Chap 9 Population Growth V2
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Population growth
Describes how the # of individuals in a population changes over time.
Individuals are added to a population through
births and immigration
(When individuals enter a subpopulation)
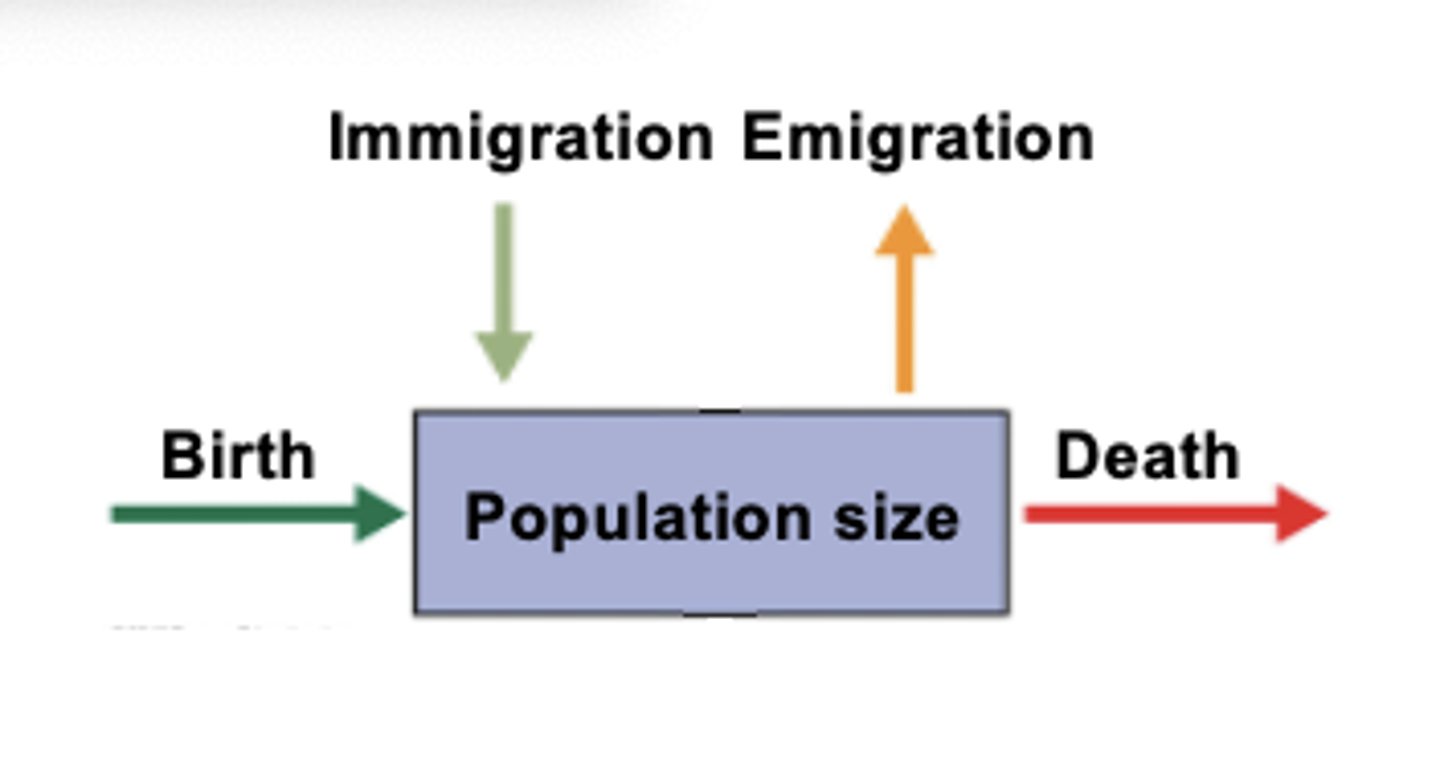
Individuals leave the population through
deaths and emigration
(When individuals leave a subpopulation)
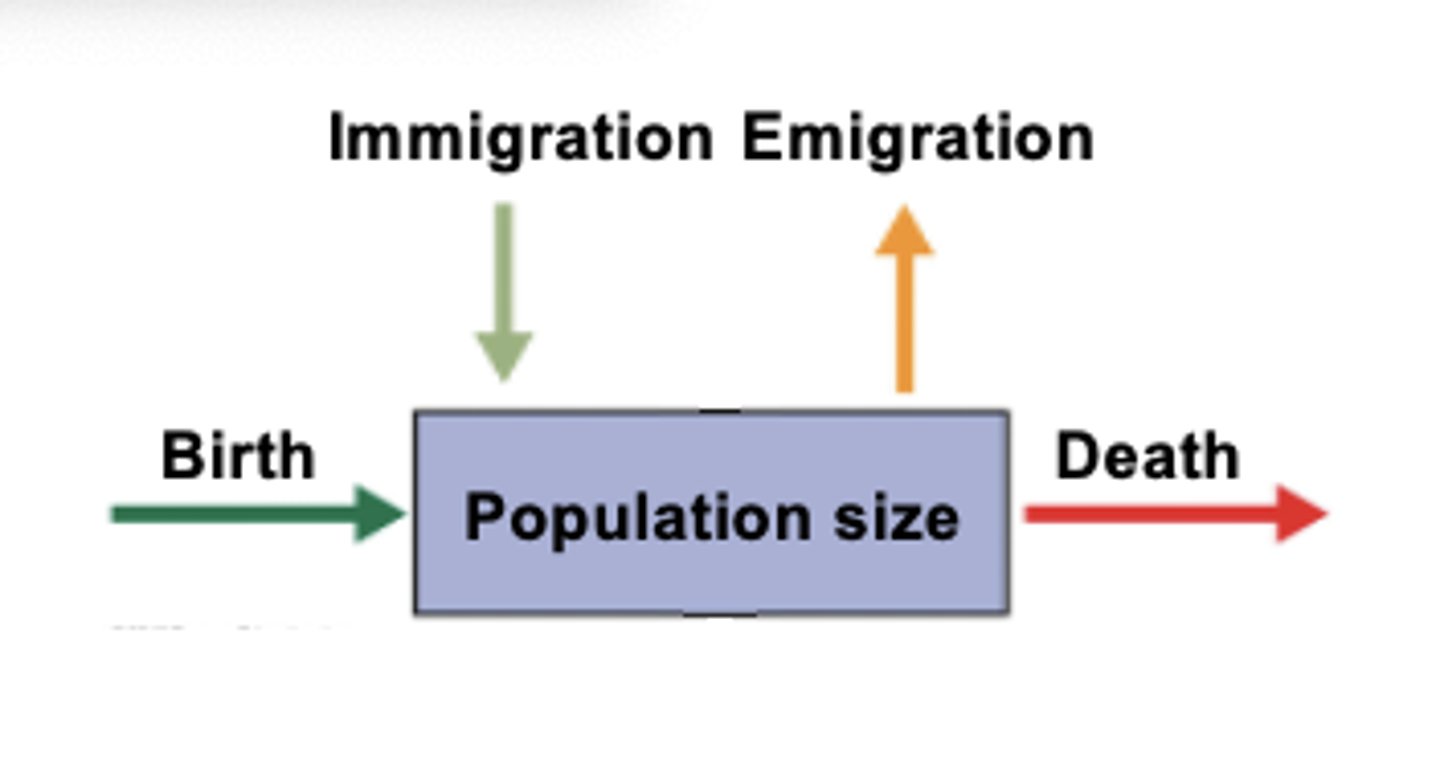
Open population
has immigration (entering) and emigration (leaving)

Closed population
does not have (or has a very low level of) immigration and emigration that doesn't influence population growth

Simple life cycle (example)
Monitor a population Hydra viridissima organisms under simple life cycle conditions
- Hydra in an aquarium (closed population)
- Most reproduction is asexual by budding
- Assume all Hydra's reproduce asexually and all have one offspring at a time
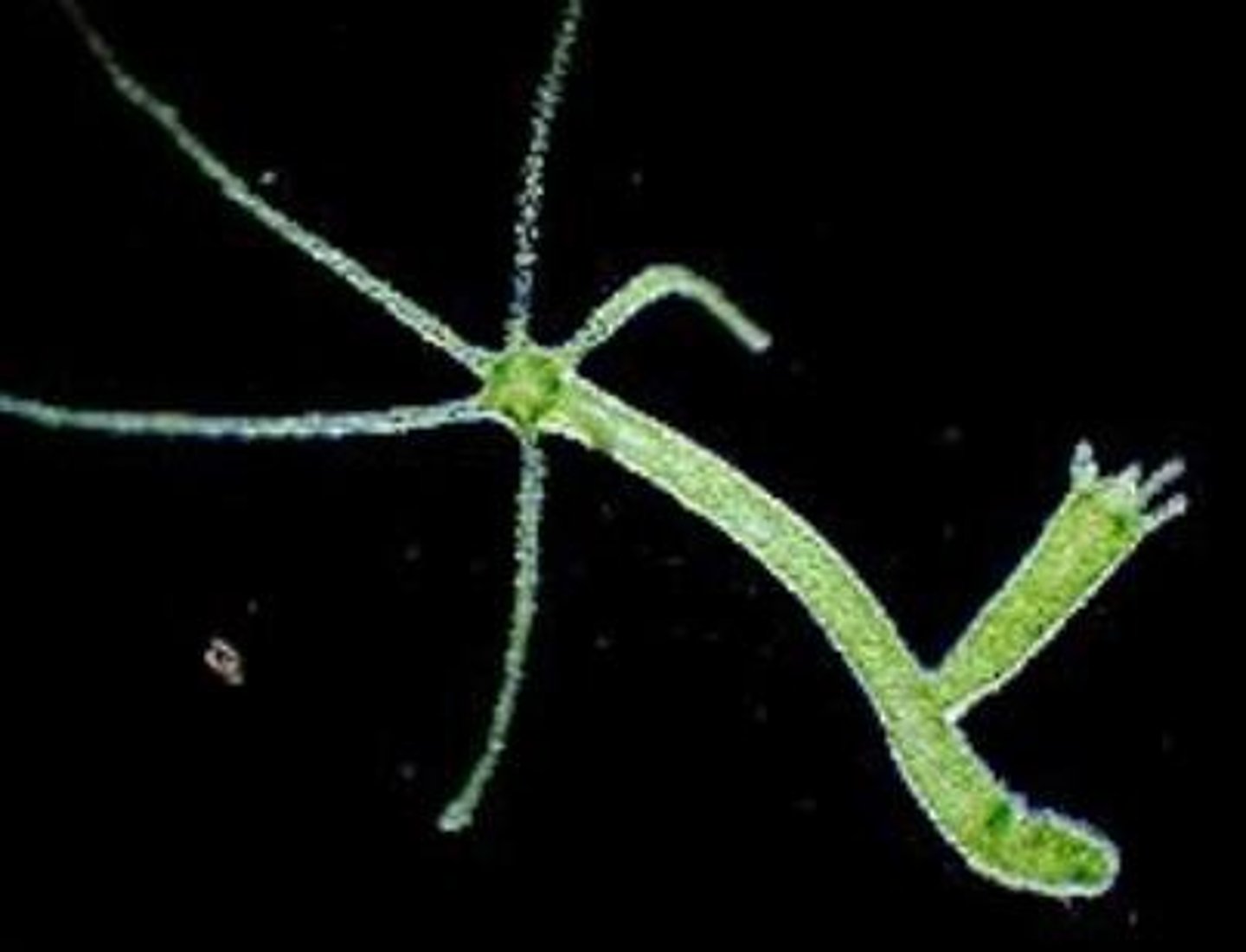

How will the hydra population size under simple life cycle conditions change over time?
hydra will probably continue growing as they will show no emigration or death
N=
the number of individuals in a population

N(t)=
Number of individuals in the population at a given time, t

t=
time

If the initial population size is 100 at time zero (day zero t= 0)
N(0)= 100
-------------------
If N is much lower than the available food supply on the environment, how will the population change over time?

If N is much lower than the avialable food supply on the environment, how will the population change over time?
If N (the number of individuals in a population) is lower than the available food, then population will have no trouble finding resources and it will probably expand if predation is not taken into account.
B=
number of new individuals produced (birthed each time interval)
D=
Number of individuals that die each time interval
In a closed population (B & D) EXAMPLE
B = 40, D = 10 each day
B and D determine the change in population size.
--------------------
N(0) + B - D= N1
100 + 40 - 10 = 130
--------------------
actual number of births and deaths depends on population size. (which changes over time)
An estimate that is independent of population size can be expressed as a rate, rather than an absolute number.
used to determine the
- per capita birthrate
- per capita death rate, d
--------------------
Since b and d are constant, they can be used to define a new parameter:
- The per capita growth rate of the population ( r= b-d)
per capita birth rate
b= B/N(0)
--------------------
EXAMPLE
- let B=40 and N(0) = 100
40/100 = 0.4
per capita death rate
d = D/N(0)
--------------------
EXAMPLE
- let D=10 and N(0) = 100
10/100 = 0.1
Exponential population growth model
dN/dt = rN
--------------------
This is differential equation can integrated and the resulting equation can be used to predict population size under conditions of exponential growth at any value of t
* Can insert value for t equal 1 day, 1 year, or 1 sec
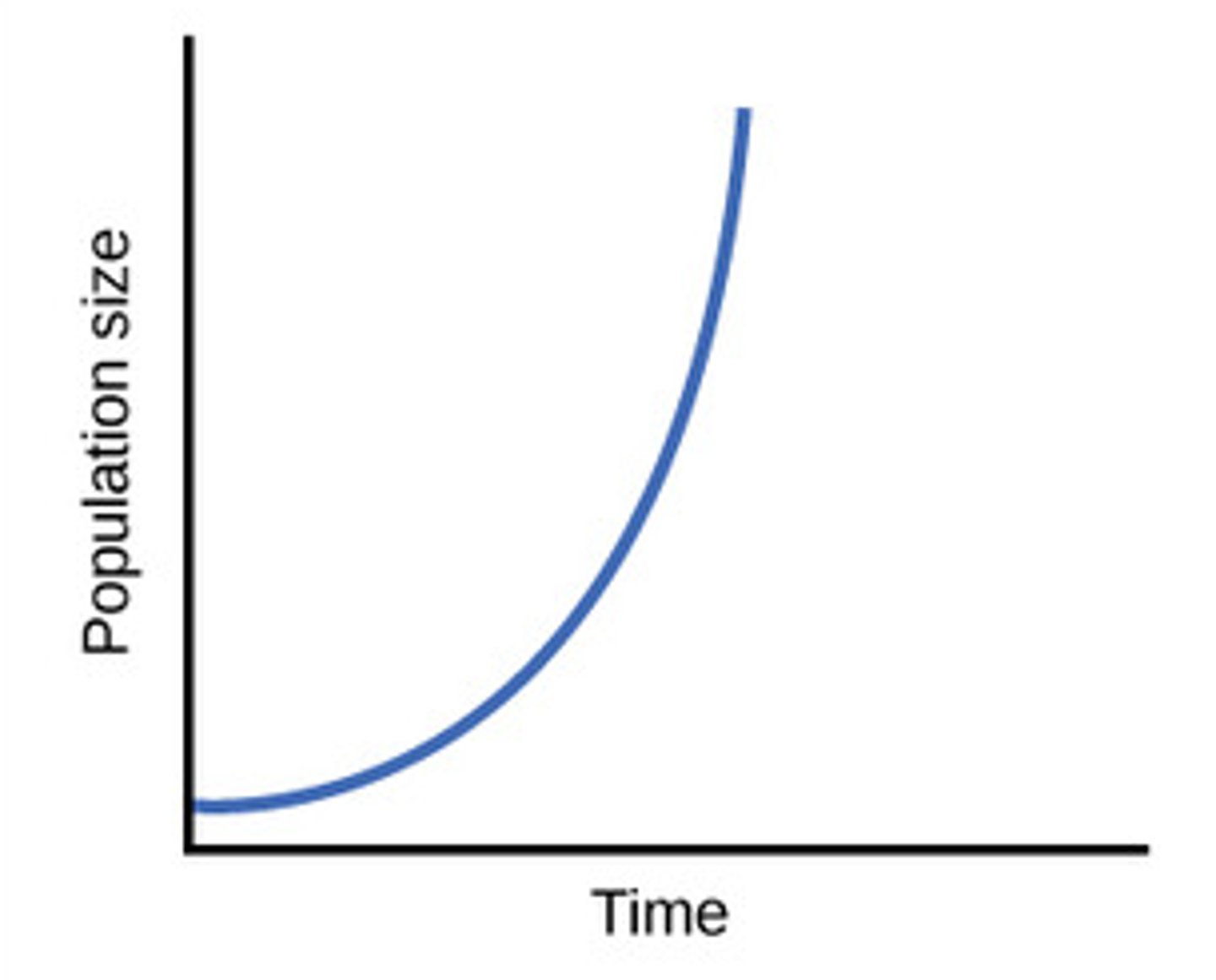
r= (exponential population growth model)
the instantaneous per capita rate of growth
- this is the rate that is intrinsic to the population
N(t)= N(0)e^rt
N(t)= number of individuals after t time units
--------------------
N(0)= initial population size at t=0
e = base of the natural logarithm, approx. (2.72)
r = Intrinsic rate of growth rate of the population.

When r= 0
What is the relationship between b and d?
What happens to the size of the population?
e(rt)= e(0)= 1,
so... N(t)= N(0).. b=d
Population growth is zero

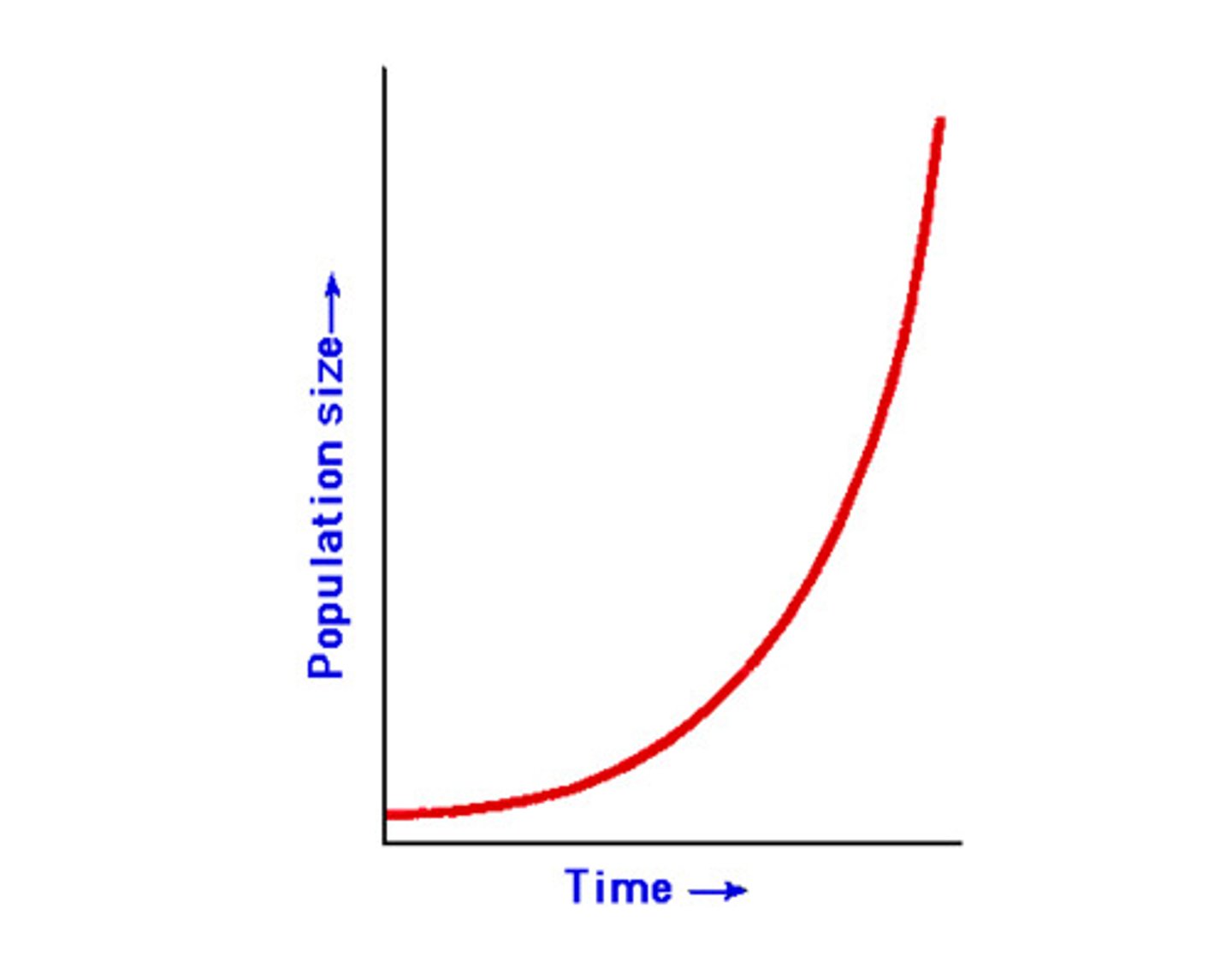
Exponential growth results in
in a continuously accelerating or decelerating rate of population growth as a function of population size.
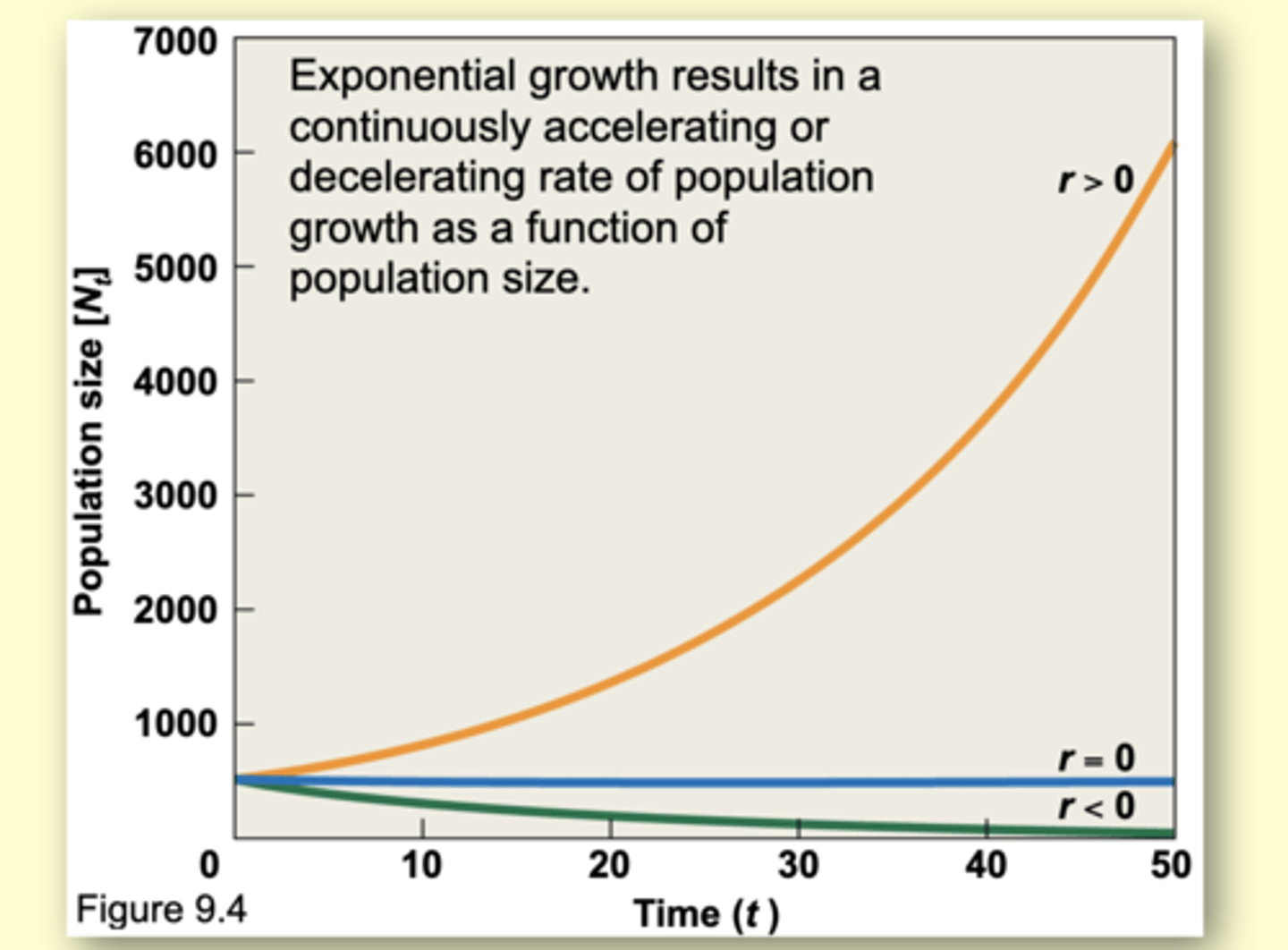
Populations that show positive exponential growth generally
- Live in favorable environments
- Are at low population densities
these (positive) conditions are present during
the process of colonization and establishment in new environments
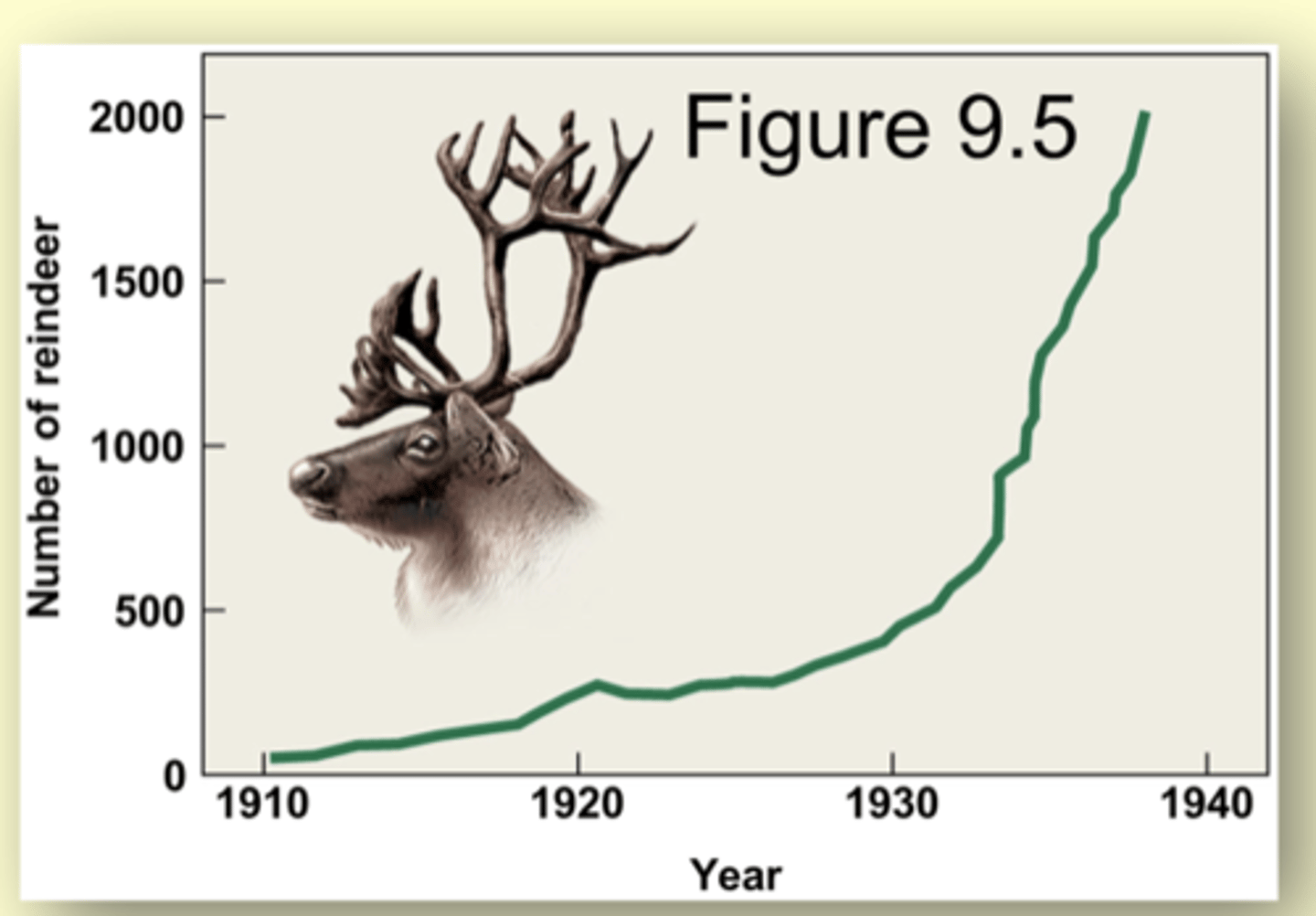
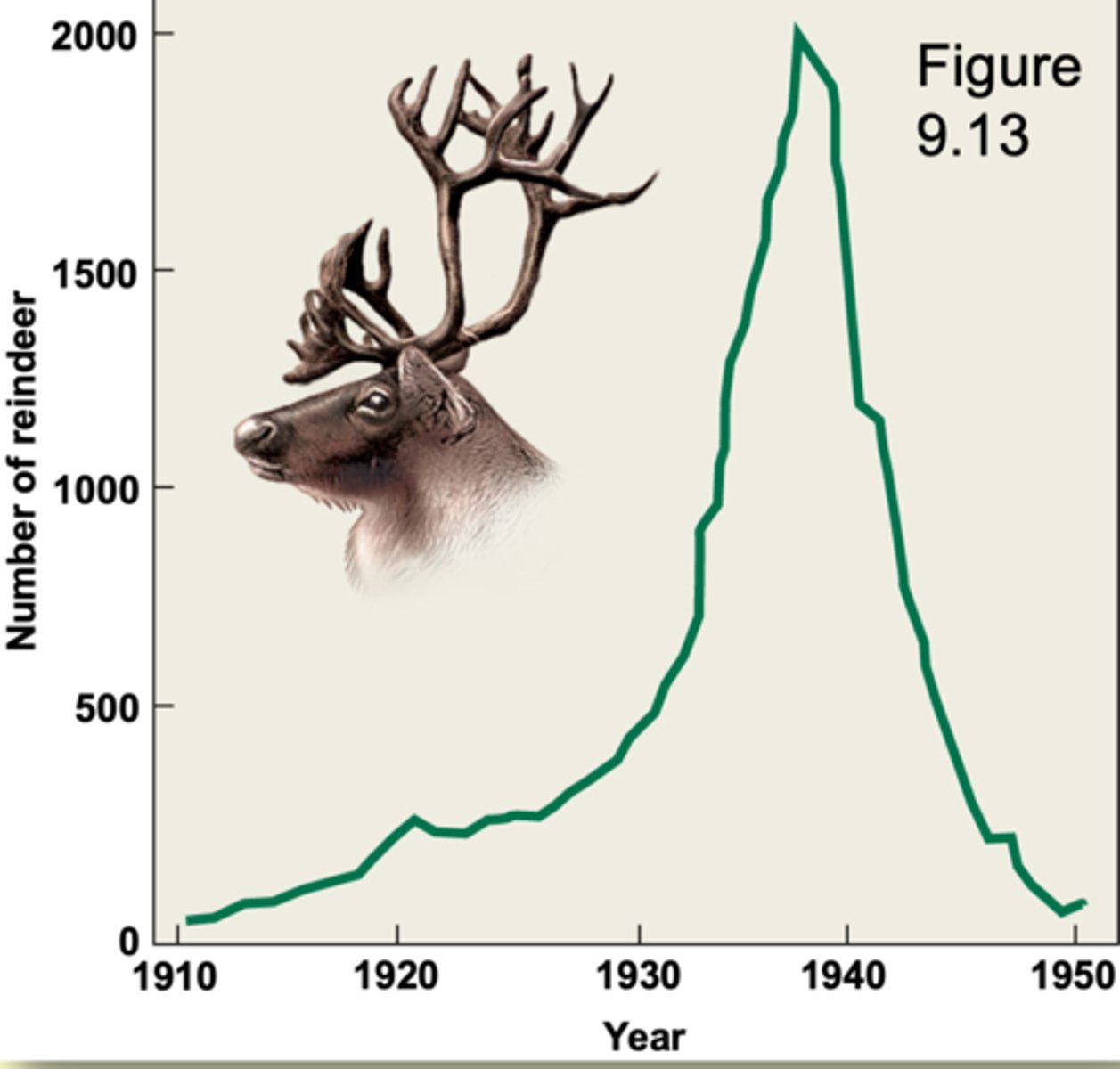
20 reindeers onto St. Paul in the Pribilof Islands, Alaska (Positive exponential growth example)
In 1911, the United States government introduced 20 reindeer (4 males and 21 females) onto the island of St. Paul in the Pribilof Islands, Alaska.
The purpose of the introduction was to provide fresh meat for the native residents.
Within 30 years, the population grew to more than 2000 individuals.
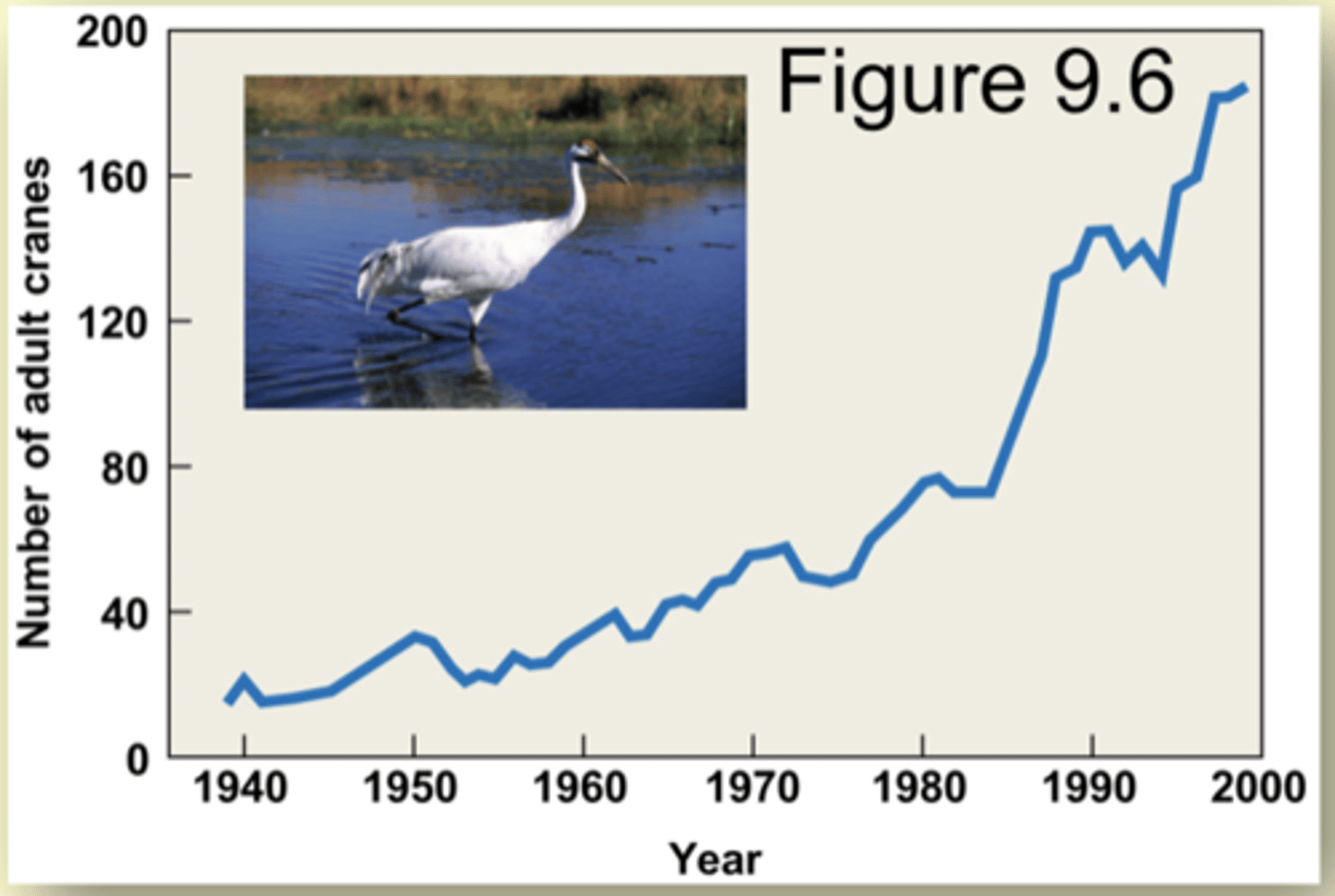
Whooping crane population (Positive exponential growth example)
- When Europeans settled in North America, the whooping crane population was estimated to be more than 10,000.
- By 1938 only 15 members of the species remained, and the species was declared endangered in 1967.
--------------------
Through conservation efforts, the population in 2000 was more than 300 individuals and showed exponential population growth.
A population is declining when deaths exceed births
r < 0
--------------------
RECAP
- r= intrinsic growth rate of a population
Why are small populations more vulnerable to extinction?
- Less of genetic variability
- Deaths of a small number of reproductive individuals can have large (negative) consequences
Extreme environment events...
can increase mortality rates and reduce population size
- if environmental conditions exceed the bounds of tolerance for the species; an extreme event could lead to extinction
types of extreme environment events
- Droughts
- Floods
- Heat waves
- Cold snaps
if environmental conditions exceed the bounds of tolerance for the species, an extreme event could lead to
extinction
--------------------
- Changes in regional and global climate
A severe resource shortage, caused by either extreme environmental conditions or overpopulation, can lead
to a population decline.
can severe resources shortage cause extinction
extinction is possible if the resource base does not recover in time for survivors to reproduce
invasive species can cause population declines (example)
EX: Reindeer on St. Paul island
- overgrazed the island severely
- herd size dropped from 2000 in 1938 to 8 in 1950
- such a population may recover or it may go extinct
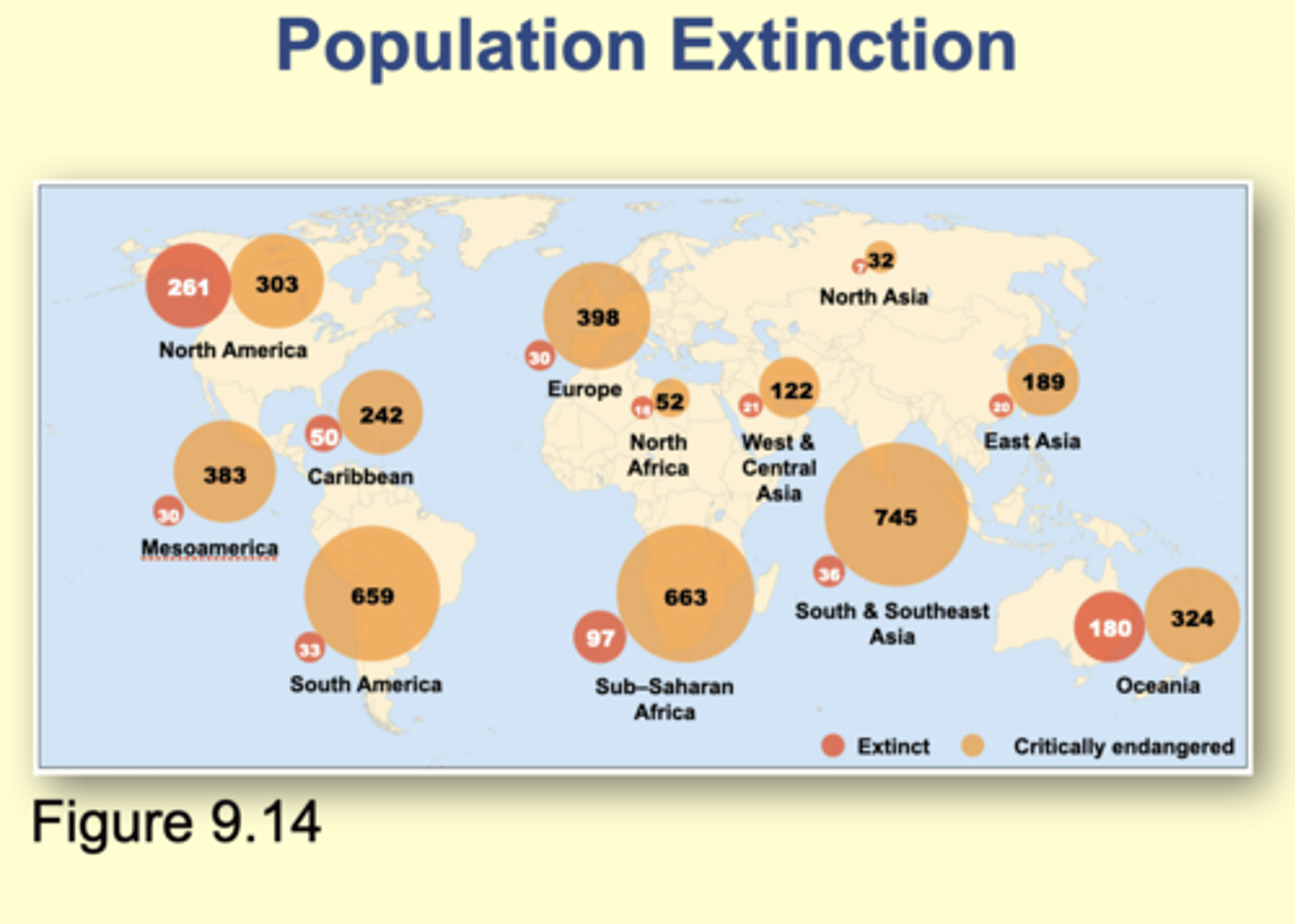
Population Extinction
fluctuations in growth rate, population size, and chance events can affect a populations risk of extinction
What is the major way that humans impact population or species-level extinctions?
Habitat destruction or modification
--------------------
Human land use changes the environment.
-Leads to decline in available habitat for many species

types of land use (human impact population)
- Cutting forests
- Draining forests
- Clearing wetlands
- Clearing land for agriculture
- Damming rivers
Rivers/Dam: Population Extinction & Humans
In the United States, about 17% of the rivers are affected by dams
About 75,000 dams impound almost 1 million km of river
Note: the Mississippi River is 3743 km in length
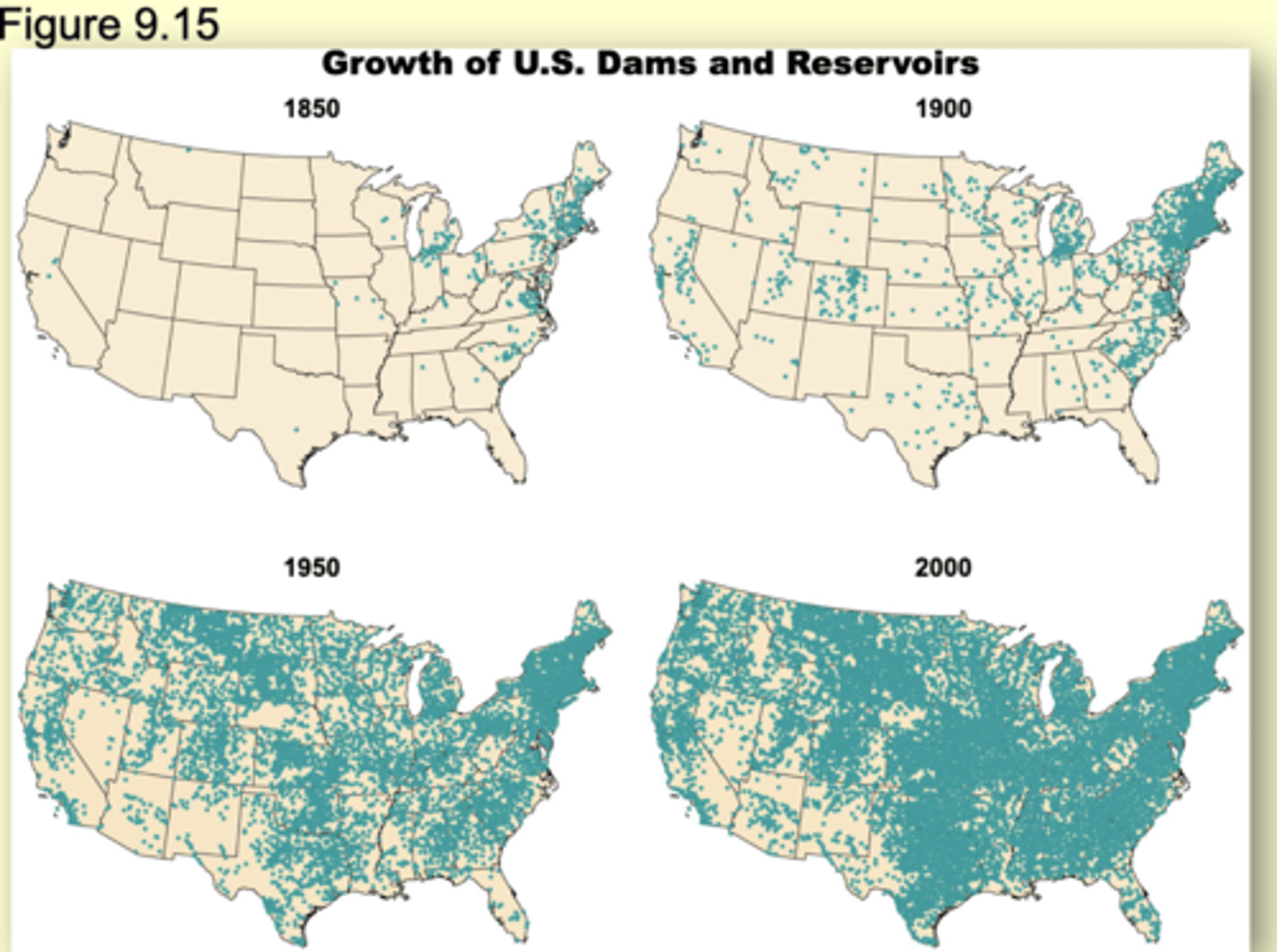
Dams affects the characteristics of water
- flow rate
- temperature
- oxygen levels
- sediment transport
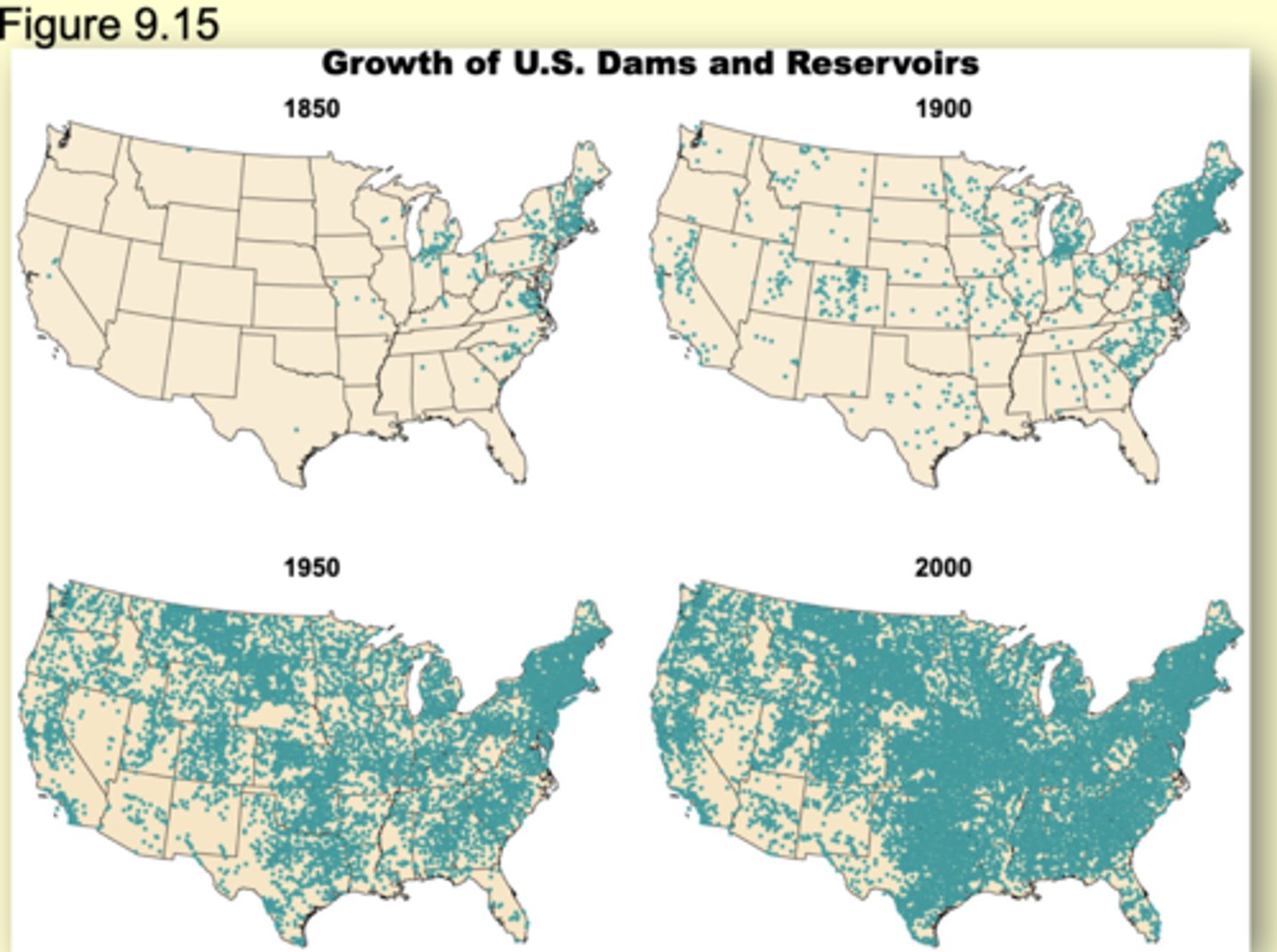
Dams negative impact on species
has an impact on species that migrate, reducing their ability to move upstream
--------------------
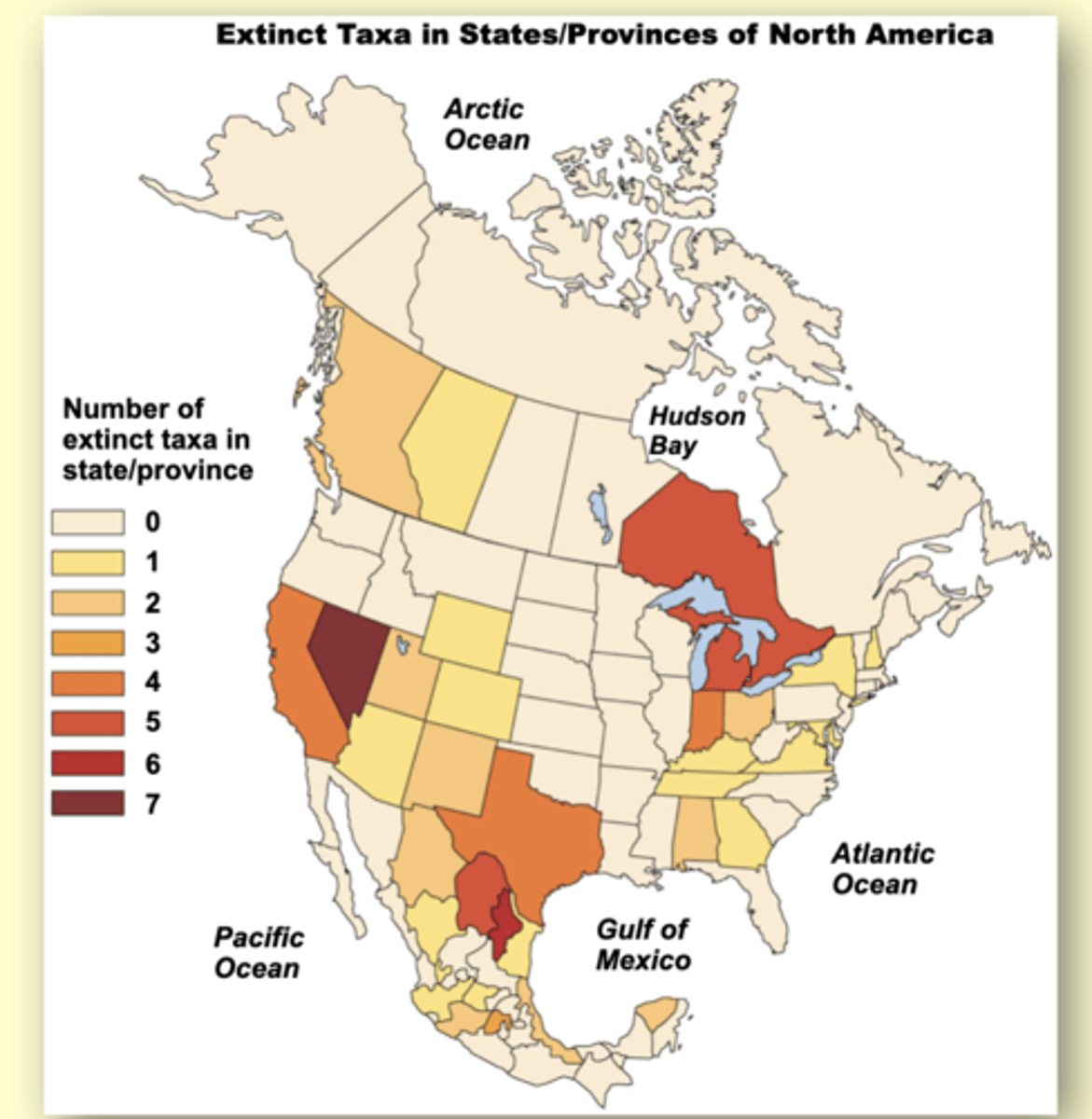
Between 1900 and 2010, 57 species and subspecies of North American freshwater fish have gone extinct.
Extinct taxa in states/provinces of North America
LOOK AT PICTURE