TEST PREP: Chapter 4; Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life; Campbell Biology; Tenth Edition
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
What are the six most important chemical elements of life?
a. carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen, phosphate, sulfur
b. carbon, nitrogen, calcium, zinc, iron, hydrogen
c. carbon, nitrogen, calcium, oxygen, phosphate, iron
d. carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, calcium, phosphate, hydrogen
e. carbon, nitrogen, sulfur, hydrogen, iron, magnesium
carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen, phosphate, sulfur
All of these elements are capable of forming strong covalent bonds, important in building large, complex molecules.
Which of the following is an organic molecule?
a. NaCl
b. Ne
c. CH4
d. H2O
e. O2
CH4
Compounds containing carbon are said to be organic.
Which element is always associated with organic chemistry?
a. hydrogen
b. oxygen
c. sulfur
d. carbon
e. nitrogen
carbon
Compounds containing carbon are said to be organic.
What is the three-dimensional shape created by hybrid orbitals that are formed when a carbon atom is covalently bonded with four other atoms?
a. a triangle with carbon in the center
b. a flat sheet with carbon in the center
c. a cube with carbon in the center
d. a tetrahedron with carbon in the center
e. All of the listed responses are possible.
a tetrahedron with carbon in the center
The pairs of bonding electrons are oriented as distantly as possible from one another in a tetrahedron with the carbon atom at the center and the other four atoms at the vertices of the tetrahedron.
What is the reason carbon atoms are the most versatile building blocks of the molecules used by living organisms?
a. Each carbon atom acts as an intersection point from which a molecule can branch off in up to four directions.
b. Carbon can combine with hydrogen to form hydrocarbons.
c. Carbon is the central atom in urea, a molecule used by many living organisms to transport wastes from the body.
d. Carbon is the central atom of carbon dioxide, a necessary molecule for photosynthesis.
e. All of the listed responses are correct.
Each carbon atom acts as an intersection point from which a molecule can branch off in up to four directions.
Carbon has the potential to form molecules that can be straight, branched, or ringed. Along with the ability to form double and triple bonds, this ability permits the formation of an almost infinite number of different molecules.
Optional: The carbon atom is tetravalent, which means that __________.
a. carbon's first electron shell holds four electrons
b. carbon readily forms ionic bonds
c. a carbon atom can complete its valence shell by forming four covalent bonds
d. carbon has a total of four electrons
e. the bond angle between each bond is 90°, forming an arrangement like the points on a compass
a carbon atom can complete its valence shell by forming four covalent bonds
With four valence electrons, carbon usually shares its four electrons in covalent bonds to complete its outer shell.
Which of the following are properties of hydrocarbons?
a. hydrophilic, good source of stored energy, consisting primarily of carbon and hydrogen
b. hydrophobic, containing numerous amine groups, polar
c. hydrophobic, polar, charged
d. hydrophilic, containing numerous carboxyl groups, nonpolar
e. hydrophobic, nonpolar, good source of stored energy
hydrophobic, nonpolar, good source of stored energy
Because they are nonpolar, hydrocarbons are hydrophobic. They also provide energy in the forms of things such as fossil fuels and fats.
The two compounds are related to each other by being __________.
a. organic compounds
b. hydrocarbons
c. double-bonded compounds
d. isomers
e. hydrocarbons, isomers, organic compounds, and double-bonded compounds
hydrocarbons, isomers, organic compounds, and double-bonded compounds
All of the listed responses are true characteristics of the two compounds.
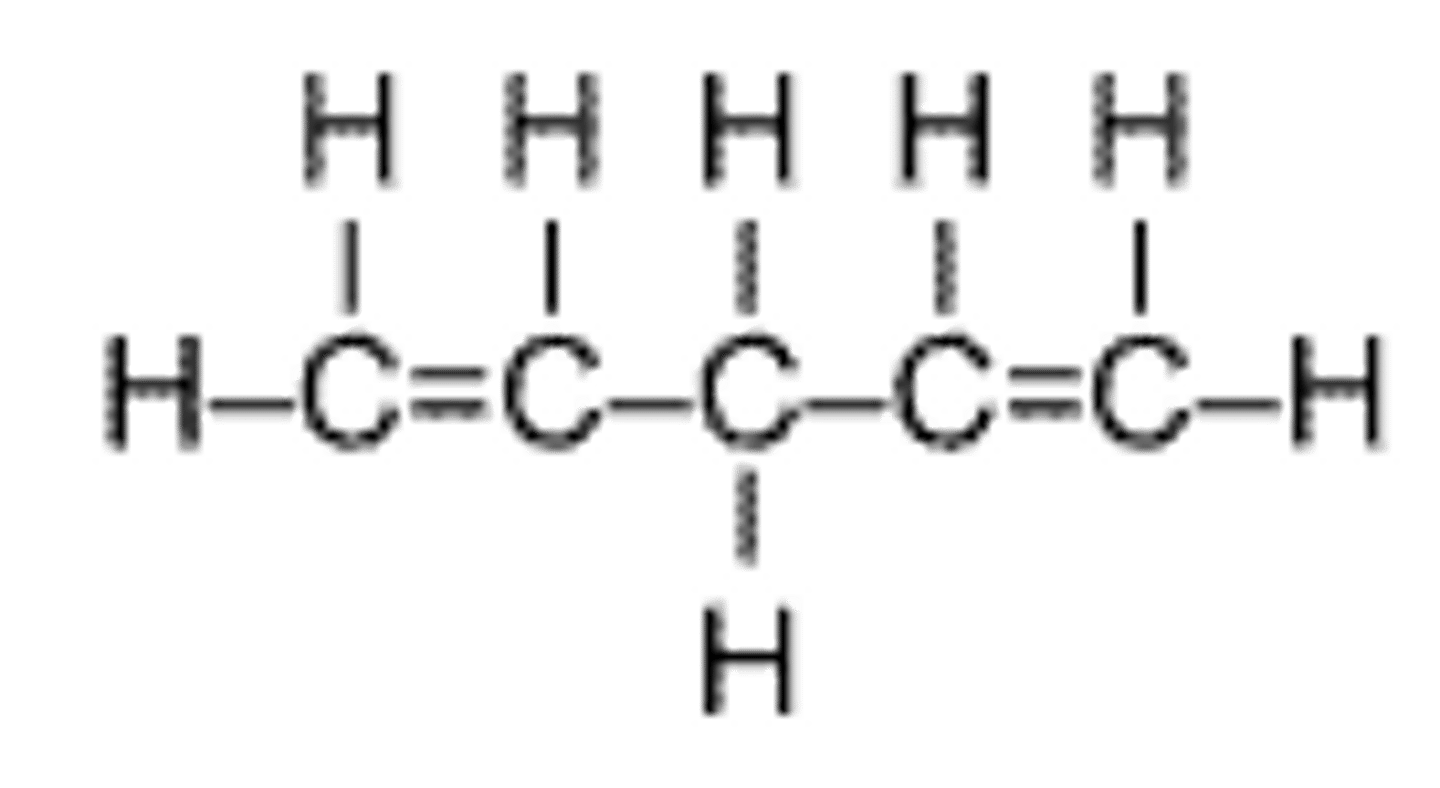
Which of the following functional groups is present in all amino acids?
a. —OPO3-2
b. —SH
c. —OH
d. —COH
e. —NH2
—NH2
This is the amino group. This group is present in all amino acids.
Which of these is found in all amino acids?
a. —COOH
b. —OH
c. —NH2
d. —COH
e. both —COOH and —NH2
both —COOH and —NH2
For a compound to be an amino acid, it must contain at least one carboxyl functional group and one amino functional group. In addition, it may contain one or more of the other functional groups.
Optional: Ethanol, propanol, and methanol are three simple alcohols. They can be grouped together because they __________.
a. increase the acidity of solutions
b. all contain a carbonyl group
c. share the same functional group: a hydroxyl
d. are hydrophobic
e. are soluble in water
share the same functional group: a hydroxyl
Alcohols are distinguished by the presence of the hydroxyl (-—OH) functional group.
Which of the following molecules has a carboxyl functional group?
a. R—NH2
b. R—OPO3-2
c. R—COOH
d. R—SH
e. R—COH
R—COOH
The molecule R—COOH contains the carboxyl functional group (—COOH). The presence of this group would make the molecule a weak acid.
Which of the following molecules is a weak base?
a. R—NH2
b. R—OH
c. R—COOH
d. R—SH
e. None of the listed responses is correct.
R—NH2
The amino group (—NH2) of R—NH2 can function as a base. It can accept a proton (H+).
Which of the following molecules is a weak acid?
a. R—COOH
b. R—NH2
c. R—OH
d. R—SH
e. None of the listed responses is correct.
R—COOH
The carboxyl group (—COOH) of R—COOH can donate a proton (H+).
Which of the following functional groups increases the solubility of organic compounds in water?
a. —NH2
b. —OH
c. —COOH
d. —COH
e. All of the listed responses are correct.
All of the listed responses are correct.
All of the listed functional groups are hydrophilic and thus increase the solubility of organic molecules in water.
Which of the following examples best describes a unique functional property of the carboxyl group?
a. Its compounds may be structural isomers with different properties.
b. It is polar as a result of the electronegative oxygen atom drawing electrons toward it.
c. Two carboxyl groups can bond covalently to help stabilize protein structure.
d. The covalent bond between oxygen and hydrogen is so polar that hydrogen ions tend to dissociate from oxygen reversibly.
e. It acts as a base.
The covalent bond between oxygen and hydrogen is so polar that hydrogen ions tend to dissociate from oxygen reversibly.
This is a property of the carboxyl group.
Optional: Which of the following functional groups is associated with a release of energy when removed from the carbon skeleton with water?
a. phosphate group
b. carboxyl group
c. amino group
d. hydroxyl group
e. sulfhydryl group
phosphate group
Cleaving a phosphate group from ATP releases energy that is used to perform many cellular functions.
Which of the following groups is capable of hydrogen bonding with an oxygen atom on another functional group?
a. carboxyl group
b. hydroxyl group
c. carbonyl group
d. amino group
e. All of the listed responses are correct.
All of the listed responses are correct.
All of the listed functional groups are polar, and thus capable of hydrogen bonding with the oxygen of another molecule.
Choose the pair of terms that correctly completes this sentence about functional groups in organic chemistry: Carboxyl is to __________ as __________ is to base.
a. hydroxyl ... amino
b. sulfhydryl ... carbonyl
c. acid ... amino
d. acid ... carbonyl
e. ketone ... phosphate
acid ... amino
A carboxyl group has acidic properties because it can donate a proton (hydrogen ion) to a solution. The amino group acts as a base because it can pick up or accept a proton (hydrogen ion) from a solution.
Optional: What is ATP's importance in the cell?
a. ATP can add phosphate groups, thereby releasing energy that can be used in cellular processes.
b. ATP stores the potential to react with water, thereby removing a phosphate group and releasing energy for cellular processes.
c. ATP contains a long hydrocarbon tail and is important in storing energy.
d. ATP stores energy in carbonyl groups. When a carbonyl group is removed, energy is released to be used in cellular processes.
e. ATP is an important component of cell membranes because it is nonpolar and hydrophobic.
ATP stores the potential to react with water, thereby removing a phosphate group and releasing energy for cellular processes.
ATP releases energy during a hydrolysis reaction that removes a phosphate group.
Organic chemistry is currently defined as
a. the study of compounds made only by living cells.
b. the study of carbon compounds.
c. the study of vital forces.
d. the study of natural (as opposed to synthetic) compounds.
e. the study of hydrocarbons.
the study of carbon compounds
Which chemical group is most likely to be responsible for an organic molecule behaving as a base (see Concept 3.3, p. 53)?
a. phosphate
b. hydroxyl
c. carboxyl
d. carbonyl
e. amino
amino
Choose the term that correctly describes the relationship between these two sugar molecules:
a. enantiomers
b. isotopes
c. structural isomers
d. cis-trans isomers
structural isomers
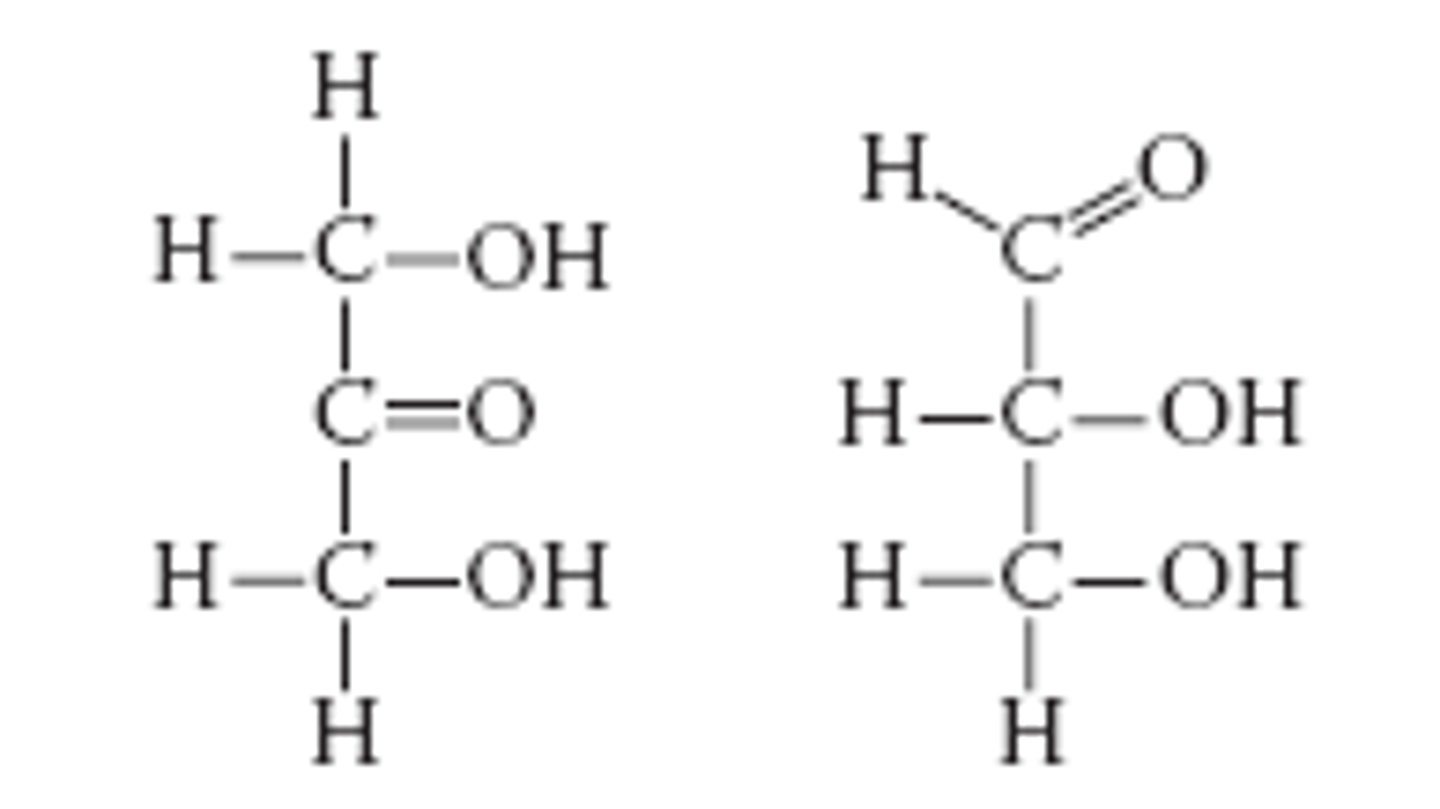
Which action could produce a carbonyl group?
a. the replacement of the -OH of a carboxyl group with hydrogen
b. the addition of a hydroxyl to a phosphate
c. the addition of a sulfhydryl to a carboxyl
d. the replacement of the nitrogen of an amine with oxygen
e. the addition of a thiol to a hydroxyl
the replacement of the -OH of a carboxyl group with hydrogen
Optional: A functional group on a molecule in solution carries two H atoms at pH 9 and three H atoms at pH 3. The functional group is probably. . .
a. carbonyl
b. carboxyl
c. sulfhydryl
d. amino
e. phosphate
amino
Amino groups take on H+ in acidic solutions.
A phosphate group contains _________ oxygen atoms.
a. 4
b. 1
c. 3
d. 2
e. 3 or 4, depending on ionization
4
Optional: _____ is formed when a Carboxyl Group is added
Acid
Optional: _____ is formed when a Hydroxyl Group is added
Alcohol
Optional: _____ is formed when a Carbonyl Group is added
Aldehyde and ketone
Although the structures of the functional groups that are most important to life vary, they share one thing in common: They _____.
a. all contain oxygen
b. always cause the carbon to which they are attached to become an asymmetric carbon, thus converting the molecule into an enantiomer
c. all are hydrophilic and increase the organic compound's water solubility
d. all have at least one double bond
e. force straight chains of carbons into closed rings of carbon
all are hydrophilic and increase the organic compound's water solubility
Optional: ____ is formed when an Amino Group is added
Amine
Amino groups ...
a. act as bases in water
b. contain nitrogen atoms
c. occur in proteins
d. just two of the preceding answers are true
e. (a), (b), and (c)
(a), (b), and (c)
Proteins contain many of these N-containing groups, which take H+ from water to become ions.
Carbon atoms are the most versatile building blocks of the molecules used by living organisms because _____.
a. carbon can combine with hydrogen to form hydrocarbons
b. each carbon atom acts as an intersection point from which a molecule can branch off in up to four directions
c. carbon is the central atom in urea, a molecule used by many living organisms to transport wastes from the body
d. carbon is the central atom of carbon dioxide, a necessary molecule for photosynthesis
e. All of the listed responses are correct
each carbon atom acts as an intersection point from which a molecule can branch off in up to four directions
Choose the pair of terms that completes this sentence about functional groups in organic chemistry: Carboxyl is to _____ as _____ is to base.
a. acid ... carbonyl
b. hydroxyl ... amino
c. acid ... amino
d. sulfhydryl ... carbonyl
e. ketone ... phosphate
acid ... amino
Optional: Citric acid makes lemons taste sour. Which of the following is a functional group that would cause a molecule such as citric acid to be acidic?
a. hydrocarbon
b. amino
c. carboxyl
d. hydroxyl
e. carbonyl
carboxyl
The carboxyl group can release a hydrogen ion when in solution.
Optional: Geometric isomers are molecules that _____.
a. differ in their molecular formulas
b. are mirror images
c. differ in the arrangement of their atoms about a double bond
d. are isomers that differ in the covalent partnerships between their atoms
e. are isomers in which one of the molecules contains an amino group and the other contains a phosphate group
differ in the arrangement of their atoms about a double bond
Glucose and hexanoic acid each contain six carbon atoms, but they have completely different properties. Glucose is a nutrient found in food; hexanoic acid is poisonous. Their differences must be due to different _____.
a. isomers
b. monomers
c. functional groups
d. quaternary structures
e. macromolecules
functional groups
How are gasoline and fat chemically similar?
Both consist largely of hydrocarbon chains.
How do isomers differ from one another?
a. Isomers differ in molecular formulas
b. Isomers differ in the arrangement or bonding of atoms
c. Isomers differ in charge
Isomers differ in the arrangement or bonding of atoms
Isomers may differ in the covalent arrangements of their atoms or the position of double bonds within the molecule and thus have different chemical properties.
How does a carbonyl group differ from a carboxyl group?
a. A carbonyl group ionizes more readily than a carboxyl group
b. A carboxyl group contains H; a carbonyl does not
c. A carbonyl group contains N; a carboxyl group doesn't
d. A carboxyl group contains oxygen; a carbonyl group doesn't
e. A carbonyl group is polar; a carboxyl group is not polar
A carboxyl group contains H; a carbonyl does not
A carbonyl group is just C=O. A carboxyl group is a carbonyl group with an OH group attached.
Optional: How does an aldehyde group differ from a ketone group?
a. The ketone is polar; the aldehyde isn't
b. The aldehyde is polar; the ketone isn't
c. The ketone occurs in sugars; the aldehyde doesn't
d. The aldehyde contains C=O; the ketone doesn't
e. Aldehydes, but not ketones, have H bound to C=O
Aldehydes, but not ketones, have H bound to C=O
Identify the functional groups.
a. Amino and carboxyl are functional groups
b. DNA and RNA are functional groups
c. Lipids and proteins are functional groups
Amino and carboxyl are functional groups
In what ways does the methyl group differ chemically from the other six important chemical groups?
The methyl group is nonpolar and not reactive. The other
six groups are called functional groups. They are each hydrophilic, increasing the solubility of organic compounds in water, and can participate in chemical reactions.
Optional: _____ is formed when a Methyl Group is added
Methylated compound
Molecules that have the same chemical formula (same numbers of each atom) but different three-dimensional shapes are called _____.
a. hydrocarbons
b. functional groups
c. enantiomers
d. isomers
e. isotopes
isomers
Isomers of carbon compounds can arise in several different ways.
Most organic compounds contain carbon and _____.
a. oxygen
b. sulfur
c. nitrogen
d. hydrogen
e. phosphate
hydrogen
Optional: _____ is formed when a Phosphate Group is added
Organic phosphate-found in ATP
_____ is formed when a Hydroxyl Group and a Carbonyl Group are added
Sugar
The functional group most closely resembling sulfhydryl is the _____ group.
a. amino
b. carboxyl
c. hydroxyl
d. phosphate
e. carbonyl
hydroxyl
Optional: The ionized or dissociated carboxyl group may be written as _____.
a. -COOH
b. -C=O
c. -OH
d. NH4+
e. -COO-
-COO-
The large diversity of shapes of biological molecules is possible because of the extensive presence of _____ in the molecules.
a. hydrogen
b. sulfur
c. nitrogen
d. carbon
e. oxygen
carbon
With four electrons to share, carbon-based molecules can be multibranching and three-dimensionally variable.
Variations in the reactive properties of different organic molecules are most closely associated with _____.
a. the orientation of the carbon skeleton, as either ringed or linear
b. the number of asymmetric carbon atoms present
c. the number of carbon atoms comprising the molecule's skeleton
d. the presence or absence of double bonds
e. the presence or absence of functional groups
the presence or absence of functional groups
Functional groups are the most common participants in chemical reactions.
Optional: What action could produce a carbonyl group?
the replacement of the -OH of a carboxyl group with hydrogen
Optional: What does the term amino acid signify about the structure of such a molecule?
It has both an amino group (-NH2), which makes it an amine, and a carboxyl group (-COOH), which makes it a carboxylic acid.
Optional: What functional group is commonly used in cells to transfer energy from one organic molecule to another?
a. hydroxyl
b. amino
c. phosphate
d. sulfhydryl
e. carboxyl
phosphate
The addition and release of phosphate groups to and from ADP and ATP is how cells store chemical energy and expend it to accomplish work.
Water is the universal medium of life on Earth, but living organisms are made up of chemicals based mostly on what elements?
a. Oxygen
b. Hydrogen
c. Carbon
d. Phosphorous
Carbon
Carbon is unparalleled in its ability to form molecules that are large, complex, and varied.
a. True
b. False
True
What are the major elements found in living organisms?
a. C, H, N, O, P, S
b. C, H, and O
c. C, H, N, P
d. C, O, P, S
C, H, N, O, P, S
Hydrocarbons are major chemical components of the substance used to fuel most of today's vehicles.
a. True
b. False
True
Which type of organic molecule are hydrocarbons associated with in cells?
a. Carbohydrates (sugars)
b. Lipids (fats)
c. Proteins (amino acids)
d. Nucleic acids (DNA)
Lipids (fats)
Which functional group affects the shape of human sex hormones that result is different physical characteristics in the human species.
a. Amino group
b. Hydroxyl group
c. Carbonyl group
d. Methyl group
Methyl group
A carbon atom is most likely to form what kind of bond(s) with other atoms?
a. ionic
b. hydrogen
c. covalent
d. ionic and hydrogen only
e. ionic, hydrogen, and covalent
covalent
Which of the following is a false statement concerning amino groups?
a. They are basic in pH.
b. They are found in amino acids.
c. They contain nitrogen.
d. They are nonpolar.
e. They are components of urea.
They are basic in pH.
How many electron pairs does carbon share in order to complete its valence shell?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
e. 8
2
Optional: A chemist wishes to make an organic molecule less acidic. Which of the following functional groups should be added to the molecule in order to do so?
a. carboxyl
b. sulfhydryl
c. hydroxyl
d. amino
e. phosphate
sulfhydryl