Bacterial Morphology, Structure of bacterial cells & bacterial spores
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Viruses are prokaryotes or eukaryotes
Neither, they’re acellular
Commensalism
One organism benefits and the other one neither benefits nor is harmed
Mutualism
Both organisms benefits from the relationship
Parasitism
One organism (parasite) benefit while the host is harmed
Resident microbiota
Microbes that are alays present on or in the host
Transient microbiota
Microorganisms that can be present under certain conditions
Opportunist
Species of resident or transient microbiota that does not normaly cause disease but can under certains conditions
Shapes of bacterias
Spherical: coccus
Rod: bacillus
Curved/spiral: spirillus
Pleomorphism
Ability of a bacteria to vary in forms under certains conditions
Cocci division
Can divide in one or more planes or randomly

Diplococci
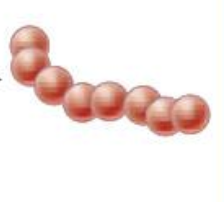
Streptococci

Tetrads; division in 2 planes

Sarcinae; division in 3 planes

Staphylococci; grape like random division planes
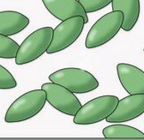
Coccobacilli: short rod (intermediate btw cocci and bacilli)
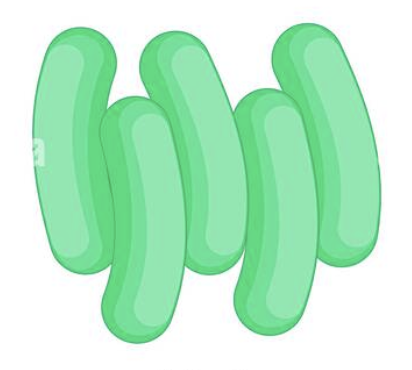
Palisades bacilli
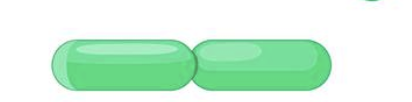
Diplobacili

Vibrio: comma sjaped

Spirillum: wavy shape

Spirochete: corkscrew
Bacteria cell structure
Internal: cytoplasm (ribosomes, nucleoid, inclusions)
Cell enveloppe (membrane usually surounded by a cell wall and also by a capsule or slime layer)
External: Flagella, pili
No single bacteria posseses all of these structures at all times
Bacterial ribosomes
Called 70S ribosomes made of a 50S (large) and 30S (small) subunit
Mainly made of ribosomalRNA(rRNA)
Small subunit contains 16S rRNA and the large 23S and 5S
Inclusions are
Small body like granules or vacuoles
Cell wall
Maintain cell shape
Protect the interior of the cell from env changes
Made of periplasmic space, peptidoglycan and outer membrane
Periplasmic space
Gap between cell membrane and cell wall (mostly in gram- smts in gram+)
Space occupied by periplasm
Digestive enzymes, transport proteins → destroy harmful substances and transport metabolites in cytoplasm
Peptidoglycan
Responsible for cell wall rigidity
Unique to bacteria
Outer membrane
Mostly in gram-
Bilayer membrane
Made of lipopolysaccharide (O side chain/antigen and lipid A)
Lipid A is responsible for what
Toxic properties (endotoxin) - fever blood vessels dilatations
O antigen is responsible for what
Provoke immune response by infected host
Difference gram- & gram+
Gram-:
Thinner cell wall
Have outer membrane
Thin layer of peptidoglycan
Gram+:
Thicker layer of peptidoglycan
Have teichoic acid (anchor wall to membrane)
Outer membrane often absent
Glycocalyx
All substances containing polysacchardies external to cell wall, provide protection
Capsule
Outside cell wall
Help resisting phagocytosis
Protect against desiccation
Help cell to adhere surfaces
Slime layer
Protect cell against drying
Bind cells together
Allow bacteria to adhere environment
Pili
Hair-like appendages, thinner and shorter than flagella
Pilli classification
Conjugation pili:
Bigger than other pili
Allow two cells to attach and conjugate
Attachment pili:
Allow cell to attach to surface
Flagella
Motile organelle
Flagella part
Filament
Basal body (embededd in cell enveloppe)
Hook (curved part link filament to basal body)
Does cocci have flagella
Rarely
When a bacteria has one flagella at one end, it’s called
Monotrichous
When a bacteria has two flagella at each end, it’s called
Amphitrichous
When a bacteria has two or more flagella at one or both end, it’s called
Lophotrichous
When a bacteria has flagella all over its surface, it’s called
Peritrichous
When a bacteria doesn’t have flagella , it’s called
Atrichous
Why spirochete coil like a corkscrew
Due to endoflagella (or axial filament)
Bacterial endospores
Resting stages produced by vegetatives cells of some bacteria
Very resistant
Can’t divide
Not metabolically active
Inside bacteria
Process that lead to endospore formation
Sporulation
What endospores will do
Develop in a new functional vegetative bacterial cell when condtions are optimal (germination)
List bacterial antigens (location, role)
Antigen A: Base of lipopolysaccharide layer of cell wall, endotoxin (fever, BV dilatation)
Antigen O: Side chain of LPS, provoke immune response
Antigen K: In capsule
Antigen F: In pili
Antigen H: in filament of flagella (flagellin)