Microbiology Chapter 2
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
168 Terms
What is the nucleus of an atom composed of?
Protons and neutrons
What substance makes up most of the mass in living organisms?
Water
Matter
anything that takes up space and has mass
Atom
the smallest chemical unit of matter
Who proposed the model in which electrons orbit a central nucleus?
Niels H. D. Bohr
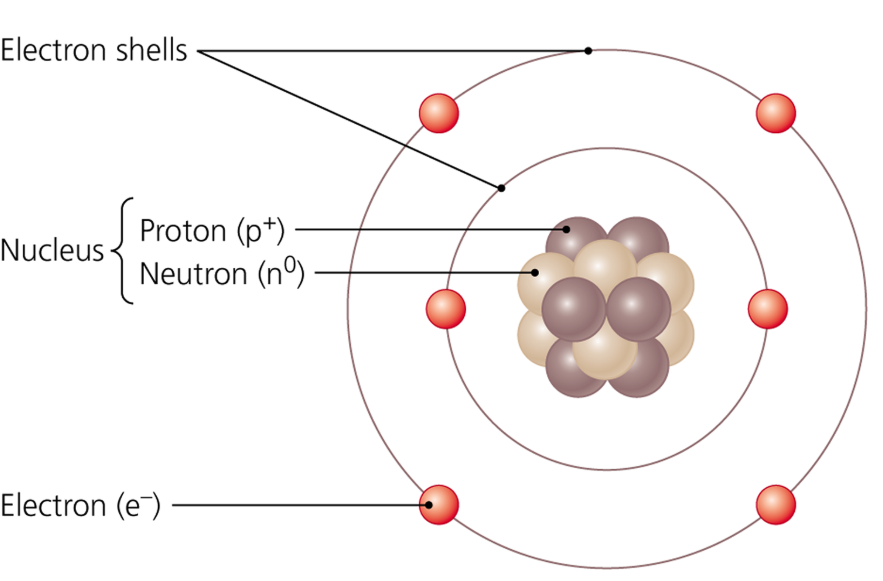
Electrons
negatively charged subatomic particles circling a nucleus
Nucleus
structure containing neutrons and protons
Neutrons
Uncharged particles
Protons
positively charged particles
Example of Bohr Model
Electron shells on outside with electrons on them, nucleus contains protons & neutrons
Element
composed of a single type of atom
Atomic number
Equal to the number of protons in the nucleus
Atomic Mass (Atomic Weight)
Sum of masses of protons, neutrons, and electrons
True or false: the sum of protons and neutrons estimates the atomic mass of an atom
TRUE → because electrons are so miniscule
Hydrogen
Sym = H
Atomic Number = 1
Atomic Mass = 1
Significance = component of organic molecules & water; H+ released by acids
Boron
Sym = B
Atomic Number = 5
Atomic Mass = 11
Significance = essential for plant growth
Carbon
Sym = C
Atomic Number = 6
Atomic Mass = 12
Significance = backbone of organic molecules
Nitrogen
Sym = N
Atomic Number = 7
Atomic Mass = 14
Significance = component of amino acids, proteins, nucleic acids
Oxygen
Sym = O
Atomic Number = 8
Atomic Mass = 16
Significance = component of organic molecules & water; OH- released by bases; aerobic metabolism
Sodium (Natrium)
Sym = Na
Atomic Number = 11
Atomic Mass = 23
Significance = principal cation outside cells
Magnesium
Sym = Mg
Atomic Number = 12
Atomic Mass = 24
Significance = component of many energy-transferring enzymes
Silicon
Sym = Si
Atomic Number = 14
Atomic Mass = 28
Significance = component of cell wall of diatoms
Phosphorus
Sym = P
Atomic Number = 15
Atomic Mass = 31
Significance = component of nucleic acids & ATP
Sulfur
Sym = S
Atomic Number = 16
Atomic Mass = 32
Significance = component of proteins
Chlorine
Sym = Cl
Atomic Number = 17
Atomic Mass = 35
Significance = principal anion outside cells
Potassium
Sym = K
Atomic Number = 19
Atomic Mass = 39
Significance = principal cation inside cells; nerve impulses
Calcium
Sym = Ca
Atomic Number = 20
Atomic Mass = 40
Significance = intracellular signaling; muscle contraction
Maganese
Sym = Mn
Atomic Number = 25
Atomic Mass = 54
Significance = enzymes; intracellular antioxidant; photosynthesis
Iron
Sym = Fe
Atomic Number = 26
Atomic Mass = 54
Significance = energy transferring proteins; transports O2 in blood
Colbalt
Sym = Co
Atomic Number = 27
Atomic Mass = 59
Significance = Vitamin B12
Copper
Sym = Cu
Atomic Number = 29
Atomic Mass = 64
Significance = enzymes; photosynthesis
Zinc
Sym = Zn
Atomic Number = 30
Atomic Mass = 65
Significance = enzymes
Molybdenum
Sym = Mo
Atomic Number = 42
Atomic Mass = 96
Significance = enzymes
Iodine
Sym = I
Atomic Number = 53
Atomic Mass = 127
Significance = brown & red algae
Isotopes
Atoms of a given element that differ in the number of neutrons in their nuclei
What are the different types of isotopes?
stable isotopes
unstable isotopes (ex: carbon-14)
radioactive isotopes → release energy during radioactive decay
What is the smallest chemical unit of matter?
atom
What atomic particles orbit around the nucleus?
electrons
The number of protons identifies an element. What characteristic tells us how many protons an atom has?
atomic number
Isotopes are forms of atoms that differ from one another by having varying numbers of what particle?
neutrons
What determines an atom’s chemical behavior?
electrons
because only they interact
What does an electron shell depict?
the PROBABLE locations of electrons at a given time
True or false: electrons occupy electron shells
TRUE
Valence electrons
electrons in the outermost shell that interact with other atoms
What is the max number of electrons for each shell?
First shell = 2 electrons
Second shell = 8 electrons
Third shell = 18 electrons
Which elements only have 1 shell?
Hydrogen & Helium
What has the same number of valence electrons in the outer shell?
Groups (families)
moving ACROSS the periodic table left to right
Electrons zip around the nucleus at about 5 million miles
per hour. Why don’t they fly off?
Electronegativity. The nucleus is positive and electrons are negative. Opposites attract.
The positively charged particles in the nucleus of an atom are called
Protons
The atomic number of an element is
the number of protons
The atomic mass of an atom is the sum of the masses of the
protons, neutrons, and electrons
The element carbon has 6 protons and 6 neutrons in its nucleus. Which of the following represents the carbon-14 isotope?
6 protons, 8 neutrons
Valence
combining capacity of an atom
General rules of valence
positive if atom has electrons to give up
negative if atom has spaces to fill
stable when outer electron shells contain eight electrons
Chemical bonds
atoms combine by sharing or transferring valence electrons
Molecule
two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds
Compound
a molecule composed of more than one element
An atom with a total of six electrons would have how many electrons in its inner shell?
Two
An atom with a total of six electrons would have how many valence electrons?
four
What do you call a molecule that contains atoms of two or more different elements?
a compound
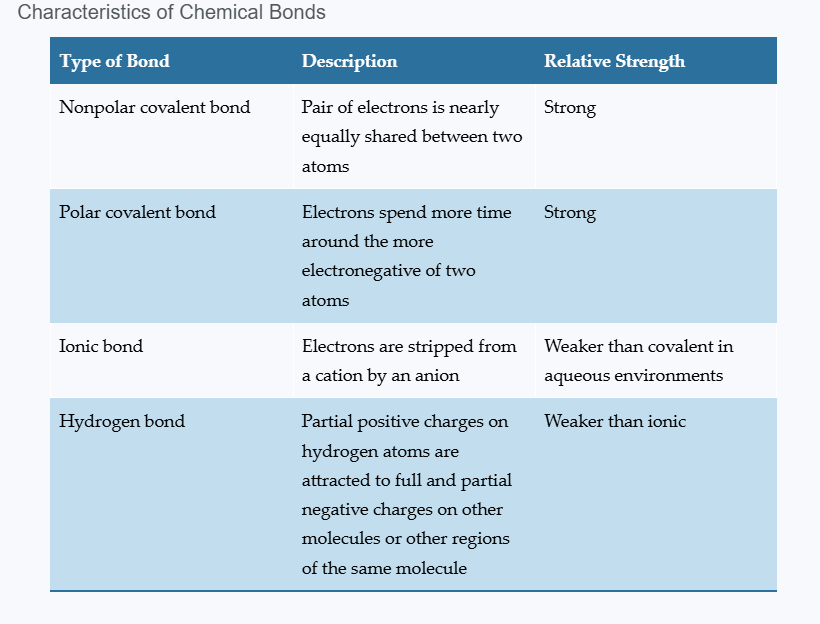
Covalent bond
sharing of a pair of electrons by two atoms
Electronegativity
attraction of an atom for electrons
more electronegative = greater pull from nucleus on electrons
higher electronegativity = right side of periodic table
lower electronegativity = bottom of periodic table bc distance between nucleus & valence shell is larger
Nonpolar covalent bond
shared electrons spend equal amounts of time around each nucleus
atoms with similar electronegativities
no poles
True or false: carbon atoms form two nonpolar covalent bonds with other atoms
FALSE - they form four
What atoms do organic compounds contain?
carbon and hydrogen
Polar covalent bonds
unequal sharing of electrons due to significantly different electronegativities
most important polar covalent bonds involve hydrogen
allows for hydrogen bonding
True or false: in polar covalent bonds, the more electronegative atom will have a partial negative, whereas the less electronegative atom will have a partial positive.
TRUE
Ionic bonds
occur when two atoms with vastly different electronegativities come together
electrons are transferred from one atom to another; NOT shared
What types of charges can atoms have (ionic bonds)?
Cation - positive
Anion - negative
they attract each other and form ionic bonds
What do ionic bonds typically form?
crystalline ionic compounds - known as salts
How does the salt crystal dissolve?
When water surrounds an ionic bond, the partial charges are attracted to the water so the ions are no longer attracted to each other.
This forms electrolytes
What is the name for an atom that has a full positive or negative charge?
ion
Ionic bonds involve electrons being donated from one atom to another. How are electrons treated in covalent bonds?
the electrons are shared
Hydrogen Bonds
electrical attraction between partially charged H+ and full or partial negative charge on same or different molecule
Can be bound to Fluorine, Oxygen, Nitrogen
weaker than covalent bonds but essential for life
help stabilize 3-D shapes of large molecules (DNA)
Summary of chemical bonds
How do atoms interact with one another to form chemical bonds?
they share or transfer valence electrons
The more electronegative an atom, the greater the pull its nucleus exerts on
electrons
What drives bonding between atoms?
completing electron valence shells
Which type of chemical bond forms between a cation and an anion?
ionic bond
Chlorine and potassium atoms form ionic bonds, carbon
atoms form nonpolar covalent bonds with nitrogen atoms,
and oxygen forms polar covalent bonds with phosphorus.
Explain why these bonds are the types they are
The Cl and K form an ionic bond due to high electronegativity difference, C and N form a covalent bond due to the least electronegativity difference, and O and P form polar covalent due to intermediate electronegativity difference.
True or false: the numbers and types of atoms never change in a chemical reaction.
TRUE → atoms are neither created or destroyed
Biochemistry involves the chemical reactions of
living things
Chemical reactions
the making or breaking of chemical bonds
Reactants
the atoms, ions, or molecules that exist at the beginning of a reaction
Products
the atoms, ions, or molecules left after the reaction is complete
Synthesis Reactions
involve the formation of larger, more complex molecules
require energy
Dehydration synthesis
two smaller molecules are joined by a covalent bond and a water molecule is formed
anabolic / endothermic
Endothermic reaction
reactions that require energy
Anabolism
all synthesis reactions in an organism
Decomposition Reactions
break bonds within larger molecules to form smaller atoms, ions, and molecules
water is added
catabolic / exothermic
Exothermic reaction
reactions that release energy
Hydrolysis
a chemical reaction in which water is used to break down a compound into smaller molecules
Catabolism
all decomposition reactions in an organism
Exchange Reactions
involve breaking and forming covalent bonds
have endothermic & exothermic steps
involve atoms moving from one molecule to another
Metabolism
the sum of all chemical reactions in an organism
Dehydration synthesis is a chemical reaction that joins two molecules through the removal of a hydrogen atom from one and hydroxide from the other, forming a new bond. What molecule is always released during this kind of reaction?
Water
Some chemical reactions require energy in order to occur. What do you call those reactions?
Endothermic
Exchange reactions contain both endothermic and exothermic steps. What other chemical reaction in living things is endothermic?
synthesis reactions
Which equation illustrates a synthesis reaction?
6H2O + 6CO2 → C6H12O6 + 6O2