OROFACIAL W2 Teeth fx, Tongue, Salivary Glands
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Crown and root of a tooth is joined at ?
CEJ - cementoenamel junction
Define Anatomical crown in comparison to Clincal crown
Anatomical crown is the whole crown of tooth that is covered by enamel regardless of whether it is erupted.
Clinical crown is the portion of the crown that is visible above gingiva
Division of root into 2 segments, 3 segments?
2 → bifurfaction
3 → trifurcation
The alveolus is also known as…
bony socket in which the tooth fits
What type of characteristics of the root offers more resistsance to displacement? Why?
long length and wide because more surface area for peridontal ligaments to attach to tooth.
Triangular shape + root lenght = high resistance to displacement
What are the 4 types of tooth tissue?
Enamel, Dentin, Cementum, Dental pulp
The hardest tissue in the human body is?
Enamel because its densely mineralized.
96% inorganic matter
What happens to our enamel as we age?
Enamel becomes thinner allowing dentin to shine through and teeth look darker.
Define dentin
Main portion of the tooth (body of tooth) composed of hard, dense, calcified tissue that is underneath enamel and cementum.
Softer than enamel but harder than cementum and bone.
Yellow in colour
Has elasticity
70% inorganic matter
Which tooth tissue is capable of repairing itself?
Dentin
What is secondary dentin?
Type of dentin that grows very slowly and it initiated by normal wear down of dentin
What is reparative dentin?
The dentin that is laid down in response to caries or trauma
What is the main function of Cementum?
provide a medium for attachment of the tooth to the alveolar bone (by PDL)
45% inorganic, 55% organic
2 types: cellular (1/3) and acellular (2/3)
What makes up the dentinocemental junction (DCJ)?
union of cementum and dentin
What is the pulp of the tooth? What are its 2 divisions?
The pulp is housed in the center of the tooth and is surrounded by dentin.
Composed of blood vessels, lymph vessels, connective tissue, nerve tissue, and ODONTOBLASTS (dentin forming cells)
Divisions:
Pulp chamber - coronal portion
Pulp canals - root portion
Pulp cavity = pulp chamber + canals
What is the chief function of odontoblasts?
Lay down primary, secondary, and reparative dentin
What kind of sensory information can be relayed from the nerves in the pulp?
Pain (not cold or heat, not pressure)
Which type of dentition is the longest?
Canines - best anchored because of its long root (maxillary canine has the longest root in the entire dentition)
How many cusps on a premolar?
2 or 3
How many cusps on a molar?
4 or 5
What characteristics act as landmarks on the crowns of teeth? (8)
Lobes (Facial and Lingual)
Lines aka developmental grooves formed when lobes fuse together
Tubercles - small elevations of enamel
Fossa - depression/concavity on a tooth
Cingulum - Lingual lobe of maxillar anterior teeth.
Pits - small pinplint holes in the enamel that occur along the lines or fossa
Cusps - mound on crown of tooth
Ridge - elevated portion of a tooth that runs in a line (on a cusp)
What are marginal ridges?
Rounded borders of enamel forming the mesial and distal shoulders of occlusal surfaces on posterior teeth and lingual surface of anterior teeth.
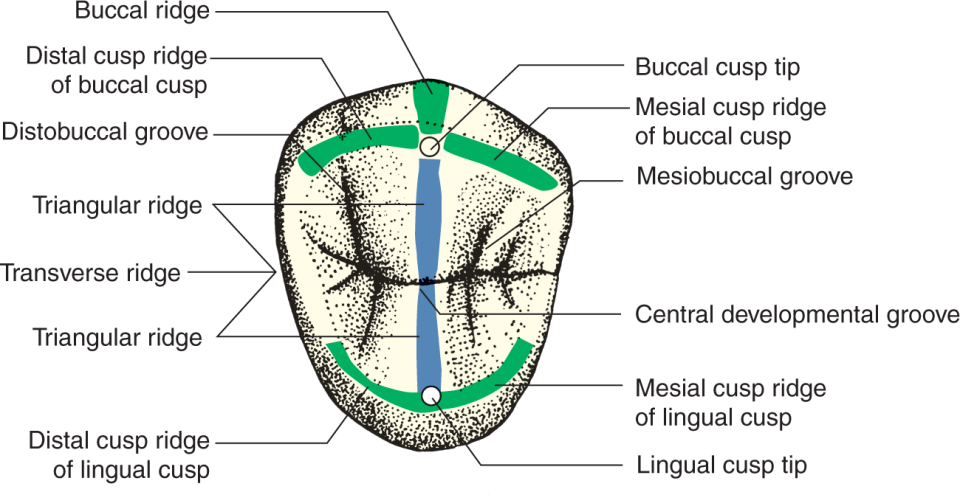
Compare and contrast the ridges on Posterior teeth
Triangular Ridge
Main ridge on each cusp that run from tip of the cusp to central part of occlusal surface
Transverse Ridge
Union of 2 triangular ridges, buccal and lingual, that CROSS the occlusal surface
The lingual groove of the anterior tooth separates…
4th lobe from labial lobes
The lingual fossa of the anterior tooth separates…
lingual lobe from the other 3 lobes
What are the 2 types of muscles of the tongue?
Intrinsic Muscle - within the tongue
Extrinsic Muscle - attached tongue to other structures
What type of epithelium is found on the tongue?
Stratified squamous epithelium
Keratinized/Parakeratinized on the dosal surface)
What are the 4 types of papillae that are scattered on the dorsum of the tongue?
Circumvallate (Vallate)
Fungiform
Filiform
Foliate
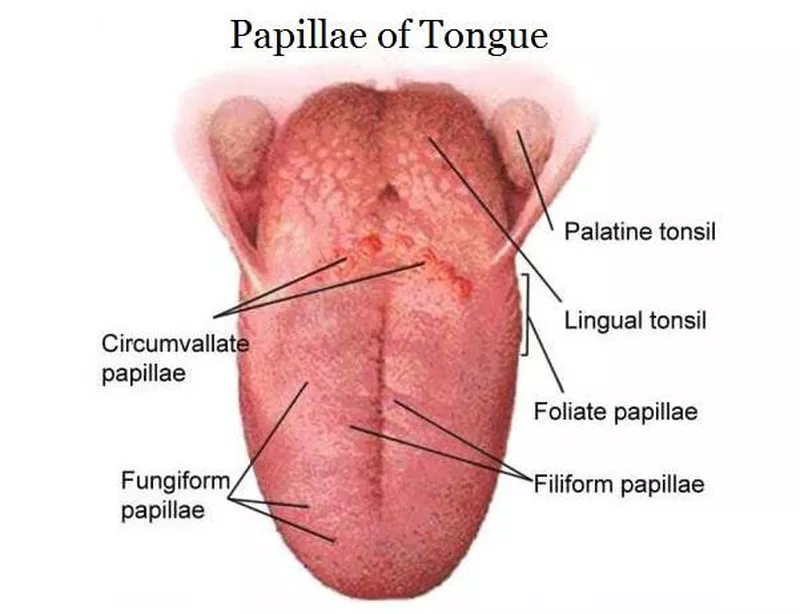
Describe Vallate (Circumvallete) papillae
V-shaped row of circular dome-shaped elevations that divides the tongue into 1/3rd posterior and 2/3rd anterior portions.
Consists of many taste buds
Small salivary glands lie beneath vallate papillae called glands of Von Ebner
Describe Fungiform papillae
Tiny round, red, reaised, spots found on the anterior 2/3rds of the tongue.
Taste buds are in these papillae
only on the dorsal side of tongue
Describe Filiform papillae
Slender, threadlike, pointed projections on the anterior 2/3rds (middle-back) of the tongue that are responsible for TACTILE SENSATION.
No taste buds
What is glossitis?
Glossitis is the inflammation of the tongue, characterized by swelling, redness, and changes in the tongue's surface texture (Very smooth)
caused by vitamine deficiency
“loss of epithelia” = smooth tongue surface
Describe Foliate papillae
reddish leaf-like folds of tissue found on the posterior 1/3rds of the tongue on the lateral sides.
in humans, foliate papillae contain fewer taste buds and they are not very well developed.
What area does oral cancer begin?
Foliate papillae
The lingual tonsils are located …
just behind the circumvallate papillae at the base of the tongue.
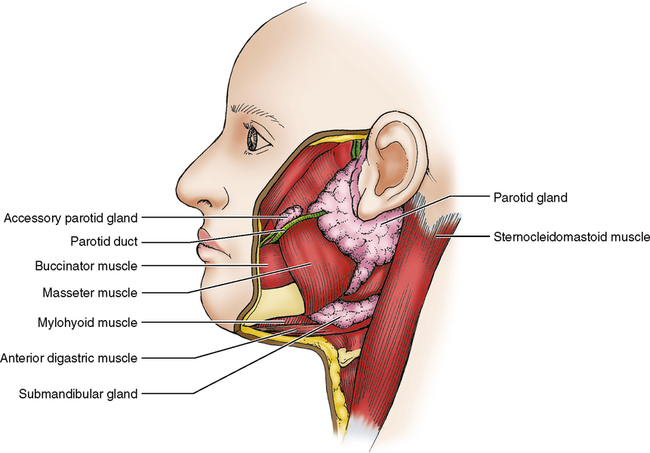
What are the 3 pairs of salivary glands?
Parotid
Submandibular
Sublingual
Describe Parotid glands, its location and the secretions from this gland.
Parotid glands are grape-like clusters of cells that secretes into tubes leading to the oral cavity. Largest salivary gland of the 3.
Location:
the surface of the masseter muscle, behind the ramus of the mandible.
Secretion:
thin, watery serous fluid
produces 25% of total resting salivary volume
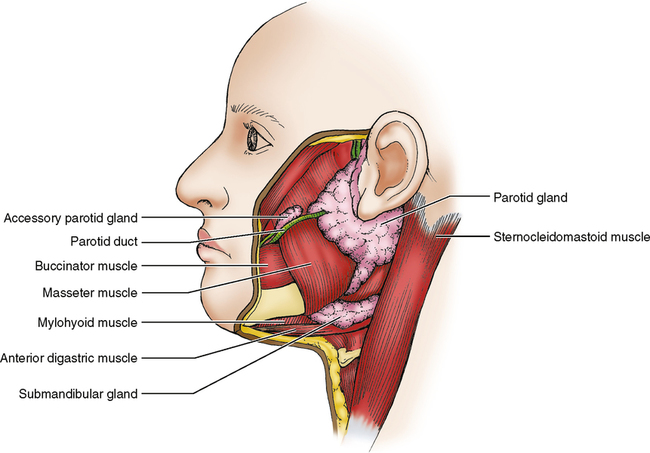
Where do the parotid gland ducts open into the oral cavity?
maxillary 2nd molars. Aka Stenson’s ducts
Describe Submandibular salivary glands, its location and the secretions from this gland.
A mixed salivary gland that produces 60-65% of resting saliva. → aka. submaxillary gland
Location:
below the body of the mandible and wraps around the mylohyoid muscle in the neck.
Secretions:
Serous and mucous secretions (thicker and stickier)
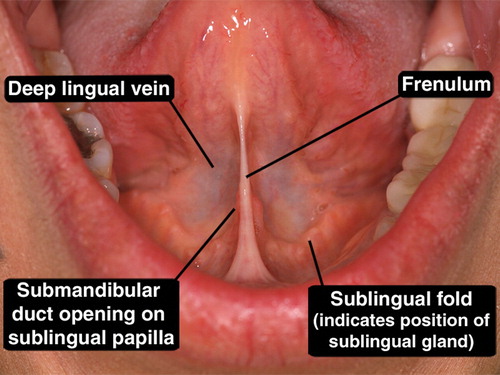
Where to the ducts of the submandibular gland open into the oral cavity?
Sublingual caruncles at the base of the lingual frenum (ventral side of tongue)
Describe Sublingual salivary glands, its location and the secretions from this gland.
Smallest salivary gland of the 3 producing 10% of saliva. Consists of mostly mucous cells with a few serous cells.
Location:
Anterior floor of the mouth next to mandibular canines
Secretion:
Thickest secretions due to the mucous cells
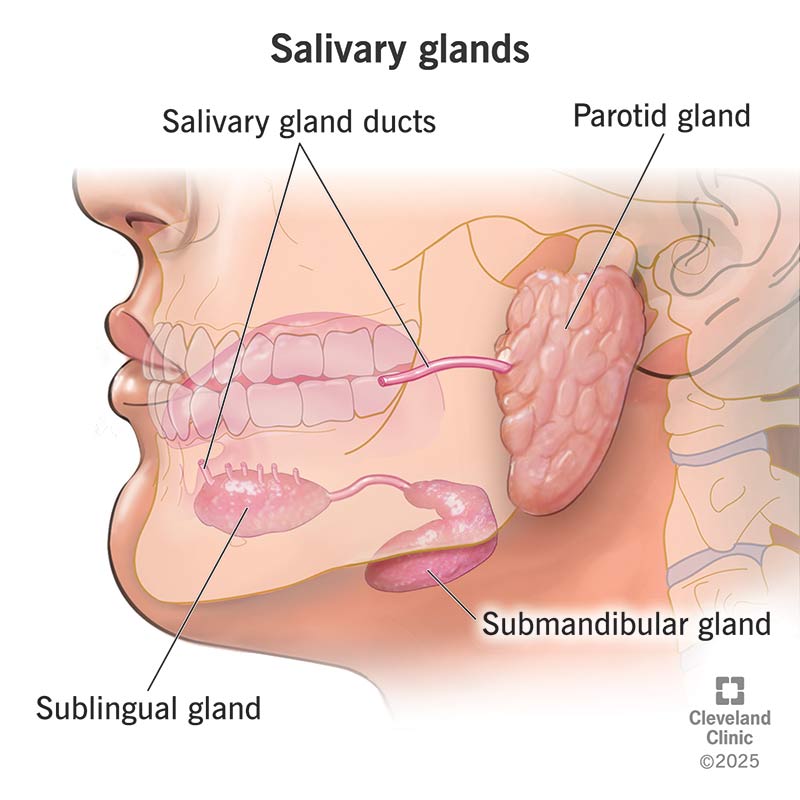
Where do the ducts of the Sublingual gland open into the oral cavity?
Opens into the submandibular duct connecting to the sublingual fold (near canines)
one major duct and several small ducts open in a line along the sublingual fold