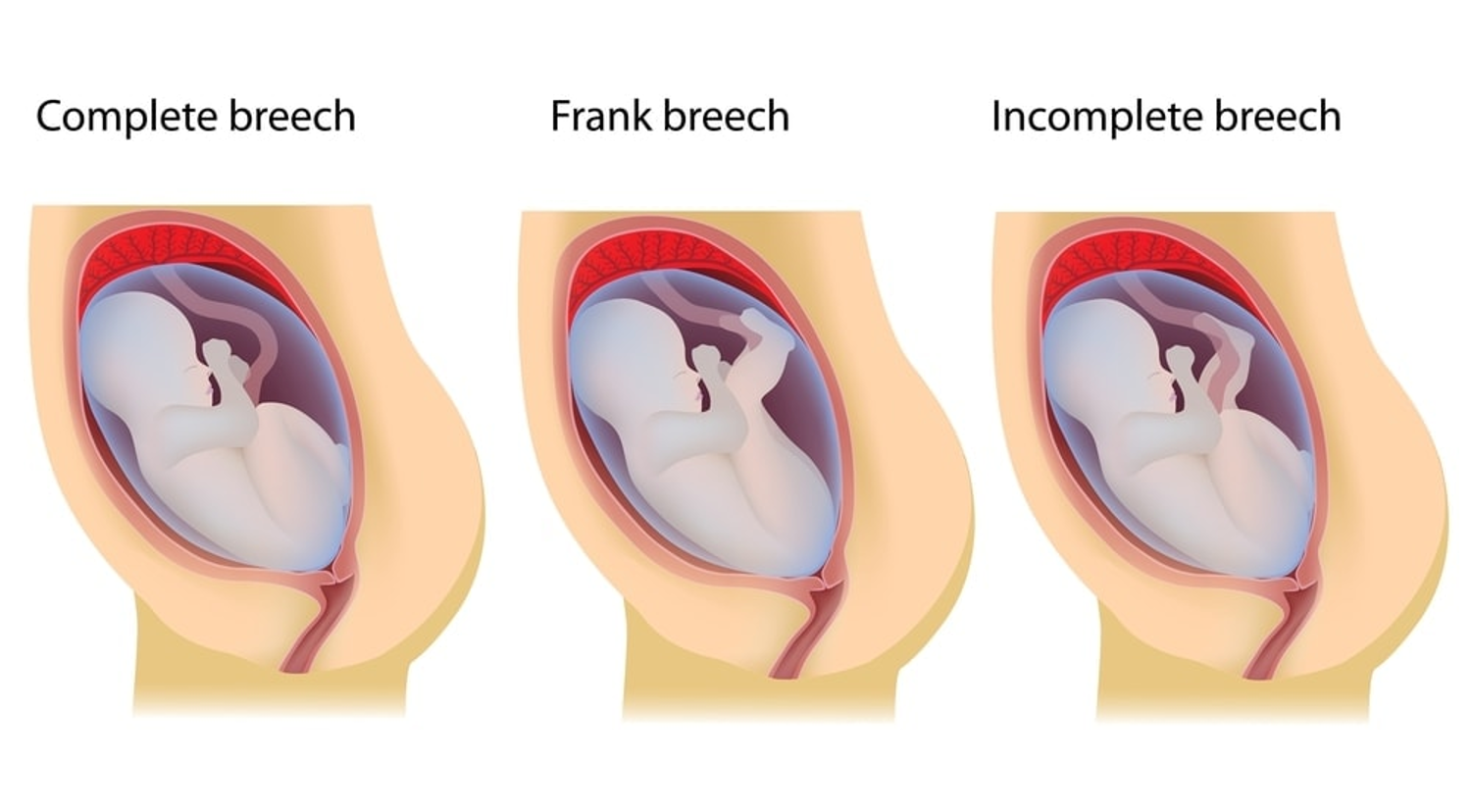
What does this refer to
the baby's legs are folded flat up against the head and his bottom is closest to the birth canal.
Frank breech
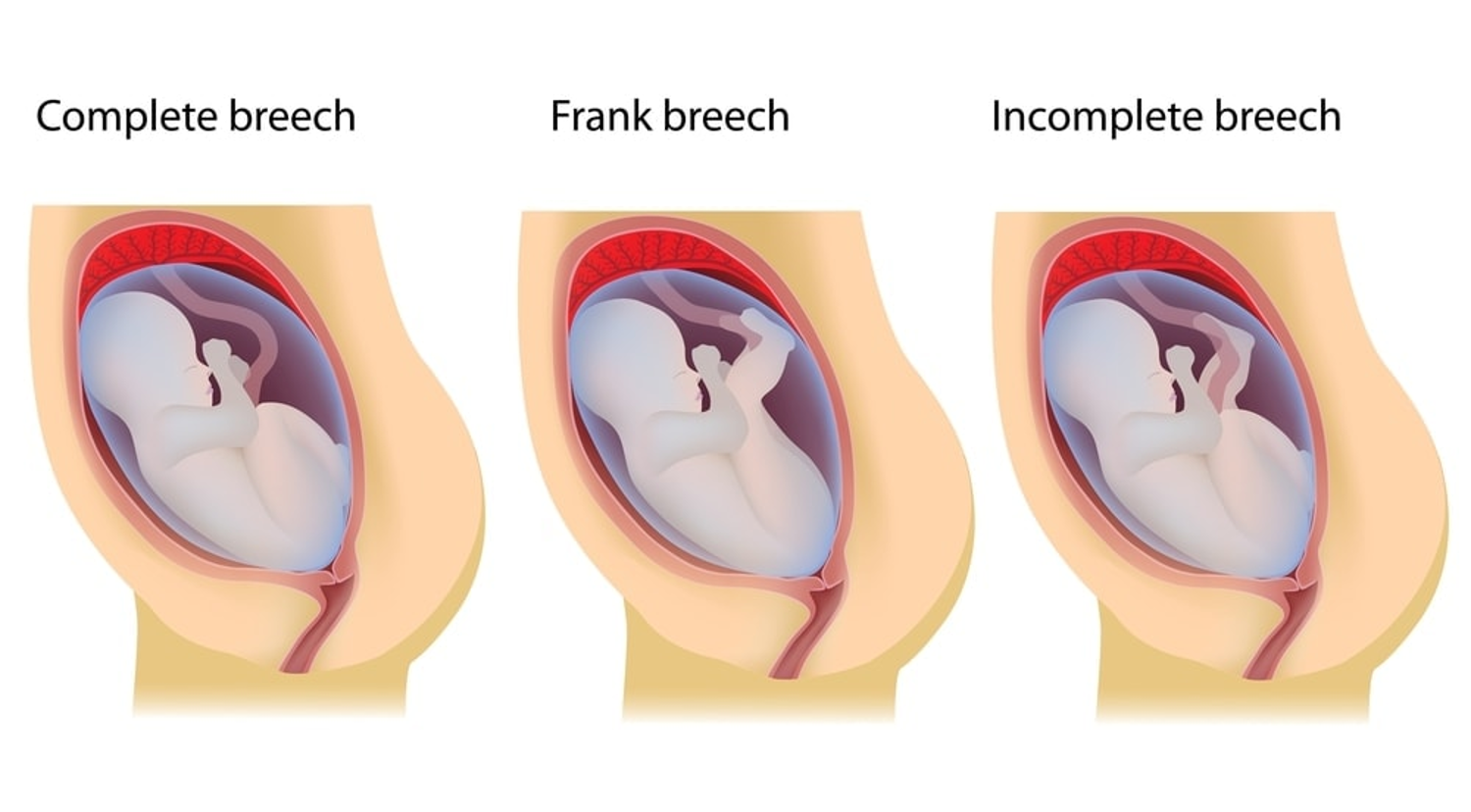
What does this refer to
where one or both feet are presenting.
Footling breech
What does this refer to
Surgical procedure by which one or more babies are delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen
(Cesarean section) C-section
What does this refer to
The most common indications (in order of frequency)
Labor dystocia
Abnormal or indeterminate (formerly, non-reassuring) fetal heart rate tracing
Fetal malpresentation
Multiple gestation
Suspected fetal macrosomia
Distress in the mother is also a consideration of vaginal v c-section delivery
C-section
What does this refer to
Also called a cervical insufficiency
Occurs when weak cervical tissue causes or contributes to premature birth or the loss of an otherwise healthy pregnancy
Incompetent cervix
What does this refer to
Difficult birth
Caused by
Large or awkwardly positioned fetus
Smallness of the maternal pelvis
Failure of the uterus and cervix to contract and expand normally
Dystocia
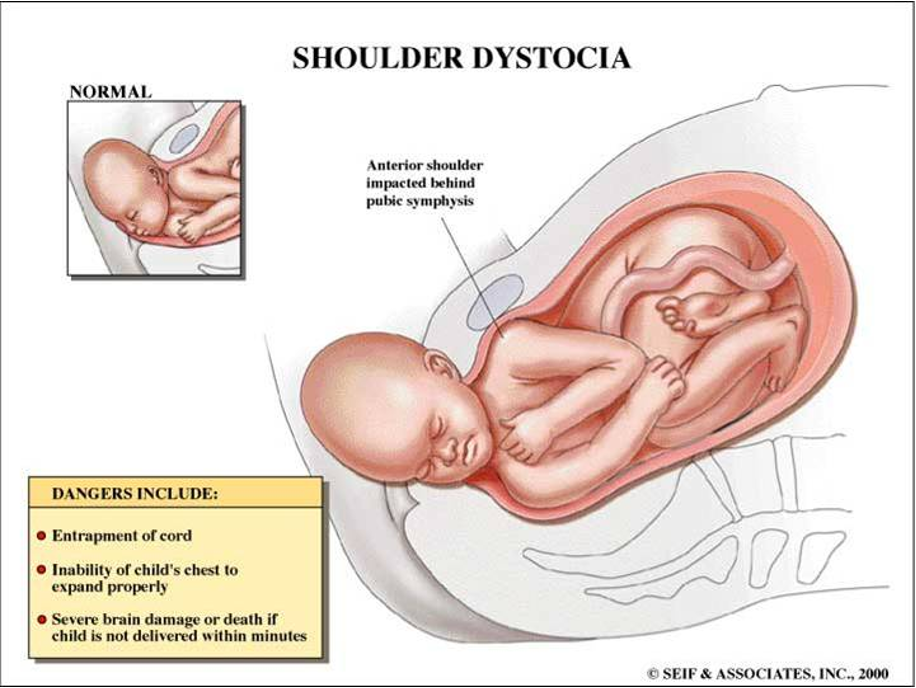
What does this refer to
A 25-year-old primigravida is pregnant with twins at 11 weeks of gestation.
She is experiencing daily nausea and vomiting of moderate intensity that is worse in the morning.
She has tried nonpharmacologic therapies with limited success.
She has also tried drinking and eating small amounts at a time and staying away from odors that make her feel nauseous.
Labs reveal a hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis.
Hyperemesis gravidarum
What does this refer to
Beyond morning sickness
Nausea AND vomiting that
Can lead to dehydration
Can result in poor weight gain
Possible maternal and fetal risks
Hyperemesis Gravidarum
What does this refer to
Some degree of nausea without vomiting in 90% of pregnancies
MC in western countries and urban areas
Slightly MC in younger, primigravid women
Less common in American Indians and Eskimos
Decreased risks with older gestational age
Epidemiology Hyperemesis Gravidarum
What does this refer to
Elevated serum concentrations of estrogen and progesterone
Genetic and familial etiology
Etiology Hyperemesis Gravidarum
What does this refer to
Physical exam
Weight loss
>5% of pre-pregnancy weight
Signs of dehydration
Orthostatic hypotension
Tachycardia
Delayed capillary refill time
Dry mucous membranes
Decreased skin turgor
Physical exam Hyperemesis Gravidarum
What does this refer to
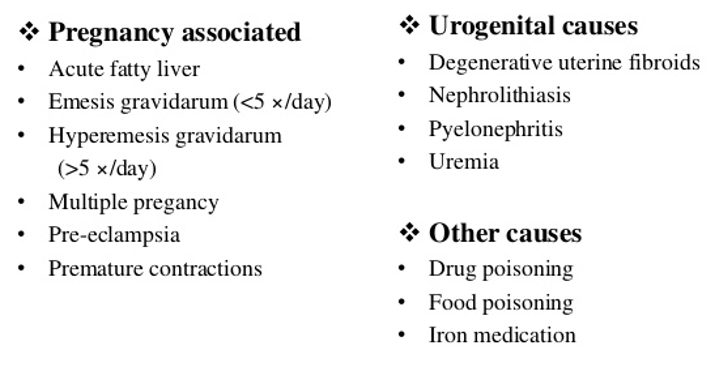
Differential diagnosis for Hyperemesis Gravidarum

What does this refer to
CBC w/ diff
↑ H/H
CMP
UA
High specific gravity (dehydration)
Ketonuria/+ serum ketones
+/- hypotension
2° hypovolemia
Workup Hyperemesis Gravidarum
What does this refer to
Behavioral
Lifestyle modifications
Eat small meals/snacks often
Eat as soon as hungry or even before feeling hungry
Aim for high protein/carbohydrate foods that are low in fat
Avoid spicy, greasy, or acidic foods
Drink cold, clear beverages and drink between meals rather than during meals
Avoid lying down right after eating
Medical
IVF for hypovolemia/dehydration
Up to 2L lactated ringers over 3-5 hours
Clinical intervention Hyperemesis Gravidarum
What does this refer to
Doxylamine-pyridoxine 1st line (H1 antagonist)
Dimenhydrinate, Meclizine, Diphenhydramine
if doxylamine-pyridoxine ineffective
Acid reducing agents
Antacids containing aluminum of calcium
Clinical pharmacotherapeutics Hyperemesis Gravidarum
What does this refer to
Most cases resolve by end of 1st trimester
Some persist up to 22 weeks and even up to delivery
Low pregnancy weight gain
Neonate small for gestational age
Preterm delivery
5-minute APGAR < 7
Prognosis Hyperemesis Gravidarum
What does this refer to
A 24-year-old woman presents to the emergency room with 6 hours of severe left lower quadrant abdominal pain and some moderate vaginal bleeding.
She is sexually active with 1 male partner and uses condoms occasionally.
She has a history of pelvic inflammatory disease.
Her last period was 7 weeks ago.
A transvaginal ultrasound is performed and shows a mass in the left adnexa.
Ectopic Pregnancy
What does this refer to
Allows the conceptus to implant and mature outside the endometrial cavity
Results in death of the fetus
Ectopic Pregnancy
What does this refer to
1-2 % of all pregnancies
1/40 pregnancies
85-90% occur in multigravida women
In U.S. more common in all races other than Caucasians
Epidemiology Ectopic Pregnancy
What does this refer to
Implantation of the ovum outside of the uterine cavity
Fallopian tube MC location
Risk Factors
Previous ectopic greatest risk factor*
Hx of PID
IUD use
Previous abdominal or tubal surgery
Hx of tubal ligation
Advanced maternal age
Etiology Ectopic Pregnancy
What does this refer to
Classic triad
Amenorrhea followed by
Pain —> Unilateral pelvic/ Lower abdominal pain
Vaginal bleeding
Clinical history Ectopic Pregnancy
What does this refer to
Lower abdominal pain on palpation
Pelvic Exam
Adnexal mass
May or may not be palpable
Cervical motion tenderness
If ruptured
May have heavy vaginal bleeding
Clinical presentation Ectopic Pregnancy
What does this refer to
Severe abd pain
Left shoulder pain (Kehr sign)
Dizziness
N/V
Acute abd signs
Signs of shock
4 symptoms independently contributed to the diagnosis of tubal rupture
Diffuse abdominal pain
Vomiting during pain
Flashing pain
Pain > 30 mins
Clinical history Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy
What does this refer to
Ruptured ovarian cyst
Appendicitis
Spontaneous or threatened abortion
Ovarian torsion
Salpingitis
Urinary tract
Differential diagnosis Ectopic Pregnancy
What does this refer to
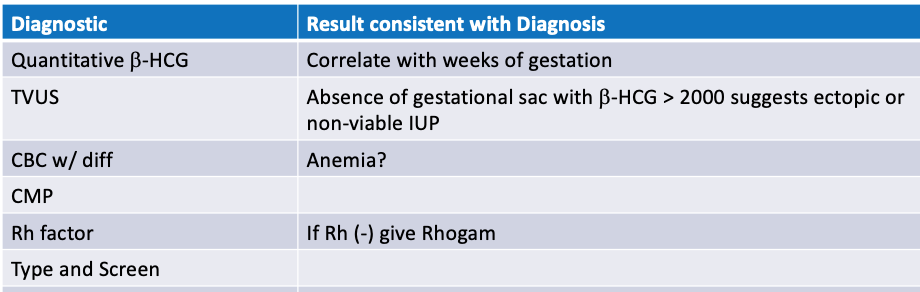
Workup Ectopic Pregnancy
What does this refer to
Methotrexate Indications
Early gestation
Gestational sac < 4cm
B-HCG < 5000
No FHT
Compliant F/U (serial B-hCG )
Must be immunocompetent
Alternative tx
Laparoscopic salpingostomy if patient does not meet criteria for medical management OR
Salpingectomy
Rhogam if Rh negative
Treatment Stable Unruptured Ectopic Pregnancy
What does this refer to
IVF
Laparoscopic Salpingectomy —> rupture
May need procedure to repair reproductive organs
Rhogam if Rh Neg
Treatment Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy (Unstable)
What does this refer to
Recurrent ectopic pregnancy (15%)
Infertility (11-62%)
Death (31/100,00)
Usually due to severe hemorrhage from intraperitoneal bleeding
Complications/prognosis Ectopic Pregnancy
What does this refer to
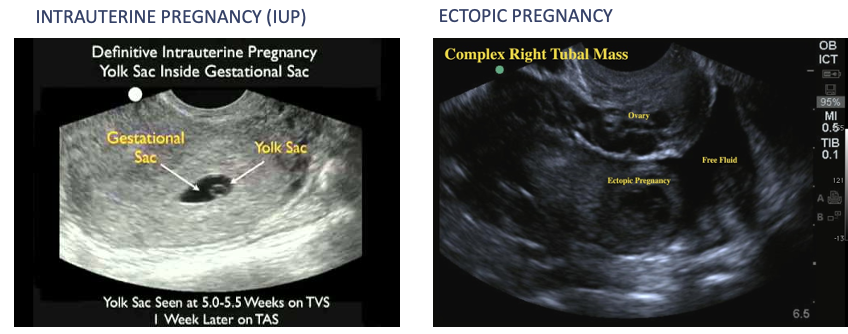
Workup – imaging Intrauterine vs Ectopic Pregnancy
What does this refer to
Intentional termination of pregnancy
In 1973 Roe v Wade – Supreme court ruled in favor of an unwed pregnant woman who sought and was denied an abortion. It was determined that this was unconstitutional.
In 2022 Roe v Wade was overturned by the Supreme court
This decision dismantled 50 years of legal protection and paved the way for individual states to curtail or outright ban abortion rights.
Induced Abortion
What does this refer to
Stopped slide 59
What does this refer to
What does this refer to
What does this refer to
What does this refer to
What does this refer to
What does this refer to
What does this refer to
What does this refer to
What does this refer to
What does this refer to
What does this refer to
What does this refer to
What does this refer to