Overview of the Human Reproductive System
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Gonads
Reproductive structures responsible for producing gametes.
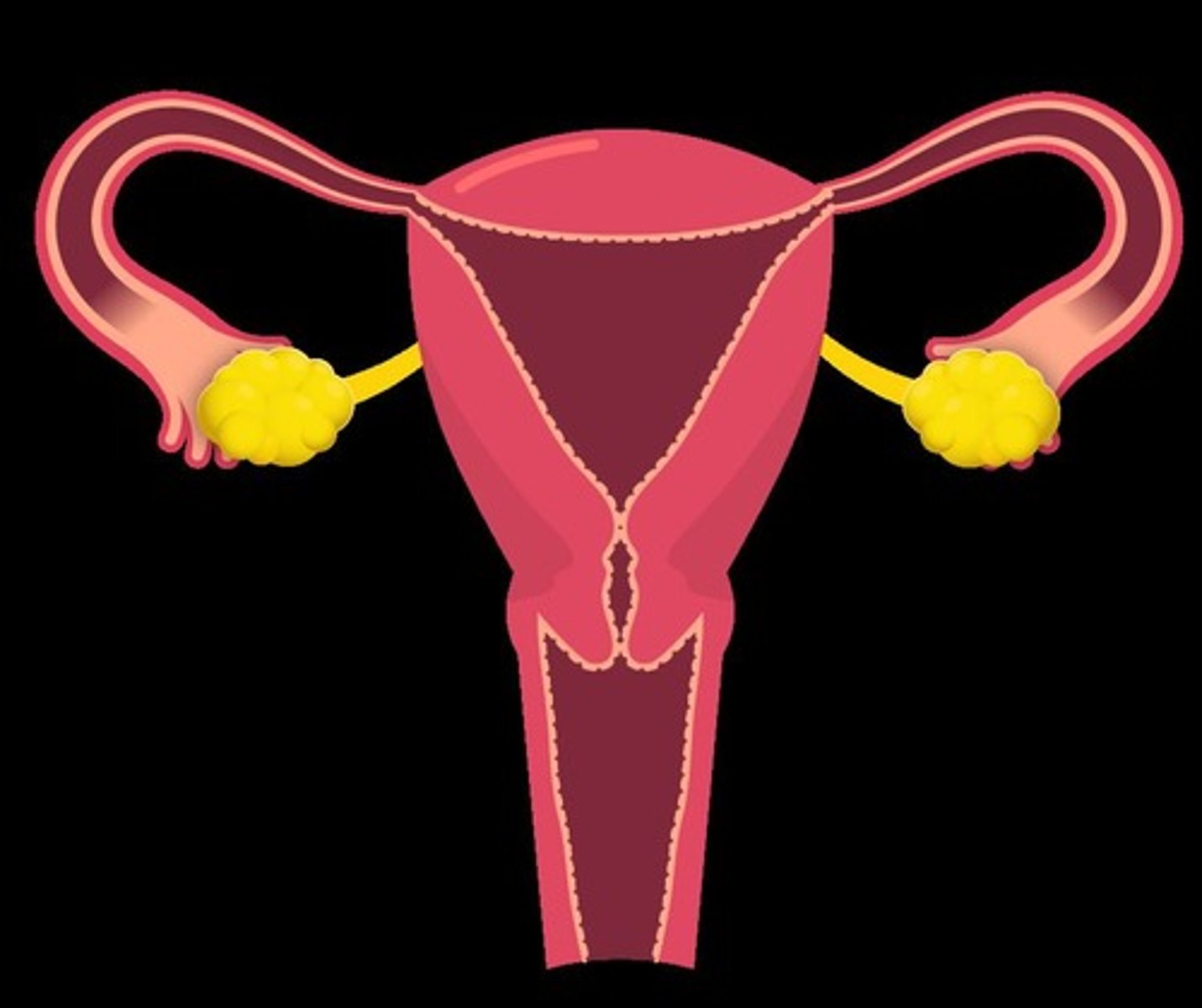
Ovary
Produces eggs (ova). Females have two ovaries.
Testis
Site of sperm and male sex hormone production enclosed within the scrotum for temperature regulation.
Somatic cell
Diploid, non-reproductive cells (E.g., muscle cells, skin cells, nerve cells).
Germ cell
Diploid cells of embryonic origin and gives rise to gametes via meiosis (E.g., spermatogonium, oogonium).
Gamete
Haploid sex cells (E.g., egg and sperm).
Viviparity
Birth to live young that receive nutrients directly from the mother's body.

Oviparity
Fertilized eggs get laid then hatch later.

Ovoviviparity
Internally fertilized eggs hatch and give birth to live young who continue to receive nutrients from the yolk of the egg.
Oviduct (Fallopian/Uterine Tube)
Responsible for moving the eggs from the ovary to the uterus; site of fertilization.
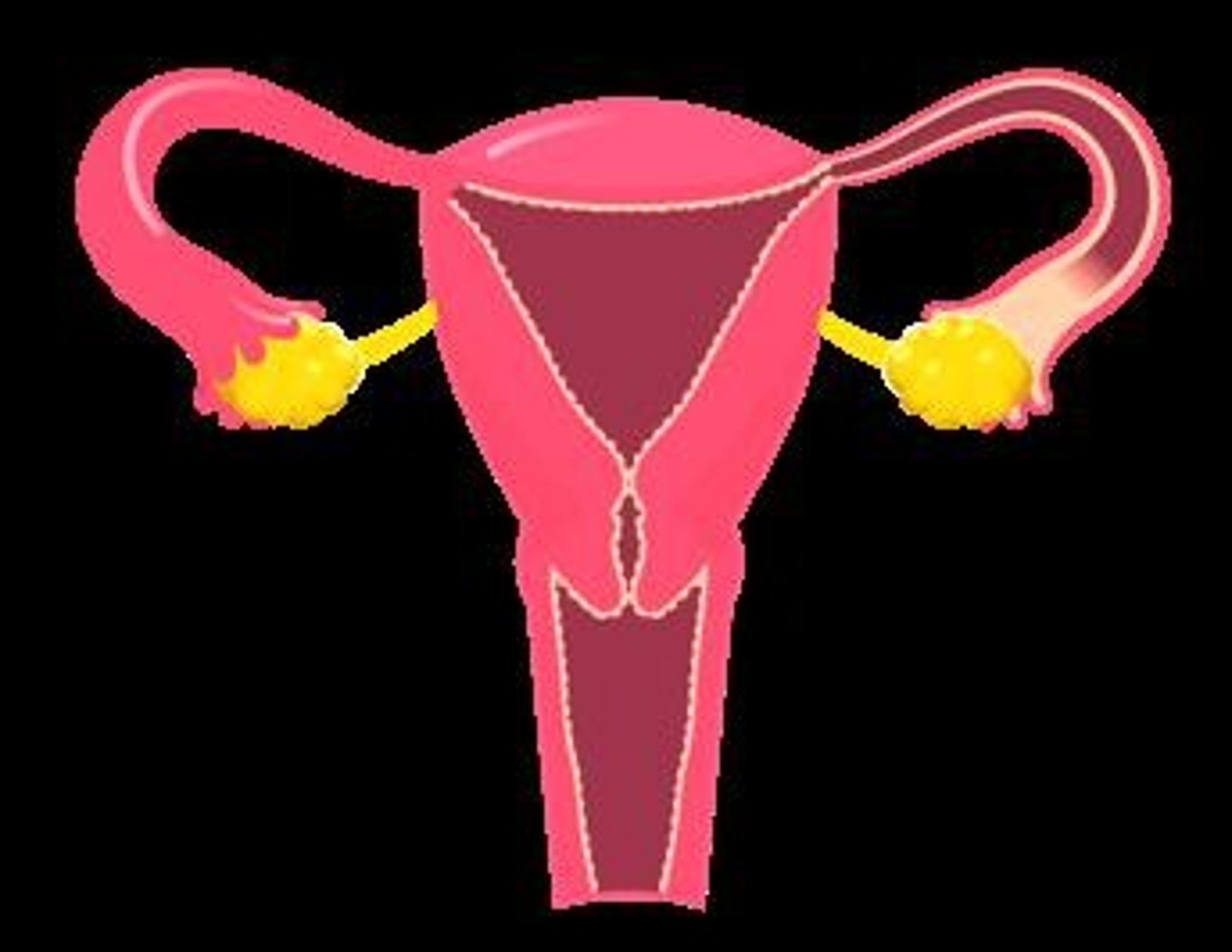
Uterus
Muscular chamber in which the embryo develops until birth.
Cervix
Connects the vagina to the uterus.
Vagina
Muscular canal that serves as a birth canal during delivery.
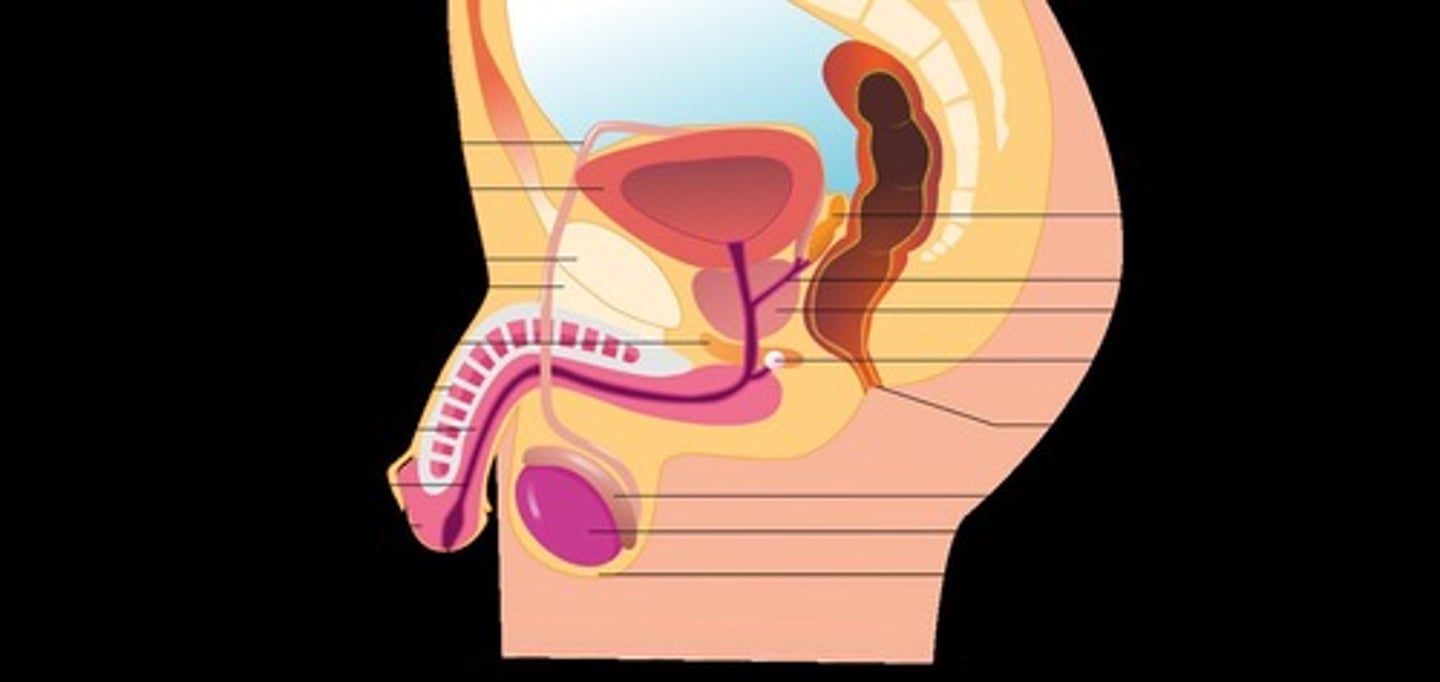
Sertoli cells
Stimulated by FSH and surround and nurture the sperm.
Interstitial cells (Leydig cells)
Secrete male hormones (E.g., testosterone and androgens) in the presence of LH.
Epididymis
Coiled tube attached to each testicle that serves as the site of final sperm maturation and storage.
Vas deferens
Transfers sperm from each epididymis to the urethra.
Seminal vesicles
Excrete fluid into the vas deferens upon ejaculation.
Penis
Transports semen into vagina.
Zygote
Fertilized egg.
Morula
A solid ball of cells resulting from the division of a zygote.
Blastocyst
A hollow ball of cells that implants in the uterus.
Acrosome
Lysosome-like organelle that penetrates the egg.
Pro-nucleus
Haploid (23 chromosomes) nucleus of the sperm or egg.
Mid-piece
Plethora of mitochondria for energy.
Tail
Flagellum that produces motion.
Oogenesis
The process of egg formation in females.
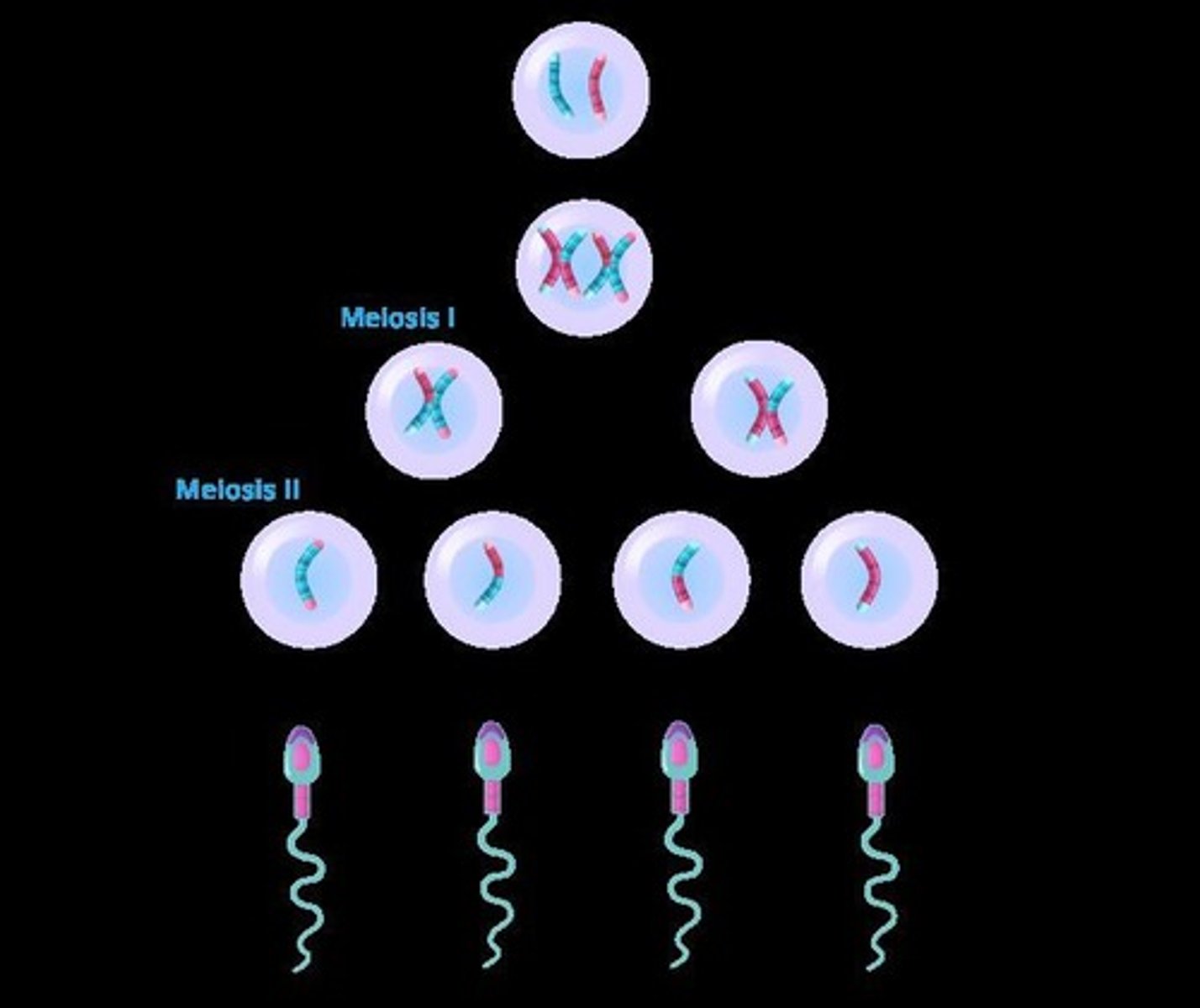
Spermatogenesis
The process of sperm formation in males.
Primary oocytes
Oogonia that have begun meiosis but stopped in prophase I, remaining until puberty.
Primordial follicle
Structure formed when primary oocytes are surrounded by a single layer of granulosa cells.
Primary follicles
Formed from primordial follicles when granulosa cells enlarge and increase in number.
Secondary follicles
Formed when fluid-filled vesicles develop and theca cells arise on the outside of the follicle.
Mature follicles
Formed when vesicles create a single antrum.
Follicular phase
The stage of the menstrual cycle involving the development of the egg and secretion of estrogen from the follicle.
Ovulation
The midcycle release of the egg, triggered by a surge of LH.
Luteal phase
The stage following ovulation characterized by secretion of estrogen and progesterone from the corpus luteum.
Secondary oocyte
The cell that results from the completion of meiosis I just before ovulation.
Meiosis II completion
Occurs only if the secondary oocyte is fertilized by a sperm cell.
Corpus luteum
The structure formed from the remaining follicle after ovulation, secreting hormones if the egg is fertilized.
Corpus albicans
The scar formed when the corpus luteum degenerates if fertilization does not occur.
Female hormonal contraception
A method that involves artificially spiking estrogen and progesterone levels to prevent ovulation and implantation.
GnRH
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone released by the hypothalamus to trigger FSH and LH release.
FSH
Follicle-stimulating hormone that stimulates Sertoli cells to promote sperm development.
LH
Luteinizing hormone that stimulates Leydig cells to release testosterone.
hCG
Human chorionic gonadotropin secreted by the placenta to maintain the corpus luteum after implantation.
Endometrium
The uterine lining that must remain intact for a successful pregnancy.
Testosterone
A hormone released by Leydig cells that is essential for male reproductive development.