Tissues- Anatomy
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
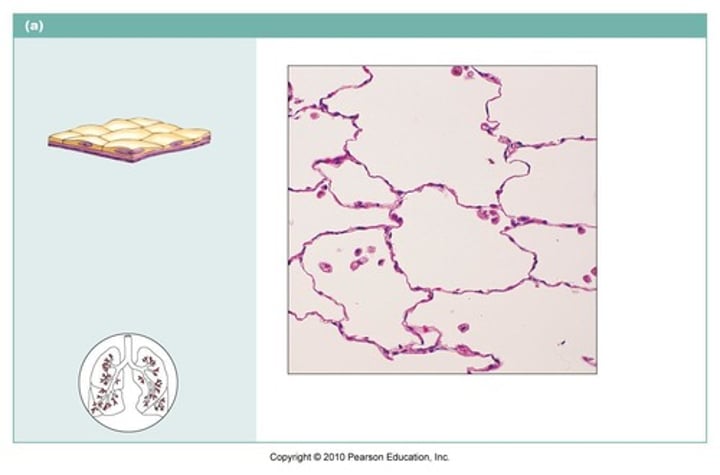
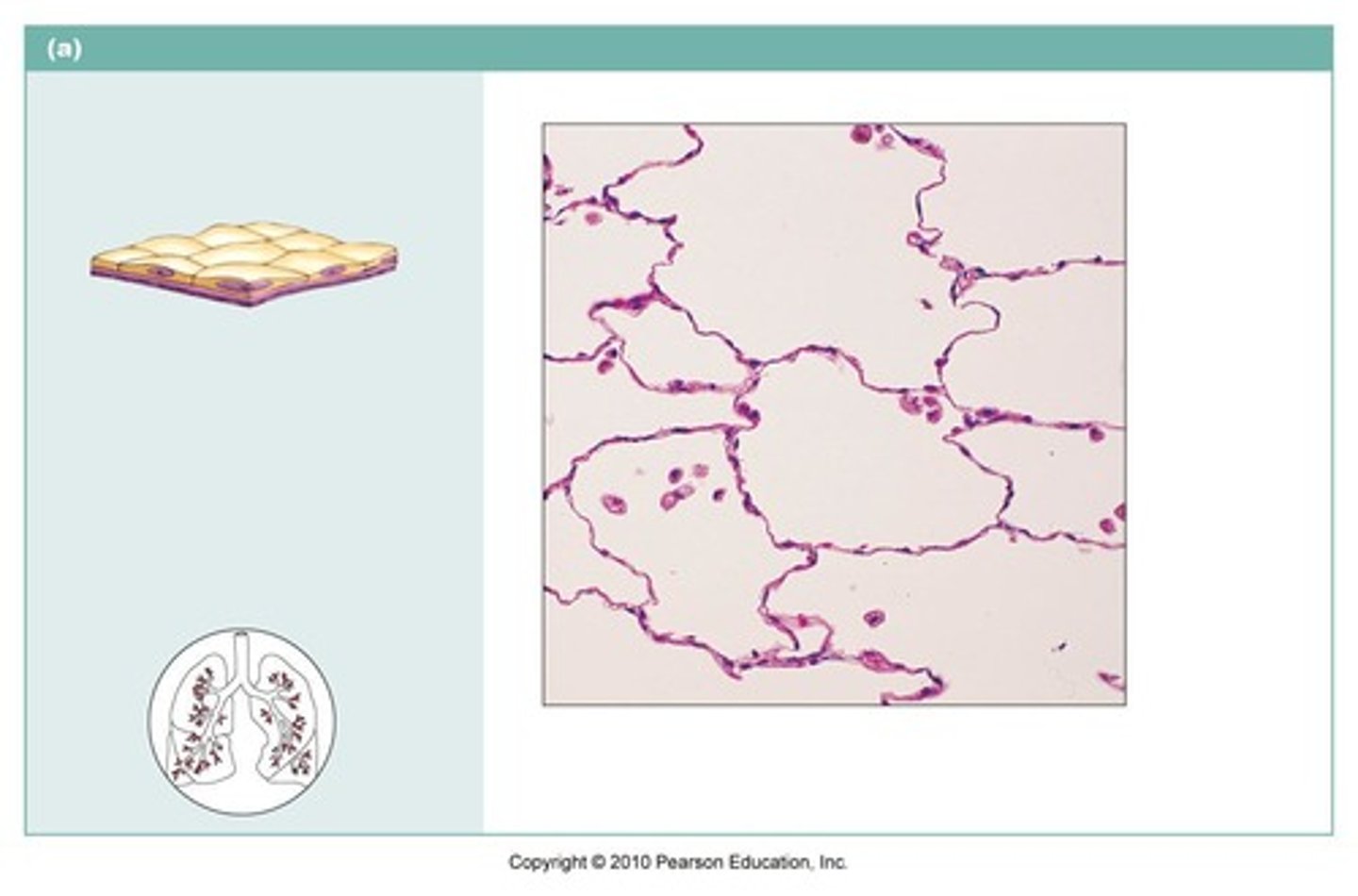
simple squamous
name the type of epithelial tissue
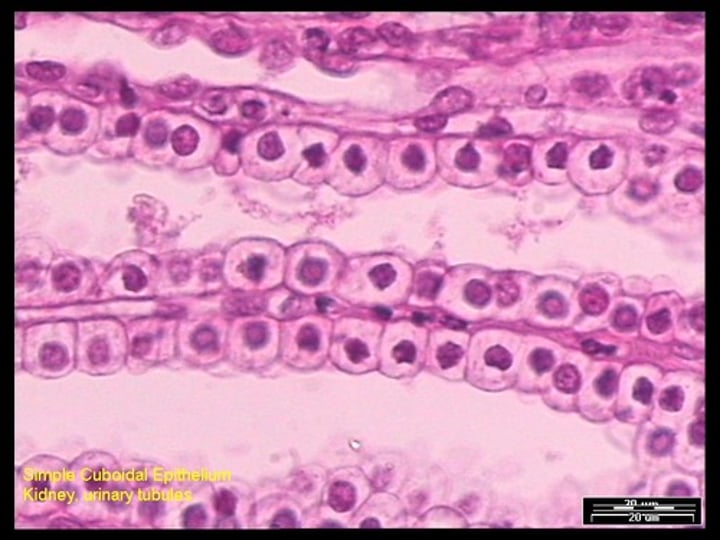
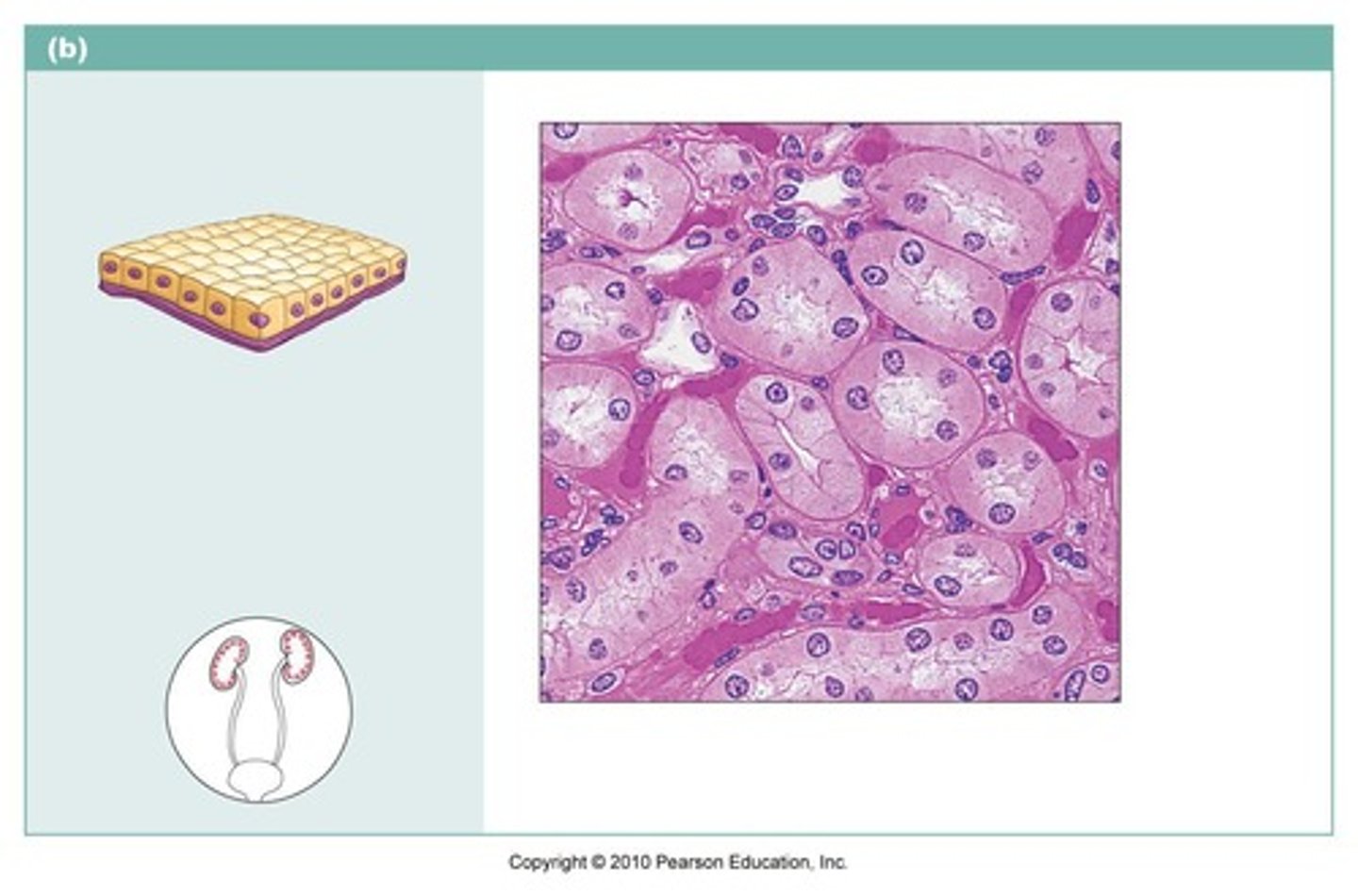
simple cuboidal
name the type of epithelial tissue
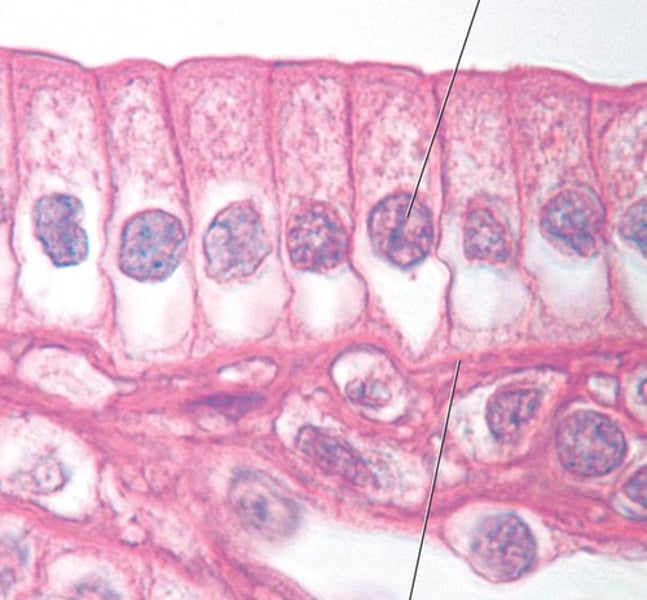
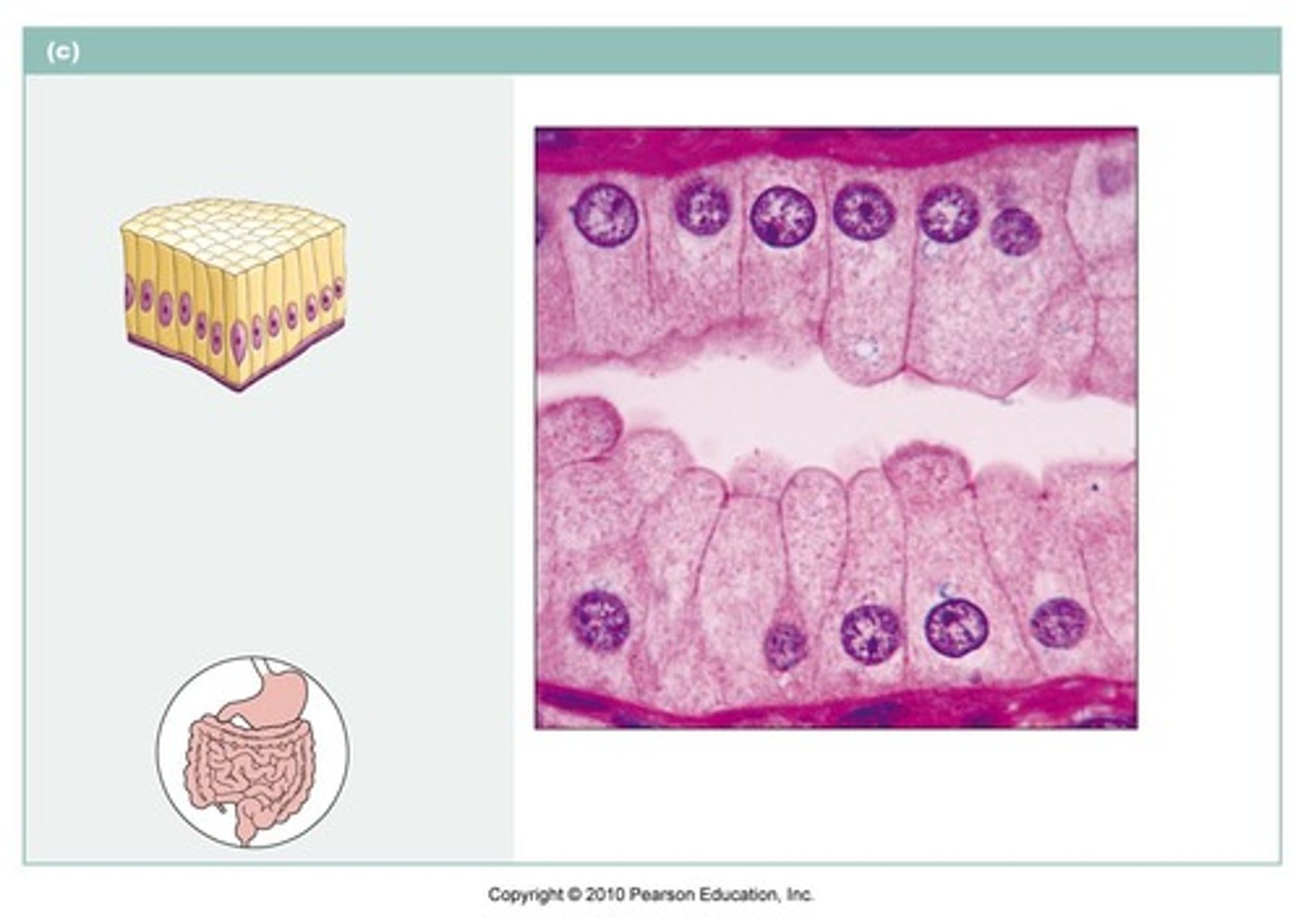
simple columnar; often ciliated
name the type of epithelial tissue
pseudostratified (ciliated)
name the type of epithelial tissue
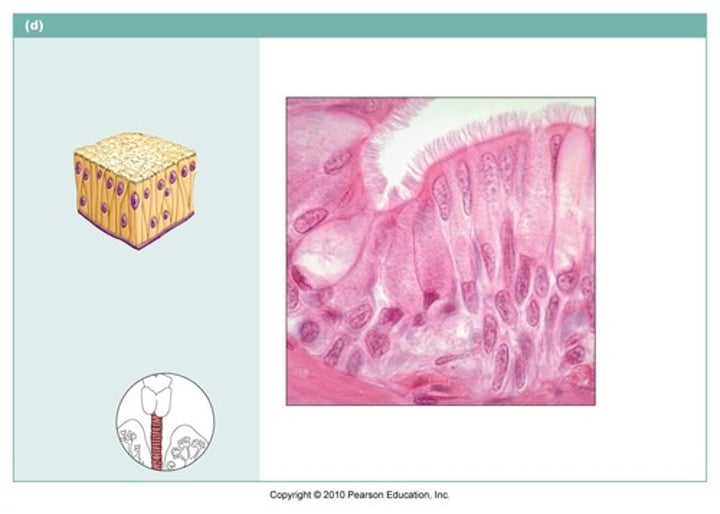
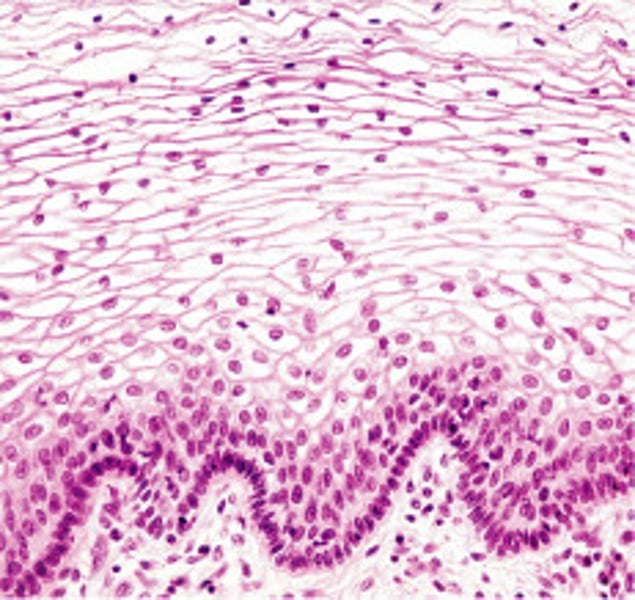
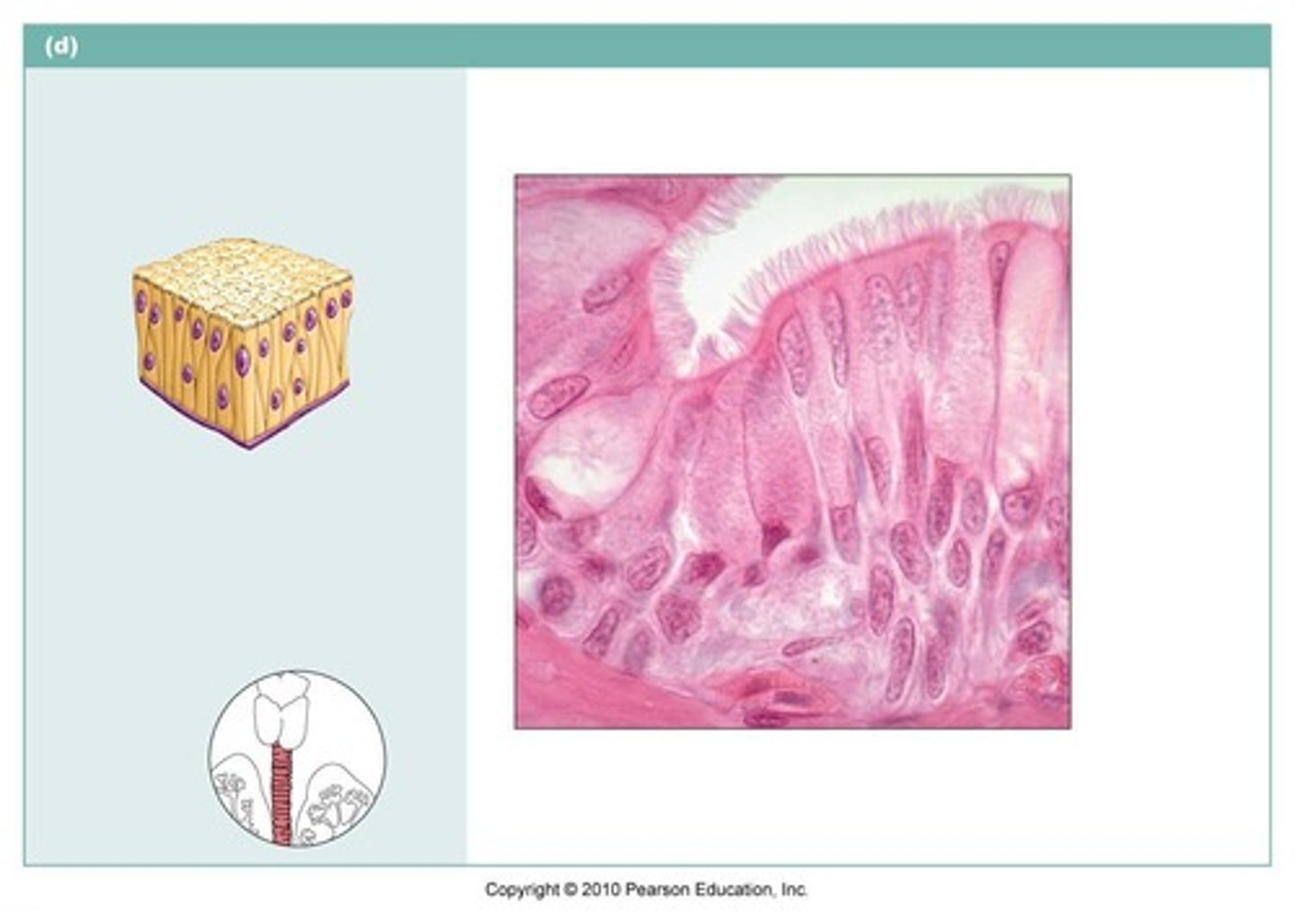
stratified squamous epithelium
name the type of epithelial tissue
Allows passage of materials by diffusion and filtration. Found in lungs and capillaries.
describe the function of this tissue type
Secretion and absorption. Found in walls of kidneys and ovaries.
describe the function of this tissue type
Absorption and secretion of mucus, enzymes, and other substances. Line the digestive tract; often ciliated.
describe the function of this tissue type (SCE)
Secretion of mucus. Ciliated variety lines the upper respiratory tract; may contain goblet cells.
describe the function of this tissue type (PS)
Protects underlying tissues in areas subject to abrasion. Ex: outer layer of skin and inside of mouth and esophagus.
describe the function of this tissue type
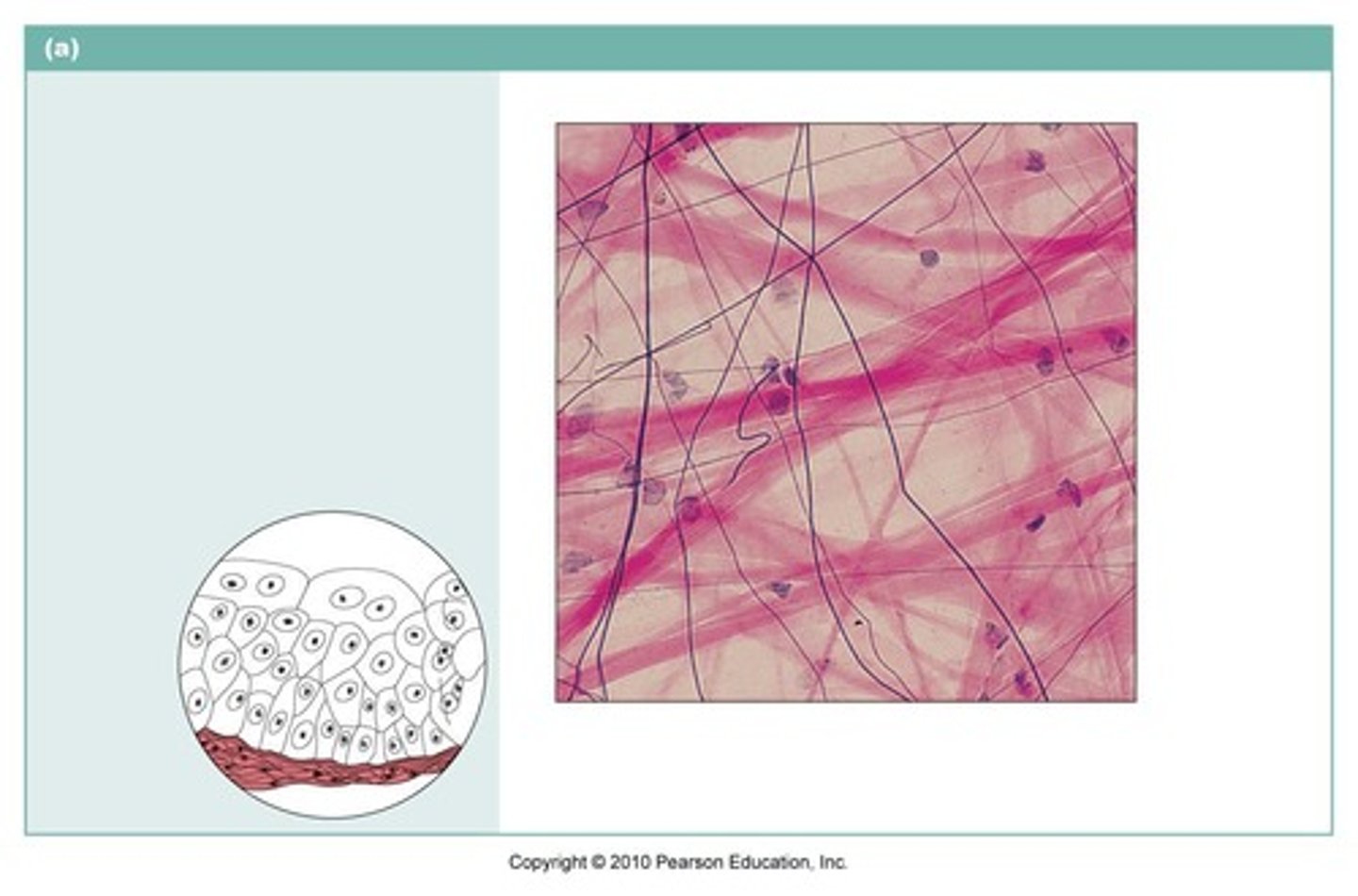
Loose connective tissue, areolar
name the type of connective tissue
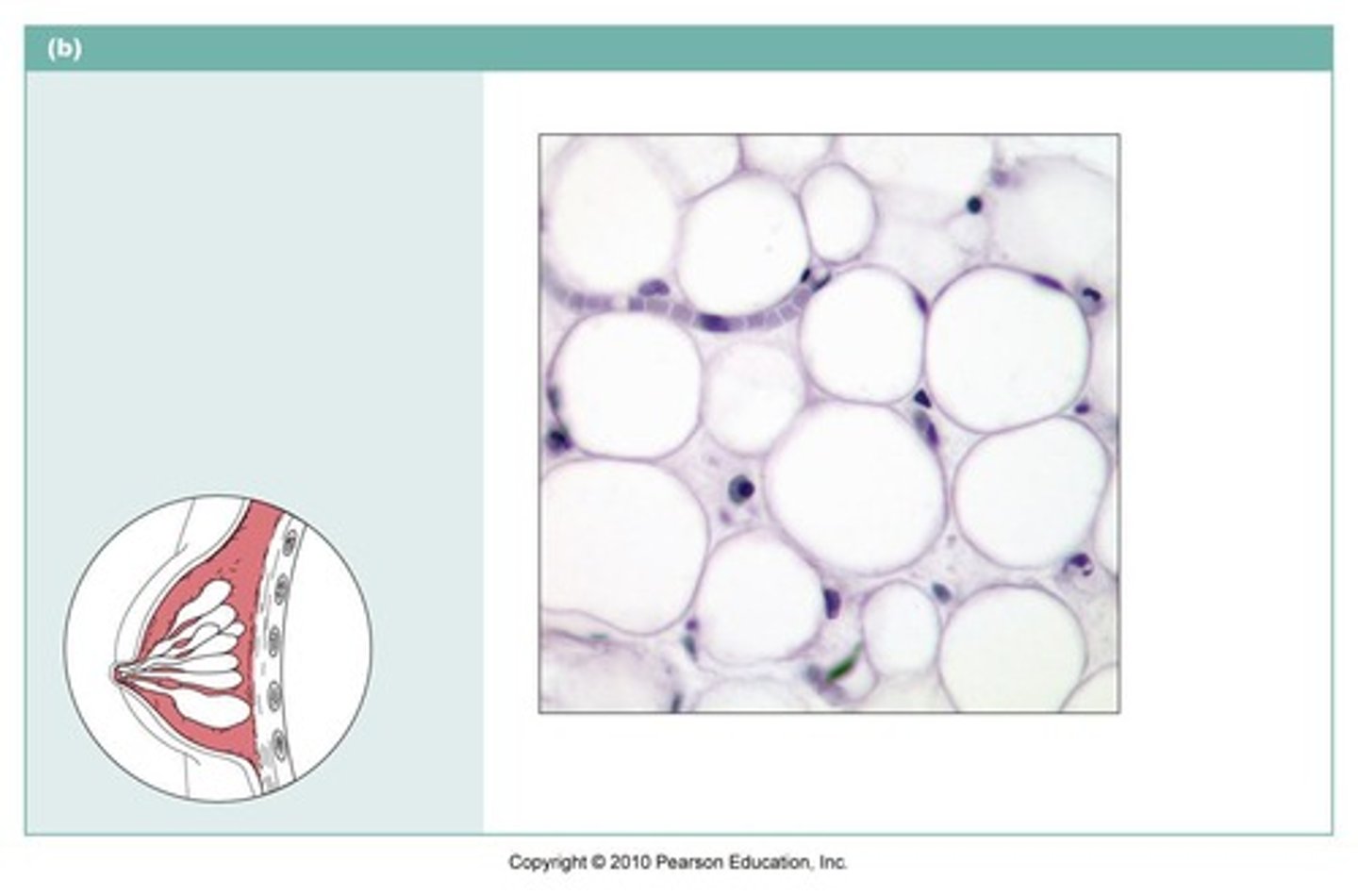
adipose
name the type of connective tissue
dense regular connective tissue
name the type of connective tissue
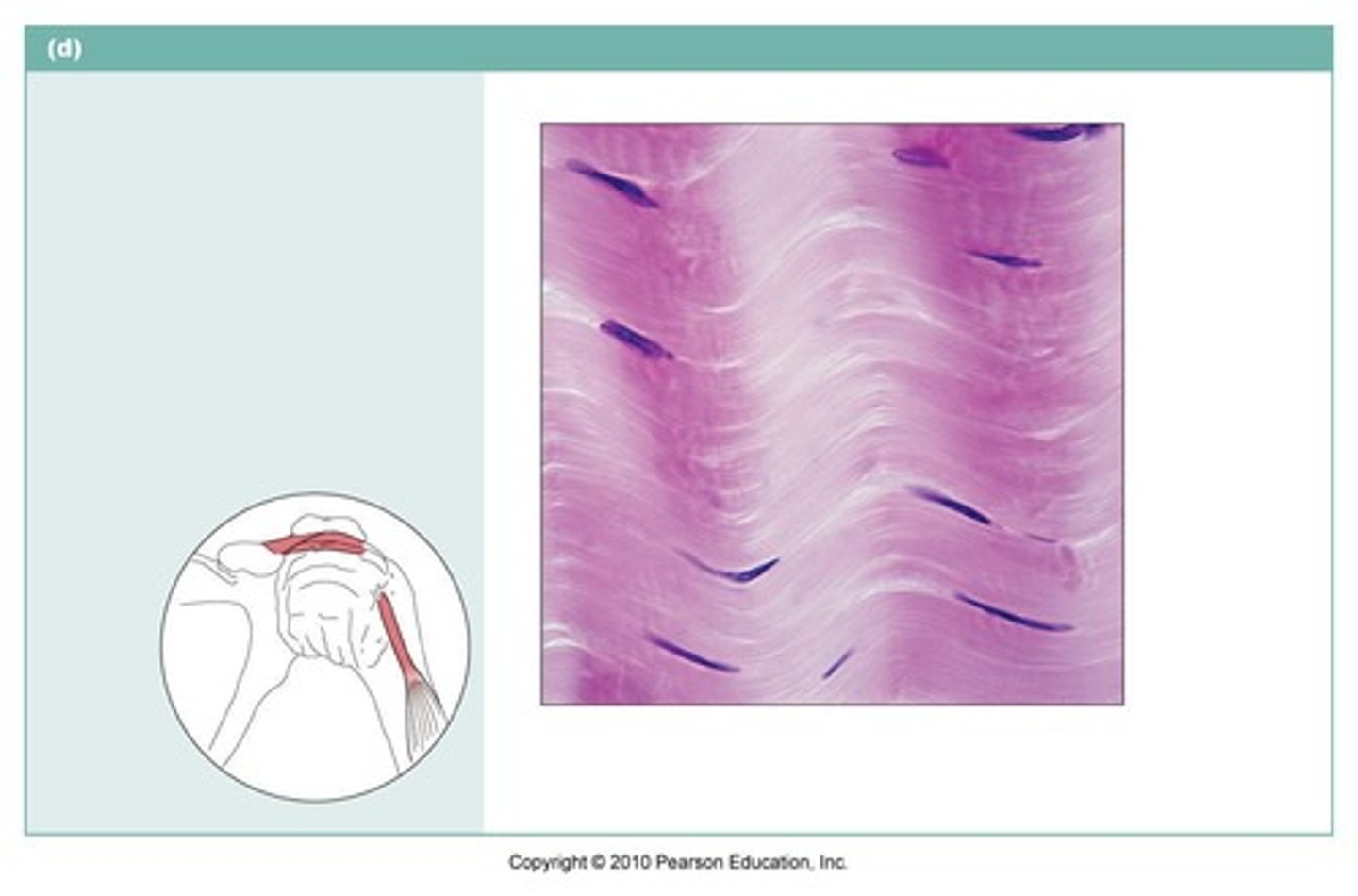
hyaline cartilage
name the type of connective tissue
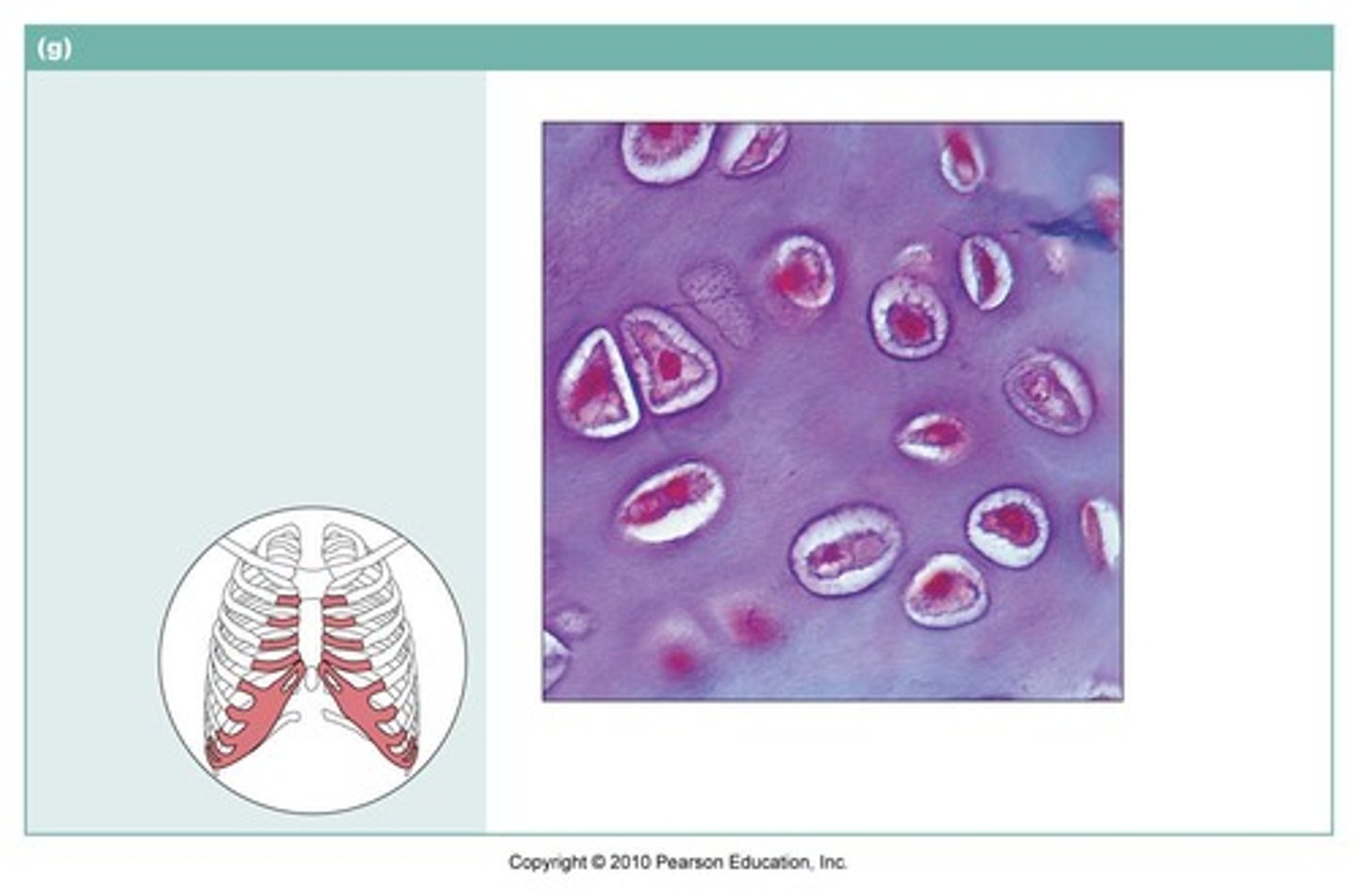
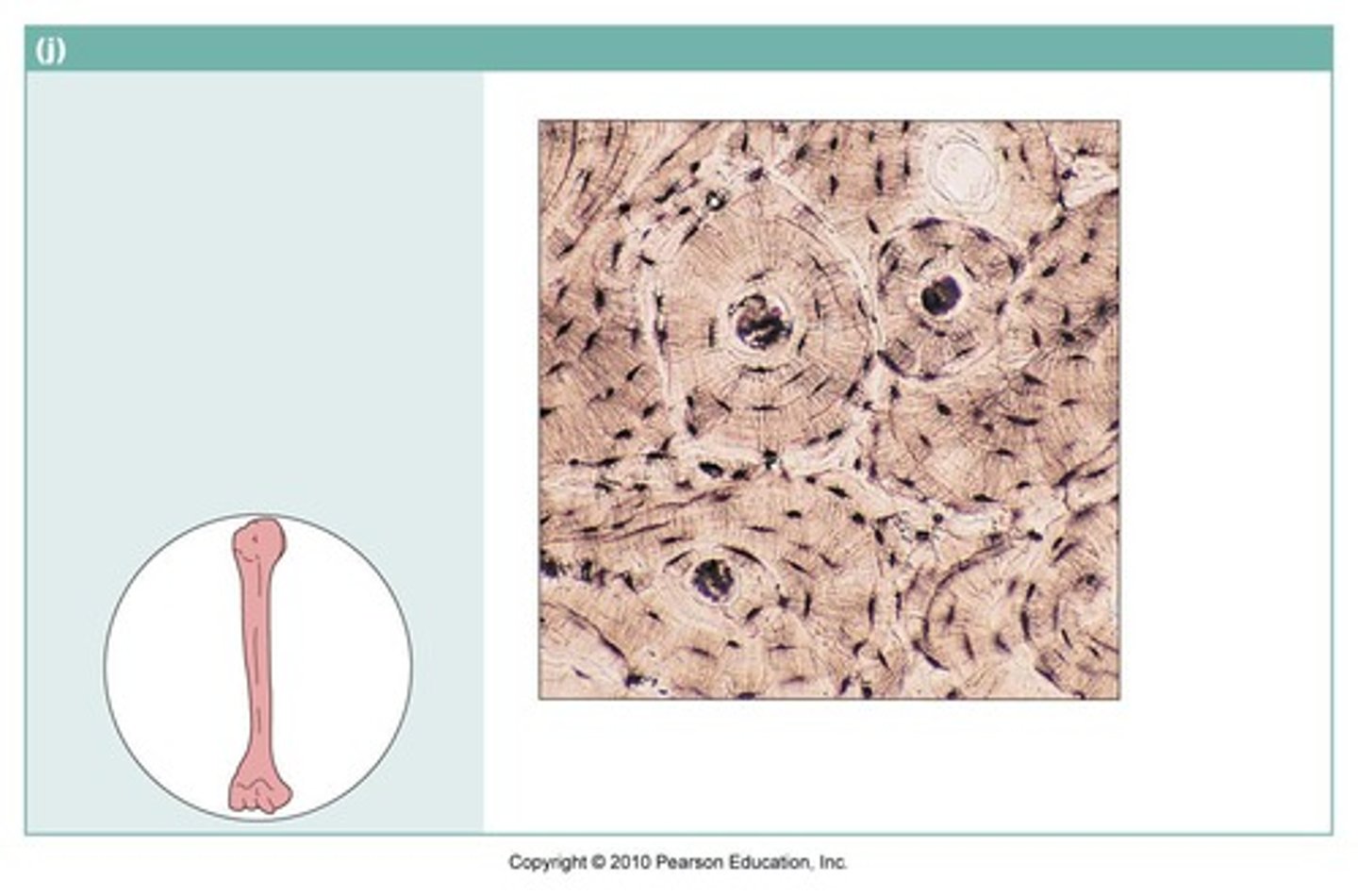
compact bone tissue
name the type of connective tissue
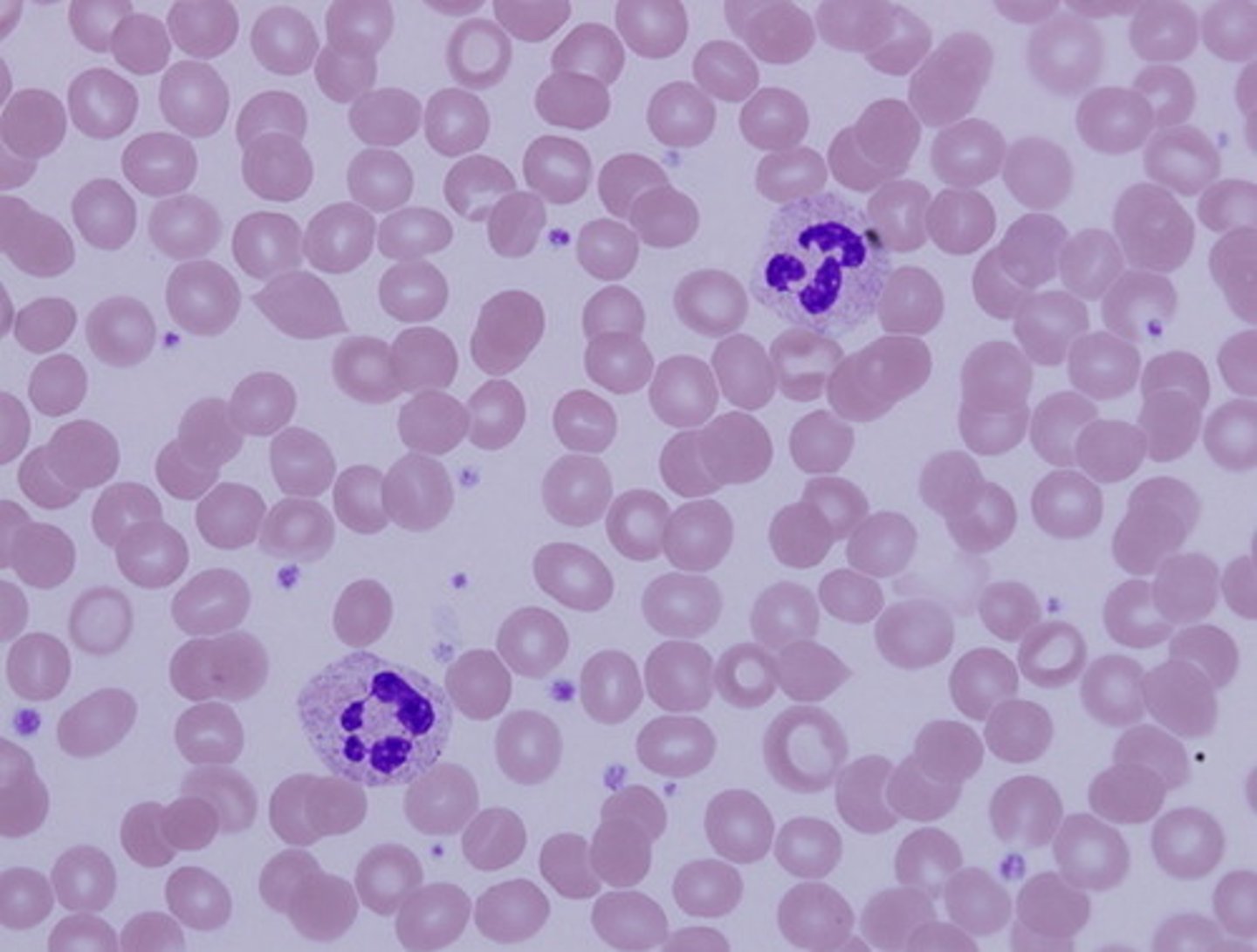
blood
name the type of connective tissue
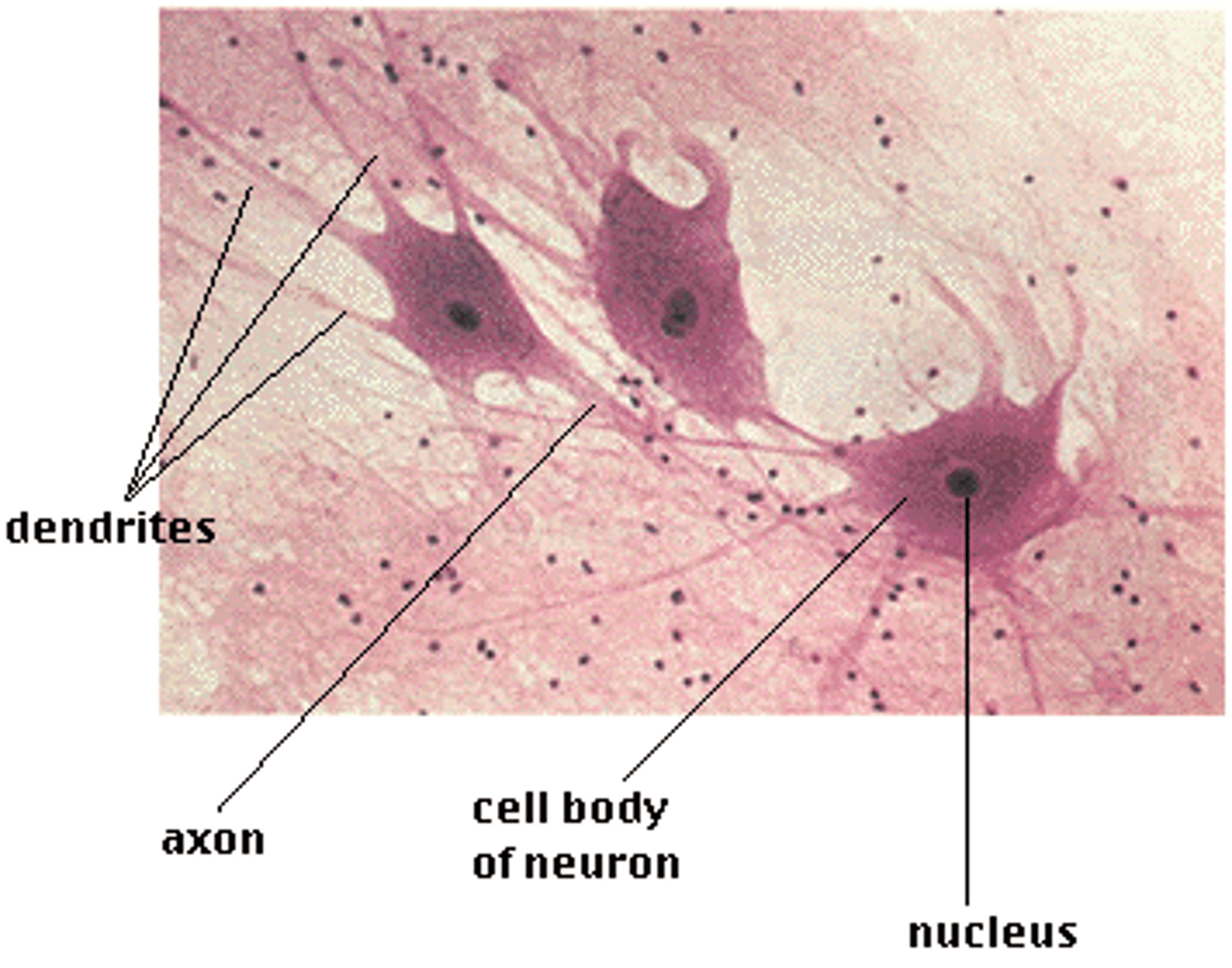
nervous tissue
name the type of tissue
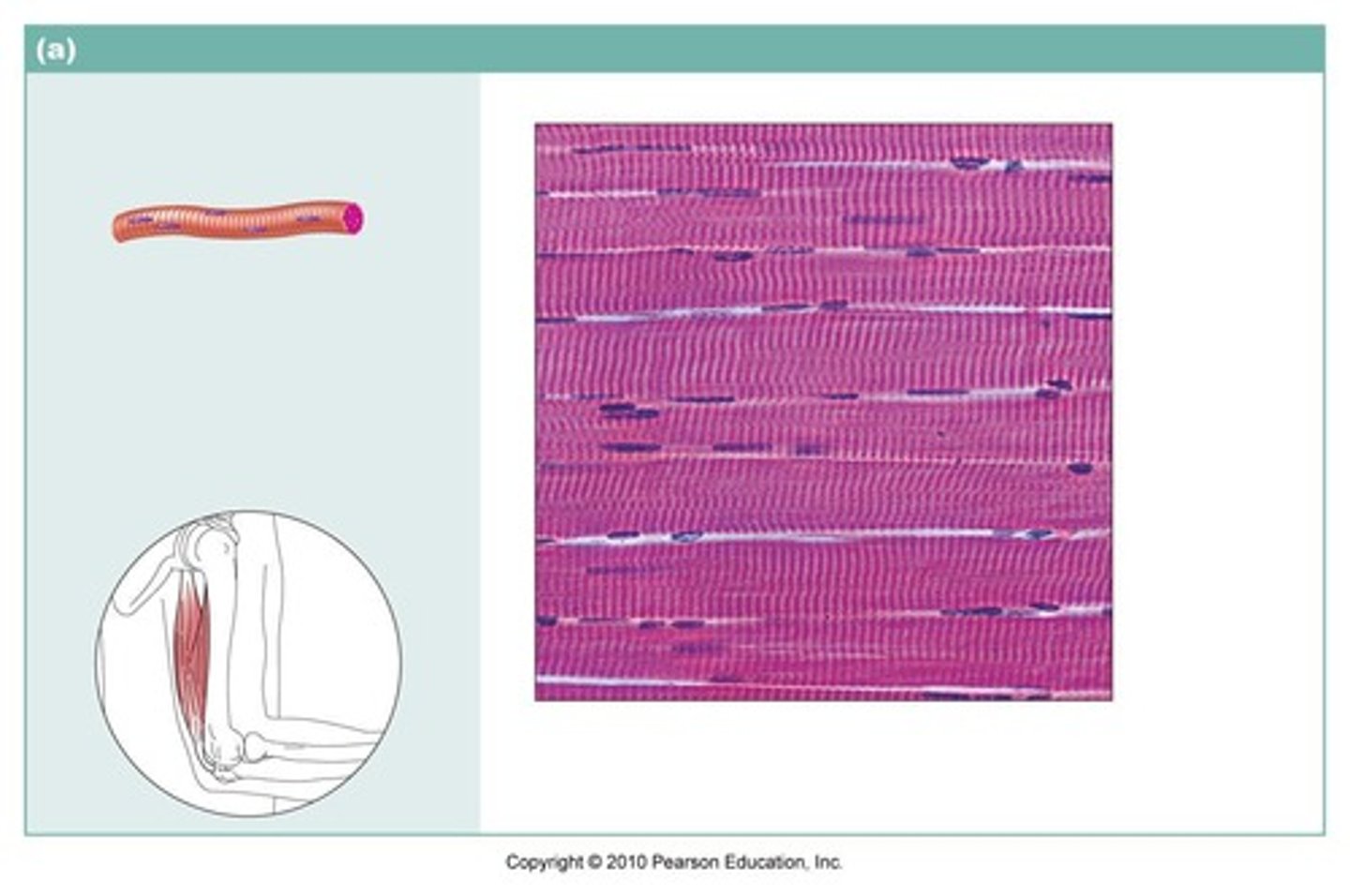
skeletal muscle
name the type of muscle tissue
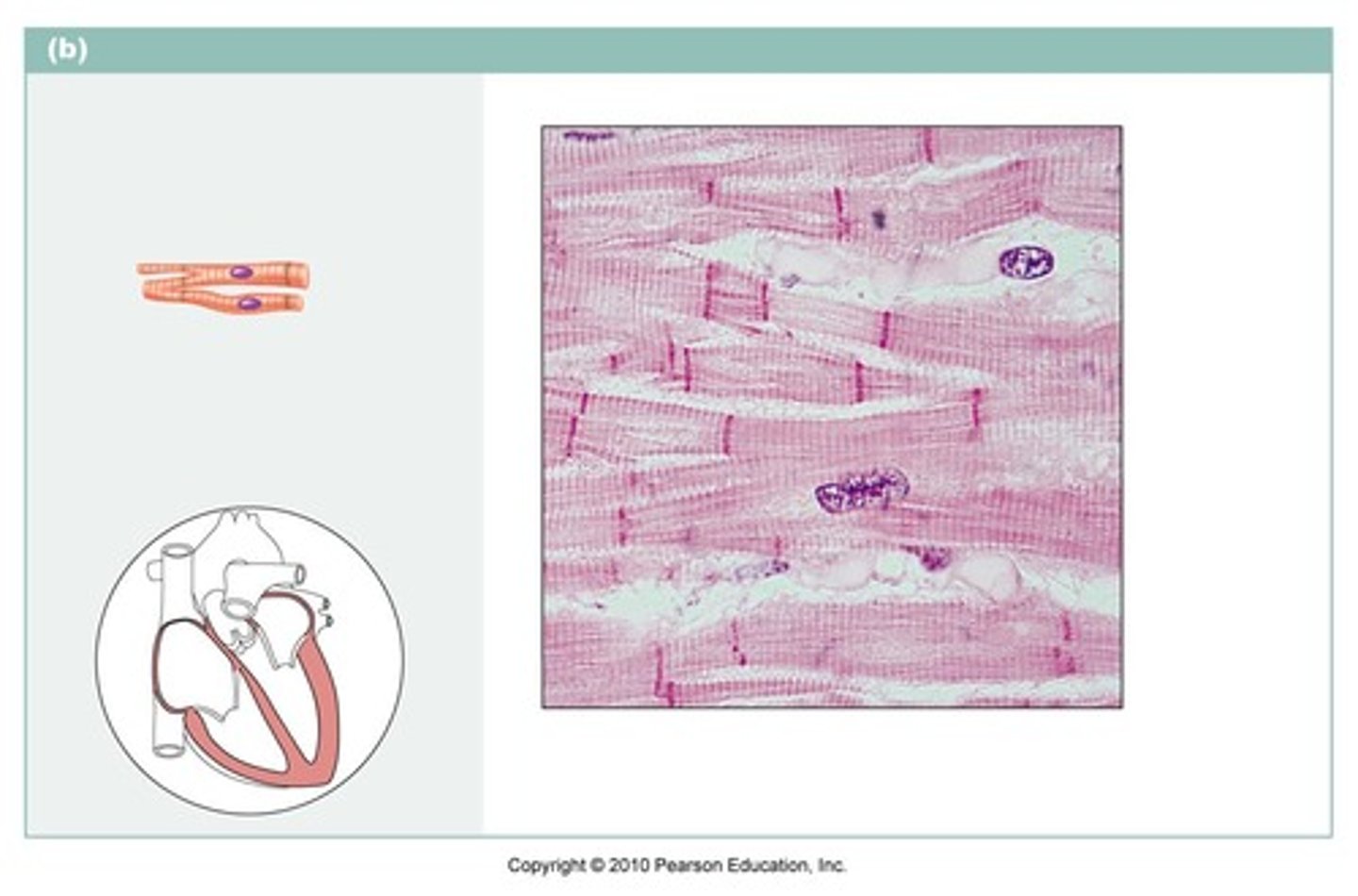
cardiac muscle
name the type of muscle tissue
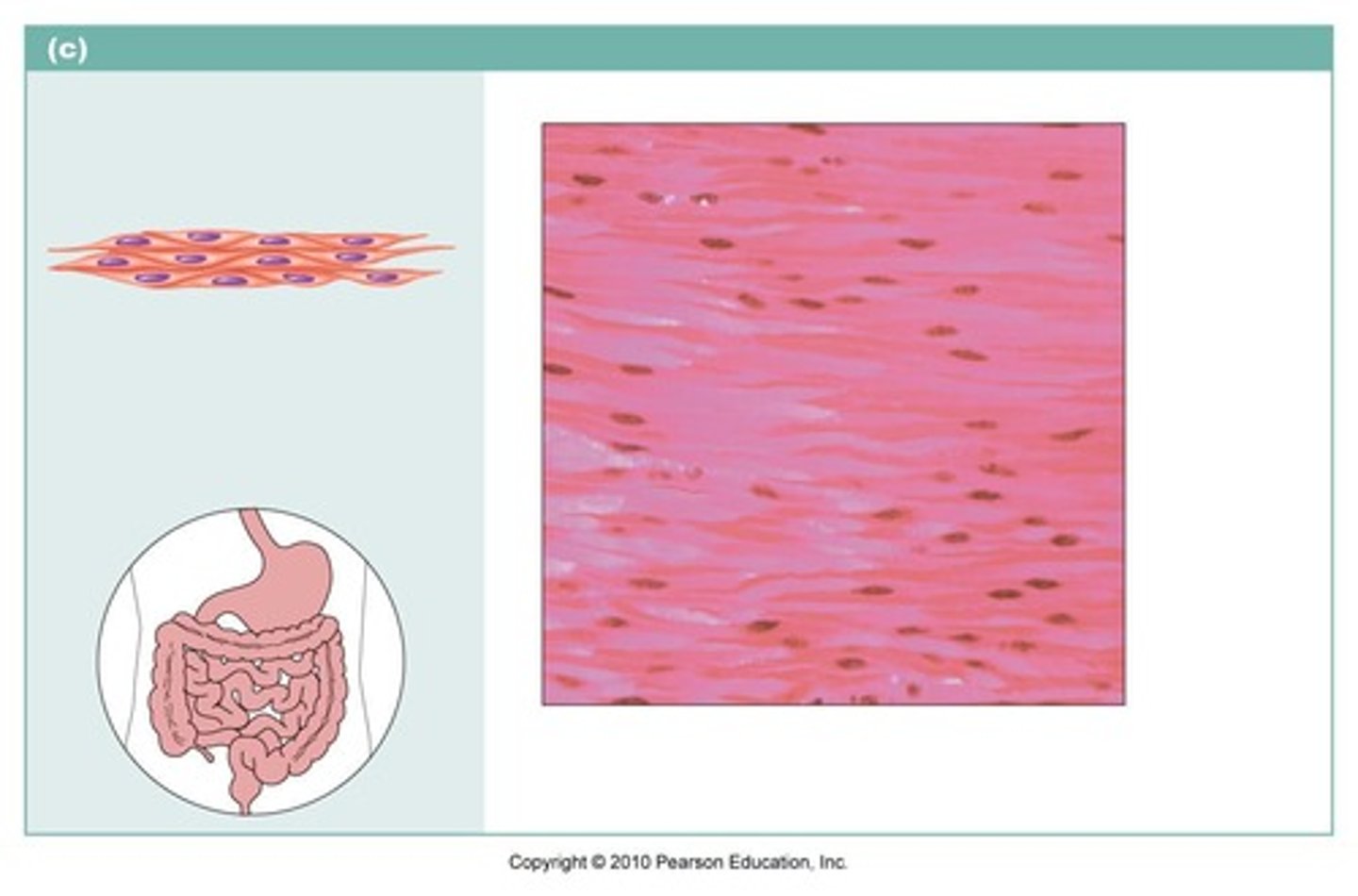
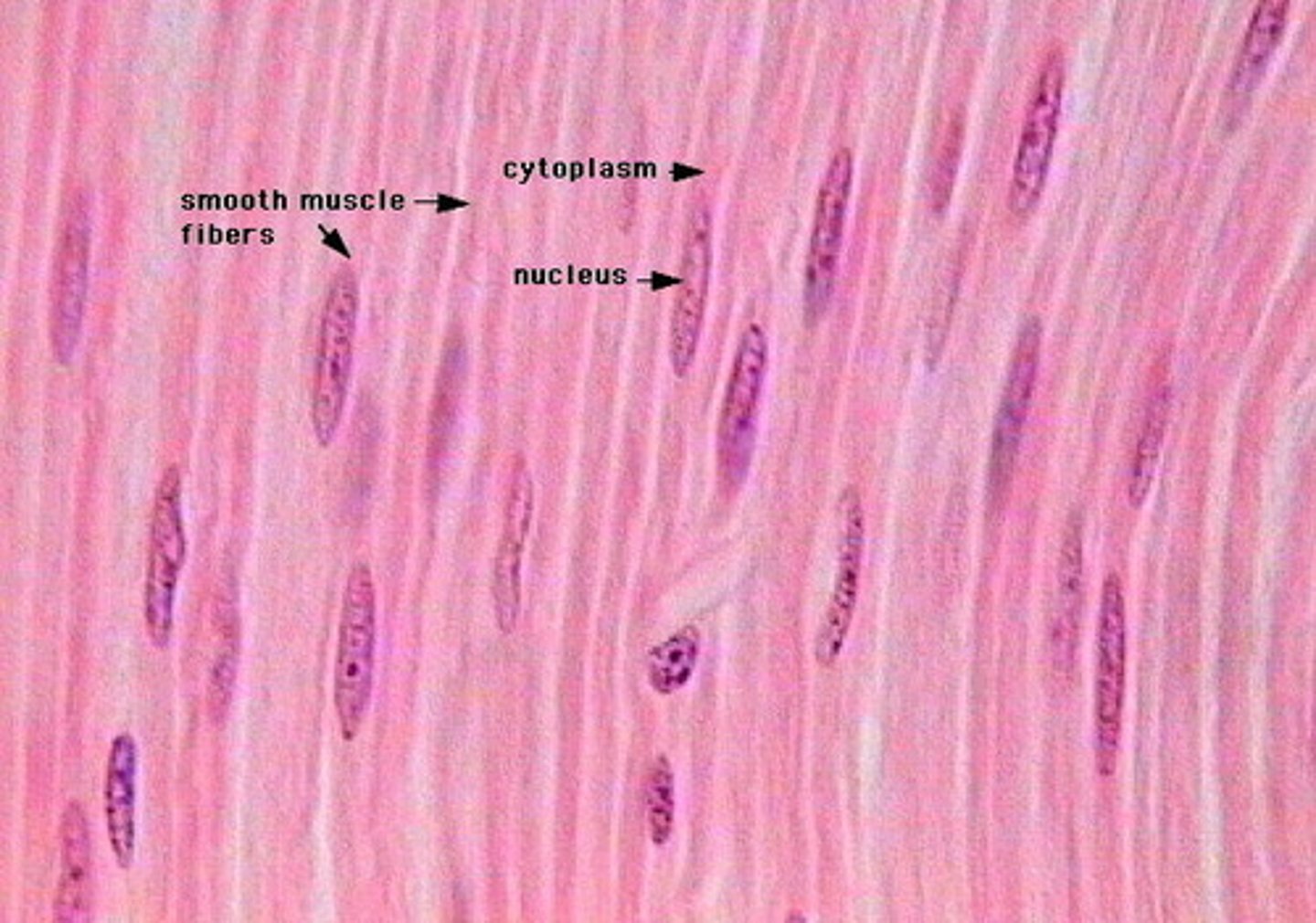
smooth muscle
name the type of muscle tissue
Skeletal
Which muscle tissue is multinucleated, striated and voluntary? (parallel bundles)
Cardiac
Which muscle tissue has intercalated disks between cells?
Hyaline
Which type of cartilage connects your ribs to your sternum?
Stratified squamous
What type of epithelial tissue provides protection with many layers of flattened cells?
simple squamous
What type of epithelial tissue lines the air sacs of lungs and the blood vessels.
Connective
What is the most abundant tissue type in the body?
simple, cuboidal, columnar
What are the three cell shapes of epithelial tissue?
Dense fibrous
What type of connective tissue makes up tendons and ligaments?
Blood
What type of tissue transports nutrients, wastes, and gases throughout the body?
They are all types of connective tissue
What do blood, bone, and fat have in common?
Nervous tissue
What type of tissue transmits electrical signals from sensory receptors to effectors?; star shaped with long cellular extensions
adipose
What type of connective tissue provides insulation for the body?
Epithelial
What category of tissue forms membranes?
Areolar
What type of connective tissue is found underneath all epithelial tissue in the body?
Avascular
Epithelial tissue is called ________________ because it does not contain blood vessels.
hyaline
What type of cartilage forms much of the fetal skeleton and has a glassy appearance?
cardiac muscle tissue
Which type of muscle tissue has intercalated disks? (branched, striated, involuntary)
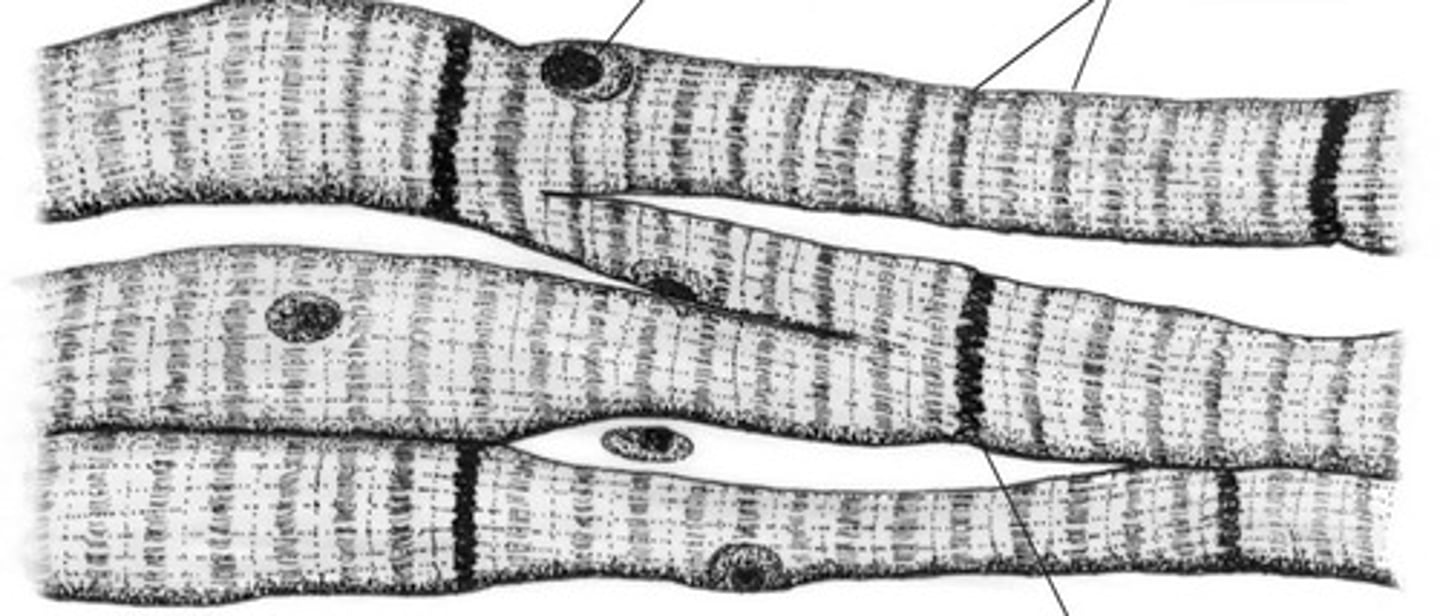
smooth muscle tissue
Which type of muscle tissue lacks striations and is involuntary?
squamous
Which cells are flattened and scale-like?
connective tissue
Blood falls into what category of tissue types?
connective
Which category of tissue usually contains a large amount of matrix?
fibers and ground substance (the gel-like fluid surrounding the cells and fibers)
What two components make up extracellular matrix?
collagen
Which fiber gives connective tissue it's tensile strength?
tissue
A group of similar cells working together to perform a specific function is called what?
pseudostratified columnar
This type of epithelial tissue appears to have multiple layers but all cells are in contact with the basement membrane
stratified squamous
What type of epithelial tissue is best at providing protection from abrasion?; found in skin (may or may not be keratinized)
Histology
the study of tissues
Bone
Consists mainly of matrix, cells live in small holes called lacunae
Skeletal
the most common type of muscle tissue
fibrocartilage
type of cartilage that makes up the disks in the spine
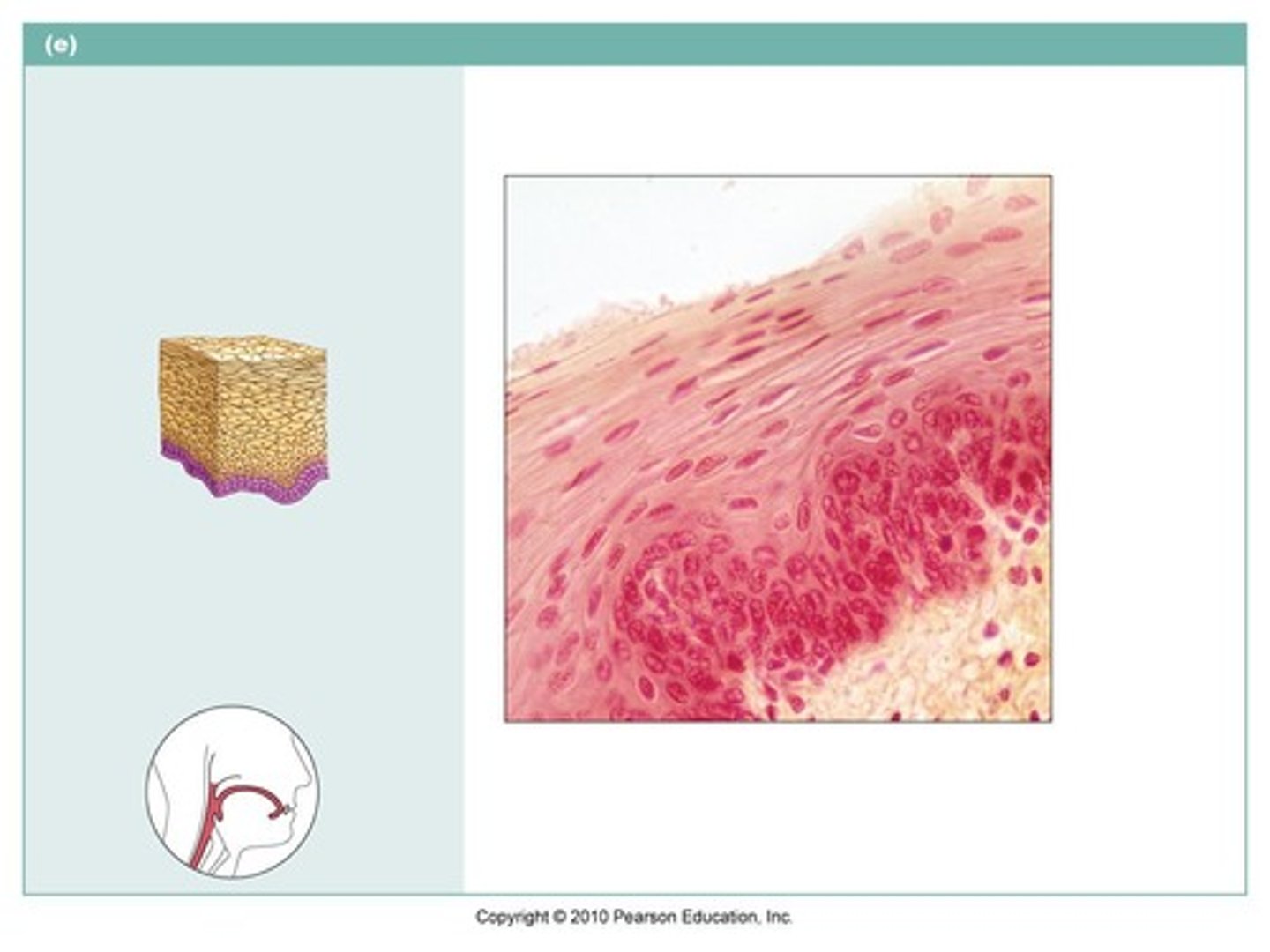
skin
stratified squamous keratinized epithelium
goblet cells
a column-shaped cell found in the respiratory and intestinal tracts, which secretes the main component of mucus.
Matrix
The non-living portion of tissue
adipose connective tissue
acts as a storage depot for fat
elastic cartilage function
maintains the shape of a structure while allowing great flexibility
reticular loose connective tissue
lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, bone marrow, and spleen)
dense irregular connective
Function: able to withstand tension exerted in many directions (irregularly arranged); provides structural strength from collagen.
Location: Fibrous capsules of organs and of joints; dermis of the skin; submucosa of digestive tract.
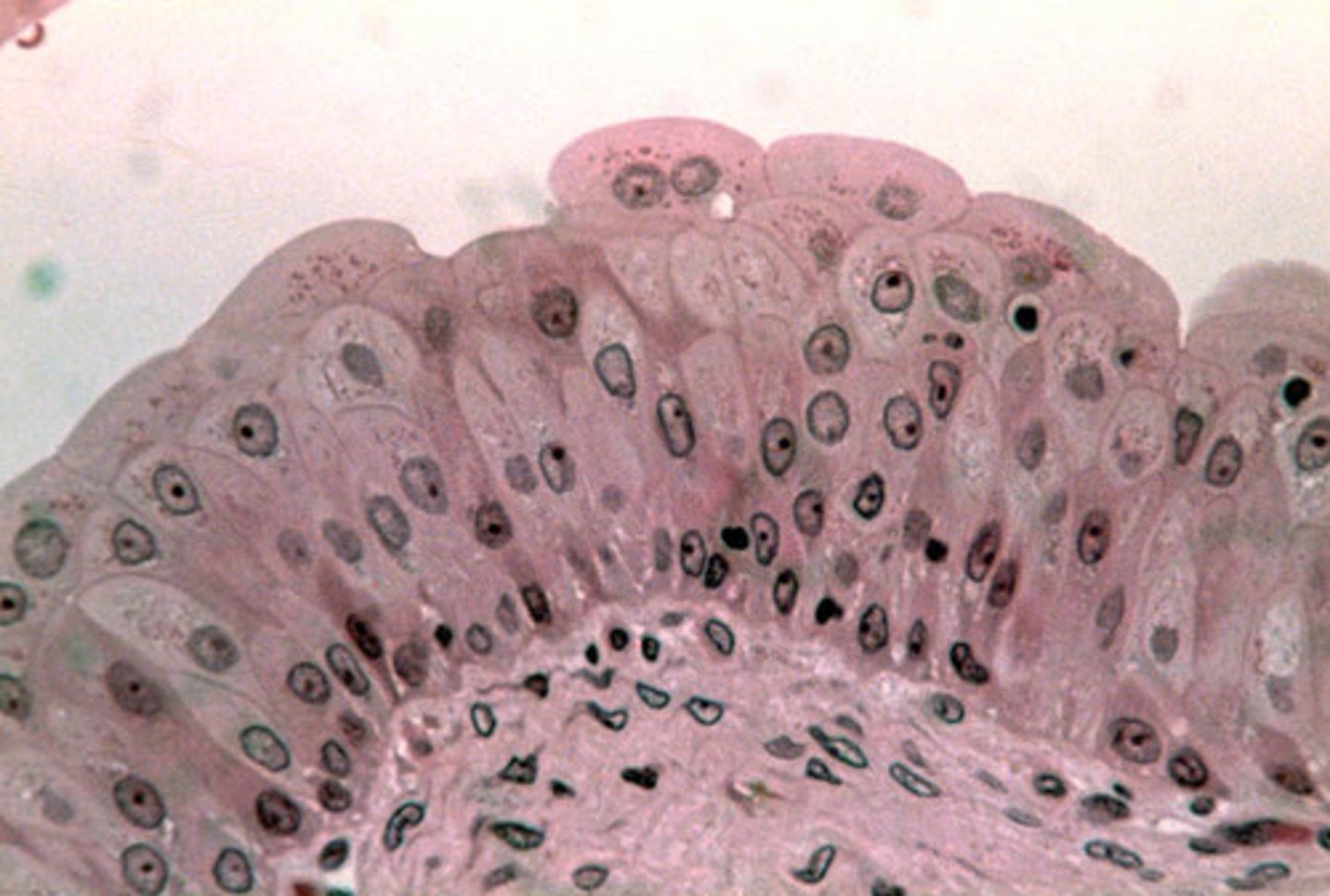
transitional epithelium function (and picture)
stretches readily and permits distension of urinary organ by contained urine; stretches and changes shape; urinary bladder
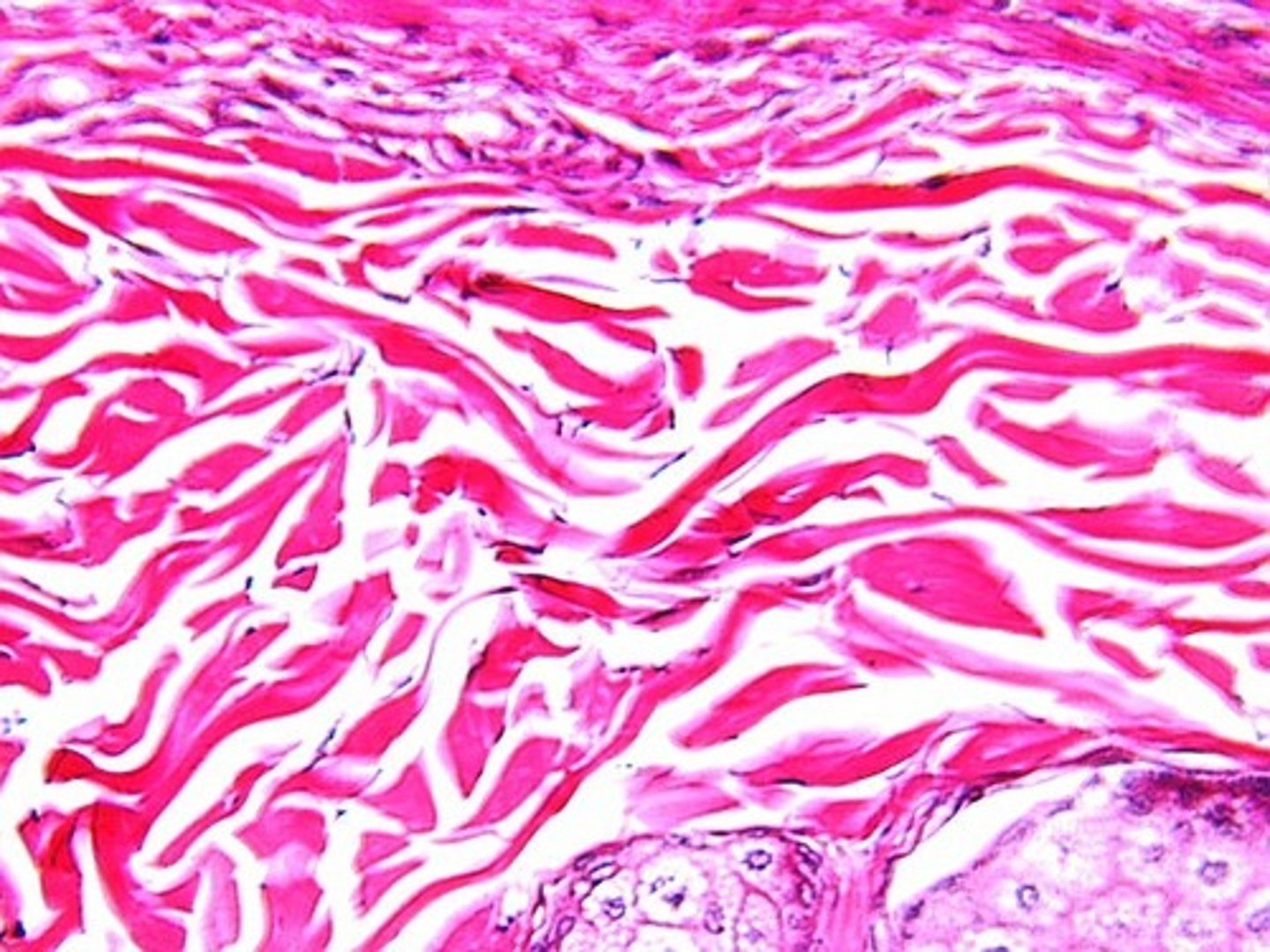
dense regular connective tissue
Function: attaches muscles to bones or to muscles; attaches bones to bones; withstands great tensile stress when pulling force is applied in one direction; densely packed containing parallel collagen fibers.
Location: tendons, most ligaments, aponeuroses
nerve tissue
star shaped cells with long cellular extensions
Haversian canal
one of a network of tubes running through compact bone that contains blood vessels and nerves
Osteocytes
mature bone cells
Chondrocytes
mature cartilage cells
Adipocytes
fat cells that make up most of the subcutaneous layer
Fibroblasts
In loose connective tissue, cells that secrete the proteins of the fibers.
Bone (osseos tissue)
stores calcium and other minerals
elastic cartilage
cartilage with abundant elastic fibers; more flexible than hyaline cartilage; found in the external ear.
hyaline cartilage
Most common type of cartilage; it is found on the ends of long bones, ribs, and nose; collagen fibers appear faint (purplish)
elastic cartilage
external ear, epiglottis
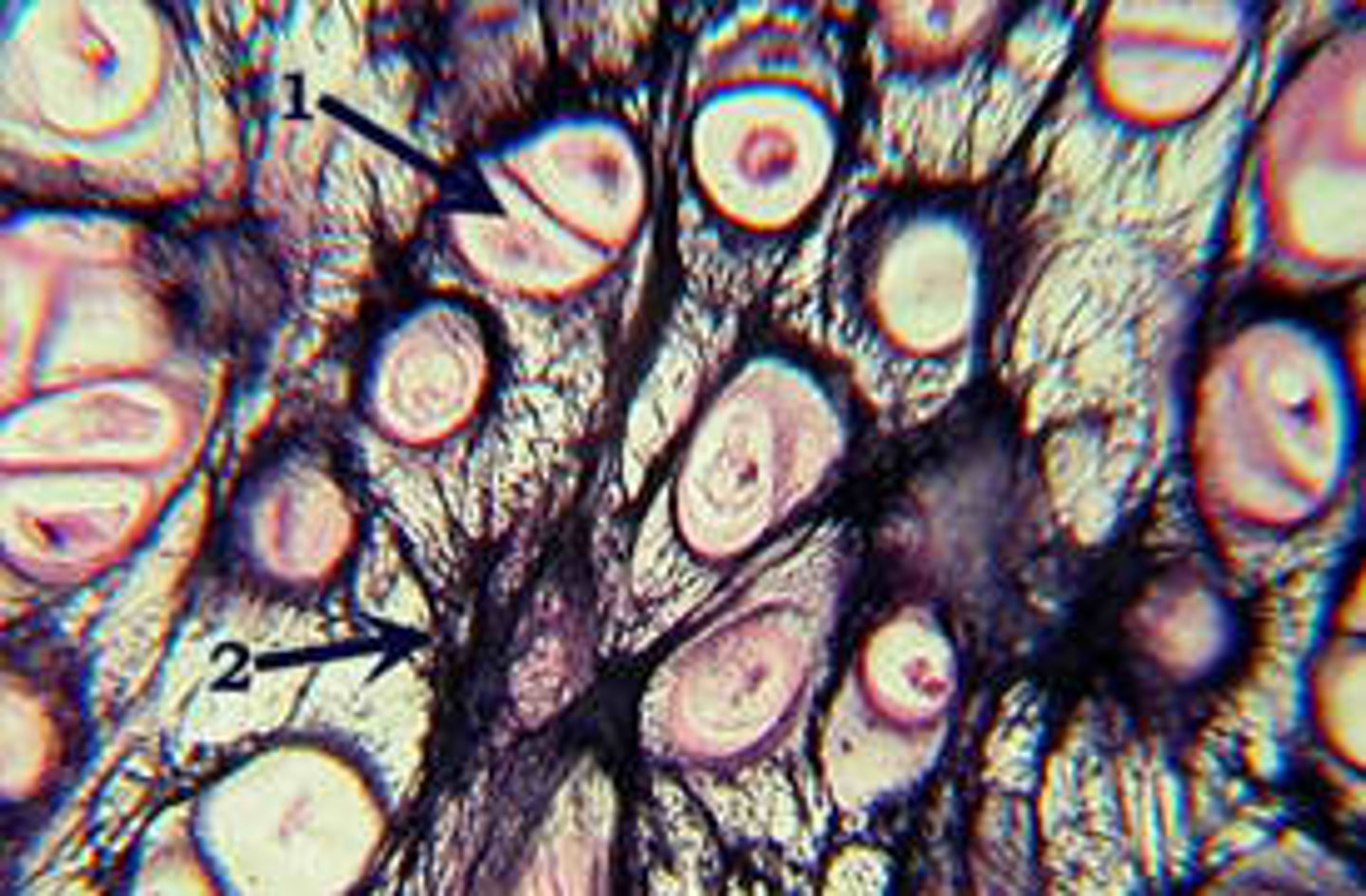
aerolar connective tissue
soft packaging material that cushions and protects body organs
intercalated discs
Attachment sites between the transverse lines between cardiac muscle cells; responsible for cell to cell communication.