Differential Staining - The Gram stain
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
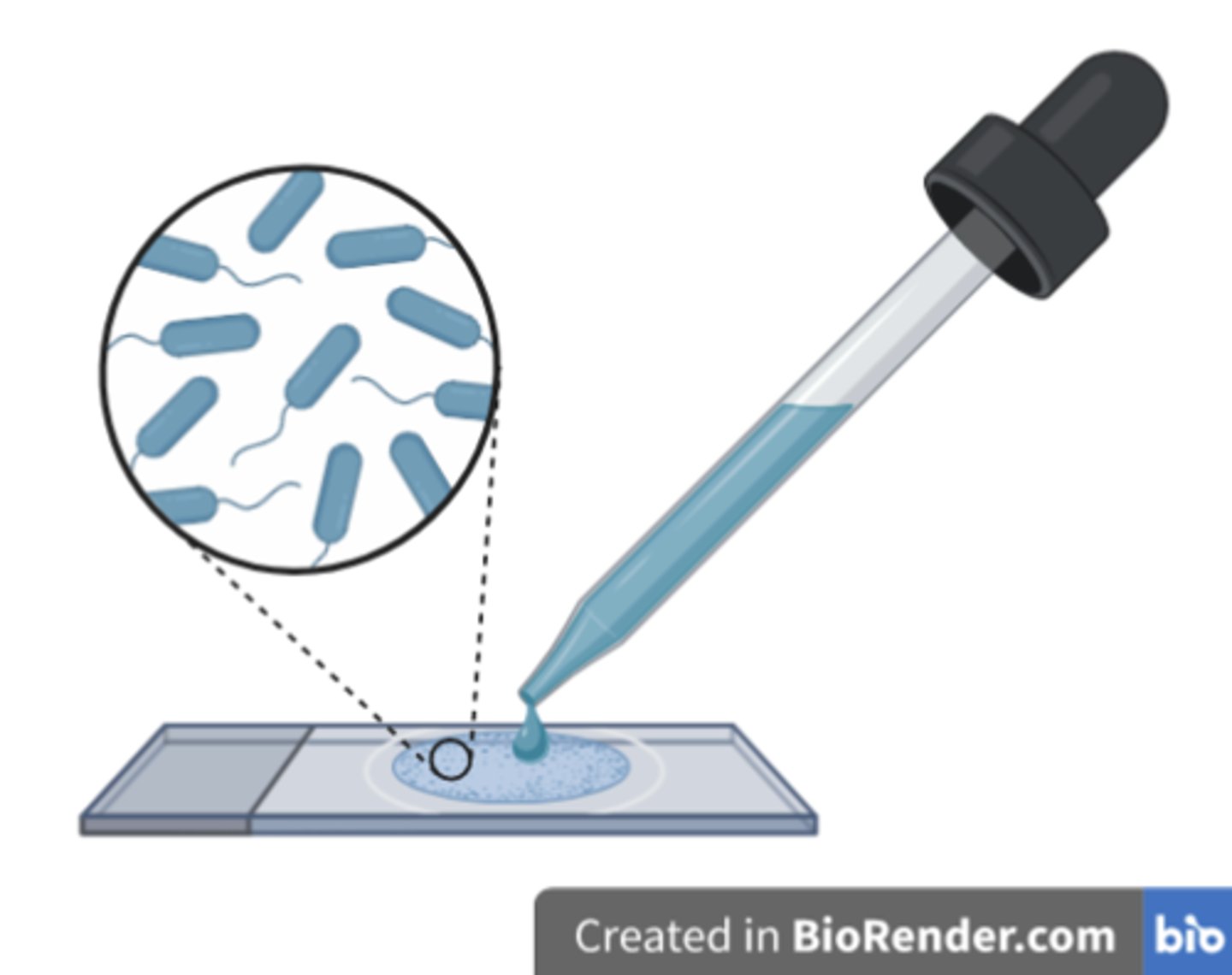
Why is it important to heat-fix your slide before the Gram stain procedure?
To kill and fix the microorganism to the slide by coagulating cellular protein.
The primary stain in the Gram stain procedure is
a) Methylene blue
b) Crystal violet
b) Crystal violet
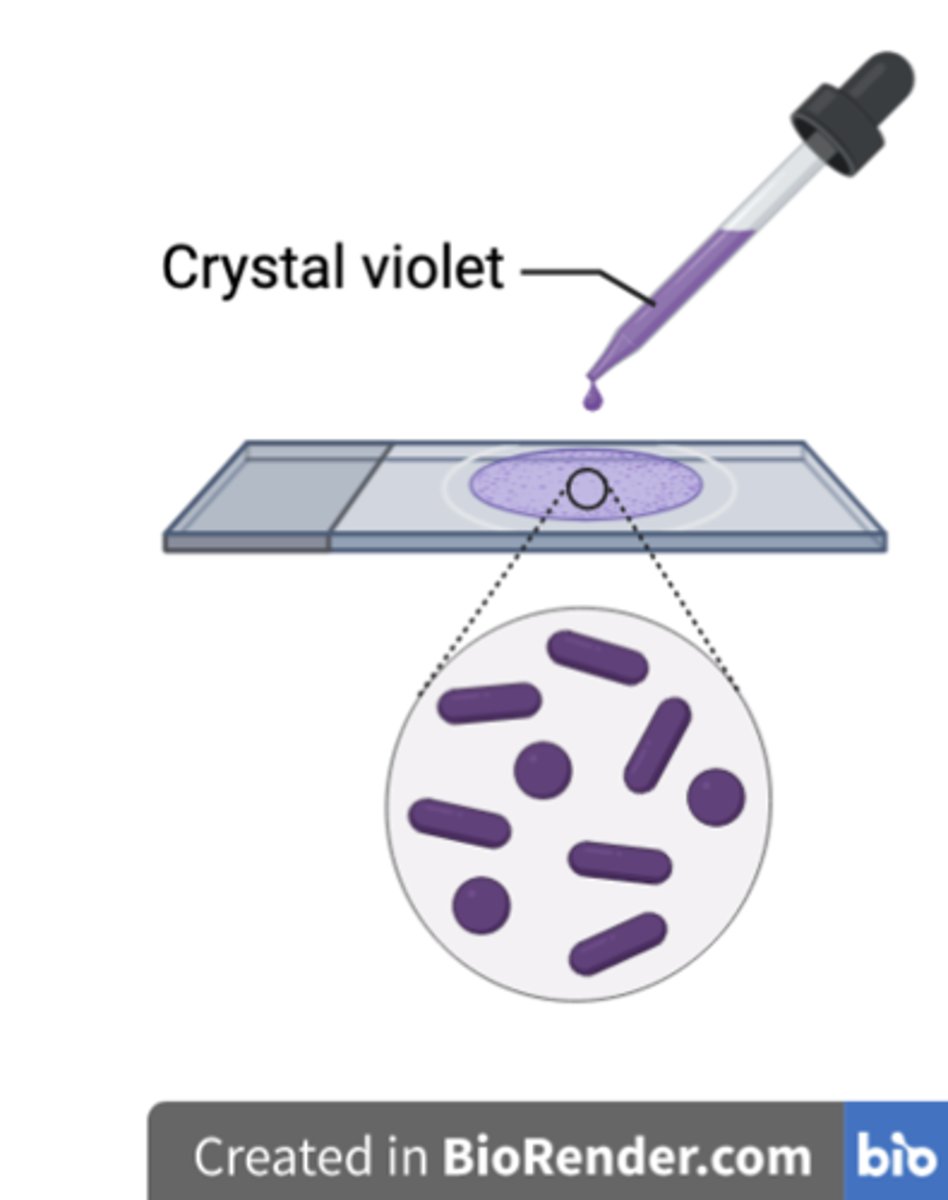
What are the four steps of Gram staining?
1. Crystal violet - the primary stain
2. Iodine - the mordant
3. Alcohol -decolorizer
4. Safranin -the counterstain

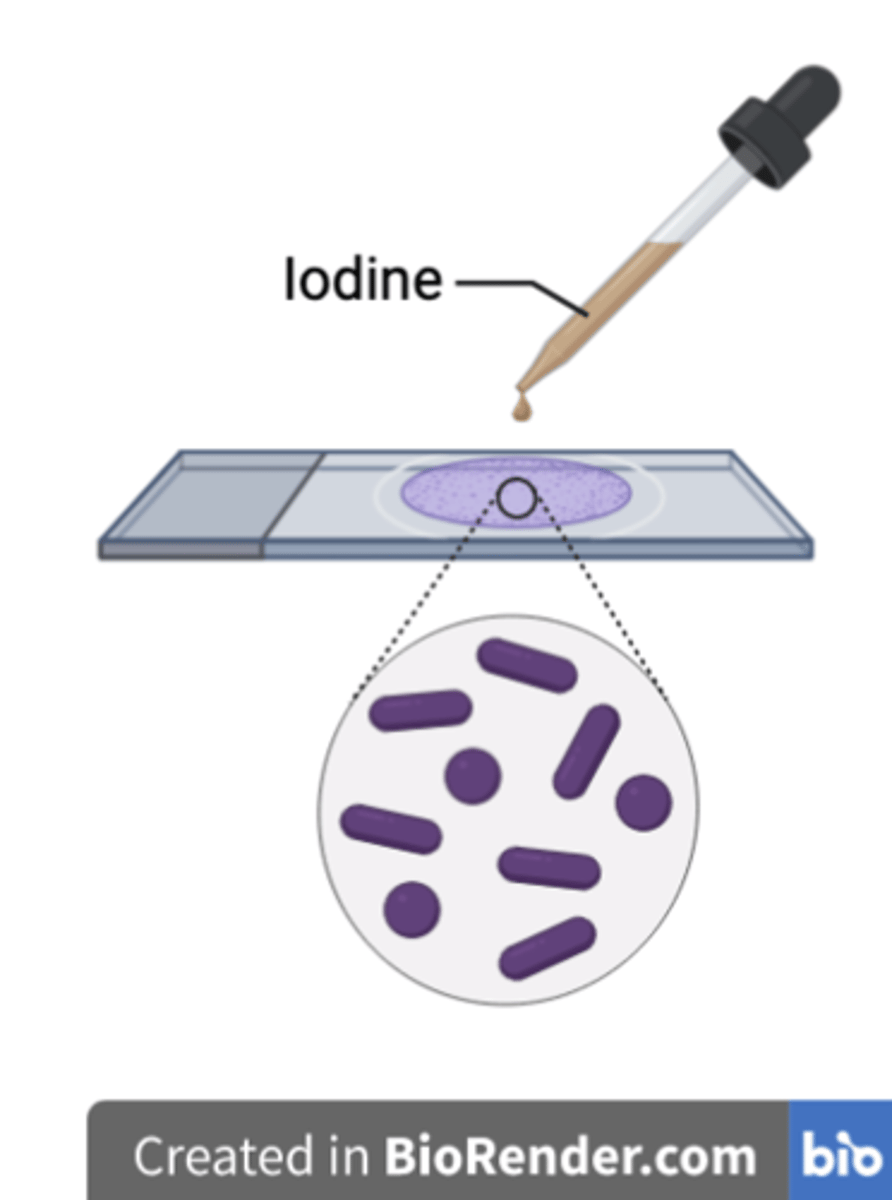
Why is iodine used after the Crystal violet step?
As a mordant, trapping the Crystal violet in the peptidoglycan wall by forming a larger complex together with it.
Why is alcohol the most important differentiating step in Gram stain?
1. Alcohol traps the Crystal violet and Iodine (CV-I) complex in the thick peptidoglycan layer of Gram positive cells, while
2. dissolving the outer lipopolysaccharide layer of Gram negative cells, allowing the CV-I complex to escape in the rinsing process
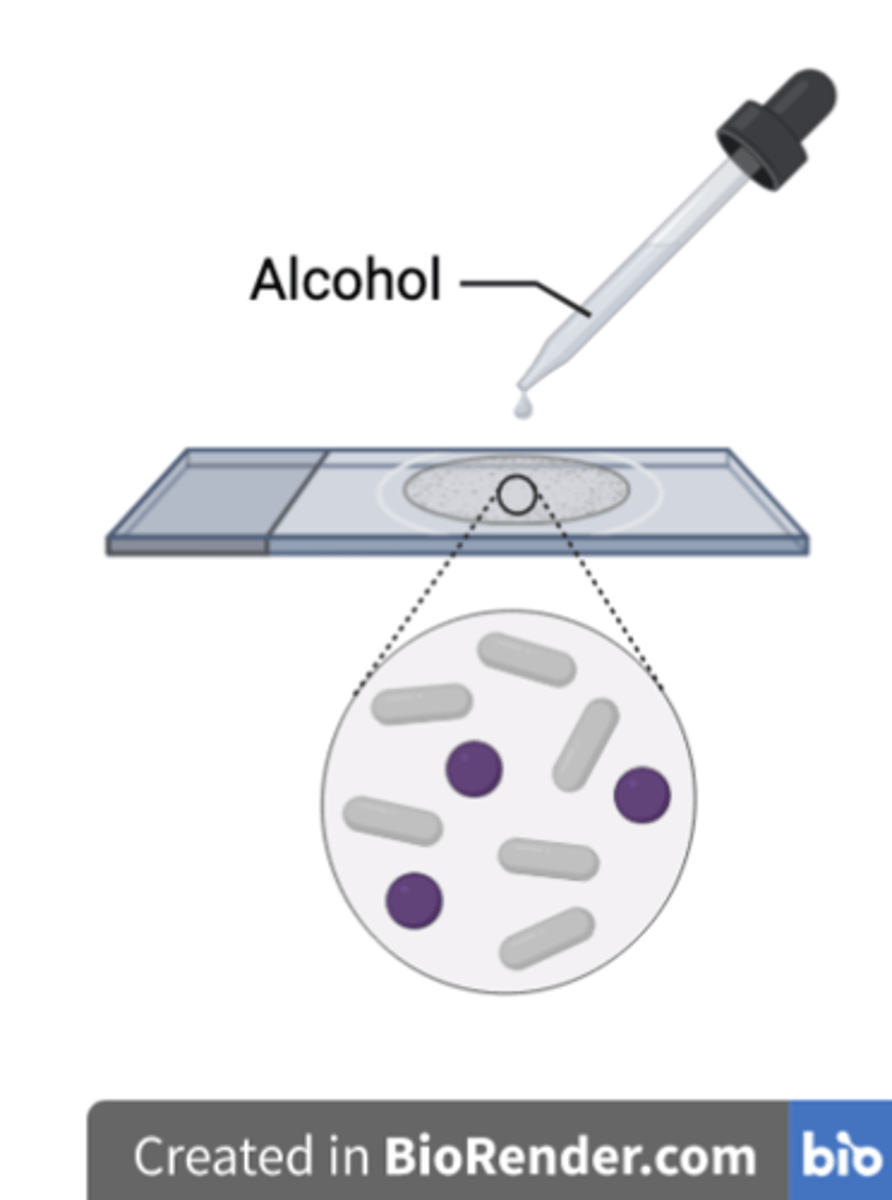
After rinsing with alcohol, what colour are
a) Gram negative cells
b) Gram positive cells?
a) Gram +, Purple
b) Gram -, Colourless
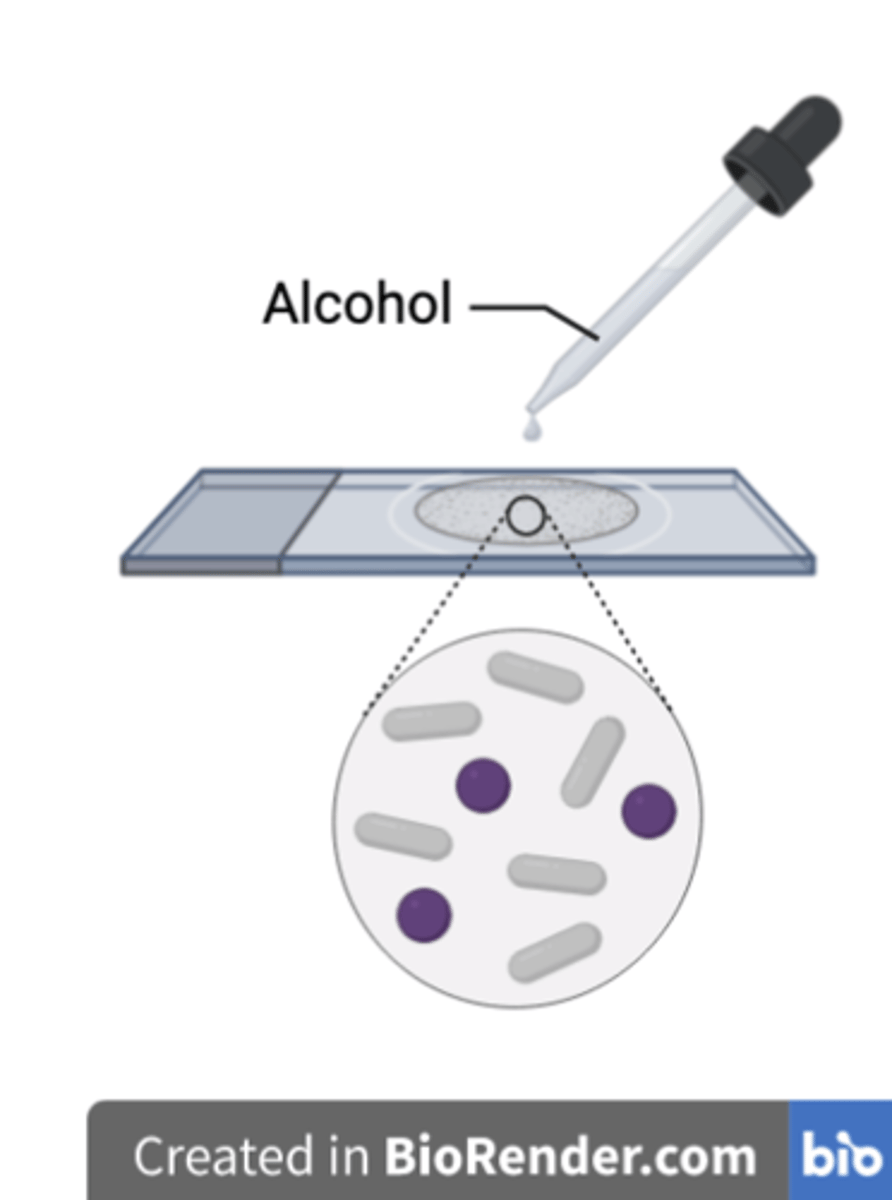
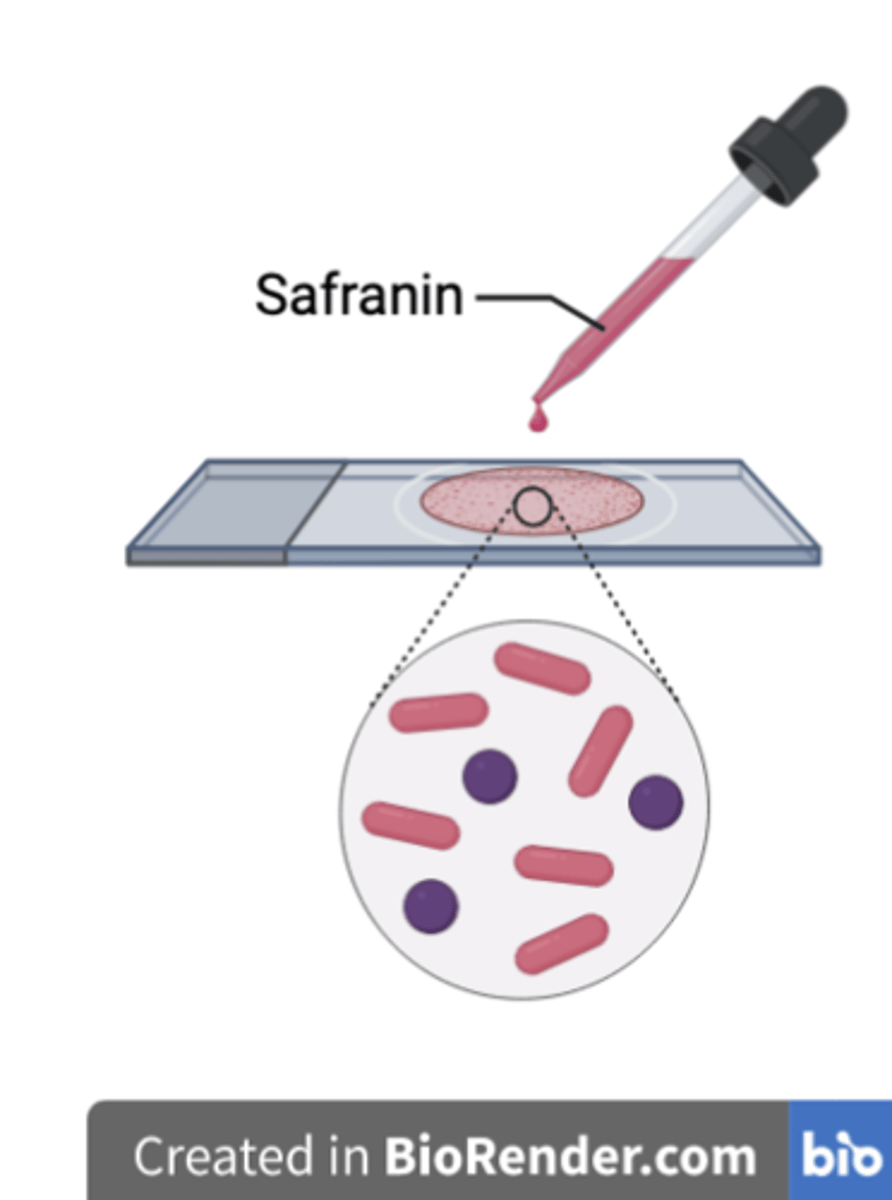
What is the purpose of counterstaining the cells after the alcohol step?
To dye the colourless Gram negative bacteria red/pink for differentiation from the Gram positive cells.
Which bacteria has a thicker peptidoglycan layer in their cell wall?
Gram positive
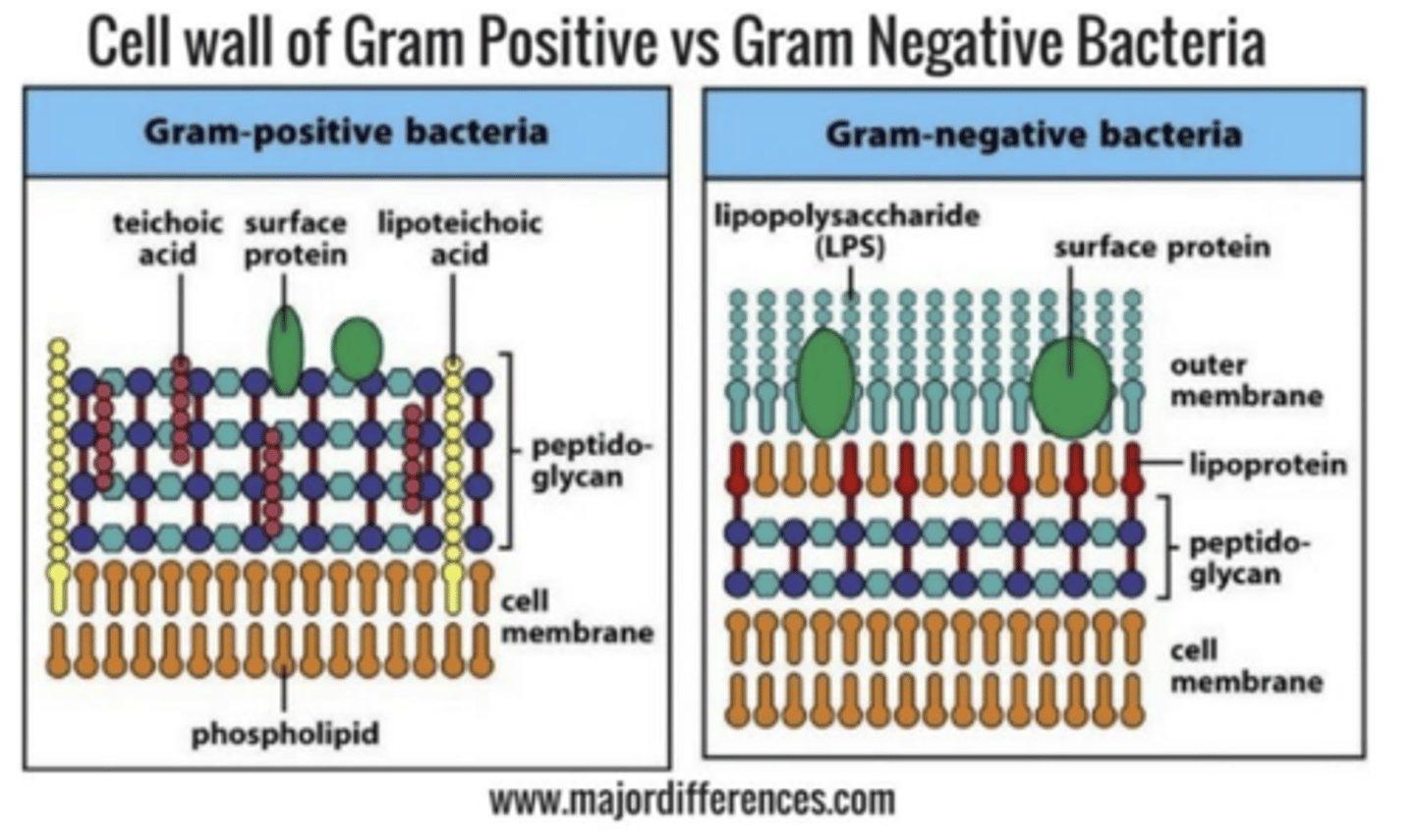
Which cell type has the ability to retain crystal violet dye after decolourisation with alcohol?
Gram positive cells (Purple)
True or false, stained red cells have the ability to retain the crystal violet.
a) True
b) False
False. Red cells (gram-negative) are unable to retain the crystal violet dye.
What is methylene blue used for?
As a simple stain, not in Gram staining.