PPI - MIDTERM 1 study guide
1/162
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
163 Terms
1917
during WWI, women were recruited to rehabilitate injured soldiers through US army medical department, division of physical reconstruction as reconstruction aides
1918
first PT with the Army was Mary McMillan at Walter Reed general hospital
-she was trained and experienced through British hospitals prior to coming to US
-she headed this 1st school of PT
1921
formation of the 1st professional association "The American Women's Physical Therapy Association" (AMWPTA) with Ms. McMillan elected as president
-and first PT journal published in US
1922
name changed to American Physiotherapy Association (APA) and men were admitted
-1st annual conference
polio epidemic
Florence (Peterson) Kendall, trained at U of Minnesota and Walter Reed Army Hospital had worked with Veterans with nerve and muscle injuries
-by 1920's she began caring for patients with polio at Baltimore Children's Hospital School under direction of PT Henry Kendall
-many PTs at that time used conservative therapy, splinting, casting, and only minor exercises, believing that frequent handling and over-treatment would harm those with polio
polio, FDR & PT
other PTs were finding that conservative treatment led to misshapen limbs and experimented with exercises in heated pools, led by the efforts of Franklin D. Roosevelt who worked with a PT (Alice Lou Plasteridge) to heal his own polio paralysis
FDR 1926
with his PT, he established Georgia Warm Springs Foundation with his funding
1927
American Orthopedic Association recommended that it be designated a permanent hydrotherapeutic center
-today known as "Roosevelt Warm Springs Institute for Rehabilitation"
1935 new requirements
minimum standard educational requirements to enter PT program
-to use the term "registered" as part of prof title, anyone joining needed to pass a written exam in joint effort between APTA and with physician prof association
-document of registered PTs was known as "American Registry of PTs"
1940
beginning of shift in PT education programs from hospital to university
1941
summer of 1941, Emma Vogel (began as reconstruction aide) was trained by Mary McMillan at Reed College
-she initiated first War Emergency Training Course of WWII that led launch of many more PT programs
-was 6 mo didactic, then 6 mo supervised practice in military hospital
1943
Special Women's Medical Service Corps Program for African-Americans launches in AZ
1947
association renamed the American Physical Therapy Association (APTA)
-congress passed a law establishing Women's Medical Specialist Corps (WMSC) within the US Army providing full military recognition for women PTs serving in armed forces
1949
first edition of muscles testing and function published by Florence and Henry Kendall
-became a standard in the field
1950s
PTs transitioned from working under a physician in autonomous professionals
1954
the 1st national standardized competency examination (7hrs)
-PTs assisted Salk with testing polio vaccine
1960s
PT programs grew to 52
-first 2 year graduate program launched at Case Western Reserve
1965
medicare and medicaid was enacted under Lyndon Johnson
-Medicare coverage NOW allowed for PT coverage via gov benefits
1969
first 2 classes of PTAs graduate and enter workforce
1972
social security administration signed into law
1973
PT assistants became part of APTA
-first PhD program in PT was established (NYU)
1975
president Ford signed into law IDEA (education of all handicapped children act) so PTs could work in school systems
1978
accreditation for PT programs moved to within APTA not AMA
-established CAPTE
1980s
target to raise degree to a post-baccalaureate degree was set as 1991
-in 1981= WWI "reconstruction aides" made veterans
-in 1985= 1st 3 people take exams for specialist certification, all in cardiopulmonary
1990
ADA (american's w disabilities act) become LAW
1993
Creighton has first professional doctor of PT program
1995
1st guide to PT practice published
2000
licensing for PTs approved in all 50 states
2003
first PTAs graduate from advanced proficiency for PTA program
2008
PTCAS launched
2009
international summit on direct access w canada and world confederation for PT
2015
all 50 states have some form of direct access
2016
clinical doctorate (DPT) only degree conferred by CAPTE accredited entry level institutions
2017
PT Licensure compact* launches w 10 states
-developed by FSBPT and APTA
2018
new mission statement "transforming society by optimizing movement to improve human experience"
2021
100th anniversary of the APTA
state the steps required to practice as a PT in the U.S.
1. graduate from accredited PT or PTA educational program
2. pass the NPTE (this is your US licensure as a PT) (for PTAs it is the PTAE)
3. obtain state licensure after meeting professional standards and taking law exam (for California= CA law exam given by PT board of California)
explain the 3 levels of PT scope of practice
1. professional (based on the professions unique body of knowledge, education, evidence)
2. jurisdiction (legal, established by federal rules and state practice act including licensure)
3. personal (individual competence, learn in depth before completing something on patient)
CAPTE
Commission on Accreditation in Physical Therapy Education
-must graduate from a CAPTE accredited school to sit for the NPTE
NPTE
National Physical Therapy Examination
-administered through FSBPT
FSBPT
Federation of State Boards of Physical Therapy
-nonprofit organization whose members are US PT licensing boards
-owns and maintains the NPTE
PTBC
PT board of California
CLE
California law examination
ABPTS
American Board of Physical Therapy Specialties
physiotherapy
physical therapy
AMA
American Medical Association
APTA
American Physical Therapy Association
ADA
Americans with Disabilities Act
profession vs professional vs professionalism
profession= occupation requiring considerable training and specialized study, the body of qualified persons in an occupation of field
professional= conforming to the standards of a profession; professional ethics, engaging in a given activity as a source of livelihood or as a career, belonging to a profession, earns living from performing an activity requiring certain level of of education/skill/training
professionalism= methods, character, or standards
how can you demonstrate professionalism in the classroom and clinic ?
class= being on time, prepped w readings/assignments finished, follow directions/rules with no food or drinks in class, being attentive to professors and classmates, working effectively in groups, bring supplies and required reading material, be respectful, working on giving/responding to feedback
clinic= respecting patients, families, their languages, cultures and customs
define and differentiate between laws and regulations and who is the primary source of jurisprudence for PTs
laws= created by statutes which originate from legislative bills originally introduced by either Senate or Assembly
regulations= standards adopted as rules by the physical therapy board of California to implement, interpret, or make specific the law enforced or administered by the physical therapy practice act. must be approved by the office of administrative law, and filed w the secretary of state and signed by governor (regulations have same effect as law)
explain the 3 levels of APTA and what they consist of
1. chapters-represent each state & DC = CPTA-California Physical Therapy Association
2. sections/academies = focus on range of pt populations, practice & policy areas including pediatrics, geriatrics, sports, orthopedics, aquatics; etc
2. special interest groups (SIGS) = offered by both chapters (CPTA) and sections (pediatrics), these represents interests or career paths
state and describe the APTA Core Values for the PT and PTA and briefly describe each
Accountability= active acceptance of the responsibility for the diverse roles, obligations, and actions of the PT and PTA including self-regulation and other behaviors that positively influence patient an client outcomes, the profession and health needs of society
Altruism= primary regard for or devotion to the interest of patients and clients, thus assuming the responsibility of placing the needs of patients and clients ahead of the PT/PTA self interest
Collaboration= working together with patients and clients, families, communities, and professionals in health and other fields to achieve shared goals
Compassion= compassion is the desire to identify with or sense something of another ones experience; a precursor of caring
Caring= the concern, empathy, and consideration for needs/values of others
Duty= commitment to meeting ones obligations to provide effective PT services
Excellence= the provision of PT services occurs when the PT/PTA consistently use current knowledge and skills while understanding personal limits
Inclusion= when PT/PTA create welcoming/equitable environment
Integrity= steadfast adherence to high ethical principles/standards, being truthful, ensuring fairness, following through on commitment
Social responsibility= promotion of a mutual trust between the profession and larger public that necessitates responding to societal needs for health/wellness (community service)
describe, define, and distinguish between the 8 principles of medical ethics
1. medical paternalism
2. autonomy
3. beneficence
4. nonmaleficence
5. justice
6. veracity/honesty
7. confidentiality
8. fidelity/loyalty
define and differential between the terms: fraud, abuse and waste and apply to PT practice
fraud= intentional deception or misrepresentation that a person makes to gain a benefit for which they are not entitled (ex: knowingly billing for services that were not furnished, falsifying documentation, altering claims forms to receive higher pay)
abuse= payment for items/services that the provider is not entitled to and for which the provider has not knowingly/intentionally misrepresented facts to obtain payment (ex: misusing codes & billing, billing for services not medically necessary)
waste=incurring unnecessary costs as a result of deficient management practices, systems, or controls (ex: duplication of services already provided elsewhere, spending on services that lack evidence of producing better outcomes compared with less expensive alternatives)
describe the elements of Kidder's test for ethical dilemmas
1. legal test
2. stench test ("gut" reaction, feels wrong)
3. front-page test (would you like this decision on the front page of paper?)
4. mom test (would your mother make this choice?)
5. professional ethics test (does it violate professional core values or code of ethics)
state and describe the elements of the APTA code of ethics for the PT/PTA
different than federal and state laws- rules ad ethics, can vary per state and profession
HCP
health care practitioner/providers
HIPAA
health insurance portability and accountability act
ICF
International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health
WHO-FIC
world health organization- family of international classifications
POC
plan of care
describe and define ICF
ICF= primary disablement model used in PT
-use of disablement in terms and concepts
-standard, consistent, universal, neutral language for diagnosis and classification for all clinicians & researchers & describing how people function in everyday lives
-need to state relationship between impairment & function clearly- can't leave it to be implied
ICF model
-moves beyond diagnosis and structural issues to consequences of disorder & impact upon persons life (understand patients function vs just their disease) w
what are the two umbrella terms in the ICF model?
function and disability
-they incorporate body functions. structures, activity, participation
-they are the result of the interaction between the persons health condition and both personal and environmental factors
who was the ICF endorsed by ?
endorsed by WHO in 2001, APTA in 2008 (Biosychological model)
ICF model parts 1 and 2
part 1= functioning and disability
-body functions and structures
-activities and participation
part 2= contextual factors
-environmental factors
-personal factors
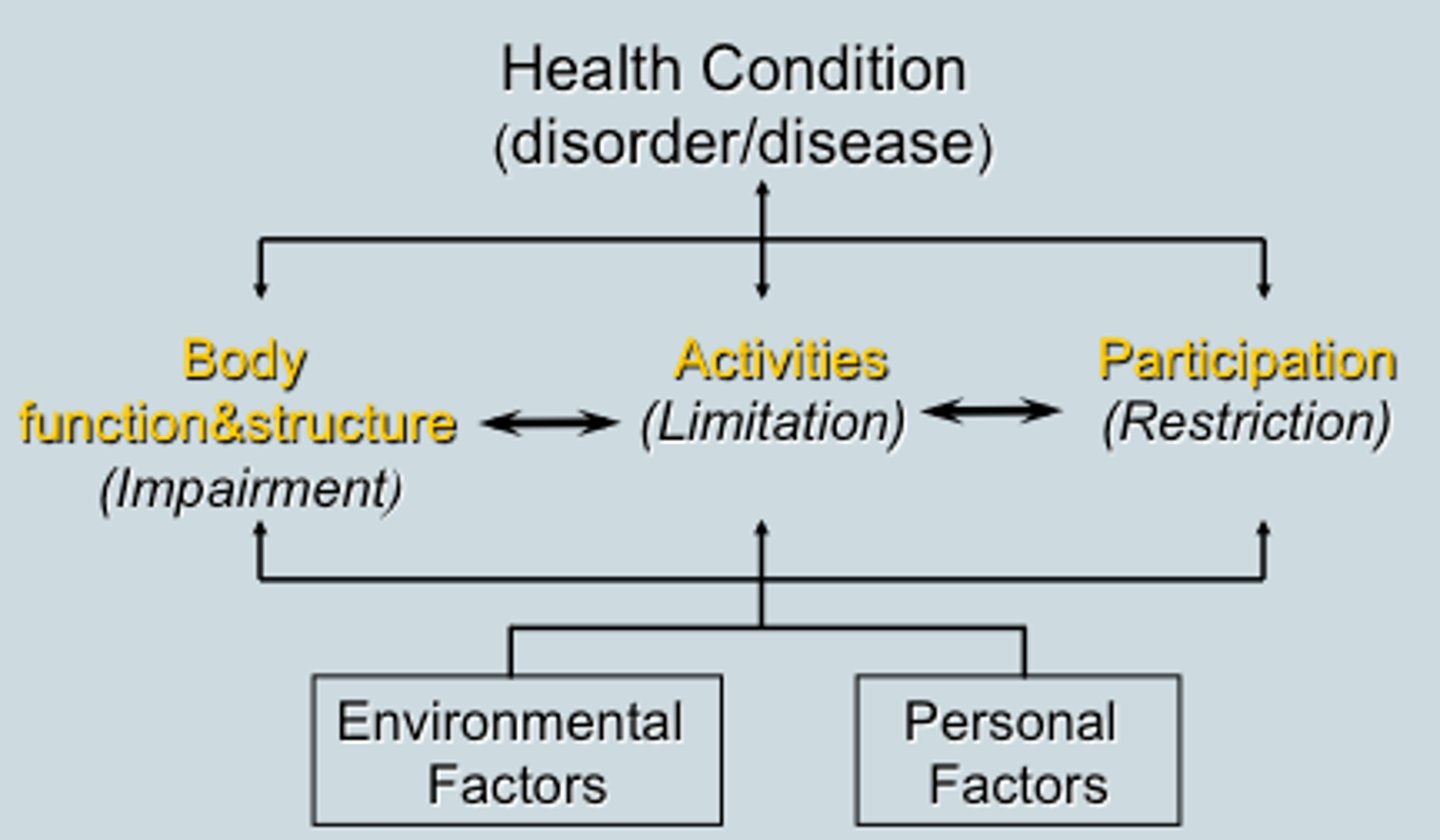
disability (ICF)
defined as dysfunction in 1 or more of these three levels:
1. impairment of body structures (limbs/organs) or functions (physiologic/psychological)
2. limitations in activities (execution of tasks)
3. restrictions of participation (involvement in life situations)
physical therapist may do what?
co-manage
consult
manage
refer
conclusion of care (discharge) planning
-important to start at beginning of episode of care, can also be within prognosis component
-determine outcome tools for baseline and ending
consumers of PT services
-patients= individuals who receive PT services for disease, disorder, condition, impairment, activity limitation or participation restriction
-clients= engage the services of a PT and who can benefit from PTs consultation, interventions, advice, health promotion, fitness, wellness, prevention services. clients may include: businesses, school systems, and other whom PTs provide service to.
-communities= groups of people that may or may not be spatially connected but who share common interests, concerns, identities
-populations= groups of people connected by their demographics and other factors; ex: ethnicity, socioeconomic status, population density
order of patient and client management model
1. examination
2. evaluation
3a. diagnosis
3b. prognosis
4. intervention
5. outcomes
what happens in an examination ?
PT conducts exam that includes=
-history (subjective and systems review)
-physical examination (tests and measures)
what is included in subjective history ?
comprehensive questioning process or completion of a patient self-administered questionnaire, and through a review of health records.
what are red flags found in patient history and physical exam that suggest the presence of a serious pathology ?
signs/symptoms found within documentation
-ex: stroke red flags= F.A.S.T
what is the most common PT note format ?
"SOAPE"
S- subjective (patient history including: HPI, MOI, DOI, PMH, C/C, PLOF, L/S, living conditions & patients goals)
O-objective (reviewing systems and performing tests/measures)
A-assessment (based on S & O, PT determines impairments, patient functional status- including activity limitations/participation restrictions)
P- plan (based on examination data, PT determines PT diagnosis, prognosis- includes goals, intervention plan)
E- education (education provided and to whom, future planned education)
what does physical examination begin with ?
begins with the systems review then follow up with any needed elements:
-cardiovascular and pulmonary systems
-integumentary systems
-musculoskeletal systems
-neuromuscular systems
-neurologic system
-communication ability, affect, cognition, language, ability to read, and learning style
-movement
why do PTs use measurements ?
-to identify impairments & potential causes of impairments in the body structures & functions, activity limitations, participation restrictions
what are the results of tests and measures ?
-inform risk identification & prevention and health promotion activities
-contribute to outcome assessment
-help PT determine change in the individuals status
tests and measures are a component of the physical exam used to ?
-confirm or reject a clinical hypothesis regarding factors that contribute to making the individuals current level of function less than optimal
-support the PTs clinical judgements about the diagnosis, prognosis, and development of an effective management plan
how many categories of tests and measures are there ?
26
what are outcome measures and what can they measure ?
when standardized tests and measures are used to determine change in outcome status during and at the end of an episode of care
May measure:
-functional status, impairments in body functions/structures, adverse outcomes & complications, morbidity & mortality, individuals self-reported outcomes, individuals satisfaction w the care/services received
PTs interpret/synthesize the history & physical exam findings to ?
-establish diagnosis from which to develop a management plan
-determine rehab prognosis (not medical), including goals for PT management
-develop management plan or plan of care if indicated
-develop a working diagnosis list as part of process used to determine whether a referral to or consultation w another health care provider is indicated
examination vs evaluation
examination= process of collecting data, synthesizing data, analyzing data, interpreting data
evaluation= process of collecting clinical decision making that occurs following the examination
**BOTH allow for determining the diagnosis, prognosis, plan of care **
what are the diagnosis classifications ?
-ICD-10= used by physicians & billing by PTs
-ICF= used by PTs for movement system categorization
-movement systems
what is prognosis ?
-the PTs determination of the predicted optimal level of improvement in function over designated time frame
- prognosis typically includes a prediction of levels of improvement during the episode in PT in determining goals/outcomes
-can be influenced by contextual factors
management plan/plan of care (POC)
-framework of PT services provided to individuals, groups/populations, based on best available evidence, clinical expertise, individuals wants/needs
-may include a POC which consists of: individuals goals, prognosis, interventions to be used including duration and frequency, summary of plans for referral or consultations to other providers
plan of care (POC)
-based on data gathered from exam and on Dx and prognosis determined by PT
-POC identified persons goals as a result of implementing the pan
example of goals for a PTs patient
"patient will ambulate for 100 ft with no assistive device using step-through gait pattern in 3 weeks in order to walk to the mailbox each day"
NOT= "gait training 20 min, stretch training with ther ex including clams x10, SLR x10, squats x10"
what is the intervention plan?
a conclusion/summary statement that relays the framework for the actual intervention approaches and techniques during patient or client encounters
why do PTs use interventions?
-to remediate impairments in all major body systems
-improve function performance
-promote improved health/wellness that lead to optimized activity, participation, quality of life
examples of procedural interventions
-adaptive & assistive technology
-manual therapy
-biophysical agents
-motor function/movement training
-functional training
-respiratory & ventilatory techniques
-therapeutic exercise
-integumentary repair & protection techniques
intervention plans specifics
frequency= how often PT services are provided to the patient or client (2 times per day, 3 times per week, daily)
duration= the amount of time the episode of care will cover (4 weeks, 8 weeks, 6 months)
outcomes
-the actual results of implementing the management plan that indicate the impact on functioning
-PTs report outcomes to demonstrate progress, for payment purposes, and to know whether goals have been met
re-examination
-includes the application of selected items from the history & physical examination and comparing them with the initial examination findings
-may be indicated more than once during a single episode of care and often is performed over the course of a disease/disorder/condition
conclusion of the episode of care
indicates the status of anticipated goals & expected outcomes in a single episode of care
-discharge vs. discontinuation
what is the difference of discharge vs discontinuation ?
discharge= is ending services provided in a single episode of care
-discharge assessment is performed in discharge note or summary to compare w initial status and provide record of pts final objective and subjective changes in status
-typically, goals/outcomes met!!
discontinuation= the process of ending services in the episode of care when:
-patient declines to continue/refuses care
-patient unable to participate due to identified barriers (medical condition, financial)
-PT determines that patient will no longer benefit from care
what is the "vehicle" that unites each of the components of the initial examination into a cohesive document ?
the use of the ICF model
the board vs the CPTA
board=
-mandate of consumer protection is the highest priority
-protection of public is paramount
-licensure is mandated
CPTA=
-primary mission is to represent members of the PT profession
-membership is voluntary
PTA
-PT is responsible for all care to the patient and all actions of the PTA
-PTA has responsibility to make sure they are being supervised correctly
-if the PTA provides care in the absence of proper supervision= violation has occurred