4 - ANATOMY OF THE ABDOMEN (BRS) 2025
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
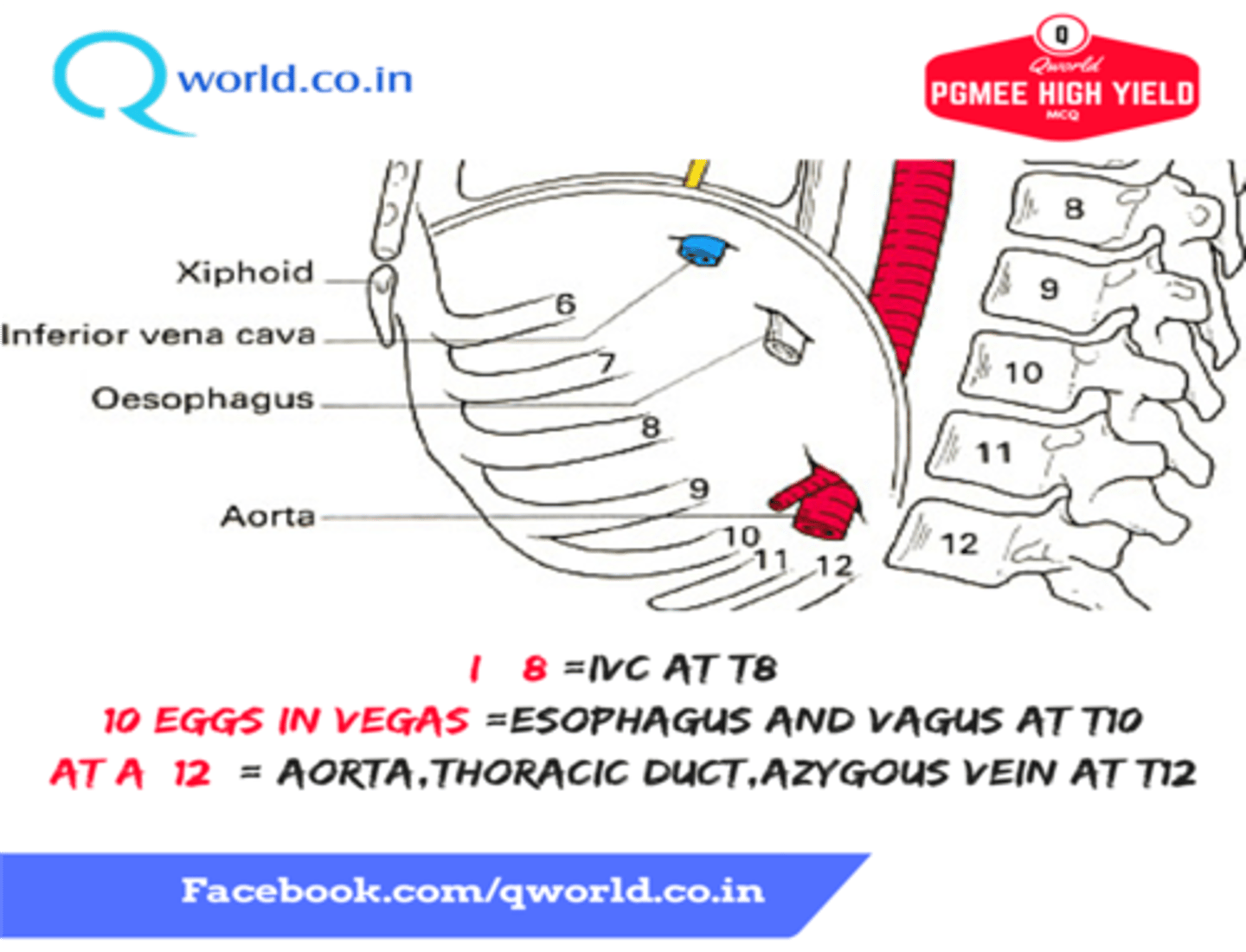
What structures pass through the aortic hiatus of the diaphragm
-Aorta
-Thoracic duct
-Azygos vein
-Greater splanchnic nerve
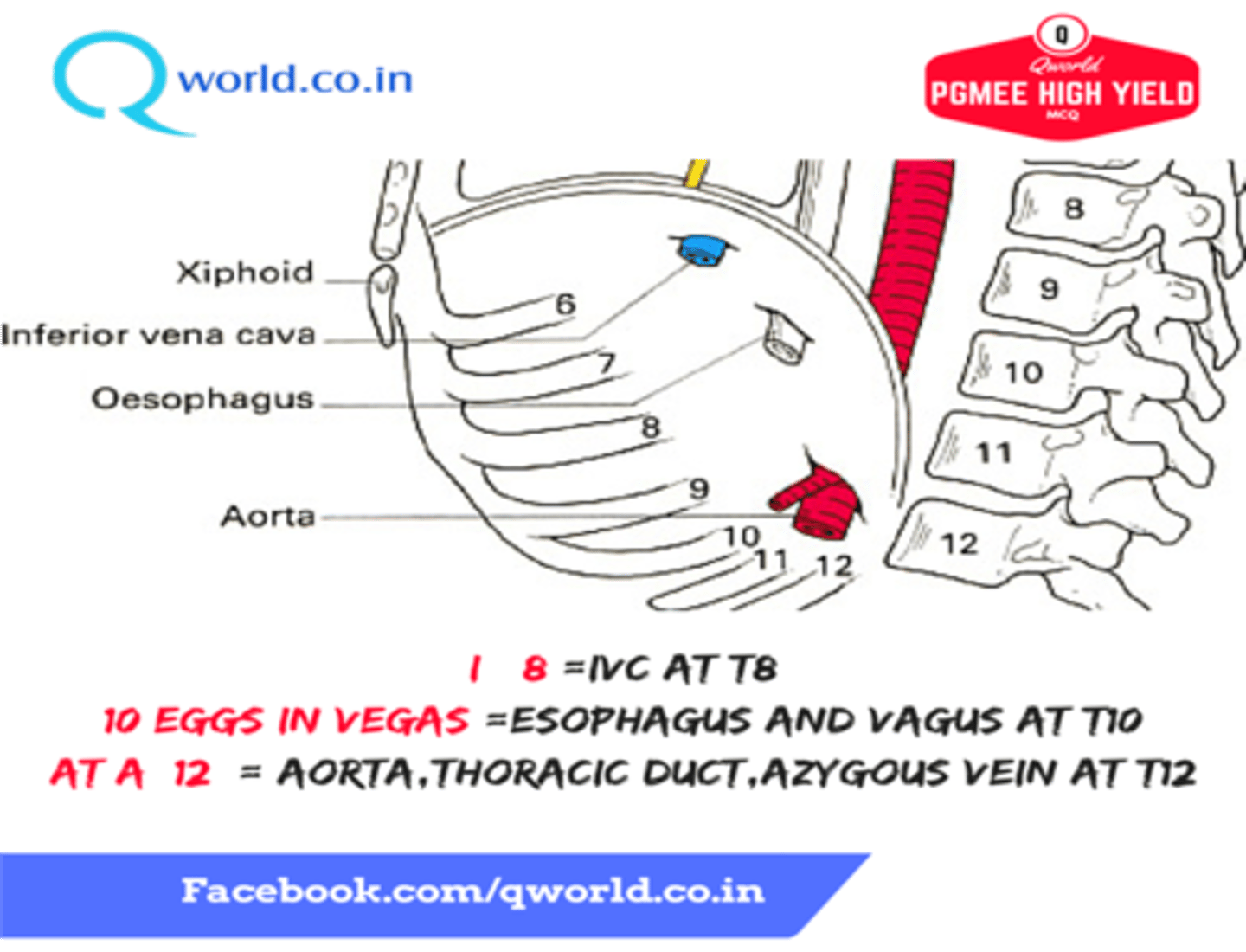
What structures pass through the esophageal hiatus of the diaphragm
-Esophagus
-Anterior and posterion trunks of the vagus nerve
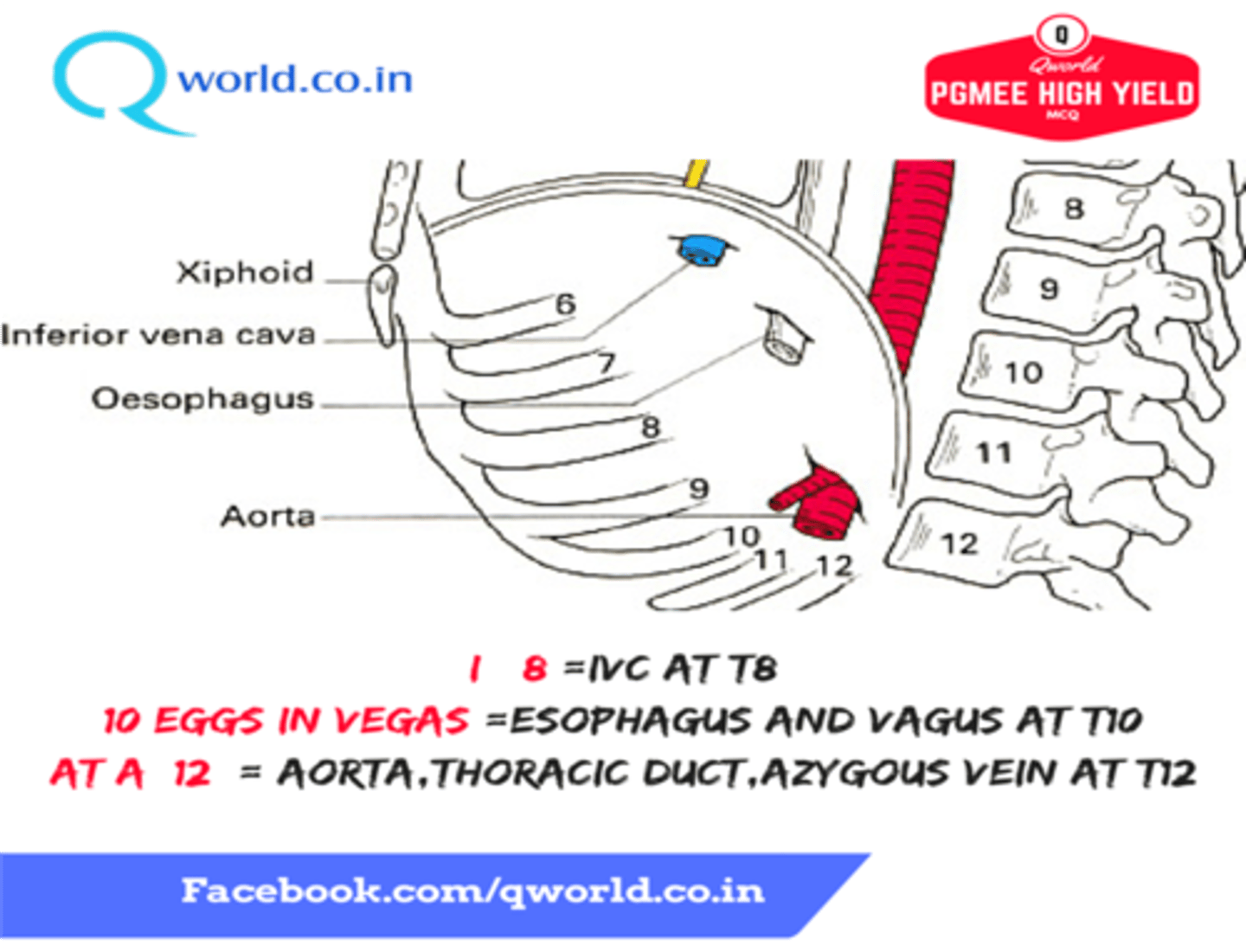
What structures pass through the vena caval hiatus of the diaphragm
-Inferior Vena Cava
-Right phrenic nerve
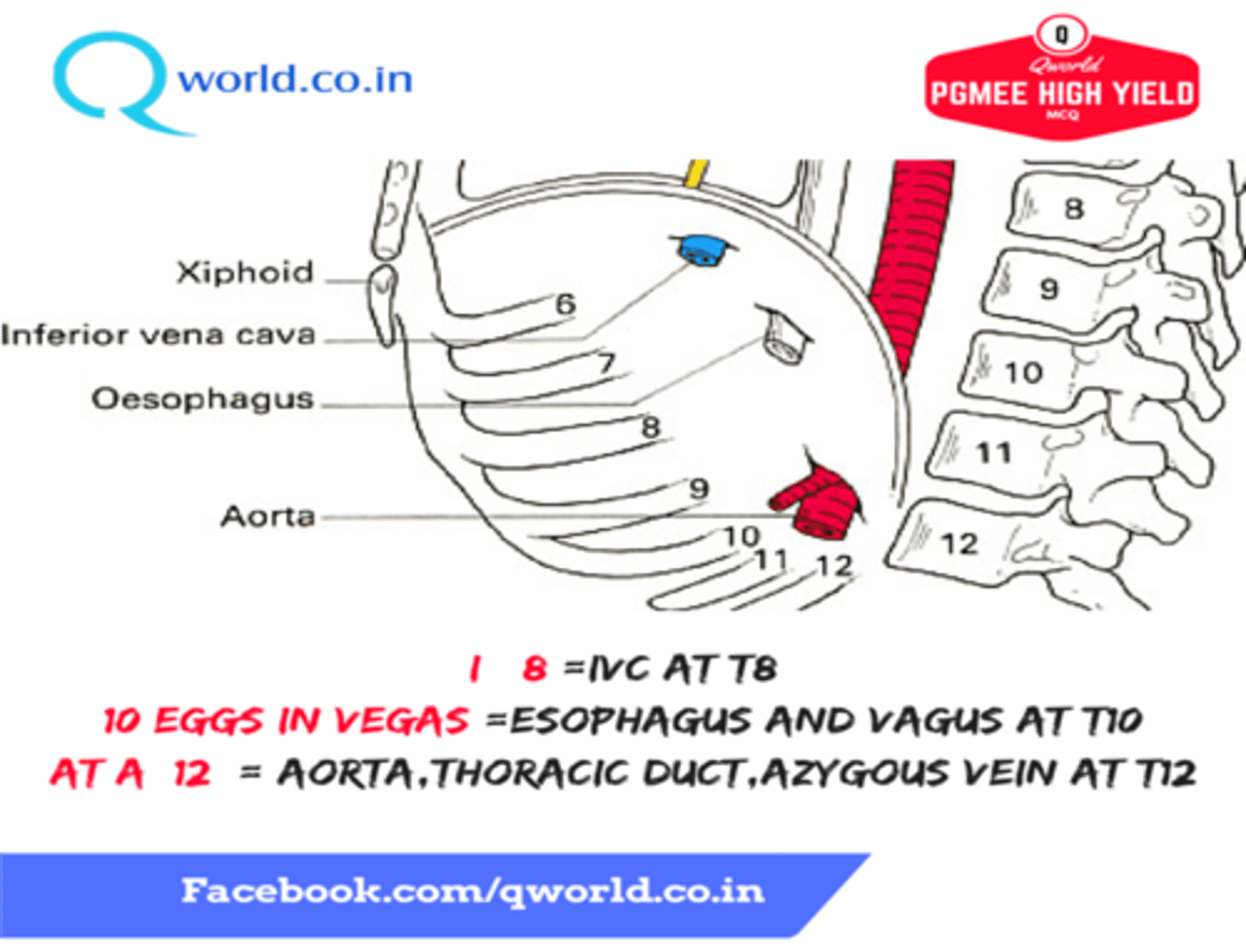
The vena caval hiatus lies in the central tendon of the diaphragm at what vertebral level?
T8
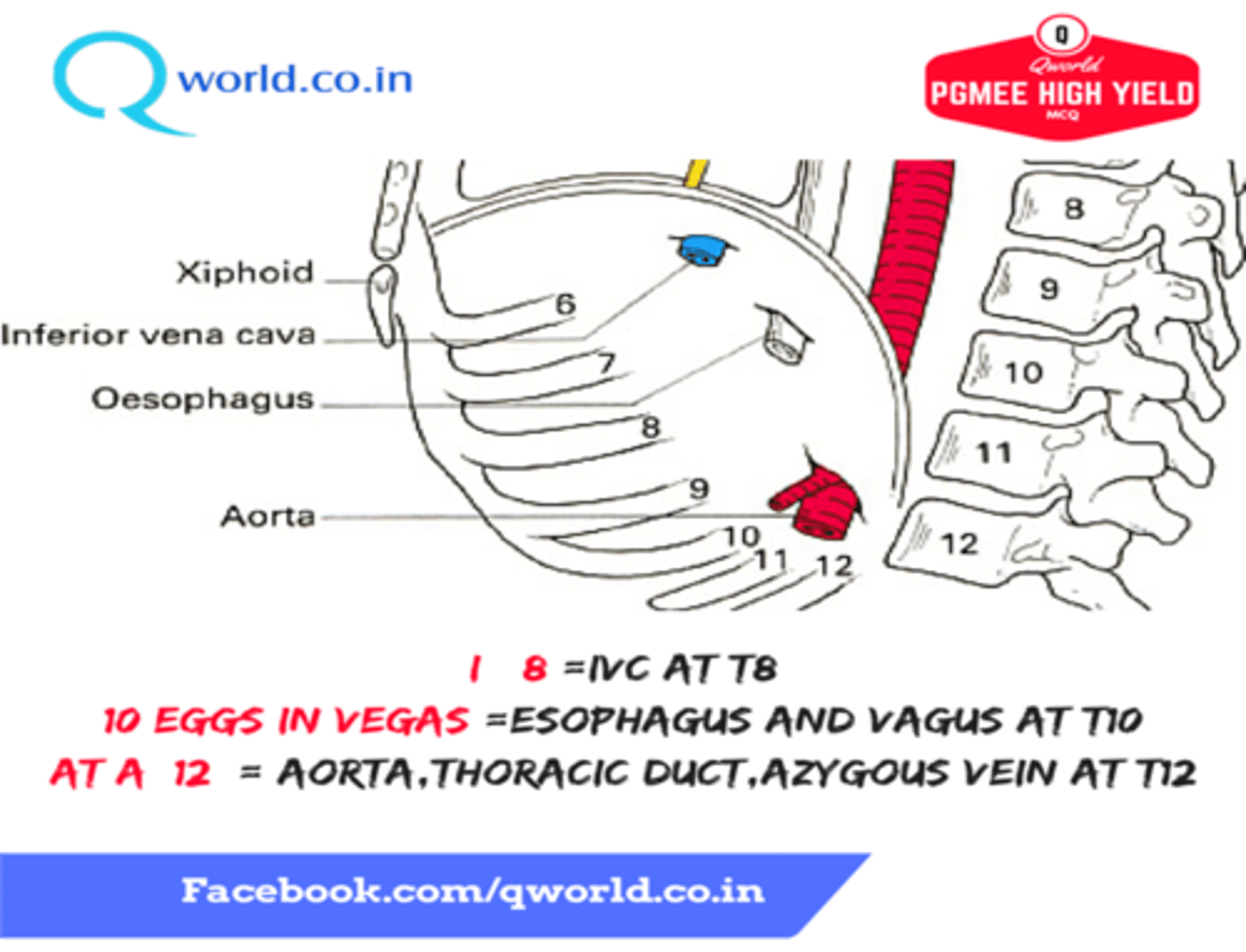
The esophageal hiatis lies in the muscular part (right crus) of the diaphragm at which vertebral level?
T10
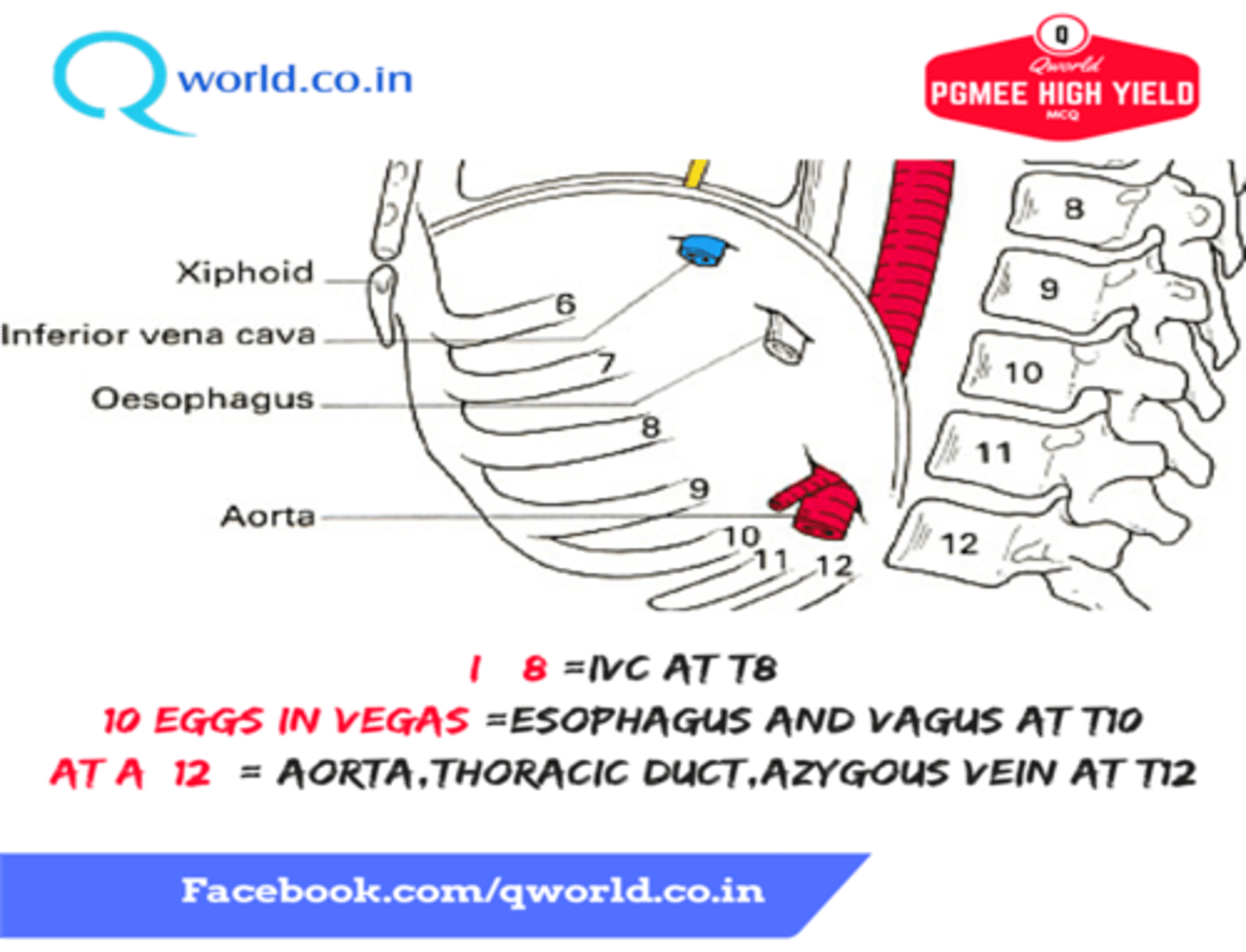
The aortic hiatus lies between the two crura of the diaphragm at which vertebral level?
T12
Which part of the pancreas is closely associated with the bile duct?
Head of the pancreas
The deep inguinal ring lies in which layer of the anterior abdominal wall?
Transversalis fascia
The deep inguinal ring lies lateral to what vessels?
Inferior epigastric vessels
The superficial inguinal ring is located in the aponeurosis of what muscle of the anterior abdominal wall?
External oblique muscle
The aponeurosis of what muscle forms the inguinal ligament and the anterior wall of the inguinal canal?
External oblique muscle
Which portion of the gallbladder is in contact with the transverse colon?
Fundus of the gallbladder
The fundus of the gallbladder is in contact posteriorly with which portion of the large intestine?
Transverse colon
Which portion of the gallbladder is in contact with the duodenum?
Body of the gallbladder
The body of the gallbladder is in contact posteriorly with what structure?
Duodenum
The retroperitoneal organs can be remembered by the mnemonic SAD PUCKER
S - Suprarenal (Adrenal) Glands
A - Aorta + Inferior Vena Cava
D - Duodenum (2nd and 3rd segments)
P - Pancreas
U - Ureters
C - Colon (Ascending + Descending)
K - Kidneys
E - Esophagus
R- Rectum
What is the only organ that directly receives preganglionic sympathetic fibers?
Adrenal (Suprarenal) gland
Which layer of the adrenal gland secretes norepinephrine?
Adrenal medulla
This condition is caused by absence of enteric ganglia in the lower part of the colon leading to dilatation of colon proximal to the inactive segment?
Hirschsprung disease (Aganglionic megacolon)
The left umbilical vein becomes the __________ of the liver after birth
Round ligament
The ___________ does not leave a fibrous remnant because it degenerates during early embryonic period
Right umbilical vein
The right and left hepatic veins drain into the ___________
Inferior Vena Cava
The right gastroepiploic vein drains into the ___________
Superior mesenteric vein
The left gastroepiploic vein drains into the _________
Splenic vein
This is the longest part of the duodenum
Transverse (Third) Part
The transverse part of the duodenum cross 3 structures (from right to left)
-IVC
-Aorta
-Vertebral column
The __________ cross the transverse part of the duodenum anteriorly
Superior mesenteric vessels
What is the afferent limb of the cremasteric reflex?
Femoral branch of genitofemoral nerve
What is the efferent limb of the cremasteric reflex?
Genital branch of genitogemoral nerve
Parasympathetic nerves to the ascending and transverse colons are supplied by __________ nerve
Vagus nerve
Parasympathetic nerves to the descending and sigmoid colons are supplied by __________ nerve
Pelvic splanchnic nerve from sacral spinal nerves (S2-S4)
What condition causes diversion of blood from the portal to the caval system?
Portal hypertension
The adrenal (suprarenal) gland is supplied by the superior, middle and inferior suprarenal arteries. From what respective arteries do these arteries arise?
-Superior Suprarenal Artery from Inferior Phrenic Artery
-Middle Suprarenal artery from Abdominal Aorta
-Inferior Suprarenal Artery from Renal Artery
The left gastroepiploic artery runs through what ligament?
Lienogastric/Gastrosplenic ligament
The splenic artery is found within what ligament?
Lienorenal ligament
The right and left gastric arteries are located within what structure?
Lesser omentum
The diaphragm is supplied by which nerves?
Phrenic nerves
Sensation from the central part of the diaphragm is perceived through what nerves?
Phrenic nerves
The peripheral part of the diaphragm receives sensory fibers from what nerves?
Lower intercostal nerves
What nerve supplies sensory fibers to the peritoneum inferior to the diaphragm?
Subcostal nerve
What are the three branches of the splenic artery?
Pa - Dorsal Pancreatic Artery
Gas - Short Gastric Arteries
Gas - Left Gastroepiploic (Gastro-omental) Arteries
What is located at the junction of the lateral one-third of the line between the umbilicus and the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS)
McBurney Point
What nerve is located near the McBurney point and is located between the internal oblique and transverse abdominal muscles
Iliohypogastric nerve
Jejunum/Ileum: Which contains more mesenteric arterial arcades?
Ileum
Jejunum/Ileum: Which has longer vasa recta?
Jejunum
Jejunum/Ileum: Which portion has tall and closely packed plicae circulares (circular folds)?
Jejunum
Jejunum/Ileum: More digestion and absorption of nutrients occur in this portion.
Jejunum
Jejunum/Ileum: Which has more fat?
Ileum
The right colic vein empties into what vein?
Superior mesenteric vein
The superior mesenteric vein joins what vein to form the portal vein?
Splenic vein
The splenic vein is joined by what vein to form the portal vein?
Superior mesenteric vein
The portal vein is formed by joining of what two veins?
-Splenic vein
-Superior mesenteric vein
What artery supplying the pancreas arises from the splenic artery and runs retroperitoneally along the superior border of the pancreas?
Dorsal pancreatic artery
Which part of the pancreas has a portion located intraperitoneally?
Tail of the pancreas
The proper hepatic artery runs within the free margin of which structure?
Lesser omentum
What artery runs within the transverse mesocolon?
Middle colic artery
What artery runs within the sigmoid mesocolon?
Sigmoid arteries
This anterior abdominal wall fold contains the remnant of umbilical artery
Medial umbilical fold
This anterior abdominal wall fold contains the remnant of the urachus
Median umbilical fold
This anterior abdominal wall fold contains the inferior epigastric vessels
Lateral umbilical fold
The medial umbilical fold contains the remnant of ____________
Umbilical artery
The median umbilical fold contains the remnant of __________
Urachus
The lateral umbilical fold contains the _____________
Inferior epigastric vessels
What structure contains the fibrous remnant of the ductus venosus?
Ligamentum venosum
The ligamentum venosum contains the fibrous remnant of what embryologic structure?
Ductus venosus
The fibrous remnant of the left umbilical vein is contained within what ligament?
Ligamentum teres hepatic
The ligamentum teres hepatic contains the fibrous remnant of which embryologic structure?
Left umbilical vein
3 veins that drain directly into the portal vein
-Splenic vein
-Superior mesenteric vein
-Left gastric (or coronary) vein
3 Tributaries of splenic vein
Pa - Pancreatic veins
Gas - Short gastric veins
Gas - Left gastroepiploic veins
3 Tributaries of the Superior Mesenteric Vein
-Middle colic vein
-Inferior pancreaticoduodenal vein
-Ileocolic vein
3 Tributaries of the Inferior Mesenteric Vein
Superior rectal vein
Sigmoid vein
Left colic vein
The lower abdominal wall, buttocks, penis, scrotum, labia majora and distal parts of vagina and anal canal drain directly into what group of lymph nodes?
Superficial inguinal lymph nodes
The testis, upper parts of vagina and anal canal drain directly into what group of lymph nodes?
Deep Inguinal Lymph Nodes
The caudate lobe drains bile into which hepatic ducts?
Right and left hepatic ducts
The liver receives blood from which 2 blood vessels?
Hepatic arteryPortal vein
The liver drains its venous blood into which blood vessel?
Hepatic vein
This structure is responsible for storing and concentrating bile?
Gallbladder
What 2 ducts combine to form the common bile duct
-Common hepatic duct
-Cystic duct
The sigmoid colon receives blood from what artery?
Inferior mesenteric artery
The sigmoid colon receives parasympathetic preganglionic fibers from what nerve?
Pelvic splanchnic nerve
The appendicular artery is a direct branch of __________ artery
Ileocolic artery
What arteries supply branches to the stomach?
-Splenic artery
-Gastroduodenal artery
-Left gastroepiploic artery
-Proper hepatic artery
What nerve carries pain fibers from the upper GI tract
Greater splanchnic nerve
Peristence of the middle portion of what fetal structure is responsible for the formation of congenital hydrocele
Processus vaginalis
Persistence of the entire processus vaginalis may lead to what condition?
Congenital indirect inguinal hernia
This fetal structure is a fetal ligament that is responsible for holding the bottom of the testis to the developing scrotum
Gubernaculum testis
This condition is characterized by the failure of the testis to descend from the abdomen to the scrotum
Cryptorchidism
Hematocele is the effusion of blood into the cavity of what structure?
Tunica vaginalis
3 structures contained in porta hepatis
-Hepatic ducts
-Hepatic arteries
-Branches of portal vein
Esophageal and gastric varices occur with dilatation of the portal-caval anastomosis between what two blood vessels?
Esophageal veinsGastric veins
Caput medusae occur with dilatation of the portal-caval anastomosis between what two blood vessels?
Paraumbilical vesselsEpigastric veins
Dilated retroperitoneal veins occur with dilatation of the portal-caval anastomosis between what two blood vessels?
-Inferior mesenteric vein tributaries
-Retroperitoneal veins
Rectal varices (hemorrhoids) occur with dilatation of the portal-caval anastomosis between what blood vessels?
Superior rectal veins
Middle and inferior rectal veins
What are the 7 rule of 2's of Meckel Diverticulum?
-Located 2 feet proximal to ileocecal junction on antimesenteric side
-Approximately 2 inches long
-Occurs in approximately 2% of population
-2 types of ectopic tissues (gastric and pancreatic)
-Presents in first 2 decades
-Most often in first 2 years
-2 times more likely in boys than girls
Which part of the pancreas is located behind the superior mesenteric vessels?
Uncinate Process
The uncinate process of the pancreas is located behind what blood vessels?
Superior Mesenteric Vessels
The superior pancreaticoduodenal artery runs between the duodenum and which part of the pancreas?
Head of the pancreas
What blood vessel is located between the duodenum and the head of the pancreas?
Superior pancreaticoduodenal artery
The portal vein runs behind which part of the pancreas?
Neck of the pancreas
Which blood vessel runs behind the neck of the pancreas?
Portal vein