Unit 2 - Short-Term Decisions Cartes | Quizlet
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What are fixed costs?
Costs that remain constant (fixed) when changes occur to the volume of activity
Graph of fixed costs against the volume of activity
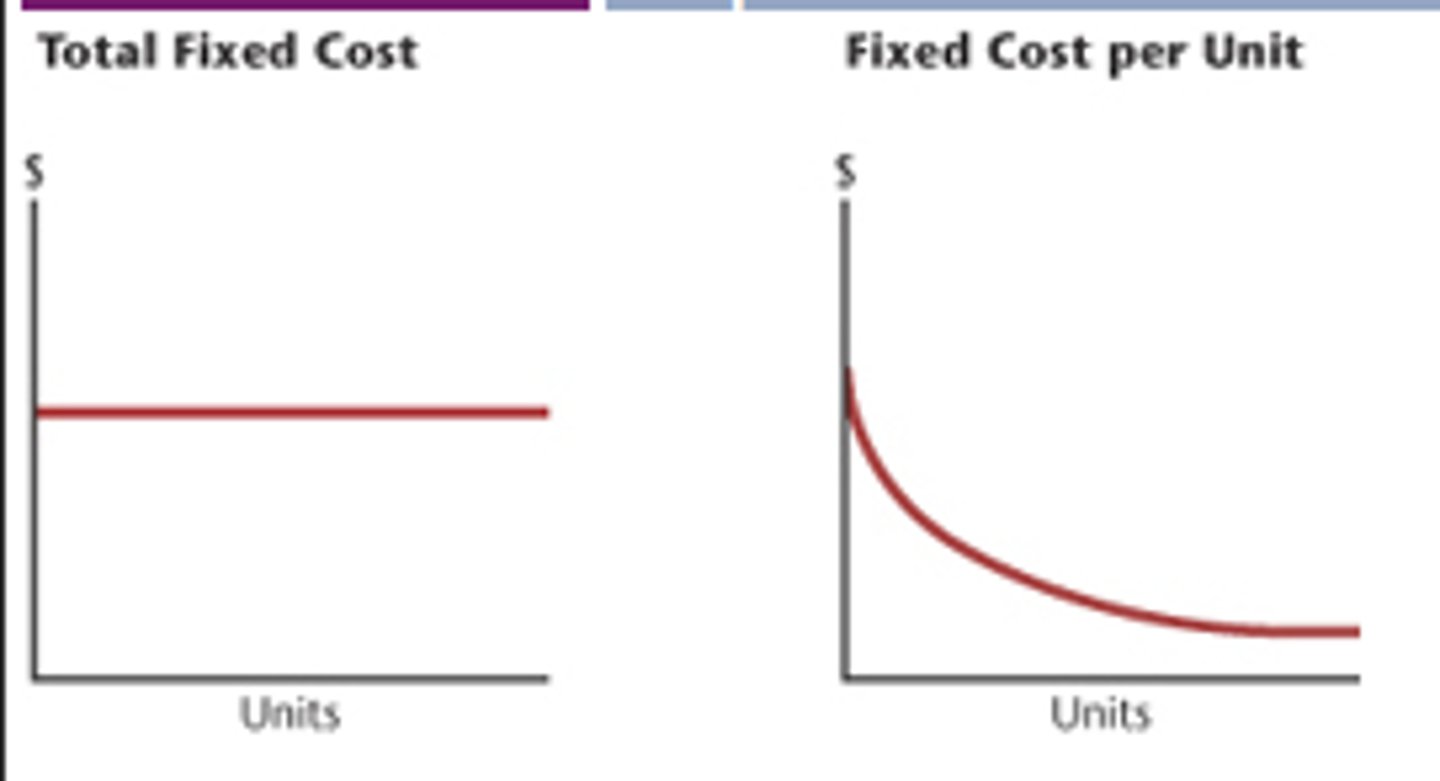
Examples of fixed costs
Rent, insurance, cleaning costs & staff salaries
What are variable costs?
Costs that vary according to the volume of activity (NOT by other circumstances)
Graph of variable costs against the volume of activity
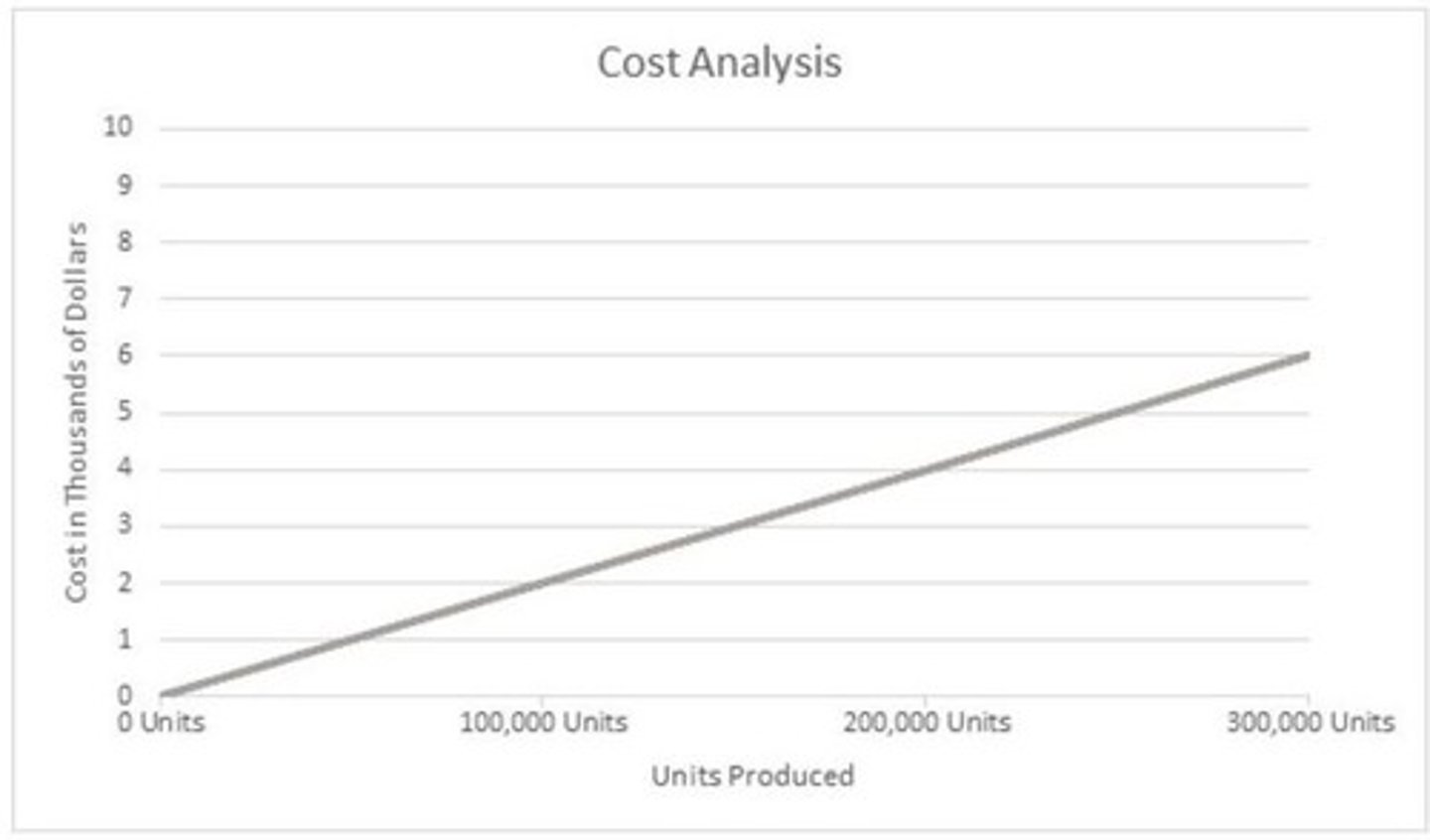
Examples of variable costs
Raw materials, shipping costs & advertising
An example of when fixed costs can be variable
When staff are paid based on their output
An example of when a fixed cost is affected by the volume of activity
When the volume of activity is so high, more space has to be rented, resulting in higher rent
What are semi-fixed (or semi-variable) costs?
When a particular cost is fixed & variable
Graph of semi-variable costs against the volume of activity
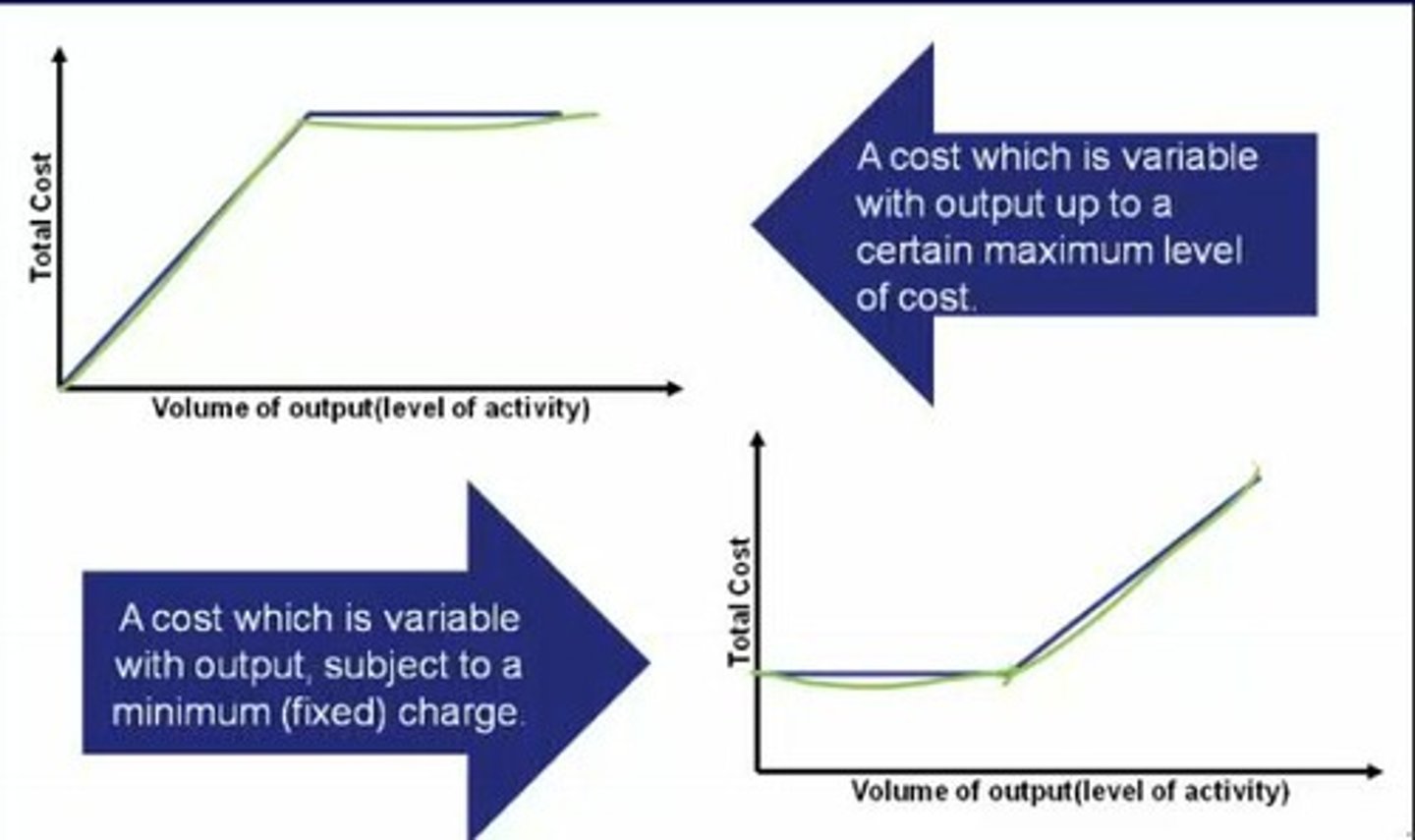
Examples of semi-fixed (or semi-variable costs)
Telephone charges (there is a fixed rental element, as well as depending on the amount of calls made)
How to analyse semi-fixed (or semi-variable costs) to find out the fixed & variable elements
Use the high-low method
How to use the high-low method
Take the highest & lowest semi-fixed (semi-variable) costs from the range of past quarterly data = New total cost - Old total cost, then the answer / Old cost (to find out the semi-fixed cost per unit)
What is the issue with using the high-low method?
It relies only on this range of information, not other factors
Graph of total cost against volume of activity
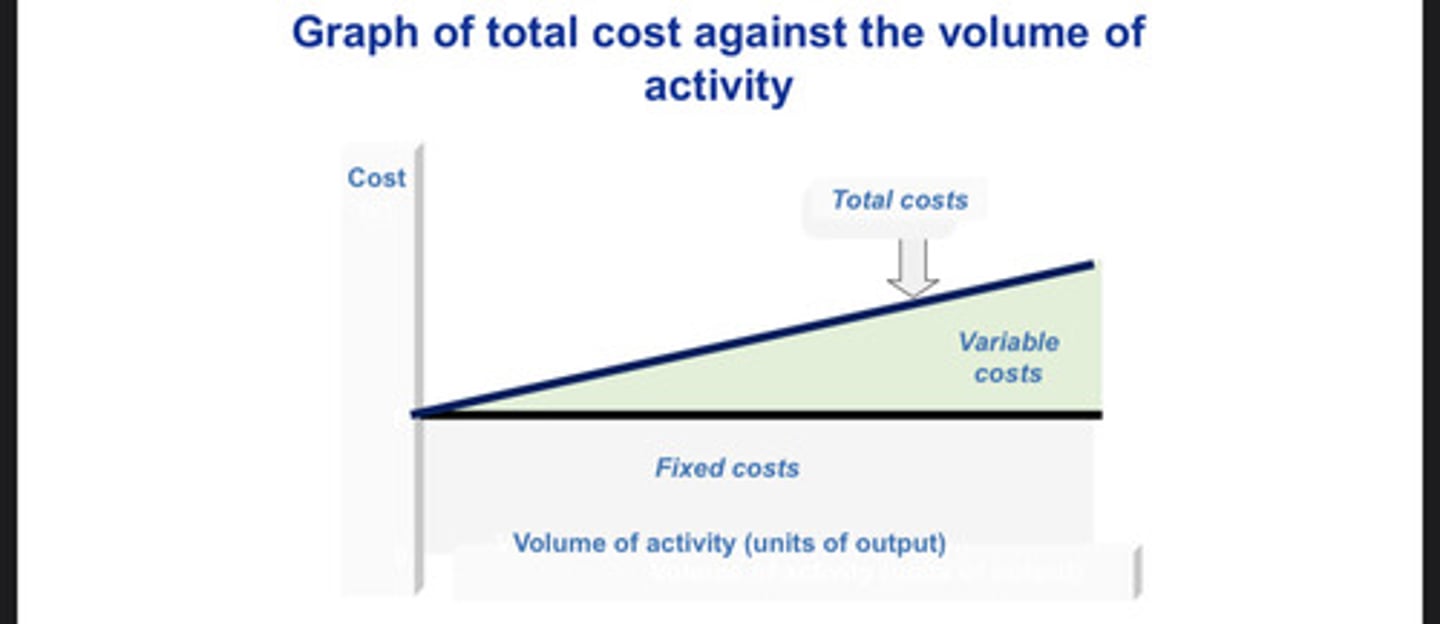
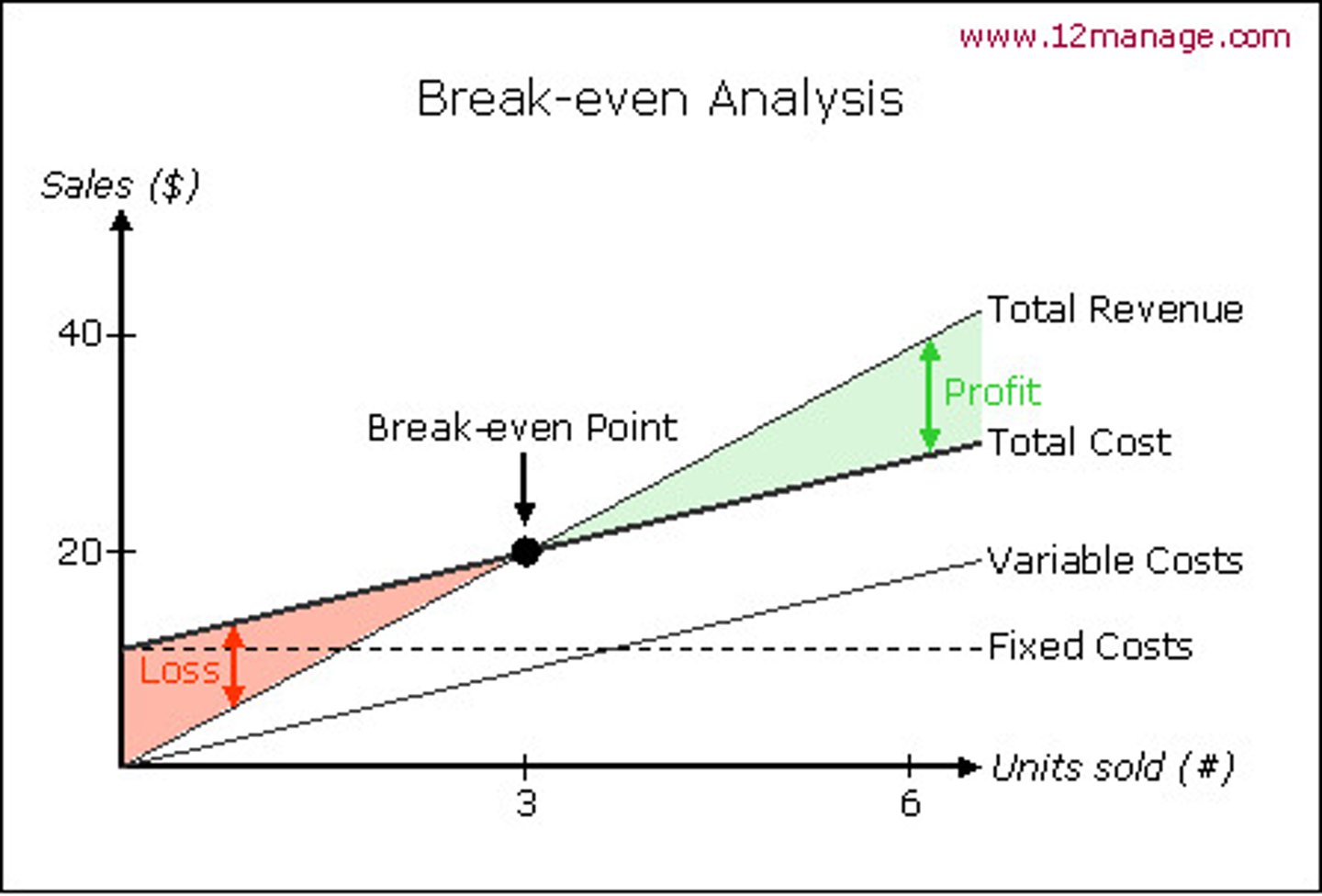
How does break-even (BE) analysis help? (1)
It can help find how many products would need to be sold, to see if this is realistic based on market research
How does break-even (BE) analysis help? (2)
To see how different pricing strategies affect break-even point
How does break-even (BE) analysis help? (3)
To highlight the impact of changes in either fixed or variable costs
How does break-even (BE) analysis help? (4)
To plan production levels (how much output before it costs too much, as well as how much equipment & staff)
What does break-even mean?
Total sales revenue = Total cost
How to calculate total sales revenue
Fixed costs + Variable costs
An example of a break-even chart
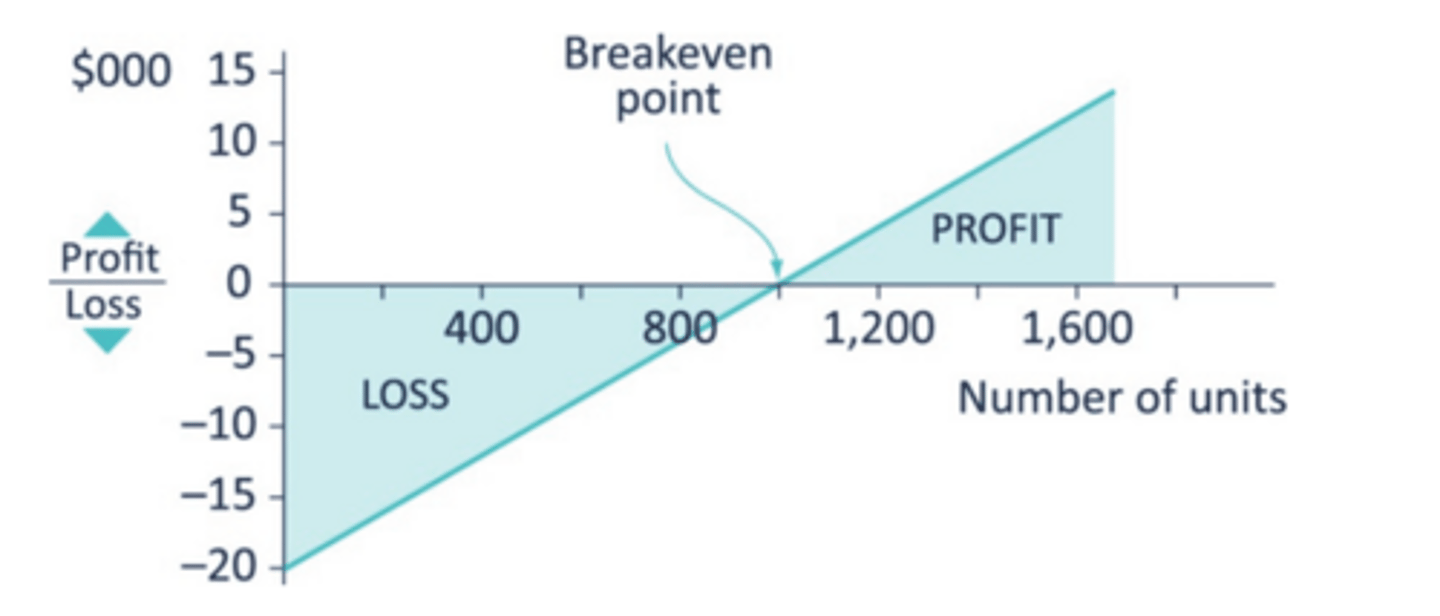
An example of a profit-volume chart (a slight variant of the break-even chart)
What is an issue with break-even charts? (1)
The line might not always be straight due to economies or diseconomies of scale at high outputs (lower or higher variable costs per unit of output)
What is an issue with break-even charts? (2)
Sales revenue per unit can decrease as volume is increased, meaning you will have to lower the price per unit
An example of a break-even chart with economies or diseconomies of scale
What is an issue with break-even analysis? (1)
Great care must be taken when making assumptions about fixed cost
What is an issue with break-even analysis? (2)
Most businesses provide more than one product (or service), so sales from additional product may affect sales of other products
How to calculate break-even point (in units)
Fixed costs / (Sales revenue per unit - Variable cost per unit)
How to calculate break-even point (when you have the contribution per unit) (in units)
Fixed costs / Contribution per unit
How to calculate break-even point (when you have the contribution per unit) (in currency)
Contribution per unit x (Revenue / Sales units)
How do you find out how a company is making operating profits?
When their load factor is higher than their break-even point
What is contribution?
How much something contributes to reaching the fixed, then to making a profit after that
How to calculate total contribution (if you don't know your contribution per unit)
Total revenue - Total variable costs
How to calculate contribution per unit (if you know your total contribution)
Total contribution / Sales units
How to calculate contribution per unit (if you don't know your total contribution)
Selling price per unit - Total variable costs per unit
How to calculate total contribution (if you already know your contribution per unit)
Contribution per unit x Number of units sold
What is the contribution margin ratio
The contribution from an activity expressed as a percentage of the sales revenue
How to calculate contribution margin ratio
(Contribution / Sales revenue) x 100
What is the margin of safety?
The extent to which the planned volume of output or sales lies above the break-even point
Graph of the margin of safety
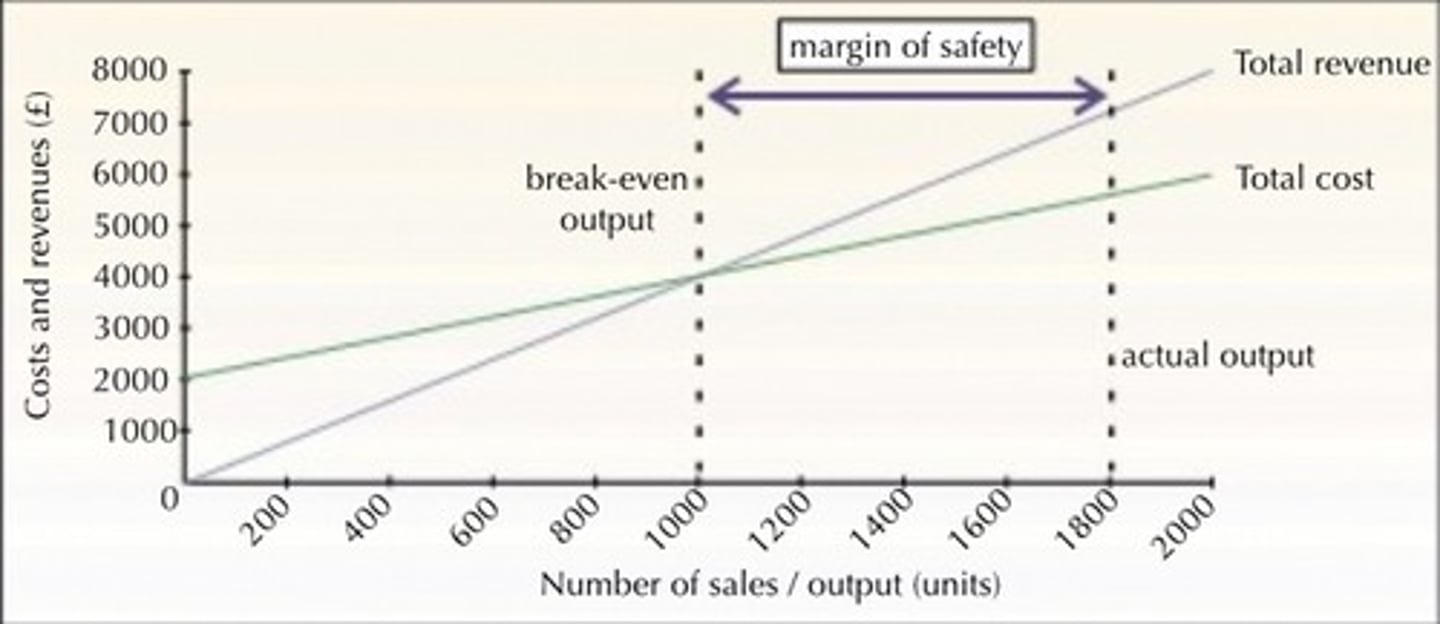
How to calculate the margin of safety (as a number)
Sales - Break-even sales
How to calculate the margin of safety (as a percentage)
Margin of safety (as a number) / Sales
What is target profit?
How many units need to be sold to make a certain amount of profit
How to calculate target profit
(Fixed overheads + Target profit) / Contribution per unit
What is the target number of units sold?
How much profit is made if a certain number of units were sold
How to calculate target number of units sold
(Amount of units sold x Contribution per unit) - Fixed costs
What is operating gearing (or operational gearing)?
The relationship between fixed costs & variable costs
What does it mean when operating gearing is high?
The fixed costs compared to the total variable costs are high
What to do when variable costs change
The answers for the fixed costs are £0 as they are irrelevant & unchanged, whilst you have to add to/remove from the difference to/from the total variable costs
What to do when fixed costs change
The answers for the fixed costs are £0 + or - the amount that is being added/removed, whilst you just have to state the same variable costs (the number is unchanged)
When giving advice on new ventures
Calculate the variable cost per unit (including semi-fixed costs), then compare it to the sales price per unit - if it is lower, it is better
What is the minimum price that can be charged?
The minimum price if the company is not to make a loss (to break even per unit)
How to calculate the minimum price that can be charged
The new variable costs
How to find the most efficient use of resources
Find out the order of the contribution per time
How to calculate the contribution per time
Contribution per unit / Time per unit